Degradation Characteristics of Reed-Based PBAT Mulch and Their Effects on Plant Growth and Soil Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Sample Mulch Film
2.3. Compost Degradation Test
- ①
- The theoretical release of the CO2 was calculated as shown in Equation (1):
- ②
- The percentage of biodegradation was based on the cumulative amount of CO2 released, and the rate of biodegradation (Dt) was evaluated by using Equation (2):
2.3.1. FTIR Analysis
2.3.2. SEM Morphology
2.3.3. Transmittance of the Films
2.3.4. Elongation at the Break of the Material
2.4. Plant Cultivation
2.4.1. Effects of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on the Soil Properties
- (1)
- Determination of the basic physical and chemical properties of the soil
- (2)
- Measurement of the soil’s enzyme activity
2.4.2. Effect of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on Plant Growth
- (1)
- Determination of the germination rate
- (2)
- Measurement of plant height, root length, and total biomass
- (3)
- Determination of the chlorophyll content
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mulch Properties
3.2. Compost Degradation
3.2.1. Composting Biodegradation
3.2.2. Infrared Analysis of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Films
3.2.3. Electron Microscopic Analysis of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films
3.3. Effects of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on the Soil’s Properties
3.3.1. PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films’ Effects on pH
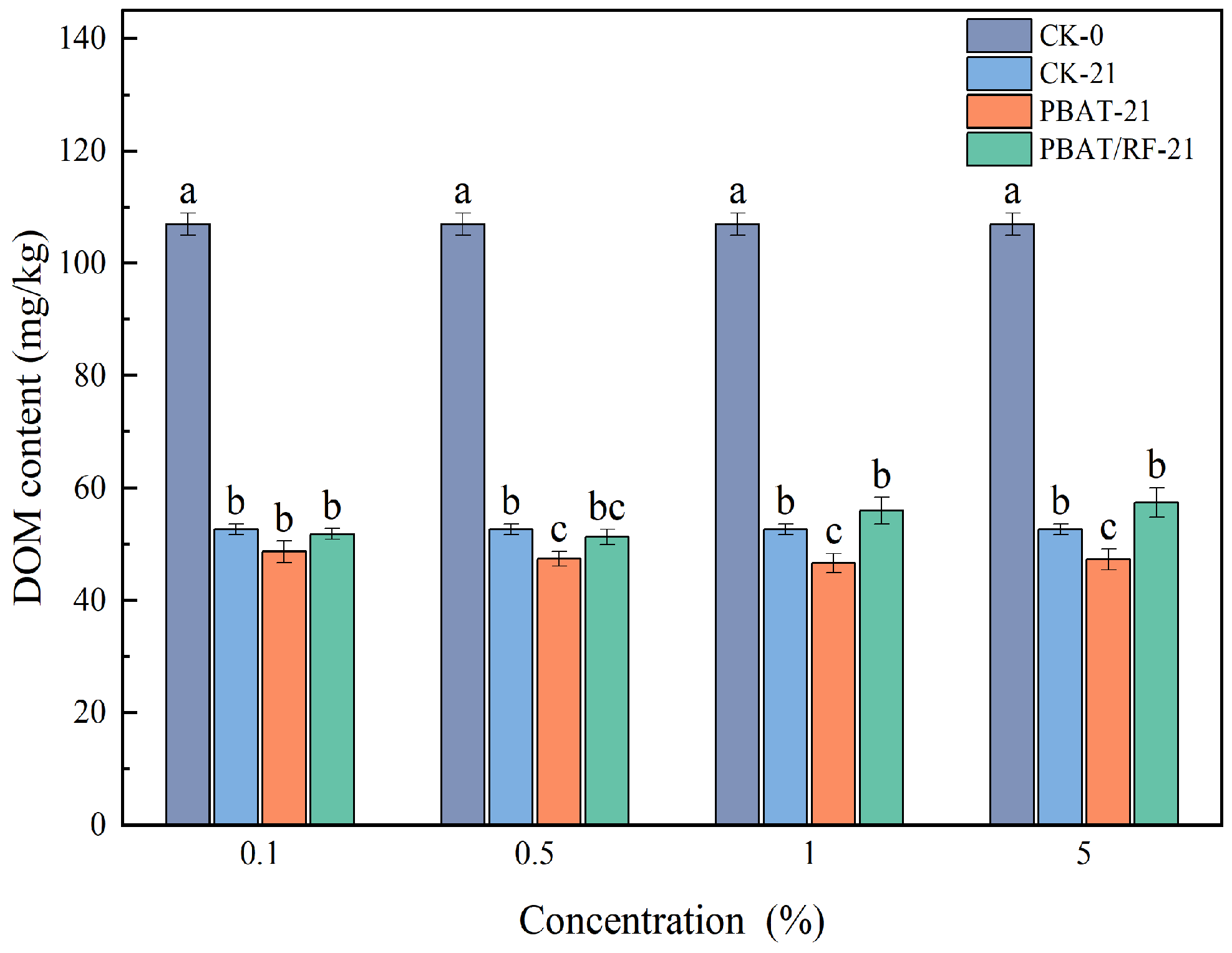
3.3.2. PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films’ Effects on DOM
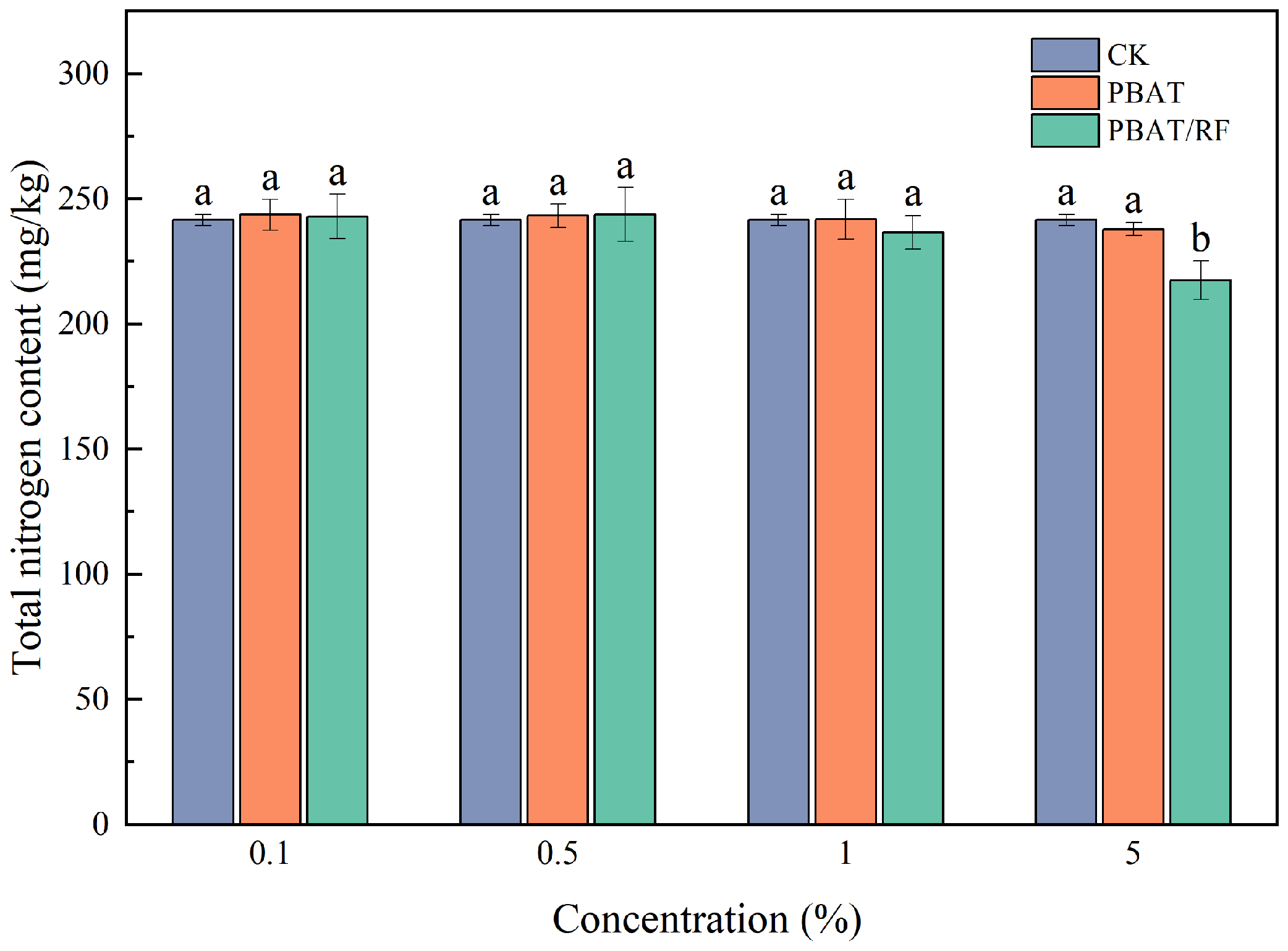
3.3.3. Effects of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on the Soil’s Total Nitrogen Contents
