Abstract
Most supervised person re-identification methods show their excellent performance, but using labeled datasets is very expensive, which limits its application in practical scenarios. To solve the scalability problem, we propose a Cross-camera Erased Feature Learning (CEFL) framework for unsupervised person re-identification that learns discriminative features from image appearances without manual annotations, where both of the cross-camera global image appearance and the local details are explored. Specifically, for the global appearance, in order to bridge the gap between images with the same identities under different cameras, we generate style-transferred images. The network is trained to classify the original images, the style-transferred images and the negative samples. To learn the partial details of the images, we generate erased images and train the network to pull the similar erased images together and push the dissimilar ones away. In addition, we joint learn the discriminative global and local information to learn a more robust model. Global and erased features are used together in feature learning which are successful conjunction of BFENet. A large number of experiments show the superiority of CEFL in unsupervised pedestrian re-identification.
1. Introduction
Person re-identification (re-ID) is a key technology in urban monitoring, which is used in public places to find the target pedestrian in video or images taken by different cameras [1]. In the past decades, most person re-identification methods have focused on distance metric learning methods [2,3,4] and feature learning methods [5,6]. Especially in recent years, deep learning methods [1,7,8,9,10,11] have been widely used for person re-identification. However, most current person re-identification methods require tremendous amount of labeled images, which is very difficult and expensive. And it also limits the scalability and usability in practical application scenarios.
To relieve the scalability problem, some unsupervised methods are proposed. To obtain supervised signals, these methods usually adopt unsupervised clustering [12,13,14,15] or generative adversarial networks [7,9] to augment datasets. Another branch of unsupervised learning methods [1,7,8,9,10,11] learn the discriminative pedestrian information from source datasets with labeled pedestrian images. However, due to the absence of supervision signal, the target dataset is still not fully explored, and the performances of these methods are thus not satisfying.
Without the annotation from the target dataset, we aim to design auxiliary task from the raw images to give supervision signal. Since there are no ground truth labels, we generate images with certain identity in unsupervised manners. To deal with the global appearance of images, Camstyle [16] is adopted, with which for each training sample, images of other camera style are generated. On the one hand, the generated images maintain the same identity information that could be viewed as positive samples. On the other hand, there are huge gaps between images of different cameras. Training one image with multiple camera style benefits the cross-camera matching and enhances the robustness of the model. To dig into the local details of images, we generated random erased images as the positive samples. As shown in Figure 1, comparing with the global appearance, the partial images of the same identity look more similar. Since the partial images are more robust to changes in pose, lighting, and perspective, the similarity between partial features are adopted to train the model in the unsupervised manner.
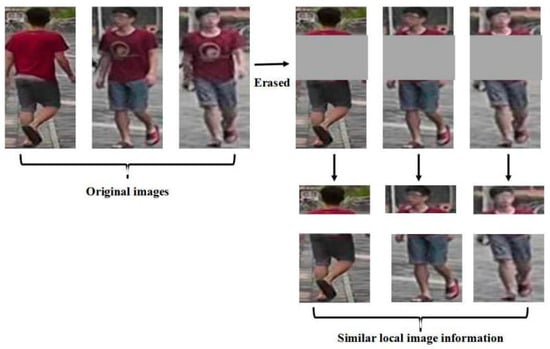
Figure 1.
The details of the remaining areas are still similar after erasing part of the original image.
With the generated images and the designed auxiliary tasks, we propose a Cross-camera Erased Feature Learning (CEFL) framework for unsupervised person re-identification. The framework can be divided into three parts: cross-camera global feature learning, erased partial feature learning, and joint global and partial feature learning. Specifically, to learn the global features, the intra-class gaps are minimized while the inter-class gaps are maximized in the global feature space. To define positive samples and negative samples and learn more discriminative features across cameras, generated images of different camera styles are utilized. To learn the partial features, a Batch Feature Erase Network (BFENet) is used to randomly erase a part of the feature maps in the same batch to force the network to learn local details of pedestrian pictures. The framework is learned to pull the similar erased feature vectors together and push away the dissimilar features. To strengthen the model and get more robust feature, we also learn the global and partial appearance jointly. We take the erased features as positive samples and determine negative samples in mini-batch image set to form a triplet for pedestrian feature determination learning.
