Controllable Fabrication of ZnO Nanorod Arrays on the Surface of Titanium Material and Their Antibacterial and Anti-Adhesion Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of ZnO Seed Layer on Ti Substrate
2.3. Preparation of Ti@ZnO Composite Material
2.4. Preparation of Bacterial Anti-Adhesive Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl Composite Surface
2.5. Preparation of Superhydrophobic-Type Antibacterial and Bacterial Anti-Adhesive Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS Composite Surface
2.6. Characterization and Measurements
2.7. Antibacterial Activity Assessment
2.8. Bacterial Anti-Adhesive Assessment
2.9. The Morphology of Bacteria Adhering on the Composite Surface
2.10. Live/Dead Bacterial Viability Assay for Antibacterial and Bacterial Anti-Adhesive Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
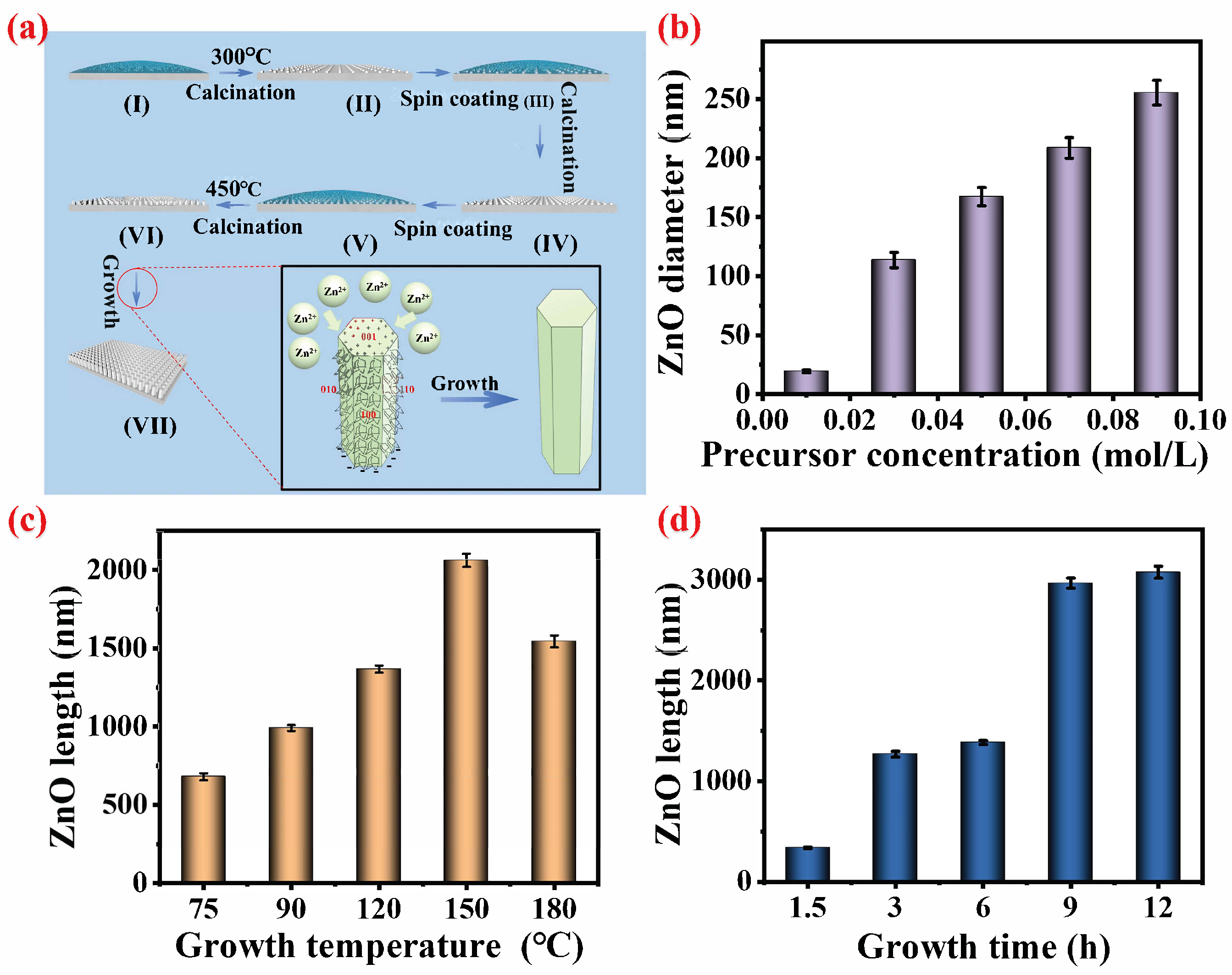
3.1. Controllable Preparation and Growth Mechanism of Ti@ZnO Arrays
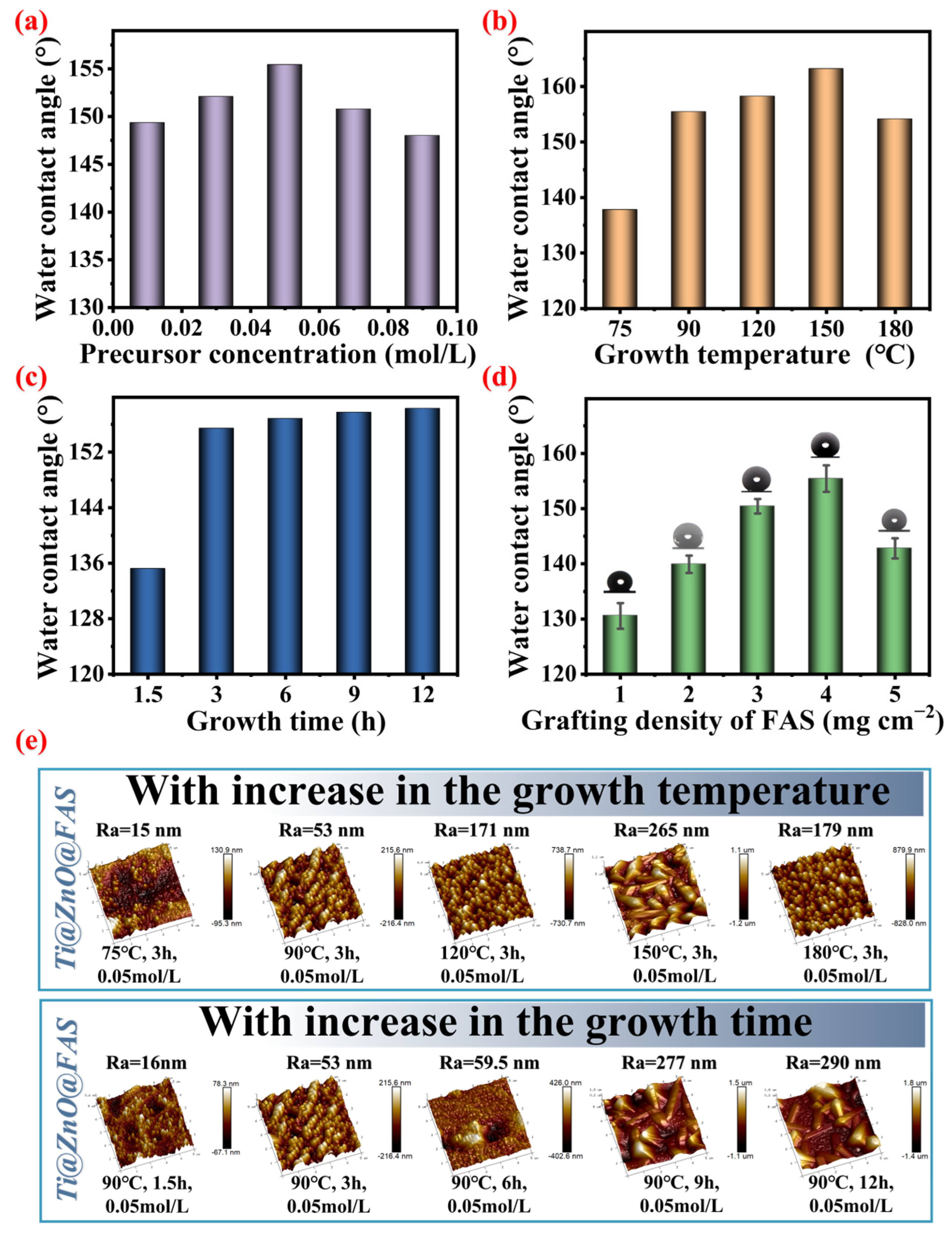
3.2. Regulation of Surface Wettability of Ti@ZnO@FAS
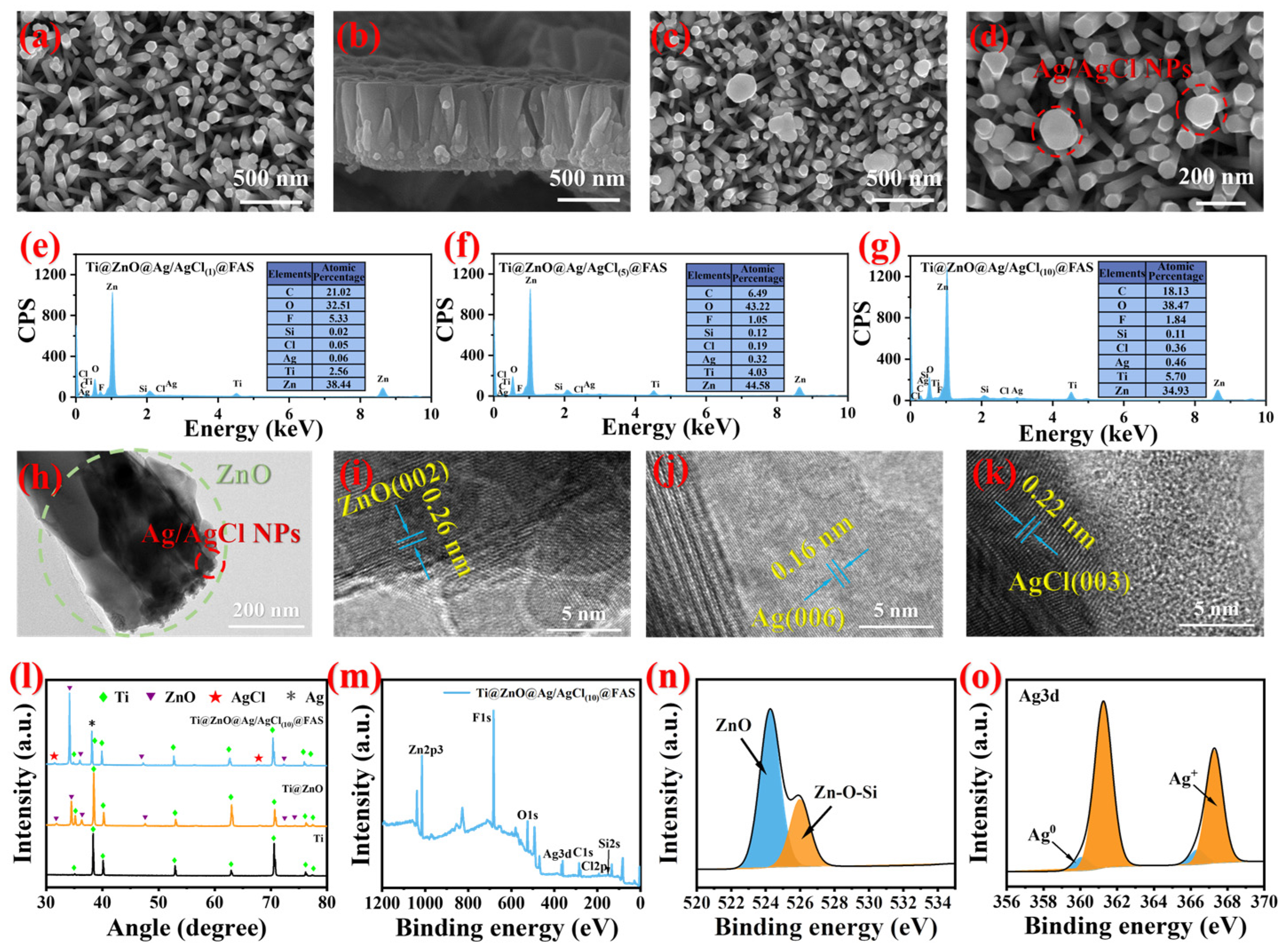
3.3. Characterization of Optimized Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS
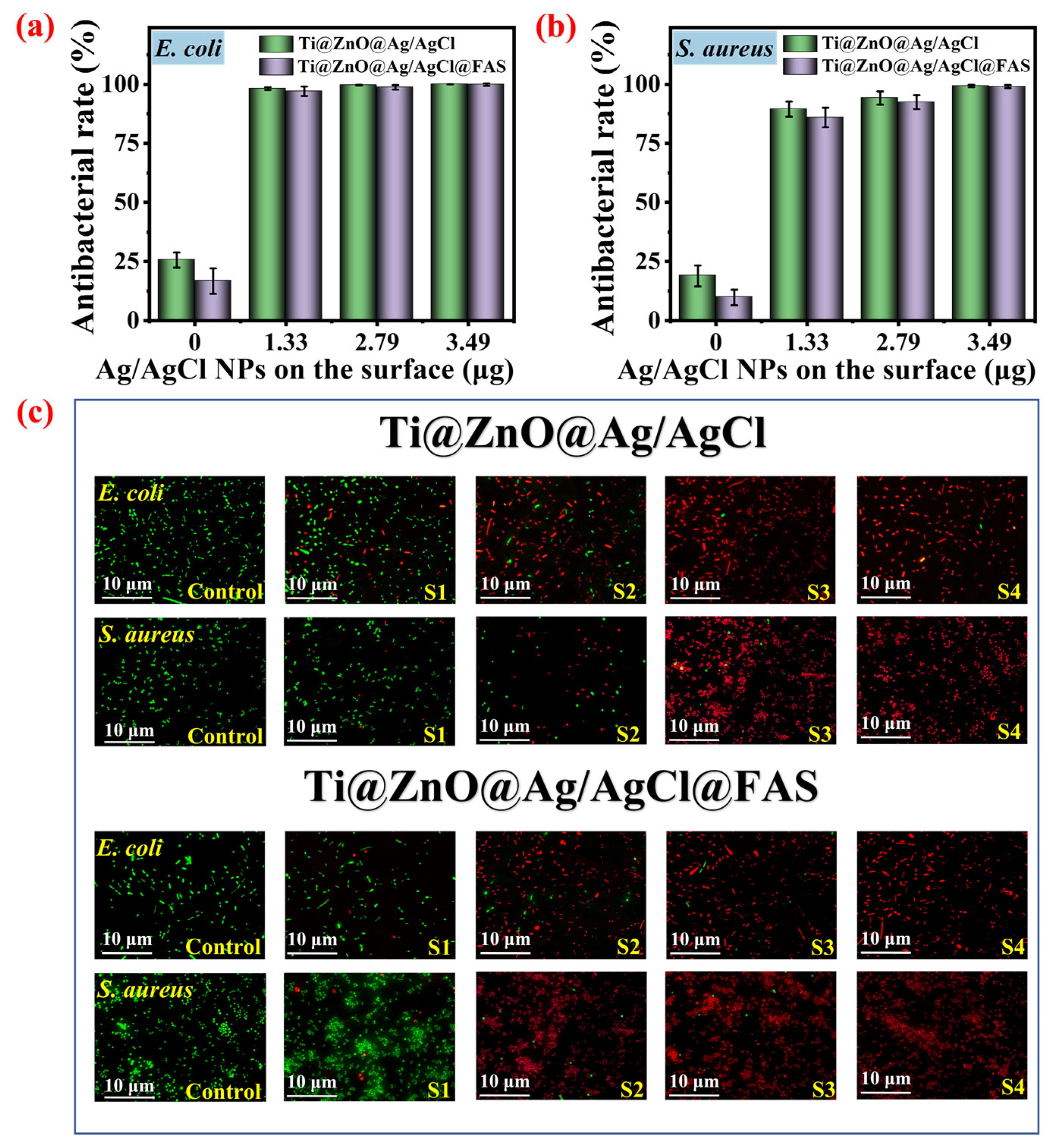
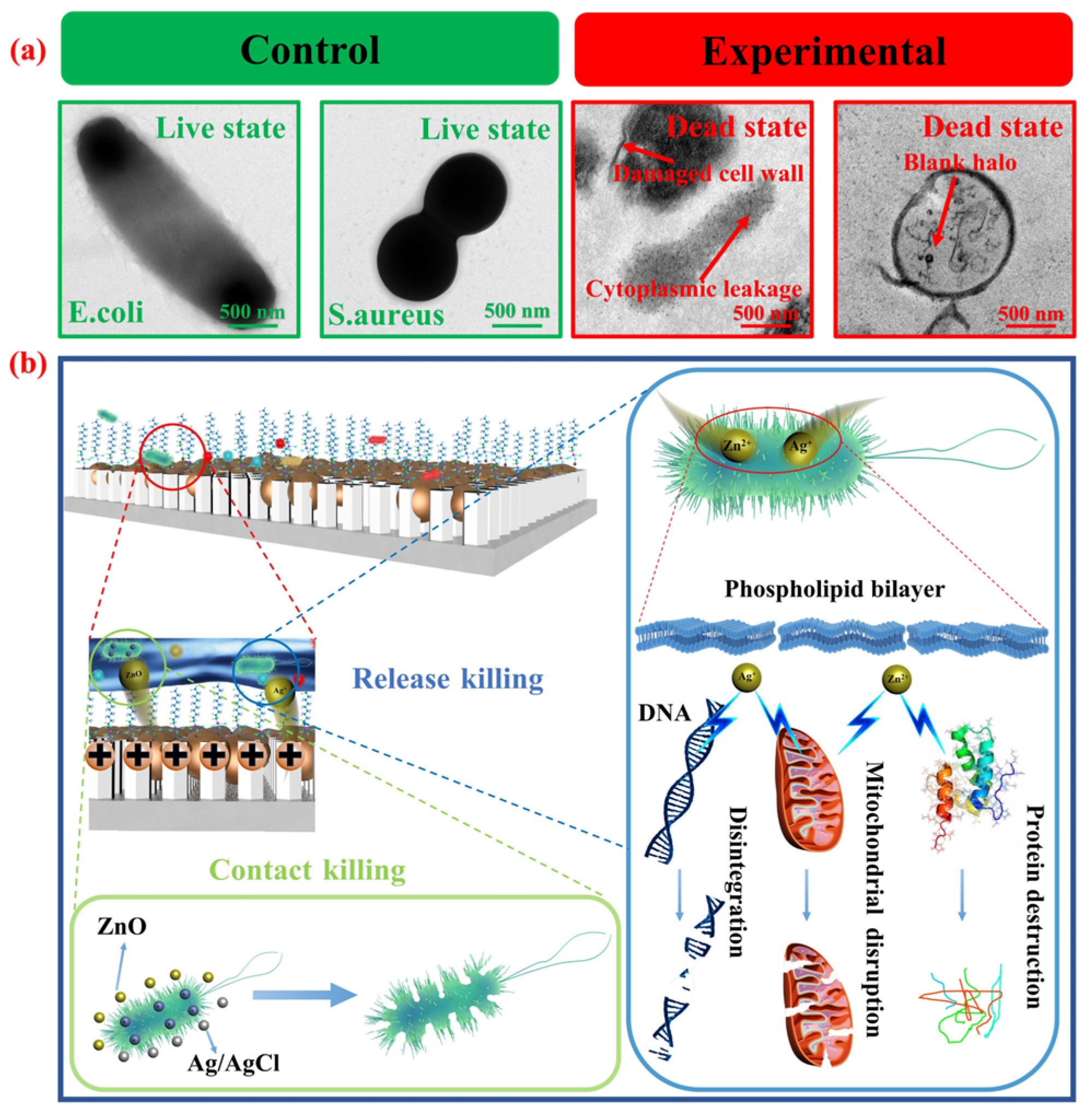
3.4. Effects of Different Ag/AgCl Loading Amounts and Surface Wettability on Antibacterial Efficacy
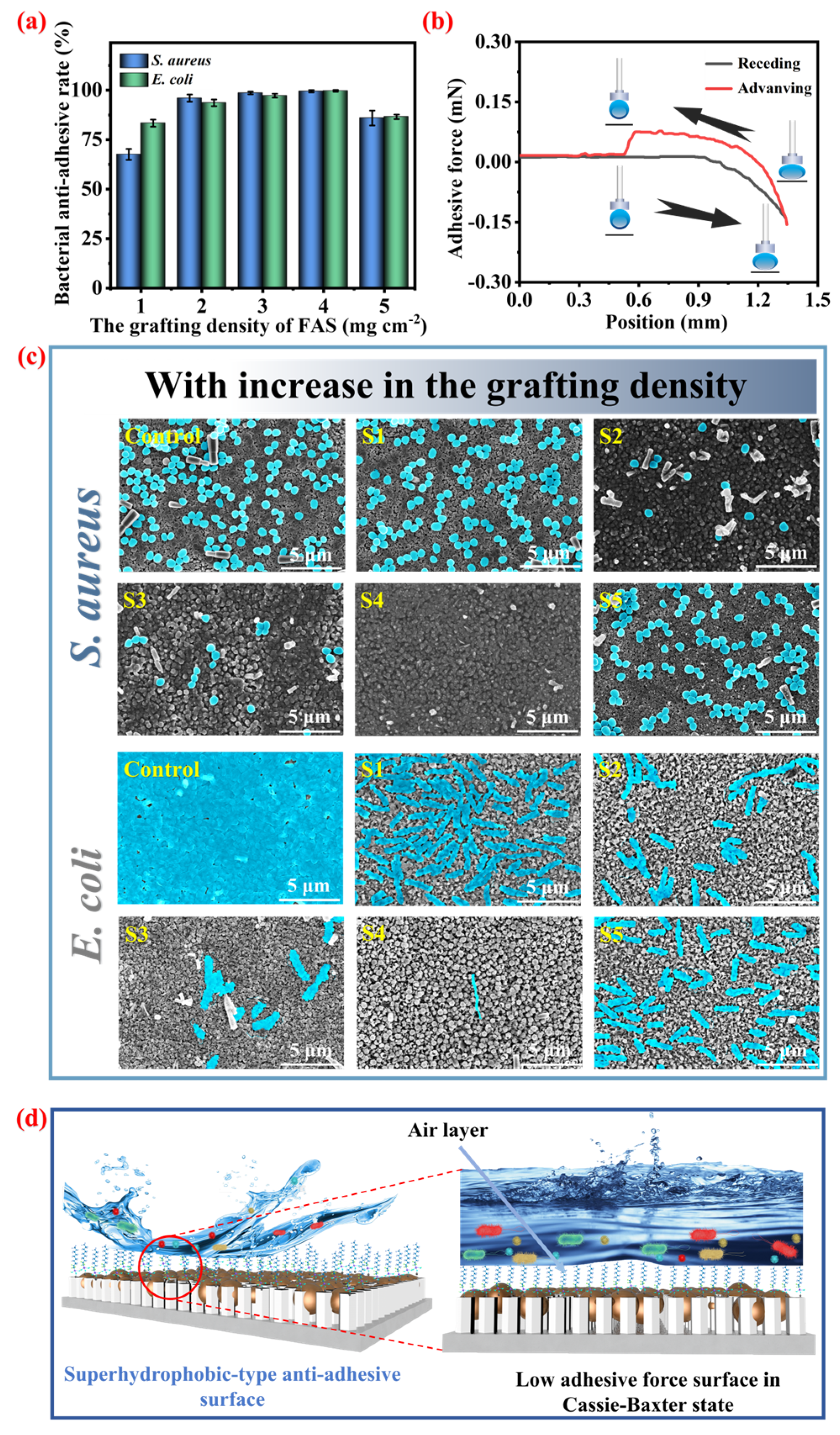
3.5. The Effect of the FAS Grafting Amount on the Bacterial Anti-Adhesion Rate of Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhen, X.; Stålsby Lundborg, C.; Sun, X.; Zhu, N.; Gu, S.; Dong, H. Economic burden of antibiotic resistance in China: A national level estimate for inpatients. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.H.; Park, J.W.; Maeng, S.K. Assessment of organic carbon migration and biofilm formation potential on polymeric tubes in contact with water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, K. Novel antibacterial metals as food contact materials: A review. Materials 2023, 16, 3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xi, Y.; Weng, Y. Recent advances in PLA-based antibacterial food packaging and its applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.Y.; Zhang, E.S.; Han, X.F.; Zhu, H.; Shi, Y.J.; Cao, Z.Q. Engineering and application perspectives on designing an antimicrobial surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21330–21341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Gao, M.; Yun, Y.; Malmsten, M.; Rotello, V.M.; Zboril, R.; Akhavan, O.; Kraskouski, A.; Amalraj, J.; Cai, X.; et al. Antibacterial nanomaterials: Mechanisms, impacts on antimicrobial resistance and design principles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L. Implant infections: Adhesion, biofilm formation and immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, D.