Abstract
The rapidly developing field of quantum dots (QDs) provides researchers with more options for imaging modalities and therapeutic strategies. In recent years, QDs were widely used as multifunctional materials for tumor imaging and therapy due to their characteristic properties such as semiconductive, zero-dimension and strong fluorescence. Nevertheless, there still exist the challenges of employing these properties of QDs for clinical diagnosis and therapy. Herein, we briefly review the development, properties and applications of QDs in tumor imaging and therapy. Future perspectives in these areas are also proposed as well.
1. Introduction
1.1. Quantum Dots
The quantum dot (QD) is defined as an artificially structured system with the capacity to load electrons [1]. Its special physicochemical properties differentiate it from other naturally occurring biogenic and anthropogenic nanoparticles [2]. QDs are one type of nanoparticles (NPs) with three characteristic properties: semiconductors, zero-dimension, and strong fluorescence. Although colloidal semiconductor QDs are single crystals with diameters of a few nanometers, their sizes and shapes can be precisely controlled by the duration, temperature, and ligand molecules during the synthetic processes [3]. The well controlled synthetic process yields QDs with composition- and size-dependent absorption and emission. Generally, as the sizes of QDs are reduced, the electronic excitations shift to higher energies (i.e., shorter wavelengths) [4], such as CdSe QDs (shown in Figure 1) [5]. Besides, physical properties of QDs influence their fluorescence emissions. The fluorescence emission of colloidal QDs on the surface of a two-dimensional slab of photonic crystals will be enhanced due to a combination of high-intensity near fields with strong coherent scattering, which is related to leaky eigenmodes of the photonic crystal (In QDs’ periodically modulated structures, an anomalous resonant phenomenon arises from periodic index modulation of the refractive index, which allows phase-matching of externally incident radiation into modes that can be re-radiated into free space). Owing to the fact that these modes possess finite lifetimes within such structures, they are called “leaky eigenmodes” [6]. Another example of the fluorescence enhancement of QDs is that when a sharp gold tip is brought within a few nanometers from a single QD cluster surface, the fluorescence of the QD in the vicinity of the tip increases about fourfold in magnitude [7].
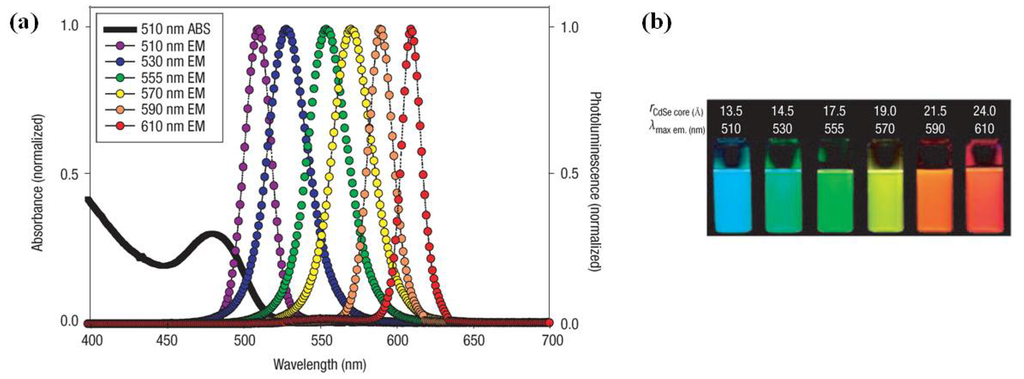
Figure 1.
(a) Absorption and emission of six different quantum dot (QD) dispersions. The black line shows the absorption of the 510 nm emitting QDs. Note that at the wavelength of lowest absorption for the 510 nm QD, ~450 nm, the molar extinction coefficient is greater than that of rhodamine red at its absorption maxima (~150,000 vs. 129,000 M−1 cm−1); (b) Photo demonstrating the size-tunable fluorescence properties and spectral range of the six QD dispersions plotted in A vs. CdSe core size. All samples were excited at 365 nm with a UV source. For the 610 nm emitting QDs, this translates into a Stokes shift of ~250 nm. r = radius. Reprinted with permission from [5]. Copyright 2005 Nature Publishing Group.
The specific properties of QDs enable them with wide applications in chemistry, chemical biology and biomedicine. In the past decade, QDs have been broadly applied in fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) analysis, gene technology, fluorescent labeling of cellular proteins, cell tracking, in vivo animal imaging and tumor biology investigation [8]. In this review, we will discuss the applications of QDs in tumor imaging and therapy.
1.2. Tumor Imaging
Tumor imaging is an imaging technology, which monitors changes of tumor cells at tissue, cellular, or sub-cellular levels. It helps people with qualitative and quantitative analyses of the biological processes of tumors in imaging aspects. The three predominant imaging modalities are optical imaging (e.g., fluorescence or non-fluorescence imaging), nuclear imaging (e.g., single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET)), and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Figure 2 and Table 1 show the development of imaging techniques and their characteristics, respectively [9]. Compared with other imaging methods, QDs have advantages of broad light spectrum emission from visible to infrared due to their controllable sizes, bright and photostable fluorescence within a few nanometers, and good water-solubility [10]. However, QDs have inherent disadvantages such as high cytotoxicity (e.g., QDs of CdSe) [10].
As one of the optical imaging modalities, fluorescence refers to relatively-longer-wavelength light (especially visible light) emitted by certain molecule after it absorbing light at a particular wavelength [9]. The fluorophores are classified into two groups in terms of their origin: Endogenous fluorophores and exogenous fluorophores. For example, NADH (reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide) is one type of endogenous fluorophores, which can indicate the metabolic status of tumor because only its reduced form has fluorescence [11]. Exogenous fluorophores are usually organic compounds with fluorogenic motifs (e.g., near-infrared (NIR) fluorophores such as heptamethine cyanines containing benzoxazole or benzothiazole motifs [12].
As the two main modalities for nuclear imaging, SPECT and PET play important roles of imaging bone metastases in miscellaneous cancers including lung cancer, thyroid cancer, renal cancer, myeloma, and neuroendocrine cancers [13]. While SPECT uses one photon with lower energy to produce three-dimensional image of tracer distribution with multiplanar images, PET uses positron-emitting radiotracers and achieves image with higher spatial resolution than that of SPECT [13]. MRI is also frequently applied in tumor imaging using dotarem or magnevist as T1 contrast media or resovist as T2 contrast medium [14]. To date, multimodalities of imaging such as PET-CT, PET-MRI have emerged and been used for the acquisition of images with higher accuracy [9].
QDs plays an increasingly important role in tumor imaging, especially near-infrared (NIR, 700–900 nm) imaging. NIR fluorescence imaging of tumor is expected to have a major impact in biomedical imaging because in the NIR region the absorbance spectra for all the biomolecules in tumor reach their minima, which provides a clear window for in vivo optical imaging of tumor [15]. In 2010, Gao et al. reported that QD800-MPA (a NIR non-cadmium QDs coated with mercaptopropionic acid with an emission wavelength of about 800 nm) had high tumor uptake and excellent contrast of tumor to surrounding tissues due to the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect of this kind of ultrasmall nanoparticles [16].
