Electroanalysis of Apocynin Part 2: Investigations on a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode in Aqueous Buffered Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Apparatus and Voltammetric Techniques
3. Results
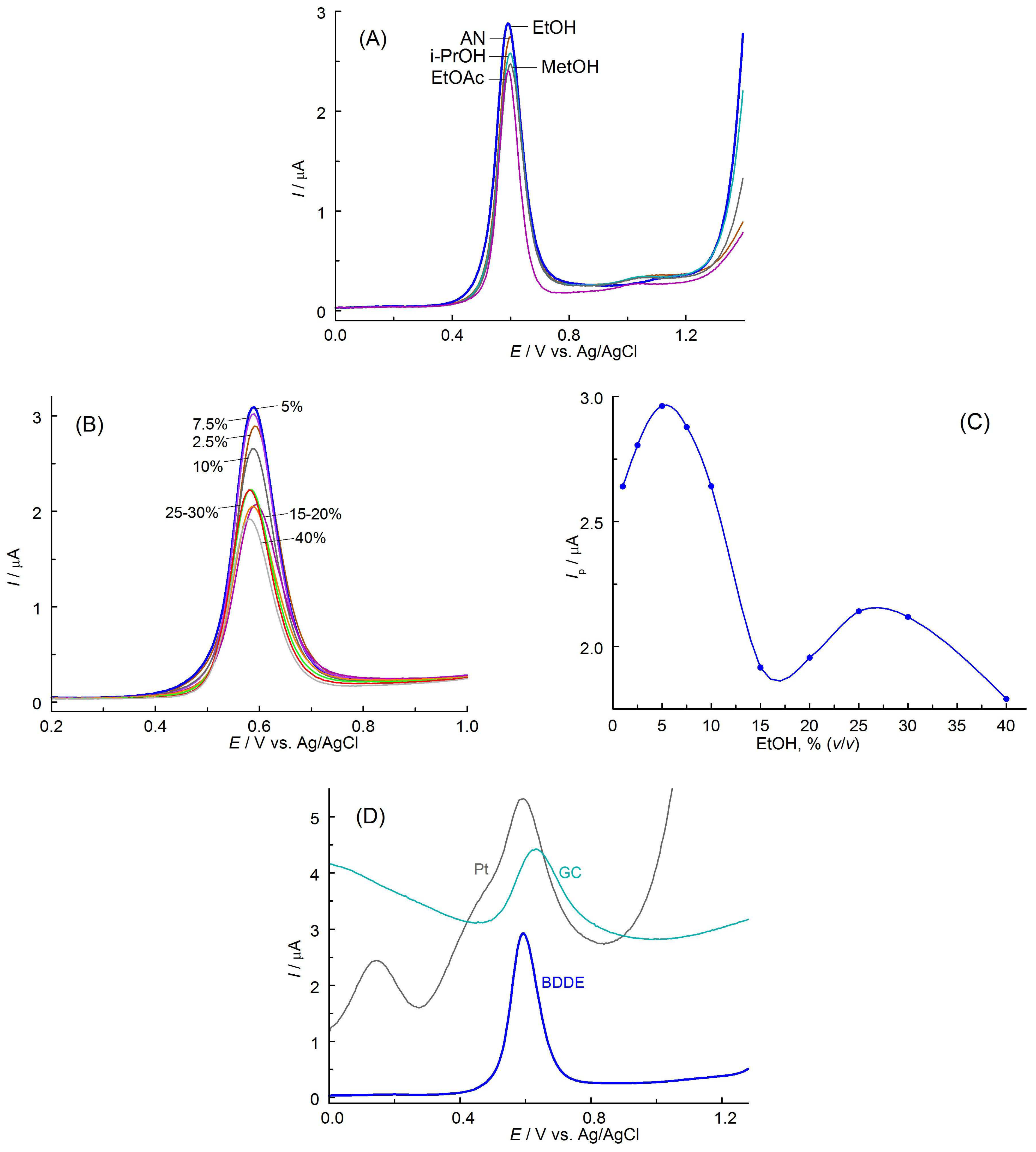
3.1. Preparation of Solutions
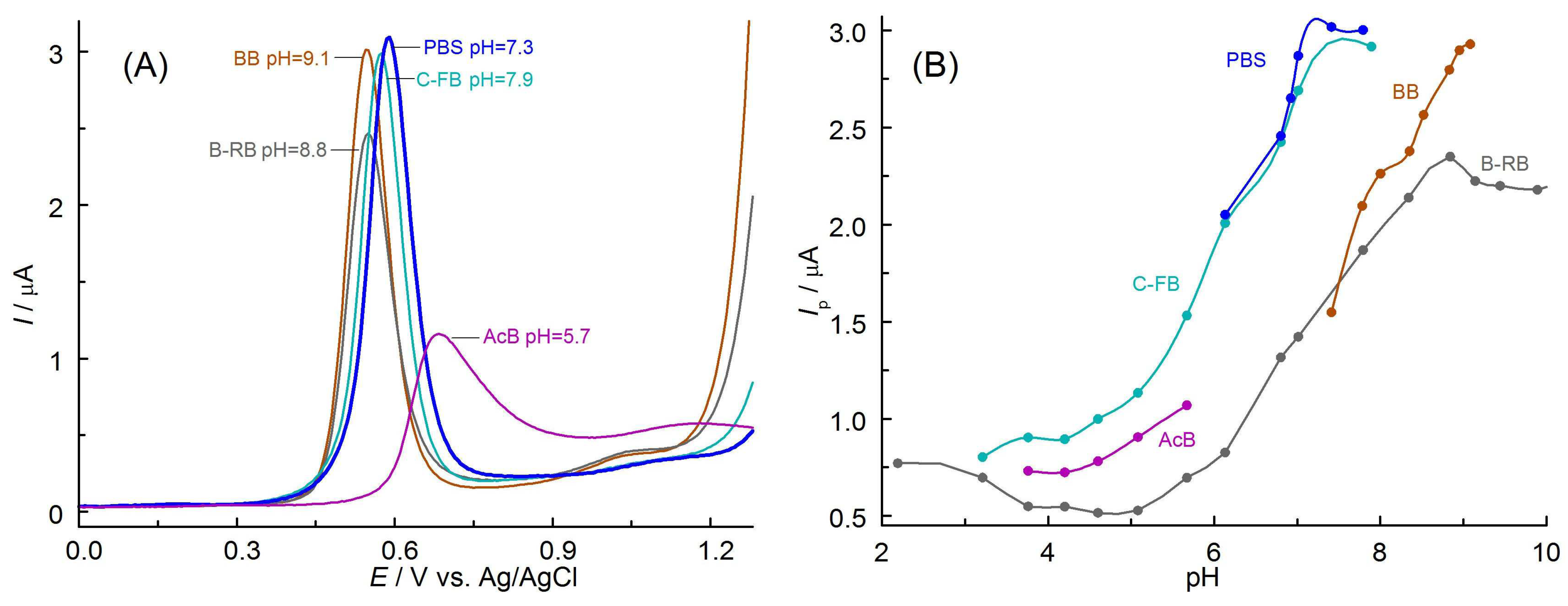
3.2. Selection of the Optimal Solution Composition and Electrode Material
3.3. Voltammetric Behavior of Apocynin
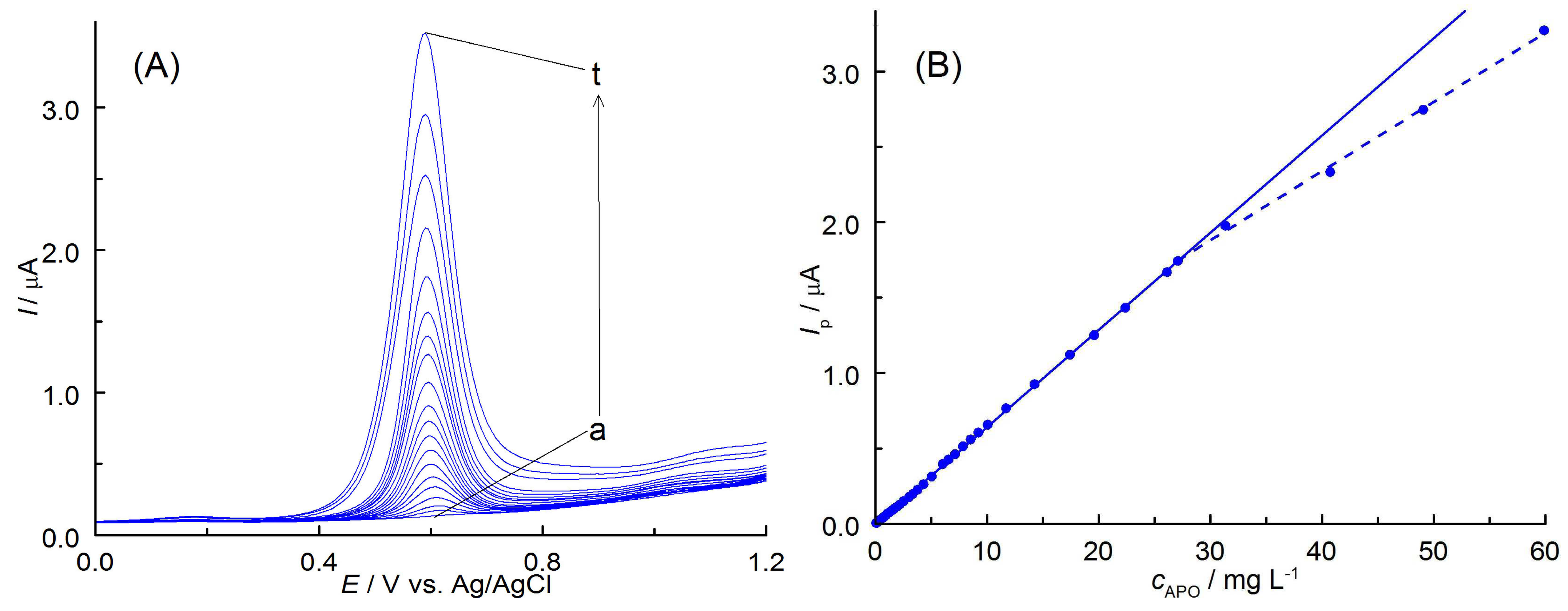
3.4. Voltammetric Determination of APO
3.4.1. Validation of the Method
3.4.2. Repeatability
3.4.3. Recovery Studies
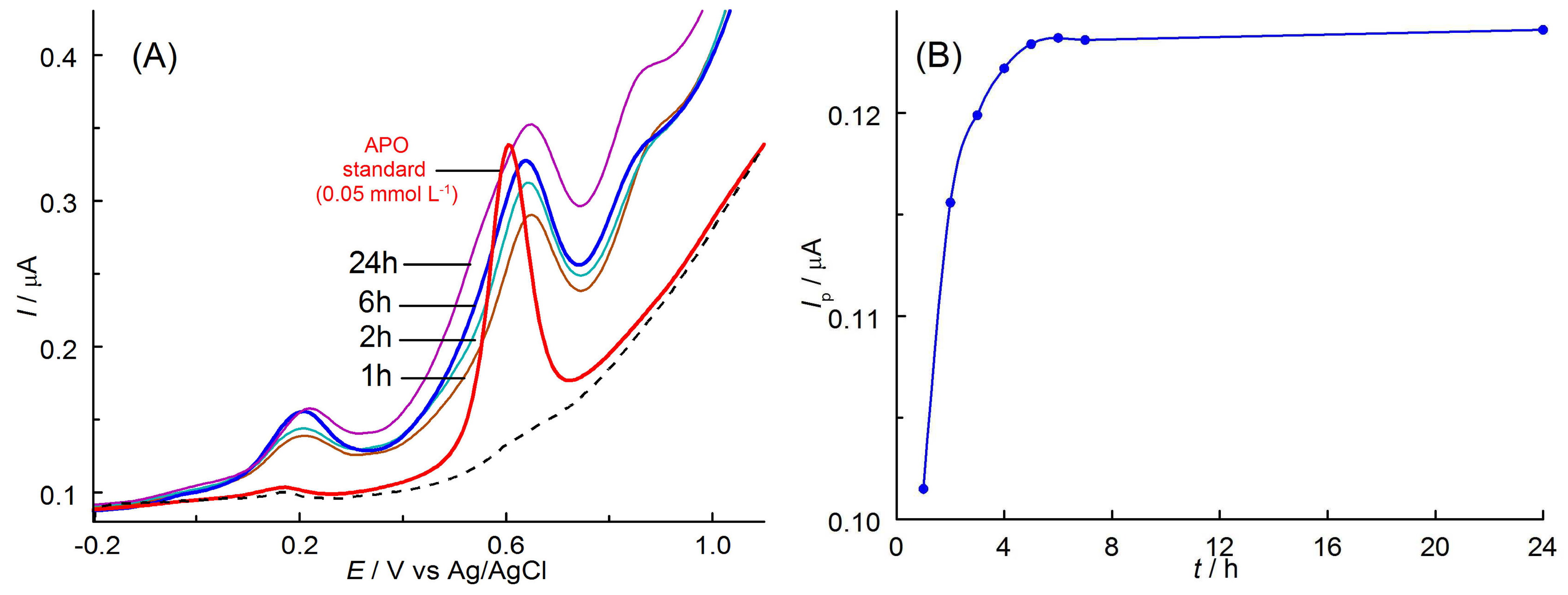
3.4.4. Extraction
3.4.5. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anter, H.M.; Hashim, I.I.A.; Awadin, W.; Meshali, M.M. Novel anti-inflammatory film as a delivery system for the external medication with bioactive phytochemical “Apocynin”. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 2981–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanska, J.; Pawliczak, R. Apocynin: Molecular aptitudes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2008, 106507, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, S.; Struppner, H. Analysis of iridoid glycosides from Picrorhiza kurroa by capillary electrophoresis and high performance liquid chromatography-Mass spectrometry. Chromatographia 2001, 53, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, J. Synthesis of apocynin dimer derivatives combining L-cysteine and alpha-lipoic acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 7, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, M.P.; Benedí, J.; Bermejo-Bescós, P.; Martin-Aragon, S. Plants with evidence-based therapeutic effects against neurodegenerative diseases. Pharm. Pharmacol. Int. J. 2019, 7, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.J.; Mock, N.M.; Averyanov, A.A. Redox- and bio-activity of apocynin (acetovanillone) in tobacco, a plant phenolic that alleviates symptoms of autoimmune diseases in animals. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 106, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancheva, D.Y.; Stoyanov, S.S.; Velcheva, E.A.; Stamboliyska, B.A.; Smelcerovic, A. DFT study on the radical scavenging capacity of apocynin with different free radicals. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 49, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, G.C.; Piton, E.; dos Santos, B.M.; da Silva, R.M.; de Almeida, A.S.; Dalenogare, D.P.; Schiefelbein, N.S.; Fialho, M.F.P.; Moresco, R.N.; dos Santos, G.T.; et al. Apocynin as an antidepressant agent: In vivo behavior and oxidative parameters modulation. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 388, 112643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chuang, C.C.; Kandaswamy, E.; Zhou, T.; Zuo, L. Role of ROS and nutritional antioxidants in human diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrônio, M.S.; Zeraik, M.L.; Da Fonseca, L.M.; Ximenes, V.F. Apocynin: Chemical and biophysical properties of a NADPH oxidase inhibitor. Molecules 2013, 18, 2821–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Moon, K.A.; Jo, H.Y.; Jeong, S.; Seon, S.H.; Jung, E.; Cho, Y.S.; Chun, E.; Lee, K.Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of apocynin, an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase, in airway inflammation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomassi, A.; Falegnami, A.; Romano, E. Talking Resilience: Embedded Natural Language Cyber-Organizations by Design. Systems 2025, 13, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, B.A.; Dogan, T.; Bolat, İ.; Ozcan, A.C.; Kocak, R. Effect of NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin on human lung cancer A549 cells via Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3, and NF-κB signaling pathway. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Diego-Otero, Y.; El Bekay, R.; García-Guirado, F.; Sánchez-Salido, L.; Giráldez-Pérez, R.M. Apocynin, a Selective NADPH Oxidase (Nox2) Inhibitor, Ameliorates Behavioural and Learning Deficits in the Fragile X Syndrome Mouse Model. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukovic, A.; Karanovic, D.; Mihailovic-Stanojevic, N.D.; Miloradovic, Z.; Brkic, P.; Zivotic, M.; Nesovic Ostojic, J.; Ivanov, M.; Kovacevic, S.; Vajic, U.J.; et al. Apocynin and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improve Renal Function and Structure in an Animal Model of CKD. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, L.; Song, Y.; Ye, X.; Fu, S.; Jiang, J.; Li, S. Improvement of Pharmacokinetics Behavior of Apocynin by Nitrone Derivatization: Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Nitrone-Apocynin and its Parent Apocynin in Rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalczuk de Oliveira, J.; Ronik, D.F.V.; Ascari, J.; Mainardes, R.M.; Khalil, N.M. A stability-indicating high performance liquid chromatography method to determine apocynin in nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 7, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandasana, H.; Chhonker, Y.S.; Bala, V.; Prasad, Y.D.; Chaitanya, T.K.; Sharma, V.L.; Bhatta, R.S. Pharmacokinetic, bioavailability, metabolism and plasma protein binding evaluation of NADPH-oxidase inhibitor apocynin using LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 985, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbull, K.A.; McAllister, D.; Gandelman, M.M.; Fung, W.Y.; Lew, T.; Brennan, L.; Lopez, N.; Morré, J.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Beckman, J.S. Diapocynin and apocynin administration fails to significantly extend survival in G93A SOD1 ALS mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalkiewicz, S.; Skorupa, A.; Jakubczyk, M.; Bębacz, K. Application of a Carbon Fiber Microelectrode as a Sensor for Apocynin Electroanalysis. Materials 2024, 17, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalkiewicz, S.; Skorupa, A.; Jakubczyk, M. Carbon materials in electroanalysis of preservatives: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.C.B.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Boron doped diamond electrode pre-treatments effect on the electrochemical oxidation of dsDNA, DNA bases, nucleotides, homopolynucleotides and biomarker 8-oxoguanine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 648, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchtefeld, R.; Luo, R.; Stine, K.; Alt, M.L.; Chernovitz, P.A.; Smith, R.E. Dose formulation and analysis of diapocynin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, F. Electroanalytical Methods: Guide to Experiments and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-642-02914-1. [Google Scholar]