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Jia, R.; Zhang, D.; Sand, W.; Wang, F.; Gu, T. Anaerobic microbiologically influenced corrosion mechanisms interpreted using bioenergetics and bioelectrochemistry: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ning, C. Latest research progress of marine microbiological corrosion and bio-fouling, and new approaches of marine anti-corrosion and anti-fouling. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grengg, C.; Mittermayr, F.; Ukrainczyk, N.; Koraimann, G.; Kienesberger, S.; Dietzel, M. Advances in concrete materials for sewer systems affected by microbial induced concrete corrosion: A review. Water Res. 2018, 134, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Du, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Song, J.; Ou, K.; Xie, G.; Yu, Z. Regulating the alkyl chain length of quaternary ammonium salt to enhance the inkjet printing performance on cationic cotton fabric with reactive dye ink. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 19750–19760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschel, A.; Otto, M. Phenol-soluble modulins and staphylococcal infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Li, F.; He, S.; Li, W.; Wu, Q.; He, J.; Ruan, R.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H. Mussel-and barnacle cement proteins-inspired dual-bionic bioadhesive with repeatable wet-tissue adhesion, multimodal self-healing, and antibacterial capability for nonpressing hemostasis and promoted wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Deng, S.; Cong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Z.; Shao, N.; Bhatti, S.A.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, J.; Gellman, S.H.; et al. Secondary amine pendant β-peptide polymers displaying potent antibacterial activity and promising therapeutic potential in treating MRSA-induced wound infections and keratitis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Chen, J.; Cheng, X.; Feng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, S.; Wan, Q.; Pei, X.; Wang, J. Multi-mechanism antibacterial strategies enabled by synergistic activity of metal–organic framework-based nanosystem for infected tissue regeneration. Small 2023, 19, 2205941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Liu, X.; Wu, S. Metal organic framework-based antibacterial agents and their underlying mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7138–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Jakob, R.P.; Marzinek, J.K.; Green, R.; Imai, Y.; Bolla, J.R.; Agustoni, E.; Robinson, C.V.; Bond, P.J.; Lewis, K.; et al. The antibiotic darobactin mimics a β-strand to inhibit outer membrane insertase. Nature 2021, 593, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wu, L.; Yan, H.; Jiang, Z.