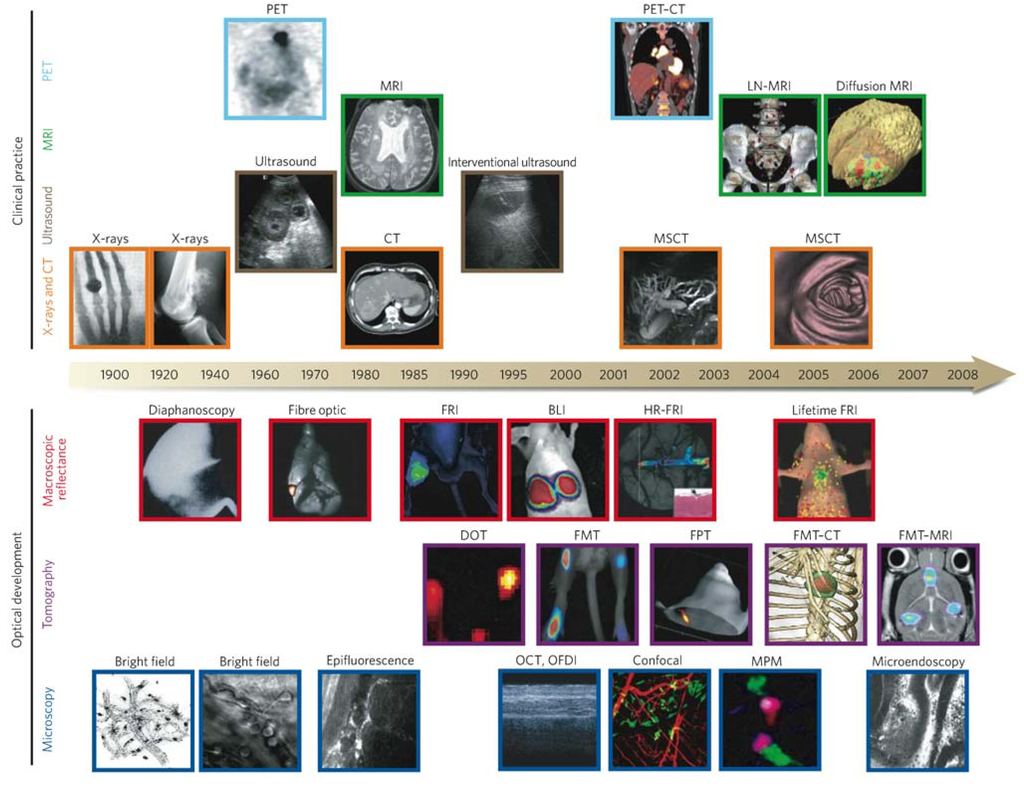
Figure 2.
Imaging technologies used in oncology. Many macroscopic imaging technologies (shown above the timeline) are in routine clinical use, and there have been huge advances in their capabilities to obtain anatomical and physiological information since the beginning of the twentieth century. Shown are some examples of bones (X-rays), soft tissue (ultrasound, MRI and CT rows), three-dimensional organs (CT and MRI rows) and physiological imaging (MRI and PET rows). Microscopic and other intravital optical techniques (shown below the timeline) have developed over the past decade and now allow studies of genetic, molecular and cellular events in vivo. Shown are surface-weighted, whole-mouse, two-dimensional techniques (macroscopic reflectance row); tomographic three-dimensional techniques, often in combination with other anatomical modalities (tomography row); and intravital microscopy techniques (microscopy row). The timeline is approximate and is not to scale. Here BLI, bioluminescence imaging; CT, computed tomography; DOT, diffuse optical tomography; FMT, fluorescence-mediated tomography; FPT, fluorescence protein tomography; FRI, fluorescence reflectance imaging; HR-FRI, high-resolution FRI; LN-MRI, lymphotropic nanoparticle-enhanced MRI; MPM, multiphoton microscopy; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MSCT, multislice CT; OCT, optical coherence tomography; OFDI, optical frequency-domain imaging; PET, positron-emission tomography. Reprinted with permission from [9]. Copyright 2008 Nature Publishing Group.

Table 1.
Overview of imaging systems. Reproduced with permission from [9]. Copyright 2008 Nature Publishing Group.
| Technique | Resolution * | Depth | Time † | Quantitative ‡ | Multi-channel | Imaging agents | Target | Cost § | Main small-animal use | Clinical use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRI | 10–100 μm | No limit | Minutes to hours | Yes | No | Paramagnetic chelates, magnetic particles | Anatomical, physiological, molecular | $$$ | Versatile imaging modality with high soft-tissue contrast | Yes |
| CT | 50 μm | No limit | Minutes | Yes | No | Iodinated molecules | Anatomical, physiological | $$ | Imaging lungs and bone | Yes |
| Ultrasound | 50 μm | cm | Seconds to minutes | Yes | No | Microbubbles | Anatomical, physiological | $$ | Vascular and interventional imaging || | Yes |
| PET | 1–2 mm | No limit | Minutes to hours | Yes | No | 18F-,64Cu- or 11C-labelled compounds | Physiological, molecular | $$$ | Versatile imaging modality with many tracers | Yes |
| SPECT | 1–2 mm | No limit | Minutes to hours | Yes | No | 99mTc- or 111In-labelled compounds | Physiological, molecular | $$ | Imaging labelled antibodies, proteins and peptides | Yes |
| Fluorescence reflectance imaging | 2–3 mm | <1 cm | Seconds to minutes | No | Yes | Photoproteins, fluorochromes | Physiological, molecular | $ | Rapid screening of molecular events in surface-based disease | Yes |
| FMT | 1 mm | <10 cm | Minutes to hours | Yes | Yes | Near-infrared fluorochromes | Physiological, molecular | $$ | Quantitative imaging of fluorochrome reporters | In development |
| Bioluminescence imaging | Several mm | cm | Minutes | No | Yes | Luciferins | Molecular | $$ | Gene expression, cell and bacterium tracking | No |
| Intravital microscopy ¶ | 1 μm | <400–800 μm | Seconds to hours | No | Yes | Photoproteins, fluorochromes | Anatomical, physiological, molecular | $$$ | All of the above at higher resolutions but limited depths and coverage | In development # |
* For high-resolution, small-animal imaging systems. (Clinical imaging systems differ.); † Time for image acquisition; ‡ Quantitative here means inherently quantitative. All approaches allow relative quantification; § Cost is based on purchase price of imaging systems in the United States: $, <US$100,000; $$, US$100,000–300,000; $$$, >US$300,000; || Interventional means used for interventional procedures such as biopsies or injection of cells under ultrasound guidance; ¶ Laser-scanning confocal or multiphoton microscopy; # For microendoscopy and skin imaging.
1.3. Tumor Therapy
Millions of people die from cancer every year, especially from lung cancer. Even though no existing method can defeat cancer, tumor therapies such as surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and photodynamic therapy (PDT) are developing dramatically nowadays. Surgery has relatively good effects for benign tumors and precancerous tumors. Advances in radiotherapy, such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), provide the capability of delivering a highly conformal distribution of radiative dose to a static, complex targeting volume [17]. Chemotherapy is widely adopted for tumor therapy and hundreds of anticancer drugs are used clinically. Typical anticancer drugs include plant extractives (e.g., taxol [18]), heavy metal complexes (e.g., cisplatin [19]), bioreductive drugs (e.g., tirapazamine, 3-amino-1,2,4-benzotriazine 1,4-dioxide or TPZ [20]), and traditional Chinese medicine [21]. In bcl-2-positive cancer cells (cancer cells expressing bcl-2), taxol induces the phosphorylation of bcl-2 and programmed cell death thereafter [22]. Cisplatin, one of the most widely used anticancer drugs, can bind with DNA to form cis-DDP/DNA adducts which induce DNA-damage and cell apoptosis [19]. Tirapazamine (TPZ), a leading bioreductive drug with selective cytotoxicity to hypoxic cells in tumor, damages the DNA inside cell with the reactive oxygen species (ROS) with its reduction product under the action of reductases in cells [20].