The main contributions of our work are as follows:
- We use generated images to reduce the gap between cameras. Generated images can provide additional supervision information for unsupervised person re-identification.
- We use BEFNet to generate erased images so that the network can learn the features of local detail. At the same time, the similarity calculation between erased parts is more accurate and more suitable for unsupervised person re-identification.
- We join to learn global and erased parts to improve the robustness of CEFL. Global and erased features are used together in feature learning which are successful conjunction of BFENet.
- We evaluated EFDL on two large datasets: Market-1501 [6] and Duke-MTMC [17]. Experiments show that our method is superior to existing unsupervised person re-identification methods.
2. Related Work
Supervised person re-identification. Most of existing methods are proposed to deal with supervised person re-identification, such as distance measures learning, subspaces learning [2,3,4], and deep learning methods [18,19]. With the rapid development of deep learning, feature learning by deep networks has become a common practice in person re-identification. Li et al. [20] combined deep siamese network architecture with pedestrian human body feature learning for the first time and achieved higher performance. Proposed methods also improved the performance of deep person re-identification. Xiao et al. [21] improved the generalization of different pedestrian scenes by using Domain Guided Dropout method. Part-based methods [19,22] achieve the most advanced performance. In part-based methods, the input feature map is divided into a fixed number of bands, and feature vectors are aggregated from these bands. BFE model [23] get better results than part-based model in supervised person re-identification. However, supervised person re-identification methods rely on a large amount of manually labeled datasets which is time-consuming and labor-intensive. It also limit the practicability and applicability of supervised methods. In this paper, BFE network is applied to unsupervised person re-identification, which strengthens the classification ability of our model.
Unsupervised person re-identification. There are few effective methods have been used in unlabeled datasets. Features of manual annotation [5,24,25] are still insufficient for guaranteeing visually invariant features. The performance of manually labeled features in unsupervised pedestrian re-identification is weak. Recently. some methods achieved better results extracting features [26,27,28] or finding base labels [29,30,31] in unlabeled datasets. An unsupervised asymmetric distance metric learning method is proposed and it is based on asymmetric K-means clustering method [30,31]. Lin et al. [32] uses the clustering method for completely unsupervised person re-identification. However, the pseudo-labels of person images obtained through clustering may assign the same pseudo-labels to similar images with different identities, which improving the difficulty of classifying pedestrians. Cross-domain transfer learning methods [1,7,8,10,11] are proposed for unsupervised person re-identification, and the performance of the model on the target dataset is improved by using other labeled dataset. Wei et al. [7] use GAN to reduce the gap between different datasets. Bak et al. [1] propose an adaptive technology that uses synthetic data to identify person. Yu et al. [33] used auxiliary datasets to generate auxiliary references for unsupervised person re-identification. However, the gap between pedestrian pictures in different datasets is really large, and the robustness of transfer learning still needs to be improved. Yang et al. [34] develops the PatchNet network to learn discriminative features at patch level and shows superior performance. However, these similar patches may be extracted from different pedestrian identities, which is still difficult to distinguish potential identity information. In our model, we partially occluding pedestrian images and the remaining feature information can still belong to the same pedestrian. In addition, dataset generated in Camstyle is directly used as positive sample for calculation, so that the operation is more direct and convenient.
