Effect of Film-Cooling-Hole Inclination on the Creep Performance of IN-738 Specimens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
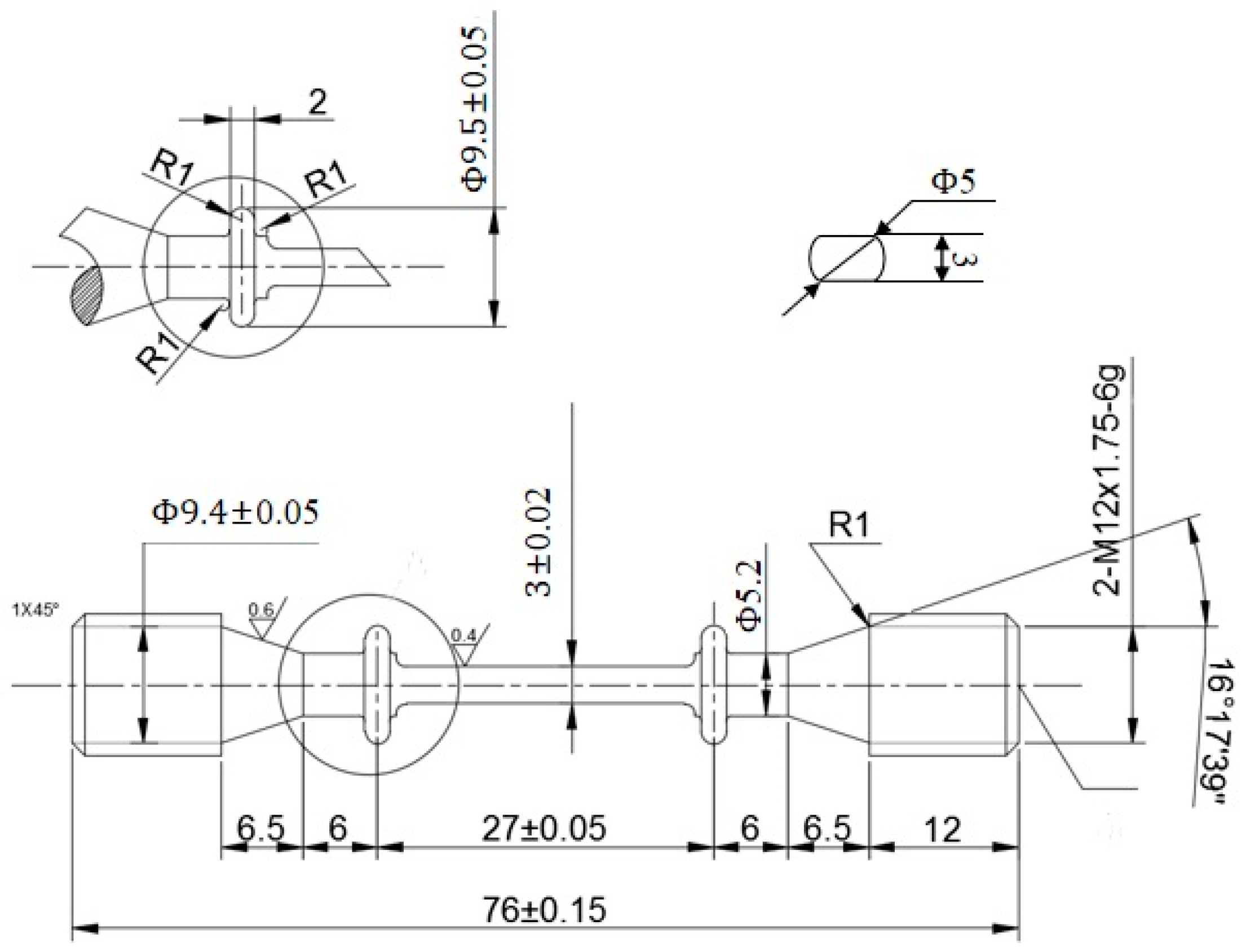
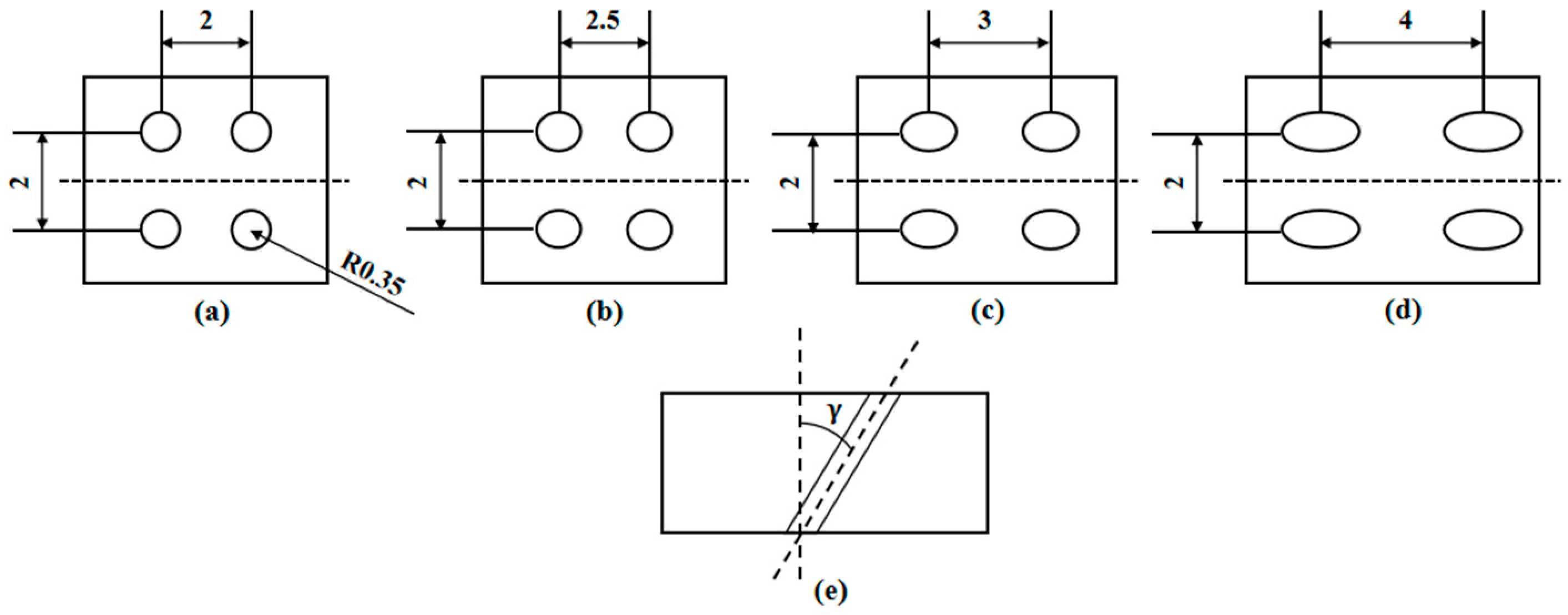
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Experimental Method
3. Results
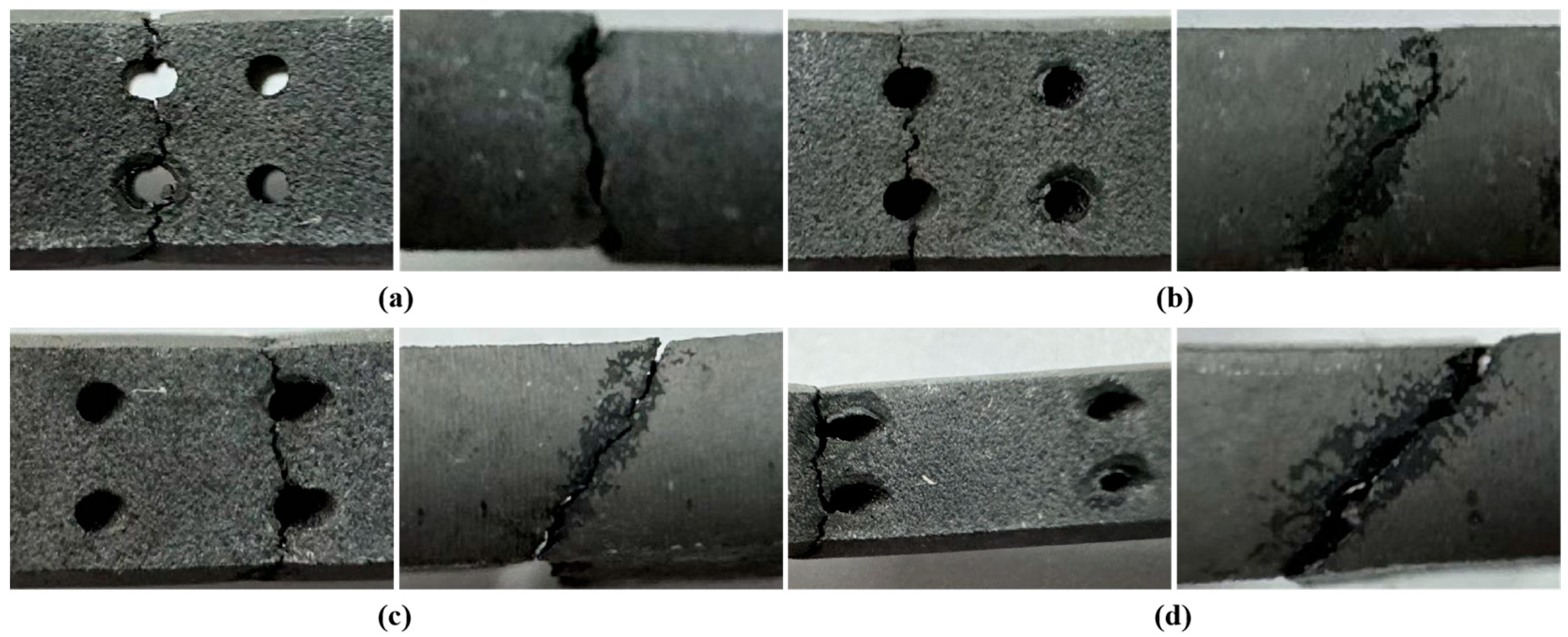