PDT has been an innovative and attractive modality for treatment of small and superficial tumors since the end of the last century [23]. After absorption of light with certain wavelength, sensitizers can induce the necrosis of tumors [23]. Some examples of QDs for PDT of tumors are discussed in the following parts.
2. QDs for Tumor Imaging
QDs, tiny light-emitting particles on nanometer scale, are new type of fluorescent probes for molecular and cellular imaging. Compared with organic dyes and fluorescent proteins, QDs have unique optical and electronic properties in cellular imaging: Wavelength-tunable emission, improved brightness of signal, resistance against photobleaching, etc. [24]. Such preponderant optical properties were not realized until the QD-based probes are equipped with war heads targeting tumor. Xingyong Wu and co-workers synthesized immunofluorescent probes by conjugating the QDs with streptavidin or IgGs (immunoglobulin Gs). Using the conjugates, they conducted comprehensive investigations on cell imaging at the targets of interest including cell surface receptors, cytoskeleton components, and nuclear antigens [25]. Up to date, QDs have been rapidly developed in tumor imaging, such as imaging tumor vasculature [15] and sentinel lymph node [26].
2.1. QDs for Imaging Membrane Receptors (Surface)
Metastases, which are responsible for most cancer deaths rather than those of primary tumors, spread tumor cells from a primary site to new distant organs [27]. Changes of membrane morphology or dynamics of membrane protein in cancer cells for cellular fluidity are critical for cancer metastasis [28]. Therefore, QDs modified with targeting ligands offer a good opportunity to track the changes of related membrane receptors. Soonhag Kim and co-workers designed a series of aptamers conjugating with different QDs to image the proteins on the membranes of cancer cells [29]. They chose three different QDs with distinct emission wavelengths of 605, 655 and 705 nm to respectively conjugate with three cancer-related aptamers-AS1411, TTA1, and MUC-1 [29]. AS1411 is an aptamer that binds to the nucleolin in the plasma membranes of cancer cells [30,31]. TTA1, which is expressed during the tissue remodeling processes including angiogenesis, inflammation, and tumor growth, binds to the extracellular matrix protein tenascin-C of cancer cells [32]. MUC-1 targets mucin, which is highly expressed by the majorities of human adenocarcinomas [33,34]. Confocal microscopic cell images were obtained with the receptors in different cells being successfully labeled with respective QD-conjugated aptamers (shown in Figure 3) [29]. Gonda et al. [28] also labeled a metastasis-promoting factor on the cell membrane called protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) with QD-conjugated anti-PAR1 antibody. By tracking the fluorescence of QDs, they photographed four stages of metastasis: cancer cells far from blood vessels in tumor, near the vessel, in the bloodstream, and adherent to the inner vascular surface in the normal tissues near tumor. With this, they successfully showed the dynamics of PAR1 movement in the whole process [28].
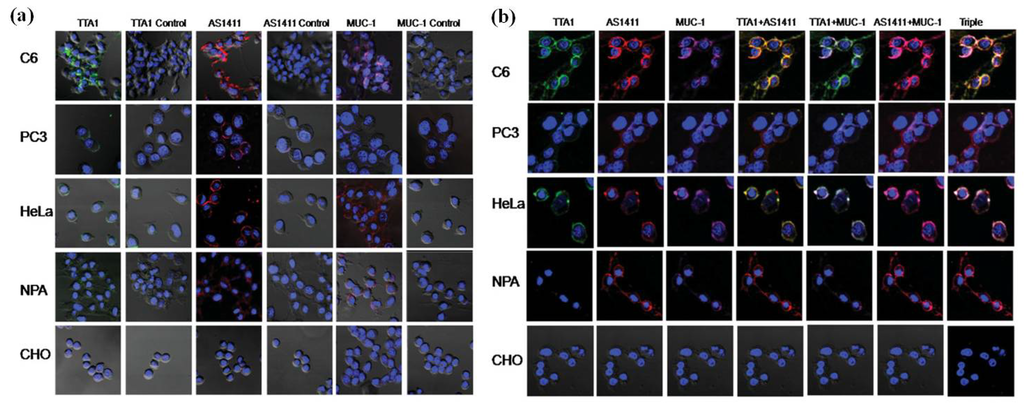
Figure 3.
Confocal microscopy imaging of cells treated with QD-aptamer conjugates. (a) A single incubation of QD605-TTA1, QD655-AS1411, or QD705-MUC-1 was applied to PC-3, HeLa, CHO, C6, and NPA cells, and confocal images were obtained. Each image was compared with the corresponding QD-control aptamers (column 1: QD-TTA1, column 2: QD-TTA1 control, column 3: QD-AS1411, column 4: QD-AS1411 control, column 5: QD-MUC-1, column 6: QDMUC- 1control); (b) Multiplex imaging of cancer cells treated simultaneously with three different types of QD-conjugated aptamers. Single images for QD-TTA1 (605 nm, light green, column 1), QD-AS1411 (655 nm, red, column 2), and QD-MUC-1(705 nm, violet, column3), dual images for QD-AS1411 and QD-TTA1 (column 4, yellow for co-localization), QD-TTA1 and QD-MUC-1 (column 5, light green for co-localization), and QD-AS1411 and QD-MUC-1 (column 6, violet for co-localization), and a triple image for QD-AS1411, QD-TTA1, and QD-MUC-1 (column 7, white for co-localization) were acquired from PC-3, HeLa, CHO, C6, and NPA cells. All figures are merged with the 40, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) image (nucleus staining, 460 nm) and cellular morphology. Reprinted with permission from [29]. Copyright 2009 John Wiley and Sons.
2.2. QDs for Imaging Cytoskeleton Components (Intracellular)
The cellular cytoskeleton, involved in many fundamental processes (e.g., locomotion and cytokinesis) of the cell, consists of actin filaments, microtubules and intermediate filaments [35]. Tumor cells are in endless division, which is related to the movement of actin filaments and microtubules [36,37]. Therefore, imaging the movement of actin filaments and microtubules in tumor cells is important for tumor imaging.
In the end of the last century, Bruchez et al. labeled the F-actin filaments with red nanocrystal probes conjugated with biotin [38]. Compared with conventional dye molecules, the nanocrystal-labeled samples showed advantages of neglectable photobleaching [38]. Wu et al. used QD 630-streptavidin (red) and QD 535-streptavidin (green) to stain microtubules and actin filaments, respectively [25]. The results indicated the QD-based probes could be bright enough and specific enough for effectively labeling fine cellular structures, and have a better performance over other probes reported (shown in Figure 4) [25]. In 2008, Higuchi et al. reported new photostable, bright QDs conjugated with anti-tubulin antibody, which could bind to microtubules and trace the dynamic movement of microtubules in living cancer cells [39].
