Tissue Equivalents Based on Cell-Seeded Biodegradable Microfluidic Constructs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Microfabrication of Tissue Scaffold

2.2. Evaluation of Cell-Seeded Construct


2.3. Staining of Flat Cell-Seeded Silk Films
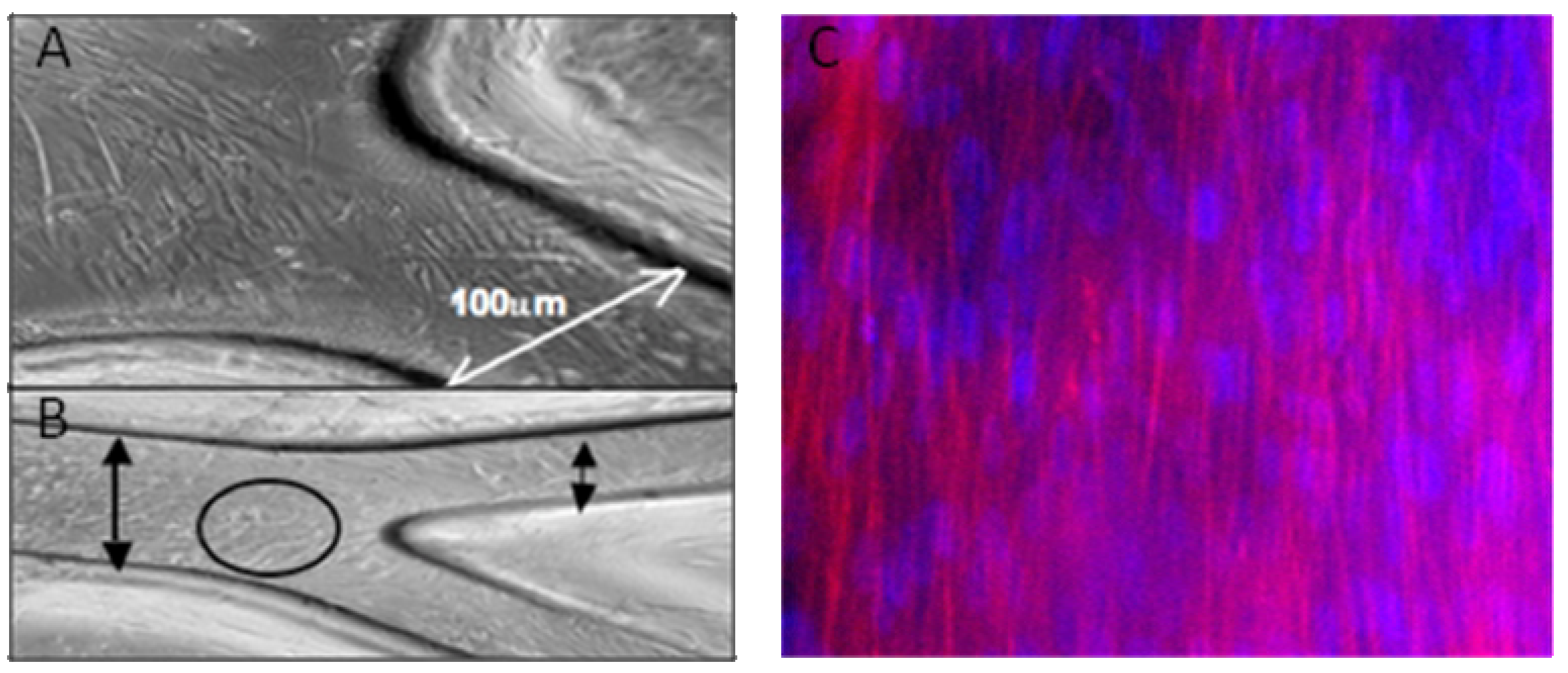
2.4. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Silk Solution
3.2. Silk Microvascular Network Scaffold Fabrication

