Abstract
Advancing the background-subtraction method in dynamic scenes is an ongoing timely goal for many researchers. Recently, background subtraction methods have been developed with deep convolutional features, which have improved their performance. However, most of these deep methods are supervised, only available for a certain scene, and have high computational cost. In contrast, the traditional background subtraction methods have low computational costs and can be applied to general scenes. Therefore, in this paper, we propose an unsupervised and concise method based on the features learned from a deep convolutional neural network to refine the traditional background subtraction methods. For the proposed method, the low-level features of an input image are extracted from the lower layer of a pretrained convolutional neural network, and the main features are retained to further establish the dynamic background model. The evaluation of the experiments on dynamic scenes demonstrates that the proposed method significantly improves the performance of traditional background subtraction methods.
1. Introduction
Background subtraction methods are widely applied in the realm of computer vision applications, for example, object tracking [1], moving object detection [2], intelligent video surveillance [3], and human–computer interaction [4]. Detailed overviews of background subtraction methods are available in [5,6]. In the past decade, several traditional background subtraction methods have been developed to segment foreground objects from the background in various video scenes. A parametric probabilistic background model, the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) [7], takes advantage of multiple normal distributions to fit the changes of pixels in order to deal with dynamic backgrounds, such as slow-moving objects, swaying trees, and water rippling. The Kernel density estimation (KDE) [8], a widely used nonparametric background method, estimates the distribution of pixels directly from the previously observed data without making any assumptions of the underlying distribution. Barnich et al. proposed using the visual background extractor (ViBe) method [9] for a sample-based background model. This method establishes the background model by aggregating previous input pixel information. The ViBe method adopts a stochastic renewal strategy for the phases of estimating and updating the background model and assumes that the information between adjacent pixels is transmitted [10]. Similarly, the pixel-based adaptive segmenter (PBAS) [11], which models the background by a history of recently observed pixel values, is also a nonparametric background modeling paradigm that introduces cybernetics to update threshold and background adaptively. The procedure for foreground detection by PBAS is similar to that by ViBe. Inspired by the low-cost and highly-efficient ViBe method, St-Charles et al. presented the local binary similarity segmenter (LOBSTER) [12] method for background subtraction, which uses a spatiotemporal binary similarity descriptor instead of relying solely on pixel intensities as its core component. The SuBSENSE method was proposed by St-Charles [13]. This method adopts the principle of sample consistency and feedback mechanism, and therefore the background model adapts to the diversity of a complex background. The fundamental idea of these traditional methods is as follows: First, establish a statistical background model with historical data. Subsequently, calculate the defined distance between a current pixel and the background. Once the pixel deviates from the background obviously, a foreground pixel is confirmed. Meanwhile, continue running the background maintenance to continuously update the background model. These methods have been widely used for detecting moving objects and they have achieved impressive results.
The robust principal component analysis (RPCA) is a popular method used in background models [14]. In models using this method, the structure of the video is decomposed into low-rank and sparse matrices, which provide a suitable framework to separate moving objects from the background. Bouwmans [15] reviewed various models based on RPCA. Recently, inspired by the impressive achievement of deep learning, some researchers applied deep neural networks for background subtraction [16]. Braham and Van Droogenbroeck [17] made use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to deal with the scene-specific problem of background subtraction, naming their model ConvNet, where the network architecture was inspired by the LeNet-5 network [18]. Their model consists of four phases: using a time median operation to extract gray background images from multiple initialization frames, generating the dataset for a specific scene, training the network, and background subtraction. In ConvNet, input image patches and corresponding background image patches are fed to the network to predict the probability of foreground pixels. Following this fundamental idea, Babaee et al. [19] trained a single CNN using various video scenes from the CD2014 dataset [20] to perform segmentation of the video sequences. Baustita et al. [21] applied a simple CNN for vehicle detection. Similarly, the input of the CNN is the observed patch image and the corresponding background patch image. The fully connected layer in the traditional convolutional network is replaced by the convolutional layer, which reduces the amount of computation and the architecture of fully convolutional networks (FCNs) can be trained end-to-end. Encouraged by the