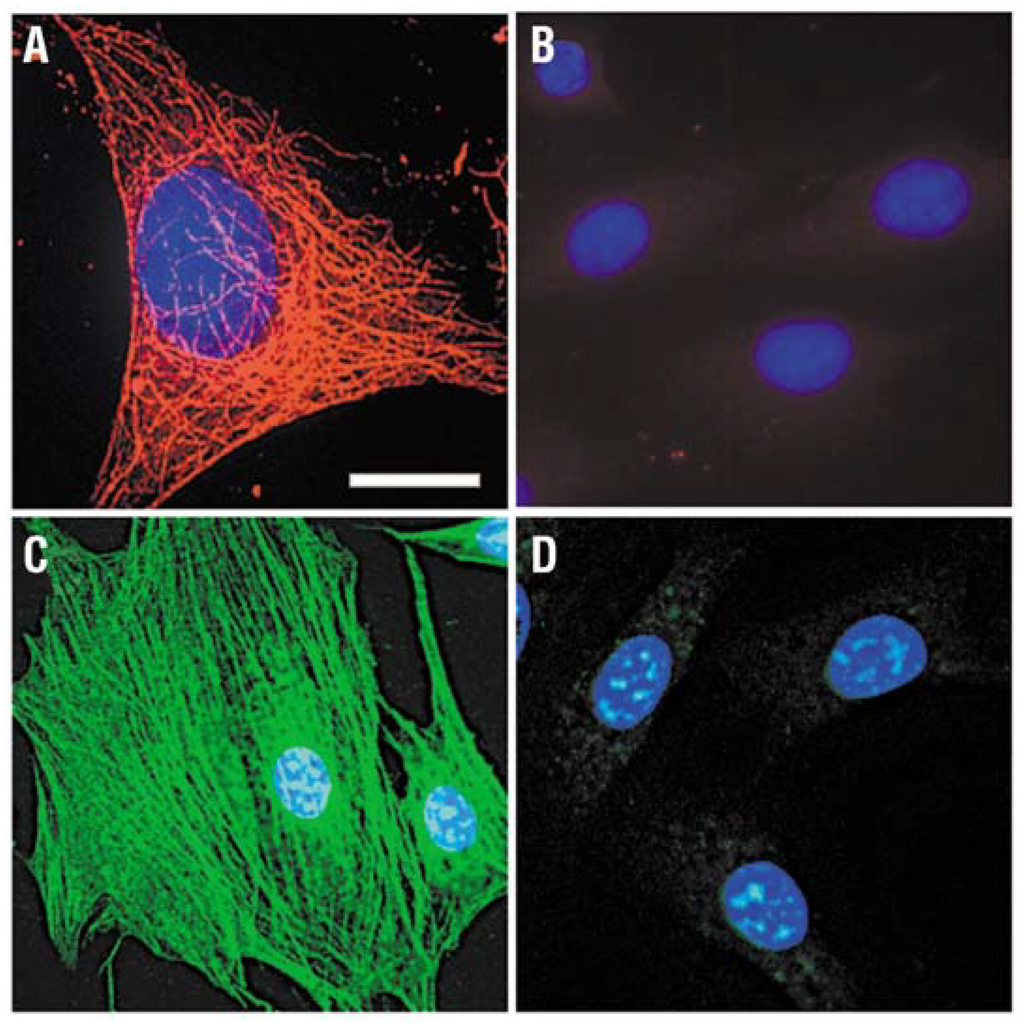
Figure 4.
Staining of cytoskeleton fibers in 3T3 mouse fibroblast cells with QD-streptavidin. (A) Microtubules were labeled with monoclonal anti-α-tubulin antibody, biotinylated anti-mouse IgG and QD 630-streptavidin (red); (B) Control for (A) without primary antibody; (C) Actin filaments were stained with biotinylated phalloidin and QD 535-streptavidin (green); (D) Control for (C) without biotin-phalloidin. The nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 blue dye. Filter sets ex. 480 ± 20 nm/em. 535 ± 10 nm and ex. 560 ± 27.5 nm/em. 635 ± 10 nm were used to observe signals of QD 535 and QD 630, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm for (A), 24 μm for (B) through (D). Reprinted with permission from [25]. Copyright 2003 Nature Publishing Group.
2.3. QDs for Imaging Nuclear Antigens (Intranuclear)
Tumor cells have some specific over-expressed nuclear antigens relating to their endless proliferation, such as PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) [40]. It was reported that QDs coated with urea or acetate groups might stain the nucleus [38]. Tang et al. used CdSe/ZnS QDs conjugated with anti-human PCNA antibody to label PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigens) in breast cancer tissues (shown in Figure 5) [40]. Xingyong Wu used QD 630-streptavidin to label the nuclei of SK-BR-3 cells successfully [25]. Labeling nuclear antigens in tumor cells with QD-conjugated bioprobes offers people with useful and reliable information for biomedical analysis and cancer diagnosis.
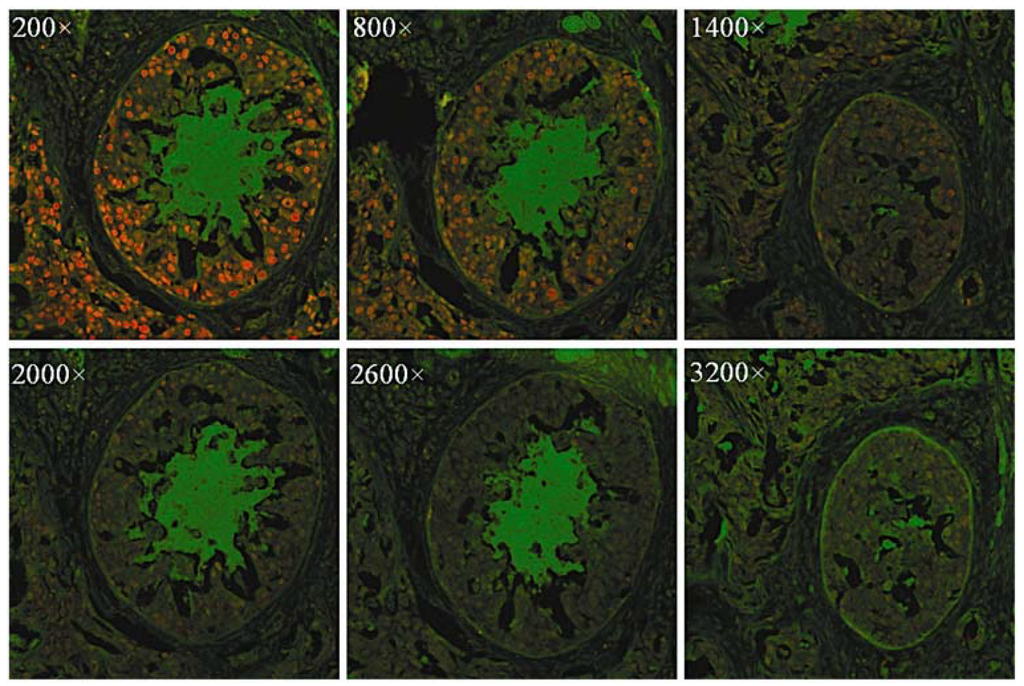
Figure 5.
Fluorescence images of breast cancer tissues labeled with CdSe/ZnS QDs. PCNA was stained red with QDs modified with the antibody. The original QD-SA concentration was about 1 μmol/L and was diluted 200–3200× before staining operations. Reprinted with permission from [40]. Copyright 2010 Society for Applied Spectroscopy.
