Learning Output Reference Model Tracking for Higher-Order Nonlinear Systems with Unknown Dynamics †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Output Model Reference Control for Unknown Dynamics Nonlinear Processes
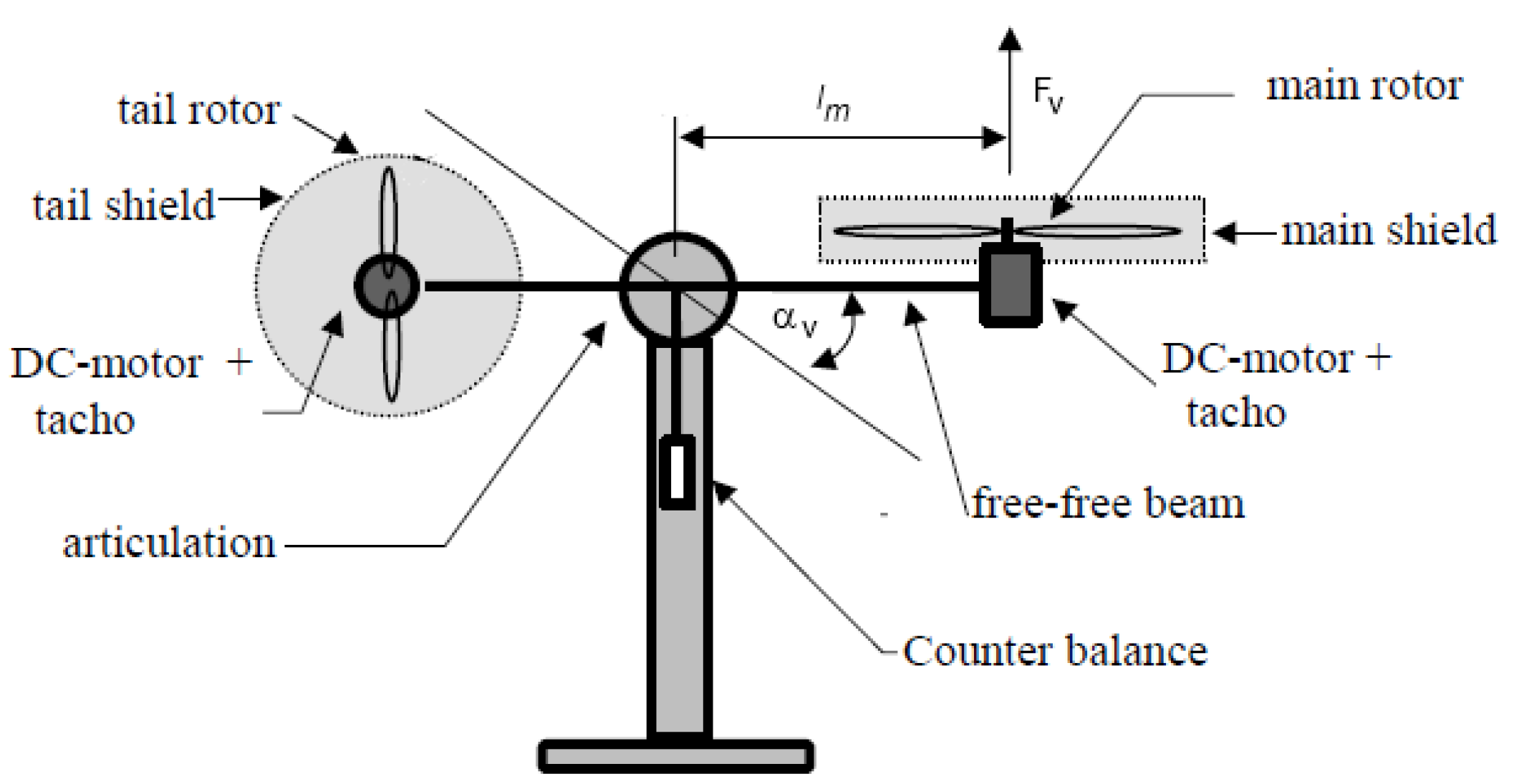
2.1. The Process
2.2. Output Reference Model Control Problem Definition