recent success of transfer learning and FCNs [22] for semantic segmentation, researchers leveraged FCNs to build background modeling. Zeng and Zhu [23] proposed a multiscale fully convolutional network architecture which utilized different layer features for background subtraction. Cinelli [24] varied different features of the ResNet [25] architectures to optimize them for background or foreground separation by exploring the advantages of FCNs. Yang et al. [26] also improved FCNs by using three atrous convolution branches with a different dilate to extract spatial information from different neighborhoods of pixels. Wang et al. presented a convolutional neural network based on a multiscale cascade [27]. In this network, a multiscale CNN model with cascade structure is adopted to model the correlation between adjacent pixels to enhance spatial correlation. The FgSegNet-M20 method [28] is based on a triplet CNN and a transposed convolutional neural network. This method uses the VGG-16 Net to embed an image in multiple scales into the feature space, and, in the decoder part, it uses a transposed convolutional network to learn a mapping from feature space to image space. Subsequent research resulted in the proposed FgSegNet-S and FgSegNet-V2. Li et al. [29] judged the location of targets in surveillance scenes using an adaptive deep neural network (ADCNN) method. Zhang et al. [30] designed a deep learned features based block-wise method with a binary spatiotemporal background model. Zhao et al. designed a deep pixel distribution learning model (DPDL) for background subtraction [31]. Lim et al. used an encoder–decoder-structured convolutional neural network for background subtraction [32]. Wang et al. used BGSNet-D to detect moving objects in the scenes where color information was not available [33]. Yu et al. [34] combined background subtraction and CNN for moving objects detection in pumping-unit scene.
The aforementioned deep neural network methods have contributed to background subtraction. However, it is evident that they have encountered several limitations. One limitation, for example, is that most of the learning algorithms are supervised methods that are merely used to deal with scene-specific situations. Therefore, for these methods, many historical video data are needed first to train the background model, and then the moving object is detected in the new video. Moreover, the trained model only detects the known targets in the category of the training set, which is an even more stringent limitation of these methods. When the unknown objects in the category appear in the current video scene, it produces incorrect judgments. Another limitation is that many of the algorithms have extremely high computational costs. For example, the deep convolutional neural network is in high demand as a computing resource, and often includes tens of millions of parameters; therefore, the computations required to train this network take a great deal of time and money. Some methods adopt an approach based on patch-wise, a method that segments an image into many patches, and then convolutes each patch separately. However, this approach generates a lot of redundancy. Some other methods adopt a fully convolutional network architecture in semantic segmentation for each pixel. Each pixel is divided into two categories: the foreground and the background. However, the computation load is still very large. Likewise, the storage space required by CNN is also relatively large. In comparison, a traditional background subtraction method (BGS) is computed with a lower computational load. Table 1 shows an overview of these methods.

Table 1.
An overview of background subtraction methods.
In this paper, a novel framework based on CNN is proposed to improve background subtraction. In the proposed method, the lower convolution layers are used to extract the general features of a video. These general features usually have multiple channels, and, in each channel, there is a lot of redundant information. A few of these channels contain the main information of the image, thus these main channels are applied to background subtraction, which not only reduces the amount of data processing, but also removes the redundant interference in the scene. Using a traditional background subtraction method to process the main features that are extracted by CNN further improves the performance of the background subtraction method. In comparison to the existing deep neural network methods of background subtraction, there are three advantages of the proposed method. First, the proposed method is a general unsupervised method, and there is no need to train models based on the historical data of specific scenarios. Second, the proposed method requires only a few calculations. Third, only one of the lower layers of the pretrained CNN is used to extract the general features of videos.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents a detailed account of the proposed method. Section 3 describes the profound experiments on a dataset of surveillance videos that verified the validity and feasibility of the proposed method. Finally, Section 4 provides some conclusions.
2. The Proposed Method
The outline of the proposed method is illustrated in Figure 1. The input image I is fed into a pretrained convolution layer to obtain a series of convolution feature images F, and then a few feature images that are closest to the original image are selected to merge a new convolution feature image . Subsequently, background subtraction methods are used to deal with and obtain the foreground image (FG).