2.4. QDs for Imaging Tumor Neovasculature (a Special Example of Tumor Imaging)
Newly formed/forming blood vessels express αvβ3 integrin, which specifically binds to arginine-glycine-aspartic (RGD) peptides. The αvβ3 integrin receptor plays an important role in tumor metastasis and tumor-induced angiogenesis, making it possible for RGD-conjugated QDs to image tumor neovasculature [41]. Employing this, Sanjiv Sam Gambhir and co-workers designed RGD-QDs for real-time intravital imaging of luminal endothelium in mouse tumor neovasculature [41]. The peptides for QDs conjugation are cyclo(RGDfC) and cyclo(RADfC). In contrast to the controls, RGD-QDs specifically bound to tumor vessel endothelium and exhibited better performance than organic dyes (shown in Figure 6). Importantly, this work of real-time imaging tumor neovasculature was performed in living subjects with an intravital microscopy, which opens the door of in vivo tumor imaging with QDs.
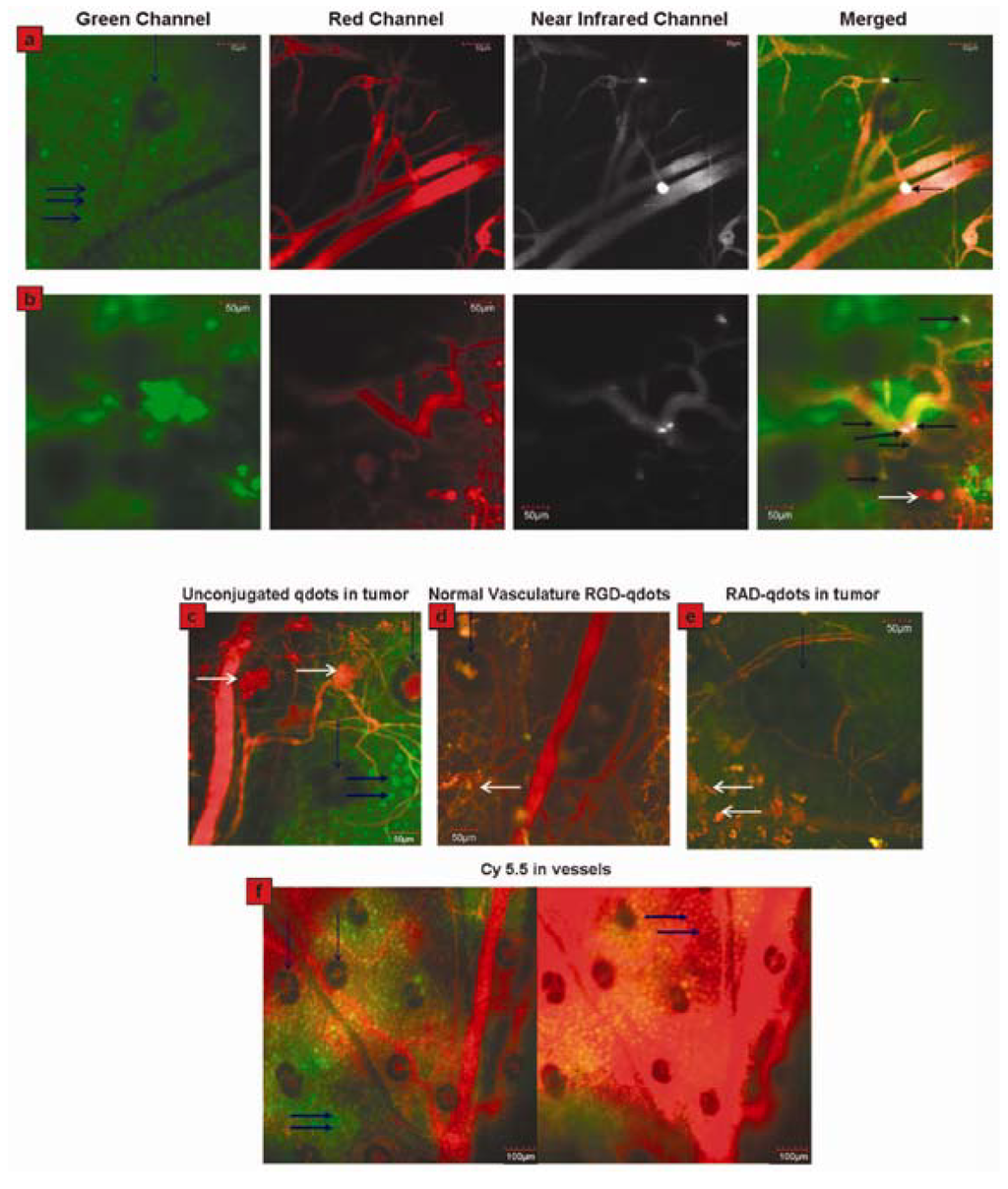
Figure 6.
Direct visualization of binding of RGD-QDs to tumor vessel endothelium and controls. (a) Panel displays different output channels of the identical imaging plane along the row with scale bars. In the green channel, individual EGFP-expressing cancer cells are visible (marked by thick horizontal blue arrows; vertical blue arrow points to a hair follicle), while the red channel outlines the tumor’s vasculature via injection of Angiosense dye. The NIR channel shows intravascularly administered QDs, which remain in the vessels (i.e., they do not extravasate). Binding events are visible by reference to bright white signal. These are demarcated by arrows in the rightmost merged image, in which all three channels have been overlaid; (b) Displays the same as (a) in a different mouse, except that six times the RGD-QDs dose has been injected. Individual cells are not generally visible. Six binding events are observed in this FOV, as marked by arrows in the merged image at right. White arrows in the bottom merged image designate areas of tissue autofluorescence. Typical images of no binding in each control condition are shown in (c–f). Tumor neovasculature containing unconjugated QDs (c), normal vasculature containing RGD-QDs (d), and tumor neovasculature containing RAD-QDs (e). (f) Tumor vasculature shortly after Cy5.5 injection (left) and ~20 min post-Cy5.5 injection (right). Individual cancer cells are visible before (left) and after dye extravasates (right, dyed red). Also see movie S6 in Supporting Information. Horizontal white arrows indicate tissue autofluorescence, vertical blue arrows denote hair follicles (which generally display autofluorescence in their center), and thick horizontal blue arrows indicate individual cancer cells. Reprinted with permission from [41]. Copyright 2008 American Chemical Society.
3. QDs for Tumor Therapy
Although relatively fewer researches on QDs for tumor therapy were reported, it is conceivable that QDs have the potentialities for tumor therapy due to their large surface areas available for the modification of functional groups or therapeutic agents such as anti-cancer drugs [42] and PDT photosensitizers (PS) [43]. Moreover, QDs themselves can also functionalize as PDT photosensitizers for tumor therapy [44]. Herein, QDs as PDT photosensitizers and anti-cancer drug-QD complexes for cancer therapy are reviewed as following. Barberi-Heyo et al. established that QDs conjugated with folic acid (FA) could be used as PS for PDT of cancer [45]. They conjugated CdTe(S)-type QDs with FA which is an optimal targeting ligand for selectively delivering the attached therapeutic agents (herein QDs as PS) to cancer tissues. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl) 2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay indicated that the survival rate of KB (human head and neck carcinoma cell line) cells incubated with FA-conjugated QDs decreased as the irradiation time or intensity increased (shown in Figure 7). The results demonstrated that CdTe(S)-type QDs had photosensitizing properties, which could be used to promote PDT effect. In their study, they mentioned that the concentration of QDs should be inferior to 10 nM and the incubation time less than 8 hour to avoid the intrinsic cytotoxicity of QDs without light irradiation.