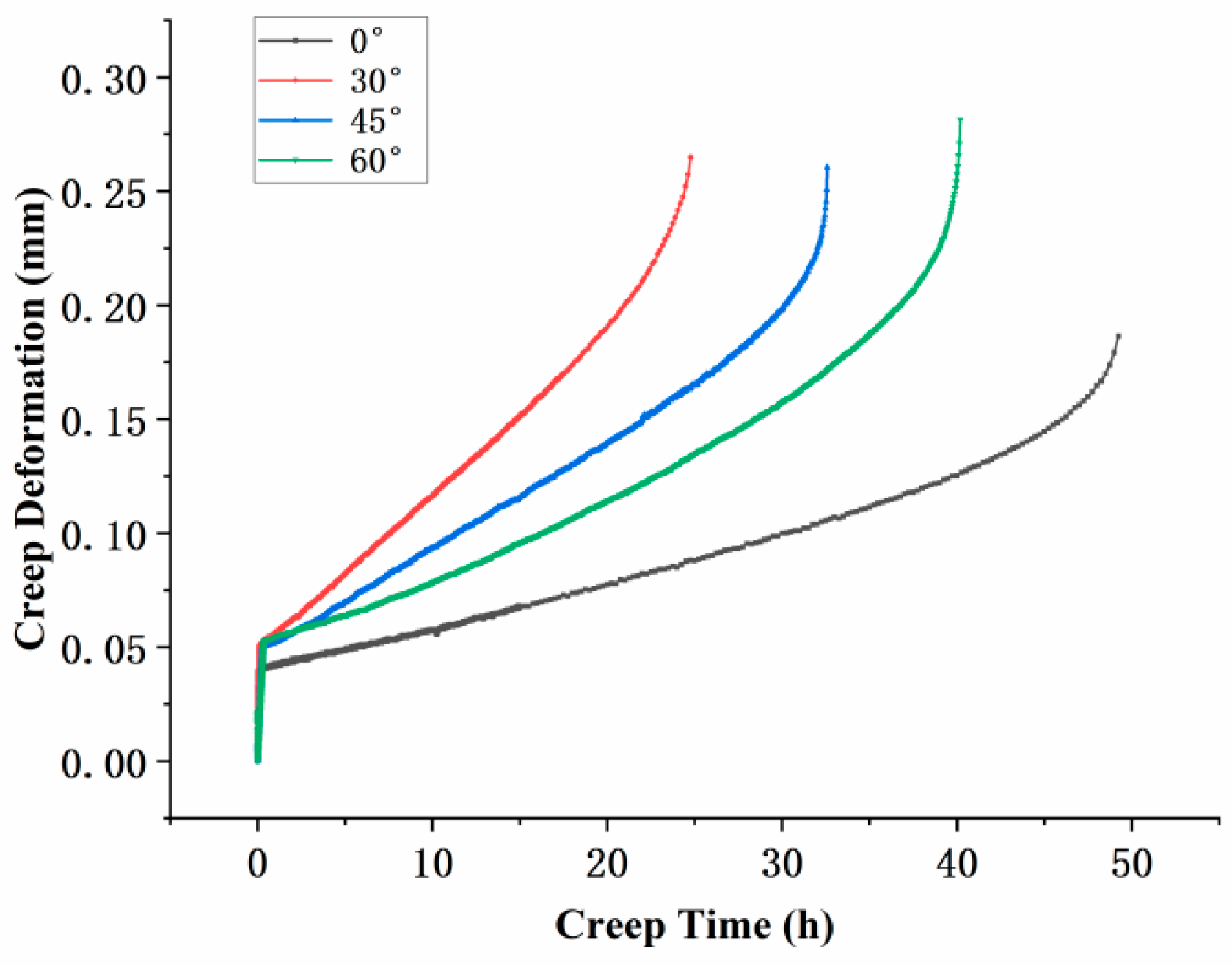
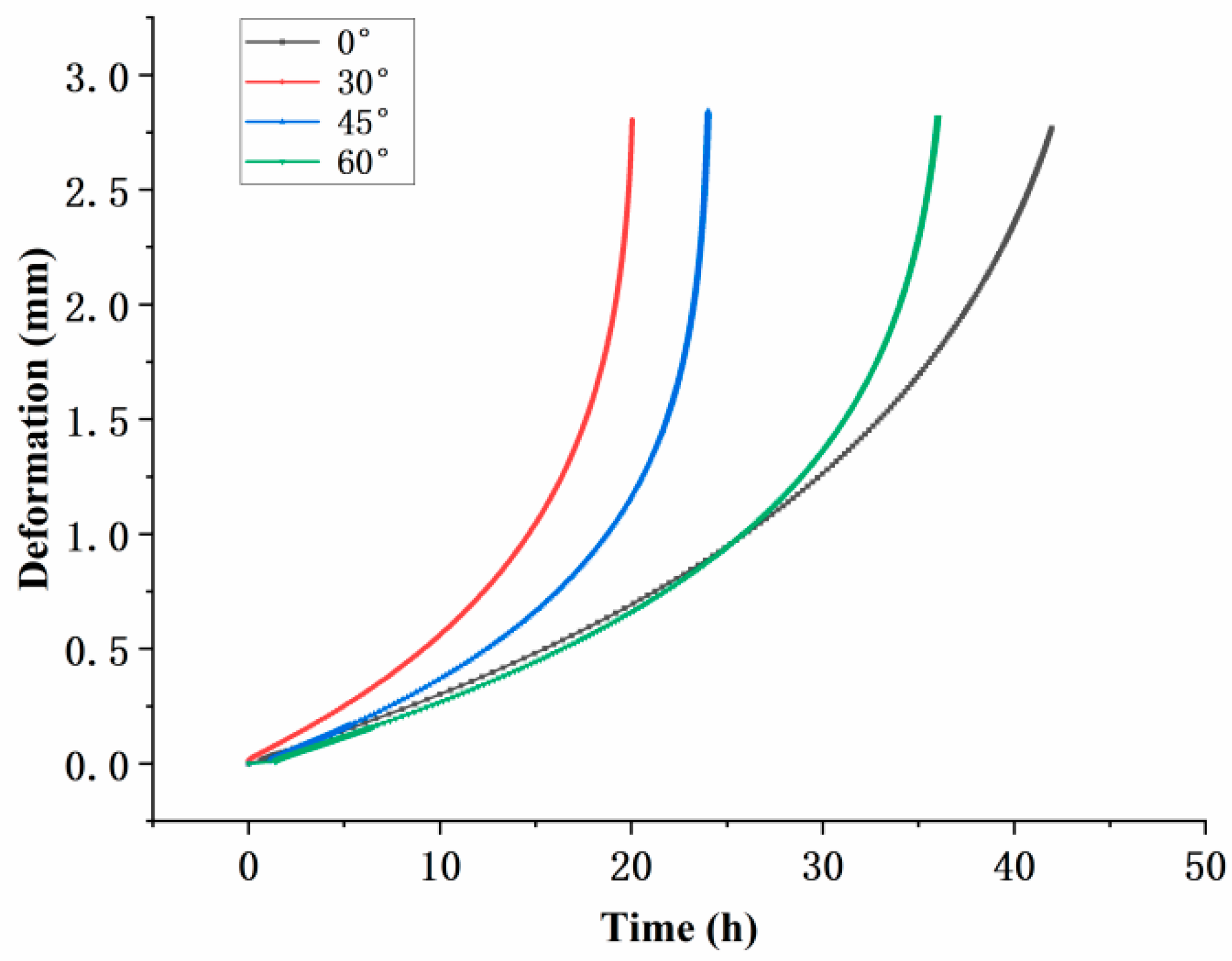
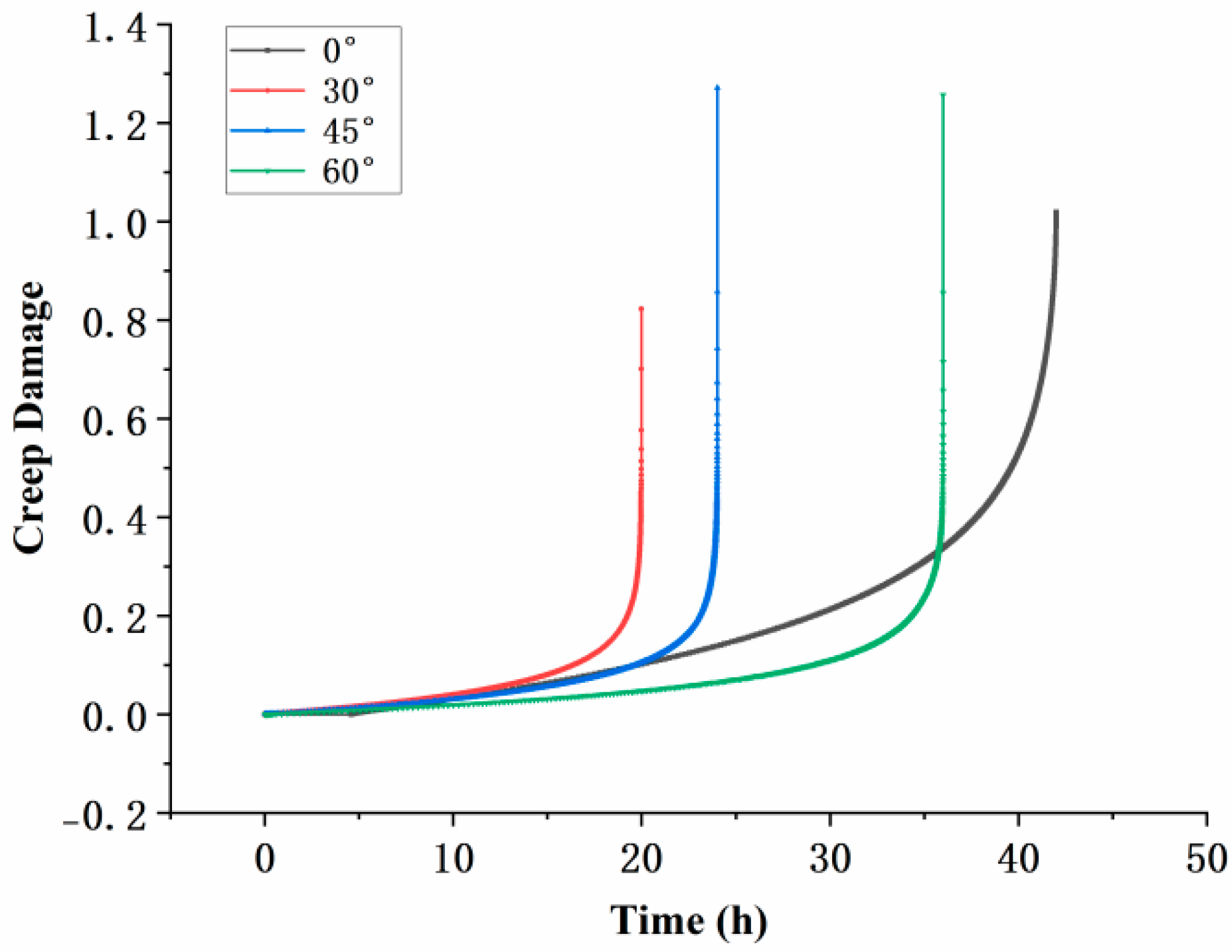
3.1. Creep Life and Deformation
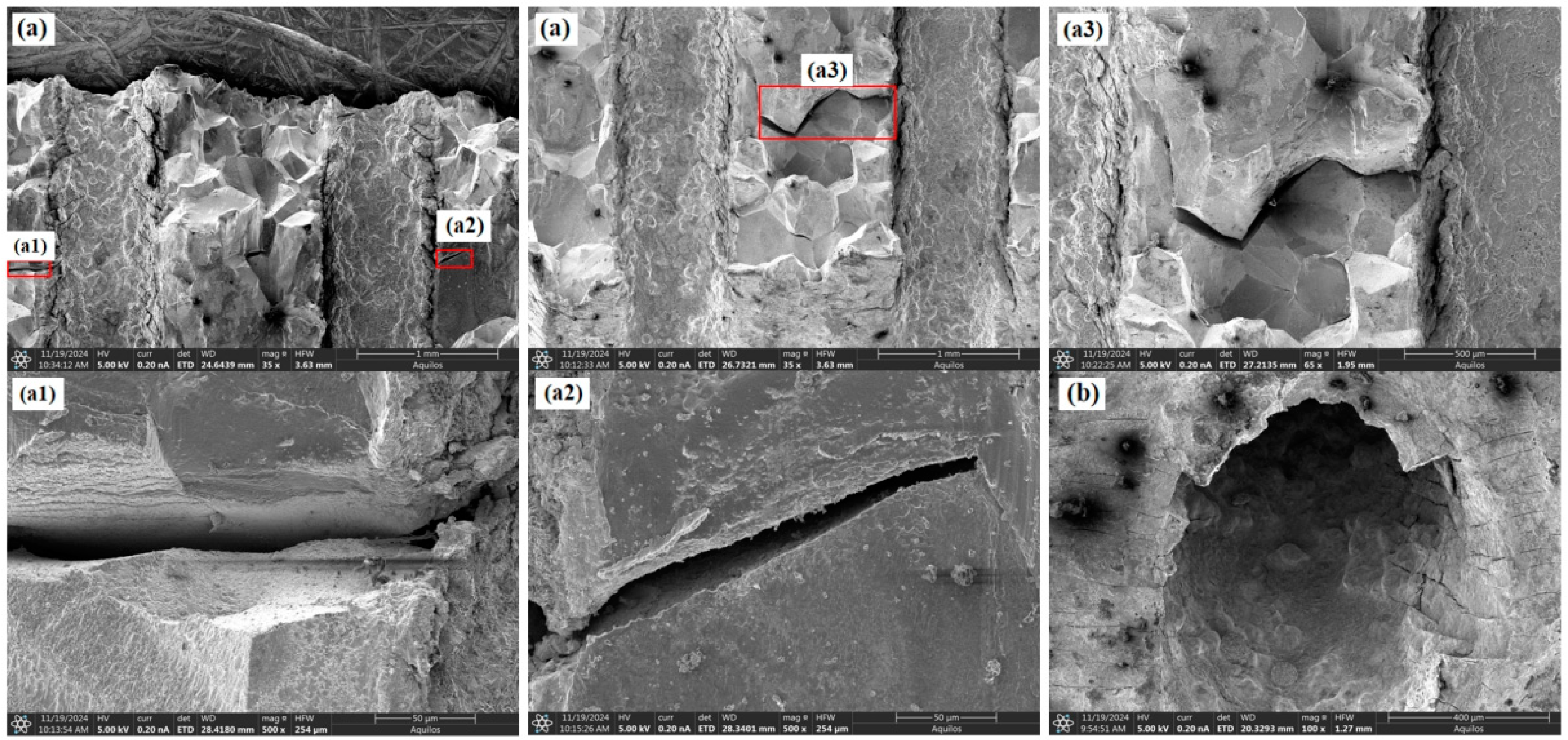
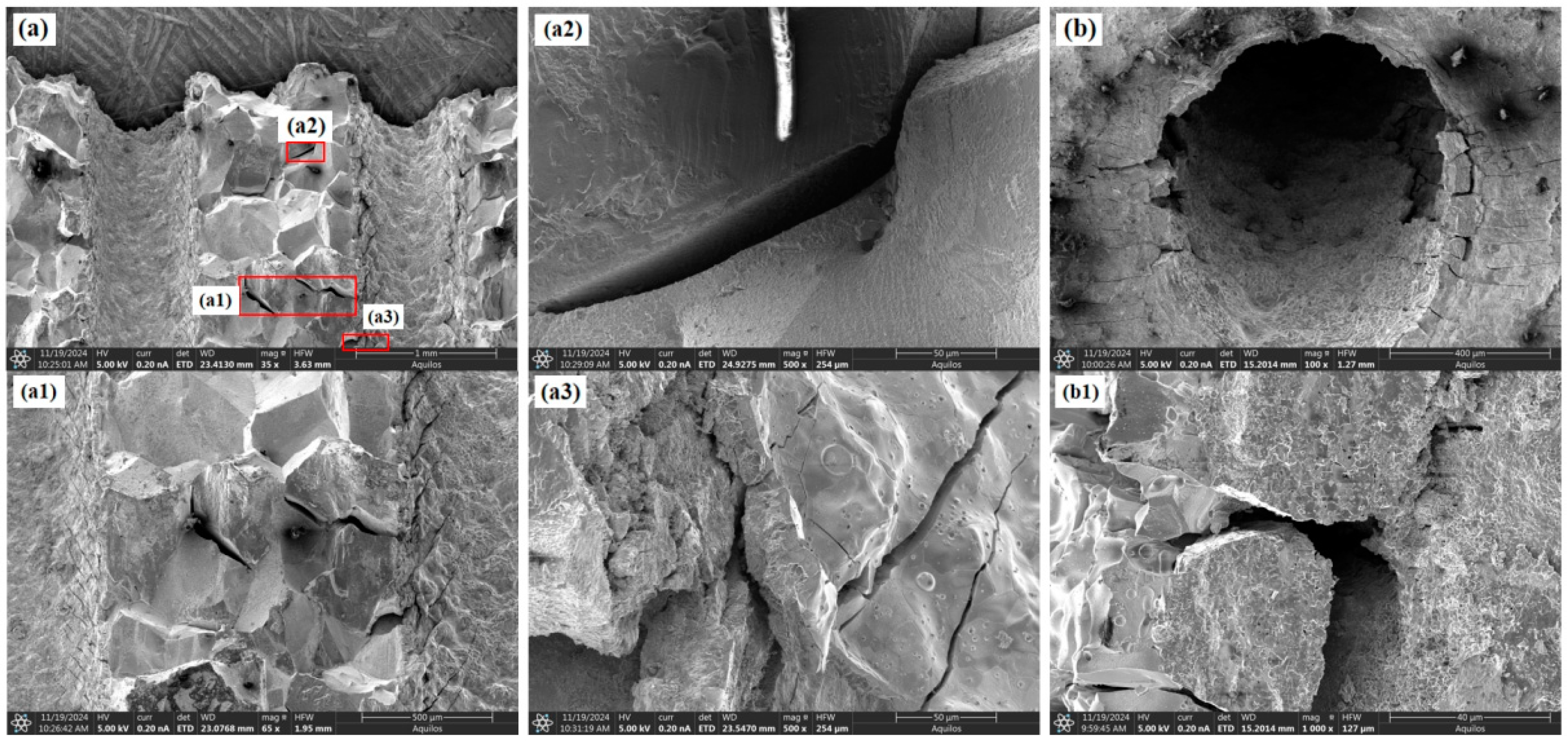
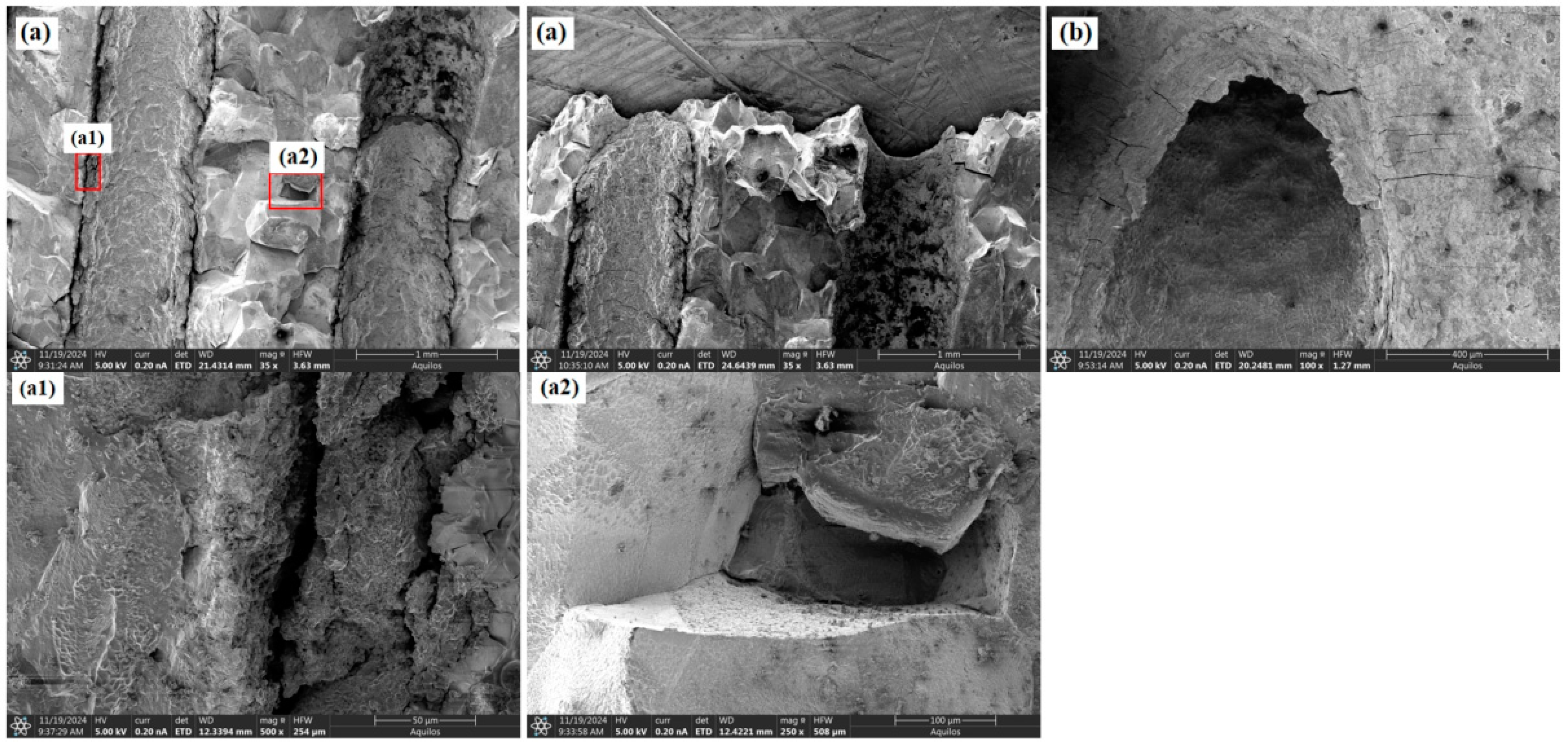
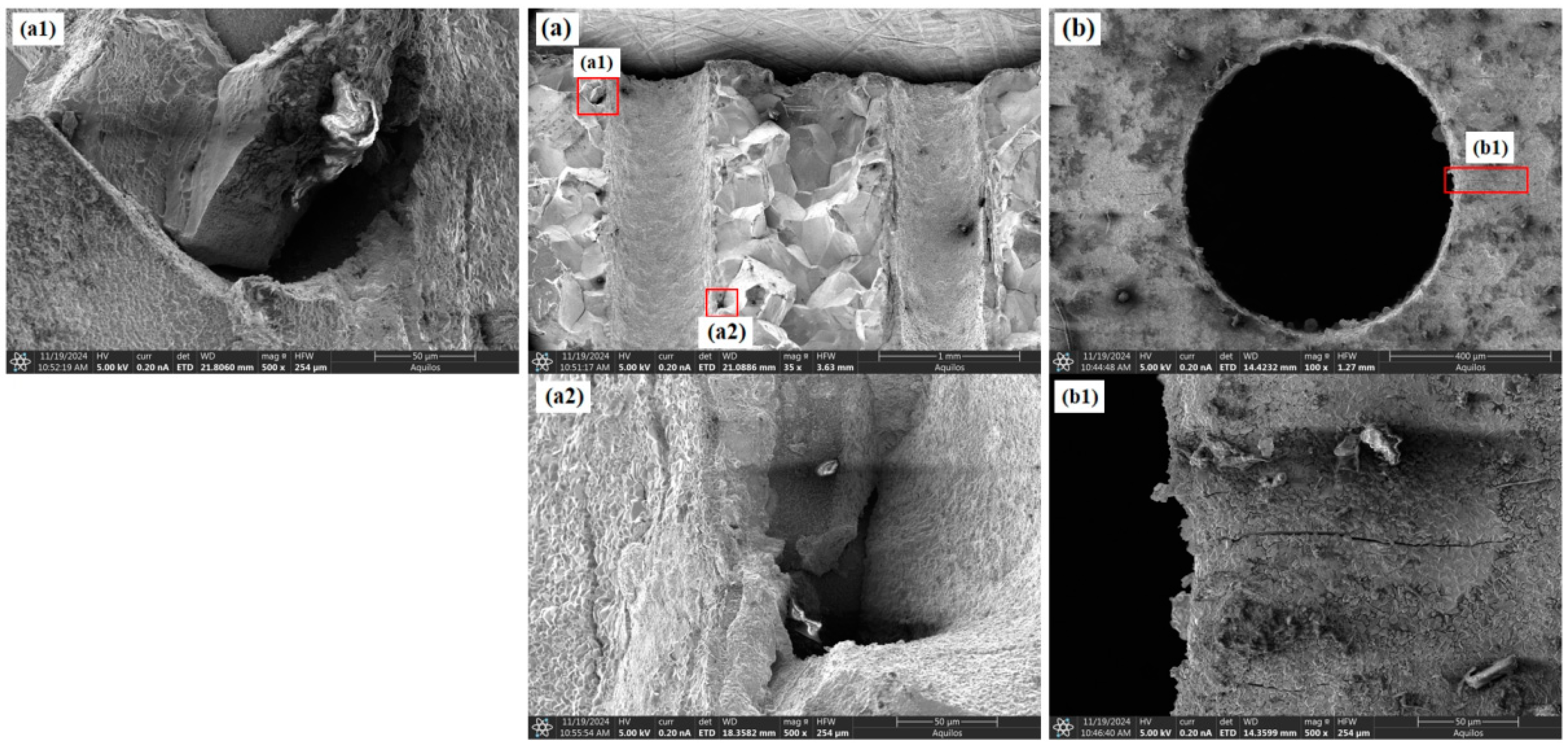
3.2. Fracture Morphology Analysis