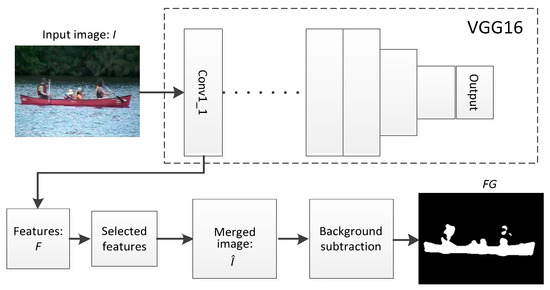
Figure 1.
The framework of the proposed method.
It is well known that CNN has made great achievements in computer vision, image processing, and other fields. Jason et al. [36] showed that the features learned by the CNN are hierarchical. Basically, general features, such as color, edge, line, and so on, are extracted from the lower layers of the neural network. More advanced specific features are extracted from the deep layers; however, these specific features only present the scene features in the corresponding training set, and they cannot be used in other scenarios. On the contrary, the lower layers are used to extract the underlying common features of other scenes. Our framework was based on the VGG16 network [37] architecture trained on ImageNet. The first convolution layer, conv1_1, of the VGG16 is applied to extract the general features of the images. The detailed configuration parameters of the conv1_1 layer used in this study are shown in Table 2. The size of the input image was W × H × 3, where W is the width and H is the height of the image. The feature images with 64 channels were generated by conv1_1, and therefore the output size was W × H × 64.

Table 2.
Parameter configuration of conv1_1 layer.
The conv1_1 captured low-level information and retained higher spatial resolution. For example, the input image I was processed by the convolution layer conv1_1 of the VGG16. Then, the feature image (F) was obtained.
Conv is the convolution operation with a kernel size of 3 × 3 and the stride is 1. F contains 64 convolution feature images, and the resolution of each convolution feature image is the same as the input image. The feature images are shown in Figure 2. Our observations of these convolution feature images show that some features take the form of noise-like images, while other features reflect the major objects of the input image, such as a canoe and people. Based on these observations, the main convolution features that best represent the input image are reserved, while other features that have a low correlation with the input image are abandoned. Consequently, some irrelevant interference factors are removed from the input image. The performance of the background subtraction method is further refined by using the reserved convolution features instead of the corresponding input images.
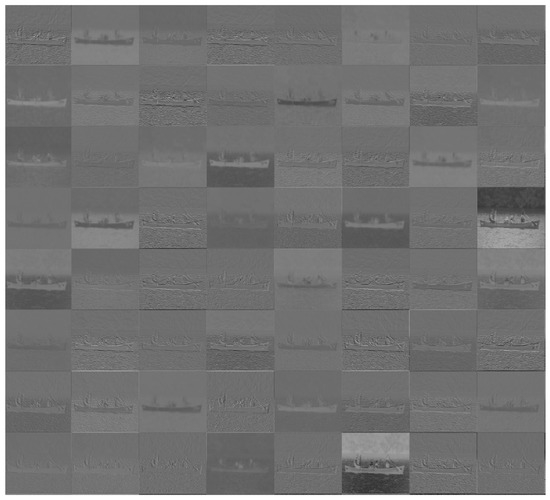
Figure 2.
CNN features of the input image extracted by conv1_1 of the VGG16.
To reduce the complexity of the computations, the two convolution feature images which have the strongest correlation with the input image are extracted to merge a new merging image. This new image is fed into the background subtraction method and replaces the input image. To evaluate the correlation strength between the convolution feature image and the input image, the value of the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is calculated for the convolution feature image and the input image. The higher is the PSNR value, the stronger is the correlation between the convolution image and the input image.
where is the maximum pixel value of the input image and the data in this study are in the range of 0–1. is 1, and MSE is the mean square error between the grayscale of input image I and the convolution feature .
where H and W are the height and width of the image, respectively; and k = 1, 2, …, 64 denotes the number of the convolution image.
The two feature images with the maximum values of PSNR are shown in Figure 3. The indices are the 32nd and 26th in Figure 2, respectively. In the same scene, the feature distributions extracted by the convolution layer for different video frames are the same. The ranking of the PSNR values which are obtained from one input frame are used as the indices of the convolution feature of the subsequent frames. Therefore, the indices of the two features with maximal PSNR only need to be computed once. Two convolution feature images of the maximum PSNR value are merged into a new image and the formula is as follows:
where , and and are the two feature images with the maximum values of PSNR. Obviously, is normalized to a range 0–1.