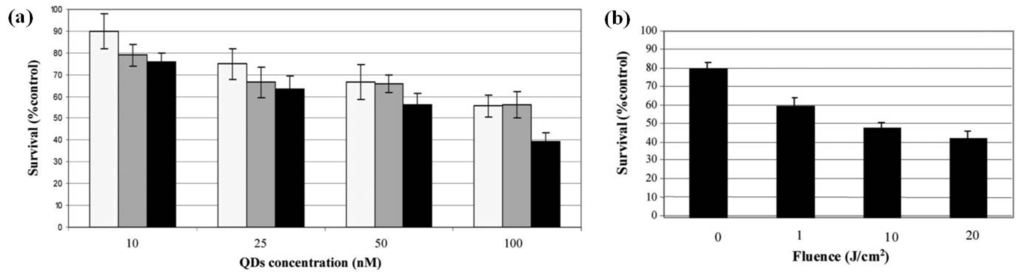
Figure 7.
(a) Measurement of PDT sensitivity of KB cells treated with FA-conjugated QD 4. Cells were exposed to QDs in a concentration range of 10–100 nM for 1 (light gray), 3 (dark grey) and 6 h (black); (b) Survival curves obtained for cells incubated with QDs at 5 nM for 3 h incubation before irradiation to increasing doses of light from 1 to 20 J cm−2. Measurement of PDT sensitivity for the QDs were obtained by MTT test (data points show the mean ± s.d., n = 6). * P < 0.05 vs. previous fluence dose. Reprinted with permission from [45]. Copyright 2011 Royal Society of Chemistry.
Taking advantage of QDs’ superior physical properties, PS-QDs conjugates can be excited with a wide range of wavelengths and avoid the PS to absorb light in the mean time (Figure 8 explains how QDs assist photosensitizers with producing singlet oxygen) [43]. Clemens Burda and co-workers used QD-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) to facilitate the excitation of a PDT photosensitizer to generate reactive 1O2 species for PDT [46]. The results demonstrated that CdSe QDs could be used to sensitize either phthalocyanines (a family of PDT agents) such as Pc4 via FRET mechanism or itself as PS via a triplet energy transfer (TET) mechanism to produce 1O2 species for PDT (shown in Figure 9).
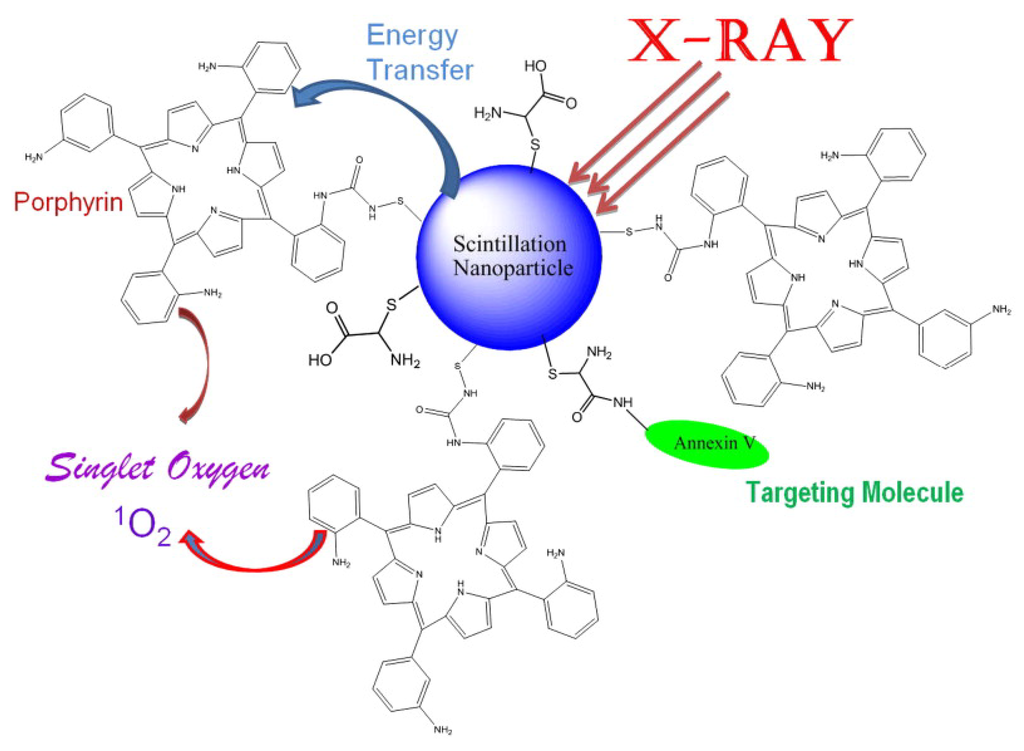
Figure 8.
Schematic presentation of the nanoparticle-based X-ray-induced PDT. Under ionizing radiation a nanoparticle starts to scintillate transferring its energy into a conjugated porphyrin molecule, which then generates singlet oxygen necessary to produce photosensitizing effect. This methodology will help to treat nodular and deeper tumors due to higher penetrating capacity of X-rays and gamma rays compared to that of visible light commonly used in PDT. Reprinted with permission from [43]. Copyright 2008 Elsevier.
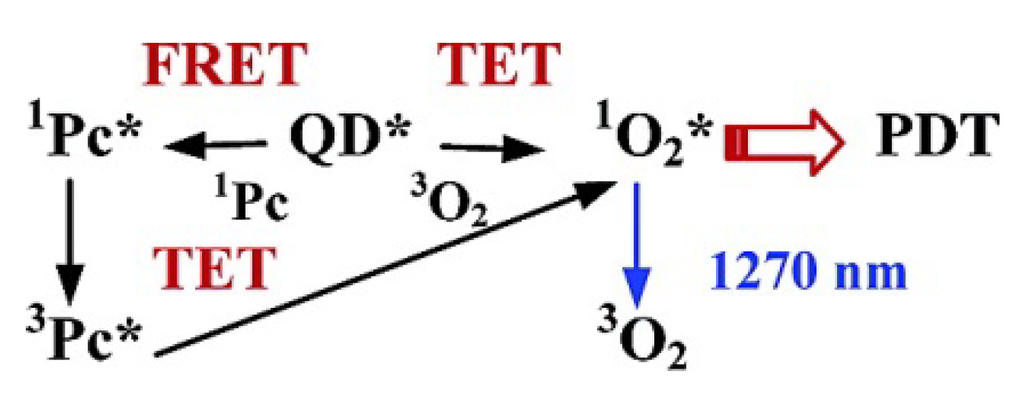
Figure 9.
Schematics of the 1O2 generation in QD-based PDT systems. Reprinted with permission from [46]. Copyright 2003 American Chemical Society.
4. Multifunctional QDs for Synchronous Tumor Imaging and Therapy
QDs have exhibited specific advantages in tumor imaging and tumor therapy. Large surface area of QDs enables them to be conjugated with different agents including targeting molecules, therapeutic chemicals, and imaging substances. Obviously, the multifunctional QDs for synchronous tumor imaging and therapy will be much more attractive and important. Sangyong Jon and co-workers reported such a multifunctional QD-aptamer (Apt)-doxorubicin (Dox) conjugate [QD-Apt(Dox)] for cancer-targeted imaging, therapy, and sensing [47]. The conjugate consists of three components: QDs, which functionalize as fluorescent agents; RNA aptamers covalently attached to the surface of QD, which serve a dual functions as targeting molecules and as drug carrying vehicles; Dox, which is a therapeutic agent for tumor cells as well as a fluorescent agent (Dox has fluorescence itself [48]). This conjugate keeps fluorescence-off state through a Bi-FRET mechanism when Dox links to QD. Fluorescence of both QD and Dox will be turned on after Dox being released from the QD-conjugate. The results indicated that QD-Apt(Dox) could differentially bind to prostate specific membrane antigen(PSMA)-expressing LNCaP cells instead of the PSMA-negative PC3 prostate adenocarcinoma cell lines due to the aptamer selectively binding to PSMA. Fluorescence microscopic cell imaging indicated that Dox was released from QD-conjugate 1.5 h after endocytosis and the targeting cells were stained with both Dox and QD (shown in Figure 10). MTT assay indicated that the QD-Apt(Dox) has LNCaP cell-targeted therapeutic ability (shown in Figure 11).