3. Solution to the ORM Tracking Problem
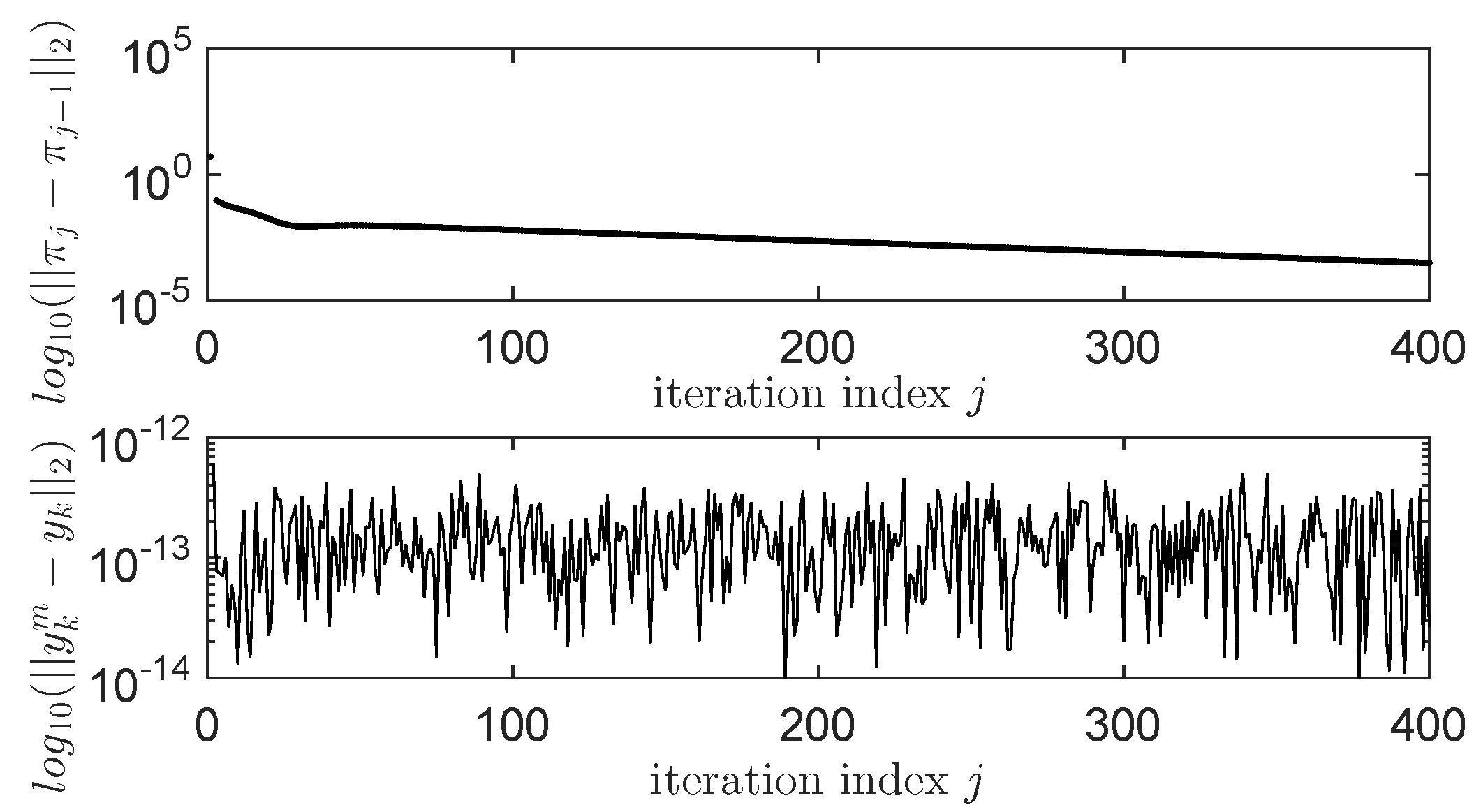
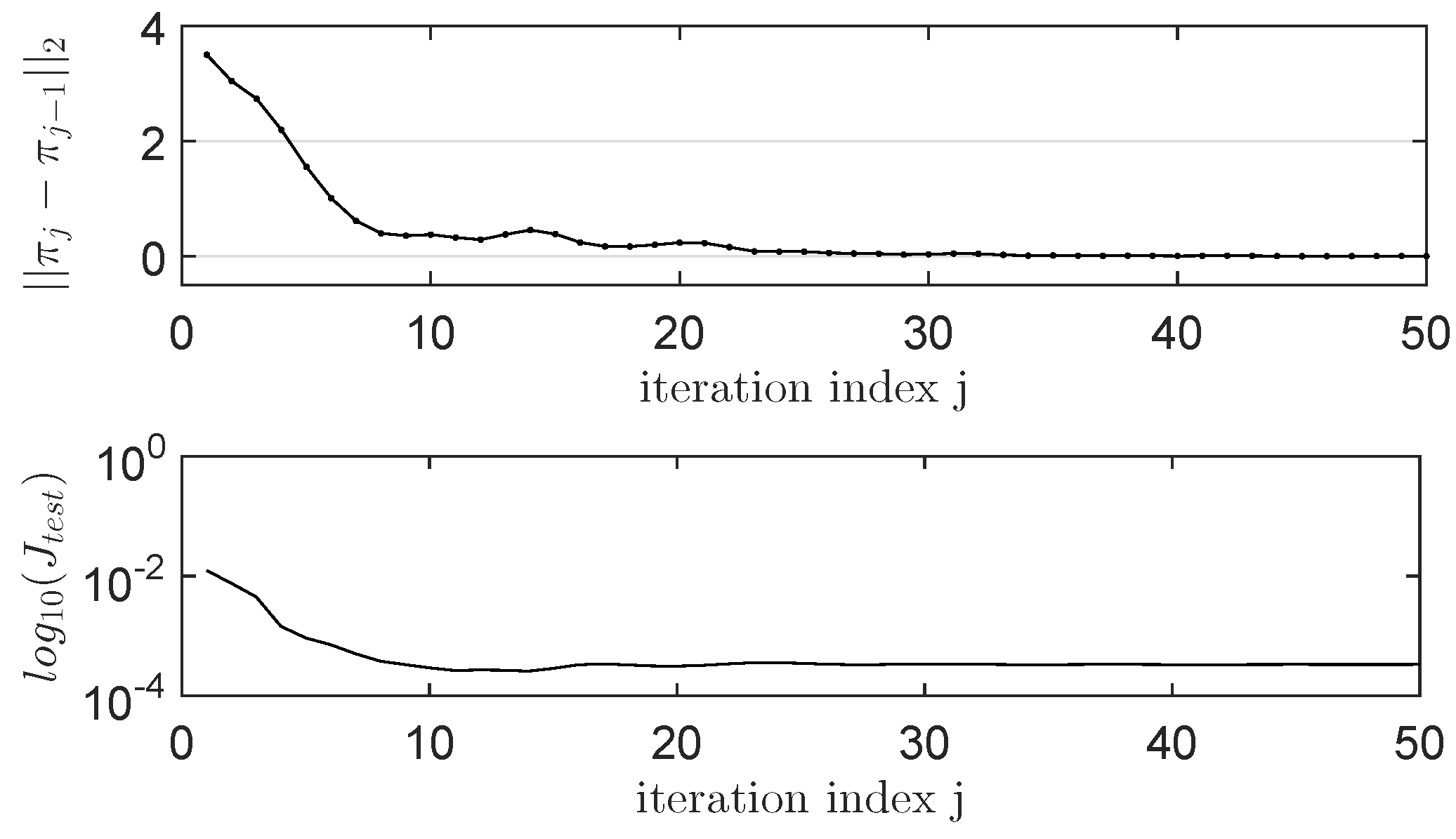
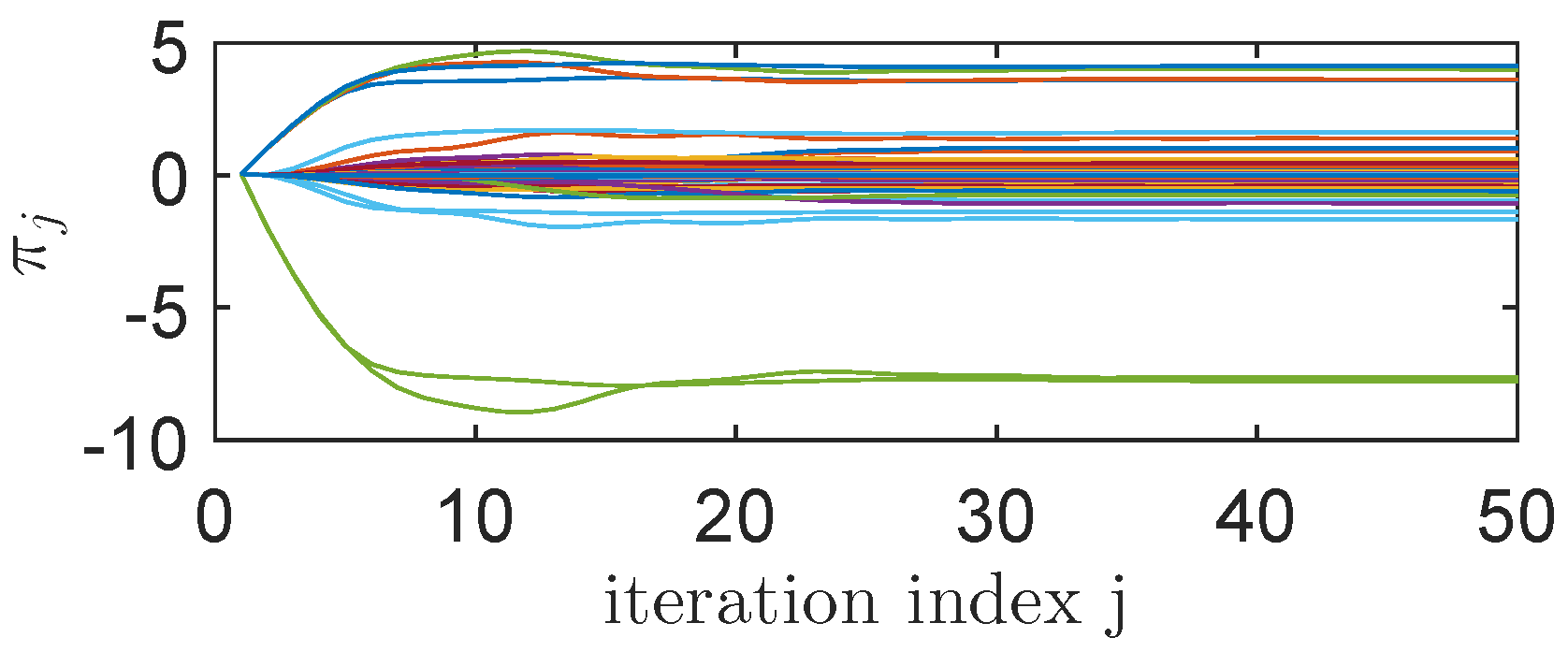
IMF-AVI Convergence Analysis with Approximation Errors for ORM Tracking
| Algorithm 1 VI-based Q-learning. |
| S1: Initialize controller and the Q-function value to , initialize iteration index |
| S2: Use one step backup equation for the Q-function as in (13) |
| S3: Improve the controller using the Equation (14) |
| S4: Set and repeat steps S2, S3, until convergence |
- (1)
- with an upper bound.
- (2)
- If there exists a solution to (8), then .
- (1)
- {} is a non-decreasing sequence for which holds, and
- (2)
- (2) and .