Figure 3.
Two CNN features with the maximal PSNR.
Once the synthetic image is obtained, the foreground binary image (FG) is finally obtained by the traditional background subtraction method.
where i and j are the position coordinates of the pixels; ; and BGS is a background subtraction method.
Algorithm 1 depicts the overall procedure of the proposed method.
| Algorithm 1: The proposed method. |
| Input: : input image of video, t = 1, 2, …, L, L is the frame number of the video; Output: : the foreground of the input image. . Calculate the PSNR values between and the grayscale image of . Find the numbers of and of . While Do and Calculate using (4) Obtain the foreground image using Equation (5) |
3. Experiments
To verify the performance of the proposed method, the dynamic background videos from CDnet [20] were used to test the method. The CDnet is an expanded change detection benchmark dataset, which provides a realistic, diverse set of videos and covers a wide range of detection challenges. The main advantage of this dataset is that it provides the ground truths for all video frames. Therefore, the dataset can be used to quantitatively evaluate the performance of various background subtraction methods and rank them. The category of dynamic background contains six videos depicting outdoor scenes with strong background motion. The details of this category are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Dynamic background videos.
The performance of the background modeling methods was evaluated at the pixel level. The background modeling methods classified pixels into foreground or background. The following six metrics were used to evaluate the performance of the background modeling methods:
where TP is the number of correctly detected foreground pixels, TN is the number of correctly detected background pixels, FP is the number of background pixels that are incorrectly marked as the foreground pixel, and FN is the number of foreground pixels that are incorrectly marked as the background pixels. F-measure is the comprehensive evaluation index which represents the weighted harmonic mean and ranges between 0 and 1. Obviously, the higher are recall, precision and F-measure, the better is the performance, while the lower are FPR, FNR, and PWC, the better is the performance.
We applied the proposed framework to the following traditional background modeling methods: GMM, SuBSENSE, PBAS, KDE, LOBSTER, and ViBe. Details for the implementation of these traditional methods are available in the BGSlibrary [38], and, consequently, these implementations were used in this study. Figure 4 presents the refinements of the traditional background subtraction methods using the proposed method for foreground detection in dynamic scenes. It is noteworthy that the convolution feature methods (BGScon) further suppressed the disturbance of dynamic background such as branch swaying, water ripple, and so on as compared with the corresponding background subtraction methods (BGS).

Figure 4.
Refinements of the background-subtraction methods on dynamic background.
Comparisons of the performance between these background subtraction methods (BGS) and the corresponding convolution feature methods (BGScon) are shown in Table 4 and illustrates that the convolution feature framework improves the performance of background subtraction methods to some extent.

Table 4.
Comparisons between BGS and BGScon by the proposed method.
To show the refinements of the traditional background subtraction methods by the proposed framework intuitively, the average values and standard deviations for F-measure, which are general international standards for binary classification, are presented in Figure 5. In the figure, the blue bars are the F-measure values of traditional background modeling methods while the red bars are the corresponding F-measure values of the convolution feature methods. The KDE method had the highest performance improvement, with an increase of more than 160%. GMM’s performance was improved by 42%, ViBe by 21%, LOBSTER by 12%, PBAS by 9%, and SuBSENSE by 0.1%. SuBSENSE, which is a state-of-the-art BGS method, had very high performance and surpassed most of the other unsupervised BGS methods. When the proposed method was applied, the performances of other background subtraction methods, with the exception of SuBSENSE, improved significantly.
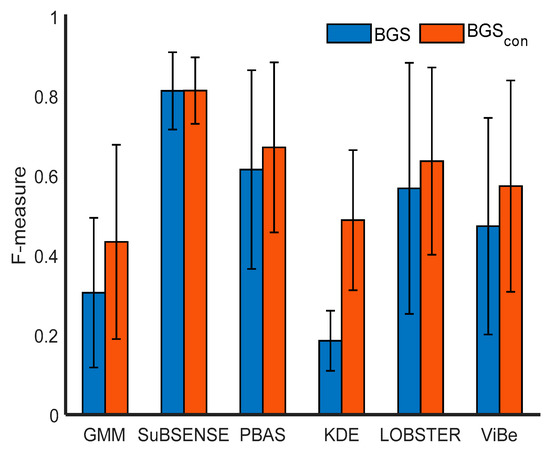
Figure 5.