3. Materials and Methods
In this section, our Cross-camera Erased Feature Learning (CEFL) framework is introduced in detail. As shown in Figure 2, our method contains three components: cross-camera global feature learning, erased partial feature learning, and joint global and partial feature learning. We develop three loss functions, so that CEFL can learn more distinguishing features in unlabeled dataset. The main structure of CEFL is introduced in Section 3.1. Cross-camera global feature learning is introduced in Section 3.2. Erased partial feature learning is introduced in Section 3.3. Joint global and partial feature learning is introduced in Section 3.4.
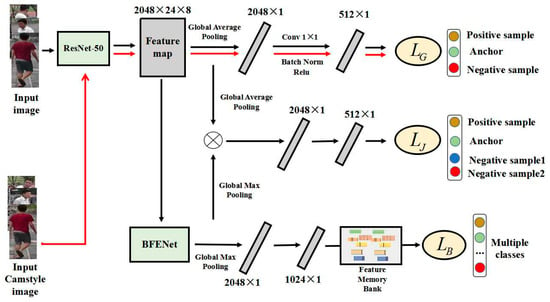
Figure 2.
The structure of our unsupervised Cross-camera Erased Feature Learning (CEFL) network. In the three branches from top to bottom, we used three different components and loss functions. Features is classified by minimizing intra-class gaps while maximizing inter-class gaps in cross-camera global feature learning. Similar erased feature vectors are pulled together and dissimilar features are pushed away in erased partial feature learning. Global features and erased features are used together in joint global and partial feature learning.
3.1. Network Structure
In this paper, we propose a new unsupervised Cross-camera Erased Feature Learning (CEFL) framework. The model framework is shown in Figure 2. CEFL model learns and uses features in different datasets to mine discriminative features on unlabeled datasets. CEFL aims to learn commonality and distinguishing features of different datasets through three branches, and combines three loss functions to provide feature differentiation guidance on unlabeled datasets.
CEFL network is divided into cross-camera global feature learning, erased partial feature learning, and joint global and partial feature learning. CEFL is pre-trained on other labeled datasets and learns common features of different datasets through pre-training process. In order to make the network mine more distinguishing features in unlabeled datasets, we add three different loss functions to three network branches, respectively. We add a quadruple loss function to discriminate pedestrians in cross-camera global feature learning. There are no identity labels used to form positive and negative samples in unsupervised datasets. Then we propose to aggregate features in mini-batch, calculate their similarity distances and sort to mine negative samples. We use image generated from Camstyle [17] to be an alternative positive sample. We use and apply the Batch Feature Erasure Network (BFENet) [23] in erased partial feature learning. BFENet consists of a global branch and a feature erasing branch. In BFE network, all images in the same batch are cropped in a consistent way. All the units inside the erased area are zeroed out. We also propose loss function to make similar erased features closer, while pushing away dissimilar erased features. Then we combine global features and erased features in joint global and partial feature learning. We use triple loss function to provide guidance for global features and erased features this network branch.
3.2. Cross-Camera Global Feature Learning
In supervised person re-identification method, the distance between pictures with same identity is usually minimized, and the distance between pictures of different identity is maximized. But there is no identity information in unsupervised person re-identification. In order to obtain more accurate category information, we classify features by minimizing intra-class gaps while maximizing inter-class gaps in feature space of the whole image. We use circular sorting to mine negative samples in mini-batch, and use different styles of pictures generated by Camstyle network as positive samples. On this basis, we propose a corresponding quadruple loss function. In this section, we will guide the cross-camera global feature learning branch to mine discriminative information on unlabeled datasets.
Selection of negative samples: We determine negative samples in mini-batch image set. If there are two pedestrian images with same identity in mini-batch, they are most likely to be the nearest neighbors to each other. In the same way, if two samples in a mini-batch are not nearest neighbors of each other, they may have different identities. Based on this concept, we add a circular sort to determine negative samples from a mini-batch set. Given a mini-batch of global sample features , ranking result of each global feature are generated based on pairwise similarity measure method. And Euclidean distance metric is used to calculate the similarity between two global features. A ranking list of is obtained by sorting the obtained similarity measurement results. Then, we traverse the sorted list in turn. For each negative sample candidate of global features , Euclidean distance measurement method is also used to calculate the sorted list of . If is not the top- nearest neighbor of , it is considered that is a negative sample of . We choose the first and second feature of ranking list as negative sample candidates in cross-camera global feature learning. And we select the first global feature of ranking list as a negative sample in joint global and partial feature learning.