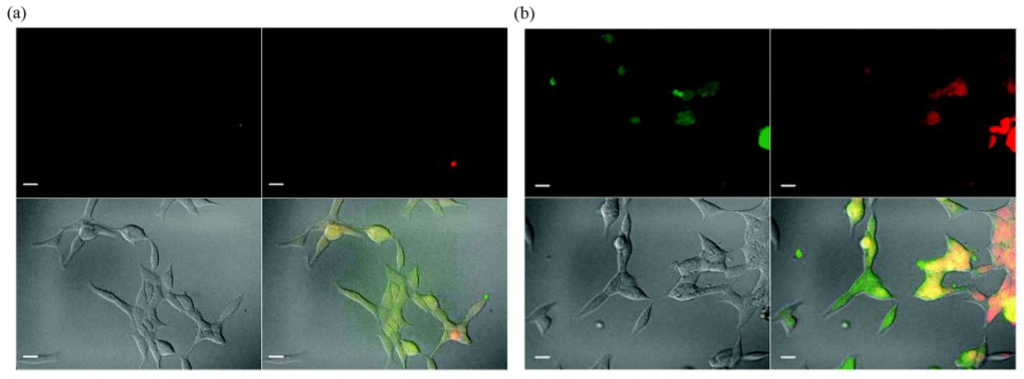
Figure 10.
Confocal laser scanning microscopy images of PSMA expressing LNCaP cells after incubation with 100 nM QD-Apt-(Dox) conjugates for 0.5 h at 37 °C, washed two times with PBS buffer, and further incubated at 37 °C for (a) 0 h and (b) 1.5 h. Dox and QD are shown in red and green, respectively, and the lower right images of each panel represents the overlay of Dox and QD fluorescent. The scale bar is 20 μm. Reprinted with permission from [47]. Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society.
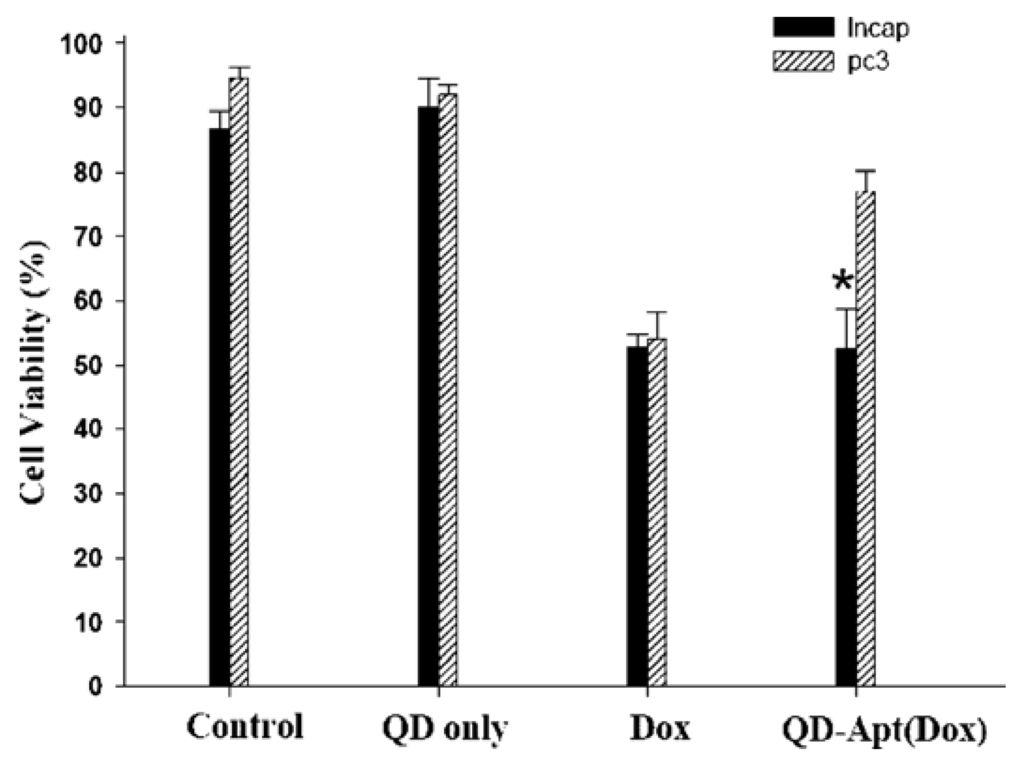
Figure 11.
Growth inhibition assay (MTT). Prostate cancer cell lines, LNCaP (PSMA+) and PC3 (PSMA−), were incubated with QD alone (1.6 μM), Dox along (5 μM), or QD-Apt(Dox) conjugates (1.6 μM), for 3 h, and the cells were washed and further incubated for 24 h prior to measurement of cell viability. Asterisk indicates significant differences between LNCaP and PC3 cells, (P < 0.005, n = 3). Reprinted with permission from [47]. Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society.
In summary, this conjugate can be used to detect cancer cells at a single cell level. It exhibits specificity and sensitivity to LNCaP cells for sensing, imaging, and therapy.
5. Conclusions
Quantum Dots, as one type of multifunctional materials, have shown promising advantages in tumor imaging and therapy due to their specific physicochemical properties. Nevertheless, they still have some non-neglectable limitations such as increased sizes after coating [49] and the cytotoxicities introduced [2,50]. As we reviewed above, some QDs have impressive effect of imaging tumor neovasculature, which is however too late for clinical diagnosis of cancer development. These call for the development of new types of QDs for the detection of important biomarkers (e.g., furin) of cancers at early stages [51]. Development of QDs in the future will not be limited to tumor imaging or therapy, but could be a combination of two or multiple functions. We envision that QDs will become one type of promising material for real-time tumor-targeted imaging and therapy in the future.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21175122, 91127036), the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (WK2060190018), and Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1108085J17).