Comparisons of the increased F-measure values.
To verify the ability of the proposed method, Neural Response Mixture (NeRM) [39] was selected for comparison. NeRM takes advantage of rich deep features extracted from the neural responses of an efficient, stochastically-formed deep neural network for constructing Gaussian mixture models to detect motion in a scene. Table 5 shows the improvement ratio of GMM by NeRM and the proposed method respectively, in which the higher the ratio, the better the performance. The most representative F-measure evaluation metric of the proposed method is better.

Table 5.
Comparisons of improvement ratio of GMM.
For further evaluating the performance of the proposed method, shadow videos are used to test. Shadow is composed of six videos with both strong and soft moving and cast shadows [20]. Table 6 shows the details of this category. The refinement results are illustrated in Figure 6. Table 7 lists the quantitative comparison results. As shown in Table 7, GMM, KDE, PBAS, LOBSTER and ViBe methods were refined in a certain degree. Since SuBSENSE had high performance, this method was not improved.

Table 6.
Shadow videos.

Figure 6.
Refinements of the background-subtraction methods on shadow videos.

Table 7.
Comparisons between BGS and BGScon by the proposed method.
Since the PSNR is simple and easy to realize, it was adopted to determine the feature images involved in the proposed method in our experiments. Structural similarity index measure (SSIM) is another well-known objective image quality metric. A simple analytical link exists between the PSNR and the SSIM and the PSNR is more sensitive to Gaussian noise than the SSIM [40]. The SSIM used to choose the convolution feature images was evaluated in the experiment as PSNR. Table 8 shows the comparison results. As can been observed, the PSNR metric was better than the SSIM.

Table 8.
Comparisons of PSNR and SSIM for GMM on dynamic scenes.
The input images of dynamic scenes usually contain a large amount of redundant information that results in deterioration of background modeling performance while the original images of a video are used to model the background. The convolution of CNN, which was pretrained on ImageNet, extracted the underlying features of the input image. The dynamic redundancy features were abandoned, and the main features were merged into a new input image. On the basis of the new image, the background model, which was built by the BGS method, had better performance. In the proposed framework, only one lower layer convolution of CNN was used. Compared with a whole CNN network, which is often hundreds of megabytes in size, one convolution layer is only several megabytes. Therefore, the performance of the traditional background subtraction method is further improved without increasing computational load. As an example, for an input image of 320 × 240 in size, the memory required to extract the convolution feature from the input image by applying the conv1_1 layer of the VGG16 is 320 × 240 × 64 = 4.9 M, and the weight is 3 × 3 × 3 × 64 = 1728.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we present an unsupervised, simple and universal framework that takes advantage of lower layer features of pretrained CNN for refinements of dynamic background subtraction methods. The framework extracts the low-level features of input images and merges the representation features of the input image into a new feature image. The background subtraction methods produce more accurate foreground object detection results by modeling the key features. To verify the performance of the proposed method, the dynamic background database was used to carry out experiments. Experiments showed that the proposed method significantly refined the traditional background subtraction methods for dynamic scenes.
