Study on Early-Age Capillary Pressure and Plastic Shrinkage Properties of High-Volume Fly Ash Concrete
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Mix Proportion
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. Electrical Resistivity
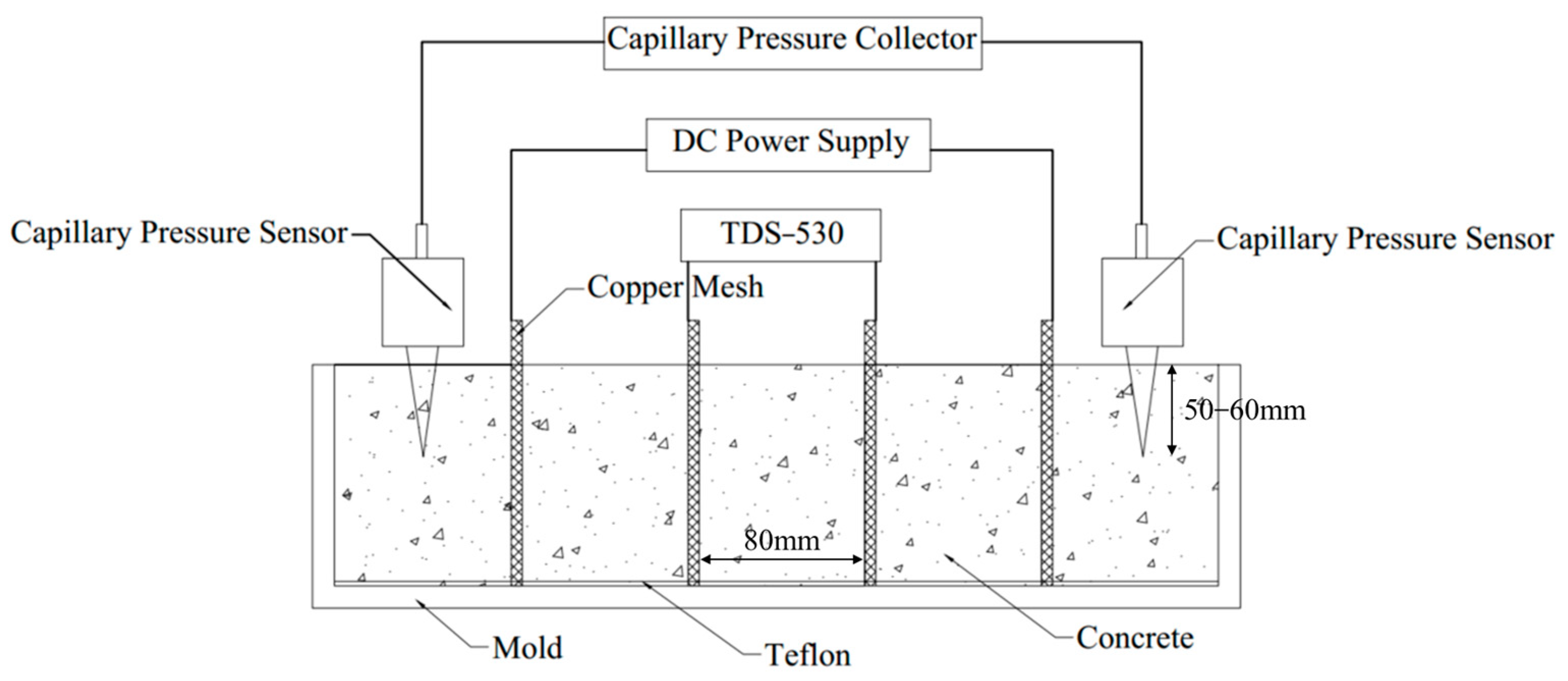
2.2.2. Capillary Pressure
2.2.3. Plastic Shrinkage
2.2.4. Heat of Hydration
3. Results
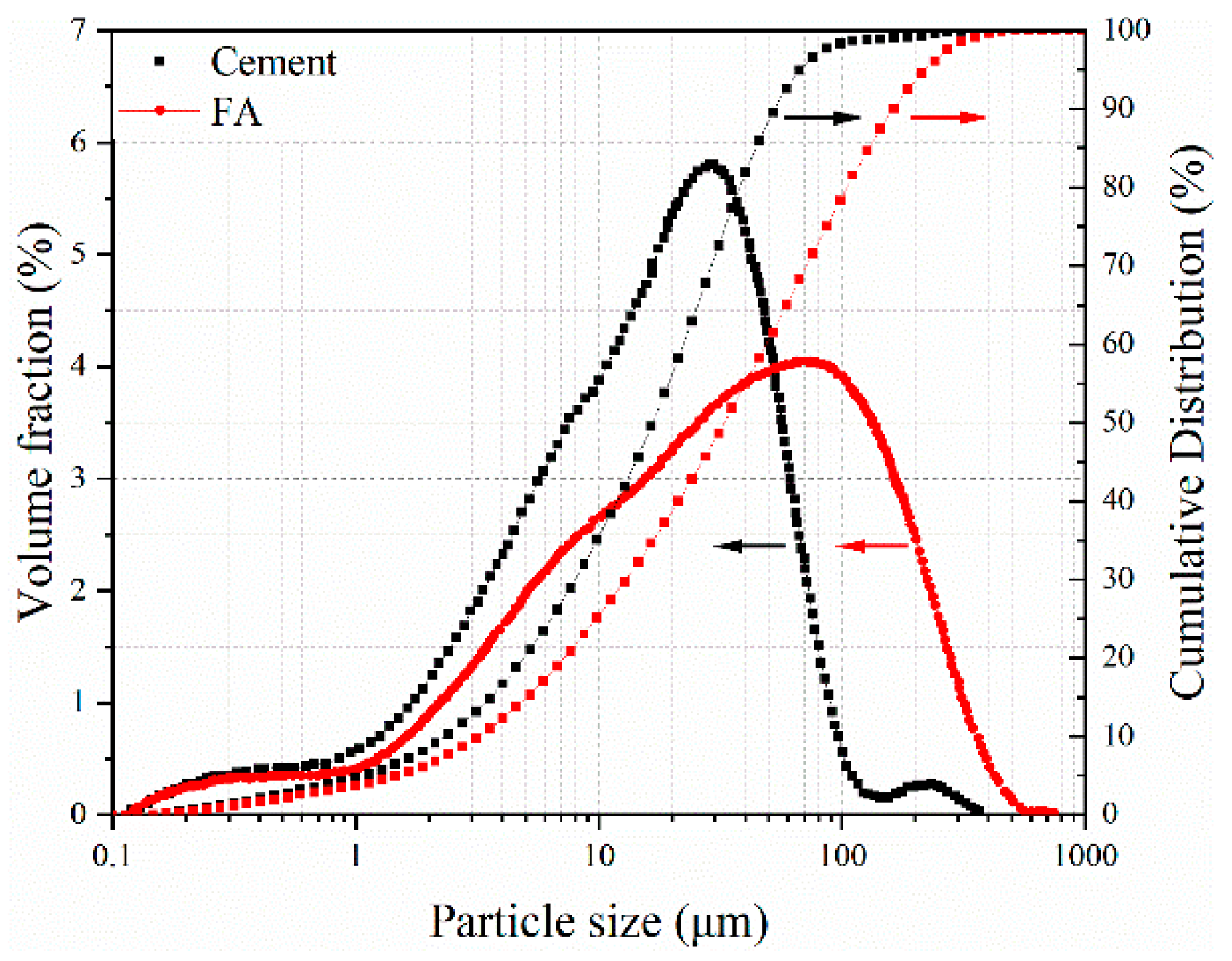
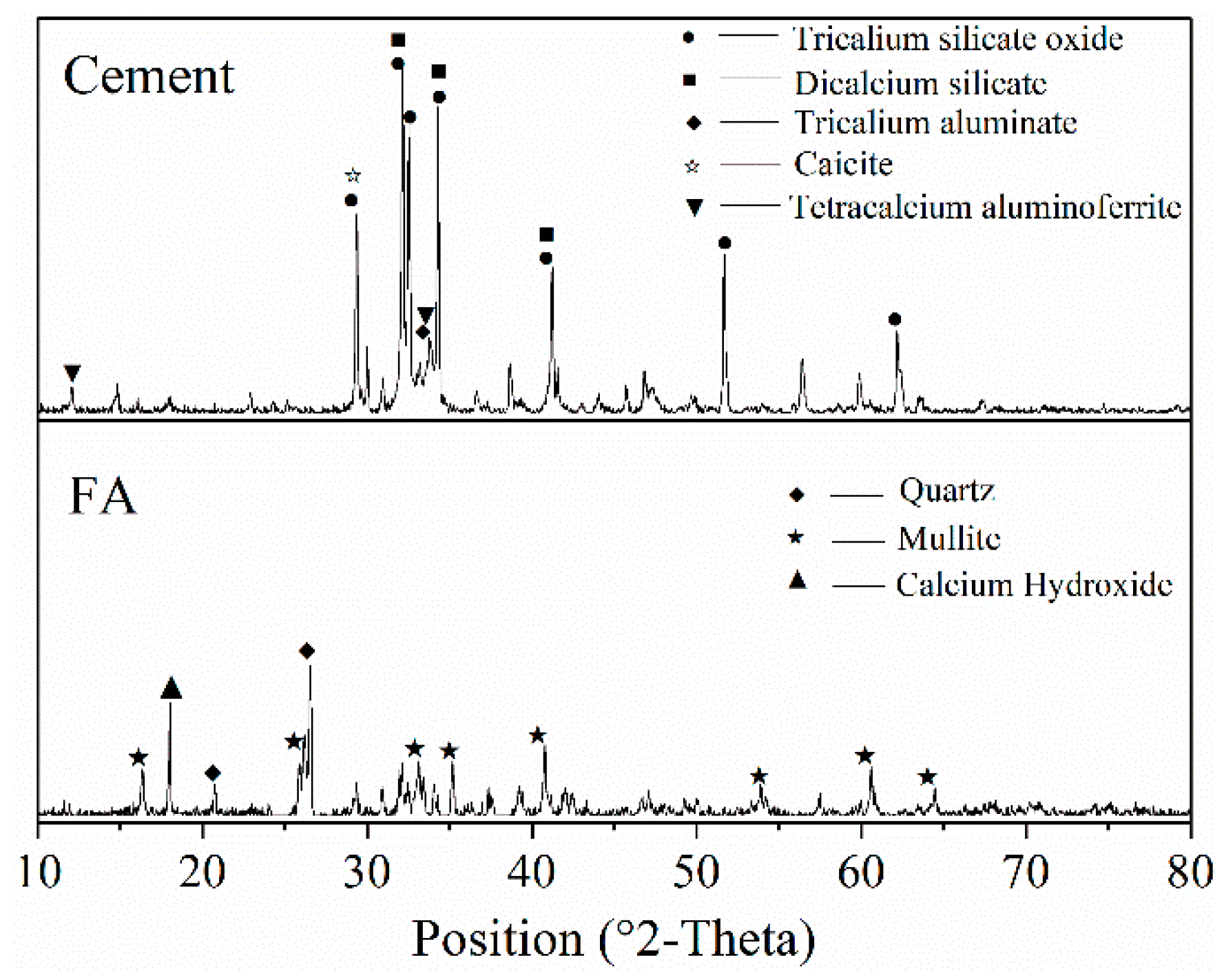
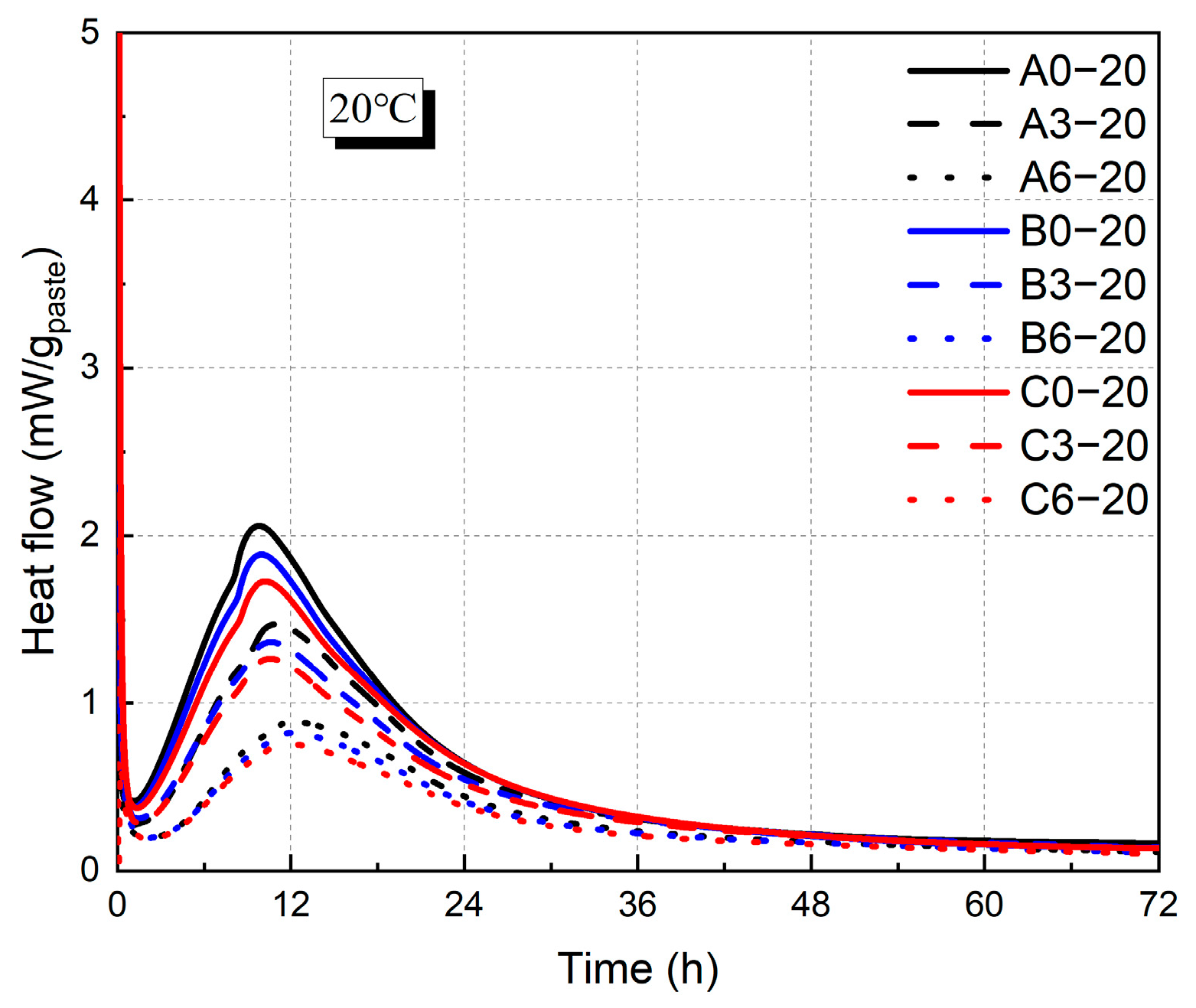
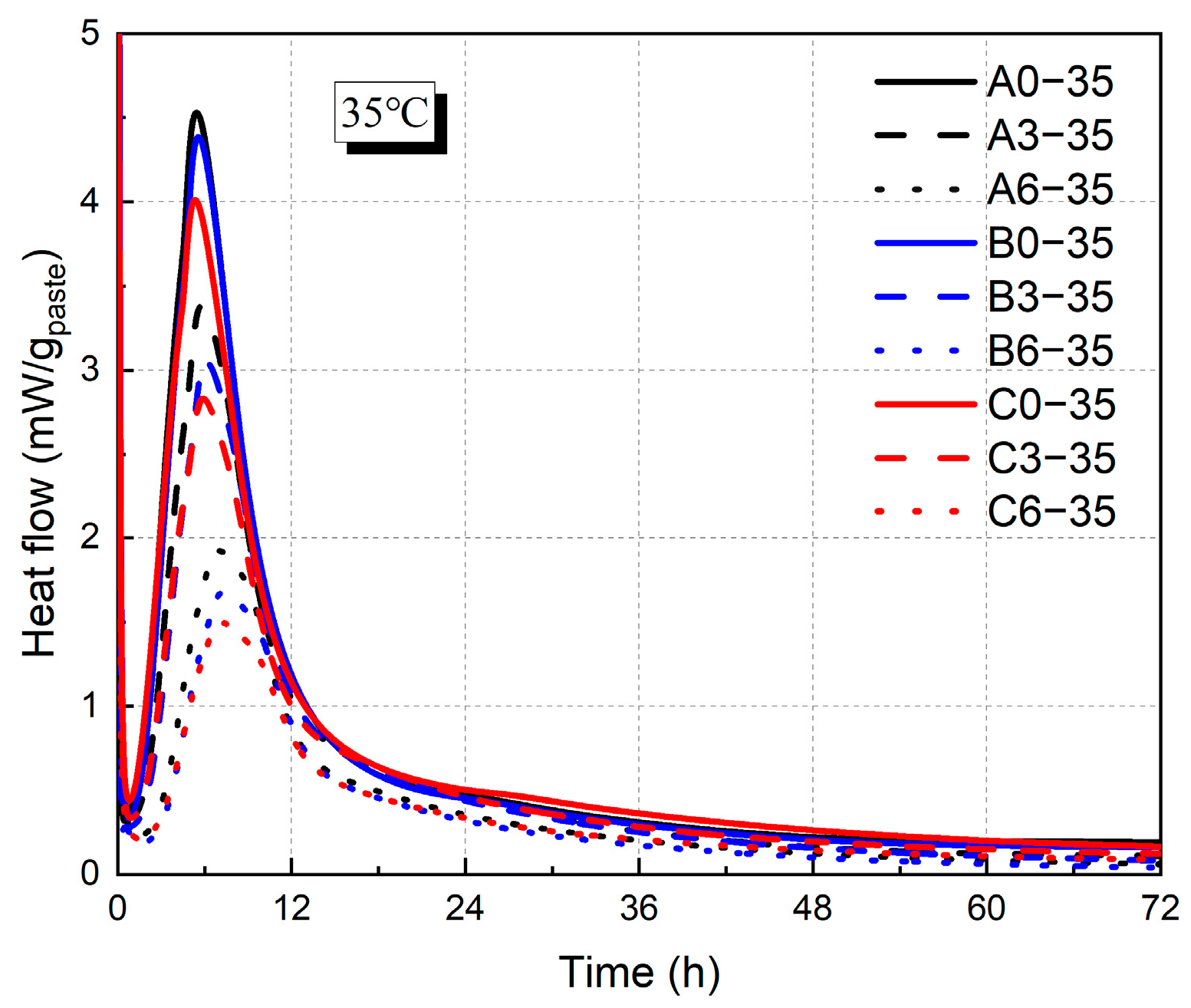
3.1. Raw Materials and the Heat of Hydration
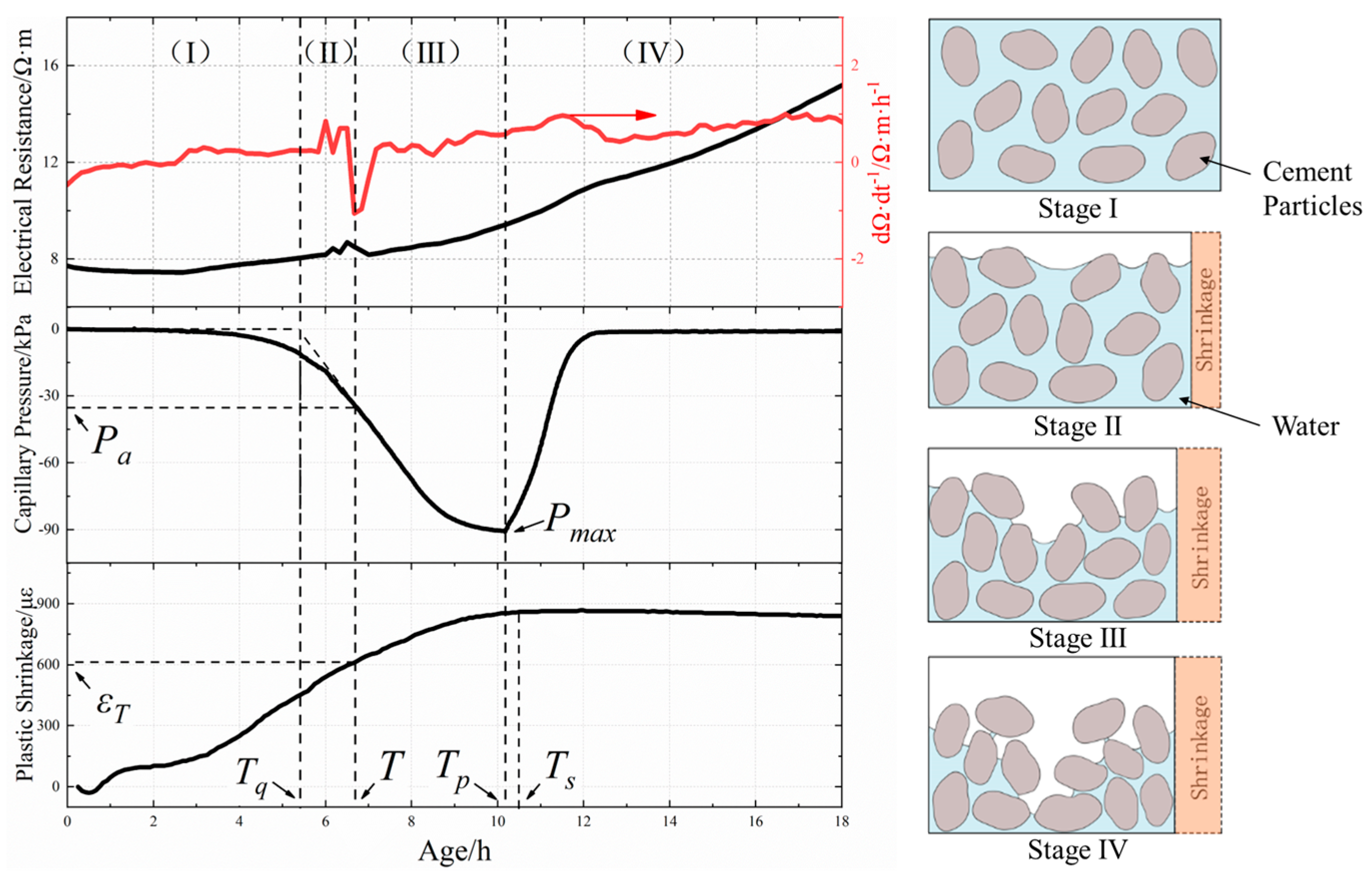
3.2. Early Age of Capillary Pressure, Resistivity, and Plastic Shrinkage of Concrete
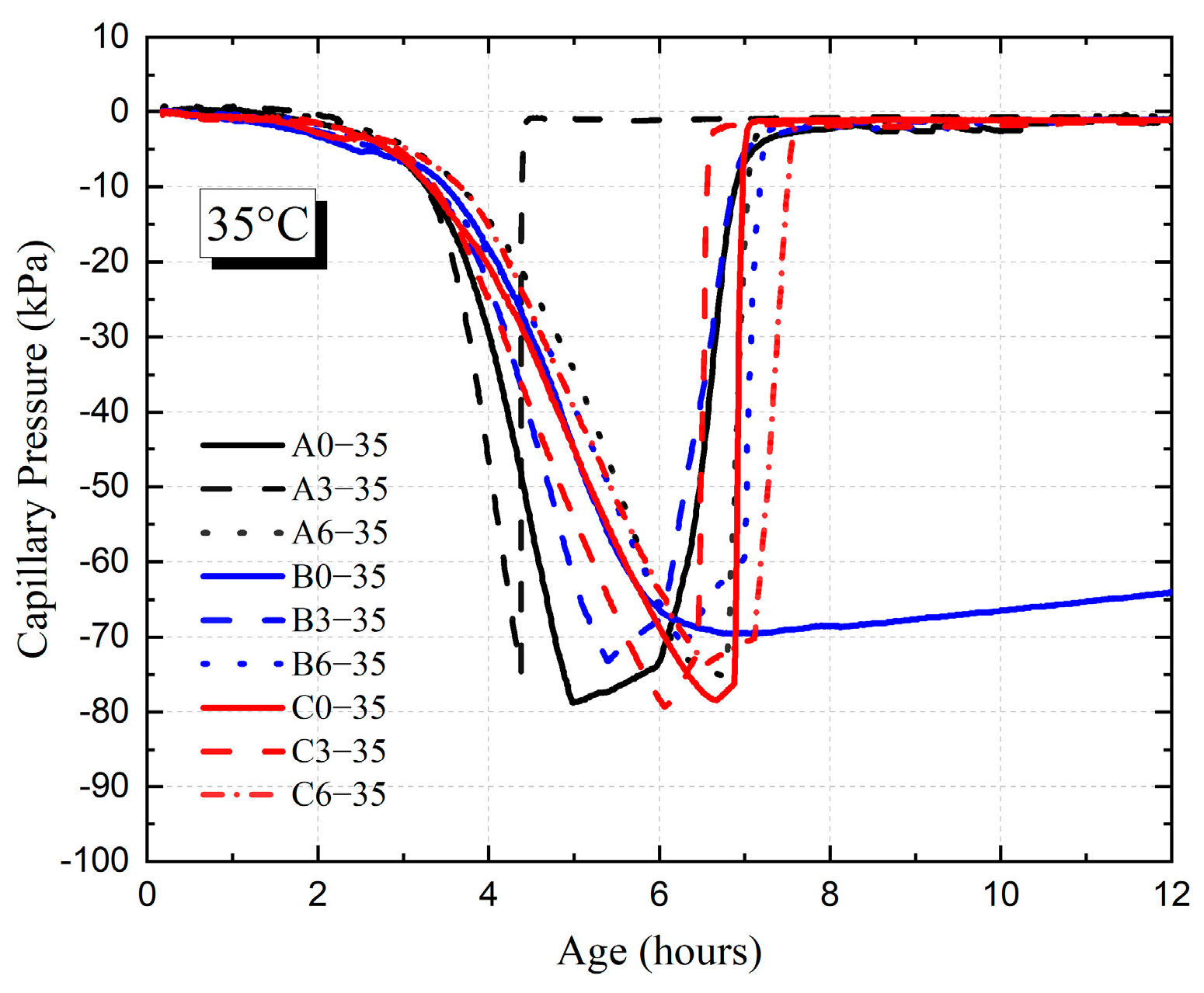
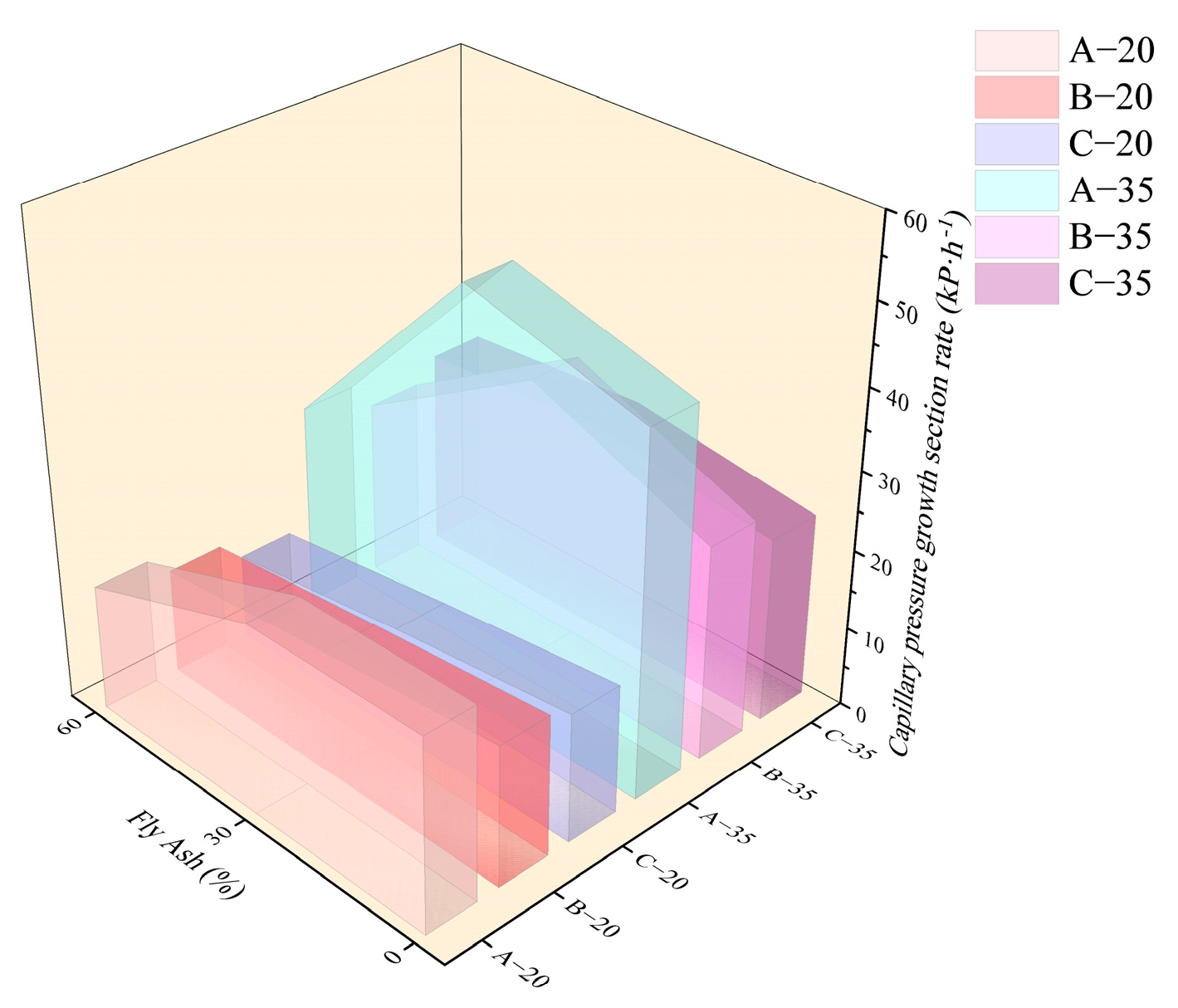
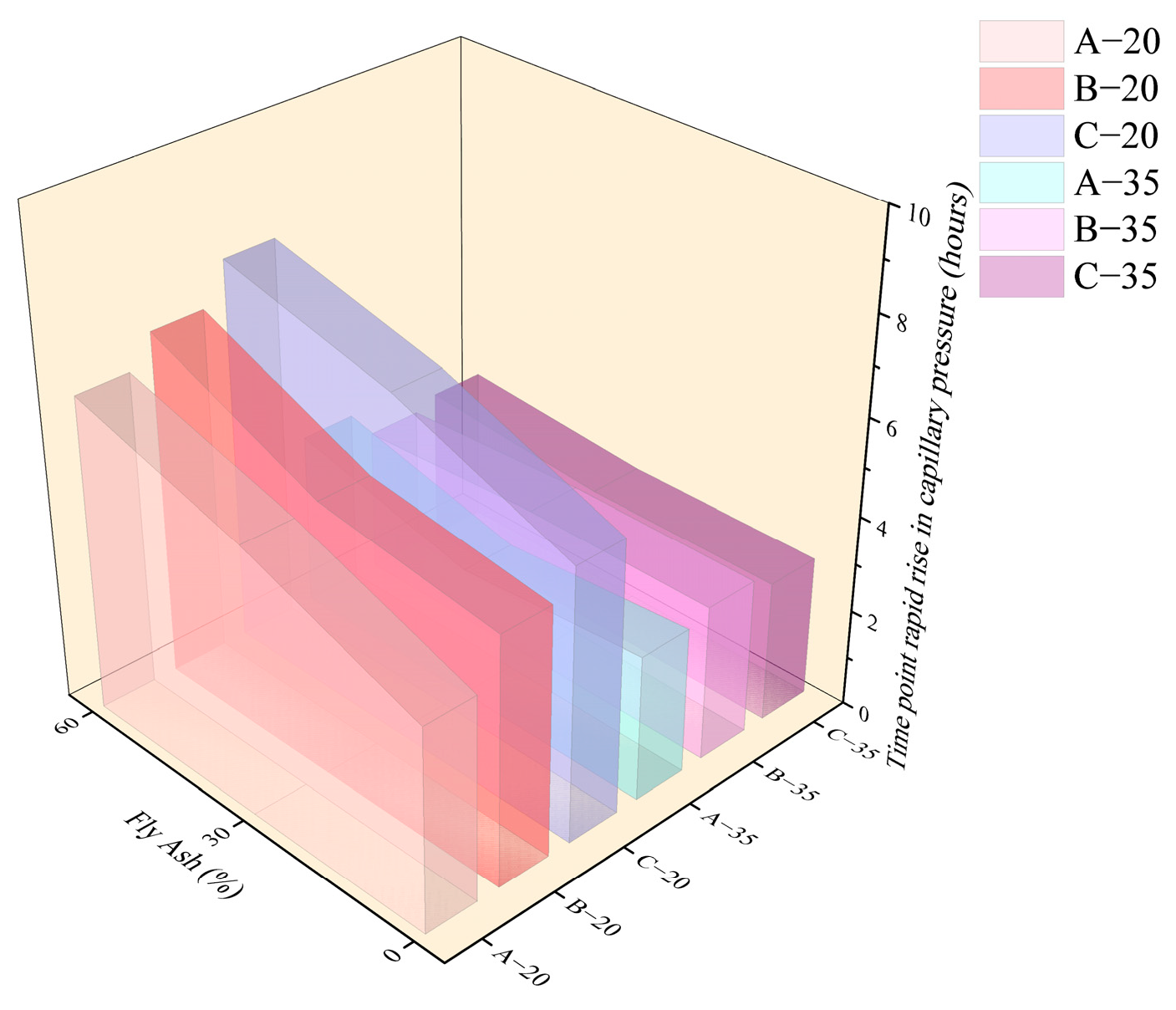
3.3. Capillary Pressure of HVFAC
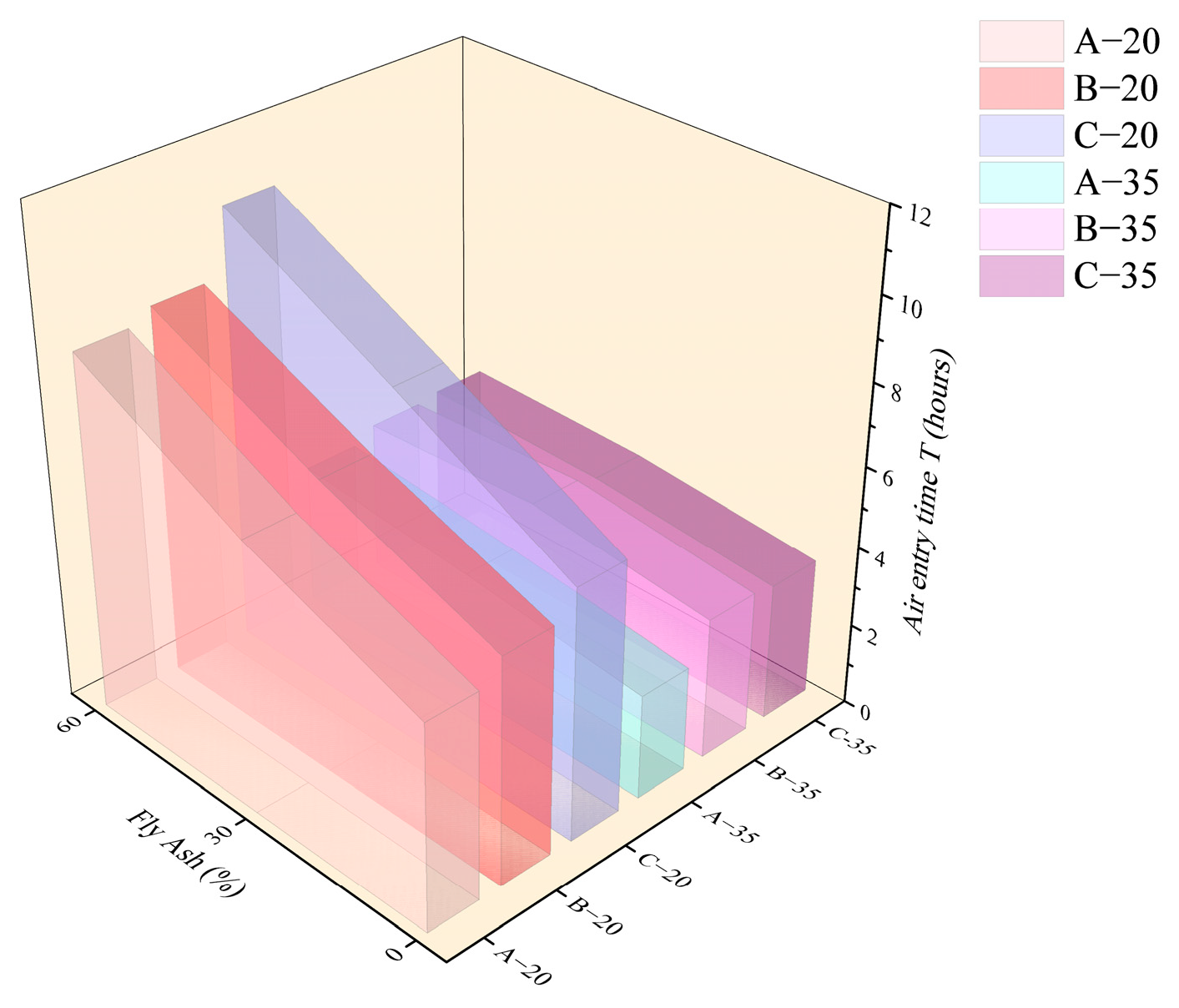
3.3.1. Effect of Fly Ash Content
3.3.2. Effect of Water–Binder Ratio
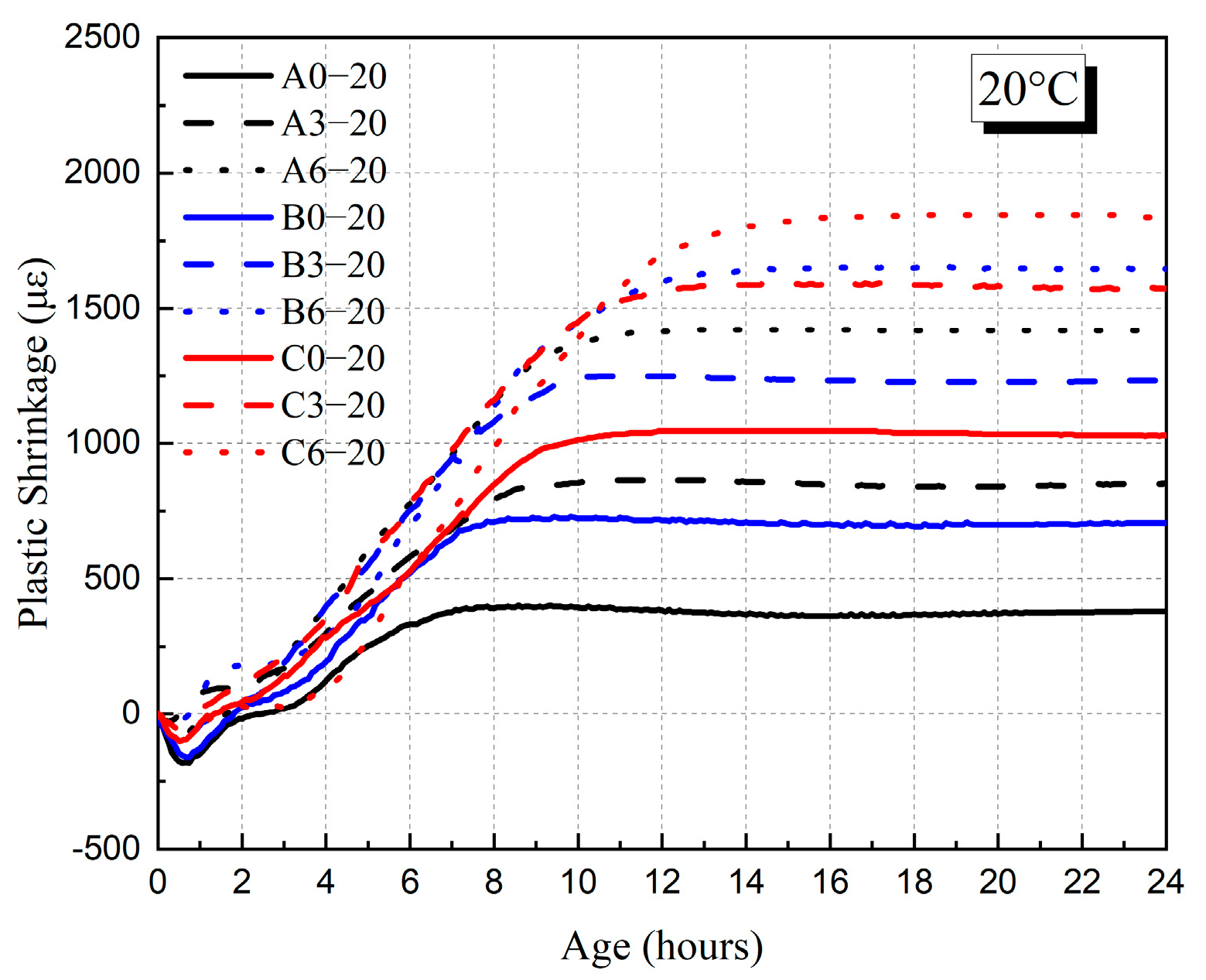
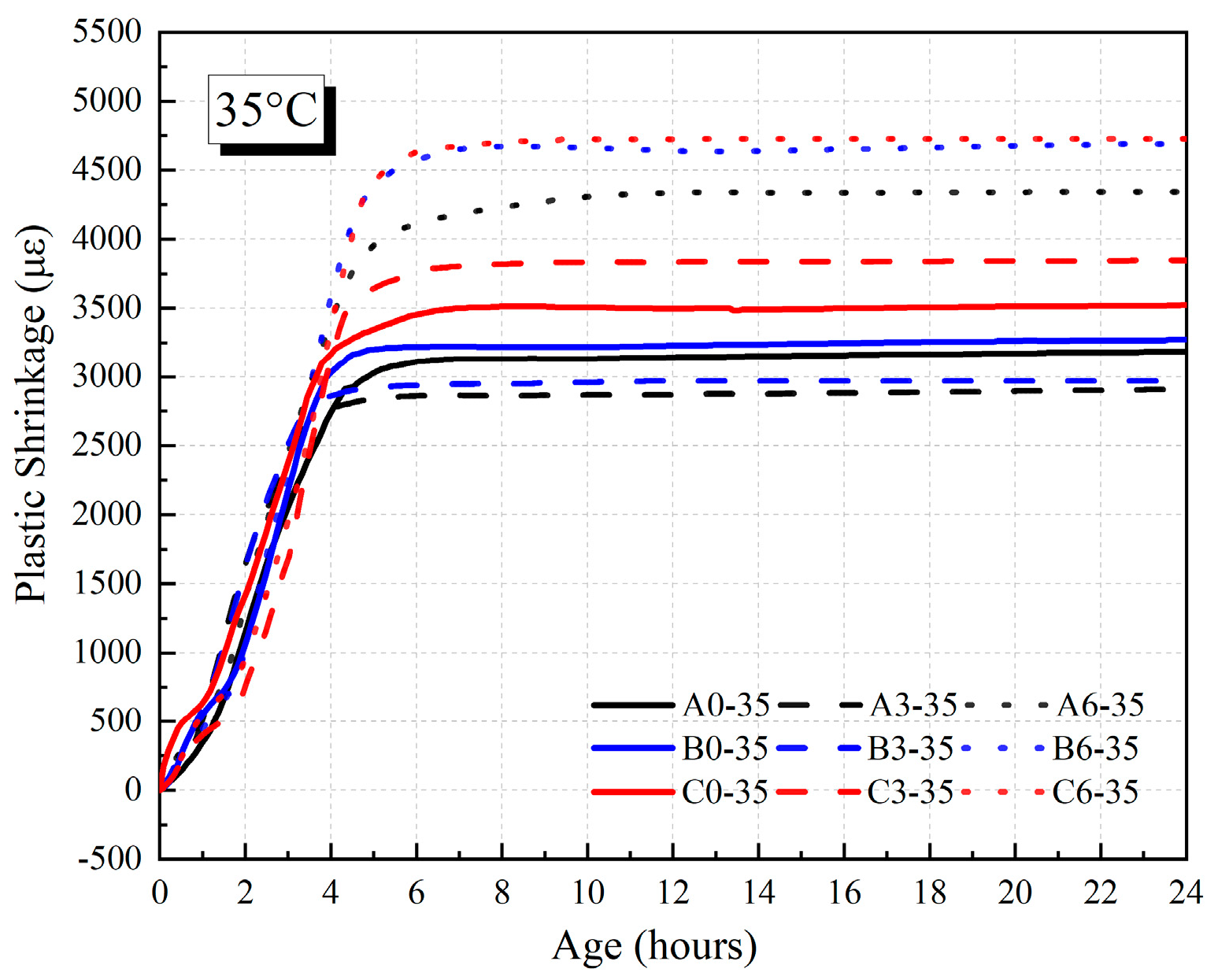
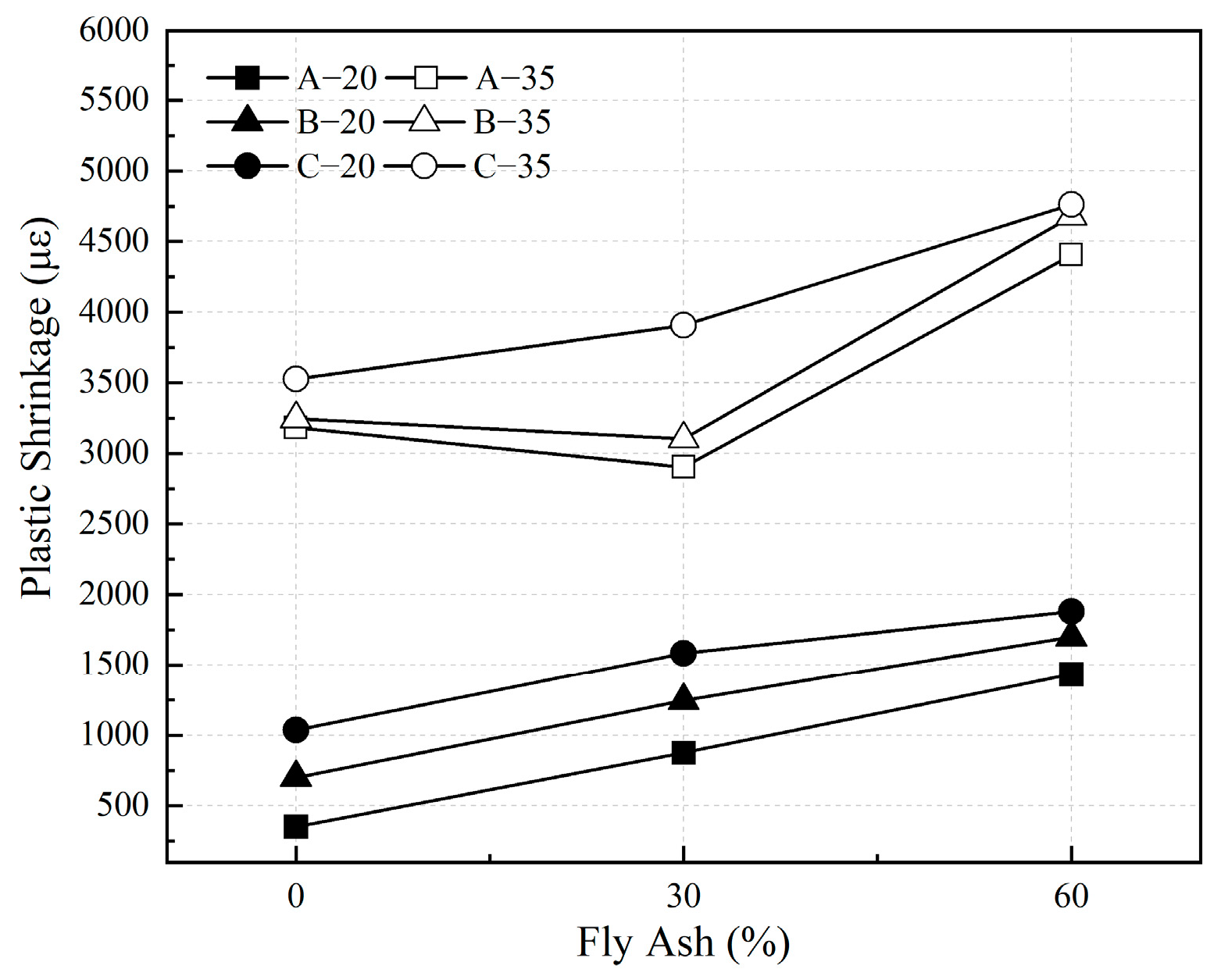
3.4. Plastic Shrinkage of HVFAC
3.4.1. Influence of Fly Ash Content
3.4.2. Influences of Water–Binder Ratio and Curing Temperature
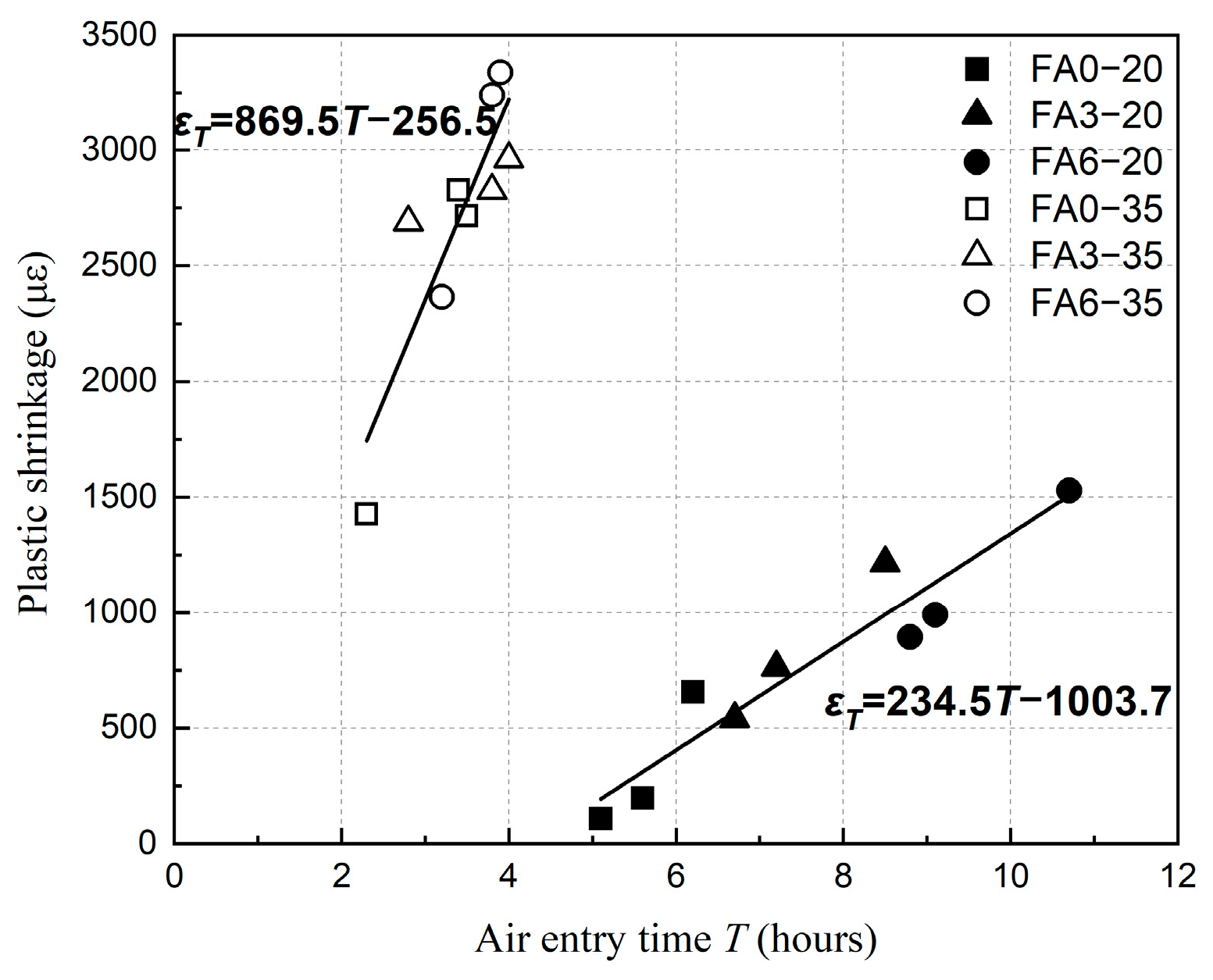
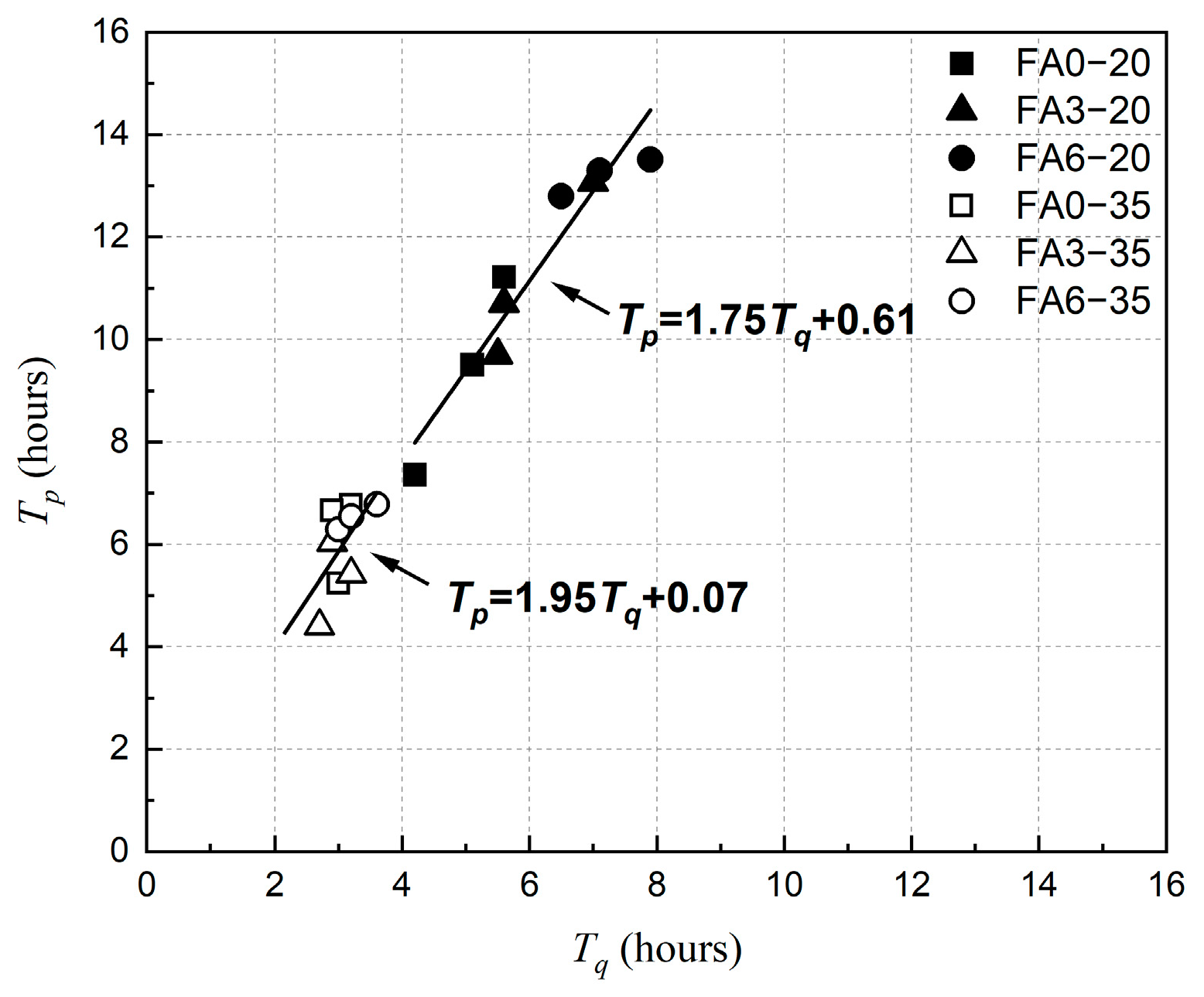
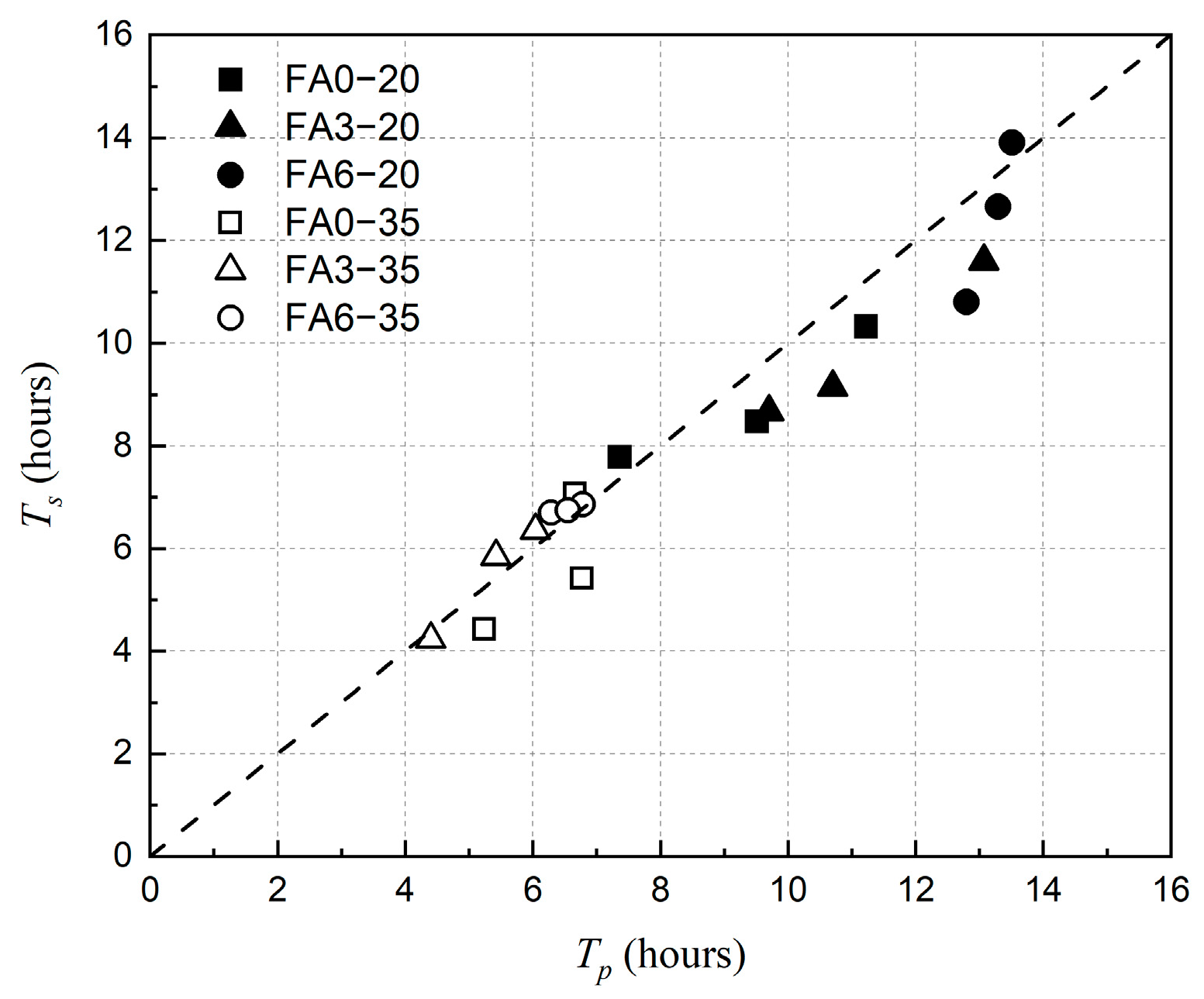
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, N.; Kumar, P.; Goyal, P. Reviewing the behaviour of high volume fly ash based self compacting concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 26, 100882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Xi, J.Y.; Qiu, P.Y.; Deng, C.L.; Li, F.X.; Wei, J.X.; Gao, P.; Yu, Q.J. Evaluation of tensile properties and cracking potential evolution of fly ash-cement mortar at early age based on digital image correlation