| Algorithm 2 IMF-AVI. |
| S1: Initialize controller and Q-function value . Initialize iteration |
| S2: Update the approximate Q-function using Equation (24) |
| S3: Improve the approximate controller using Equation (25) |
| S4: Set and repeat steps S2, S3, until convergence |
4. Validation Case Studies
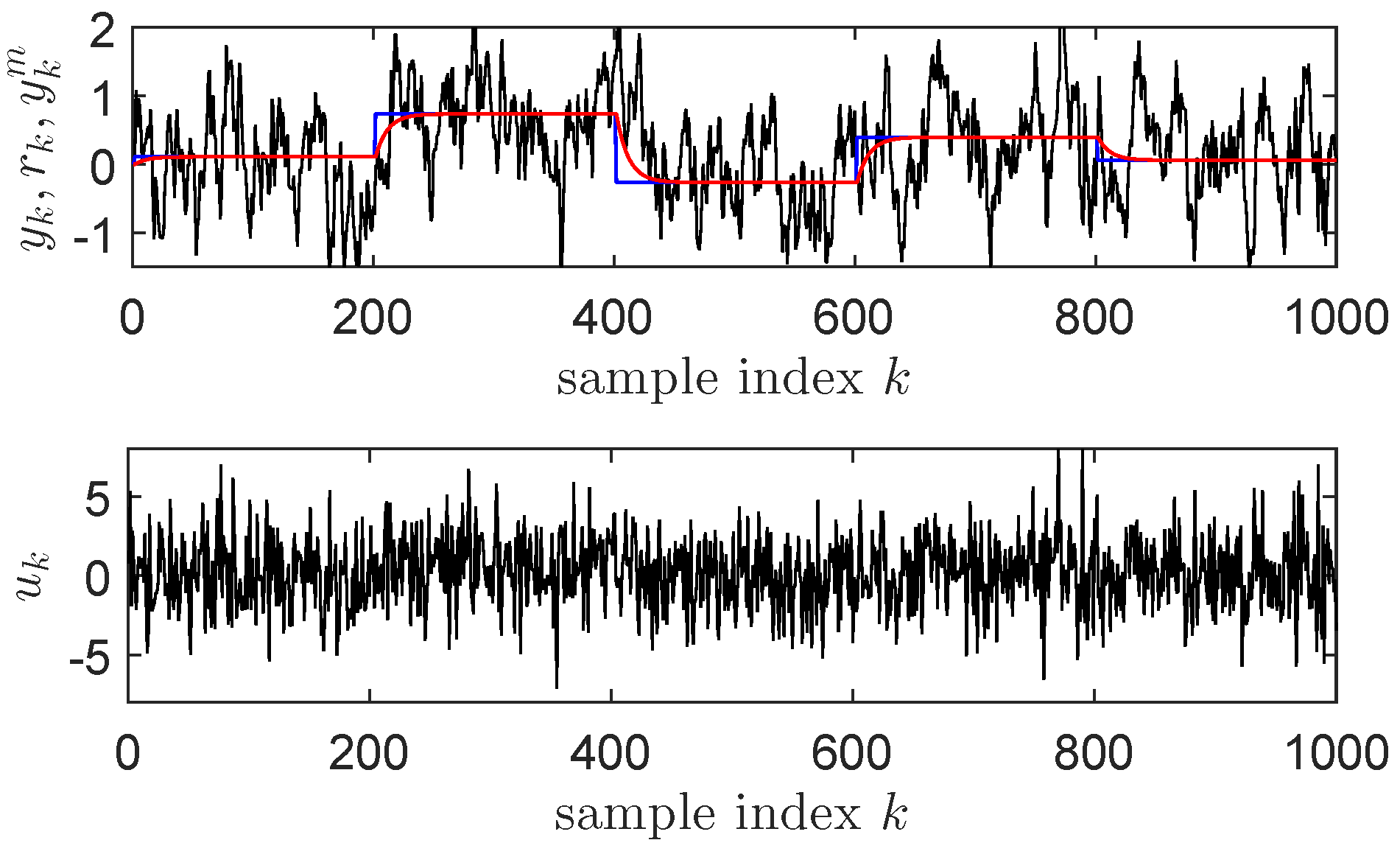
4.1. ORM Tracking for a Linear Process
4.2. IMF-AVI on the Nonlinear TITOAS Aerodynamic System
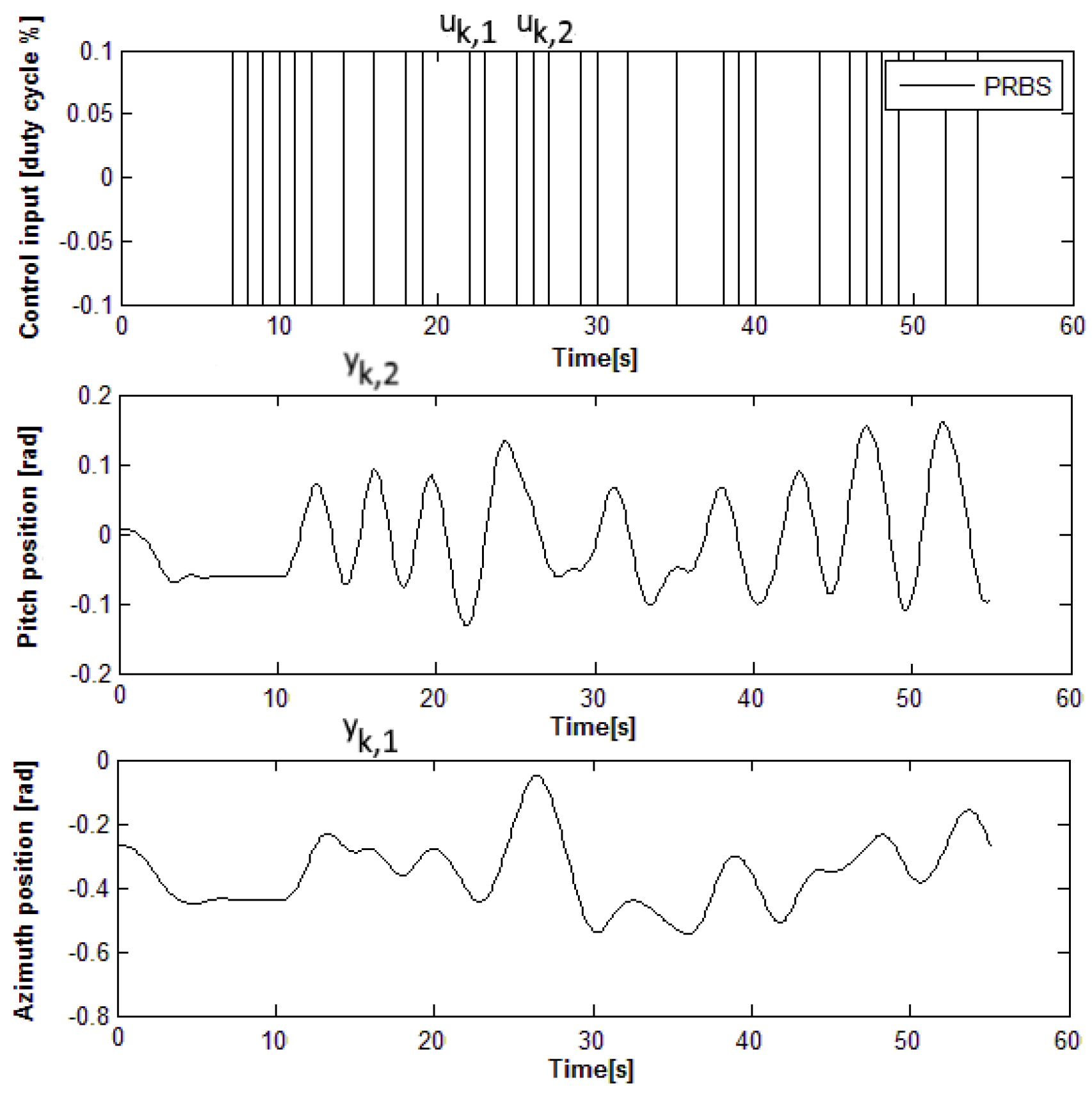
4.3. Initial Controller with Model-Free VRFT
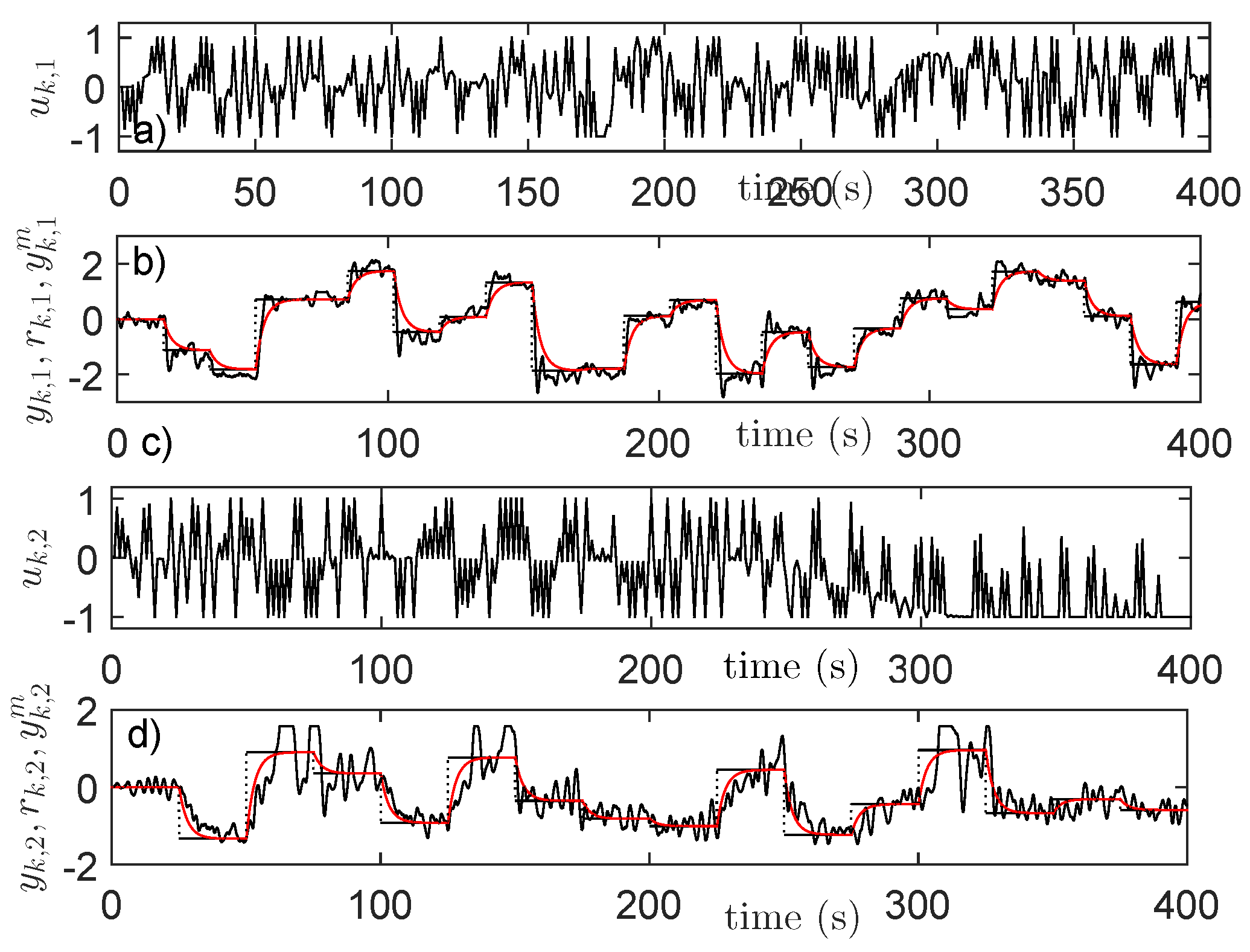
4.4. Input–State–Output Data Collection
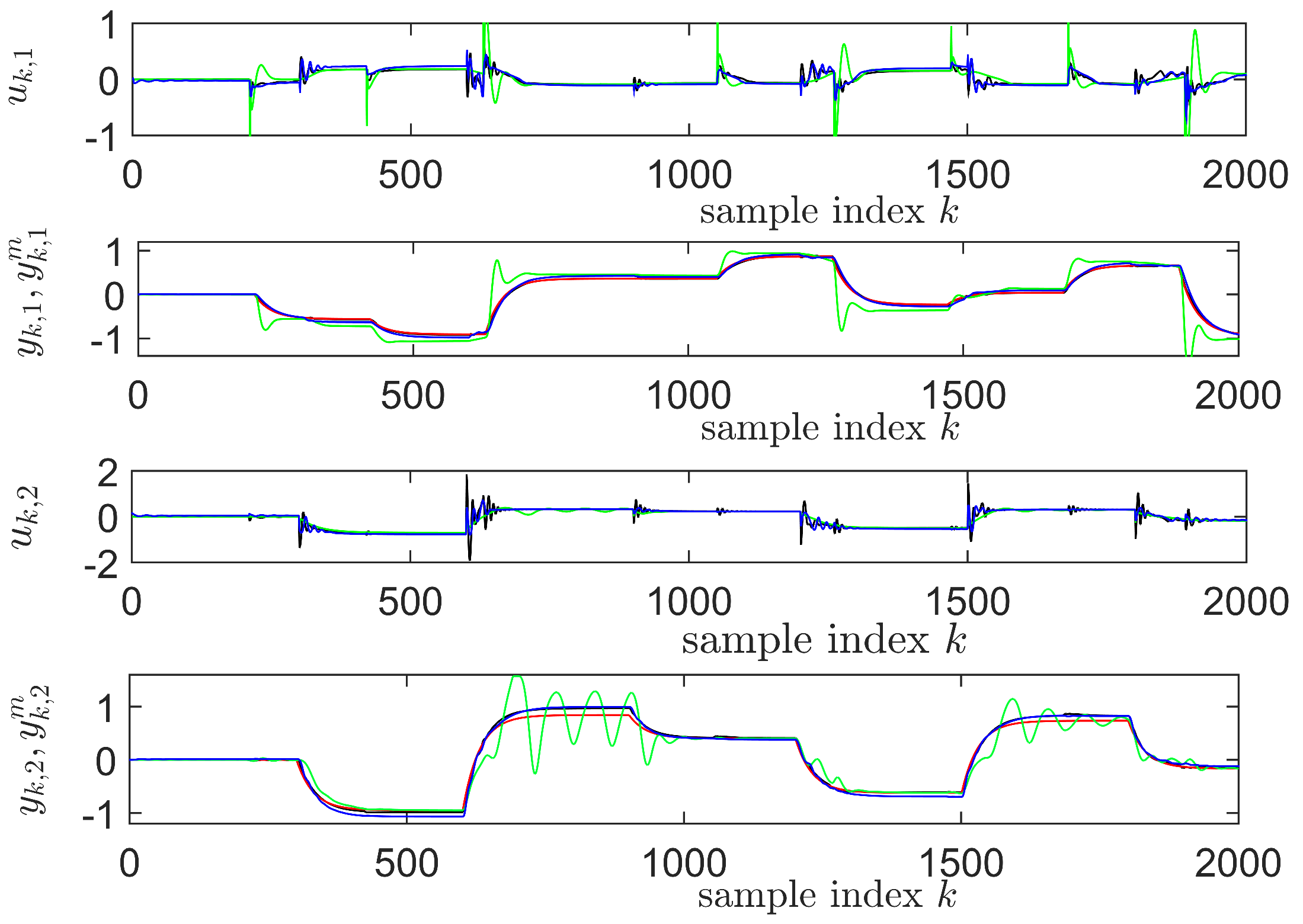
4.5. Learning State-Feedback Controllers with Linearly Parameterized IMF-AVI
4.6. Learning State-Feedback Controllers with Nonlinearly Parameterized IMF-AVI Using NNs
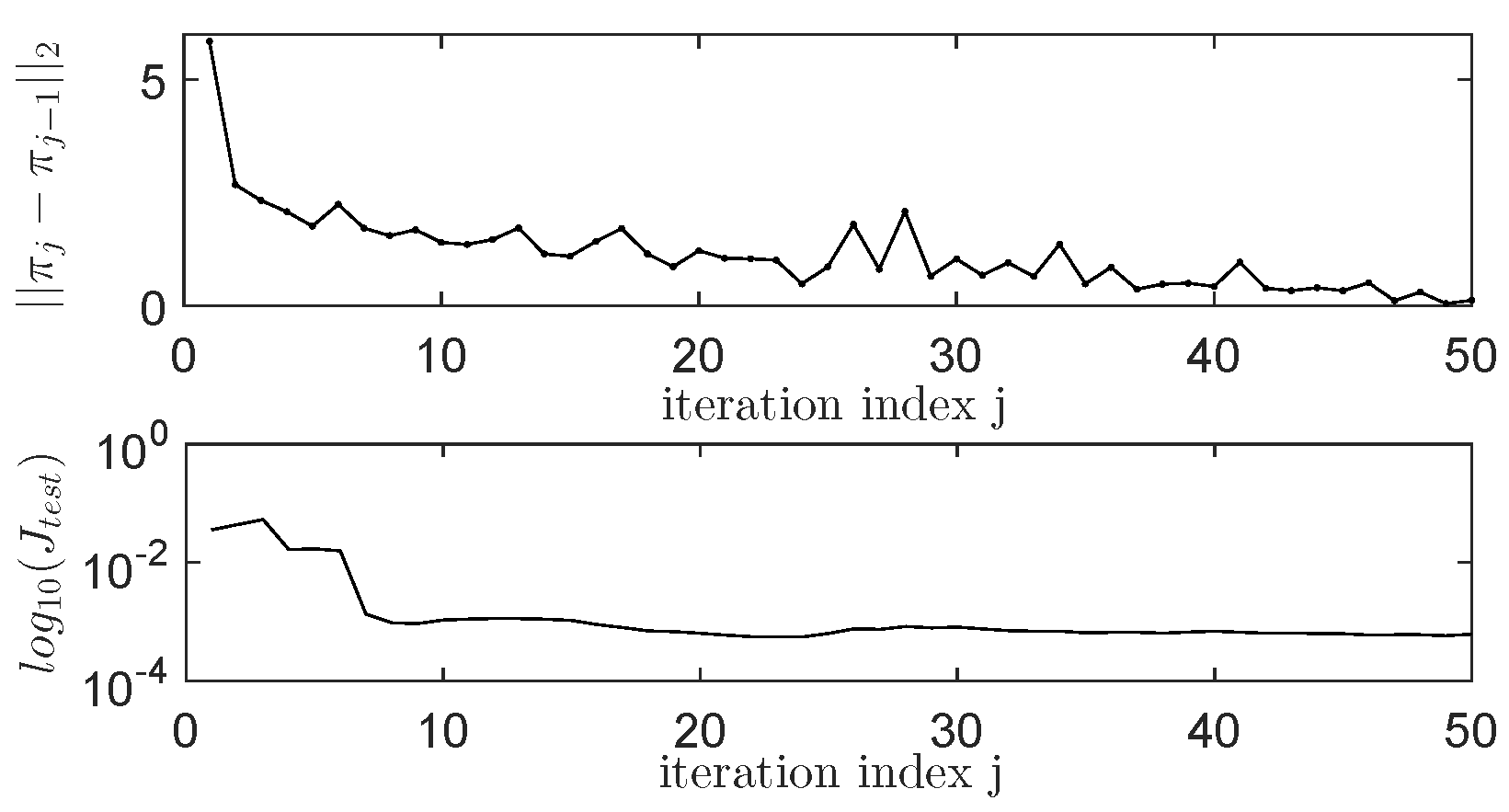
4.7. Comments on the Obtained Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radac, M.B.; Precup, R.E.; Petriu, E.M. Model-free primitive-based iterative learning control approach to trajectory tracking of MIMO systems with experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsekas, D.P.; Tsitsiklis, J.N. Neuro-Dynamic Programming; Athena Scientific: Belmont, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D. Adaptive dynamic programming: an introduction. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2009, 4, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.; Vrabie, D.; Vamvoudakis, K.G. Reinforcement learning and feedback control: Using natural decision methods to design optimal adaptive controllers. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2012, 32, 76–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, F.; Vrabie, D.; Vamvoudakis, K.G. Reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for feedback control. IEEE Circ. Syst. Mag. 2009, 9, 76–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Cox, C.J.; Lendaris, G.G.; Saeks, R. Adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2002, 32, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiumarsi, B.; Lewis, F.L.; Naghibi-Sistani, M.B.; Karimpour, A. Optimal tracking control of unknown discrete-time linear systems using input–output measured data. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2015, 45, 2270–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiumarsi, B.; Lewis, F.L.; Modares, H.; Karimpour, A.; Naghibi-Sistani, M.B. Reinforcement Q-learning for optimal tracking control of linear discrete-time systems with unknown dynamics. Automatica 2014, 50, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.B.; Precup, R.E.; Roman, R.C. Model-free control performance improvement using virtual reference feedback tuning and reinforcement Q-learning. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2017, 48, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, T.; Radac, M.B. Parameterized value iteration for output reference model tracking of a high order nonlinear aerodynamic system. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Akko, Israel, 1–4 July 2019; pp. 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, D.; Geurts, P.; Wehenkel, L. Tree-based batch mode reinforcement learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2005, 6, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, R.; Riedmiller, M. Reinforcement learning in feedback control. Challenges and benchmarks from technical process control. Mach. Learn. 2011, 84, 137–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, B.; Liu, D. A supervised actor critic approach for adaptive cruise control. Soft Comput. 2013, 17, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Yang, R.; Li, Y.; Sharma, S. Adaptive neural network control of AUVs with Control input nonlinearities using reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2017, 47, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hou, Z.; Lian, C.; He, H. Online learning control using adaptive critic designs with sparse kernel machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 762–775. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Ni, Z.; Fu, J. A three-network architecture for on-line learning and optimization based on adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing 2012, 78, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modares, H.; Lewis, F.L.; Jiang, Z.P. H∞ Tracking control of completely unknown continuous-time systems via off-policy reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 2550–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Modares, H.; Chai, T.; Lewis, F.L.; Xie, L. Off-policy reinforcement learning for synchronization in multiagent graphical games. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 2434–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsekas, D. Value and policy iterations in optimal control and adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wunsch, D.; Yin, Y. Hamiltonian-driven adaptive dynamic programming for continuous nonlinear dynamical systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalapurkar, R.; Andrews, L.; Walters, P.; Dixon, W.E. Model-based reinforcement learning for infinite horizon approximate optimal tracking. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.B.; Precup, R.E. Data-driven MIMO Model-free reference tracking control with nonlinear state-feedback and fractional order controllers. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 73, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campi, M.C.; Lecchini, A.; Savaresi, S.M. Virtual Reference Feedback Tuning: A direct method for the design of feedback controllers. Automatica 2002, 38, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, H. Iterative Feedback Tuning—An overview. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2002, 16, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, P.; Pipeleers, G.; Swevers, J.L. Model-free iterative learning control for LTI systems and experimental validation on a linear motor test setup. In Proceedings of the 2011 American Control Conference (ACC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 4287–4292. [Google Scholar]
- Radac, M.B.; Precup, R.E. Optimal behavior prediction using a primitive-based data-driven model-free iterative learning control approach. Comput. Ind. 2015, 74, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.; Hou, Z.S.; Jin, S.; Huang, B. An improved data-driven point-to-point ILC using additional on-line control inputs with experimental verification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2017, 49, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouaissa, H.; Fliess, M.; Join, C. On ramp metering: towards a better understanding of ALINEA via model-free control. Int. J. Control 2017, 90, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.S.; Liu, S.; Tian, T. Lazy-learning-based data-driven model-free adaptive predictive control for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 1914–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.B.; Precup, R.E.; Roman, R.C. Data-driven model reference control of MIMO vertical tank systems with model-free VRFT and Q-learning. ISA Trans. 2018, 73, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolder, J.; Kleinendorst, S.; Oomen, T. Data-driven multivariable ILC: enhanced performance by eliminating L and Q filters. Int. J. Robot. Nonlinear Control 2018, 28, 3728–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, R.; Gao, F.; Liu, D. An indirect data-driven method for trajectory tracking control of a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4121–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, B.J.; Noel, M.M. Control of a bioreactor using a new partially supervised reinforcement learning algorithm. J. Proc. Control 2018, 69, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, H.; Armesto, L.; Sala, A. Fitted q-function control methodology based on takagi-sugeno systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Tech. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Fu, H.; Wu, M. Data-driven adaptive dynamic programming for partially observable nonzero-sum games via Q-learning method. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Zhang, Y. Learning-based robust tracking control of quadrotor with time-varying and coupling uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, G.H. Model-free adaptive control design for nonlinear discrete-time processes with reinforcement learning techniques. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2018, 49, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Q. Data-driven iterative feedforward tuning for a wafer stage: A high-order approach based on instrumental variables. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 2019, 66, 3106–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofinas, P.; Dounis, A. Fuzzy Q-learning agent for online tuning of PID controller for DC motor speed control. Algorithms 2018, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E. Three-level hierarchical model-free learning approach to trajectory tracking control. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2016, 55, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E. Data-based two-degree-of-freedom iterative control approach to constrained non-linear systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 2015, 9, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, M.; Clempner, J.B. Measuring the emotional state among interacting agents: A game theory approach using reinforcement learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 97, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.L.; de Souza, S.R.; Souza, M.J.F.; Bazzan, A.L.C. A reinforcement learning-based multi-agent framework applied for solving routing and scheduling problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 131, 148–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E.; Hedrea, E.-L.; Mituletu, I.-C. Data-driven model-free model-reference nonlinear virtual state feedback control from input-output data. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Zadar, Croatia, 19–22 June 2018; pp. 332–338. [Google Scholar]