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Kong, D.; et al. Microchannelled alkylated chitosan sponge to treat noncompressible hemorrhages and facilitate wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Alford, M.A.; Haney, E.F. Antibiofilm activity of host defence peptides: Complexity provides opportunities. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Gao, P.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Yan, A.; Kao, R.Y.-T.; Sun, H. Multi-target mode of action of silver against staphylococcus aureus endows it with capability to combat antibiotic resistance. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.C.; Li, G.F.; Su, M.M.; Liang, H. Scutellaria baicalensis polysaccharide-mediated green synthesis of smaller silver nanoparticles with enhanced antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 45289–45306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Feng, W.; Xu, W.; Yu, L.; Xiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J. The coppery age: Copper (Cu)-involved nanotheranostics. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.; Lv, M.; Xiu, P.; Huynh, T.; Zhang, M.; Castelli, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C.; Fang, H.; et al. Destructive extraction of phospholipids from escherichia coli membranes by graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotech 2013, 8, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, M.; Xu, F.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shen, K.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y. Graphdiyne-modified TiO2 nanofibers with osteoinductive and enhanced photocatalytic antibacterial activities to prevent implant infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitasovic, T.; Caniglia, G.; Eghtesadi, N.; Ceccato, M.; Bojesen, E.D.; Gosewinkel, U.; Neusser, G.; Rupp, U.; Walther, P.; Kranz, C.; et al. Antibacterial action of Zn2+ ions driven by the In vivo formed ZnO nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. 2024, 16, 30847–30859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindha, B.; Mohammad, K.; Okla Kokilavani, S.; Sabariselvan, L.; Saud, S.A.; Mostafa, A.; Abdel, M.; Sudheer, K.S. Dynamic Ag-mediated electron transfer confined ZnO nanorods for boosted photocatalytic bacterial disinfection. J. Clean. Prod 2024, 451, 141908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellappan, L.K.; Manoharan, S. Fabrication of bioinspired keratin/sodium alginate based biopolymeric mat loaded with herbal drug and green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as