- Gosser, D.K. Cyclic Voltammetry; Simulation and Analysis of Reaction Mechanisms; VCH Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993; ISBN 1-56081-026-2. [Google Scholar]
- Brett, C.M.A.; Oliveira Brett, M.A. Electrochemistry. Principles, Methods, and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; ISBN 0-19-855389-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.; Varela, H.; Torresi, R.M.; Tremiliosi-Filho, G. Electrode passivation caused by polymerization of different phenolic compounds. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureta-Zanartu, M.S.; Bustos, P.; Berrıos, C.; Diez, M.C.; Mora, M.L.; Gutierrez, C. Electrooxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenol and other polychlorinated phenols at a glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, M.; Lu, F. Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance investigation of surface fouling due to phenol oxidation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 444, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, H.; Ueda, M.; Nagano, S.; Tsujino, Y.; Koyama, J.; Osakai, T. Mechanistic Study of the Oxidation of Caffeic Acid by Digital Simulation of Cyclic Voltammograms. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 303, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Compton, R.G. An Approach to the Electroanalysis of Electrode Passivating Analytes: The Determination of Phenol. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 3508–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimoni, E.; Brunetti, B. Presenting Analytical Performances of Electrochemical Sensors. Some Suggestions. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocak, J.; Bond, A.M.; Mitchell, S.; Scollary, G. A statistical overview of standard (IUPAC and ACS) and new procedures for determining the limits of detection and quantification: Application to voltammetric and stripping techniques. Pure Appl. Chem. 1997, 69, 297–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Real-time electrochemical monitoring: Toward green analytical chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Guidelines for Standard Method Performance Requirements AOAC Official Methods of Analysis. Appendix F, pp. 1–18. 2016. Available online: https://www.aoac.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/app_f.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2025).





