Study of Operational Parameters on Indium Electrowinning Using a Ti Cathode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
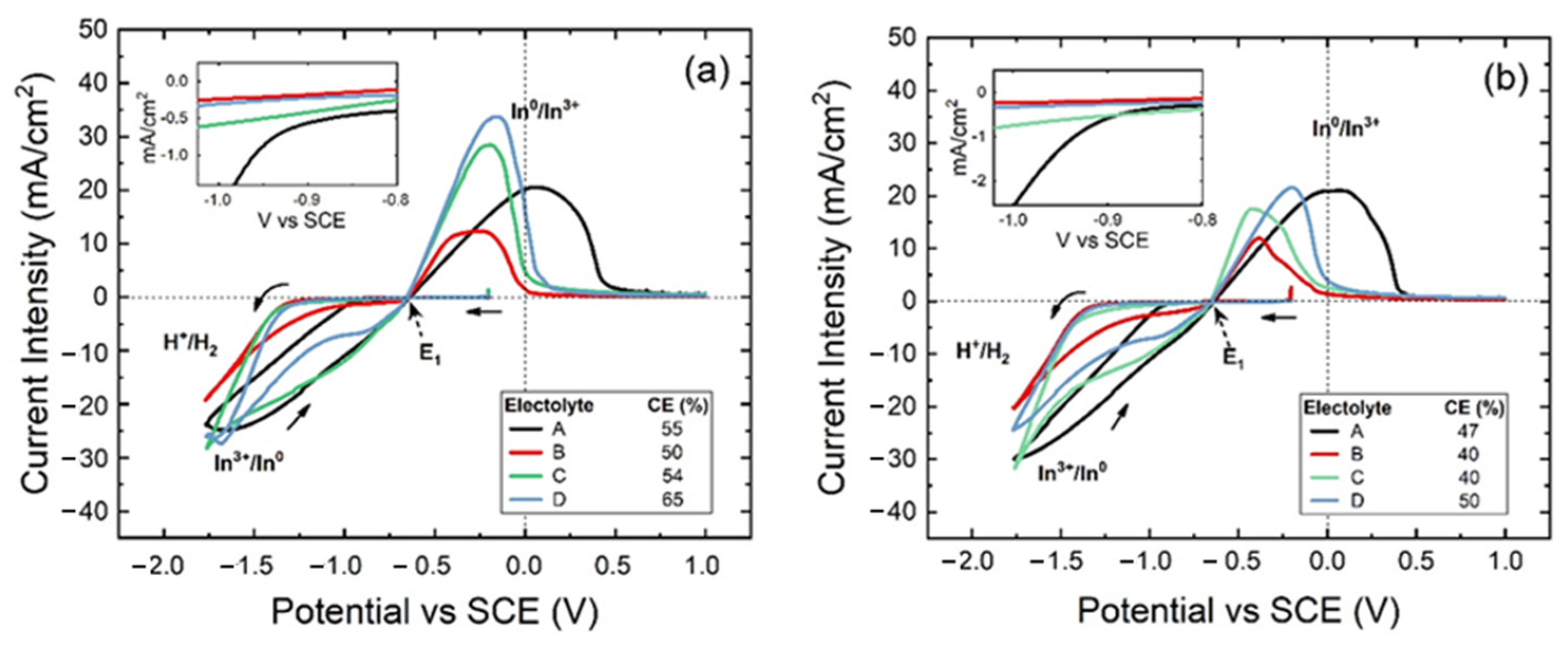
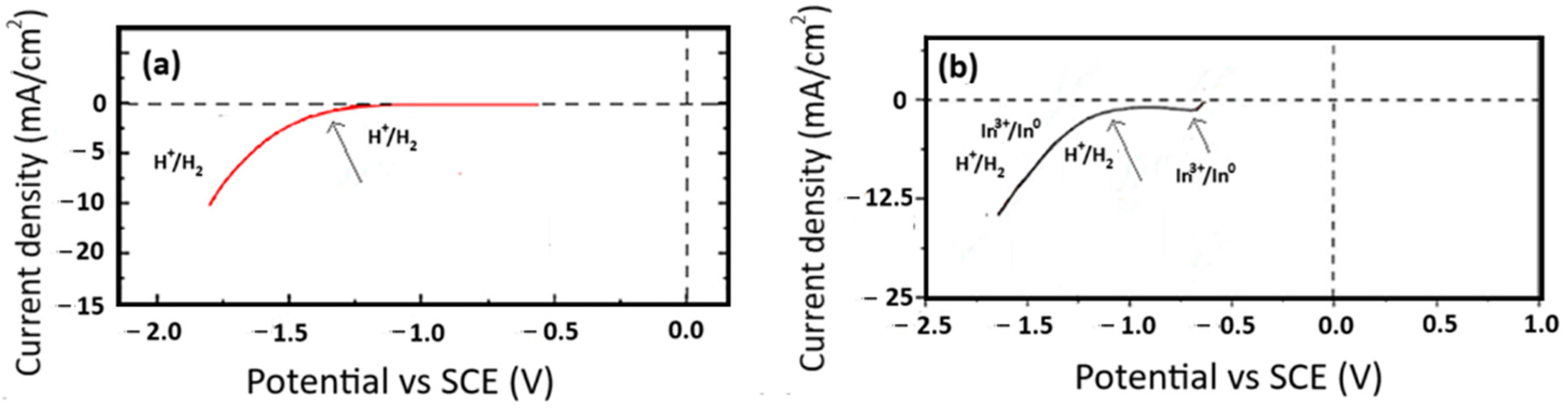
3.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
3.2. Galvanostatic Tests
3.2.1. Current Density Effect
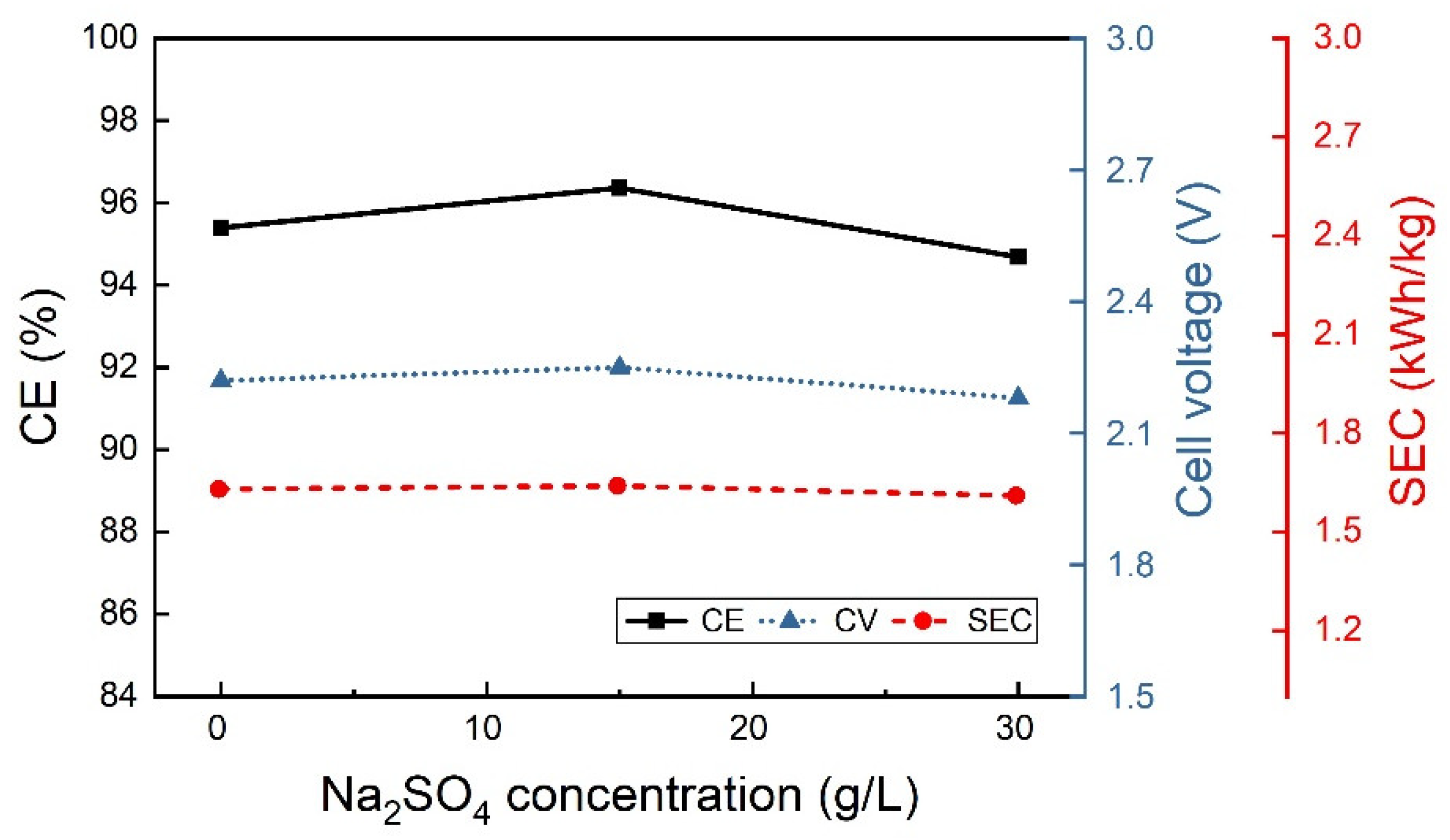
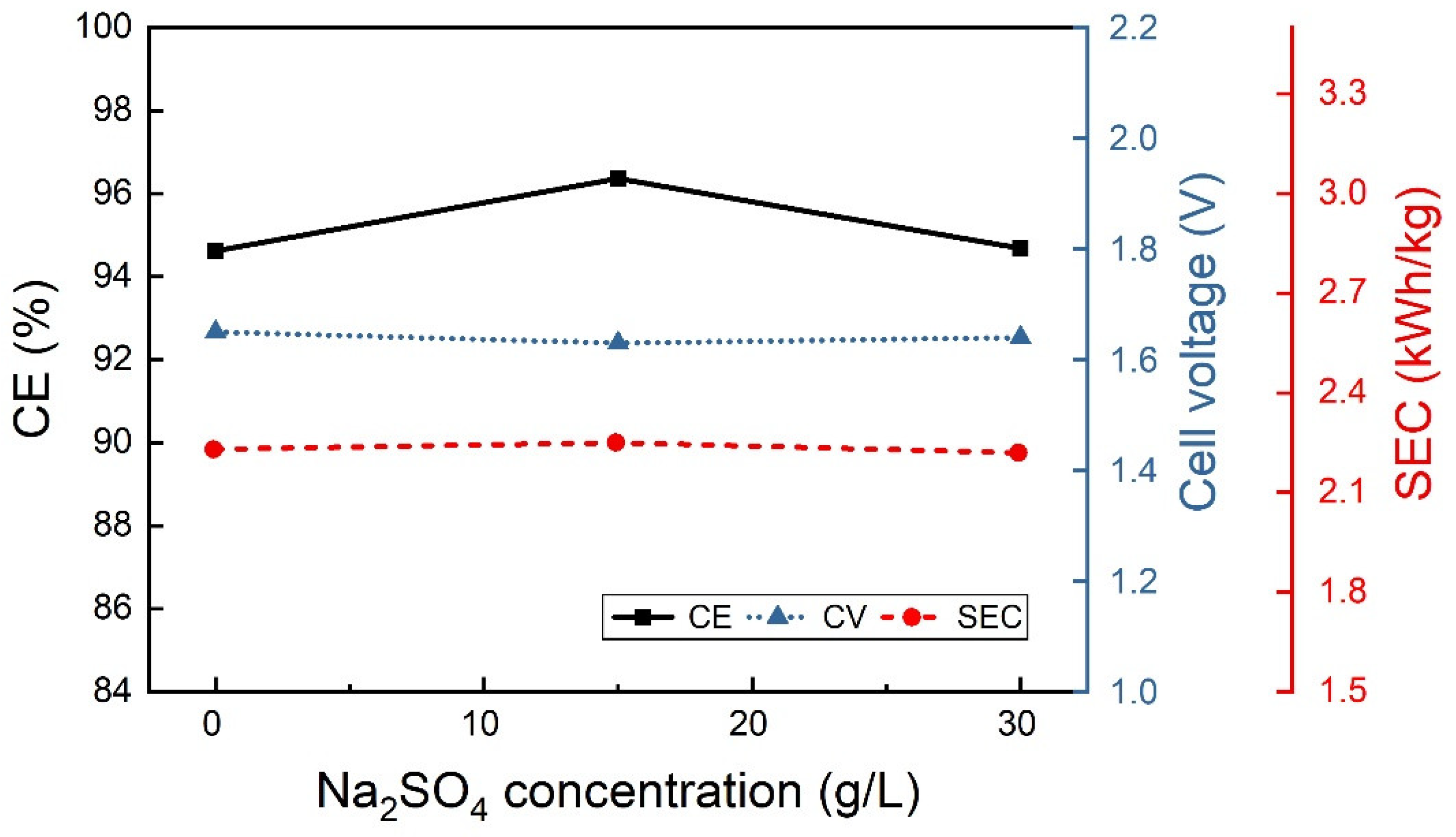
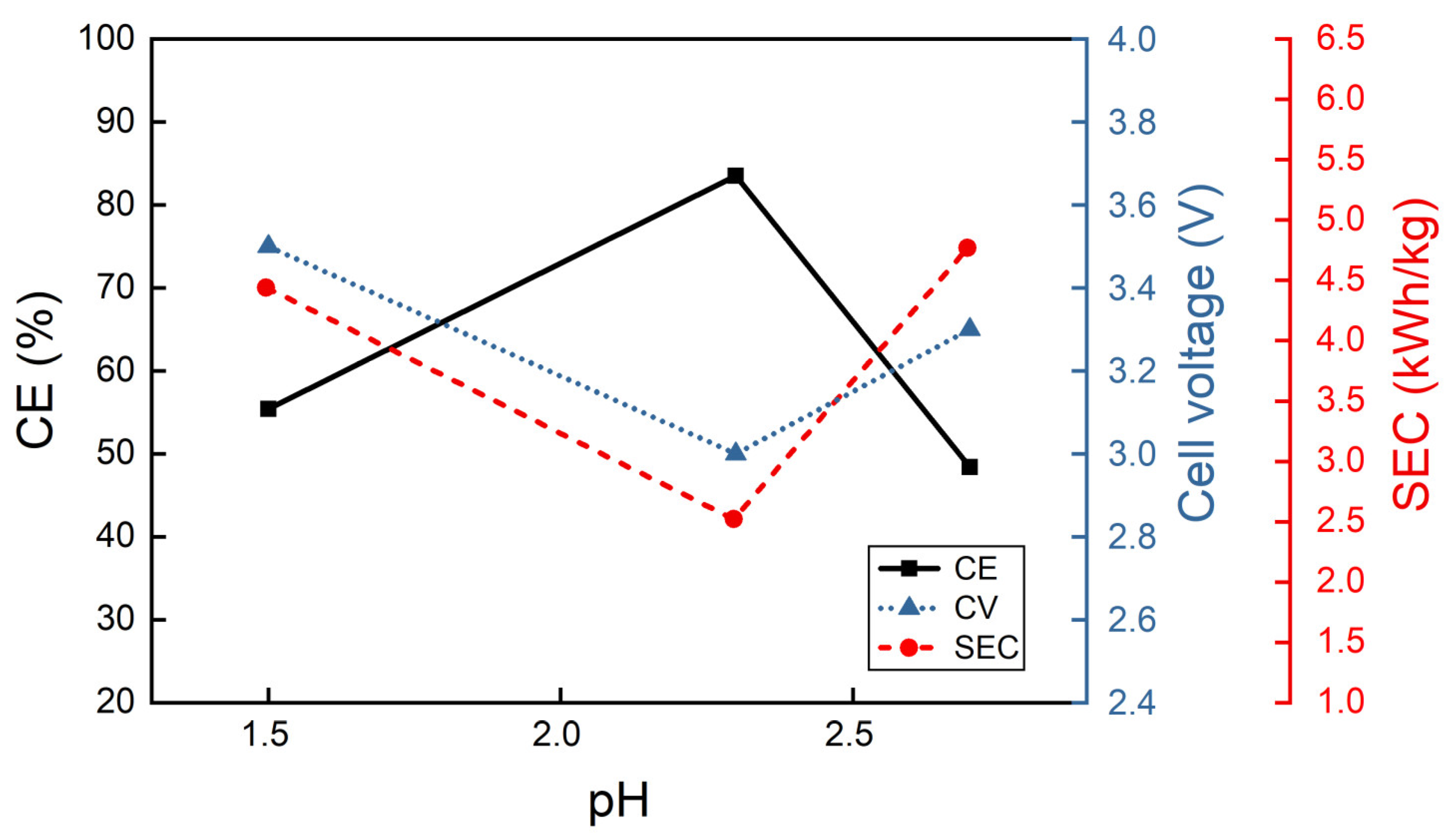
3.2.2. Effect of the Electrolyte Composition
3.2.3. Effect of the Cathodic Surface Pretreatment
3.2.4. Temperature Effect
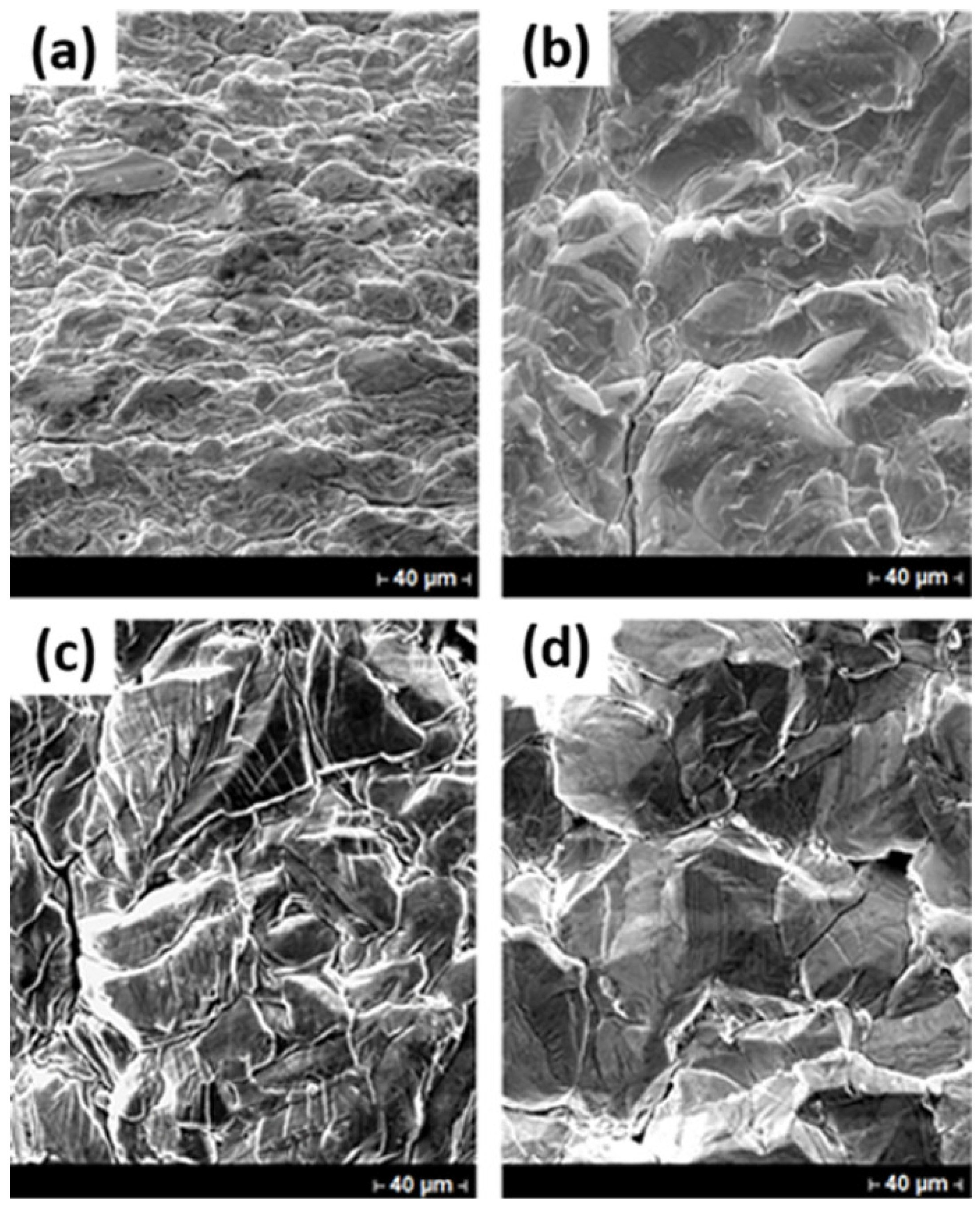
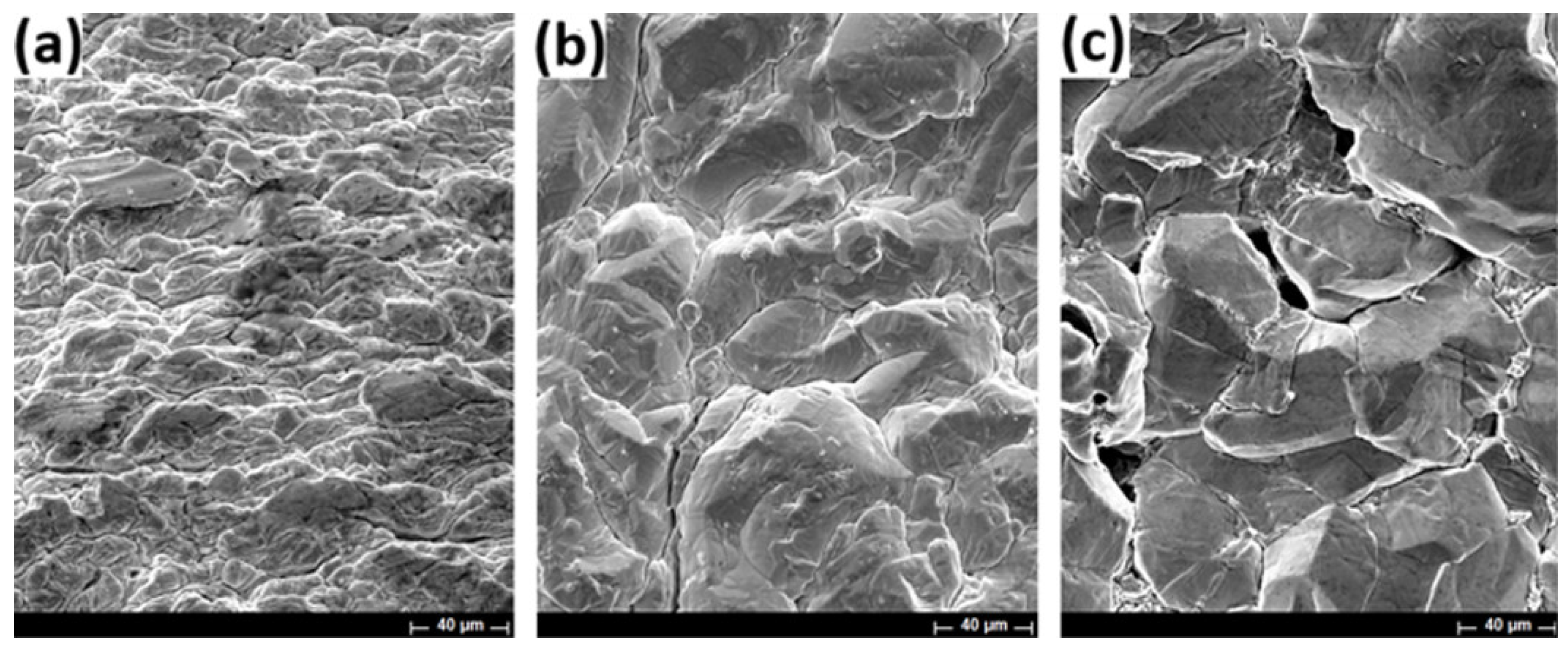
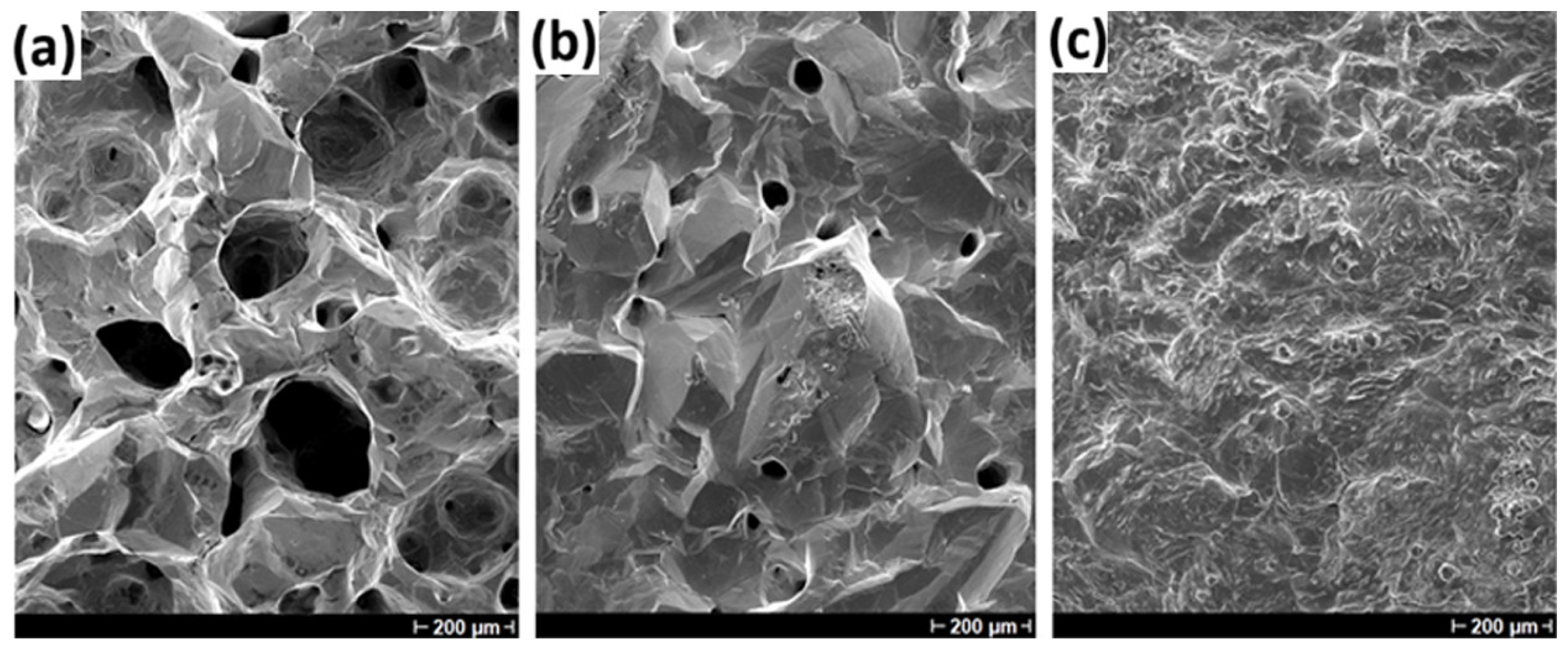
3.3. SEM Evaluation of Indium Deposits
3.4. XRD Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, X.; Mathews, J.A.; Li, J. Urban Mining of E-Waste is Becoming More Cost-Effective Than Virgin Mining. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4835–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethurajan, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Fontana, D.; Akcil, A.; Deveci, H.; Batinic, B.; Leal, J.P.; Gasche, T.A.; Kucuker, M.A.; Kuchta, K.; et al. Recent advances on hydrometallurgical recovery of critical and precious elements from end of life electronic wastes—A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 212–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Benedetti, M.F.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Recovery technologies for indium, gallium, and germanium from end-of-life products (electronic waste)—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluczka, J. A Review on the Recovery and Separation of Gallium and Indium from Waste. Resources 2024, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Hofmann, H.; Hagelüken, C.; Hool, A. Critical raw materials: A perspective from the materials science community. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2018, 17, e00074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, F.J. Recent Advances in Indium Recovery. Metals 2024, 14, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, D.; Forte, F.; De Carolis, R.; Grosso, M. Materials recovery from waste liquid crystal displays: A focus on indium. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Lee, C.G. Commercial indium recovery processes development from various e-(industry) waste through the insightful integration of valorization processes: A perspective. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Agcasulu, I.; Swain, B. Resources, Conservation & Recycling Valorization of waste LCD and recovery of critical raw material for circular economy: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 622–637. [Google Scholar]
- Ciacci, L.; Werner, T.T.; Vassura, I.; Passarini, F. Backlighting the European Indium Recycling Potentials. J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zuo, T. Recycling of indium from waste LCD: A promising non-crushing leaching with the aid of ultrasonic wave. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, M.; Xu, G.; Li, J.; Zeng, X. Securing Indium Utilization for High-Tech and Renewable Energy Industries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 2611–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciro, E.; Dell’Era, A.; Razzi, M.; Lupi, C. Optimization of indium electrowinning from sulfate solutions on Ni cathode. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuong, I.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, X. Estimating the Evolution of Urban Mining Resources in Hong Kong, Up to the Year 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciro, E.; Alzate, A.; López, E.; Serna, C.; Gonzalez, O. Neodymium recovery from scrap magnet using ammonium persulfate. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.; Rocchetti, L.; Fonti, V.; Ruello, M.L.; Beolchini, F. Secondary indium production from end-of-life liquid crystal displays. Curr. Top. Solid State Phys. 2016, 13, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, L.; Amato, A.; Beolchini, F. Recovery of indium from liquid crystal displays. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 116, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Ma, E.; Xu, Z. Application of pyrolysis process to remove and recover liquid crystal and films from waste liquid crystal display glass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 243, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Wang, S.; Ren, H.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yan, X.; Guo, J.; Gu, W.; Su, R.; Liang, B.; et al. Indium recovery from waste liquid crystal displays by polyvinyl chloride waste. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 102836–102843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.; Lu, R.; Xu, Z. An efficient rough vacuum-chlorinated separation method for the recovery of indium from waste liquid crystal display panels. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 3395–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. Vacuum pyrolysis characteristics and kinetic analysis of liquid crystal from scrap liquid crystal display panels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 327, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, P.; Xie, P.; Shang, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Chemosphere Heat-activated persulfate oxidation of methyl- and ethyl-parabens: Effect, kinetics, and mechanism. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qiu, K. Vacuum co-pyrolysis of Chinese fir sawdust and waste printed circuit boards. Part II: Influence of heating conditions. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2015, 111, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Mishra, C.; Hong, H.S.; Cho, S.-S. Beneficiation and recovery of indium from liquid-crystal-display glass by hydrometallurgy. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Retegan, T.; Ekberg, C. Indium recovery from discarded LCD panel glass by solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 137, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, L. Recovery of indium from used indium-tin oxide (ITO) targets. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Guo, Y.; Qiao, Q. Recovery of indium from scrap TFT-LCDs by solvent extraction. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.V.M.; Fuchs, M.S.; Pinheiro, D.K.; Tanabe, E.H.; Bertuol, D.A. Recovery of indium from LCD screens of discarded cell phones. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Mishra, C.; Hong, H.S.; Cho, S.-S. Treatment of indium–tin–oxide etching wastewater and recovery of In, Mo, Sn and Cu by liquid–liquid extraction and wet chemical reduction: A laboratory scale sustainable commercial green process. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4418–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souada, M.; Louage, C.; Doisy, J.; Meunier, L.; Benderrag, A.; Ouddane, B.; Bellayer, S.; Nuns, N.; Traisnel, M.; Maschke, U. Extraction of indium-tin oxide from end-of-life LCD panels using ultrasound assisted acid leaching. UltrasonSonochem. 2018, 40, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowkar, M.J.; Bahaloo-horeh, N.; Mousavi, S.M. Bioleaching of indium from discarded liquid crystal displays. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lv, Z.; He, J.; Song, J. Electrochemical upcycling of indium-gallium-zinc oxide scraps. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 191, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fang, W.; Rao, T.; Qi, Y.; Dong, H.; Ma, R.; Xiong, Y. Efficient and fast recovery of indium with phosphate-functionalized polyaniline porous carbon self-supported electrode by electrosorption-deposition strategy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, C.; Pilone, D. In(III) hydrometallurgical recovery from secondary materials by solvent