Phase Changes of Monosulfoaluminate in NaCl Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. XRD, STXM, and XANES
2.3. Spectral Deconvolution for Quantification and Thermodynamic Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reference XANES Spectra of Synthesized AFm and AFt Phases
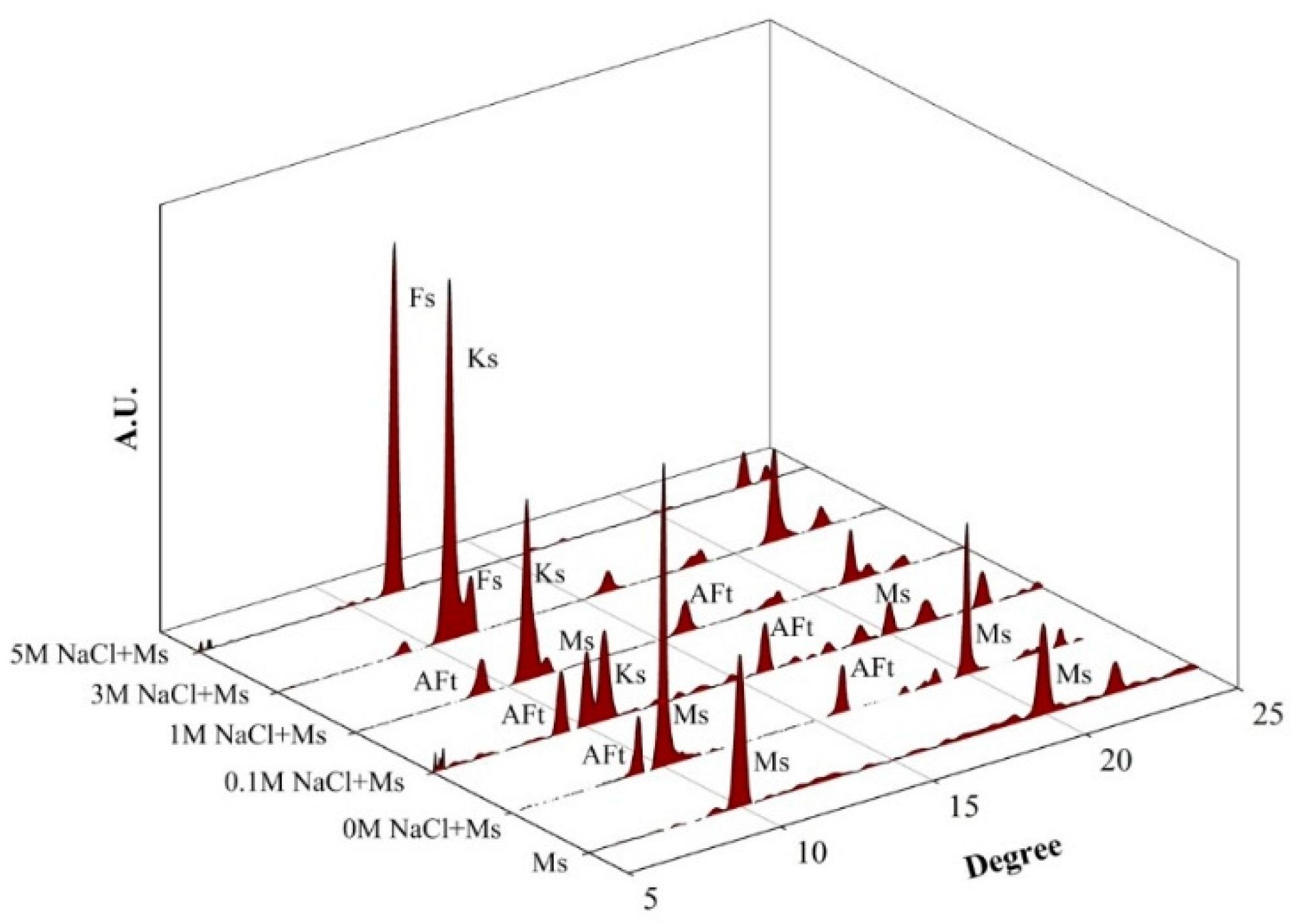
3.2. Phase Identification of NaCl-Reacted Monosulfoaluminate Sample Using XRD
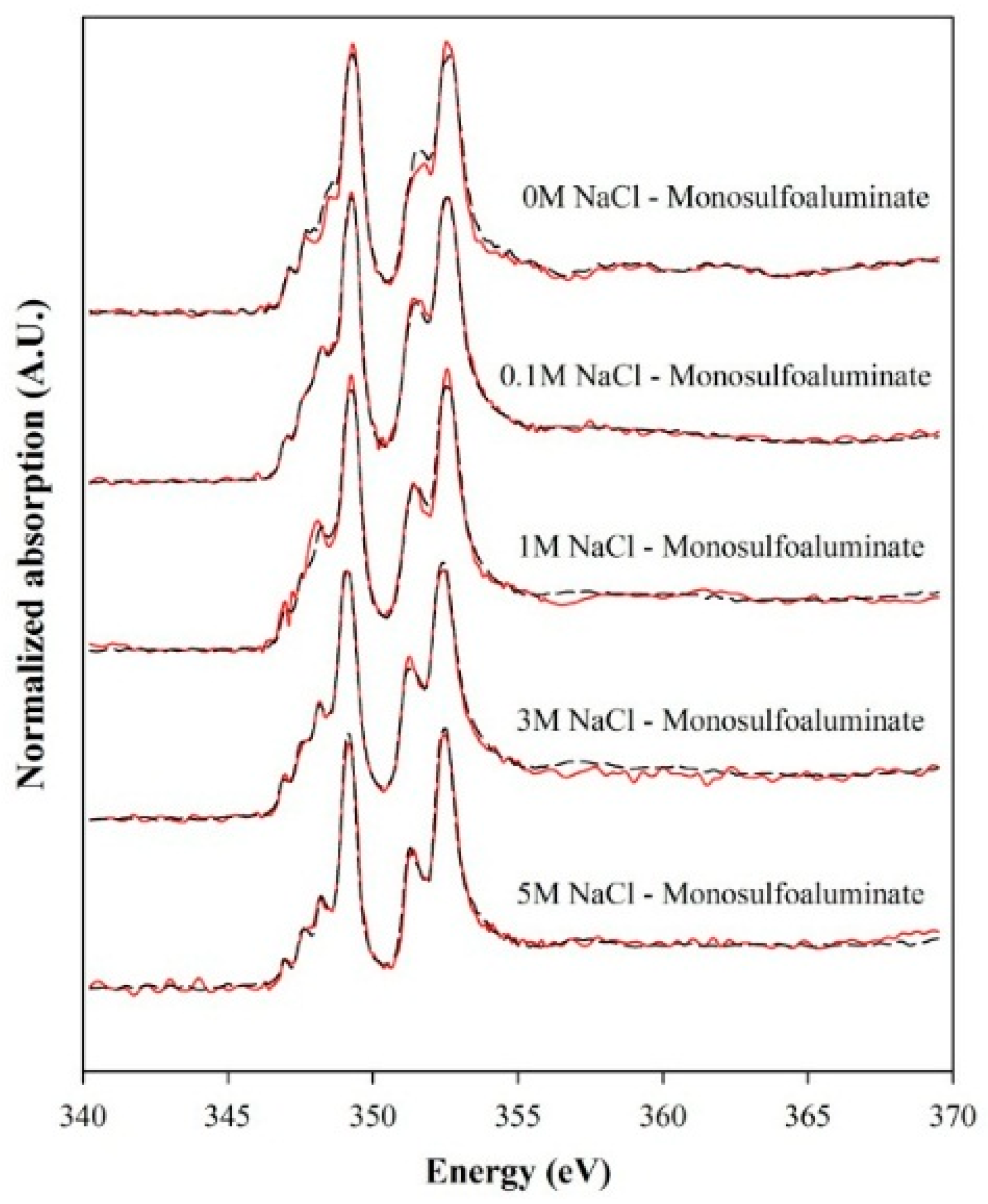
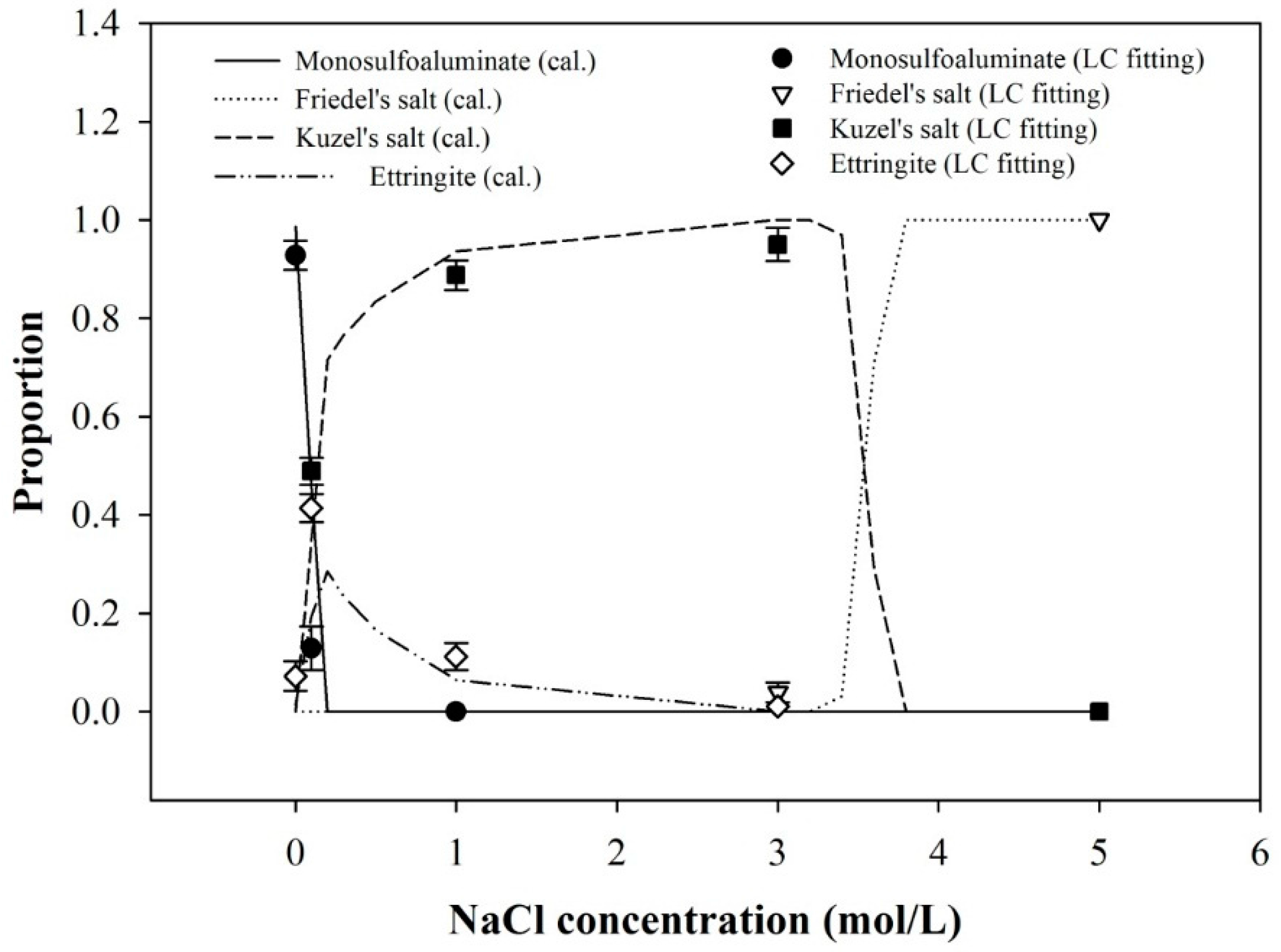
3.3. Deconvolution of XANES and Thermodynamic Calculation
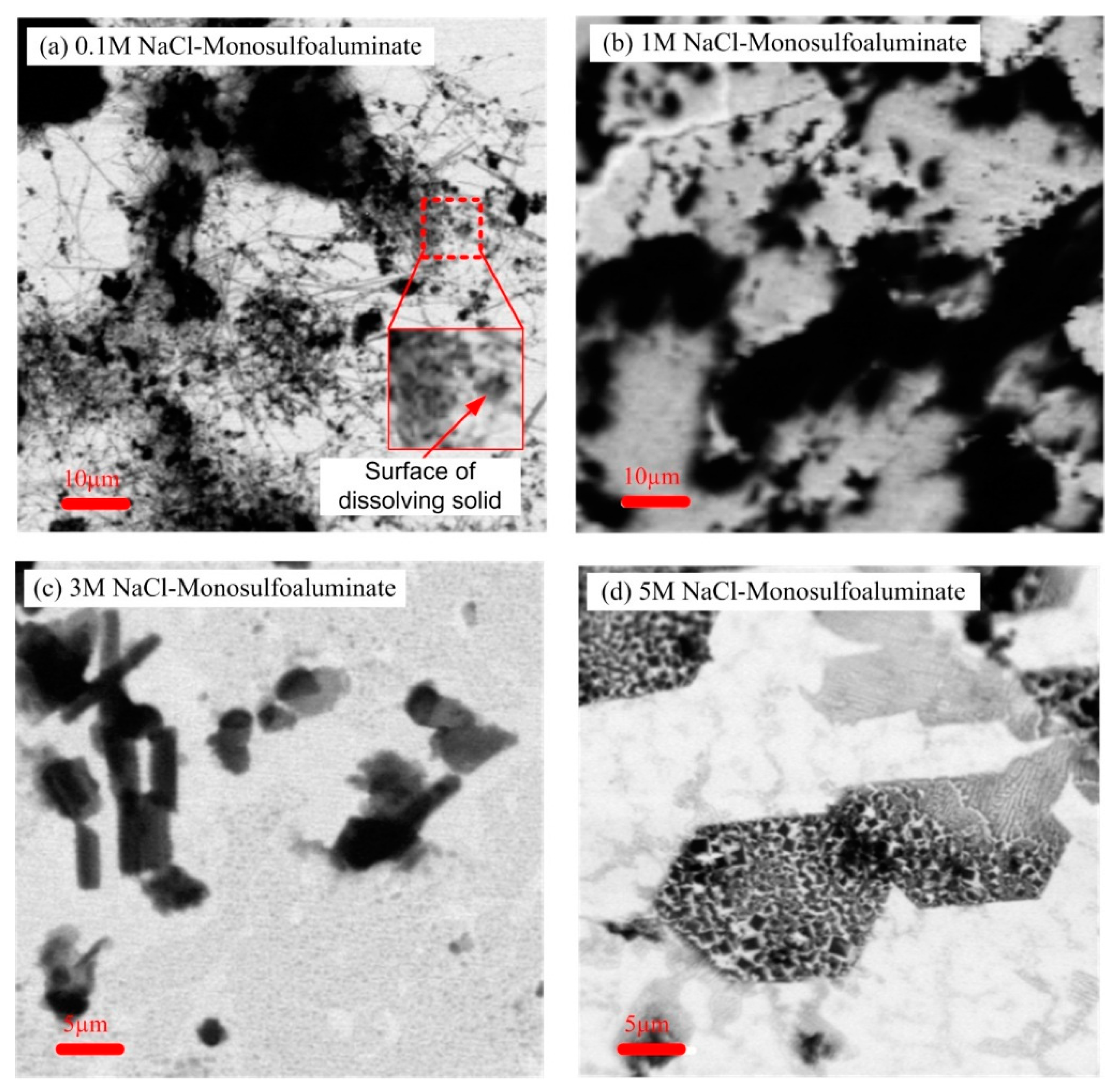
3.4. STXM Results
4. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gjørv, O.E. Durability and Service Life of Concrete Structures; Japan Concrete Engineering Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2002; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, P.K.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Concrete: Microstructure, Properties, and Materials; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.; Bothe, J. The system CaO-Al2O3-CaCl2-H2O at 23 ± 2 °C and the mechanisms of chloride binding