method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, C.; Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.W.; Setunge, S. Performance of high volume fly ash concrete incorporating additives: A systematic literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 120606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Delsaute, B.; Lu, T.S.; Kostiuchenko, A.; Staquet, S.; Ye, G. A comparative study on the mechanical properties, autogenous shrinkage and cracking proneness of alkali-activated concrete and ordinary Portland cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 292, 123418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, T.; Ramaswamy, A. A review on fly ash characteristics—Towards promoting high volume utilization in developing sustainable concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.P.; Yao, J.K.; Huang, S.L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.T.; Ni, T.Y.; Yang, Z.B. Study on early-age tensile properties of high volume fly ash concrete. Mater. Struct. 2022, 55, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhu, X.H.; Liu, D.S.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, M. Modification of water absorption and pore structure of high-volume fly ash cement pastes by incorporating nanosilica. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 33, 101638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Davis, J.M.; Ley, M.T.; Kang, S.; Amrollahi, P. Fly ash particle characterization for predicting concrete compressive strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghourchian, S.; Wyrzykowski, M.; Plamondon, M.; Lura, P. On the mechanism of plastic shrinkage cracking in fresh cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 115, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghourchian, S.; Wyrzykowski, M.; Lura, P. A poromechanics model for plastic shrinkage of fresh cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 109, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghourchian, S.; Wyrzykowski, M.; Baquerizo, L.; Lura, P. Susceptibility of Portland cement and blended cement concretes to plastic shrinkage cracking. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 85, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, B.I.; Wong, H.W.; Ishida, T.; Nassif, A.Y. Thermal stress of high volume fly-ash (HVFA) concrete made with limestone aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sato, R.; Kawai, K. Autogenous shrinkage of high-strength concrete containing silica fume under drying at early ages. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.H.; Tang, J.H.; Hu, Z.L.; Yao, T.; Li, H.; Liu, J.P. Restraint effect of steel bar on early-age shrinkage of steel bar-mortar composites. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Fang, C.; Ali, M.S.M.; Visintin, P. Characterizations of autogenous and drying shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): An experimental study. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 91, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, D.P.; Garboczi, E.J.; Lu, Y.; Martys, N.; Sakulich, A.R.; Weiss, W.J. Modeling of the influence of transverse cracking on chloride penetration into concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 38, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaee, K.; Farzadnia, N.; Khayat, K.H. Coupled effect of expansive agent and curing on mechanical and shrinkage properties of fiber-reinforced Eco-Crete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.G.; Ha, S.; Weiss, W.J. Experimental and Numerical Quantification of Plastic Settlement in Fresh Cementitious Systems. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boghossian, E.; Wegner, L.D. Use of flax fibres to reduce plastic shrinkage cracking in concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, M.B.; Alexander, M.G.; Beushausen, H.D. Corrosion in cracked and uncracked concrete—Influence of crack width, concrete quality and crack reopening. Mag. Concr. Res. 2010, 62, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Mendes, J.; Nagaratnam, B.; Lim, M. A new four stage model of capillary pressure in early age concrete: Insights from high capacity tensiometers br. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 161, 106955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.K.; Hu, N.; Ben, S.J.; Zhao, H.T.; Chen, S.; Xiang, Y. Multiscale prediction model for autogenous shrinkage of early-age concrete incorporating high volume fly ash. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowik, V.; Hübner, T.; Schmidt, M.; Villmann, B. Simulation of capillary shrinkage cracking in cement-like materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowik, V.; Schmidt, M.; Fritzsch, R. Capillary pressure in fresh cement-based materials and identification of the air entry value. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongtanakitcharoen, T.; Naaman, A.E. Unrestrained early age shrinkage of concrete with polypropylene, PVA, and carbon fibers. Mater. Struct. 2007, 40, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, J.; Rozière, E.; Grondin, F.; Loukili, A. Influence of shrinkage-reducing admixtures on plastic and long-term shrinkage. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarter, W.J.; Curran, P.N. The electrical response characteristics of setting cement paste. Mag. Concr. Res. 1984, 36, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, W.P.S. Influence of mix and environment on plastic shrinkage cracking. Mag. Concr. Res. 2003, 55, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Ghods, P.; Isgor, O.B. Numerical Study on the Effect of Cracking on Surface Resistivity of Plain and Reinforced Concrete Elements. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayahi, F.; Emborg, M.; Hedlund, H.; Cwirzen, A. Effect of Admixtures on Mechanism of Plastic Shrinkage Cracking in Self-Consolidating Concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2020, 117, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; van Zyl, J.; Combrinck, R. The influence of temperature on the cracking of plastic concrete. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Concrete Repair, Rehabilitation and Retrofitting (ICCRRR 2022), Cape Town, South Africa, 3–5 October 2022; p. 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowik, V.; Schmidt, M.; Kässler, D.; Eiserbeck, M. Capillary Pressure Monitoring in Plastic Concrete for Controlling Early-Age Shrinkage Cracking. Transp. Res. Record. 2014, 2441, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ 52-2006; Standard for Technical Requirements and Test Method of Sand and Crushed Stone (or Gravel) for Ordinary Concrete. Ministry of Construction: Beijing, China, 2006.
- JGJ/T 10-2011; Technical Specification for Concrete Pumping Construction. Building & Construction Industry Standard: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Liu, L.Y.; Xu, J.X.; Yin, T.J.; Wang, Y.; Chu, H.Q. Improving electrical and piezoresistive properties of cement-based composites by combined addition of nano carbon black and nickel nanofiber. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50082-2009; The Test Method of Long-Term and Durability on Ordinary Concrete. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of PRC: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Ghourchian, S.; Wyrzykowski, M.; Lura, P. The bleeding test: A simple method for obtaining the permeability and bulk modulus of fresh concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 89, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.D.A.; Shehata, M.H.; Shashiprakash, S.G.; Hopkins, D.S.; Cail, K. Use