Laser-Based Characterization and Classification of Functional Alloy Materials (AlCuPbSiSnZn) Using Calibration-Free Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and a Laser Ablation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer for Electrotechnical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Sample Preparation
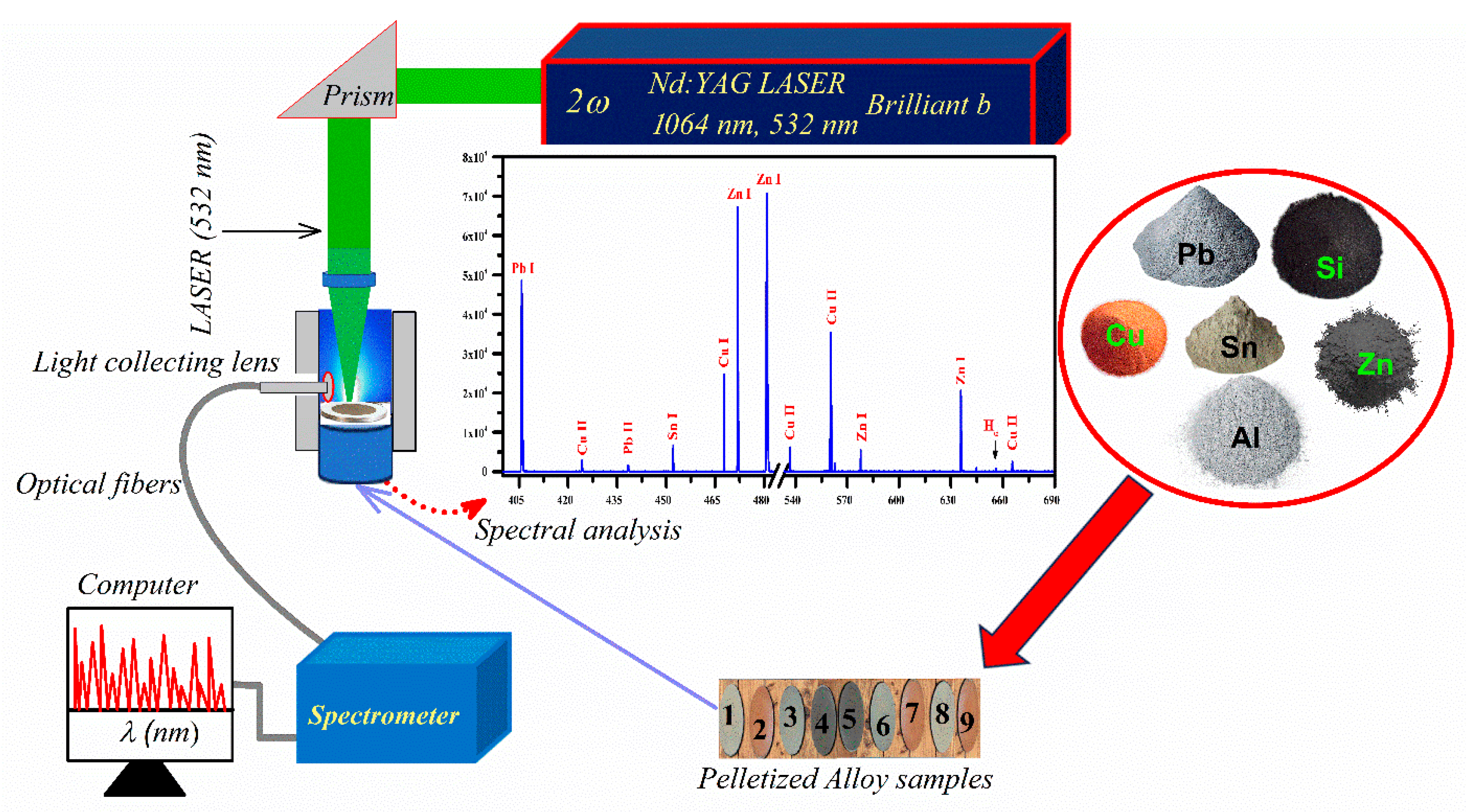
2.2. LIBS Experimental Methods
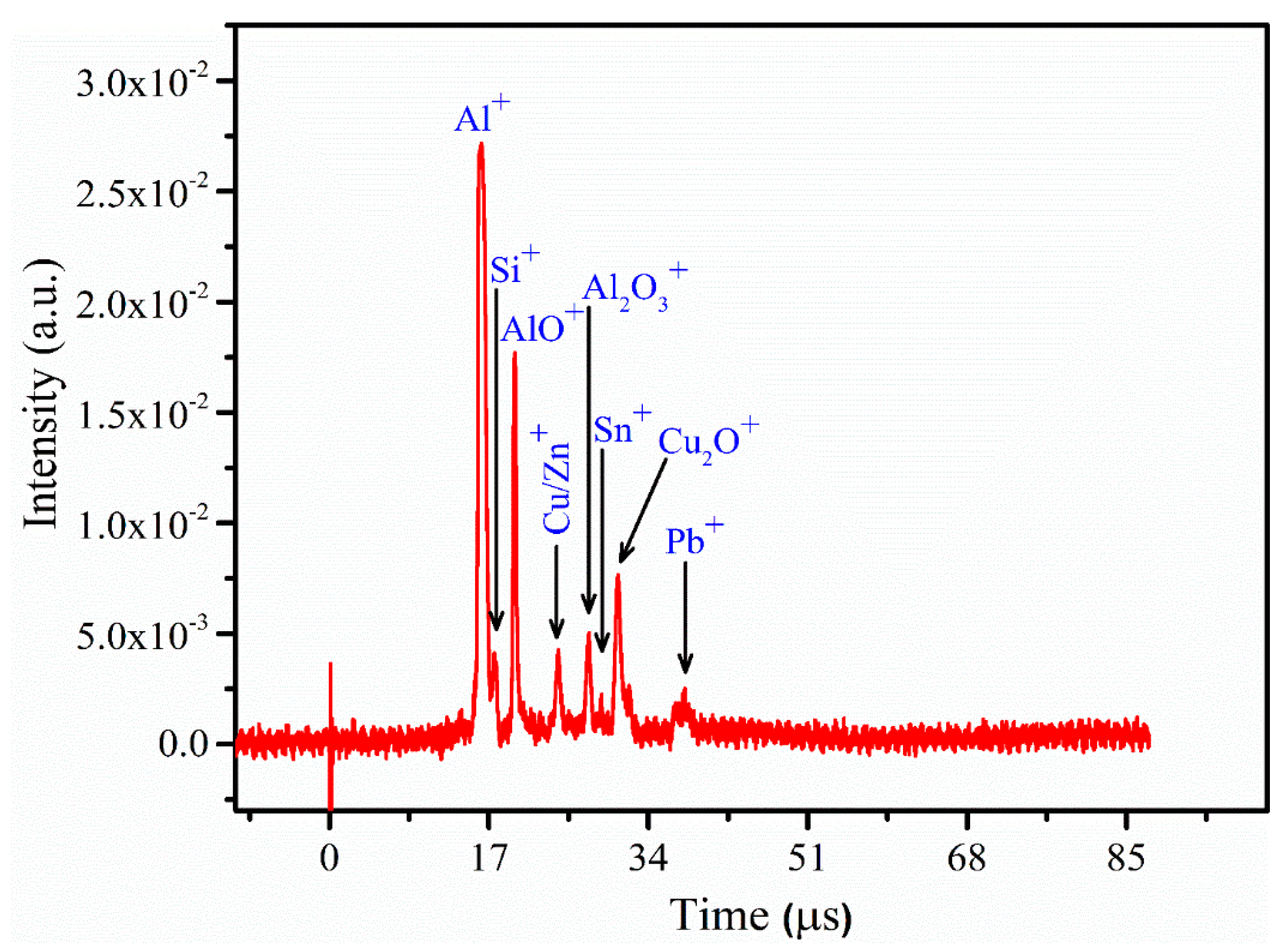
2.3. LA-TOF-MS Spectrometric Studies
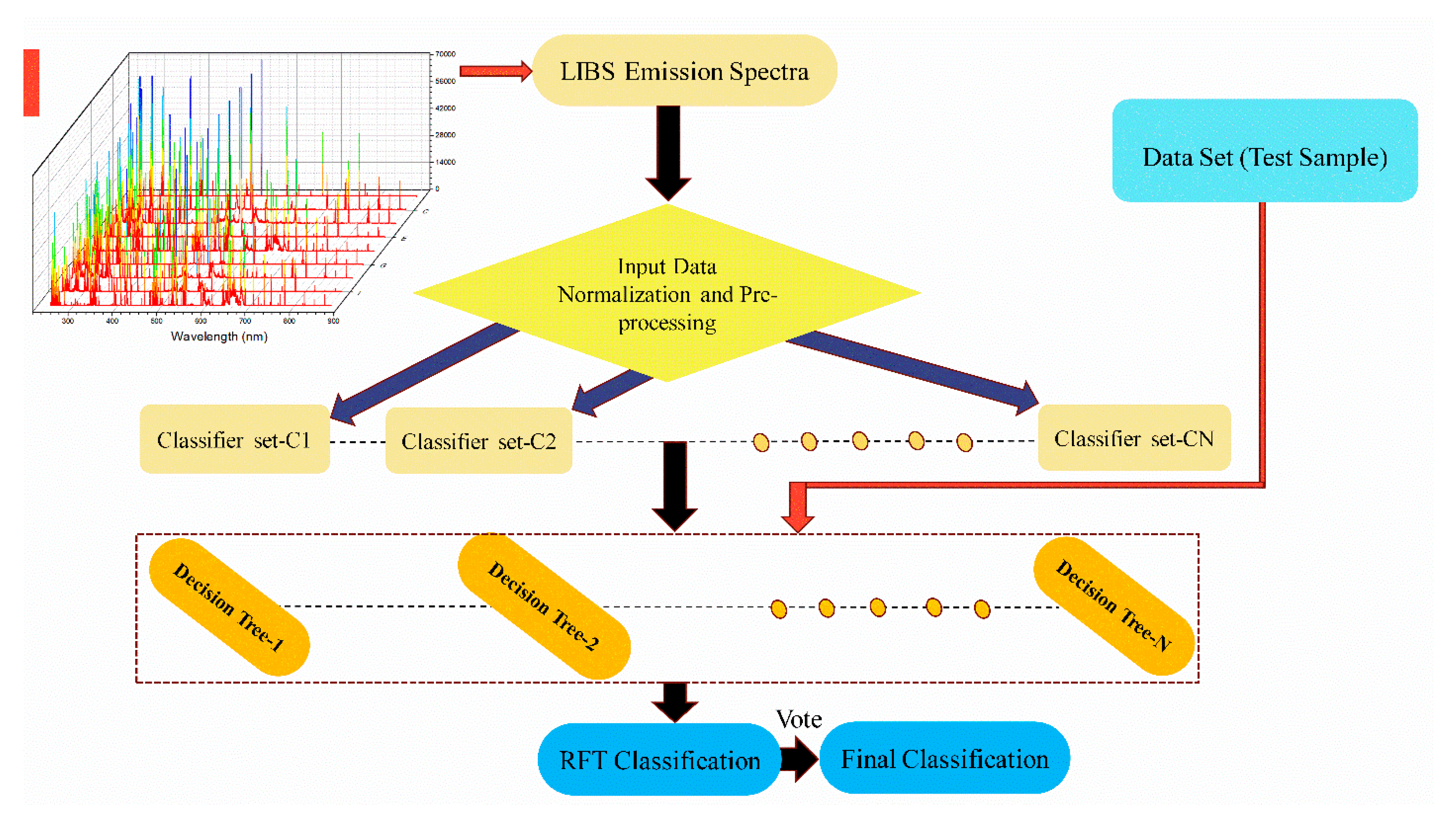
2.4. Random Forest Technique
3. Results
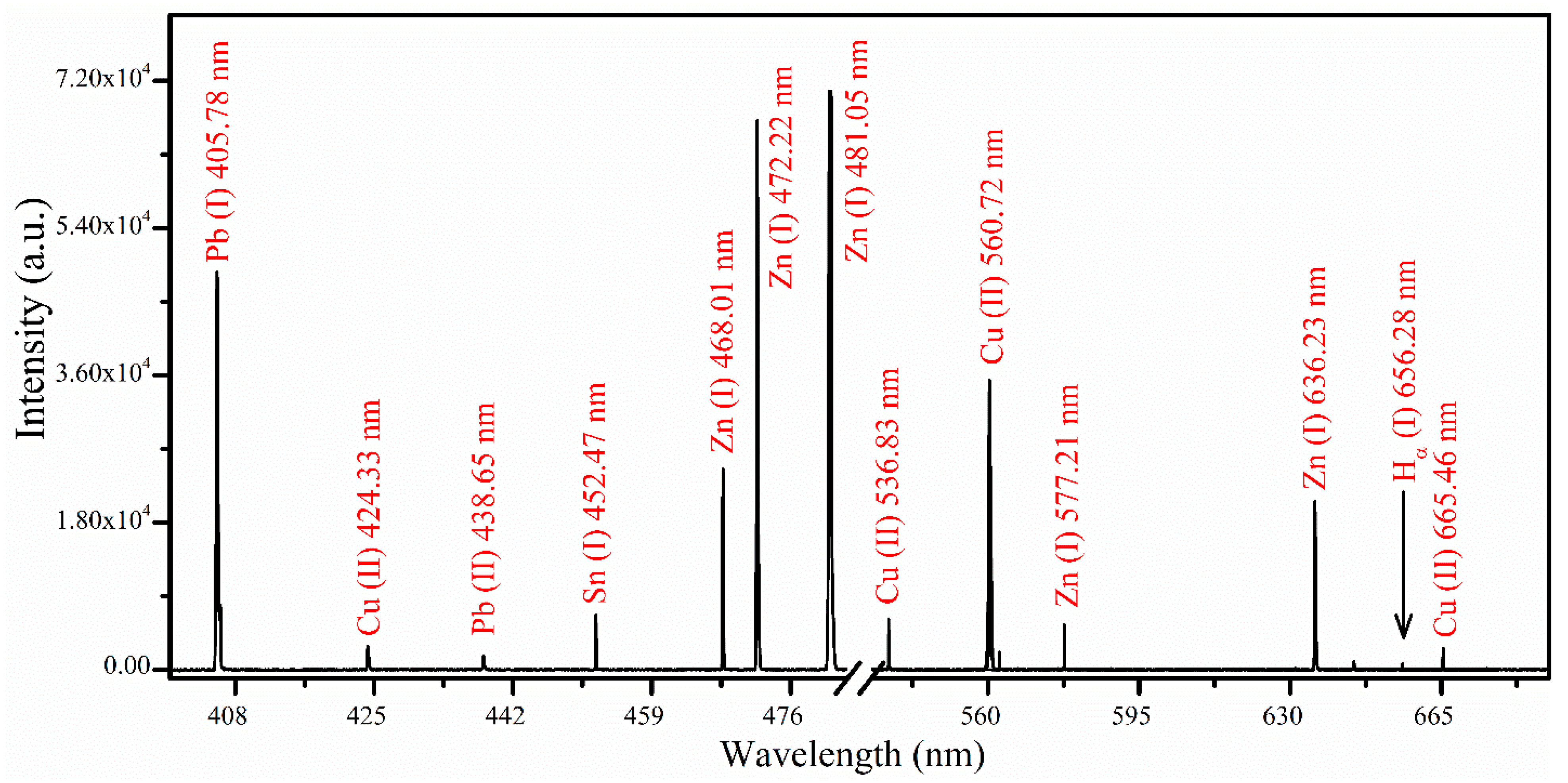
3.1. Analytical Plasma and Spectral Analysis
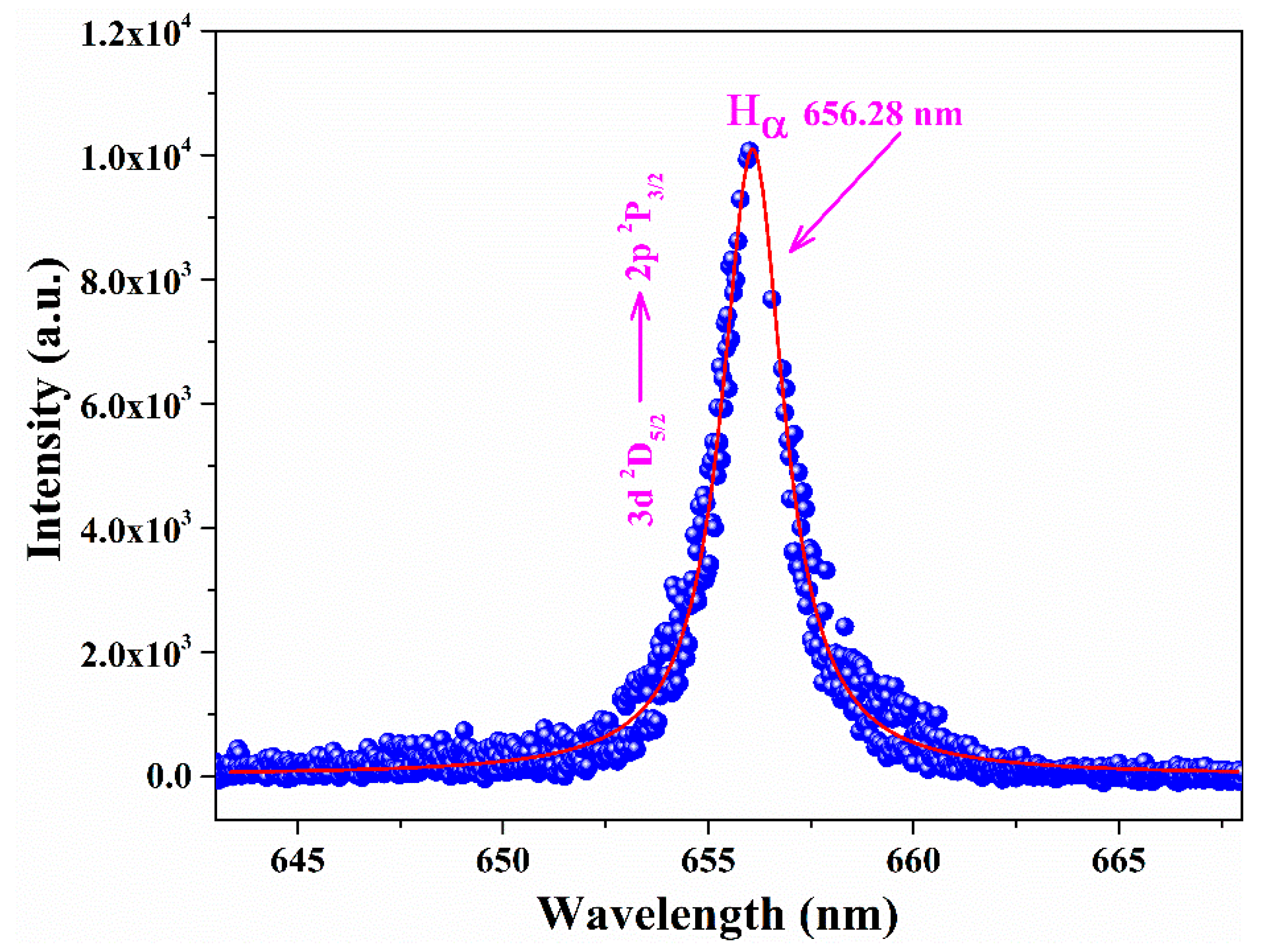
3.2. Analytical Plasma Characterization
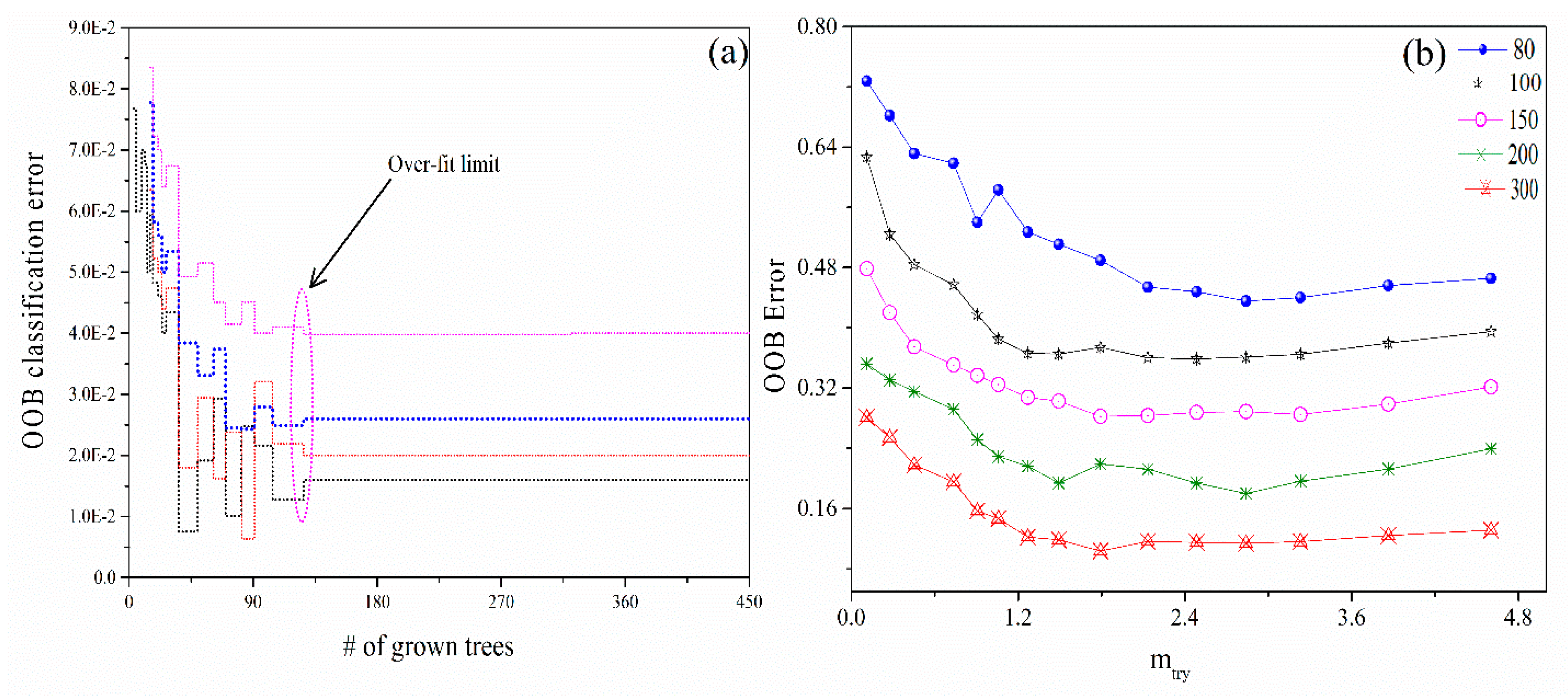
3.3. RFT Parameter Optimization
3.4. RFT Classification and Validation
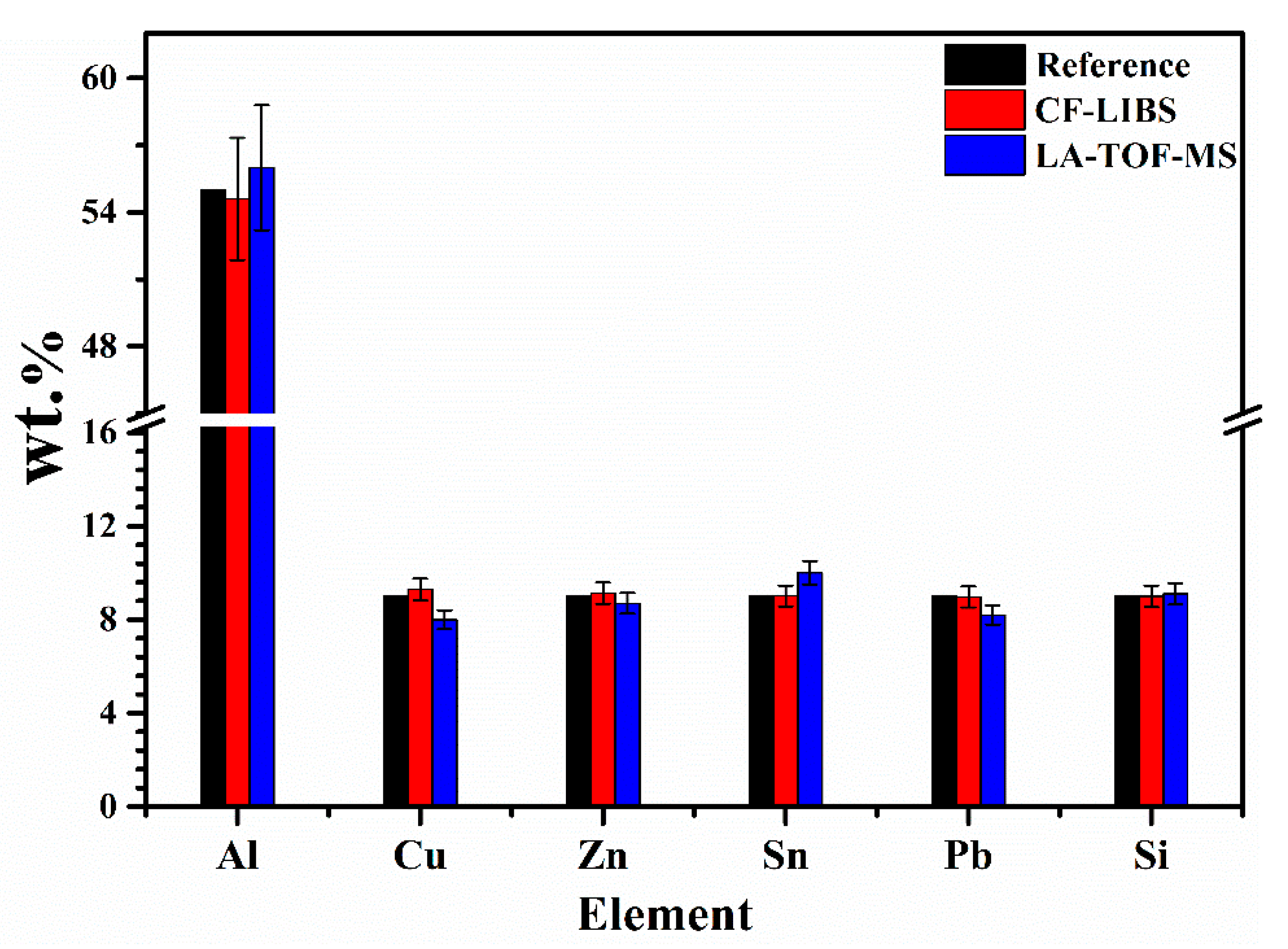
3.5. Quantitative Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, J.R. Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys; ASM International: Metal Park, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Iida, T.; Nohira, T.; Ito, Y. RBS analysis of Sm–Ni alloy films prepared by molten salt electrochemical process. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 386, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Liaqat, U.; Umar, Z.A.; Ahmed, R.; Baig, M.A. Elemental analysis of cement by calibration-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (CF-LIBS) and comparison with laser ablation–time-of-flight–mass spectrometry (LA-TOF-MS), energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX), X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF), and proton induced X-ray emission spectrometry (PIXE). Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 1951–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cai, S.; Forrest, W.C.; Mohr, E.; Yang, Q.; Forrest, M.L. Forrest, Development and validation of an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) method for quantitative analysis of platinum in plasma, urine, and tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 70, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oropeza, D.; Gonzalez, J.J.; Chirinos, J.R.; Zorba, V.; Rogel, E.; Ovalles, C.; López-Linares, F. Elemental analysis of asphaltenes using simultaneous laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)–laser ablation inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (LA-ICP-OES). Appl. Spectrosc. 2019, 73, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, V.; Vadrucci, M.; Fantoni, R.; Chiari, M.; Mazzinghi, A.; Gorghinian, A. Applications of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for cultural heritage: A comparison with X-ray fluorescence and particle induced X-ray emission techniques. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2018, 149, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doménech-Carbó, A.; Mödlinger, M.; Ghiara, G. Determining the composition of the metallic core of historical objects from surface XRF spectrometry data. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2024, 220, 107030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quackatz, L.; Griesche, A.; Kannengiesser, T. Spatially resolved EDS, XRF, and LIBS measurements of the chemical composition of duplex stainless steel welds: A comparison of methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2022, 193, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Pathak, A.; Chauhan, D.; Dubey, N.; Rai, A.; Prasad, R. An efficient approach of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and ICAP-AES to detect the elemental profile of Ocimum L. species. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giacomo, A.; Dell’aglio, M.; De Pascale, O.; Gaudiuso, R.; Teghil, R.; Santagata, A.; Parisi, G. ns- and fs-LIBS of copper-based alloys: A different approach. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7677–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciucci, A.; Corsi, M.; Palleschi, V.; Rastelli, S.; Salvetti, A.; Tognoni, E. New procedure for quantitative elemental analysis by laser-induced plasma spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 1999, 53, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognoni, E.; Palleschi, V.; Corsi, M.; Cristoforetti, G. Quantitative micro-analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: A review of the experimental approaches. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2002, 57, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedwig, R.; Tanra, I.; Karnadi, I.; Pardede, M.; Marpaung, A.M.; Lie, Z.S.; Kurniawan, K.H.; Suliyanti, M.M.; Lie, T.J.; Kagawa, K. Suppression of self-absorption effect in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by employing a Penning-like energy transfer process in helium ambient gas. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 9259–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legnaioli, S.; Campanella, B.; Poggialini, F.; Pagnotta, S.; Harith, M.; Abdel-Salam, Z.; Palleschi, V. Industrial applications of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: A review. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1014–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giacomo, A.; Dell’Aglio, M.; De Pascale, O.; Capitelli, M. From single pulse to double pulse ns-laser induced breakdown spectroscopy under water: Elemental analysis of aqueous solutions and submerged solid samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2007, 62, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miziolek, A.W.; Palleschi, V.; Schechter, I. Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cremers, D.A.; Radziemski, L.J. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Galbács, G.; Gornushkin, I.B.; Smith, B.W.; Winefordner, J.D. Semi-quantitative analysis of binary alloys using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and a new calibration approach based on linear correlation. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2001, 56, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, V.K.; Mridul, K.; Nayak, R.; Alti, K.; Kartha, V.B.; Santhosh, C.; Gupta, G.P.; Suri, B.M. Calibration-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for quantitative elemental analysis of materials. Pramana-J. Phys. 2012, 79, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognoni, E.; Cristoforetti, G.; Legnaioli, S.; Palleschi, V. Calibration-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: State of the art. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2010, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yang, G.; Sun, X.; Qu, D.; Li, S.; Chen, G.; Li, C.; Tian, D.; Yao, L. Discrimination of rocks by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with Random Forest (RF). J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2023, 38, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Liaqat, U.; Yaqoob, K.; Ahmed, R.; Umar, Z.A.; Baig, M.A. Combination of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and time–of–flight mass spectrometry for the quantification of CoCrFeNiMo high entropy alloys. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2022, 198, 106562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Baig, M.A.; Waqas, M.; Liaqat, U. Analytical techniques for detecting rare earth elements in geological ores: Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), MFA-LIBS, thermal LIBS, laser ablation time-of-flight mass spectrometry, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy. Minerals 2024, 14, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Baig, M.A.; Ahmed, R.; Waqas, M. Isotopic Analysis of Zinc Plasma using Laser-Ablation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2025, 512, 117442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Ali, R.; Waqas, M.; Liaqat, U.; Ahmad, R.; Umar, Z.A.; Baig, M.A. Analysis of rare earth ores using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and laser ablation time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Minerals 2023, 13, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Online transient stability margin prediction of power systems with wind farms using ensemble regression trees. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2021, 31, e13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Atomic Spectra Database Lines Data; NIST: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Alfarraj, B.A.; Bhatt, C.R.; Yueh, F.Y.; Singh, J.P. Evaluation of optical depths and self-absorption of strontium and aluminum emission lines in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, I.; Burgio, L.M.; Corsi, M.; Fantoni, R.; Palleschi, V.; Salvetti, A.; Squarcialupi, M.C.; Tognoni, E. Self-calibrated quantitative elemental analysis by laser-induced plasma spectroscopy: Application to pigment analysis. J. Cult. Herit. 2000, 1, S281–S286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, C.; Bengoechea, J.; Aguilera, J. Influence of the optical depth on spectral line emission from laser-induced plasmas. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2001, 56, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, D.D.; Miguel, R.; Di Rocco, H.; García, F.A.; Pardini, L.; Legnaioli, S.; Lorenzetti, G.; Palleschi, V. Quantitative analysis of metals in waste foundry sands by calibration free-laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2017, 131, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.-Y.; Herrera, K.K.; Omenetto, N.; Smith, B.W.; Winefordner, J. On the usefulness of a duplicating mirror to evaluate self-absorption effects in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2009, 64, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjević, N.; Ivković, M.; Sakan, N. Hydrogen Balmer lines for low electron number density plasma diagnostics. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2012, 76, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomba, J.; D’Angelo, C.; Bertuccelli, D.; Bertuccelli, G. Spectroscopic characterization of laser induced breakdown in aluminium–lithium alloy samples for quantitative determination of traces. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2001, 56, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiuso, R.; Dell’aglio, M.; De Pascale, O.; Senesi, G.S.; De Giacomo, A. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy for elemental analysis in environmental, cultural heritage and space applications: A review of methods and results. Sensors 2010, 10, 7434–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Képeš, E.; Vrábel, J.; Siozos, P.; Pinon, V.; Pavlidis, P.; Anglos, D.; Chen, T.; Sun, L.; Lu, G.; Díaz-Romero, D.J.; et al. Quantification of alloying elements in steel targets: The LIBS 2022 regression contest. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2023, 206, 106710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yang, Q.; He, X.; Li, J.; Ling, D.; Wei, D.; Liao, Y. Spectral filtering method for improvement of detection accuracy of Mg, Cu, Mn and Cr elements in aluminum alloys using femtosecond LIBS. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 32230–32236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, W.T.Y. Improved LIBS limit of detection of Be, Mg, Si, Mn, Fe and Cu in aluminum alloy samples using a portable Echelle spectrometer with ICCD camera. Opt. Laser Technol. 2008, 40, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubmer, G.; Kitzberger, R.; Mörwald, K. Application of LIBS to the in-line process control of liquid high-alloy steel under pressure. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Rai, A.K.; Kumar, T.; Tarai, A.; Gundawar, G.M.K. Compositional analysis of copper and iron-based alloys using LIBS coupled with chemometric method. Anal. Sci. 2023, 40, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

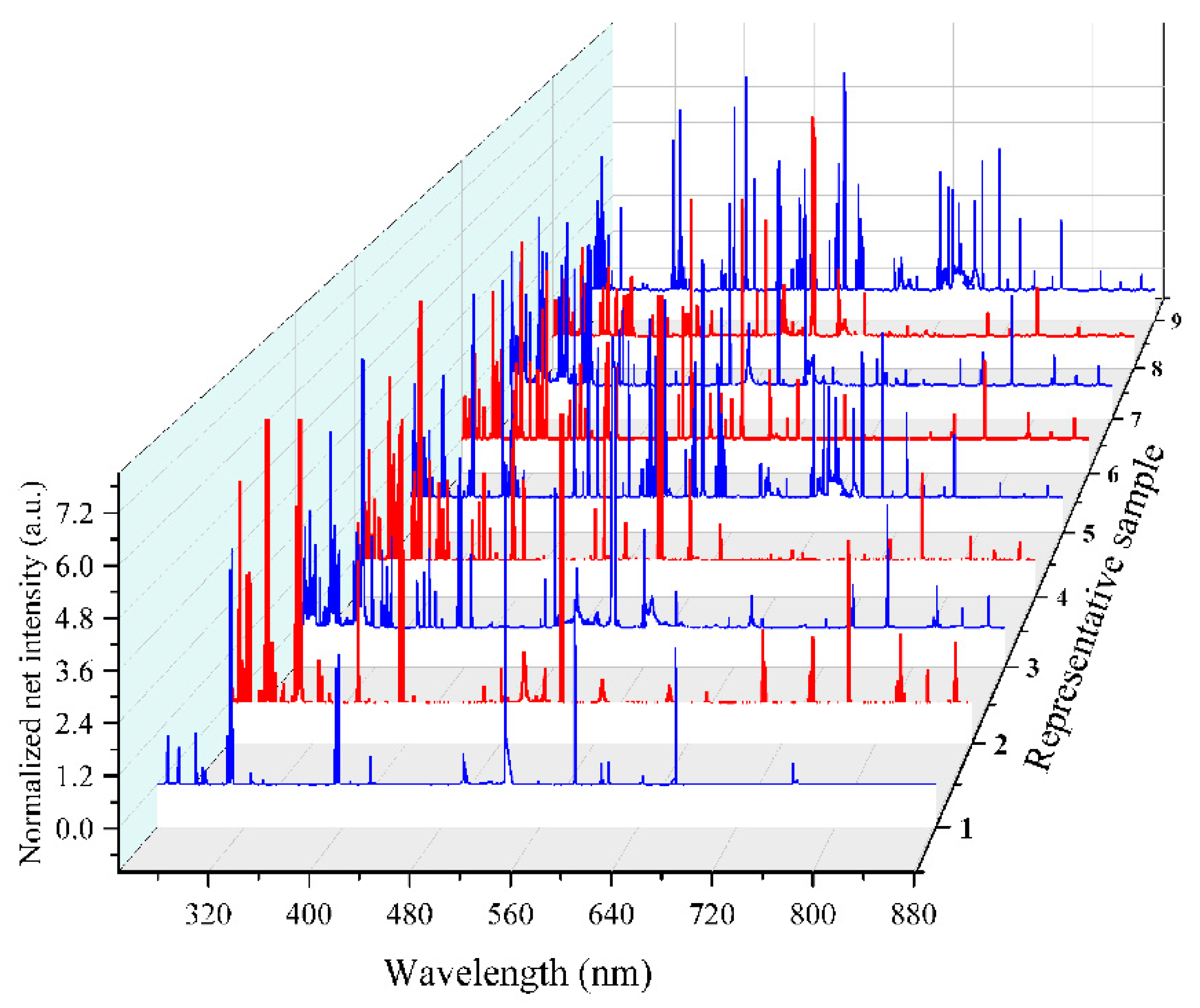
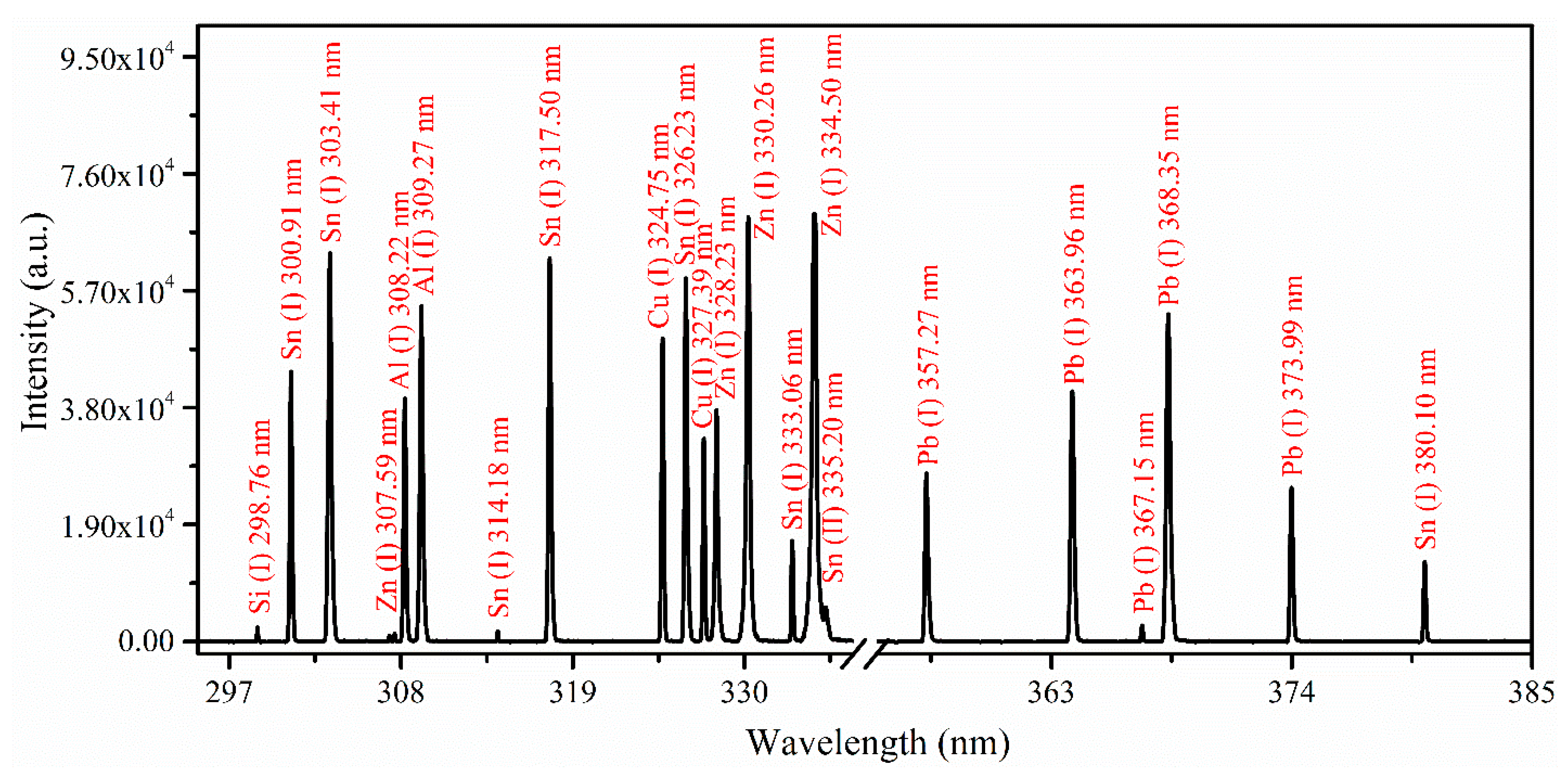



| Sample | Element Chemical Composition (wt.%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Copper | Lead | Silicon | Tin | Zinc | |
| 1 | 99.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 97.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 95 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 85 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 70 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 6 | 55 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| 7 | 40 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 8 | 25 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| 9 | 5 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| Wavelength λ (nm) | Transition | Transition Probability ) | Upper Energy Level ) | Statistical Weight (2Jk + 1) | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Level | Lower Level | ||||||
