Green Synthesis and Particle Size Control of High-Purity Alumina Based on Hydrolysis of Alkyl Aluminum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Experimental Method
2.3. Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
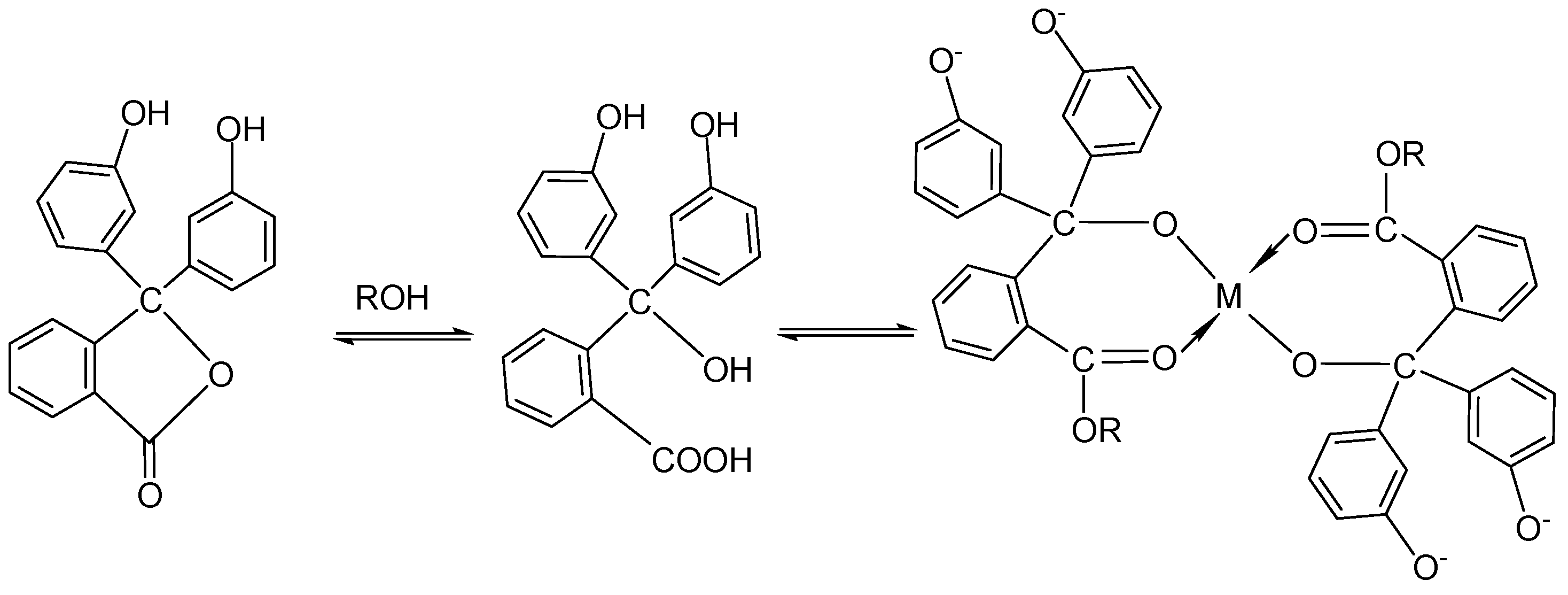
3.1. Synthesis of Aluminum Isopropoxide
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
3.1.2. Elemental Content Analysis
3.2. Hydrolysis of Aluminum Isopropoxide
3.3. Calcination of Hydrolysis Products
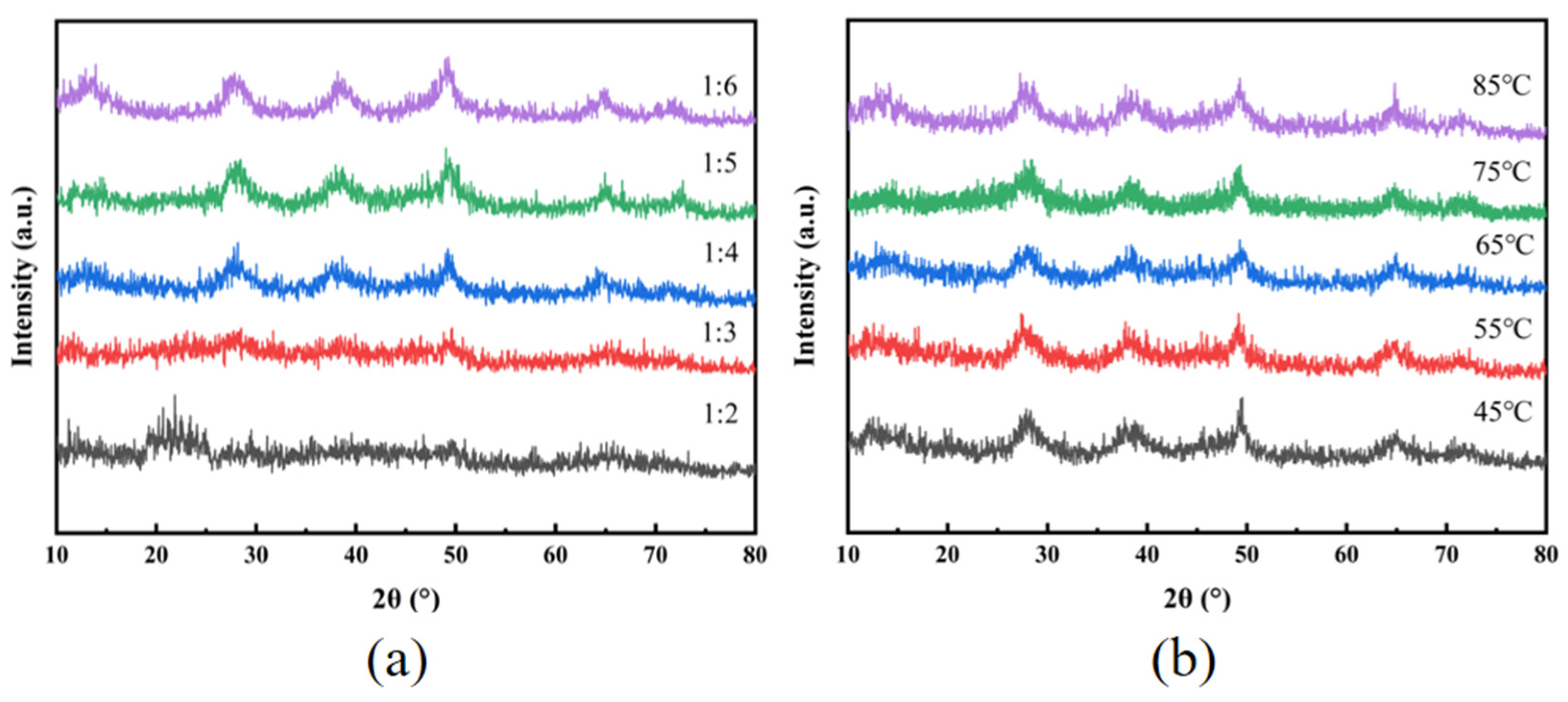
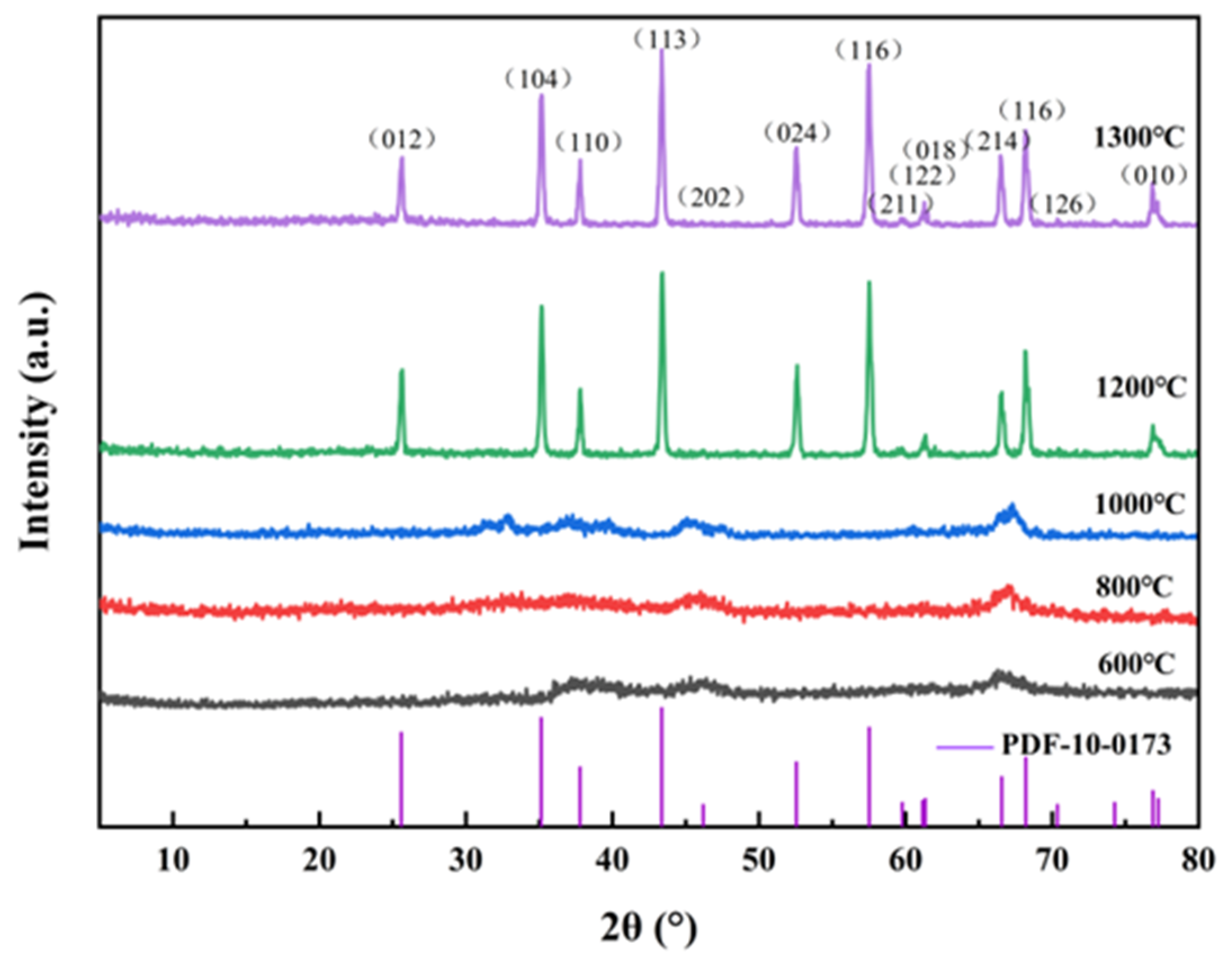
3.3.1. XRD Analysis
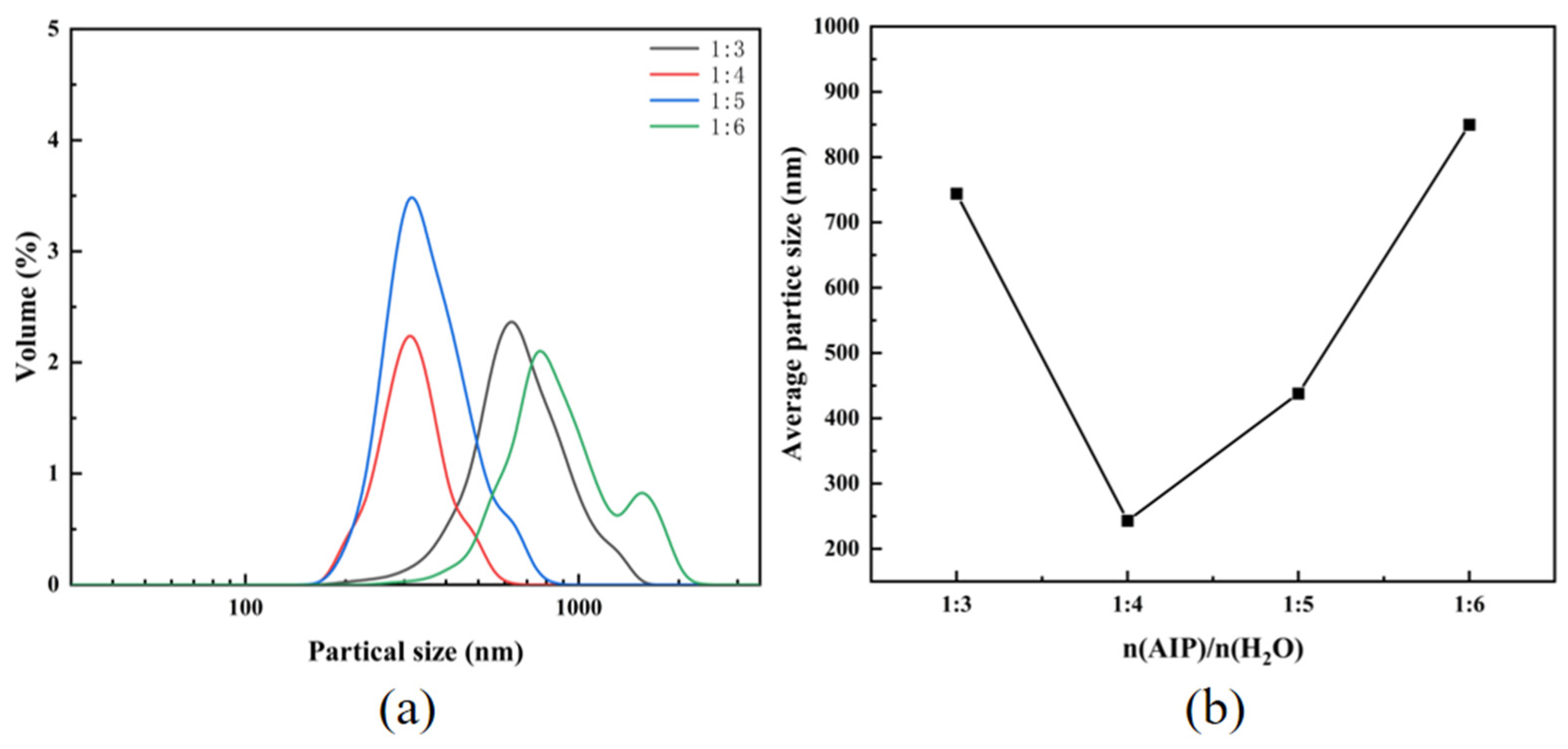
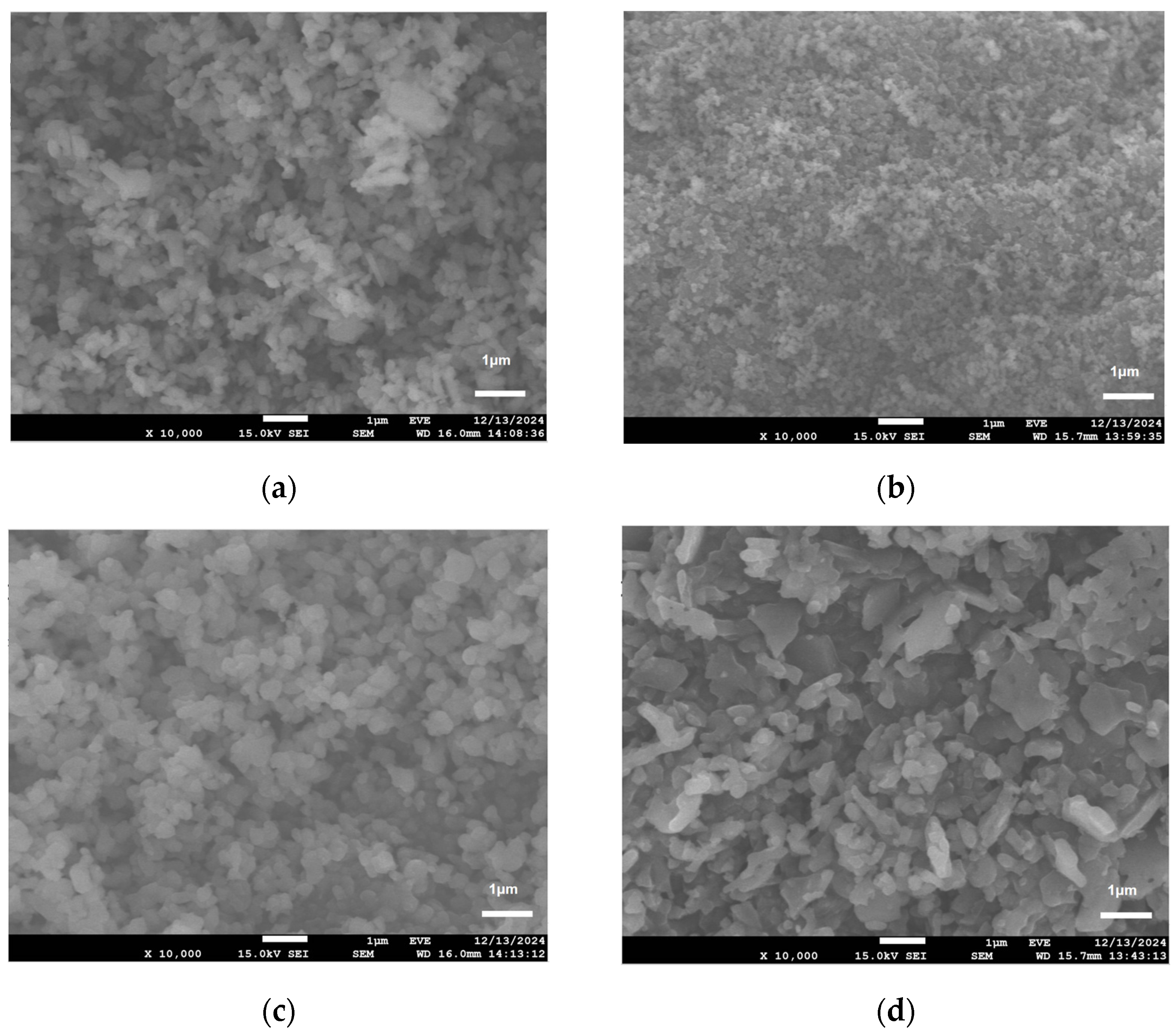
3.3.2. Particle Size and Morphology Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, X.F.; Xu, B.J.; Huang, C.J. Preparation of High Purity Alumina Technology Overview. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 734–737, 2496–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, S.; Greg, P. High Purity Alumina—Current and Future Production. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 43, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasakan, P.; Rajendran, V.; Rauta, P.R.; Sahu, B.B.; Panda, B.K. Direct Synthesis of Nano Alumina from Natural Bauxite. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 67, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasyuk, G.P.; Azarova, L.A.; Belan, V.N.; Semenov, E.A.; Kharatyan, S.Y. Methods for High-Purity Aluminum Oxide Production for Growth of Leucosapphire Crystals (Review). Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2019, 53, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.-K.; Choi, H.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, T.J.; Kang, M.; Lee, W.G.; Kim, H.D.; Park, J.W. Purification of Al(OH)3 synthesized by Bayer process for preparation of high purity alumina as sapphire raw material. J. Cryst. Growth 2013, 373, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Li, T.; Hreniak, D. Fabrication of submicron grained alumina transparent ceramics with high bending strength and low dielectric loss. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.B.; Dai, J.S.; Xu, L.N.; Wang, X.H. Advance of Sintering Methods of High Purity Alumina Ceramics. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 703, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri, S.; Rezaei, M.; Garbarino, G.; Busca, G. Facile synthesis of a mesoporous alumina and its application as a support of Ni-based autothermal reforming catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 3456–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenić, M.; Bacoș, T.B.; Milivojević, A.; Adžić, V.; Ciopec, M.; Nemeş, N.S.; Negrea, A.; Cioablă, A.E. α-Al2O3 Functionalized with Lithium Ions Especially Useful as Inert Catalyst Bed Supports. Mol. Online 2025, 30, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cokic, S.; Meerbeek, B.V.; Vleugels, J.; Zhang, F. Novel zirconia ceramics for dental implant materials. J. Mater. Sci. Annd Technol. 2025, 210, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P.P.; Gong, Y.L.; Xiang, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Li, Q.; Su, Y.H.; Leng, Y.X. Biocompatibility study of Fe-doped zirconia-toughened alumina ceramic for artificial joints. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 20108–20117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, V.L.; Colin, J.; Fabiana, L.; Li, H.Y.; Sylvain, N.; Ballif, C.; Ingenito, A.; Leon, J.J.D. Ultrathin ALD Aluminum Oxide Thin Films Suppress the Thermal Shrinkage of Battery Separator Membranes. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 45582–45589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. The application of Al2O3 in separators and solid electrolytes of lithium-ion battery: A review. Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 71, 103575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandapat, N.; Ghosh, S. Effect of alumina impurity on microstructure and properties of alumina based conventionally brazed joints. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2020, 27, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Tan, R.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Song, W. Coatings on Lithium Battery Separators: A Strategy to Inhibit Lithium Dendrites Growth. Molecules 2023, 28, 7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.J.; Yi, Y.K.; Kim, S.J.; Tran, T.; Kim, M.J. Production of micro-crystalline boehmite from hydrothermal processing of Bayer plant alumina tri-hydrate. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletnev, P.M.; Pogrebenkov, V.M.; Vereshchagin, V.I.; Tyul’kin, D.S. Corundum Refractory Material in Alumina-Binder Resistant to High-Temperature Deformation. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2018, 59, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y. Analysis of the Performances of a New Type of Alumina Nanocomposite Structural Material Designed for the Thermal Insulation of High-Rise Buildings. Fdmp-Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 2023, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W., Jr.; Powertrain, F.-M. Alumina Insulators for High Voltage Automotive Ignition Systems. In Processing, Properties, and Design of Advanced Ceramics and Composites; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 259, pp. 359–370. [Google Scholar]
- Aldbea, F.W.; Va’Zques-Va’Zquez, C.; Abobaker, M.A.; Alsteeni, A.Y.; Saad, A.; Sharma, A.; Singh, P.K.; Diantoro, M.; May, M.; Abdullah, T. Structural and optical properties of α aluminum oxide prepared by sol-gel method. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2025, 71, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogojan, R.; Andronescu, E.; Ghiulicǎ, C.; Vasile, B.T. Synthesis and characterization of alumina nano-powder obtained by sol-gel method. UPB Sci. Bull. Ser. B Chem. Mater. Sci. 2011, 73, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shakirzyanov, R.I.; Garanin, Y.A.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Shlimas, D.I.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Zhamikhanova, D.K. Study of Phase Composition and Microstructure of Porous Alumina Ceramics Derived from Hydrothermal Powders. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 155, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.G.; Wang, R.