3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Cell Seeding
3.5. Cell Staining
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Khademhosseini, A.; Borenstein, J.T. Micro and Nanoengineering of the Cell Microenvironment; Toner, M., Takayama, S., Eds.; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rouwkema, J.; Rivron, N.; Blitterswijk, C. Vascularization in tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabodi, M.; Choi, N.W.; Gleghorn, J.P.; Lee, D.; Bonassar, L; Stroock, A.D. A microfluidic biomaterial. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 127, 13788–13789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druecke, D.; Langer, S.; Lamme, E.; Pieper, J.; Ugarkovic, M.; Steinau, H.; Homann, H. Neovascularization of poly(ether ester) block co-polymer scaffolds in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 68, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Park, H.; Engelmayr, G.C.; Moretti, M.; Freed, L.E. Effects of regulatory factors on engineered cardiac tissue in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, T.; Peters, M.; Ennett, A.; Mooney, D. Polymeric system for dual growth factor delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borenstein, J.T.; Terai, H.; King, K.R.; Weinberg, E.J.; Kaazempur-Mofrad, M.R.; Vacanti, J.P. Microfabrication technology for vascularized tissue engineering. Biomed. Microdevices 2002, 4, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armani, D.; Liu, C. Microfabrication technology for polycaprolactone, a biodegradable polymer. IEEE J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 10, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- King, K.R.; Wang, C.C.; Shin, M.; Vacanti, J.P.; Borenstein, J.T. Biodegradable polymer microfluidics for tissue engineering microvasculature. MRS Symp. Proc. 2002, 729, U1.4. [Google Scholar]
- King, K.R.; Wang, C.C.; Kaazempur-Mofrad, M.R.; Vacanti, J.P.; Borenstein, J.T. Biodegradable microfluidics. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bettinger, C.J.; Weinberg, E.J.; Wang, Y.; Kulig, K.; Vacanti, J.P.; Borenstein, J.T.; Langer, R. Three dimensional microfluidic tissue engineering scaffolds using a flexible biodegradable polymer. Adv. Mater. 2006, 16, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidowski, C.; Kaazempur-Mofrad, M.R.; Borenstein, J.T.; Vacanti, J.P.; Langer, R.; Wang, Y. Endothelialized microvasculature based on a biodegradable elastomer. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettinger, C.J.; Orrick, B.K.; Langer, R.; Borenstein, J.T. Tunable contact guidance using feature geometry in biodegradable substrates. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2558–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenberg, S.; Rouwkema, J.; Macdonald, M.; Gerfein, E.; Kohane, D.; Darland, D.; Marini, R.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Mulligan, R.; D’Amore, P.; Langer, R. Engineering vascularized skeletal muscle tissue. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Bettinger, C.J.; Cyr, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Langer, R.; Borenstein, J.T.; Kaplan, D. Silk fibroin microfluidic devices. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2847–2850. [Google Scholar]
- Lokmic, Z.; Mitchell, G. Engineering the microcirculation. Tissue Eng. B 2008, 14, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, G.; Diaz, F.; Jakuba, C.; Calabro, T.; Horan, R.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Richmond, J.; Kaplan, D. Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.; Aronson, S. Suture reaction in the human cornea, sclera, and ocular muscle. Arch. Opthalmol. 1969, 82, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondar, B.; Fucs, S.; Motta, A.; Migliaresi, C.; Kirkpatrick, C. Functionality of endothelial cells on silk fibroin nets: Comparative study of micro- and nanometic fibre size. Biomaterials 2008, 28, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Vepari, C.; Jin, H.; Kim, H.; Kaplan, D. Electrospun silk-BMP-2 scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3115–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, B.; Jianmei, X.; Qilong, S.; Chuanxia, D.; Jiangchao, Z.W. On the growth model of the capillaries in the porous silk fibroin films. J. Mater. Sci., Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, S.; McCarthy, M.; Gronowicz, G.; Kaplan, D. Functionalized silk-based biomaterials for bone formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 54, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuniff, P.; Fossey, S.; Auerbach, M.; Song, J.; Kaplan, D.; Adams, W.; Eby, R.; Mahoney, D.; Vezie, D. Mechanical and thermal properties of dragline silk from the spider, Nephlia clavipes. Polym. Adv. Tech. 1994, 5, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoura, N.; Tsukada, M.; Nagura, M. Physico-chemical properties of silk fibroin membrane as a biomaterial. Biomaterials 1990, 11, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Kluge, J.A.; Uppal, N.; Omenetto, F.; Kaplan, D.L. Insoluble and flexible silk films containing glycerol. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Park, J.; Karageorgiou, V.; Kim, U.; Valluzzi, R.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D. Water-stable silk films with reduced-sheet content. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.; Kim, U.; Park, J.; Jin, H. Concentrated aqueous silk fibroin solution and use thereof. US Pat. 20,070,187,862, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lovett, M.; Cannizzaro, C.; Daheron, L.; Messmer, B.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D. Silk fibroin microtubes for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5271–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, I.M.; Leung, A. Development of a 3-D Model System for Studying the Angiogenesis of Wound Healing. In Angiogenesis Protocols: Methods in Molecular Biology, 2nd ed.; Martin, S., Murray, C., Eds.; Humana Press, Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 467, pp. 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, J.T.; Cheung, W.; Hartman, L.; Kaazempur-Mofrad, M.R.; King, K.R.; Sevy, A.; Shin, M.; Weinberg, E.J.; Vacanti, J.P. Living three-dimensional micro fabricated constructs for the replacement of vital organ function. In Proceedings of the Transducers, Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, 12th International Conference, Boston, MA, 8–12 June 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1754–1757.
© 2010 by the authors. Licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Borenstein, J.T.; Megley, K.; Wall, K.; Pritchard, E.M.; Truong, D.; Kaplan, D.L.; Tao, S.L.; Herman, I.M. Tissue Equivalents Based on Cell-Seeded Biodegradable Microfluidic Constructs. Materials 2010, 3, 1833-1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3031833
Borenstein JT, Megley K, Wall K, Pritchard EM, Truong D, Kaplan DL, Tao SL, Herman IM. Tissue Equivalents Based on Cell-Seeded Biodegradable Microfluidic Constructs. Materials. 2010; 3(3):1833-1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3031833
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorenstein, Jeffrey T., Katie Megley, Kimberly Wall, Eleanor M. Pritchard, David Truong, David L. Kaplan, Sarah L. Tao, and Ira M. Herman. 2010. "Tissue Equivalents Based on Cell-Seeded Biodegradable Microfluidic Constructs" Materials 3, no. 3: 1833-1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3031833
APA StyleBorenstein, J. T., Megley, K., Wall, K., Pritchard, E. M., Truong, D., Kaplan, D. L., Tao, S. L., & Herman, I. M. (2010). Tissue Equivalents Based on Cell-Seeded Biodegradable Microfluidic Constructs. Materials, 3(3), 1833-1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3031833