Author Contributions
T.Y. contributed to the paper writing and revision. J.Y. and W.L. made some supplements and revision. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (61876029).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Suresh, S.; Deepak, P.; Chitra, K. An efficient low cost background subtraction method to extract foreground object during human tracking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Circuits, Power and Computing Technologies, Nagercoil, India, 20–21 March 2014; pp. 1432–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, C.; Yu, W. Moving object detection by detecting contiguous outliers in the low-rank representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unzueta, L.; Nieto, M.; Cortés, A.; Barandiaran, J.; Otaegui, O.; Sánchez, P. Adaptive multi-cue background subtraction for robust vehicle counting and classification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 13, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Li, S.-Y. Algorithm and architecture design of human-machine interaction in foreground object detection with dynamic scene. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2013, 23, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmans, T. Traditional and recent approaches in background modeling for foreground detection: An overview. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2014, 11, 31–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobral, A.; Vacavant, A. A comprehensive review of background subtraction algorithms evaluated with synthetic and real videos. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2014, 122, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, C.; Grimson, W.E.L. Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 1999, 2, 246–252. [Google Scholar]
- Elgammal, A.; Duraiswami, R.; Harwood, D.; Davis, L.S. Background and foreground modeling using nonparametric kernel density estimation for visual surveillance. Proc. IEEE 2002, 90, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnich, O.; Droogenbroeck, M.V. ViBe: A universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droogenbroeck, M.V.; Paquot, O. Background subtraction: Experiments and improvements for ViBe. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, M.; Tiefenbacher, P.; Rigoll, G. Background segmentation with feedback: The pixel-based adaptive segmenter. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- St-Charles, P.-L.; Bilodeau, G.-A. Improving background subtraction using local binary similarity patterns. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA, 24–26 March 2014; pp. 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- St-Charles, P.-L.; Bilodeau, G.-A.; Bergevin, R. Flexible background subtraction with selfbalanced local sensitivity? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Candes, E.J.; Li, X.; Ma, Y. Robust principal component analysis. J. ACM 2011, 58, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmans, T.; Sobral, A.; Javed, S.; Jung, S.K.; Zahzah, E. Decomposition into low-rank plus additive matrices for background/foreground separation: A review for a comparative evaluation with a large-scale dataset. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2017, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmans, T.; Javed, S.; Sultana, M.; Jung, S.K. Deep neural network concepts for background subtraction: A systematic review and comparative evaluation. Neural Netw. 2019, 117, 8–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braham, M.; Droogenbroeck, M.V. Deep background subtraction with scene-specific convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), Bratislava, Slovakia, 23–25 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaee, M.; Dinh, D.T.; Rigoll, G. A deep convolutional neural network for video sequence background subtraction. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 76, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jodoin, P.-M.; Porikli, F.; Janusz, K.; Benezeth, Y.; Ishwar, P. Cdnet 2014: An expanded change detection benchmark datase. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, C.M.; Dy, C.A.; Manalac, M.I.; Orbe, R.A.; Cordel, M. Convolutional neural network for vehicle detection in low resolution traffic videos. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), Bali, Indonesia, 9–11 May 2016; pp. 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, D.; Zhu, M. Background subtraction using multiscale fully convolutional network. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 16010–16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, L.P. Anomaly Detection in Surveillance Videos Using Deep Residual Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, J. Deep background modeling using fully convolutional network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Jodoin, P.-M. Interactive deep learning method for segmenting moving objects. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 96, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.A.; Keles, H.Y. Foreground segmentation using a triplet convolutional neural network for multiscale feature encoding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.02225. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ye, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C. Adaptive deep convolutional neural networks for scene-specific object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2017, 16, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, F.; Zhao, L. Deep learning driven blockwise moving object detection with binary scene modeling. Neurocomputing 2015, 168, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cham, T.-J.; Ren, X.; Cai, J.; Zhu, H. Background subtraction based on deep pixel distribution learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), San Diego, CA, USA, 23–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, K.; Jang, W.-D.; Kim, C.-S. Background subtraction using encoder-decoder structured convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Lecce, Italy, 29 August–1 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Dong, X.; Zhao, P.; Feng, X. Background subtraction on depth videos with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Yang, J.; Lu, W. Combining Background Subtraction and Convolutional Neural Network for Anomaly Detection in Pumping-Unit Surveillance. Algorithms 2019, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Zhu, M.; Kuijper, A. Combining background subtraction algorithms with convolutional neural network. J. Electron. Imaging 2019, 28, 013011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosinski, J.; Clune, J.; Bengio, Y.; Lipson, H. How transferable are features in deep neural networks? In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 3320–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for largescale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Sobral, A. Bgslibrary: An opencv c++ background subtraction library. In Proceedings of the Ix Workshop De Visao Computacional, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 3–5 June 2013; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee, M.J.; Siva, P.; Fieguth, P.; Wong, A. Embedded motion detection via neural response mixture background modeling. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 837–844. [Google Scholar]
- Hore, A.; Ziou, D. Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).