Effect of Annealing Conditions of High-Energy Ball-Milled Sm(Fe, Co, Ti)12 Alloys Doped with Zr on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure of Arc-Melting Alloys
Structure and Magnetic Properties of High-Energy Ball Milling (HEBM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popa, D.C.; Szabó, L. Securing Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Needs for Sustainable Energy Initiatives. Materials 2024, 17, 5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A European Green Deal. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/strategy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Podmiljšak, B.; Saje, B.; Jenuš, P.; Tomše, T.; Kobe, S.; Žužek, K.; Šturm, S. The Future of Permanent-Magnet-Based Electric Motors: How Will Rare Earths Affect Electrification? Materials 2024, 17, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippas, A.; Sempros, G.; Sarafidis, C. Critical rare earths: The future of Nd & Dy and prospects of end-of-life product recycling. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 4058–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, M. China’s Rare Earths Production Forecasting and Sustainable Development Policy Implications. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mooij, D.B.; Buschow, K.H.J. Some Novel Ternary ThMn12-Type Compounds. J. Less Common Met. 1988, 136, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.-S.; Coey, J.M.D. Chapter 1 Magnetic Properties of Ternary Rare-Earth Transition-Metal Compounds. In Handbook of Magnetic Materials; Buschow, K.H.J., Ed.; North Holland Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; Volume 6, pp. 1–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, K.; Tawara, Y.; Osugi, R.; Shimao, M. Magnetic Properties of Fe-rich Rare-earth Intermetallic Compounds with a ThMn12 Structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 5714–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Magnetic Properties of Sm-Fe-Ti-V Alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1990, 87, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xu, S.; Xu, C.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. Tuning Fe2Ti Distribution to Enhance Extrinsic Magnetic Properties of SmFe12-Based Magnets. Crystals 2024, 14, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Magnetically Hard Anisotropic RFe10Si2 Powders with Representing Combinations of Sm, Ce and Zr. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 422, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengdeejing, A.; Chen, Y. Improving Thermodynamic Stability of SmFe12-Type Permanent Magnets from High Entropy Effect. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2021, 42, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Yamagishi, K.; Homma, M. High Coercivity in Melt-Spun SmFe10(TiV)2 Ribbons. Materials Transactions. JIM 1989, 30, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Kojima, A.; Yamagishi, K.; Homma, M. High Coercivity in Melt-Spun SmFe10(Ti,M)2 Ribbons (M=V/Cr/Mn/Mo). IEEE Trans. Magn. 1990, 26, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Kim, A.; Liu, N.C.; Sellmyer, D.J. Magnetic and Structural Studies in Sm-Fe-Ti Magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 4954–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozman, P.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K. Intrinsic Magnetic Properties of (Sm,Gd)Fe12-Based Compounds with Minimized Addition of Ti. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 855, 157491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.-P.; Li, H.-S.; Gavigan, J.P.; Coey, J.M.D. Intrinsic Magnetic Properties of the Iron-Rich ThMn12-Structure Alloys R(Fe11Ti); R=Y, Nd, Sm, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm and Lu. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1989, 1, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coehoorn, R. Electronic structure and magnetism of transition-metal-stabilized YFe12-xMx intermetallic compound. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 11790–11797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J. Permanent Magnet Materials Based on Tetragonal Rare Earth Compounds of the Type RFe12−xMx. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1991, 100, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozman, P.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hirosawa, S.; Hono, K. Intrinsic Magnetic Properties of Sm(FeCo)11Ti and Zr-Substituted Sm1-yZr (Fe0.8Co0.2)11.5Ti0.5 Compounds with ThMn12 Structure toward the Development of Permanent Magnets. Acta Mater. 2018, 153, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.F.; Sinha, V.K.; Xu, Y.; Elbicki, J.M.; Boltich, E.B.; Wallace, W.E.; Sankar, S.G.; Laughlin, D.E. Magnetic and Structural Properties of SmTiFe11-xCox Alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1988, 75, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hirosawa, S.; Hono, K. Intrinsic Hard Magnetic Properties of Sm(Fe1−xCox)12 Compound with the ThMn12 Structure. Scr. Mater. 