in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1549–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csizmadia, J.; Balözs, G.; Tamás, F.D. Chloride ion binding capacity of aluminoferrites. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delagrave, A.; Marchand, J.; Ollivier, J.P.; Julien, S.; Hazrati, K. Chloride binding capacity of various hydrated cement paste systems. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1997, 6, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, H.; Yamada, K.; Takahashi, H.; Zibara, H. Chloride binding of cement estimated by binding isotherms of hydrates. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2005, 3, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luping, T.; Nilsson, L.O. Chloride binding capacity and binding isotherms of OPC pastes and mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, A.K.; Scantlebury, J.D.; Lyon, S.B. The binding of chloride ions by sulphate resistant Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritthart, J. Chloride binding in cement II. The influence of the hydroxide concentration in the pore solution of hardened cement paste on chloride binding. Cem. Concr. Res. 1989, 19, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. The influence of sulphates on chloride binding and pore solution chemistry. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shi, C.; De Schutter, G.; Audenaert, K.; Deng, D. Chloride binding of cement-based materials subjected to external chloride environment-a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibara, H.; Hooton, D.; Yamada, K.; Thomas, M.D.A. Roles of cement mineral phases in chloride binding. Cem. Sci. Conc. Technol. 2002, 56, 384–391. [Google Scholar]
- Balonis, M.; Lothenbach, B.; Le Saout, G.; Glasser, F.P. Impact of chloride on the mineralogy of hydrated Portland cement systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, F.P.; Kindness, A.; Stronach, S.A. Stability and solubility relationships in AFm phases: Part I. chloride, sulfate and hydroxide. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, A.K.; Scantlebury, J.D.; Lyon, S.B. Mechanism of Friedel’s salt formation in cements rich in tri-calcium aluminate. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.R.; Macphee, D.E.; Chudek, J.A.; Hunter, G.; Lannegrand, R.; Talero, R.; Scrimgeour, S.N. Studies using 27Al MAS NMR of AFm and AFt phases and the formation of Friedel’s salt. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnin-Yauri, U.A.; Glasser, F.P. Friedel’s salt, Ca2Al(OH)6(Cl,OH)·2H2O: Its solid solutions and their role in chloride binding. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbah, A.; Cau-dit-Coumes, C.; Renaudin, G.; Frizon, F.; Leroux, F. Uptake of chloride and carbonate ions by calcium monosulfoaluminate hydrate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipavec, A.; Vuk, T.; Gabrovšek, R.; Kaučič, V. Chloride binding into hydrated blended cements: The influence of limestone and alkalinity. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 48, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, D.; Ye, J. Study on the expansion of concrete under attack of sulfate and sulfate–chloride ions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 39, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerdt, K.; Colombo, A.; Coppola, L.; Justnes, H.; Geiker, M. Impact of the associated cation on chloride binding of Portland cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 68, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, I.; Perron, L.; Glasser, F.P. Impact of chloride-rich environments on cement paste mineralogy. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 68, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschei, T.; Lothenbach, B.; Glasser, F. The AFm phase in Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, R.B.; Palmer, C.D. Solubility of ettringite (Ca6[Al(OH)6]2(SO4)3·26H2O) at 5–75 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X’Pert HighScore, version 2.2 b; Plus Software: Almelo, The Netherlands, 2006.
- AXis 2000-Analysis of X-ray Images and Spectra, versions pre-8.3; McMaster University: Lewis Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2006.
- Ha, J.; Chae, S.; Chou, K.W.; Tyliszczak, T.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Effect of polymers on the nanostructure and on the carbonation of calcium silicate hydrates: A scanning transmission X-ray microscopy study. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculation; version 2; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999.