4. Numerical Analysis
4.1. Creep Damage Constitutive Model
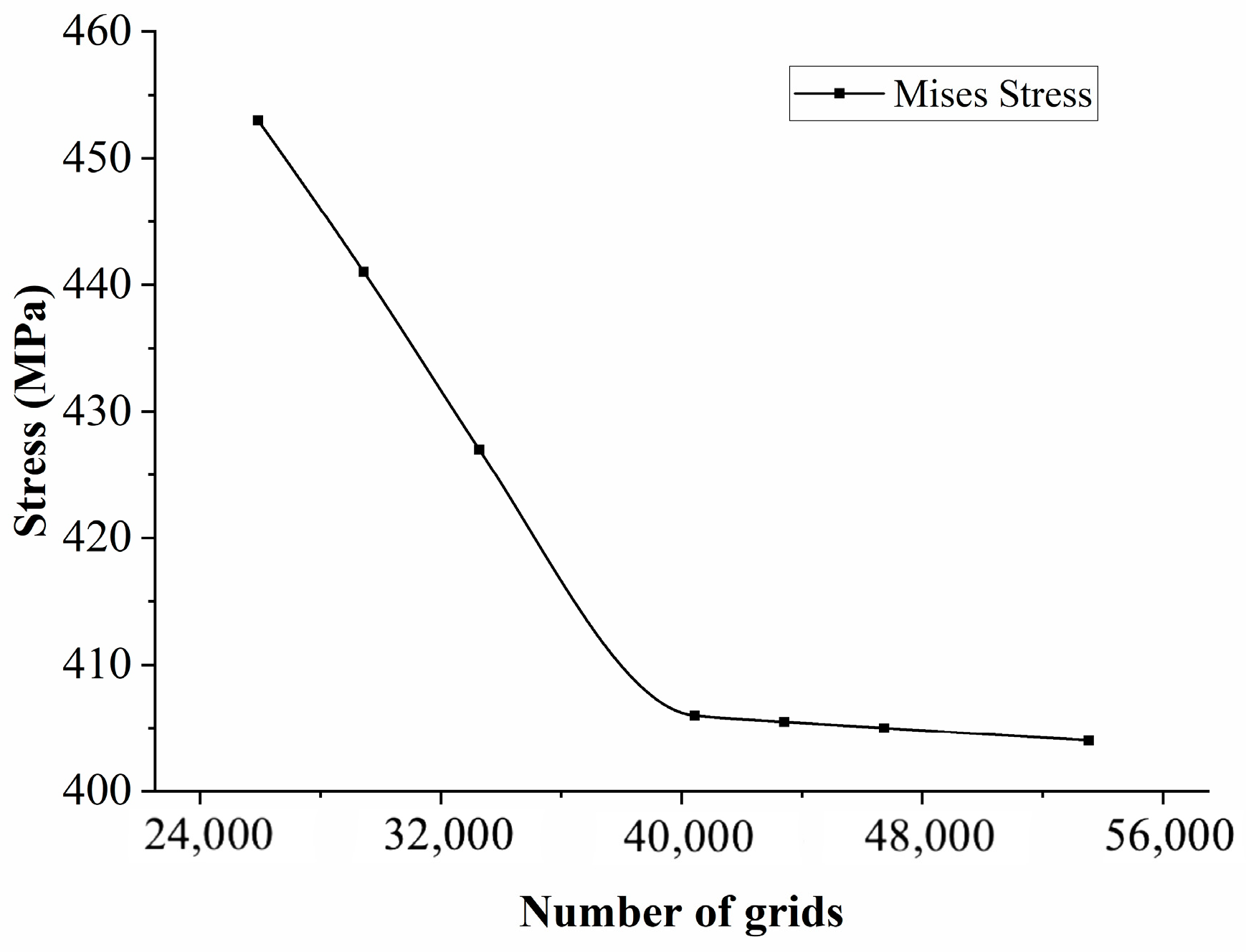
4.2. Finite Element Simulation
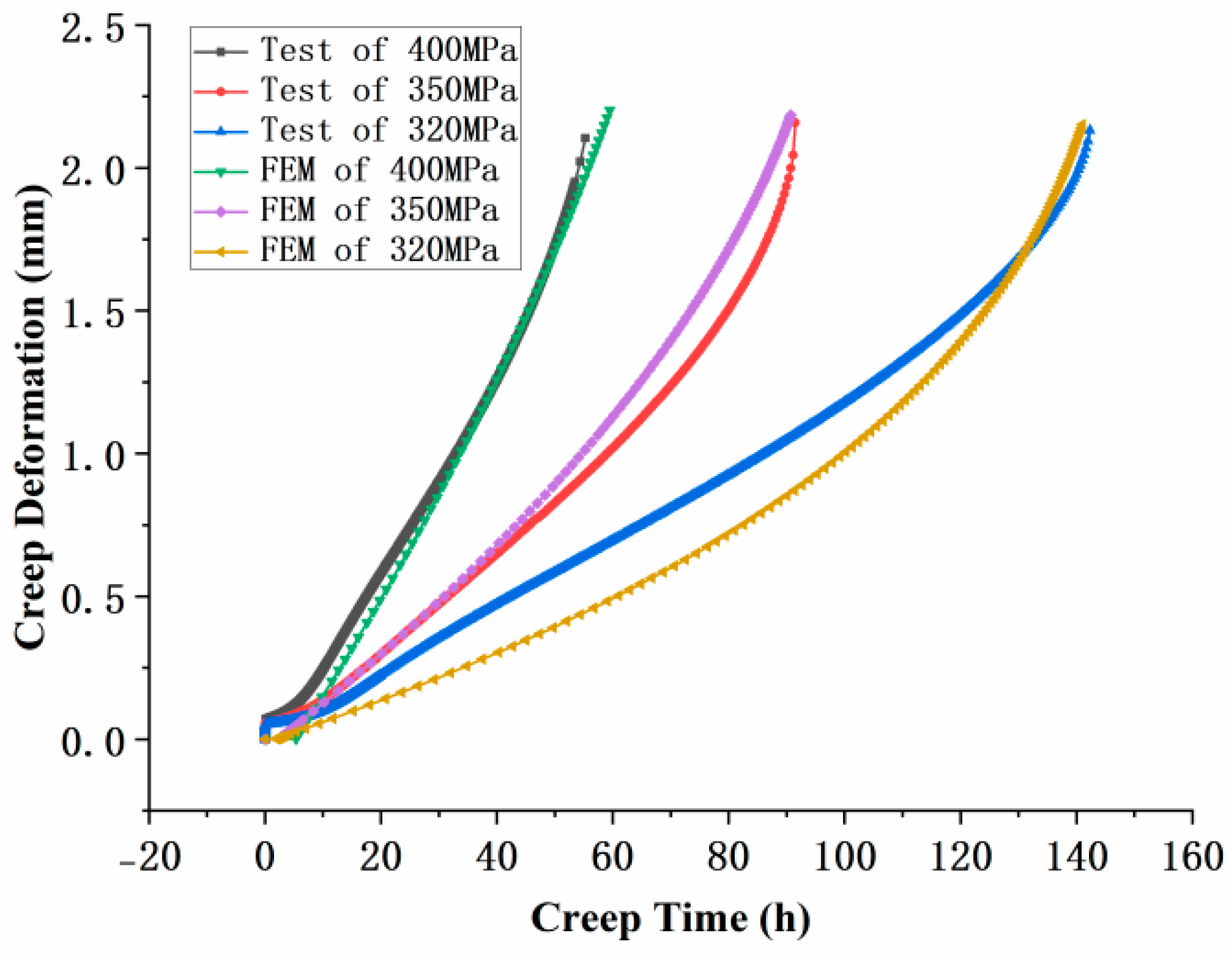
4.3. Results Analysis
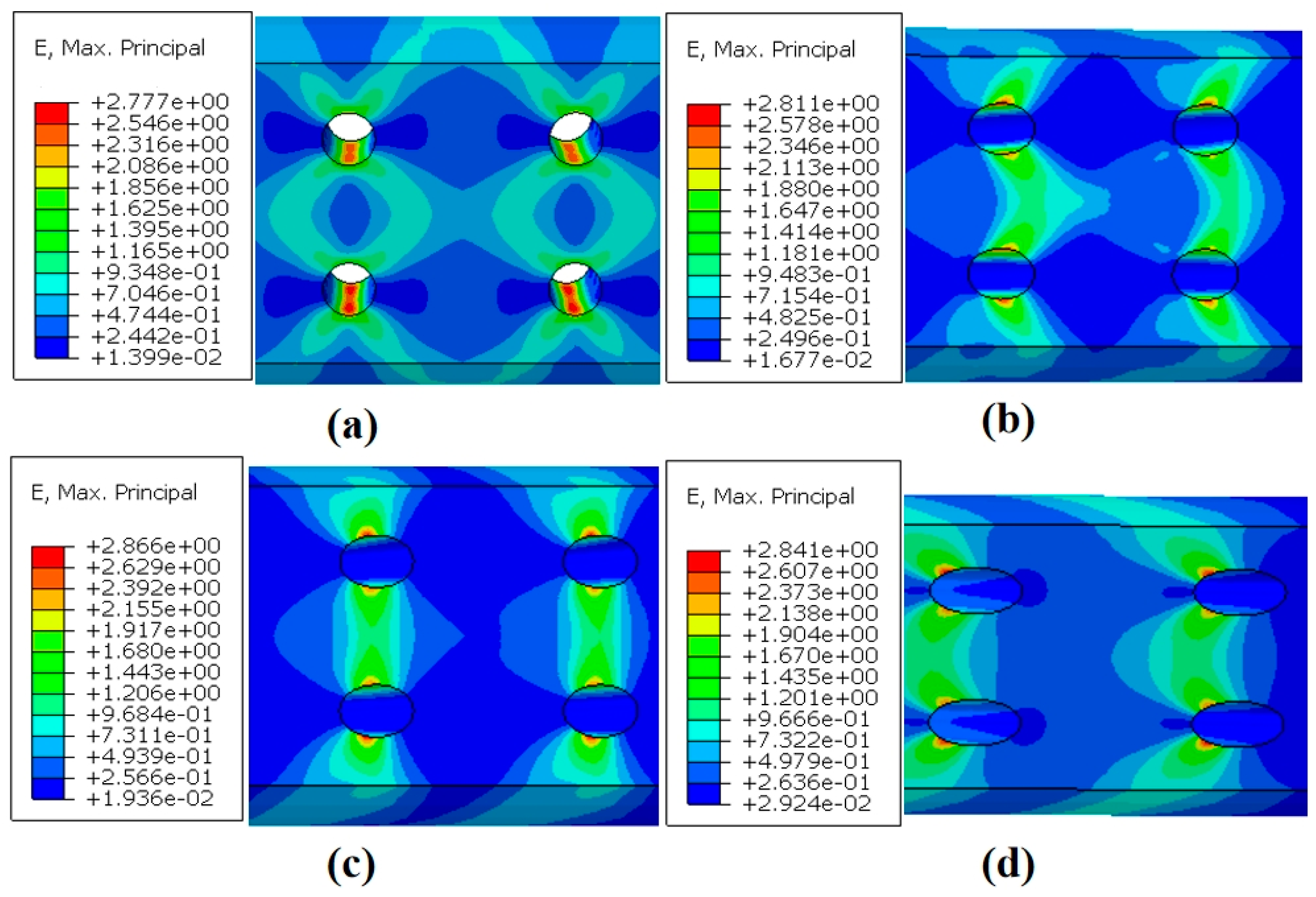
4.3.1. Strain Analysis
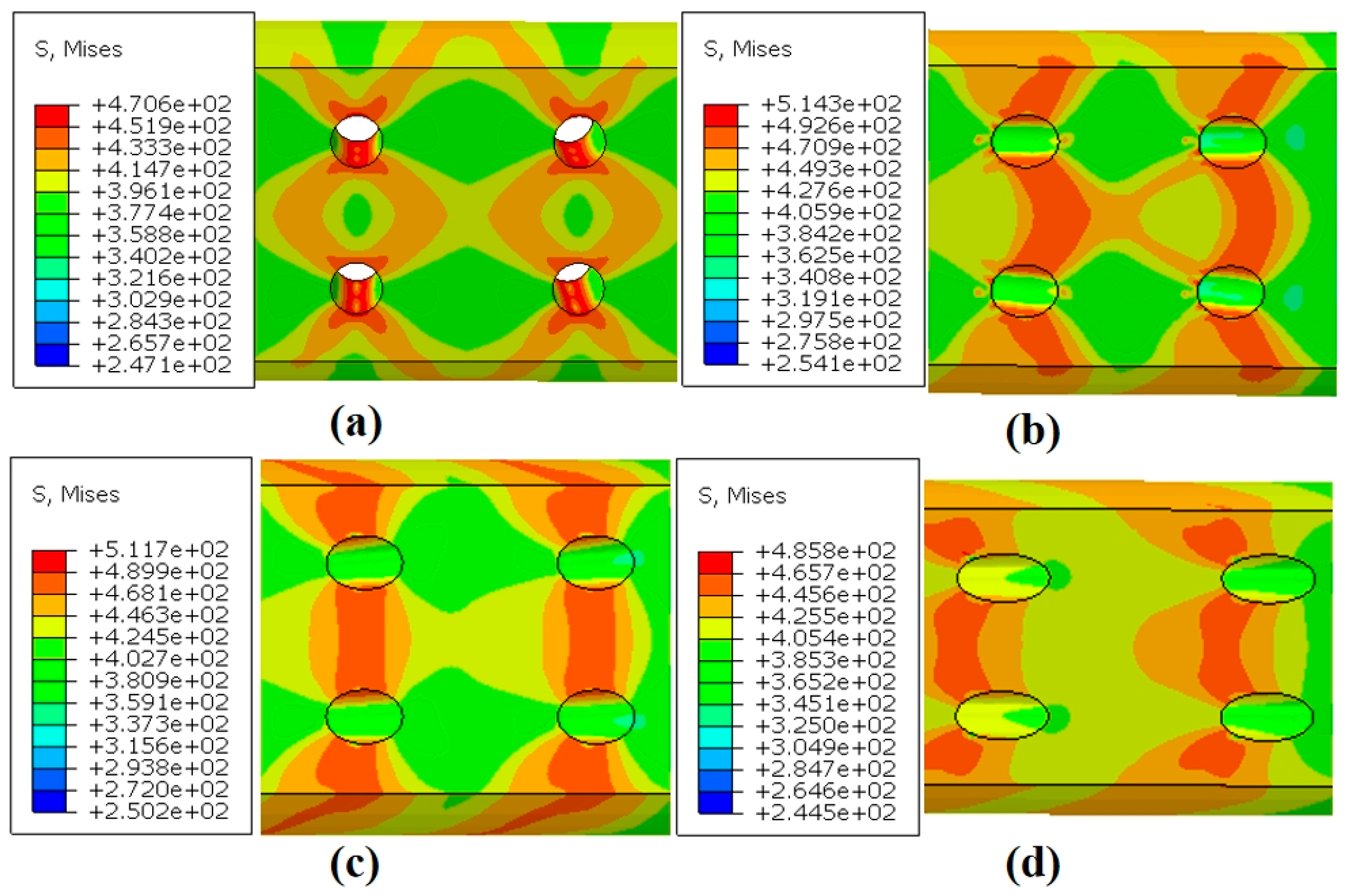
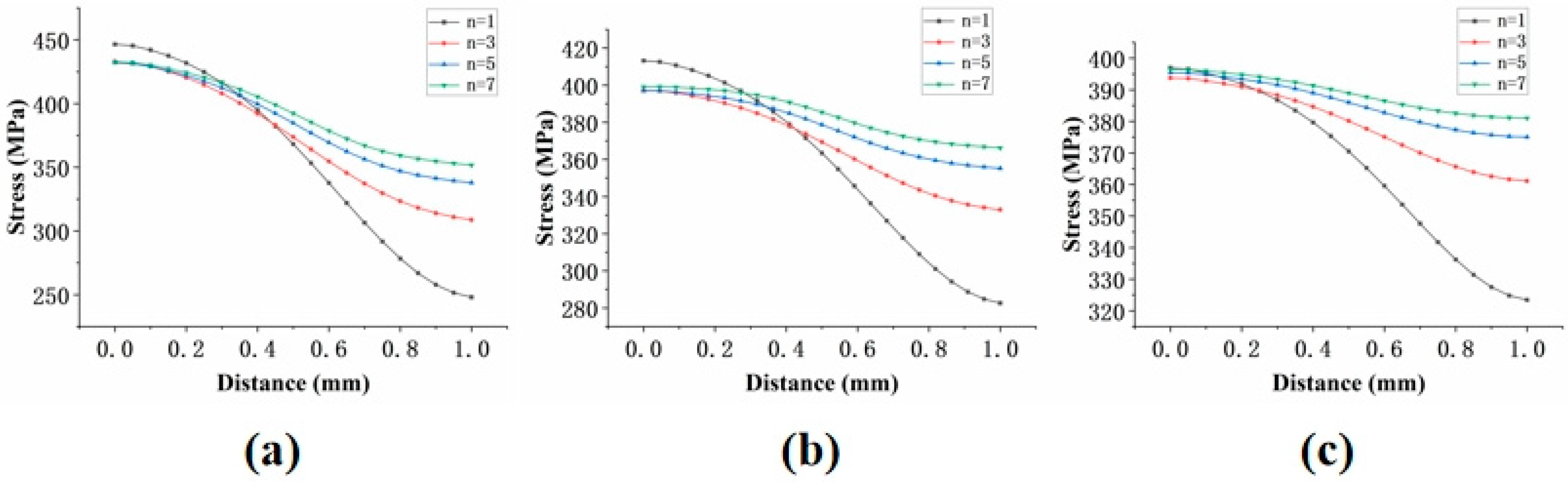
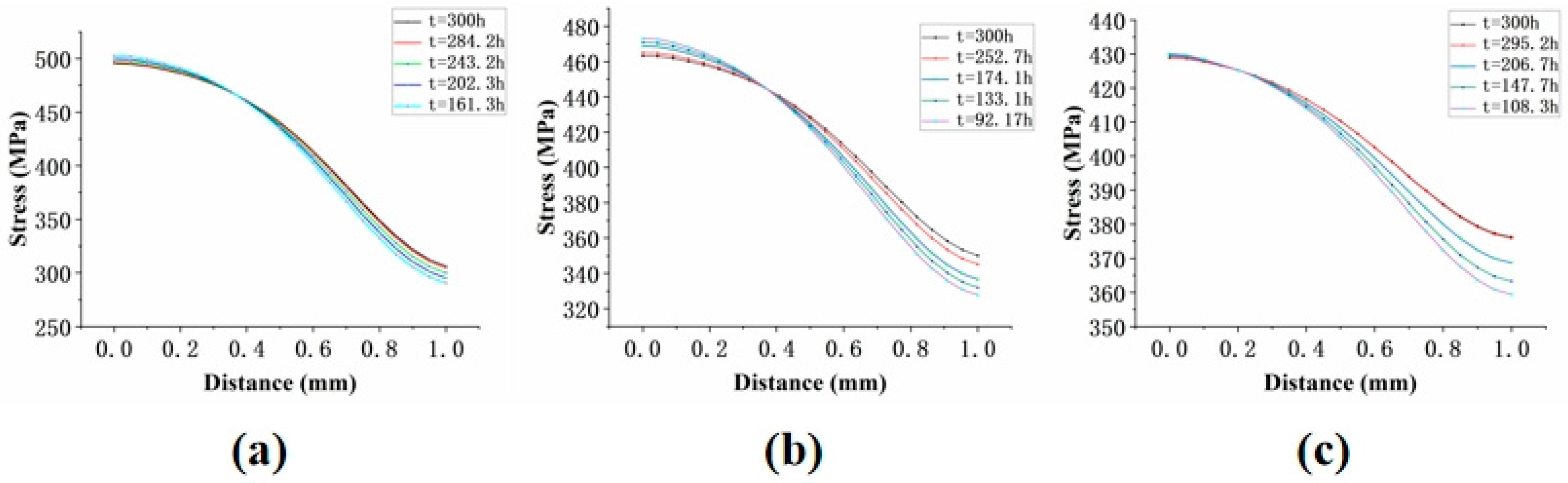