Selection of positive samples: Since the probability of finding two images with same identity is really low in a mini-batch set, we directly use the pedestrian images generated in Camstyle [34] as the positive samples. By adopting Camstyle [34], for each original training image, images with styles of other cameras are generated. As shown in Figure 3, these generated images maintain the original identity information while benefit the cross-camera feature learning. The loss function of global feature learning is defined as follows:
where is the positive sample feature replaced by the generated image, and are negative sample features. and are threshold parameters, where , . We choose the first and second feature of ranking list as negative sample candidates , , respectively.

Figure 3.
Examples of images generated by Camstyle.
Discussion: It is very unlikely that pedestrian images in mini-batch have same identity, when a part of the images is randomly sampled from a large number of pedestrian images. Then we can know that it is even less likely that both negative samples belong to the same person. At the same time, we use circular sorting mechanism to select the first and second global feature of the ranking list. In this way, we determine that the identities of these two negative samples are different. The second term of this loss function is to learn absolute distance between positive and negative samples. This loss function can help model learn better representations.
3.3. Erased Partial Feature Learning
Images of the same pedestrian under different cameras may look different in global appearance, since they have different camera views, lightings, etc. However, since they are of the same pedestrian, their local details could be similar. Therefore, for each training sample, we erase a part of the pedestrian image and train the model to learn from the retained partial image. In BFDL branch, batch feature eraser (BFE) network is proposed to randomly erase a part of feature maps in each mini-batch. In supervised person re-identification learning method, elements of same classes are closer in the feature space and farther away from different classes to enhance the discrimination of elements [35,36]. In CEFL, we propose to draw similar erased features closer while pushing dissimilarity erased features away in the feature space, as shown in Figure 4.
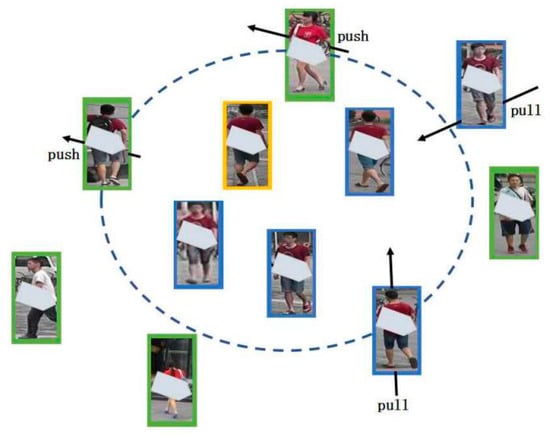
Figure 4.
Similar classes are drawn closer and dissimilar classes are pushed away.
The erased features are extracted by BFE network, as shown in Figure 2. Then we need to compare each unlabeled erased feature with other features to find similar features, which is difficult to handle in mini-batch optimization of deep learning. Therefore, we used erased feature memory bank [36] to store these erased features. At the same time, erased feature memory bank is updated during the training process. Function of the erased feature memory bank is as follows:
where is the number of images in the training dataset, is the training epoch, and is the updating rate of , is the latest erased feature extracted by BFE. means the erased feature memory bank is in initial state. The erased feature memory bank is updated in batches during the training phase.
Then the erased features are extracted and normalized by the subsequent network layer, as shown in Figure 2. For each erased feature, the loss function is defined as follows:
where is the nearest-neighbor feature set: features closest to feature (Euclidean distance) in the erased feature memory bank. By minimizing the loss function , EFDL can bring the feature that similar to the feature closer, while pushing the dissimilar feature away.