- Bond, K.A.; Heath, T.G.; Tweed, C.J. HATCHES: A referenced thermodynamic database for chemical equilibrium studies. Nirex Rep. 1997, 379. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterji, S. Mechanism of the CaCl2 attack on Portland cement concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1978, 8, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaudin, G.; Kubel, F.; Rivera, J.P.; Francois, M. Structural phase transition and high temperature phase structure of Friedels salt, 3CaO∙Al2O3∙CaCl2∙10H2O. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1937–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapin, J.P.; Renaudin, G.; Elkaim, E.; Francois, M. Structural transition of Friedel’s salt 3CaO∙Al2O3∙CaCl2∙10H2O studied by synchrotron powder diffraction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.D.; Jakobsen, H.J.; Skibsted, J. Characterization of the α-β phase transition in Friedel’s salt (Ca2Al(OH)6Cl∙2H2O) by variable-temperature 27Al MAS NMR spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 6676–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balonis, M.; Glasser, F.P. The density of cement phases. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothe, J.V. PHREEQC modeling of Friedel’s salt equilibria at 23 ± 1 °C. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, E.; Dähn, R.; Vespa, M.; Lothenbach, B. Micro-spectroscopic investigation of Al and S speciation in hardened cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naftel, S.J.; Sham, T.K.; Yiu, Y.M.; Yates, B.W. Calcium L-edge XANES study of some calcium compounds. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2001, 8, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newville, M. IFEFFIT: Interactive XAFS analysis and FEFF fitting. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2001, 8, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.F.W.; Famy, C.; Scrivener, K.L. Delayed ettringite formation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
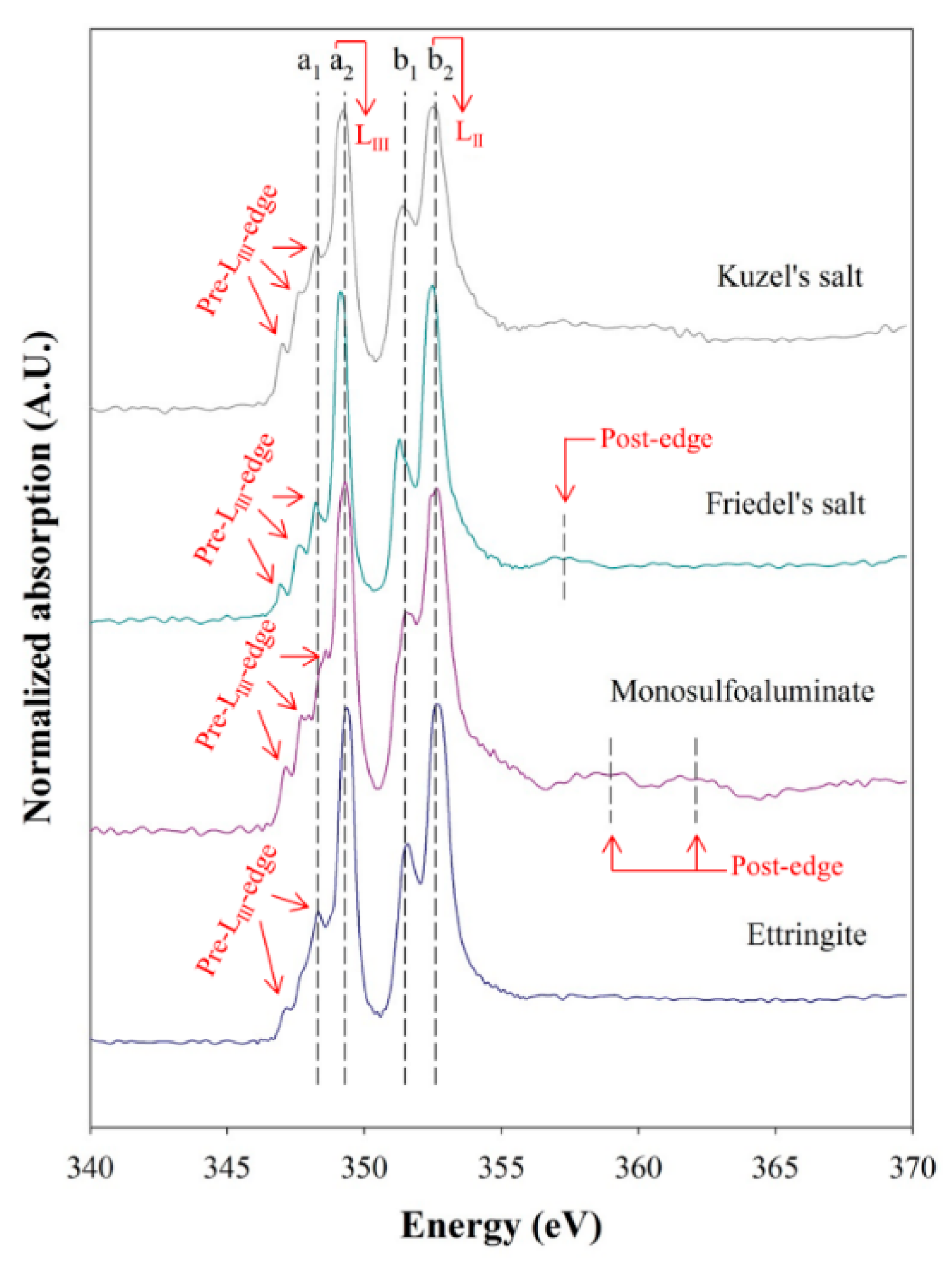