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Xu, M.H.; Ma, M.L. Preparation of Superfine Alumina Powders via Hydrothermal Method. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 726, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Zhao, Y.T.; Jia, Z.H.; Xu, L. Preparation of High Pure and Micron-Sized α-Al2O3 Powder by Activated Aluminium Hydrolysis Method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 988, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Sakaki, S.; Nakayama, A.; Kishida, H.; Ozaki, H.; Hattori, T.; Sakatani, Y. New technology and application development of alkoxide-derived high purity alumina. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2022, 104, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.A.S.; Lima, E.S.; Louro, L.H.L.; Neto, C.A.D.C. Synthesis of Powders Nanometer Al2O3 Method by Sol-Gel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2012, 727–728, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.C.; Lee, S.J. Fabrication of Activated Alumina Using Aluminum Hydroxide by a Hydrothermal Process. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2013, 50, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemkowska, W.; Basiak, D.; Kunicki, A.; Zawada, A.; Kurtycz, P.; Olszyna, A. Controlled synthesis of alumina using trialkylaluminum as starting materials. Main Group Chem. 2014, 13, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunde, G.B.; Yadav, G.D. Green approach in the sol–gel synthesis of defect free unsupported mesoporous alumina films. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 224, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, K.M.S. Formation of mesoporous alumina via hydrolysis of modified aluminum isopropoxide in presence of CTAB cationic surfactant. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2874–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.d.R.; Rosset, M.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Tenório, J.A.S. Production of High-Purity Alumina by Combining Solvent Extraction and Precipitation Techniques. Min. Metall. Explor. 2024, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cam, A.; Turan, M.D. Iron Removal from Bauxite by Oxalic Acid and Further Al Extraction by High-Pressure Alkali Leaching. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinnan, Y.; Huixin, J.; Fuzhong, W.; Weijie, W.; Qian, Y. Preparation of High-purity Alumina via Hydrolysis of Aluminum Isopropoxide after Desilication with Lanthanum Oxide. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 898, 012–022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, E.E.; Levin, Y.I.; Strel’nikova, I.E.; Amelina, A.E. Synthesis and purification of aluminum isopropylate. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 87, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.F.; Cheng, S.; Liu, H. Size-controlled synthesis of alumina nanoparticles through an additive-free reverse cation–anion double hydrolysis method. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.Q.; Wu, X.Z.; Xue, T.; Li, G.; Wang, W.W.