extraction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Xing, P.; Ma, B.; Liu, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Separation and Recovery of Valuable Elements from Spent CIGS Materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19816–19823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, Y.S.; Niewersch, C.; Lenz, M.; Kül, Z.Z.; Corvini, P.F.X.; Schäffer, A.; Wintgens, T. Recycling of indium from CIGS photovoltaic cells: Potential of combining acid-resistant nanofiltration with liquid-liquid extraction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13412–13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.; Huang, Y. Electrochemical removal of indium ions from aqueous solution using iron electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Swain, B.; Cho, S.S.; Lee, C.G. A validation experiment on indium recovery by electrowinning of aqueous electrolytes: Optimization of electrolyte composition. Mater. Test. 2016, 58, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Oh, Y. Analysis of ionic equilibria and electrowinning of indium from chloride solutions. Scand. J. Metall. 2004, 33, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Reuter, K.; Amhed, S.; Deligianni, L.; Romankiw, L.T.; Jaime, S.; Grand, P.P.; Charrier, V. Electrodeposition of indium on Copper for CIS and CIGS solar cell applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, D57–D61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidman, S.B.; Munäoz, A.G.; Bessone, J.B. Electrodeposition of indium and zinc on aluminium. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1999, 29, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-F.; Wang, Y.-S. Indium recovery in an electrochemical flow reactor. Simulation and experiment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 3516–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, W.W.; Fischer, D.; Tomney, M.R.; Pye, C.C. Indium(III) hydration in aqueous solutions of perchlorate, nitrate and sulfate. Raman and infrared spectroscopic studies and ab-initio molecular orbital calculations of indium(III)–water cluster. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys 2004, 6, 5145–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, C.; Frisch, G. Complexation equilibria of indium in aqueous chloride, sulfate and nitrate solutions: An electrochemical investigation. J. Solution Chem. 2017, 46, 1928–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Era, A.; Ciro Zuleta, E.; Pasquali, M.; Lupi, C. Process parameters affecting the efficiency of indium electrowinning results from sulfate baths. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 193, 105296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, F.C.; Gabe, D.R. Electrode reactions during the electrodeposition of indium from acid sulphate solutions. Surf. Technol. 1978, 6, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrecek, B.; Markovac, V. Studies of the Electrochemical Kinetics of Indium. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1962, 109, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, F.C.; Gabe, D.R. The electrodeposition of indium. Surf. Technol. 1979, 8, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Rehim, S.S.; Mostafa, M.A.; Ahmed, A.M. Structural studies on electrodeposited indium on steel surfaces. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1988, 7, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, G.; Fan, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Pan, J.; Wang, R. Preparation of high purity indium by chemical purification: Focus on removal of Cd, Pb, Sn and removal mechanism. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 200, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, B.; Nagy, S.; Kékesi, T. The recycling of pure metallic indium from waste LCD screens by a combined hydro-electrometallurgical method. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 213, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciro, E.; Dell’Era, A.; Pasquali, M.; Lupi, C. Indium electrowinning kinetics on titanium, aluminum and copper supports from sulfate solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 885, 115099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xing, H. Electrochemical Mechanism of the Preparation of High-Purity Indium by Electrodeposition. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 871420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciro, E.; Dell’Era, A.; Pasquali, M.; Lupi, C. Indium electrowinning study from sulfate aqueous solution using different metal cathodes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciro, E.; Dell’Era, A.; Lupi, C. Indium Electrowinning from Sulfate Solutions: The Influence of Cathodic Support on the Process Effectiveness. Mining Metall. Explor. 2023, 40, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, J.P. On the role of boric-acid in the Watts bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1986, 133, 2491–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasekar, N.P.; Haridoss, P.; Seshadri, S.K.; Sundararajan, G. Influence of mode of electrodeposition, current density and saccharin on the microstructure and hardness of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 291, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhouiete, A.; Boumendjel, S.; Sobhi, N.E.H. Effect of current density on the microstructure and morphology of the electrodeposited nickel coatings. Turk. J. Chem. 2021, 45, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, T.; Chen, C.Y.; Mark Chang, T.F.; Yamane, D.; Ito, H.; Machida, K.; Masu, K.; Sone, M. Effect of current density on micro-mechanical property of electrodeposited gold film evaluated by micro-compression. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 436, 128315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





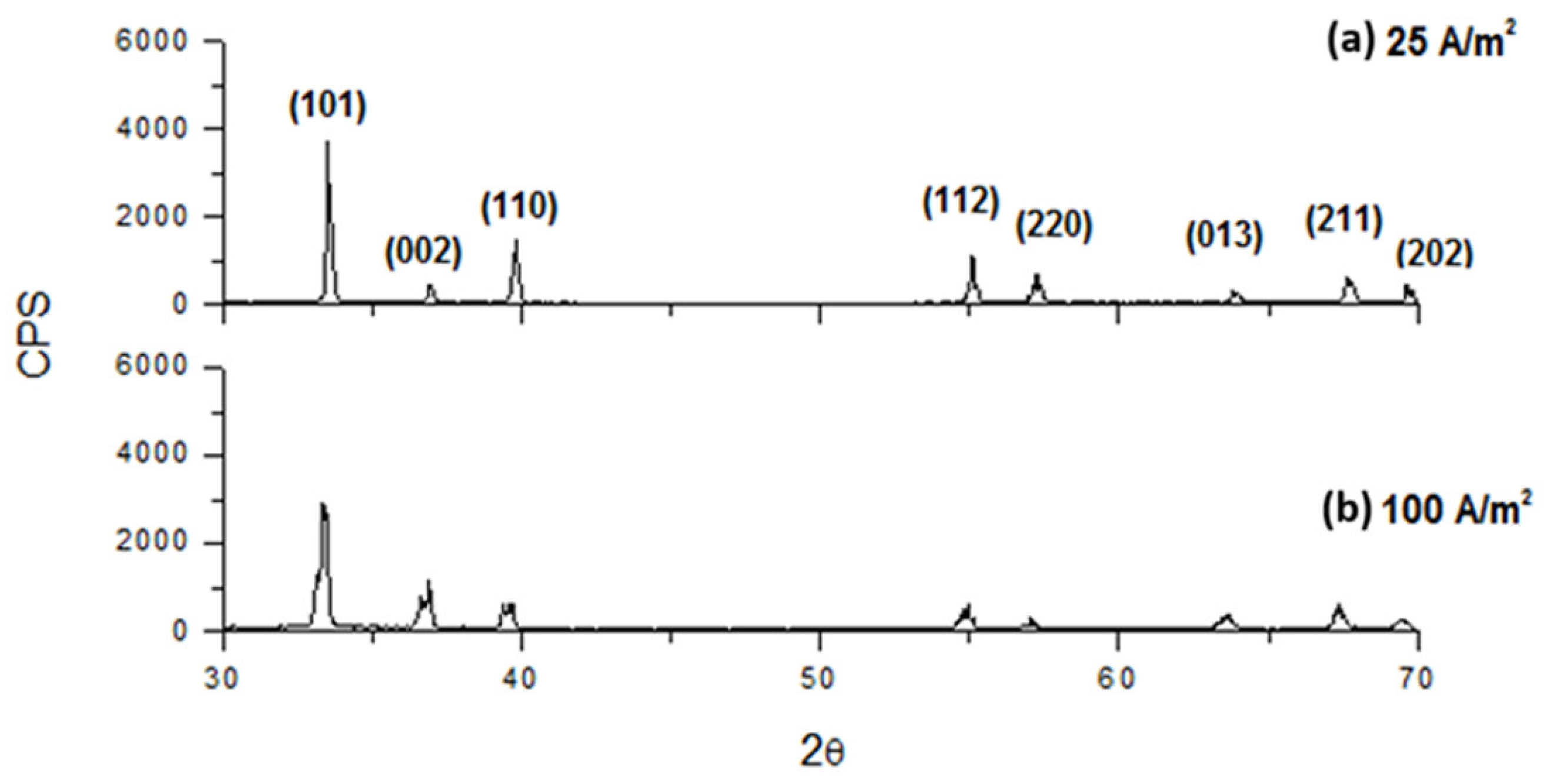