| Mineral Name | AFm Phase | AFt Phase | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Friedel’s Salt | Kuzel’s Salt | MonosulfoalumInate | Ettringite | ||
| Intensity ratio | a2/a1 | 2.77 | 1.36 | 1.87 | 2.56 |
| b2/b1 | 1.86 | 1.23 | 1.93 | 1.70 | |
| Peak position (eV) | Pre-LIII-edge | 346.9 347.6 348.2 | 347.0 347.6 348.3 | 347.1 347.8 348.6 | 347.2 348.3 |
| LIII-edge | 349.2 | 349.2 | 349.3 | 349.4 | |
| Pre-LII-edge | 351.3 | 351.37 | 351.6 | 351.6 | |
| LII-edges | 352.5 | 352.57 | 352.6 | 352.6 | |
| Post-edge | 357.3 | N.D. | 359.0362.1 | N.D. | |
| Atomic distribution in the first shell of Ca |  |  | |||
| NaCl Solution | Monosulfoaluminate | Friedel’s Salt | Kuzel’s Salt | Ettringite | R-Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 M | 0.928 ± 0.030 | N.D. | N.D. | 0.072 ± 0.030 | 0.0061 |
| 0.1 M | 0.129 ± 0.044 | N.D. | 0.489 ± 0.027 | 0.414 ± 0.028 | 0.0011 |
| 1.0 M | 0 ± 0 | N.D. | 0.888 ± 0.030 | 0.112 ± 0.027 | 0.0055 |
| 3.0 M | N.D. | 0.039 ± 0.020 | 0.950 ± 0.034 | 0.011 ± 0.010 | 0.0022 |
| 5.0 M | N.D. | 1 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | N.D. | 0.0042 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, S.; Ha, J.; Chae, S.R.; Kilcoyne, D.A.; Jun, Y.; Oh, J.E.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Phase Changes of Monosulfoaluminate in NaCl Aqueous Solution. Materials 2016, 9, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050401
Yoon S, Ha J, Chae SR, Kilcoyne DA, Jun Y, Oh JE, Monteiro PJM. Phase Changes of Monosulfoaluminate in NaCl Aqueous Solution. Materials. 2016; 9(5):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050401
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Seyoon, Juyoung Ha, Sejung Rosie Chae, David A. Kilcoyne, Yubin Jun, Jae Eun Oh, and Paulo J.M. Monteiro. 2016. "Phase Changes of Monosulfoaluminate in NaCl Aqueous Solution" Materials 9, no. 5: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050401
APA StyleYoon, S., Ha, J., Chae, S. R., Kilcoyne, D. A., Jun, Y., Oh, J. E., & Monteiro, P. J. M. (2016). Phase Changes of Monosulfoaluminate in NaCl Aqueous Solution. Materials, 9(5), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050401