of ternary cementitious systems containing silica fume and fly ash in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, C.A.; Fajardo, G.; Monroy, S.; Duran-Herrera, A.; Valdez, P.; Magniont, C. Comparative study between natural and PVA fibers to reduce plastic shrinkage cracking in cement-based composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Tian, Q.; Li, H.; Sun, S.W.; Deng, W.L. The relationship between capillary pressure and tensile strength of fresh cementitious materials under water evaporation. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 78, 107678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Slowik, V.; Schmidt, M.; Fritzsch, R. Early age concrete curing based on capillary pressure measurement. Beton-Und Stahlbetonbau 2007, 102, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, Z.Q.; Liu, B.; Zhao, F.; Tang, S.W.; Jin, M.M. Effects of Fly Ash Dosage on Shrinkage, Crack Resistance and Fractal Characteristics of Face Slab Concrete. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.J.; Shah, S.P.; Phuaksuk, P. Plastic shrinkage cracking in concrete materials—Influence of fly ash and fibers. ACI Mater. J. 2001, 98, 458–464. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, K.F.; Fen-Chong, T.; Dangla, P. Pore structure characterization of cement pastes blended with high-volume fly-ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Tam, C.T.; Leow, M.P. Effect of water-to-cementitious materials ratio and silica fume on the autogenous shrinkage of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayali, O.; Haque, M.N.; Zhu, B. Drying shrinkage of fibre-reinforced lightweight aggregate concrete containing fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhong, M.Q.; Bryan, M.; Yang, C.H.; Wang, C.