3.4. Joint Global and Partial Feature Learning
Joint global and partial feature learning is used to learn more robust features which can make the model generate similar embeddings for both the original image and the erased partial image. For each original global image, we regard the erased feature as positive sample, and select the first global feature of ranking list as a negative sample . For the extracted global feature , the loss function is defined as follows:
To summarize, the loss objective of our CEFL framework is formulated by:
4. Results
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Protocol
In order to evaluate the performance of the CEFL model, here we evaluate two datasets in the experiments, i.e., Market-1501 [6] and DukeMTMC-reID [17]. The Market-1501 [6] dataset includes 1501 identities captured by six cameras and 32,668 detected pedestrian rectangles under six camera viewpoints. In this dataset, each pedestrian contains at least two camera viewpoints. The training set is consisted of 751 identities and each identity include 17.2 training data in average. The test set is composed of 19,732 images of 750 identities. The pedestrian detection rectangle in the gallery is detected by DPM. Here, we use mean Average Precision (mAP) to evaluate person re-identification algorithms. The DukeMTMC-reID [17] dataset consists 36,411 images of 1404 identities. With those images collected by eight cameras. And each image is sampled every 120 frames from the video. This dataset is composed of 16,552 training images, 2228 query images and 17,661 gallery images. Half of the identities is randomly sampled as training sets while the others as test sets. DukeMTMC-reID offers human labeled bounding boxes.
For each query image, we calculate the Euclidean distance between query image and pedestrian image in gallery. Then we arrange them in descending order according to the Euclidean distance, and use the Cumulative Match Characteristic (CMC) curve to show the performance. In terms of performance measurement, we use the Rank-1 accuracy and the mean Average Precision (mAp).
4.2. Implementation Details
We pre-trained ResNet50 on the MSMT17 [7] dataset. The input pedestrian images are resized to 384 × 128. Batch size is set to 40 and learning rate is set to le-3. In GFDL branch, we generated one positive sample and two negative sample for each image, is set to 10. In BFDL branch, is set to 0.1, and is set to 25. The entire training process is terminated in 60 epochs.
4.3. Comparison with the State-of-the-Art
CEFL is experimented on Market-1501 [6] and DukeMTMC-reID [17], and experimental results are compared with other unsupervised person re-identification methods. Comparison results are shown in the following tables: Table 1 shows the comparison results on the Market-1501 [6] dataset, and Table 2 shows the comparison results on the DukeMTMC-reID [17] dataset.

Table 1.
Comparison with existing methods on Market1501.

Table 2.
Comparison with existing methods on DukeMTMC-reID.
Compared with manual labeling methods (LOMO [5], BoW [6], and UMDL [10]), performance of our method is beyond these methods. This is because CEFL model can learn robust features. Our proposed method outperforms clustering-based methods (PUL [29], CAMEL [30], DECAMEL [31], and BUC [32]) significantly on both datasets. Clustering-based methods mainly identify pedestrians by assigning the same pseudo-labels to similar pedestrian images. But these similar pedestrian images may have different identities, which affects the discrimination of pedestrians. Other details in the erased feature map are used for matching, in CEFL, which strengthens the ability of feature discrimination.
Compared with transfer learning methods (PTGAN [7], SPGAN + LMP [9], TJ-AIDJ [8], HHL [11], MAR [33], and PAUL [34]), our proposed method outperforms these methods. Due to the large gap between different datasets, it is still difficult to apply the model to the target domain. The CEFL model performs feature discrimination learning by extracting the global features and the erased features. Then the similarity measurement method can strengthen the generalization ability between different unlabeled datasets.