2017, 138, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, L.; Schnitzke, K.; Wecker, J. High coercivity in mechanically alloyed Sm-Fe-V magnets with a ThMn12 crystal structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1990, 56, 868–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Tang, X.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Srinithi, A.K.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K. Origin of coercivity in an anisotropic Sm(Fe,Ti,V)12-based sintered magnet. Acta Mater. 2021, 217, 117161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.H.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, X.; Song, Y.; Si, P.; Choi, C.J.; Cho, Y.R.; Park, J. Anisotropic SmFe10V2 Bulk Magnets with Enhanced Coercivity via Ball Milling Process. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wen, L.; Pan, A.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Liao, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X. First-Principles Study of Ti-Doping Effects on Hard Magnetic Properties of RFe11Ti Magnets. Crystals 2024, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirba, I.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Choi, I.-J.; Choi, J.-H.; Uh, H.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Kwon, S.-J.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K. SmFe12-Based Hard Magnetic Alloys Prepared by Reduction-Diffusion Process. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 861, 157993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozman, P.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ogawa, D.; Hirosawa, S.; Hono, K. The Effect of Zr Substitution on Saturation Magnetization in (Sm1-XZrx)(Fe0.8Co0.2)12 Compound with the ThMn12 Structure. Acta Mater. 2019, 178, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozman, P.; Sepehri-Amin, H.; Hono, K. Prospects for the Development of SmFe12-Based Permanent Magnets with a ThMn12-Type Phase. Scr. Mater. 2021, 194, 113686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.F.; Hou, Y.H.; Li, H.F.; Chai, W.X.; Wu, Z.J.; Feng, Q.; Li, W.; Pang, Z.S.; Ma, L.; Yu, H.B.; et al. Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Exchange-Coupled Nanocomposite Sm0.75Zr0.25(Fe0.8Co0.2)11Ti Alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 571, 170578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.T.; Qian, H.-D.; Park, J.; Choi, C.-J.; Kim, C.S. Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of Fe-Rich Sm(Fe0.8Co0.2)11Ti Permanent Magnetic Materials. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2019, 74, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, M.; Sanada, N.; Sakurada, S. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Rapidly Quenched (Sm,R)(Fe,Co)11.4Ti0.6 (R = Y, Zr) with ThMn12 Structure. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 035036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Suzuki, S.; Kuno, T.; Urushibata, K.; Sakuma, N.; Yano, M.; Shouji, T.; Kato, A.; Manabe, A. The Stability of Newly Developed (R,Zr)(Fe,Co)12−xTix Alloys for Permanent Magnets. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 694, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Feng, H.; Zhao, H.; Xu, S. Magnetic Properties and Microstructure of Ce and Zr Synergetic Stabilizing Ti-Lean SmFe12-Based Strip-Casting Flakes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2024, 599, 172100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Hawai, T.; Ono, K. (Sm,Zr)xFe12−xMx (M=Zr,Ti,Co) for Permanent-Magnet Applications: Ab Initio Material Design Integrated with Experimental Characterization. Phys. Rev. App. 2020, 13, 064028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, A.; Söderlind, P.; Moore, E.; Perron, A. Thermodynamics and Magnetism of SmFe12 Compound Doped with Zr, Ce, Co and Ni: An Ab Initio Study. Metals 2024, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Cid, A.; Salazar, D.; Schönhöbel, A.M.; Garitaonandia, J.S.; Barandiaran, J.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Magnetic properties and phase stability of tetragonal Ce1−xSmxFe9Co2Ti 1:12 phase for permanent magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 749, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, N.; Wu, Q.; Pan, M.; Zhang, S.; Ge, H. Role and optimization of thermal annealing in Sm0.74Zr0.26(Fe0.8Co0.2)11Ti alloys with ThMn12 structure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 549, 169065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjoka, M.; Sarafidis, C.; Niarchos, D.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Evolution of microstructure and magnetic properties in annealed high energy ball milled Sm(Fe, Co, Ti)12 compounds doped, with Zr. In Proceedings of the 64th of Annual Conference on Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–8 November 2019; Abstract Book. p. 603. [Google Scholar]