4.3.2. Stress Analysis
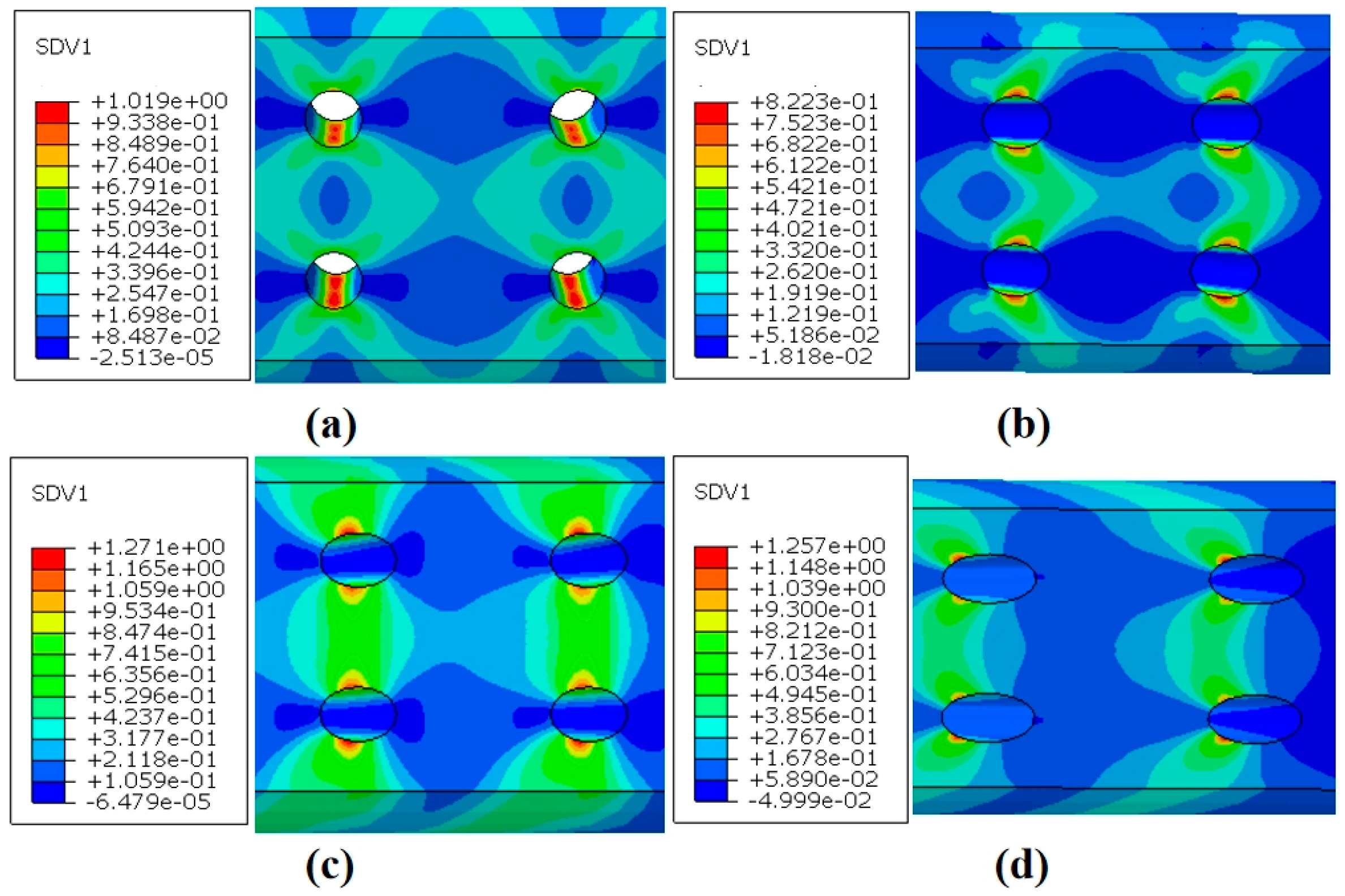
4.3.3. Creep Damage Analysis
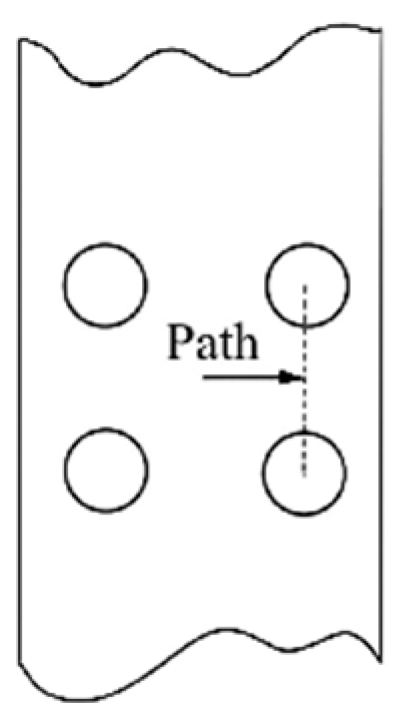
4.3.4. Simulation Path Analysis
5. Discussion
- Obtain material parameters through uniaxial creep tests.
- Use finite element simulations to determine the node location and obtain the stress value at the node.
- Calculate the creep life using the Formula (5) and compare the results with experimental data for validation.
6. Conclusions
- Under identical testing conditions, the inclination angle of film-cooling holes has a significant impact on the creep performance of the specimens. The creep life decreases in the order of 0° > 60° > 45° > 30°. SEM observations of the fracture surfaces revealed that the creep fracture in specimens with film-cooling holes is primarily caused by stress concentration at the hole edges, with cracks typically initiating at these locations. The creep fracture mode is a dimple-type failure, which occurs in regions of stress concentration around the film-cooling holes.
- Numerical analyses of specimens with different inclination angles showed that the presence of film-cooling holes disrupts the geometric continuity of the specimens, leading to localized concentrations of strain, stress, and damage around the holes. The simulated fracture paths were highly consistent with the actual crack paths observed in the specimens.