| Method | Application | Linear Range (mg L−1) | LOD (mg L−1) | LOQ (mg L−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-UV | rat plasma | 0.2–100 | nd 1 | 0.2 | [16] |
| HPLC-PDA | bovine serum albumin nanoparticles | 5–100 | 0.078 | 0.238 | [17] |
| LC–MS/MS | rat and human plasma | 1 × 10−4–1 | nd 1 | 1 × 10−4 | [18] |
| DPV (CF) | herbal extracts | 0.449–43.2 | 0.148 | 0.449 | [20] |
| DPV (BDDE) | herbal extracts | 0.213–27.08 | 0.071 | 0.213 | This work |
| Sample | APO Taken/mg L−1 | (1) APO Found/mg L−1 | (2)RSD/% (n = 5) | (3)R/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control 1 | 0.2221 | 0.2212 ± 0.001 | 0.35 | 99.6 |
| Control 2 | 0.9872 | 0.9959 ± 0.0095 | 0.77 | 100.9 |
| Control 3 | 2.356 | 2.405 ± 0.034 | 1.13 | 102.1 |
| Kutki | – | 1.352 ± 0.042 mg g−1 | 1.85 | – |
| Kutki with APO added | 0.333 mg g−1 | 1.699 ± 0.06 mg g−1 | 2.92 | 510.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skorupa, A.; Jakubczyk, M.; Michalkiewicz, S. Electroanalysis of Apocynin Part 2: Investigations on a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode in Aqueous Buffered Solutions. Materials 2025, 18, 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092044
Skorupa A, Jakubczyk M, Michalkiewicz S. Electroanalysis of Apocynin Part 2: Investigations on a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode in Aqueous Buffered Solutions. Materials. 2025; 18(9):2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092044
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkorupa, Agata, Magdalena Jakubczyk, and Slawomir Michalkiewicz. 2025. "Electroanalysis of Apocynin Part 2: Investigations on a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode in Aqueous Buffered Solutions" Materials 18, no. 9: 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092044
APA StyleSkorupa, A., Jakubczyk, M., & Michalkiewicz, S. (2025). Electroanalysis of Apocynin Part 2: Investigations on a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode in Aqueous Buffered Solutions. Materials, 18(9), 2044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18092044