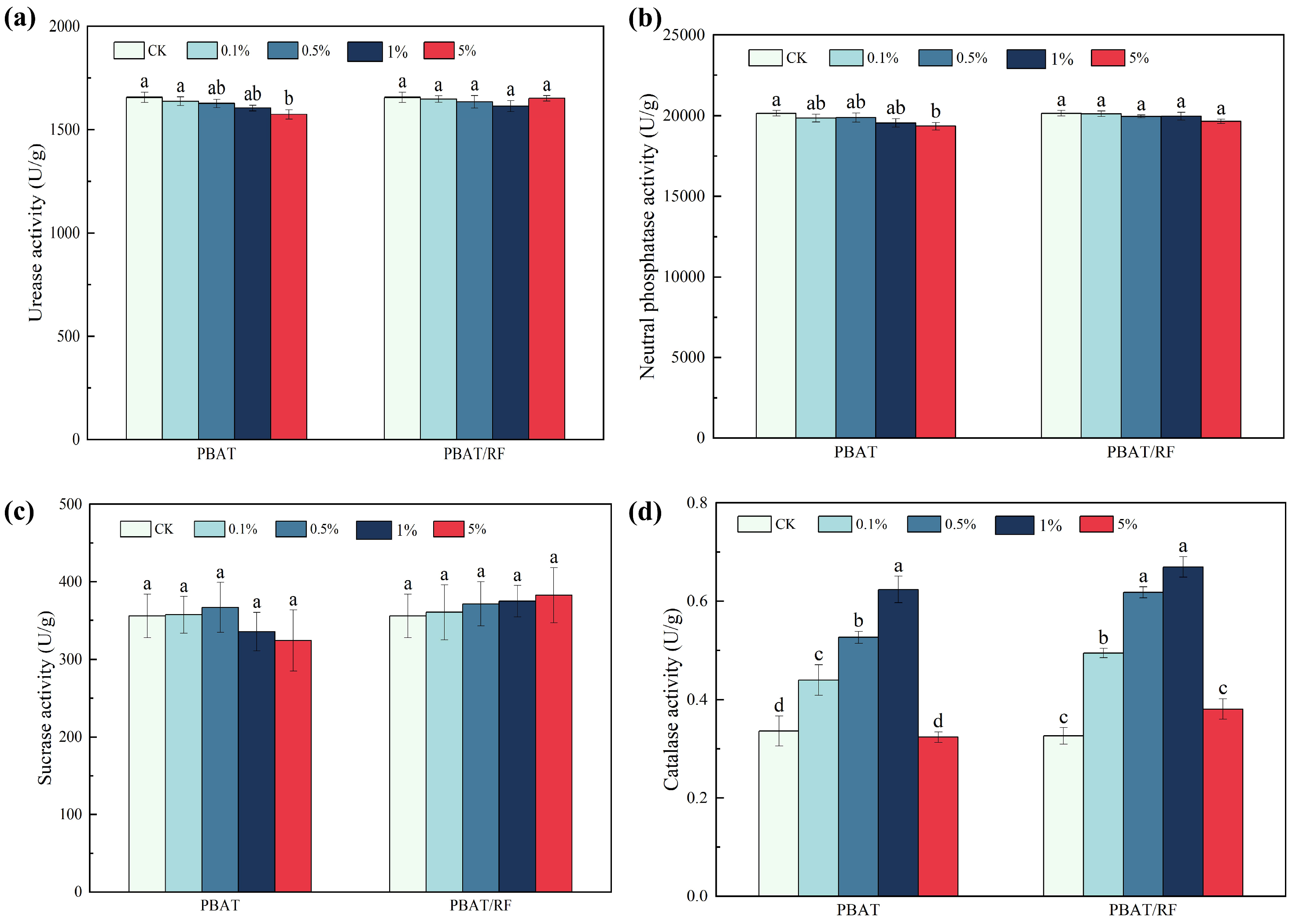
3.3.4. Effects of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on the Soil’s Enzyme Activities
3.4. Effects of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on Soybean Growth
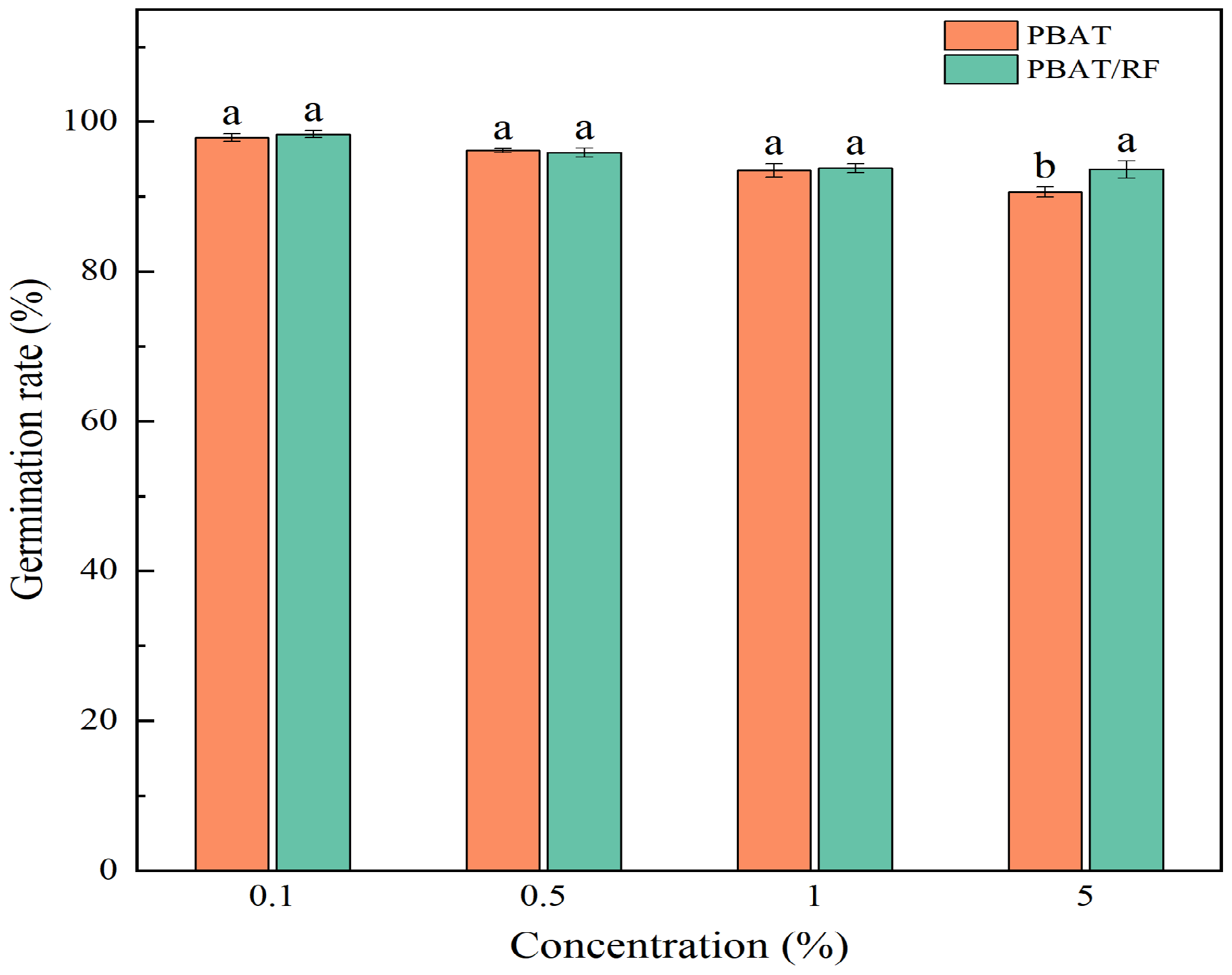
3.4.1. Effects of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on the Germination of the Soybeans
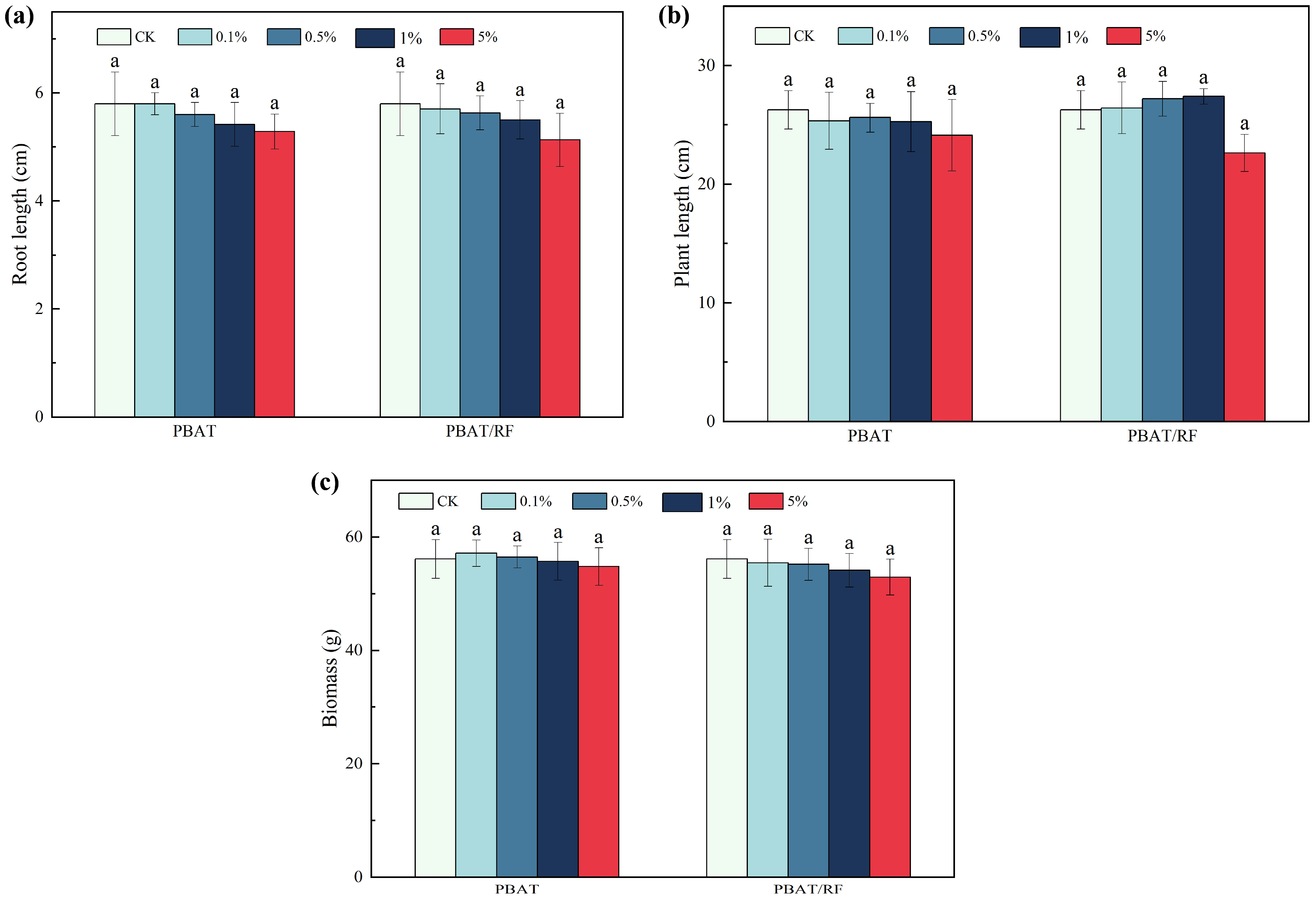
3.4.2. Effects of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on Soybean Root Length, Plant Height, and Biomass
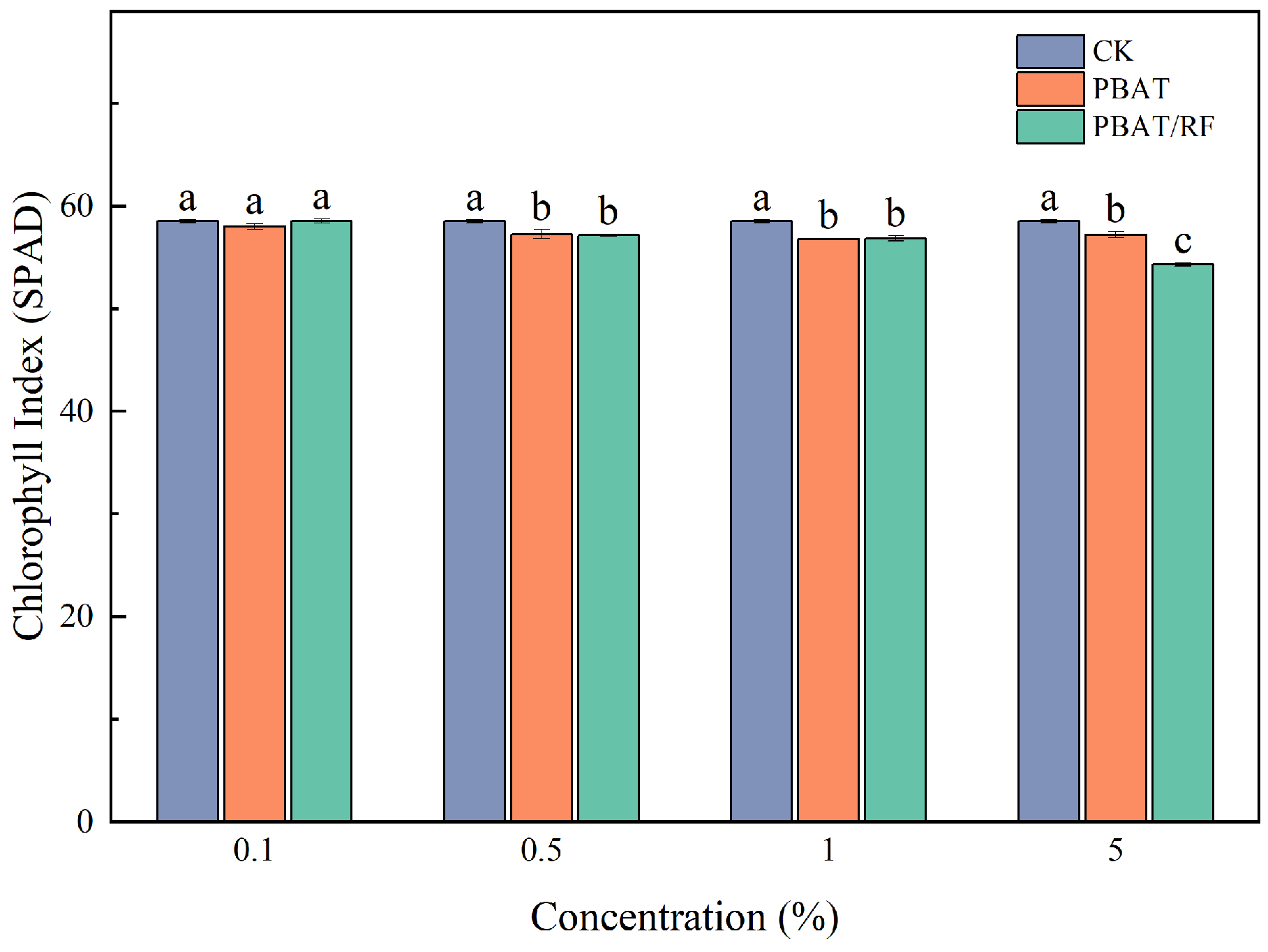
3.4.3. Effects of the PBAT and PBAT/RF Mulch Films on Plant Chlorophyll
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, F.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Luo, C.-L.; Zhang, X.-F.; Li, X.-Y.; Li, F.-M.; Xiong, L.-B.; Kavagi, L.; Nguluu, S.N.; et al. Ridge-furrow plastic-mulching with balanced fertilization in rainfed maize (Zea mays L.): An adaptive management in east African Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 236, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.B.; Bai, W.B.; Li, X.; Duan, F.Y.; Hou, P.; Zhao, R.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhao, M.; Li, S.K.; Song, J.Q. Effects of plastic film mulching on leaf metabolic profiles of maize in the loess plateau with two planting densities. Acta Agron. 2021, 47, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Yi, Y.J.; Tan, Z.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.R. Research Progress of Biodegradable Mulch in China. Plast. Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.Z.; Xu, Z.M. Status and management of cotton field film pollution. China Cotton 1992, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.H.; Zhu, H.W. Overview of the research and application of paper mulch. China Pulp Pap. 2002, 21, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano-Ruiz, H.; Martin-Closas, L.; Pelacho, A.M. Biodegradable plastic mulches: Impact on the agricultural biotic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.; Katsarava, R.; Puiggalí, J. Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Biodegradable Polymers Derived from Diols and Dicarboxylic Acids: From Polyesters to Poly(ester amide)s. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 7064–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.F.; Vilela, C.; Fonseca, A.C.; Matos, M.; Freire, C.S.; Gruter, G.J.M.; Silvestre, A.J. Biobased polyesters and other polymers from 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid: A tribute to furan excellency. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 6096. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Flury, M.; Chang, Y.; Wang, J. Agronomic performance of polyethylene and biodegradable plastic film mulches in a maize cropping system in a humid continental climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Maani, A.; Sojoudi, H.; Heuzey, M.C.; Carreau, P.J. Interfacial and rheological properties of PLA/PBAT and PLA/PBSA blends and their morphological stability under shear flow. J. Rheol. 2015, 59, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Jin, T.; Zhang, H.; Peng, J.; Zuo, N.; Huang, Y.; Han, Y.; Tian, C.; Yang, Y.; Peng, K.; et al. Deciphering the diversity and functions of plastisphere bacterial communities in plastic-mulching croplands of subtropical China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 422, 126865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Jin, T.; Zou, T.; Xu, L.; Xi, B.; Xu, D.; He, J.; Xiong, L.; Tang, C.; Peng, J. Current