- Campestrini, L.; Eckhard, D.; Gevers, M.; Bazanella, M. Virtual reference tuning for non-minimum phase plants. Automatica 2011, 47, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tamimi, A.; Lewis, F.L.; Abu-Khalaf, M. Discrete-time nonlinear HJB Solution using approximate dynamic programming: Convergence proof. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Cybern. 2008, 38, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantzer, A. Relaxed dynamic programming in switching systems. IEEE Proc. Control Theory Appl. 2006, 153, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inteco, LTD. Two Rotor Aerodynamical System; User’s Manual; Inteco, LTD: Krakow, Poland, 2007; Available online: http://ee.sharif.edu/~lcsl/lab/Tras_um_PCI.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2019).
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E. Data-driven model-free slip control of anti-lock braking systems using reinforcement Q-learning. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillicrap, T.P.; Hunt, J.J.; Pritzel, A.; Heess, N.; Erez, T.; Tassa, Y.; Silver, D.; Wierstra, D. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. Mach. Learn. 2016, arXiv:1509.02971. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Hagen, S.; Krose, B. Neural Q-learning. Neural Comput. Appl. 2003, 12, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.B.; Precup, R.E. Data-Driven model-free tracking reinforcement learning control with VRFT-based adaptive actor-critic. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierks, T.; Jagannathan, S. Online optimal control of affine nonlinear discrete-time systems with unknown internal dynamics by using time-based policy update. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, A. Theoretical and numerical analysis of approximate dynamic programming with approximation errors. J. Gui Control Dyn. 2016, 39, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, A. Revisiting approximate dynamic programming and its convergence. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radac, M.-B.; Lala, T. Learning Output Reference Model Tracking for Higher-Order Nonlinear Systems with Unknown Dynamics. Algorithms 2019, 12, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12060121
Radac M-B, Lala T. Learning Output Reference Model Tracking for Higher-Order Nonlinear Systems with Unknown Dynamics. Algorithms. 2019; 12(6):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12060121
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadac, Mircea-Bogdan, and Timotei Lala. 2019. "Learning Output Reference Model Tracking for Higher-Order Nonlinear Systems with Unknown Dynamics" Algorithms 12, no. 6: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12060121
APA StyleRadac, M.-B., & Lala, T. (2019). Learning Output Reference Model Tracking for Higher-Order Nonlinear Systems with Unknown Dynamics. Algorithms, 12(6), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12060121