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhang, Z.L. Investigation of effects of Portland cement fineness and alkali content on concrete plastic shrinkage cracking. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Alimi, W.O.; Adeoluwa Oladapo, E.; Imran, M.; Kazmi, Z.A. Behavior of drying and plastic shrinkage of Portland cement concrete prepared and cured under harsh field. Dev. Built. Environ. 2023, 16, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Baghabra Al-Amoudi, O.S.; Maslehuddin, M. Effect of placement temperature and curing method on plastic shrinkage of plain and pozzolanic cement concretes under hot weather. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, D.A.; Ramirez, A.D.; Rodríguez, C.R.; Petroche, D.M.; Boero, A.J.; Duque-Rivera, J. Environmental impacts, life cycle assessment and potential improvement measures for cement production: A literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, R.; Choudhary, K.; Srivastava, A.; Sangwan, K.S.; Singh, M. Environmental impact assessment of fly ash and silica fume based geopolymer concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippiatt, N.; Ling, T.-C.; Pan, S.-Y. Towards carbon-neutral construction materials: Carbonation of cement-based materials and the future perspective. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 28, 101062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sieve Aperture (mm) | Sieve Residue (g) | Separate Sieve (%) | Cumulative Sieve (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.75 | 11 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| 2.36 | 31 | 6.3 | 8.5 |
| 1.18 | 56 | 11.2 | 19.7 |
| 0.6 | 146 | 29.3 | 49.0 |
| 0.3 | 214 | 43.0 | 92 |
| 0.15 | 26 | 5.2 | 97.2 |
| Sieve Aperture (mm) | Sieve Residue (g) | Separate SIEVE (%) | Cumulative Sieve (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.5 | 775 | 22.4 | 22.4 |
| 4.75 | 2516 | 72.9 | 95.3 |
| 2.36 | 151 | 4.4 | 99.7 |
