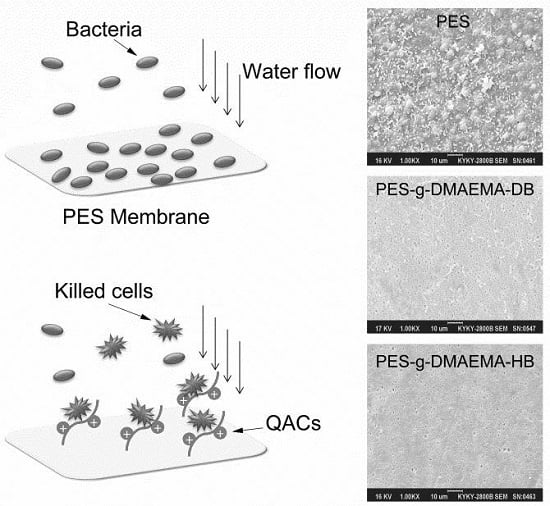
Surface Functionalization of Polyethersulfone Membrane with Quaternary Ammonium Salts for Contact-Active Antibacterial and Anti-Biofouling Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Surface Chemical Composition
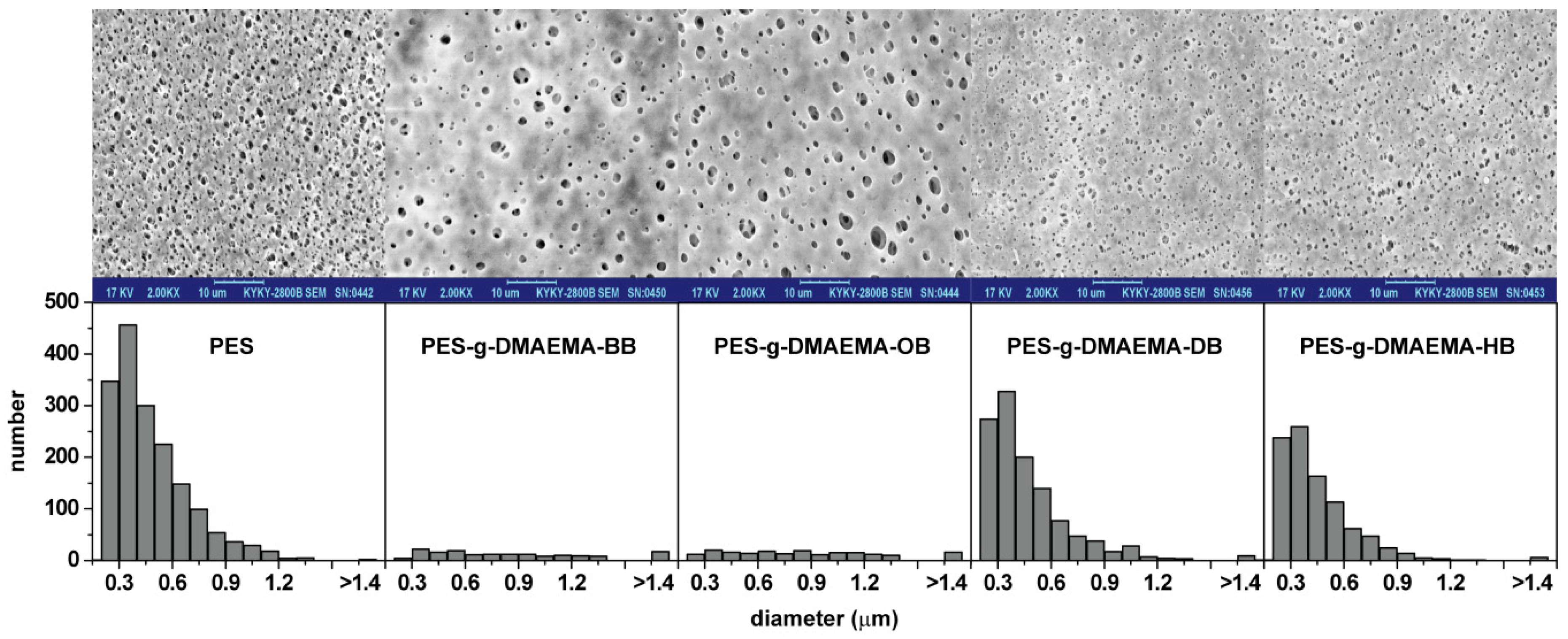
2.2. Surface Morphology
2.3. Antibacterial and Anti-Adhesion Activity
2.4. Anti-Fouling Performance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
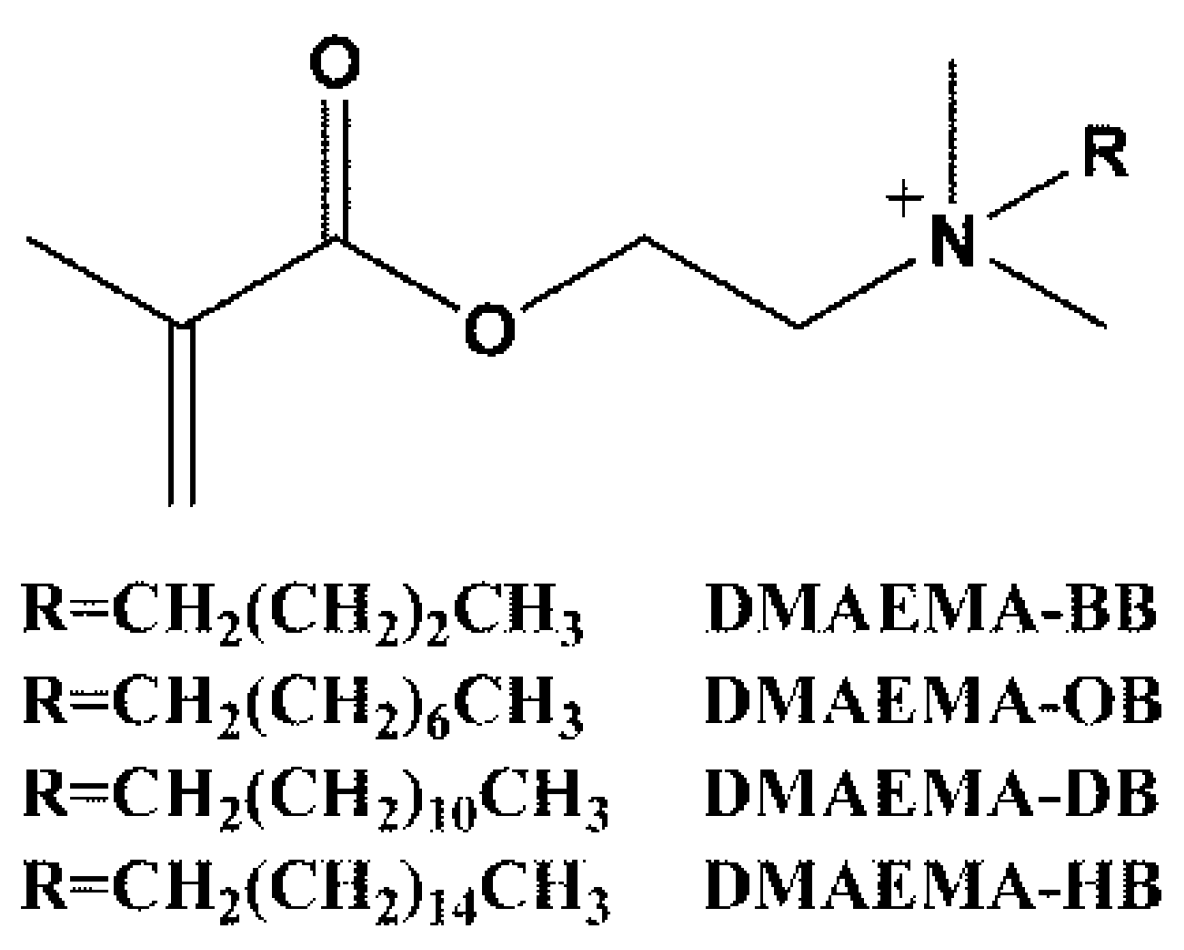
3.2. Synthesis of Quaternary Ammonium Salts Monomers
3.3. Membrane Modification by Photografting
3.4. Membrane Characterization
3.5. Bacteria Tests
3.6. Filtration Experiment With a Bacterial Solution
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PES | polyethersulfone |
| DMAEMA | dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate |
| QACs | quaternary ammonium compounds |
| CAAM | Contact-active antibacterial material |
| XPS | X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy |
| SEM | Electron Microscopy |
| ATR-FTIR | attenuated total reflectance spectrophotometer |
| GA | grafting amount |
| RFR | higher relative flux recovery |
References
- Mark, A.S.; Paul, W.B.; Menachem, E.; John, G.G.; Benito, J.M.; Anne, M.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Vasanth, D.; Pugazhenthi, G.; Uppaluri, R. Fabrication and properties of low cost ceramic microfiltration membranes for separation of oil and bacteria from its solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A. Membrane technology: Developments in ultrafiltration technologies. Filtr. Sep. 2012, 49, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semião, A.J.C.; Habimana, O.; Casey, E. Bacterial adhesion onto nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: Effect of permeate flux. Water Res. 2014, 63, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Shon, H.K.; Cho, J. Biofouling characteristics using flow field-flow fractionation: Effect of bacteria and membrane properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham-Meyer, K.; Goeres, D.M.; Hamilton, M.A. Comparative evaluation of biofilm disinfectant efficacy tests. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 70, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, J.Y. Antimicrobial biocides in the healthcare environment: Efficacy, usage, policies, and perceived problems. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2005, 1, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Stojicic, S.; Qian, W.; Olsen, I.; Haapasalo, M. The synergistic antimicrobial effect by mechanical agitation and two chlorhexidine preparations on biofilm bacteria. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickery, K.; Ngo, Q.D.; Zou, J.; Cossart, Y.E. The effect of multiple cycles of contamination, detergent washing, and disinfection on the development of biofilm in endoscope tubing. Am. J. Infect. Control 2009, 37, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frota, M.N.; Ticona, E.M.; Neves, A.V.; Marques, R.P.; Braga, S.L.; Valente, G. On-line cleaning technique for mitigation of biofouling in heat exchangers: A case study of a hydroelectric power plant in Brazil. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2014, 53, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequette, Y.; Boels, G.; Clarisse, M.; Faille, C. Using enzymes to remove biofilms of bacterial isolates sampled in the food-industry. Biofouling 2010, 26, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donlan, R.M. Preventing biofilms of clinically relevant organisms using bacteriophage. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.; McAuliffe, O.; Ross, R.P.; Coffey, A. Prevention of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and reduction in established biofilm density using a combination of phage K and modified derivatives. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 54, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razi, F.; Sawada, I.; Ohmukai, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. The improvement of antibiofouling efficiency of polyethersulfone membrane by functionalization with zwitterionic monomers. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Improving the water flux and bio-fouling resistance of reverse osmosis (RO) membrane through surface modification by zwitterionic polymer. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, P.; Guan, C.; Song, X.; Zhang, Q.; Leong, S.S.J.; Tang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Chang, M.W.; Wang, K.; et al. Hollow Fiber Membrane Decorated with Ag/MWNTs: Toward Effective Water Disinfection and Biofouling Control. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 10033–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahab, N.A.; Shukry, N. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial properties of grafted sugarcane bagasse/silver nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Sasson, M.; Lu, X.; Bar-Zeev, E.; Zodrow, K.R.; Nejati, S.; Qi, G.; Giannelis, E.P.; Elimelech, M. In situ formation of silver nanoparticles on thin-film composite reverse osmosis membranes for biofouling mitigation. Water Res. 2014, 62, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, S.; Yücel Falco, C.; Belgacem, M.N.; Bras, J. Surface cationized cellulose nanofibrils for the production of contact active antimicrobial surfaces. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H. Dual-function antibacterial surfaces for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2015, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, G.; Lu, T.; Li, J.; Qiao, Y.; Ning, C.; Zhang, X.; Chu, P.K.; Liu, X. Influence of sulfur content on bone formation and antibacterial ability of sulfonated PEEK. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Sun, S.; Dong, A.; Hao, Y.; Shi, S.; Sun, Z.; Gao, G.; Chen, Y. Developing of a novel antibacterial agent by functionalization of graphene oxide with guanidine polymer with enhanced antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Zepeda-Velazquez, L.; Brook, M.A. Tunable, antibacterial activity of silicone polyether surfactants. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 132, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siedenbiedel, F.; Tiller, J.C. Antimicrobial Polymers in Solution and on Surfaces: Overview and Functional Principles. Polymers 2012, 4, 46–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; Fernández-García, M. Polymeric materials with antimicrobial activity. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 281–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y. Antimicrobial polymeric materials with quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3626–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadida, T.; Kroupitski, Y.; Peiper, U.M.; Bendikov, T.; Sela, S.; Poverenov, E. Air-ozonolysis to generate contact active antimicrobial surfaces: Activation of polyethylene and polystyrene followed by covalent graft of quaternary ammonium salts. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Ye, X.Y.; Yao, K.; Ji, J.; Xu, Z.K. Effects of quaternization on the morphological stability and antibacterial activity of electrospun poly(DMAEMA-co-AMA) nanofibers. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 133, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, C.; Ma, H.; Li, R.; Dong, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. Surface modification of APA-TFC membrane with quaternary ammonium cation and salicylaldehyde to improve performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 457, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Zhu, L.P.; Xu, Y.Y.; Yi, Z.; Zhu, B.K. A novel positively charged nanofiltration membrane prepared from N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate by quaternization cross-linking. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 374, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiankanga, M.; Canb, W.; Xinyuana, S. Effect of Polymeric Quarternary Ammonium Salt Content on Morphology and Properties of Polymeric Quarternary Ammonium Salt/Polyethersulfone Blend Membrane. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2009, 5, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Wu, D.; Fu, R. Studies on the synthesis and antibacterial activities of polymeric quaternary ammonium salts from dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emin, C.; Remigy, J.C.; Lahitte, J.F. Influence of UV grafting conditions and gel formation on the loading and stabilization of palladium nanoparticles in photografted polyethersulfone membrane for catalytic reactions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, R.; Antón, E.; Ulbricht, M. Tuning the nanofiltration performance of thin film strong polyelectrolyte hydrogel composite membranes by photo-grafting conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Shin, H.S.; Park, K.; Han, D.K. Surface grafting of blood compatible zwitterionic poly(ethylene glycol) on diamond-like carbon-coated stent. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas, I.; Collado, S.; Gutiérrez, A.; Díaz, M. Fouling mechanisms of Pseudomonas putida on PES microfiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 465, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goei, R.; Lim, T.T. Ag-decorated TiO2 photocatalytic membrane with hierarchical architecture: Photocatalytic and anti-bacterial activities. Water Res. 2014, 59, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

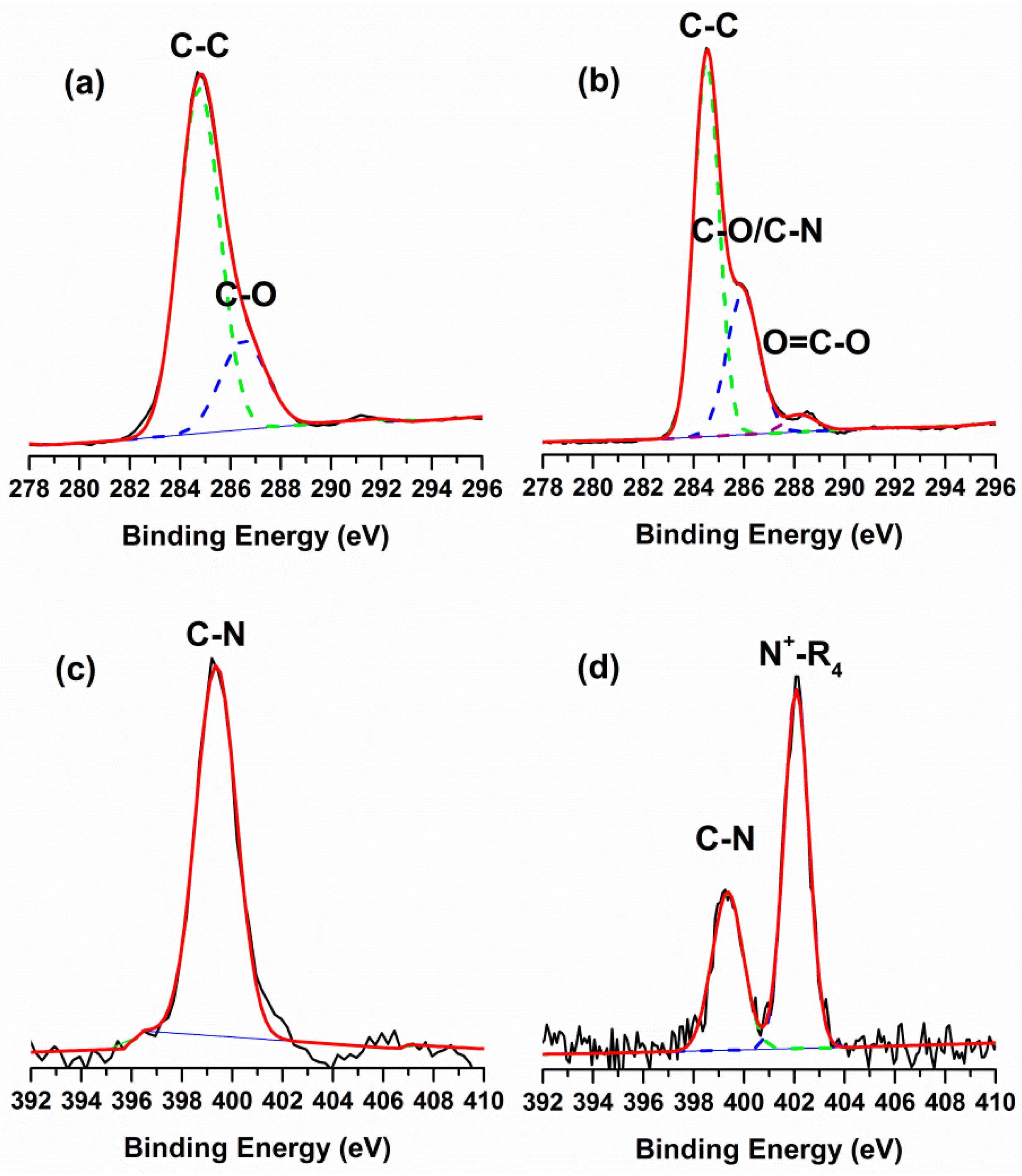
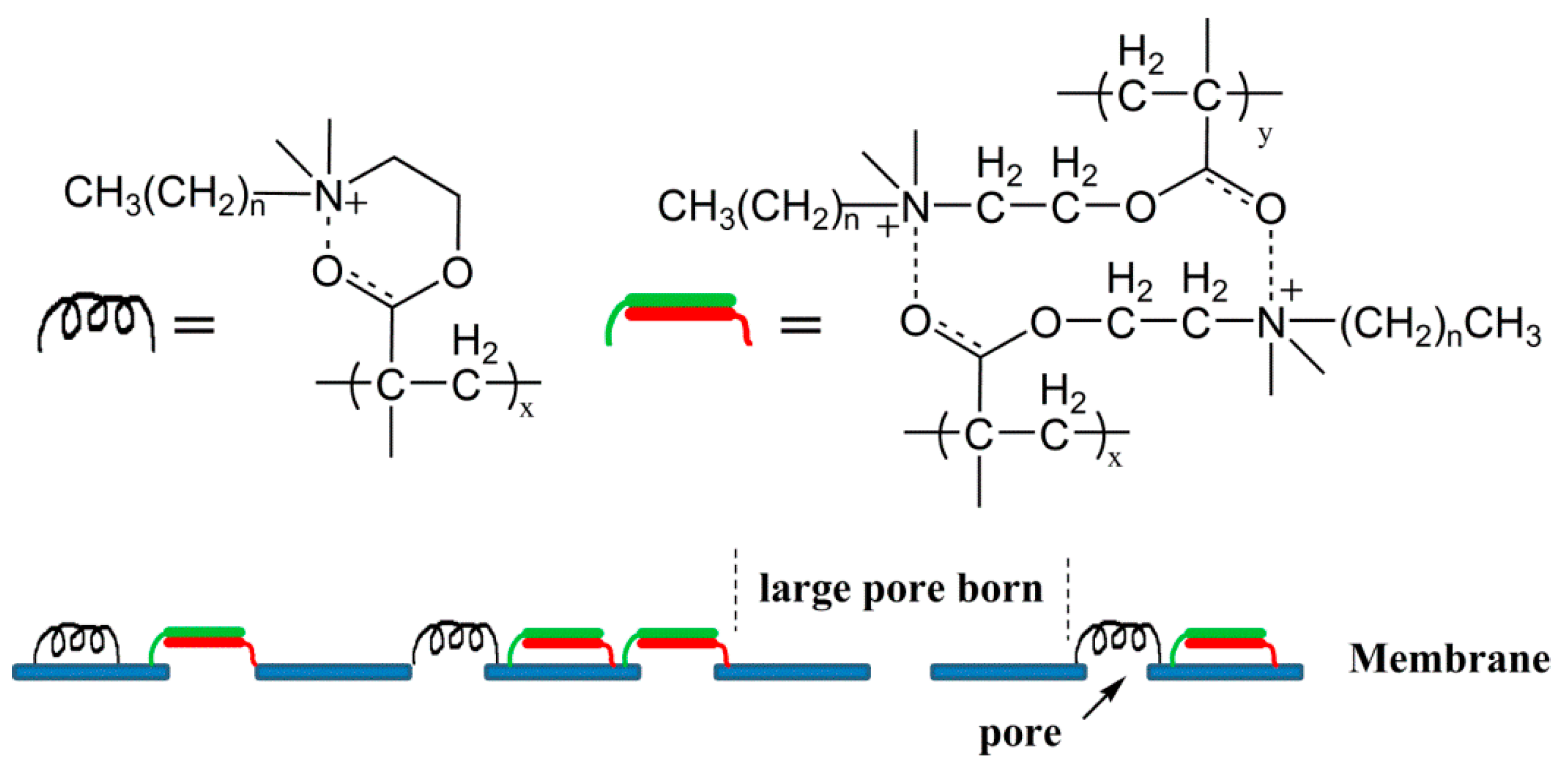

| Membrane | C (%) | O (%) | N (%) | S (%) | C/N | GA (μg/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | 72.20 | 18.01 | 4.89 | 4.70 | 14.76 | – |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-BB | 77.89 | 16.14 | 3.83 | 2.14 | 20.34 | 193.6 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-OB | 76.88 | 15.99 | 3.49 | 3.64 | 22.05 | 203.8 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-DB | 76.85 | 17.29 | 3.08 | 2.77 | 24.95 | 560.5 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-HB | 78.30 | 16.54 | 2.53 | 2.63 | 30.95 | 835.7 |
| Membrane | Log CFU/mL Reduction | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| PES | 0.16 ± 0.06 | 0.19 ± 0.05 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-BB | 1.03 ± 0.21 | 1.10 ± 0.25 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-OB | 2.06 ± 0.31 | 3.90 ± 0.09 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-DB | 3.05 ± 0.39 | 5.40 ± 0.39 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-HB | 3.21 ± 0.12 | 5.15 ± 0.09 |
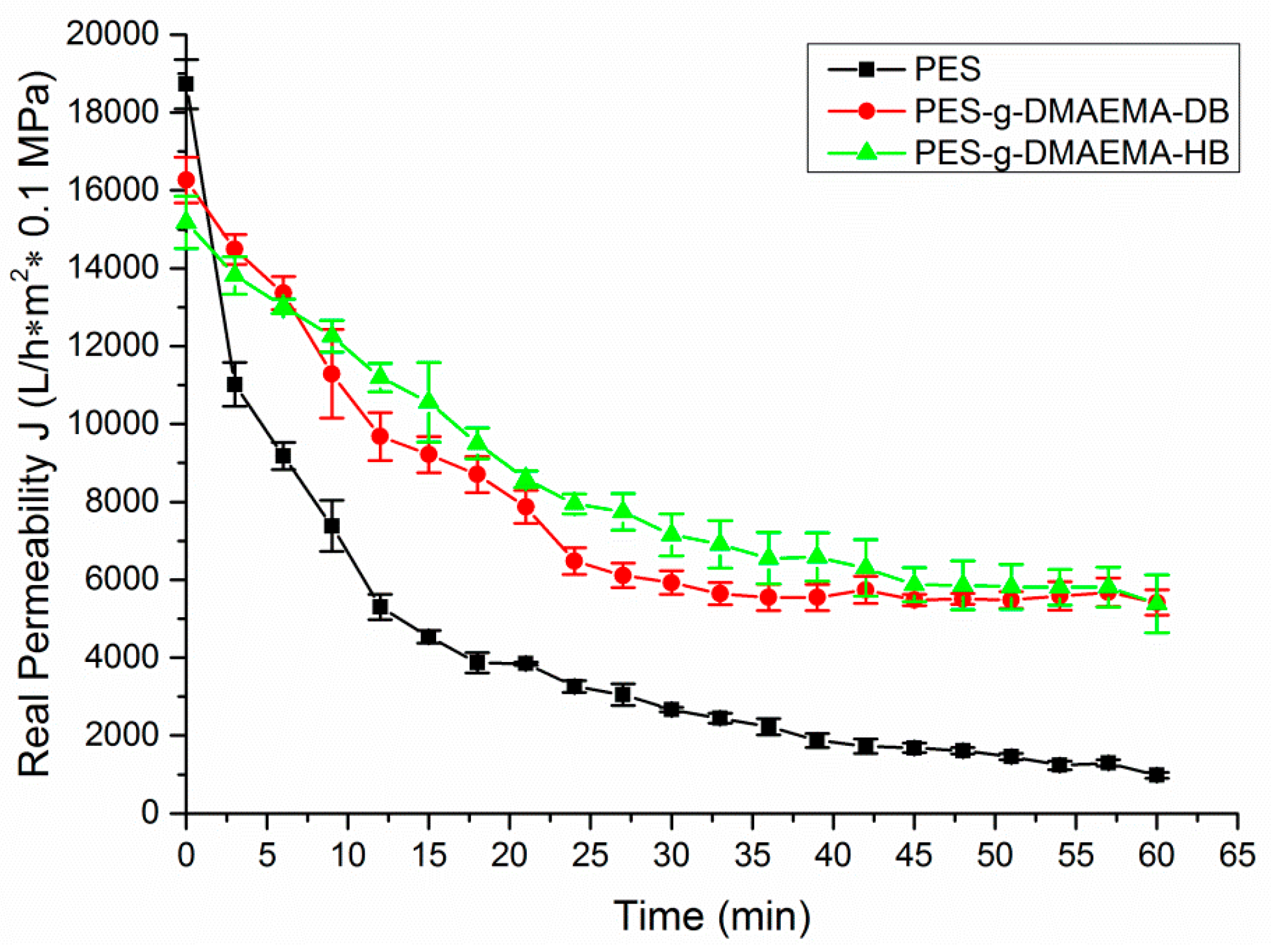