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.M.; Tang, Y.; He, M.Y. Morphological Controlled Growth of Nanosized Boehmite with Enhanced Aspect Ratios in an Organic Additive-Free Cationic–Anionic Double Hydrolysis Method. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 5166–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Yin, J.L.; Liu, W.; Gao, H.; Yang, J.L. Hydrolysis Process and Mechanism of Magnesium Aluminate Alkoxides. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 197, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Bartholomew, C.H.; Woodfield, B.F. Facile synthesis of mesoporous γ-alumina with tunable pore size: The effects of water to aluminum molar ratio in hydrolysis of aluminum alkoxides. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 183, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Han, J.Y.; Hyun, D.E.; Jung, M.G.; Koo, S.M.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.N.; Lee, D.W.; Shin, W.H.; Oh, J.M. Effects of particle size and flow properties on the performance of ceramic-coated separators in Lithium-ion batteries. Powder Technol. 2024, 445, 120139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademann, J. Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. Reagents for High-Throughput Solid-Phase and Solution-Phase Organic Synthesis. Edited by Peter Wipf. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 45, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ning, G.; Li, J.S.; Lin, Y. The Novel and Effective Method of Removing of Trace Iron Impurity from Aluminum Isopropoxide for Nano-alumina. In Proceedings of the 2006 1st IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Zhuhai, China, 18–21 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