| Tin (Sn): | |||||||
| 300.91 | 5p6s 3P1 → 5p2 3P1 | 3.8 | 34,914.282 | 3 | 3 | D | |
| 303.41 | 5p6s 3P0 → 5p2 3P1 | 20 | 34,640.758 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 314.18 | 5p5d 3P1 → 5p2 1S0 | 1.9 | 48,981.934 | 3 | 1 | ||
| 333.06 | 5p6s 3P2 → 5p2 1D2 | 2.0 | 38,628.876 | 5 | 5 | ||
| 380.10 | 5p6s 3P1 → 5p2 1D2 | 2.8 | 34,914.282 | 3 | 5 | ||
| 452.47 | 5p6s 1P1 → 5p2 1S0 | 2.6 | 39,257.053 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Zinc (Zn): | |||||||
| 328.23 | 4s4d 3D1 → 4s4p 3P0 | 9.0 | 62,768.7462 | 3 | 1 | B | |
| 330.25 | 4s4d 3D2 → 4s4p 3P1 | 12 | 62,772.0144 | 5 | 3 | ||
| 334.50 | 4s4d 3D3 → 4s4p 3P2 | 17 | 62,776.9809 | 7 | 5 | ||
| 468.01 | 4s5s 3S1 → 4s4p 3P0 | 1.6 | 53,672.2398 | 3 | 1 | NR | |
| 472.21 | 4s5s 3S1 → 4s4p 3P1 | 4.6 | 53,672.2398 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 481.05 | 4s5s 3S1 → 4s4p 3P2 | 7.0 | 53,672.2398 | 3 | 5 | ||
| 577.21 | 4s7p 3P2 → 4s5s 3S1 | 0.08 | 70,992.3040 | 5 | 3 | ||
| 636.23 | 4s4d 1D2 → 4s4p 1P1 | 4.7 | 62,458.5323 | 5 | 3 | C | |
| Element | Wavelength λ (nm) | Akgk (108) s−1 | Ek (eV) | Te (eV) | Calculated | Observed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb (I) | 368.3 | 1.37 | 4.33 | 0.89 | 0.67 | 0.68 |
| 283.3 | 1.50 | 4.37 | ||||
| Si (I) | 250.7 | 2.74 | 4.95 | 0.42 | 0.41 | |
| 288.2 | 6.51 | 5.08 | ||||
| Zn (I) | 468.01 | 0.16 | 6.65 | 2.85 | 2.73 | |
| 472.22 | 0.46 | 6.65 |
| Sample Type | RFT Results Based on OOB | RFT Classification Based on 10-Fold (Cross-Validation) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Sensitivity | Accuracy | Recall | Classification | Accuracy | RMSE | |
| 1 | 100% (1.00~10/10) | 0.9952 | 0.9976 | 96.91% | 93.6 | 0.9476 | 1.228 |
| 2 | 0.9865 | 0.9971 | 91.67% | 95 | 0.8971 | 0.851 | |
| 3 | 0.9976 | 0.9874 | 98.70% | 94 | 0.8879 | 0.899 | |
| 4 | 0.9874 | 0.9975 | 95.23% | 92 | 0.9677 | 0.978 | |
| 5 | 0.9471 | 0.9576 | 91.92% | 88 | 0.9576 | 1.199 | |
| 6 | 0.9972 | 0.9878 | 92.78% | 94.5 | 0.9878 | 0.965 | |