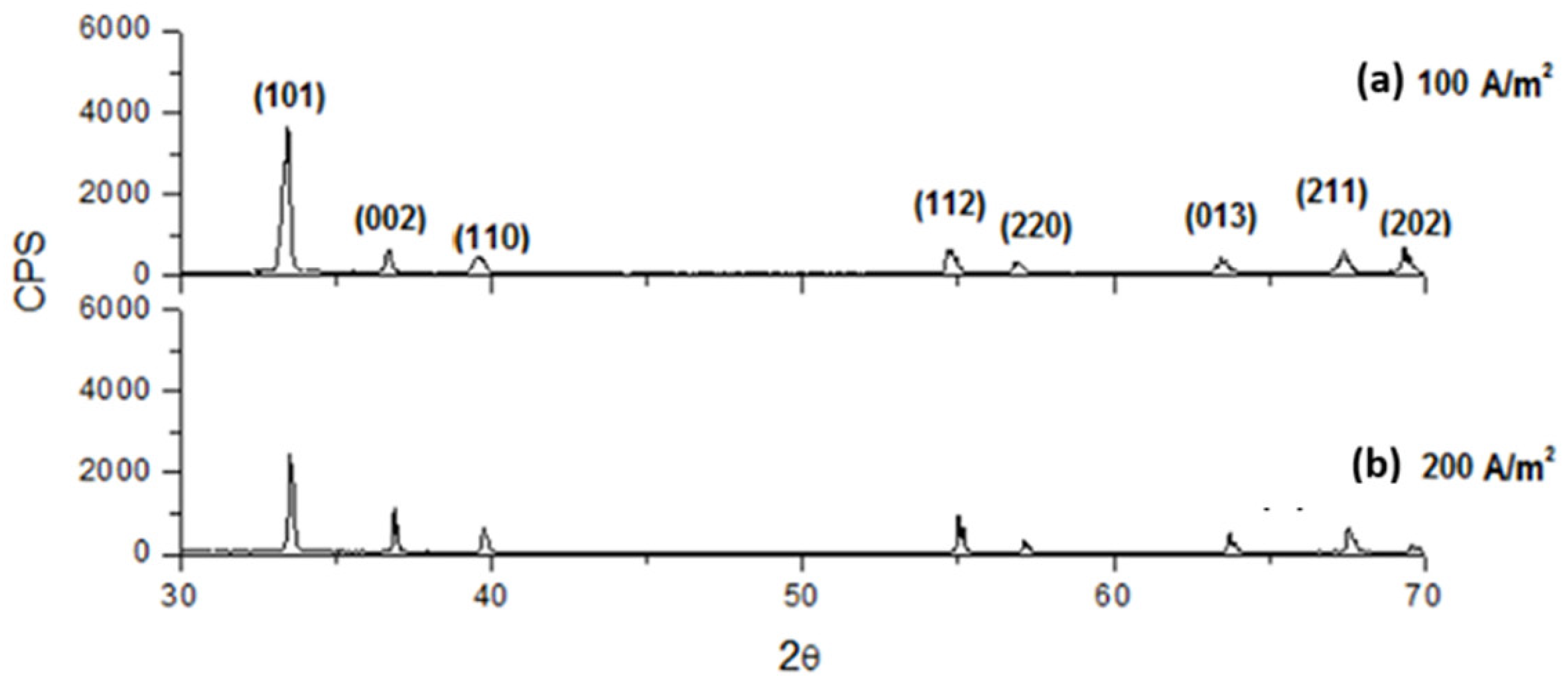

| H3BO3 (g/L) | Na2SO4 (g/L) | CD (A/m2) | CE (%) | SEC (kWh/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 100 | 59.0 | 3.5 |
| 5 | 0 | 100 | 63.0 | 2.7 |
| 40 | 0 | 100 | 83.5 | 2.5 |
| 0 | 0 | 150 | 43.8 | 5.5 |
| 40 | 0 | 150 | 63.5 | 3.7 |
| 0 | 30 | 100 | 33.1 | 6.5 |
| 40 | 30 | 100 | 23.7 | 9.1 |
| Pretreatment | CD (A/m2) | CV (V) | CE (%) | SEC (kWh/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 100 | 2.4 | 63.0 | 2.7 |
| Etching | 100 | 3.1 | 77.6 | 2.8 |
| - | 150 | 3.5 | 43.8 | 5.5 |
| Etching | 150 | 3.2 | 79.3 | 2.8 |
| - | 200 | 3.4 | 38.1 | 6.2 |
| Etching | 200 | 3.5 | 71.8 | 3.4 |
| Temperature (°C) | Current Density (A/m2) | CV (V) | SEC (kWh/kg) | CE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 150 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 77.3 |
| 25 | 200 | 4.0 | 3.8 | 74.2 |
| 40 | 150 | 3.6 | 2.8 | 79.3 |
| 40 | 200 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 71.3 |
| 60 | 150 | 3.4 | 2.8 | 85.0 |
| 60 | 200 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 71.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lupi, C.; Ciro, E.; Dell’Era, A. Study of Operational Parameters on Indium Electrowinning Using a Ti Cathode. Materials 2025, 18, 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092089
Lupi C, Ciro E, Dell’Era A. Study of Operational Parameters on Indium Electrowinning Using a Ti Cathode. Materials. 2025; 18(9):2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092089
Chicago/Turabian StyleLupi, Carla, Erwin Ciro, and Alessandro Dell’Era. 2025. "Study of Operational Parameters on Indium Electrowinning Using a Ti Cathode" Materials 18, no. 9: 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092089
APA StyleLupi, C., Ciro, E., & Dell’Era, A. (2025). Study of Operational Parameters on Indium Electrowinning Using a Ti Cathode. Materials, 18(9), 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092089