- Sundar, R.S.; Deevi, S.C. Soft magnetic FeCo alloys: Alloy development, processing, and properties. Int. Mater. Rev. 2005, 50, 157–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, C.N.; Takeshita, T. Hydrogenation and nitrogenation of SmFe2. J. Alloys Compd. 1993, 194, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K.; Sagawa, M. The origin of coercivity decrease in fine grained Nd Fe B sintered magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Labisz, K.; Jonda, E.; Klimpel, A. Comparison of the surface alloying of the 32CrMoV12-28 tool steel using TiC and WC powder. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 191, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.; Rinko, E.; Prost, T.; Horn, T.; Ledford, C.; Rock, C.; Anderson, I. Processing of Alnico Magnets by Additive Manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

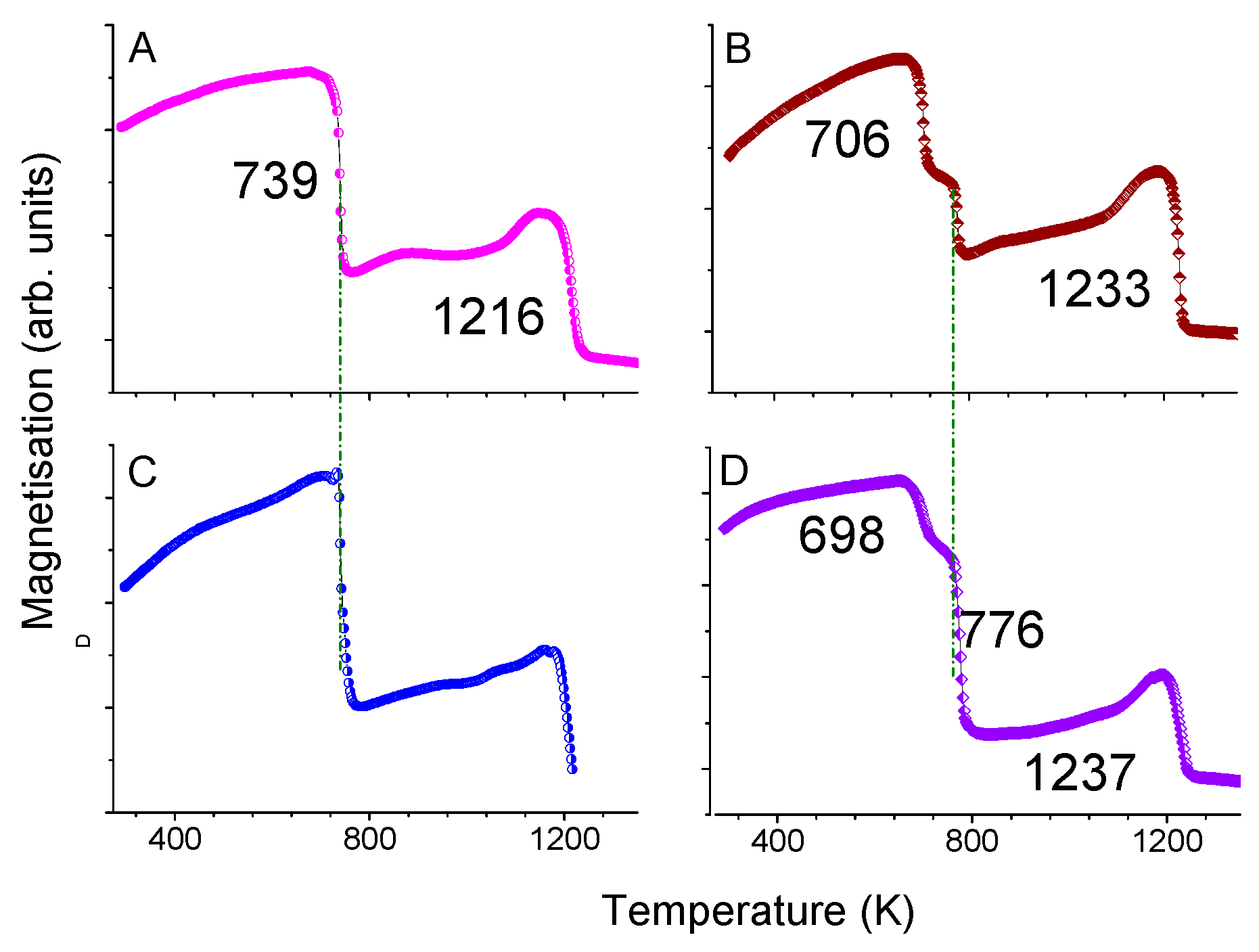

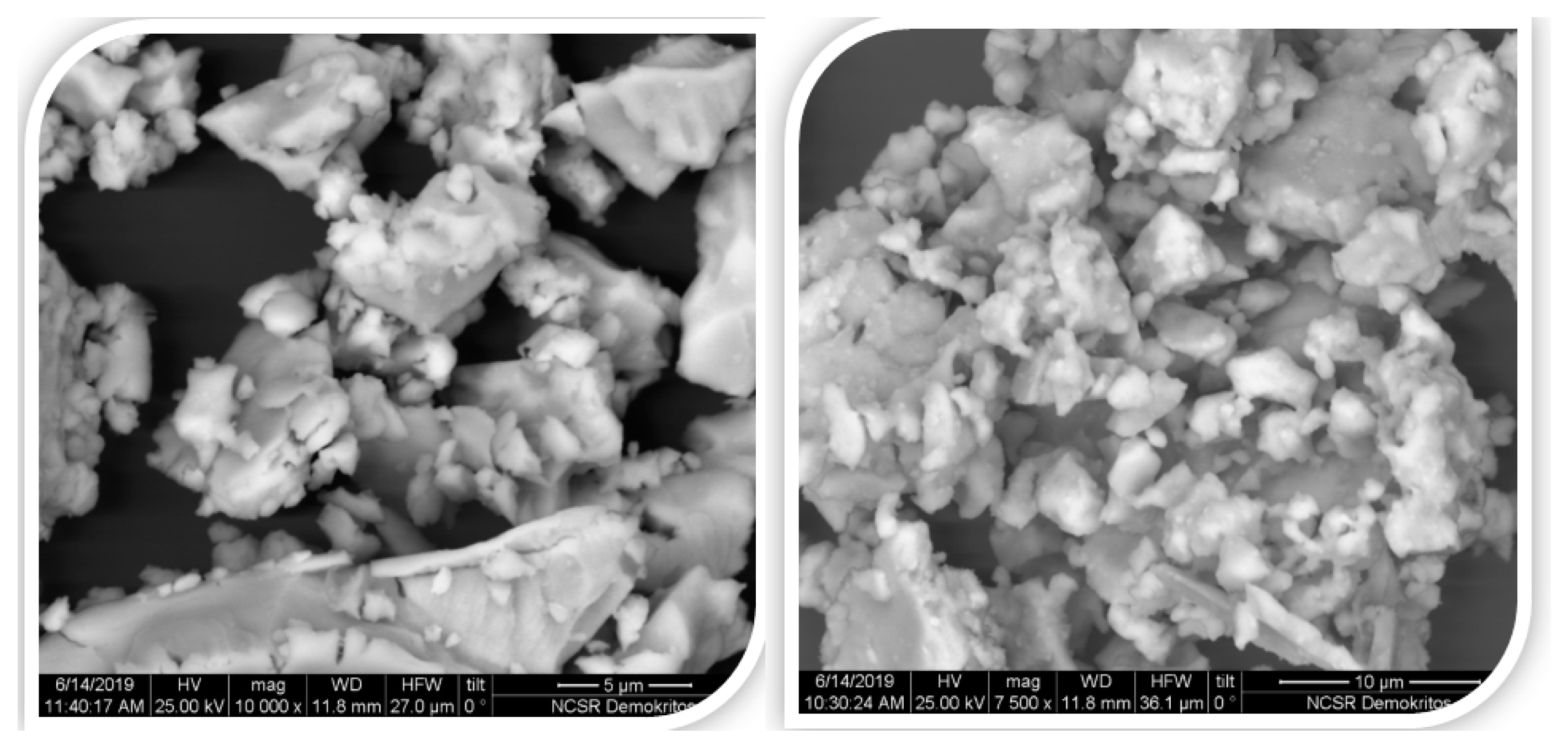
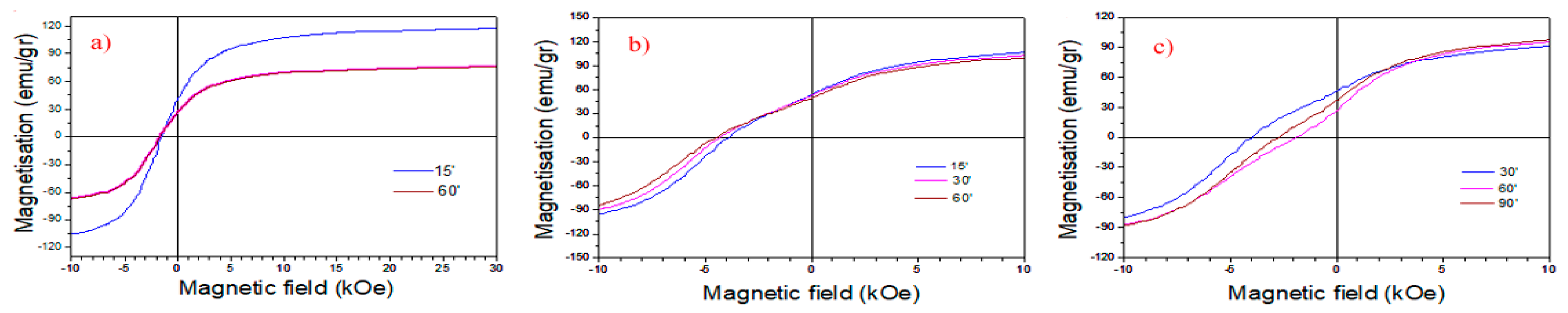
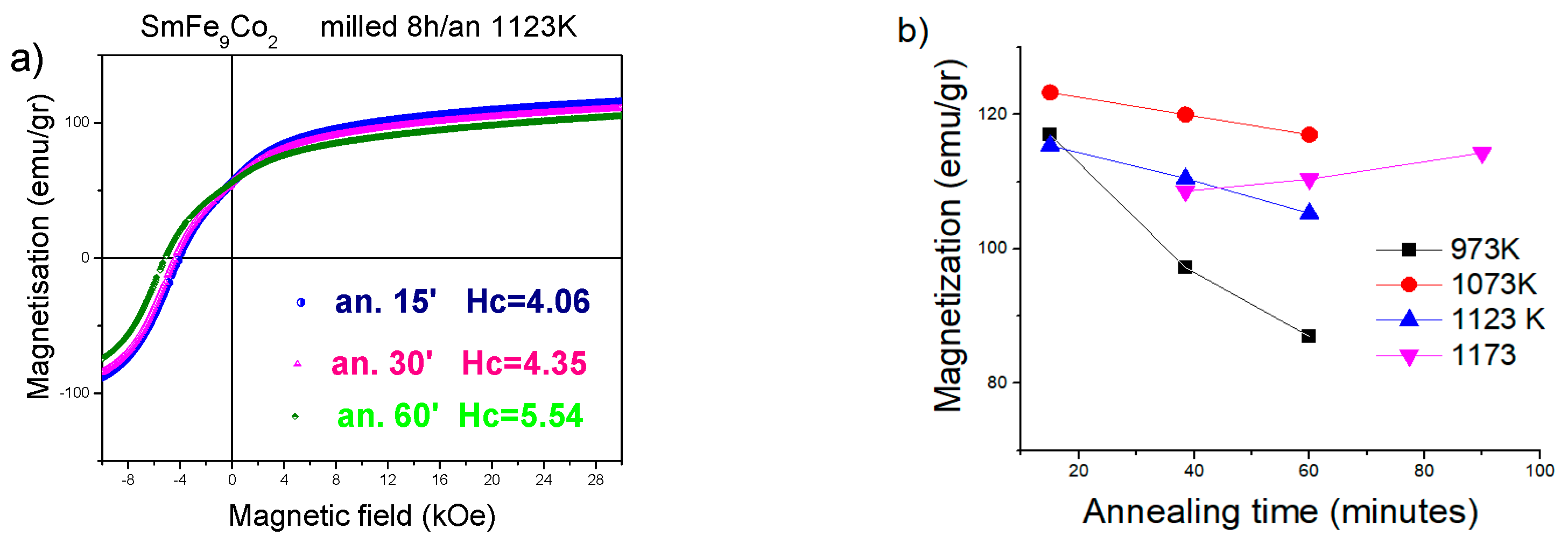


| Sample B Ann. at 1123 K | Sample C Ann. at 1098 K | Sample D Ann. at 1123 K | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ann. time | Hc (kOe) | M3T (emu/gr) | Hc (kOe) | M3T (emu/gr) | Hc (kOe) | M3T (emu/gr) |
| 15 m | 4.01 | 120.9 | 3.0 | 122.8 | 4.05 | 120.8 |
| 30 min | 4.05 | 120.7 | 3.1 | 122.1 | 3.29 | 105.5 |
| 60 min | 4.37 | 93.6 | 3.5 | 118.4 | 2.76 | 125.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gjoka, M.; Sarafidis, C.; Niarchos, D.; Hadjipanayis, G. Effect of Annealing Conditions of High-Energy Ball-Milled Sm(Fe, Co, Ti)12 Alloys Doped with Zr on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071642
Gjoka M, Sarafidis C, Niarchos D, Hadjipanayis G. Effect of Annealing Conditions of High-Energy Ball-Milled Sm(Fe, Co, Ti)12 Alloys Doped with Zr on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071642
Chicago/Turabian StyleGjoka, Margarit, Charalampos Sarafidis, Dimitrios Niarchos, and George Hadjipanayis. 2025. "Effect of Annealing Conditions of High-Energy Ball-Milled Sm(Fe, Co, Ti)12 Alloys Doped with Zr on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties" Materials 18, no. 7: 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071642
APA StyleGjoka, M., Sarafidis, C., Niarchos, D., & Hadjipanayis, G. (2025). Effect of Annealing Conditions of High-Energy Ball-Milled Sm(Fe, Co, Ti)12 Alloys Doped with Zr on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties. Materials, 18(7), 1642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071642