a dual drug antimicrobial wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Jha, M.K.; Ghimire, J.; Koirala, A.R.; Shrestha, R.M.; Sharma, R.K.; Pant, B.; Park, M.; Pant, H.R. Decoration of Zinc Oxide Nanorods into the Surface of Activated Carbon Obtained from Agricultural Waste for Effective Removal of Methylene Blue Dye. Materials 2020, 13, 5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasert, A.; Sontikaew, S.; Sriprapai, D.; Chuangchote, S. Polypropylene/ZnO Nanocomposites: Mechanical Properties, Photocatalytic Dye Degradation, and Antibacterial Property. Materials. 2020, 13, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Guo, R.; Cheng, Q.; Cheng, X. Synthesis of magnetic CuO/MnFe2O4 nanocompisite and its high activity for degradation of levofloxacin by activation of persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.V.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Kumar, P.S.; Din, A.T.M.; Jalil, A.A. Vo D-VN Green synthesis of ZrO2 nanoparticles and nanocomposites for biomedical and environmental applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1309–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Cui, L.; Tian, Y.; Xia, L.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Bagley, D.M.; Sun, J.; Fan, M. A novel and high-performance double Z-scheme photocatalyst ZnO-SnO2-Zn2SnO4 for effective removal of the biological toxicity of antibiotics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.H.; Liu, H.C.; Lin, J.C. Surface modification of polyurethane membrane with various hydrophilic monomers and N-halamine: Surface characterization and antimicrobial properties evaluation. Polymers 2021, 13, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Hu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W. A review on recent trends of the antibacterial nonwovens air filter materials: Classification, fabrication, and application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Ahmadi, S.; Akhavan, O.; Luque, R. Silver and gold nanoparticles for antimicrobial purposes against multi-drug resistance bacteria. Materials 2022, 15, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Asadi, M.; Akhavan, O. Graphene-based nanomaterials in fighting the most challenging viruses and immunogenic disorders. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 54–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q.; Wu, D.; Ma, R.; Liu, X.; et al. Antibiotic-like activity of atomic layer boron nitride for combating resistant bacteria. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 7674–7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, K.; Canales, D.; Amigo, N.; Montoille, L.; Cament, A.; Rivas, L.M.; Gil-Castell, O.; Reyes, P.; Ulloa, M.T.; Ribes-Greus, A.; et al. Effective antimicrobial materials based on low-density polyethylene (LDPE) with zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Compos Part B Eng. 2019, 172, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzi, M.; Sportelli, M.C.; Torsi, L.; Picca, R.A.; Cioffi, N. Synthesis and antimicrobial applications of ZnO nanostructures: A review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 10881–10902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J.; Igarashi, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Kokugan, T.; Shimizu, M. Evaluation of growth inhibitory effect of ceramics powder slurry on bacteria by conductance method. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1995, 28, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, D.D.; Nguyen-Tri, P.; Le, K.H.; Nguyen, P.T.M.; Nguyen, M.D.-B.; Vo, A.T.K.; Nguyen, M.T.H.; Chang, S.W.; Tran, L.D.; Chung, W.J.; et al. Effects of antibacterial ZnO nanoparticles on the performance of a chitosan/gum arabic edible coating for post-harvest banana preservation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 151, 106057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.H.; Xu, X.; Ma, A.P.Y.; Liu, F.; Ng, A.M.C.; Shen, Z.; Gethings, L.A.; Guo, M.Y.; Djurišić, A.B.; Lee, P.K.H.; et al. Toxicity of ZnO and TiO2 to Escherichia coli cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, A.; Park, S.H.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Jhee, K.H.; Sohn, Y.; Jang, E.S. Antimicrobial activity of ZnO nanoplates and its Ag nanocomposites: Insight into an ROS-mediated antibacterial mechanism under UV light. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 267, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shan, M.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Li, L. Antimicrobial properties of heterojunction BiSnSbO6-ZnO composites in wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 55498–55512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T.; Manna, A.C. Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, H. Halloysite nanotubes supported Ag and ZnO nanoparticles with synergistically enhanced antibacterial activity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Xiao, Z.; Luo, Y.; Luo, Y. Carboxymethyl cellulose capped zinc oxide nanoparticles dispersed in ionic liquid and its antimicrobial effects against foodborne pathogens. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 6, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lin, J.; Lin, J.; Hua, Z.; Hu, F.; Ouyang, L. Active bacterial anti-adhesion strategy based on directional transportation of droplet self-actuated by Laplace pressure gradient on self-actuated and infrared sensing responsive platform. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Y. Robust biomimetic hierarchical diamond architecture with a self-cleaning, antibacterial, and antibiofouling surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24432–24441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.K.; Lu, X.; Min, Y.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Akbulut, M. Bacterially Antiadhesive, Optically transparent surfaces inspired from rice leaves. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19274–19281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Zuo, J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Feng, T.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. Difference and association of antibacterial and bacterial anti-adhesive performances between smart Ag/AgCl/TiO2 composite surfaces with switchable wettability. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cai, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, N.; Xie, M.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z. Anti-liquid-Interfering and bacterially antiadhesive strategy for highly stretchable and ultrasensitive strain sensors based on Cassie-Baxter wetting state. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Mawignon, F.J.; Hussain, M.; Ange, N.K.; Lu, S.; Hafezi, M.; Dong, G. Economic friendly ZnO-based UV sensors using hydrothermal growth: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraleoni-Morgera, A.; Cesini, I.; Kumar, P.; Oddo, C.M. Hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorods as promising materials for low cost electronic skin. ChemNanoMat 2019, 6, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Fu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X. Recent progress in ZnO-based nanostructures for photocatalytic antimicrobial in water treatment: A review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.T.; Aslam, M.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Salah, N.; Hameed, A. The assessment of the photocatalytic activity of magnetically retrievable ZnO coated γ-Fe2O3 in sunlight exposure. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.; Zereffa, E.A.; Tadesse, A.; Murthy, H.C.A. A review on enhancing the antibacterial activity of ZnO: Mechanisms and microscopic investigation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakimińska, A.; Macyk, W. Photochemical transformations of AgCl in the context of its eventual photocatalytic applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 445, 115048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znaidi, L.; Soler Illia, G.J.A.A.; Benyahia, S.; Sanchez, C.; Kanaev, A.V. Oriented ZnO thin films synthesis by sol–gel process for laser application. Thin Solid Films 2003, 428, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znaidi, L. Sol–gel-deposited ZnO thin films: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 174, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugunan, A.; Warad, H.C.; Boman, M.; Dutta, J. Zinc oxide nanowires in chemical bath on seeded substrates: Role of hexamine. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, G.; Asif, M.H.; Zainelabdin, A.; Zaman, S.; Nur, O. Willander M, Influence of pH, precursor concentration, growth time, and temperature on the morphology of ZnO nanostructures grown by the hydrothermal method. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 269692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Diao, P.; Wang, X.; Cai, S. The effect of hydrothermal growth temperature on preparation and photoelectrochemical performance of ZnO nanorod array films. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 3210–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demes, T.; Ternon, C.; Morisot, F.; Riassetto, D.; Legallais, M.; Roussel, H.; Langlet, M. Mechanisms involved in the hydrothermal growth of ultra-thin and high aspect ratio ZnO nanowires. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 410, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Bian, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Sun, K.; Yu, D. Controllable growth of well-aligned ZnO nanorod arrays by low-temperature wet chemical bath deposition method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.H.; Hu, J.; Li, S.S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Shi, J.; Li, X.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Chen, Y. Improved seedless hydrothermal synthesis of dense and ultralong ZnO nanowires. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 245601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, S.; Mao, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, C.; Cohick, Z.; Huang, P.-H.; Huang, T.J. In situ fabrication of 3D Ag@ZnO nanostructures for microfluidic surface-enhanced raman scattering systems. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12175–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. High-quality oriented ZnO films grown by sol–gel process assisted with ZnO seed layer. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poortinga, A.T.; Bos, R.; Norde, W.; Busscher, H.J. Electric double layer interactions in bacterial adhesion to surfaces. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2002, 47, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, L.; Zheng, A.; Cao, L.; Wen, J.; Su, T.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, X. Multifunctionalized carbon-fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone implant for rapid osseointegration under infected environment. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 24, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, H.; Liu, L.; Sun, D.D. Dimension induced intrinsic physio-electrical effects of nanostructured TiO2 on its antibacterial properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-W.; Cao, A.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Superior antibacterial activity of zinc oxide/graphene oxide composites originating from high zinc concentration localized around bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2791–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Dong, S.; Xu, W.; Tu, S.; Yan, L.; Zhao, C.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Antibacterial hydrogels. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, M.; Geszke-Moritz, M. The newest achievements in synthesis, immobilization and practical applications of antibacterial nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 596–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS Composite Materials | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sample | Ag/AgCl Content | FAS Content |
| Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS(1) | 3.49 ug | 1 mg cm−2 |
| Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS(2) | 3.49 ug | 2 mg cm−2 |
| Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS(3) | 3.49 ug | 3 mg cm−2 |
| Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS(4) | 3.49 ug | 4 mg cm−2 |
| Ti@ZnO@Ag/AgCl@FAS(5) | 3.49 ug | 5 mg cm−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, S.; Li, J.; Fan, O.; Lin, F.; Xie, J.; Lin, J. Controllable Fabrication of ZnO Nanorod Arrays on the Surface of Titanium Material and Their Antibacterial and Anti-Adhesion Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071645
Kong S, Li J, Fan O, Lin F, Xie J, Lin J. Controllable Fabrication of ZnO Nanorod Arrays on the Surface of Titanium Material and Their Antibacterial and Anti-Adhesion Properties. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071645
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Sifang, Jialin Li, Ouyang Fan, Feng Lin, Jiayin Xie, and Jing Lin. 2025. "Controllable Fabrication of ZnO Nanorod Arrays on the Surface of Titanium Material and Their Antibacterial and Anti-Adhesion Properties" Materials 18, no. 7: 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071645
APA StyleKong, S., Li, J., Fan, O., Lin, F., Xie, J., & Lin, J. (2025). Controllable Fabrication of ZnO Nanorod Arrays on the Surface of Titanium Material and Their Antibacterial and Anti-Adhesion Properties. Materials, 18(7), 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071645