4.4. Experimental Details Analysis
The effect of the parameters in loss function . We perform experiments on two datasets (Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID), and used Rank-1 accuracy as the evaluation index. If the value of is too small, CEFL may choose a negative sample which has the same identity of the query image. The wrong selection of negative sample can reduce the classification ability of CEFL. The performance of the model can be reduced if the value of is too large, as shown in Figure 5. Setting appropriate values is more helpful to find negative samples with different identity. Experiments show that the CEFL network performance better than others when is set to 10, as shown in Figure 5.
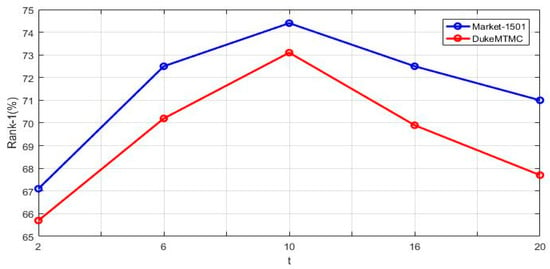
Figure 5.
The effect of the parameters in loss function .
The effect of the parameters in loss function . We perform experiments on two datasets (Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID), and used Rank-1 accuracy as the evaluation index. The value of means that there are erased features are regarded as similar features of the target pedestrian features. If the value of is too large, features with different ID may be judged into the same class, which resulting in performance degradation. Similarly, if the value of is too small, CEFL may lose some similar features. Losing similar features is not conducive to the subsequent process of CEFL network. In CEFL, we set different values of to judge the influence of the parameters . Experiments on two dataset show that the CEFL performance better than others when the value of is set to 25, as shown in Figure 6.
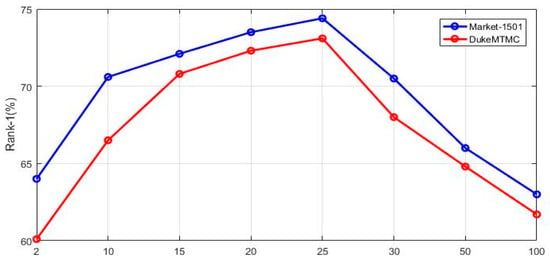
Figure 6.
The effect of the parameters in loss function .
In order to further explore the impact of CEFL, we evaluate the effects of three network components on two classic datasets respectively. Experiments on two dataset show that the CEFL performance better when the three network branches work together, as shown in Table 3. We test Cross-camera global feature Learning (CL) and Erased partial feature Learning (EL), as shown in Table 3. GL classifies features by minimizing intra-class gaps while maximizing inter-class gaps in global feature space. In EL similar erased feature vectors are pulled together and dissimilar features are pushed away. The result of ‘GL+EL’ is clearly better than ‘CL’ or ‘EL’ on both datasets. This is because combining ‘GL’ and ‘EL’ can provide more effective learning guidance to the network. The result of CEFL shows the best performance on two datasets. This is because joint global and partial feature learning can combine global features and erased features together.

Table 3.