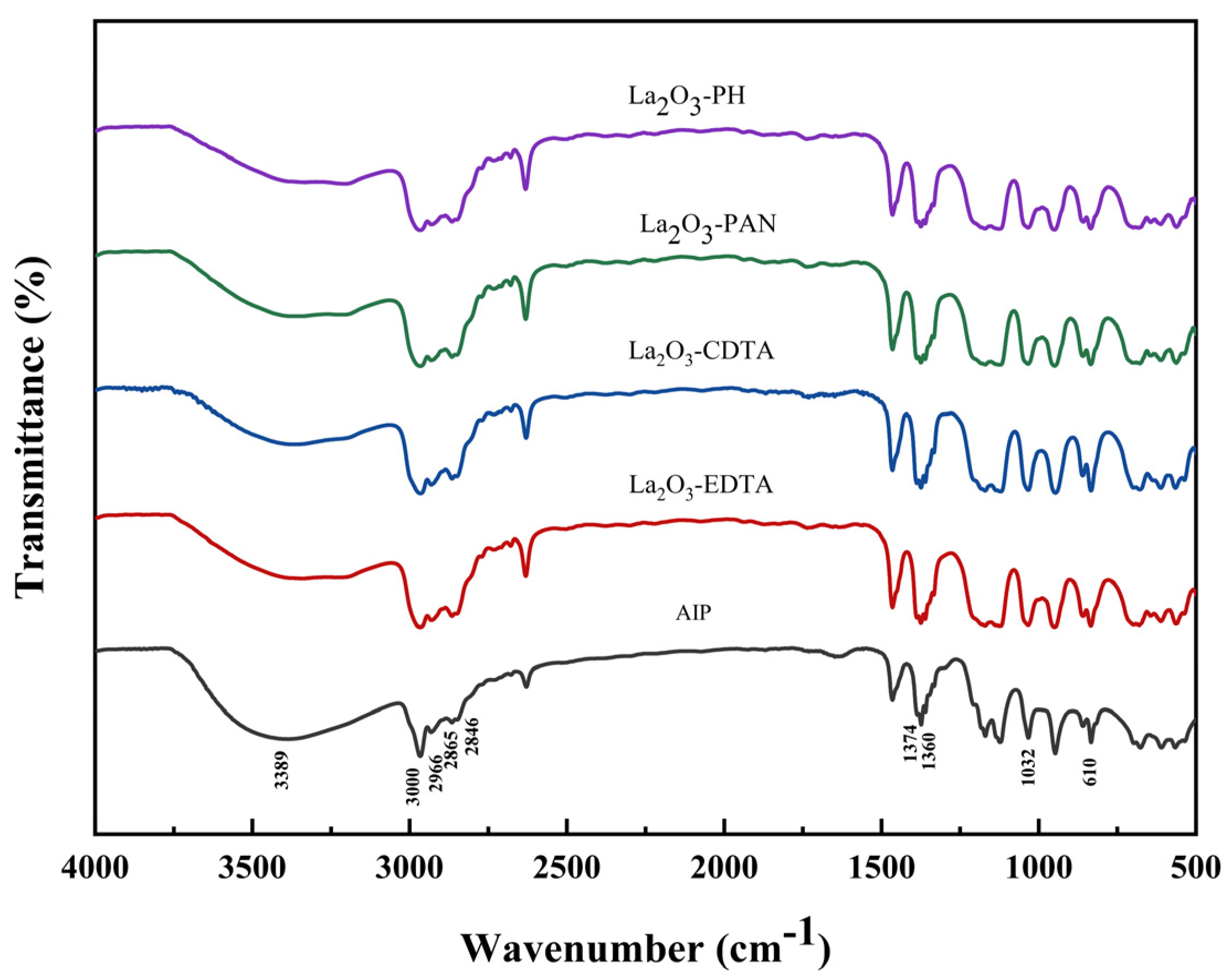
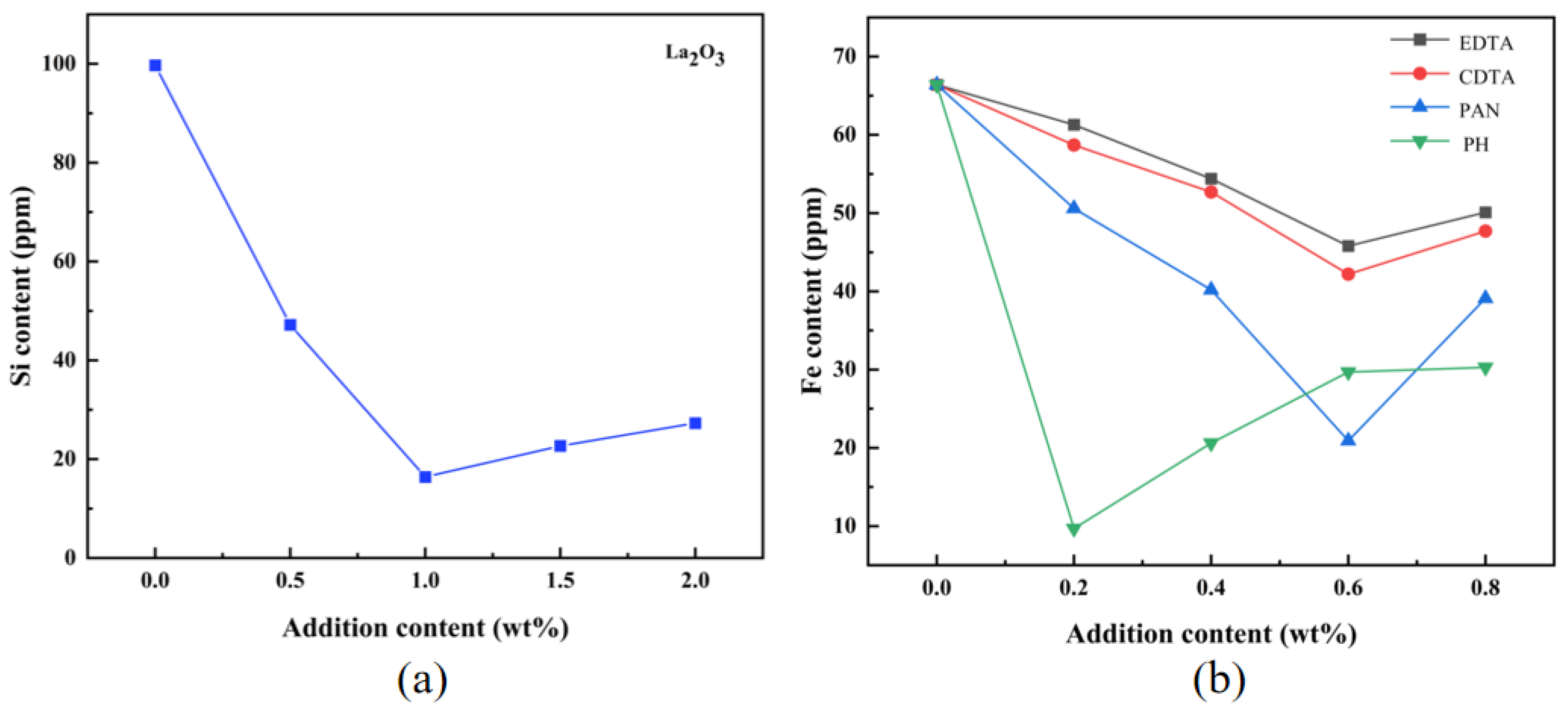

| Impurity Content (ppm) | Fe | Si | Na | Ca | Mg | Cu | Al (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| scavengers-free | 66.4 | 99.7 | 12.9 | 18.4 | 8.4 | <1 | 99.97932 |
| CDTA+ La2O3 | 45.7 | 16.5 | 12.9 | 18.4 | 8.4 | <1 | 99.98971 |
| PAN+ La2O3 | 20.7 | 16.4 | 13.0 | 18.2 | 8.3 | <1 | 99.99227 |
| PH+ La2O3 | 9.7 | 16.7 | 12.8 | 17.9 | 8.2 | <1 | 99.99337 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, H. Green Synthesis and Particle Size Control of High-Purity Alumina Based on Hydrolysis of Alkyl Aluminum. Materials 2025, 18, 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092100
Zheng S, Lu Y, Zhao H. Green Synthesis and Particle Size Control of High-Purity Alumina Based on Hydrolysis of Alkyl Aluminum. Materials. 2025; 18(9):2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092100
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Shuang, Yao Lu, and Huanyu Zhao. 2025. "Green Synthesis and Particle Size Control of High-Purity Alumina Based on Hydrolysis of Alkyl Aluminum" Materials 18, no. 9: 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092100
APA StyleZheng, S., Lu, Y., & Zhao, H. (2025). Green Synthesis and Particle Size Control of High-Purity Alumina Based on Hydrolysis of Alkyl Aluminum. Materials, 18(9), 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092100