progress on plastic/microplastic degradation: Fact influences and mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafea, L.; Yap, J.; Beriot, N.; Felde, V.J.M.N.L.; Okoffo, E.D.; Enyoh, C.E.; Peth, S. Microplastics in agroecosystems: A review of effects on soil biota and key soil functions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2023, 186, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantis, L.J.; Adamczyk, S.; Velmala, S.M.; Adamczyk, B.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.; Bosker, T. Comparing the impact of microplastics derived from a biodegradable and a conventional plastic mulch on plant performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.; Devetter, L.; Ghimire, S.; Hayes, D.G. Suitability of Biodegradable Plastic Mulches for Organic and Sustainable Agricultural Production Systems. Hortscience 2017, 52, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Chen, C.; Song, B.; Shen, M.; Gong, J. A review of biodegradable plastics to biodegradable microplastics: Another ecological threat to soil environments? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y. Interactions of microplastics and cadmium on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in an agricultural soil. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.H.; Liu, W.T.; Shi, R.Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.T.; Zheng, Z.Q. Effect of polyethylene and polylactic acid microplastics on growth and physiological biochemistry and metabolism of soybeans. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 435, 129057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gui, H.; Banfield, C.C.; Wen, Y.; Zang, H.; Dippold, M.A.; Charlton, A.; Jones, D.L. The microplastisphere: Biodegradable microplastics addition alters soil microbial community structure and function. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroi, F.; Tachibana, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Kasuya, K.-I. Influences of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) on soil microbiota and plant growth. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 129, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanna, S.; Laura, O.; Selene, C.; Aldo, V. Application of Biotests for the Determination of Soil Ecotoxicity after Exposure to Biodegradable Plastics. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Yu, H.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. A review on the occurrence and influence of biodegradable microplastics in soil ecosystems: Are biodegradable plastics substitute or threat? Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zantis, L.J.; Rombach, A.; Adamczyk, S.; Velmala, S.M.; Adamczyk, B.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.; Bosker, T. Species-dependent responses of crop plants to polystyrene microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 1.1–1.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Yang, X.; Riksen, M.; Xu, M.; Geissen, V. Response of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) growth to soil contaminated with microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Feng, K.; Li, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Q. Enhanced Biodegradation Rate of Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Composites Using Reed Fiber. Polymers 2024, 16, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 6672-2001; Plastics Film and Sheeting—Determination of Thickness by Mechanical Scanning. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2001.