| Series | No. | FA (%) | W/B | Unit Mass (kg/m3) | fc (MPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | FA | Water | Sand | Gravel | SP | |||||
| A | A0 | 0 | 0.4 | 450 | 0 | 180 | 654 | 1113 | 0.675 | 70.8 |
| A3 | 30 | 310 | 133 | 177 | 634 | 1096 | 0.576 | 51.2 | ||
| A6 | 60 | 174 | 262 | 174 | 634 | 1078 | 0.828 | 26.6 | ||
| B | B0 | 0 | 0.5 | 360 | 0 | 180 | 698 | 1139 | 0.684 | 58.5 |
| B3 | 30 | 249 | 107 | 178 | 689 | 1125 | 0.640 | 35.7 | ||
| B6 | 60 | 140 | 211 | 175 | 681 | 1110 | 0.684 | 17.4 | ||
| C | C0 | 0 | 0.6 | 300 | 0 | 180 | 736 | 1152 | 0.600 | 41.9 |
| C3 | 30 | 208 | 89 | 1178 | 728 | 1140 | 0.564 | 25.9 | ||
| C6 | 60 | 1117 | 176 | 176 | 721 | 1128 | 0.573 | 12.8 | ||
| Material | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 22.6 | 5.04 | 3.33 | 61.57 | 2.65 | 2.31 | 2.50 |
| Fly ash | 42.77 | 30.28 | 6.08 | 14.00 | 2.26 | 0.81 | 3.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Cai, Q. Study on Early-Age Capillary Pressure and Plastic Shrinkage Properties of High-Volume Fly Ash Concrete. Materials 2025, 18, 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081884
Liu J, Yu X, Wang S, Yang J, Cai Q. Study on Early-Age Capillary Pressure and Plastic Shrinkage Properties of High-Volume Fly Ash Concrete. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081884
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jintao, Xinyang Yu, Shaojiang Wang, Jie Yang, and Qianni Cai. 2025. "Study on Early-Age Capillary Pressure and Plastic Shrinkage Properties of High-Volume Fly Ash Concrete" Materials 18, no. 8: 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081884
APA StyleLiu, J., Yu, X., Wang, S., Yang, J., & Cai, Q. (2025). Study on Early-Age Capillary Pressure and Plastic Shrinkage Properties of High-Volume Fly Ash Concrete. Materials, 18(8), 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081884