References
- Hanson, R.; Kouwenhoven, L.P.; Petta, J.R.; Tarucha, S.; Vandersypen, L.M.K. Spins in few-electron quantum dots. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2007, 79, 1217–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, R. A toxicologic review of quantum dots: Toxicity depends on physicochemical and environmental factors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalet, X.; Pinaud, F.F.; Bentolila, L.A.; Tsay, J.M.; Doose, S.; Li, J.J.; Sundaresan, G.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Weiss, S. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 2005, 307, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir, T.M.; Mansour, M.M.H.; Kazmierczak, S.C.; Azzazy, H.M.E. Quantum dots: Heralding a brighter future for clinical diagnostics. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 1755–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medintz, I.L.; Uyeda, H.T.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, N.; Zhang, W.; Mathias, P.C.; Chow, E.; Soares, J.; Malyarchuk, V.; Smith, A.D.; Cunningham, B.T. Enhanced fluorescence emission from quantum dots on a photonic crystal surface. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.M.; Festy, F.; Richards, D. Tip-enhanced fluorescence imaging of quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 183101:1–183101:3. [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson, T.; Bakhshi, R.; Petrova, D.; Pocock, R.; Imani, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4717–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissleder, R.; Pittet, M.J. Imaging in the era of molecular oncology. Nature 2008, 452, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, Y.; Peymani, P.; Afifi, S. Quantum dot: Magic nanoparticle for imaging, detection and targeting. Acta Biomed. 2009, 80, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stringari, C.; Nourse, J.L.; Flanagan, L.A.; Gratton, E. Phasor fluorescence lifetime microscopy of free and protein-bound nadh reveals neural stem cell differentiation potential. PLoS One 2012, 7, e48014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangioni, J.V. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, S.; Gnanasegaran, G.; Cook, G.J.R. Miscellaneous cancers (lung, thyroid, renal cancer, myeloma, and neuroendocrine tumors): Role of spect and pet in imaging bone metastases. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2009, 39, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Brechbiel, M.; Choyke, P.L. Macromolecular mri contrast agents for imaging tumor angiogenesis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 60, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.B.; Shin, D.W.; Chen, K.; Gheysens, O.; Cao, Q.Z.; Wang, S.X.; Gambhir, S.S.; Chen, X.Y. Peptide-labeled near-infrared quantum dots for imaging tumor vasculature in living subjects. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.H.; Chen, K.; Xie, R.G.; Xie, J.; Lee, S.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, X.G.; Chen, X.Y. Ultrasmall near-infrared non-cadmium quantum dots for in vivo tumor imaging. Small 2010, 6, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.B. Radiotherapy of mobile tumors. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2006, 16, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-Bubb, J.; Croteau, R.; Williams, R.M. The early stages of taxol biosynthesis: An interim report on the synthesis and identification of early pathway metabolites. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.F.; Shinde, S.S.; Hay, M.P.; Denny, W.A. Potentiation of the cytotoxicity of the anticancer agent tirapazamine by benzotriazine n-oxides: The role of redox equilibria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efferth, T.; Li, P.C.H.; Konkimalla, V.S.B.; Kaina, B. From traditional chinese medicine to rational cancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, S.Y.; Hour, T.C.; Lin, S.R.; Yu, D.S. Taxol synergizes with antioxidants in inhibiting hormal refractory prostate cancer cell growth. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2010, 28, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.A.; Evans, D.H.; Abraharnse, H. Photodynamic therapy (PDT): A short review on cellular mechanisms and cancer research applications for pdt. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2009, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.H.; Yang, L.L.; Petros, J.A.; Marshal, F.F.; Simons, J.W.; Nie, S.M. In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.Y.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, J.Q.; Haley, K.N.; Treadway, J.A.; Larson, J.P.; Ge, N.F.; Peale, F.; Bruchez, M.P. Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballou, B.; Ernst, L.A.; Andreko, S.; Harper, T.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.J.; Waggoner, A.S.; Bruchez, M.P. Sentinel lymph node imaging using quantum dots in mouse tumor models. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, A.F.; Groom, A.C.; MacDonald, I.C. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonda, K.; Watanabe, T.M.; Ohuchi, N.; Higuchi, H. In vivo nano-imaging of membrane dynamics in metastatic tumor cells using quantum dots. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 2750–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.J.; Chae, J.R.; Cho, Y.L.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, S. Multiplex imaging of single tumor cells using quantum-dot-conjugated aptamers. Small 2009, 5, 2519–2522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christian, S.; Pilch, J.; Akerman, M.E.; Porkka, K.; Laakkonen, P.; Ruoslahti, E. Nucleolin expressed at the cell surface is a marker of endothelial cells in angiogenic blood vessels. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Girvan, A.C.; Casson, L.K.; Pierce, W.M.; Qian, N.; Thomas, S.D.; Bates, P.J. As1411 alters the localization of a complex containing protein arginine methyltransferase 5 and nucleolin. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10491–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, D.A.; Chen, H.; Hicke, B.J.; Swiderek, K.M.; Gold, L. A tenascin-c aptamer identified by tumor cell selex: Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15416–15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borbas, K.E.; Ferreira, C.S.M.; Perkins, A.; Bruce, J.I.; Missailidis, S. Design and synthesis of mono- and multimeric targeted radiopharmaceuticals based on novel cyclen ligands coupled to anti-muc1 aptamers for the diagnostic imaging and targeted radiotherapy of cancer. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.S.M.; Matthews, C.S.; Missailidis, S. DNA aptamers that bind to muc1 tumour marker: Design and characterization of muc1-binding single-stranded DNA aptamers. Tumor Biol. 2006, 27, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettstein, G.; Bellaye, P.S.; Micheau, O.; Bonniaud, P. Small heat shock proteins and the cytoskeleton: An essential interplay for cell integrity? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1680–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, Y.W.; Koh, C.G. Actin cytoskeleton dynamics and the cell division cycle. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, P.; Tirnauer, J.S. Tumor suppressor interactions with microtubules: Keeping cell polarity and cell division on track. Dis. Model. Mech. 2010, 3, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchez, M.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss, S.; Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ybo, J.; Kambara, T.; Gonda, K.; Higuchi, H. Intracellular imaging of targeted proteins labeled with quantum dots. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 3563–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Chen, C.A.; Peng, J.; Tang, H.W.; Liu, C.M.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Pang, D.W. Evaluation of the bioconjugation efficiency of different quantum dots as probes for immunostaining tumor-marker proteins. Appl. Spectrosc. 2010, 64, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.R.; Cheng, Z.; De, A.; Koh, A.L.; Sinclair, R.; Gambhir, S.S. Real-time intravital imaging of rgd-quantum dot binding to luminal endothelium in mouse tumor neovasculature. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhyner, M.N.; Smith, A.M.; Gao, X.H.; Mao, H.; Yang, L.L.; Nie, S.M. Quantum dots and multifunctional nanoparticles: New contrast agents for tumor imaging. Nanomedicine 2006, 1, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juzenas, P.; Chen, W.; Sun, Y.P.; Coelho, M.A.N.; Generalov, R.; Generalova, N.; Christensen, I.L. Quantum dots and nanoparticles for photodynamic and radiation therapies of cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1600–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakalova, R.; Ohba, H.; Zhelev, Z.; Nagase, T.; Jose, R.; Ishikawa, M.; Baba, Y. Quantum dot anti-cd conjugates: Are they potential photosensitizers or potentiators of classical photosensitizing agents in photodynamic therapy of cancer? Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosini, V.; Bastogne, T.; Frochot, C.; Schneider, R.; Francois, A.; Guillemin, F.; Barberi-Heyo, M. Quantum dot-folic acid conjugates as potential photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy of cancer. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2011, 10, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samia, A.C.S.; Chen, X.B.; Burda, C. Semiconductor quantum dots for photodynamic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15736–15737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagalkot, V.; Zhang, L.; Levy-Nissenbaum, E.; Jon, S.; Kantoff, P.W.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Quantum dot–aptamer conjugates for synchronous cancer imaging, therapy, and sensing of drug delivery based on bi-fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3065–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, E.R.; Frechet, J.M.J. Ph-responsive copolymer assemblies for controlled release of doxorubicin. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klostranec, J.M.; Chan, W.C.W. Quantum dots in biological and biomedical research: Recent progress and present challenges. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yee, D.; Wang, C. Quantum dots for cancer diagnosis and therapy: Biological and clinical perspectives. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.L.; Ren, H.J.; Rao, J.H. A biocompatible condensation reaction for controlled assembly of nanostructures in living cells. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2013 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).