Components analysis of CEFL.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes an unsupervised Cross-camera Erased Feature Learning (CEFL) model and proves the effectiveness of CEFL in unsupervised person re-identification. At the same time, three feature learning loss functions are upgraded and used to provide effective guidance of CEFL. These loss functions can help strengthen the feature discrimination ability of CEFL. In this article. CEFL is divided into three components: cross-camera global feature learning, erased partial feature learning and joint global and partial feature learning. Three components can learn features of unlabeled dataset. Cross-camera global feature learning is designed to minimize the gap between similar global features and maximize the gap between different global features. BFENet is added to help CEFL learn more details of features by erasing part feature map. And a loss function is proposed to draw closer to similar features and push away dissimilar features in erased partial feature learning. Joint branch connects erased features with global features and improves a loss function to learn discriminant features on unlabeled dataset. A large number of experiments show the effectiveness of CEFL in unsupervised person re-identification.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W.; methodology, S.W.; resources, L.G.; validation, S.W. and L.G.; writing—original draft, S.W.; writing—review & editing, S.W. and L.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61672329) and the Key Research and Development Foundation of Shandong Province (Nos. 2017GGX10117, 2017CXGC0703).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bak, S.; Carr, P.; LaLonde, J.-F. Domain adaptation through synthesis for unsupervised person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, W.-S.; Lai, J.-H. Person Re-Identification by Camera Correlation Aware Feature Augmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Gong, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, S. Person Re-Identification by Discriminative Selection in Video Ranking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 2501–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gong, S.; Zhu, X.; Xiang, T. Human-in-the-Loop Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Volume 9908, pp. 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.Z. Person re-identification by Local Maximal Occurrence representation and metric learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q.; Liang, Z.; Liyue, S.; Lu, T.; ShengJin, W.; et al. Scalable Person Re-identification: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Person Transfer GAN to Bridge Domain Gap for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S.; Li, W. Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning 3641 for unsupervised person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2275–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Zheng, L.; Ye, Q.; Kang, G.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, J. Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person reidentification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 994–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Peixi, P.; Tao, X.; Yaowei, W.; Massimiliano, P.; Shaogang, G.; Tiejun, H.; Yonghong, T. Unsupervised cross-dataset transfer learning for person reidentification. In Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Generalizing a person retrieval model hetero-and homogeneously. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 172–188. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.-X.; Wu, A.; Zheng, W.-S. Crossview asymmetric metric learning for unsupervised person reidentification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-X.; Wu, A.; Zheng, W.-S. Unsupervised person re-identification by deep asymmetric metric embedding. Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 956–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, X.; Zheng, L.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y. A Bottom-up Clustering Approach to Unsupervised Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–28 January 2019; pp. 8738–8745. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, W.; Wu, A.; Guo, X.; Gong, S.; Lai, J. Unsupervised Person Re-identification by Soft Multi-label Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 2148–2157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Camera Style Adaptation for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 172–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ergys, R.; Francesco, S.; Roger, Z.; Rita, C.; Carlo, T. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2285–2294. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, S.W. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 480–496. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhao, R.; Xiao, T.; Wang, X. Deepreid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 27th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), OhioComp, DC, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Li, H.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X. Learning deep feature representations with domain guided dropout for person reidentification. In Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1249–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Person re-identificaiton by multi-channel parts-based cnn with improved triplet loss function. In Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1335–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Chen, M.C.; Gu, X.; Zhu, S.; Tan, P. Batch DropBlock Network for Person Re-identification and Beyond. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Systems, Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–25 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Michela, F.; Loris, B.; Alessandro, P.; Vittorio, M.; Marco, C. Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tetsu, M.; Takahiro, O.; Einoshin, S.; Yoichi, S. Hierarchical gaussian descriptor for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Song, M.; Tao, D.; Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; Bu, J. Semi-supervised coupled dictionary learning for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 27th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), OhioComp, DC, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 3550–3557. [Google Scholar]
- Elyor, K.; Tao, X.; Shaogang, G. Dictionary learning with iterative laplacian regularisation for unsupervised person re-identification. Brit. Mac. Vis. Confer. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyor, K.; Tao, X.; Zhenyong, F.; Shaogang, G. Person re-identification by unsupervised l1 graph learning. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 178–195. [Google Scholar]
- Hehe, F.; Liang, Z.; Yi, Y. Unsupervised person re-identification: Clustering and fine-tuning. Trans. Pat. Ana. Mac. Intel. 2017, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yifan, S.; Liang, Z.; Weijian, D.; Shengjin, W. Svdnet for pedestrian retrieval. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3800–3808. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, J. Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person reidentification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Xing, J.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Pose-driven deep convolutional model for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3960–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Huang, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y. Pose invariant embedding for deep person re-identification. Trans. Imag. Process. 2017, 4500–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yu, H.-X.; Wu, A.; Zheng, W.-S. Patch-based Discriminative Feature Learning for Unsupervised Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3633–3642. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, M.; Raj, B.; Song, L. Sphereface: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Volume 9911, pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).