| Membrane | Initial Water Flux (J0, L/h·m2· 0.1 MPa) | Water Flux Reduction after Modification 1, % | Final Water Flux after 60 min Filtration (J, L/h·m2· 0.1 MPa) | Water Flux after Filtration External Cleaning (J′, L/h·m2· 0.1 MPa) | Relative Flux Recovery 2 (RFR, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | 1.87 × 104 | – | 9.80 × 102 | 1.03 × 104 | 55.1 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-BB | 6.50 × 103 | 34.8 | – | – | – |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-OB | 5.80 × 103 | 31.0 | – | – | – |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-DB | 1.62 × 104 | 86.6 | 5.41 × 103 | 1.43 × 104 | 88.3 |
| PES-g-DMAEMA-HB | 1.51 × 104 | 80.7 | 5.38 × 103 | 1.40 × 104 | 92.7 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Lin, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, F.; Liu, C.; Tian, F. Surface Functionalization of Polyethersulfone Membrane with Quaternary Ammonium Salts for Contact-Active Antibacterial and Anti-Biofouling Properties. Materials 2016, 9, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050376
Hu X, Lin X, Zhao H, Chen Z, Yang J, Li F, Liu C, Tian F. Surface Functionalization of Polyethersulfone Membrane with Quaternary Ammonium Salts for Contact-Active Antibacterial and Anti-Biofouling Properties. Materials. 2016; 9(5):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050376
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiao, Xiaohui Lin, Huabing Zhao, Zihao Chen, Jian Yang, Fan Li, Changjun Liu, and Feng Tian. 2016. "Surface Functionalization of Polyethersulfone Membrane with Quaternary Ammonium Salts for Contact-Active Antibacterial and Anti-Biofouling Properties" Materials 9, no. 5: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050376
APA StyleHu, X., Lin, X., Zhao, H., Chen, Z., Yang, J., Li, F., Liu, C., & Tian, F. (2016). Surface Functionalization of Polyethersulfone Membrane with Quaternary Ammonium Salts for Contact-Active Antibacterial and Anti-Biofouling Properties. Materials, 9(5), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050376