| 7 | 0.9877 | 0.9779 | 94.92% | 98 | 1.2778 | 0.981 | |
| 8 | 1.0000 | 0.9972 | 98.80% | 99.6 | 0.9972 | 0.982 | |
| 9 | 0.9979 | 1.0000 | 97.23% | 100 | 0.9998 | 1.309 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fayyaz, A.; Waqas, M.; Fatima, K.; Naseem, K.; Asghar, H.; Ahmed, R.; Umar, Z.A.; Baig, M.A. Laser-Based Characterization and Classification of Functional Alloy Materials (AlCuPbSiSnZn) Using Calibration-Free Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and a Laser Ablation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer for Electrotechnical Applications. Materials 2025, 18, 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092092
Fayyaz A, Waqas M, Fatima K, Naseem K, Asghar H, Ahmed R, Umar ZA, Baig MA. Laser-Based Characterization and Classification of Functional Alloy Materials (AlCuPbSiSnZn) Using Calibration-Free Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and a Laser Ablation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer for Electrotechnical Applications. Materials. 2025; 18(9):2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092092
Chicago/Turabian StyleFayyaz, Amir, Muhammad Waqas, Kiran Fatima, Kashif Naseem, Haroon Asghar, Rizwan Ahmed, Zeshan Adeel Umar, and Muhammad Aslam Baig. 2025. "Laser-Based Characterization and Classification of Functional Alloy Materials (AlCuPbSiSnZn) Using Calibration-Free Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and a Laser Ablation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer for Electrotechnical Applications" Materials 18, no. 9: 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092092
APA StyleFayyaz, A., Waqas, M., Fatima, K., Naseem, K., Asghar, H., Ahmed, R., Umar, Z. A., & Baig, M. A. (2025). Laser-Based Characterization and Classification of Functional Alloy Materials (AlCuPbSiSnZn) Using Calibration-Free Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and a Laser Ablation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer for Electrotechnical Applications. Materials, 18(9), 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092092