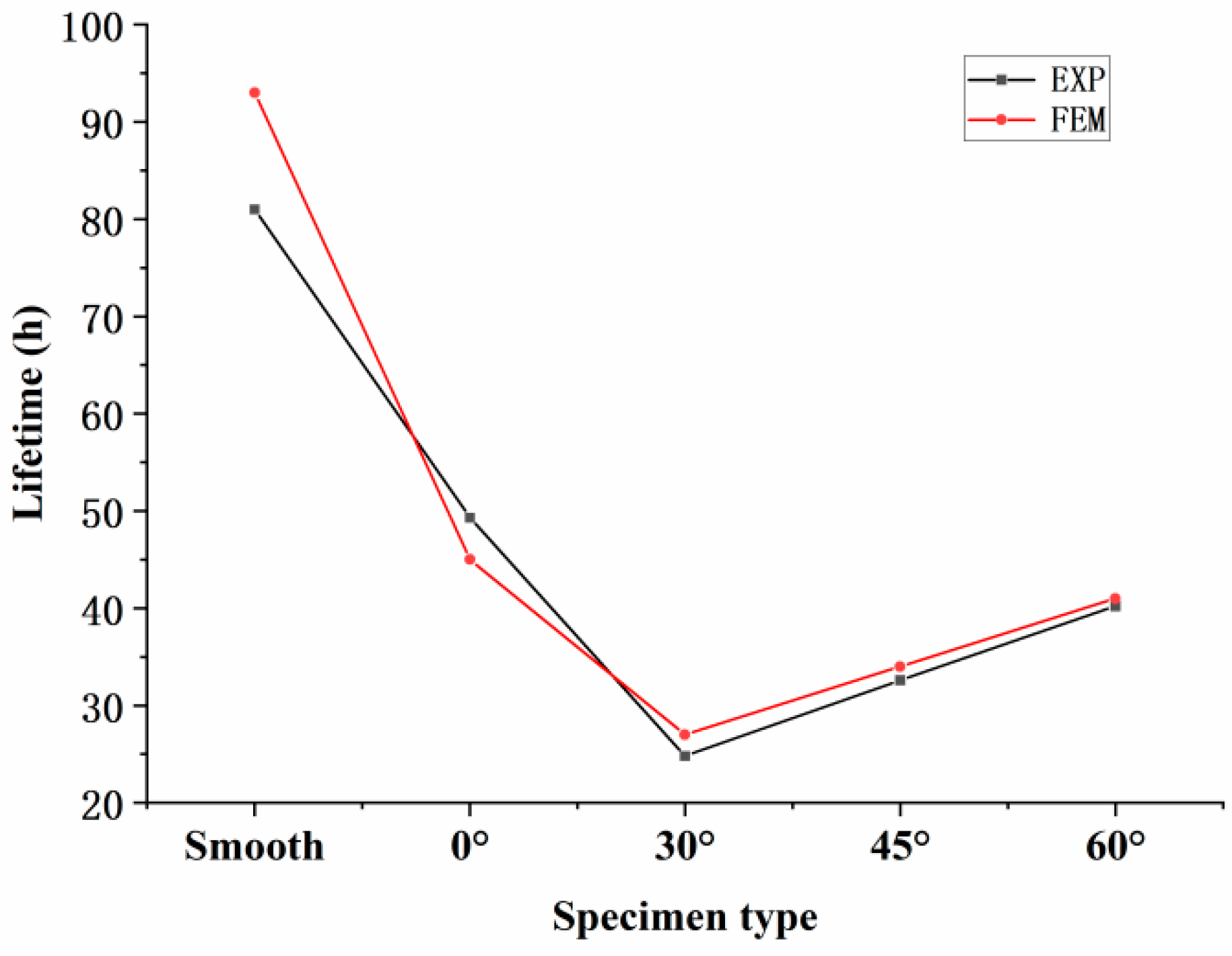
- The node stress method was used to predict the creep rupture life of specimens with different film-cooling-hole inclination angles. The predicted results agreed well with the experimental data, demonstrating that the node stress method provides high accuracy for creep life prediction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, H.D.; Ren, J.; Li, X.Y.; Tan, Q. Status and Development Trend of the Heavy Duty Gas Turbine. Proc. CSEE 2014, 34, 5096–5102. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.Z. Review and Prospect of Developments of Cast Superalloys and Technology of Aeroengine Turbine Blade. Aeronaut. Manuf. Technol. 2002, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Tao, C.H.; Kong, Z.Q. Damage Behavior of Film Holes of DD6 Single Crystal Superalloy by Electro-Stream Machining. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2019, 48, 3190–3194. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.L.; Tao, C.H.; Liu, C.J.; Hu, C.Y.; Chen, X. Investigation of Processing Methods and Development of Gas Holes of Engine Blade. Mater. Rep. 2013, 27, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.F.; Xu, Y.M.; Liu, X.L.; Sun, R.J. Anisotropic creep behavior of Ni-based single crystal superalloy with film cooling hole drilled by a femtosecond laser along different crystal orientations. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 163, 109258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.N.; Gao, H.S.; Wen, Z.X.; Pei, H.Q.; Li, Z.W.; Zhao, Y.C.; Yue, Z.F. Creep characteristics of directionally solidified turbine blades based on the difference in original casting characteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 884, 161055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.M.; Yue, Z.F.; Wen, Z. Creep damage evolution in a modeling specimen of nickel-based single crystal superalloys air-cooled blades. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 477, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Gao, H.S.; Wen, Z.X.; Liu, D.S.; Yue, Z.F. Creep Behavior of Thin-Walled Plate with Cooling Holes of Nickel-Based Single Crystal Superalloy DD6 Under High Temperature. J. Aerosp. Power 2014, 29, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.X.; He, J.Y.; Wen, Z.X.; Liang, J.W. Effects of Slant Angle of Film Hole on Fatigue Properties of Single Crystal Superalloy. J. Propuls. Technol. 2021, 42, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.X.; He, J.Y.; Liang, J.W. Creep rupture mechanism and microstructure evolution around film-cooling holes in nickel-based single crystal superalloy specimen. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 235, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; He, J.Y.; Liang, J.W. Anisotropic creep fracture mechanism and microstructural evolution in nickel-based single crystal specimen with a center film hole. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2020, 108, 102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Lv, M.H.; Wen, Z.X. A unified creep life prediction method and fracture mechanism of high-temperature alloys under multiaxial stress. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 149, 107262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Wang, D.F.; Li, L. Effect of film cooling hole shape on creep properties of CMSX-10 plate specimens. J. Aerosp. Power 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.C.; Jiang, R.; Gong, H.X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.P.; Zha, H.Y.; Song, Y.D. Effect of film cooling holes on creep properties of nickel-based single crystal superalloy. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2024, 45, 301–317. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.K.; Xu, Y.M.; Hu, C.Y.; Liu, X.L. Effect of film-hole configuration on creep rupture behavior of a second generation nickel-based single crystal superalloys. Mater. Charact. 2017, 130, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.W.; Wen, Z.X.; Yue, Z.F. Numerical Simulation on the Creep Damage Evolution of Nickel-Based Single Crystal Specimens with Slant-Angled Film Cooling Holes. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2015, 44, 2656–2660. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, G.A.; Nikbin, K.M.; Biglari, F. Finite element analysis of notched bar skeletal point stresses and dimension changes due to creep. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2004, 27, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Liu, Y. Prediction of Multi-Axial Creep Life for P92 Steel Notched Bars Using the Time-Hardening Model and Skeletal Point Stress Method. J. Mech. Strength 2019, 41, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.X.; Liang, J.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Pei, H.Q.; Wen, S.F.; Yue, Z.F. Prediction method for creep life of thin-wall specimen with film cooling holes in Ni-based single-crystal superalloy. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 141, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.X.; Pei, H.Q.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.W.; Yue, Z.F. A combined CP theory and TCD for predicting fatigue lifetime in single-crystal superalloy plates with film cooling holes. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 111, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Wen, Z.X.; Pei, H.Q.; Yue, Z.F. Equivalent model of close-packed film cooling holes in nickel-based single crystal cooled blade based on crystallographic theory. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.X.; Huang, S.; Gao, H.S.; Yue, Z.F. Experimental investigation on low cycle fatigue properties of GH3536 alloy with film cooling holes in different drilling processes. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 82, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, M.; Ajabshir, S.Z.; Sofia, D.; Barletta, D.; Poletto, M. Experimental Metrics of the Powder Layer Quality in the Selective Laser Sintering Process. Powder Technol. 2023, 419, 118346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H.; Shang, D.G.; Yin, X.; Li, M.; Chen, F.; Sun, G.Q.; Sun, W. A novel fatigue-oxidation-creep life prediction method under non-proportional loading. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 131, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Wen, Z.; Pei, H.; Gao, H. Creep properties of a U-type notch plate in Ni-based superalloy. Mater. Und Werkst. 2019, 50, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Laha, K.; Mathew, M.D. Creep Life Prediction of Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel under Multiaxial State of Stress. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Structural Integrity (ICONS), Kalpakkam, India, 4–7 February 2014; Indira Gandhi Ctr Atom Res: Kalpakkam, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.X.; Wang, J.P.; Wen, Z.X.; Liu, D.S.; Yue, Z.F. V-Notched Bar Creep Life Prediction: GH3536 Ni-Based Superalloy Under Multiaxial Stress State. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Element | wt (%) | Element | wt (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0.16 | Al | 3.3 |
| Si | 0.22 | Fe | 0.3 |
| Mn | 0.15 | Mo | 1.7 |
| W | 2.45 | Ti | 3.4 |
| S | 0.005 | Zr | 0.07 |
| Cr | 15.93 | Ta | 1.6 |
| Ni | Balance | Nb | 0.8 |
| Co | 8.3 | B | 0.008 |
| A | B | n | k | φ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.72 | 4.28 | 20.61 |
| Specimen | Node Stress | Test Life | Predicted Life | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth | 350 MPa | 81 h | 93 h | 14.8% |
| 0° | 415 MPa | 49.3 h | 45 h | 8.7% |
| 30° | 466 MPa | 24.8 h | 27 h | 8.9% |
| 45° | 444 MPa | 32.6 h | 34 h | 4.3% |
| 60° | 425 MPa | 40.2 h | 41 h | 2.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, J.; Li, H.; Chu, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, K. Effect of Film-Cooling-Hole Inclination on the Creep Performance of IN-738 Specimens. Materials 2025, 18, 1737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081737
Yang H, Zhang Q, Lv J, Li H, Chu T, Chen S, Wang K. Effect of Film-Cooling-Hole Inclination on the Creep Performance of IN-738 Specimens. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081737
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hao, Qin Zhang, Jinke Lv, Han Li, Tiange Chu, Shaoyang Chen, and Ke Wang. 2025. "Effect of Film-Cooling-Hole Inclination on the Creep Performance of IN-738 Specimens" Materials 18, no. 8: 1737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081737
APA StyleYang, H., Zhang, Q., Lv, J., Li, H., Chu, T., Chen, S., & Wang, K. (2025). Effect of Film-Cooling-Hole Inclination on the Creep Performance of IN-738 Specimens. Materials, 18(8), 1737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081737