- GB/T19277-2011; Determination of the Ultimate Aerobic Biodegradability of Plastic Materials Under Controlled Composting Conditions-Method by Analysis of Evolved Carbon Dioxide-Part 1: General Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- GB/T 1040.2-2006; Plastic—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastic. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Sintim, H.Y.; Bary, A.I.; Hayes, D.G.; Wadsworth, L.C.; Flury, M. In situ degradation of biodegradable plastic mulch films in compost and agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, J.; Lach, R.; Grellmann, W.; Susan, A.B.H.; Saiter, J.; Henning, S.; Katiyar, V.; Adhikari, R. Compostable composites of wheat stalk micro- and nanocrystalline cellulose and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate): Surface properties and degradation behavior. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Feng, C.; Na, H.; Liu, F.; Xue, L.; Zhu, J. Effect of large sized reed fillers on properties and degradability of PBAT composites. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhao, S.; Shi, H.; Zhu, Y.; Teng, Y.; Jiang, G.; Liu, S. Combined effects of microplastics and cadmium on the soil-plant system: Phytotoxicity, Cd accumulation and microbial activity. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 121960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cao, Y.; Fan, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ren, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Feng, Y. Degradation characteristics of polybutylene adipate terephthalic acid (PBAT) and its effect on soil physicochemical properties: A comparative study with several polyethylene (PE) mulch films. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Liang, C.; Xue, S.; Chen, H.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Response of soil dissolved organic matter to microplastic addition in Chinese loess soil. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Han, L.; Liu, W.; Ding, Y. Microplastics regulate soil microbial activities: Evidence from catalase, dehydrogenase, and fluorescein diacetate hydrolase. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, Y.S.K.; Rajagopalan, U.M.; Kadono, H.; Li, D. Effects of microplastics on lentil (Lens culinaris) seed germination and seedling growth. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, R.; Dai, W.; Luan, Y.; Li, J. Impacts of Micro(nano)plastics on Terrestrial Plants: Germination, Growth, and Litter. Plants 2023, 12, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żołnowski, A.C.; Rolka, E.; Kalinowski, Ł. Effects of Organic Amendments on the Morphology and Chemical Composition of Black Mustard (Sinapis nigra L.) Grown on Soil Contaminated with Copper. Agronomy 2024, 14, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, H.; Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Yin, T.; Liu, X. Responses of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth and soil properties to conventional non-biodegradable and new biodegradable microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122897. [Google Scholar]

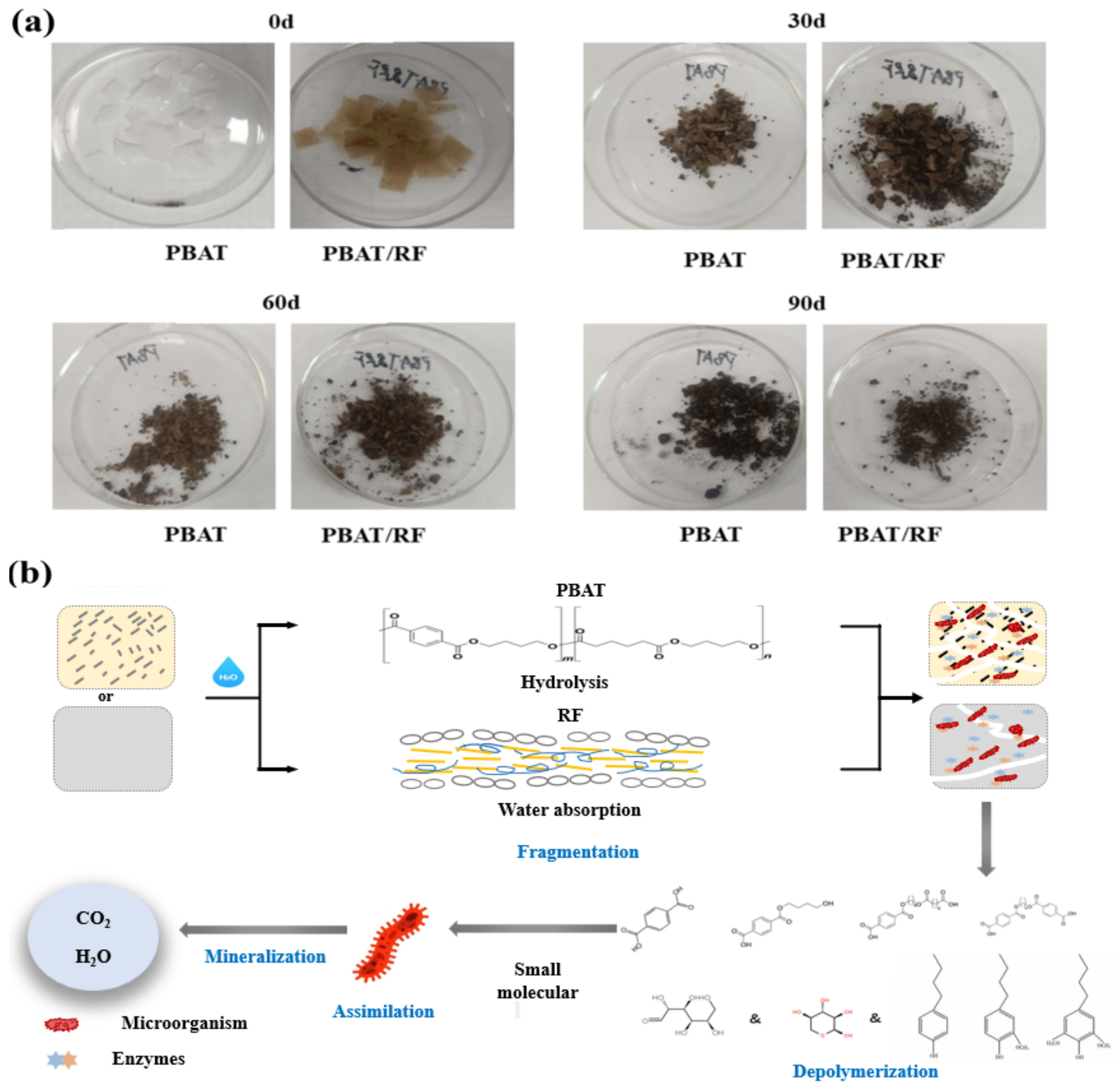
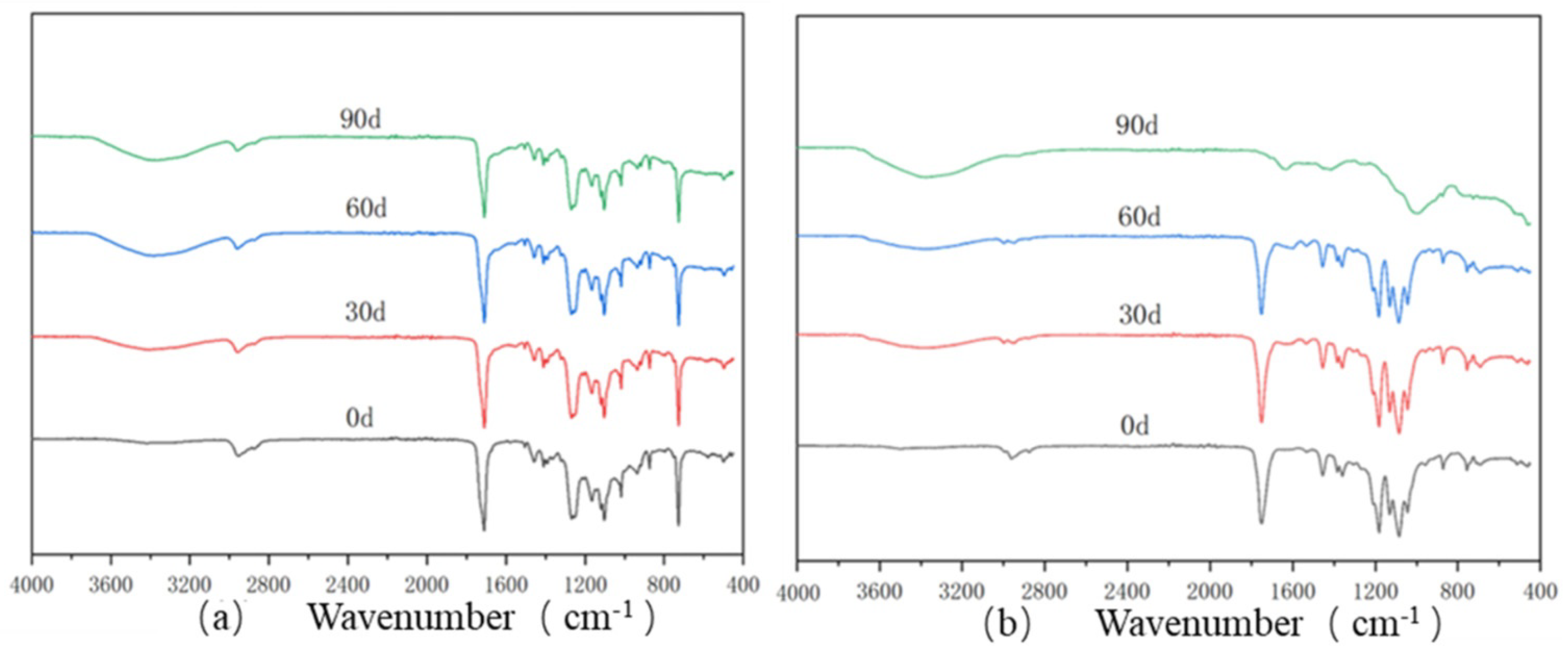
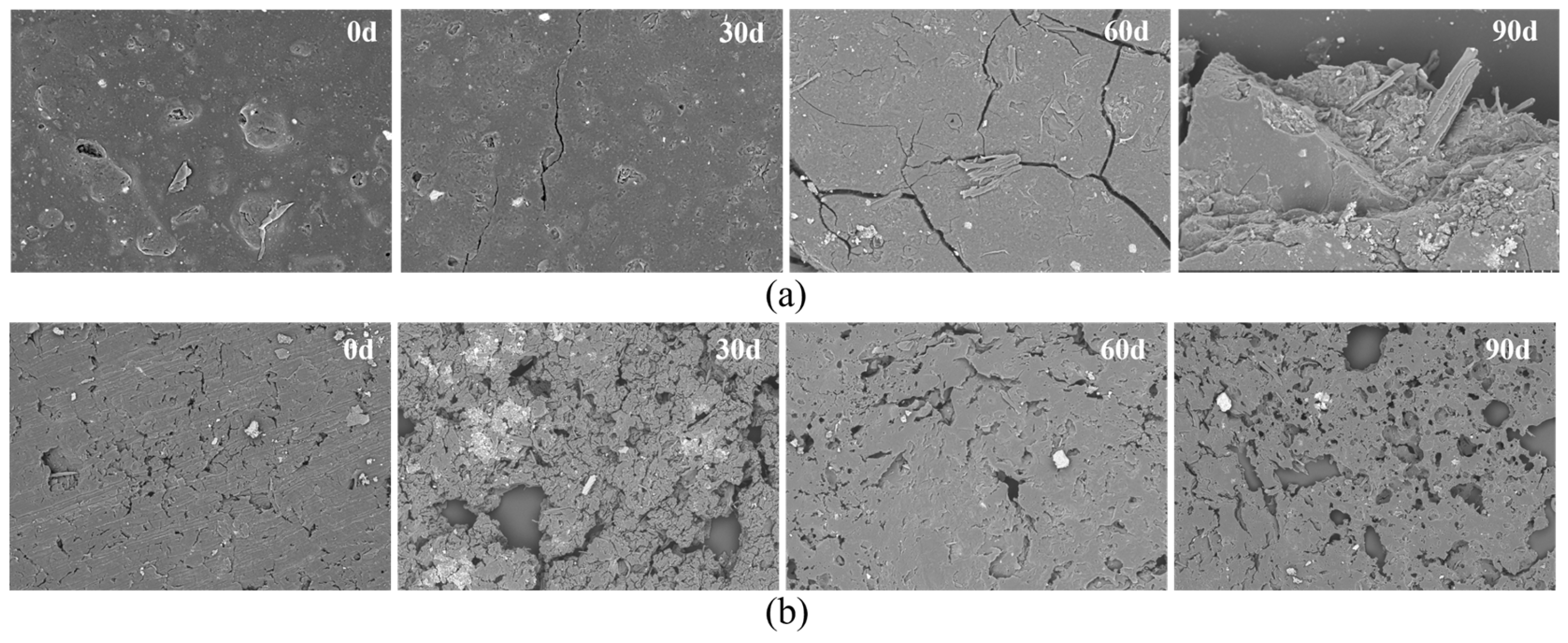
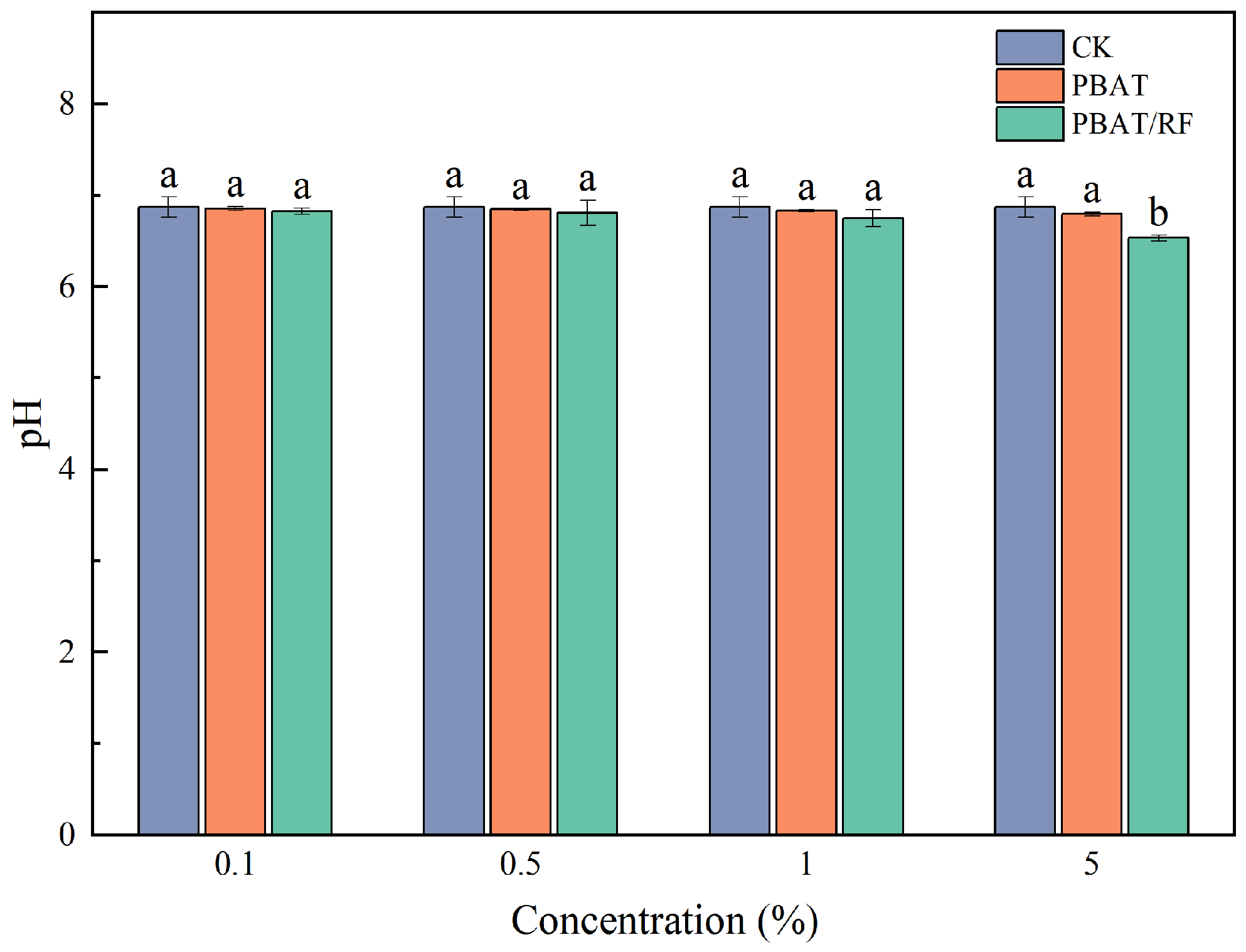
| Project | Type of Sample | Weight of Sample (g) | Weight of Compost (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | - | - | 300 |
| CEL | cellulose | 50 | 300 |
| RF | reed fibers | 50 | 300 |
| PBAT | PBAT | 50 | 300 |
| PBAT/RF | PBAT/RF | 50 | 300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xie, J. Degradation Characteristics of Reed-Based PBAT Mulch and Their Effects on Plant Growth and Soil Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071477
Wang Y, Zhang Q, Huang Y, Xu J, Xie J. Degradation Characteristics of Reed-Based PBAT Mulch and Their Effects on Plant Growth and Soil Properties. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071477
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yipeng, Qiuxia Zhang, Yinghao Huang, Jia Xu, and Jixing Xie. 2025. "Degradation Characteristics of Reed-Based PBAT Mulch and Their Effects on Plant Growth and Soil Properties" Materials 18, no. 7: 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071477
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, Q., Huang, Y., Xu, J., & Xie, J. (2025). Degradation Characteristics of Reed-Based PBAT Mulch and Their Effects on Plant Growth and Soil Properties. Materials, 18(7), 1477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071477






