Hot Deformation Behavior via Isothermal Compression and Constitutive Model of GH2132 Superalloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. True Stress-True Strain Curves
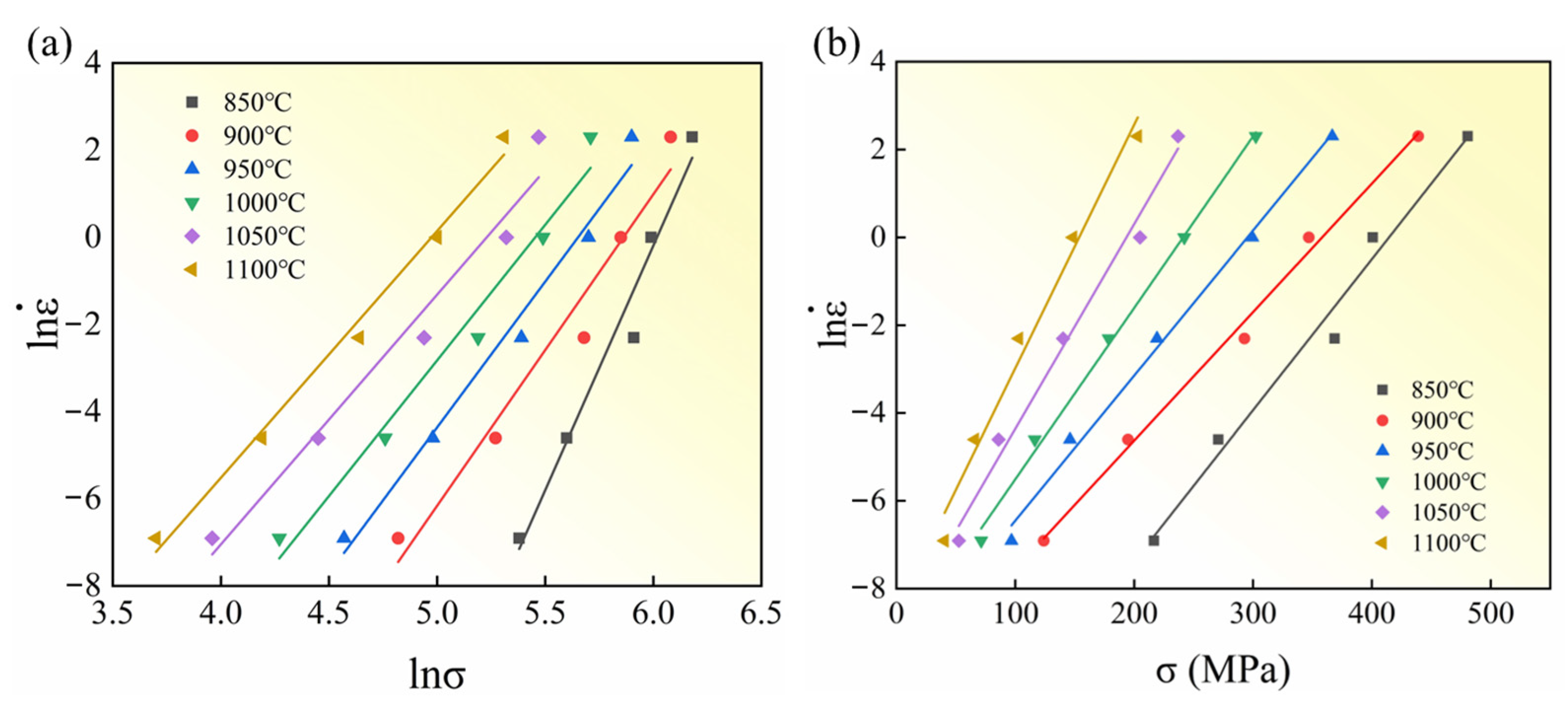
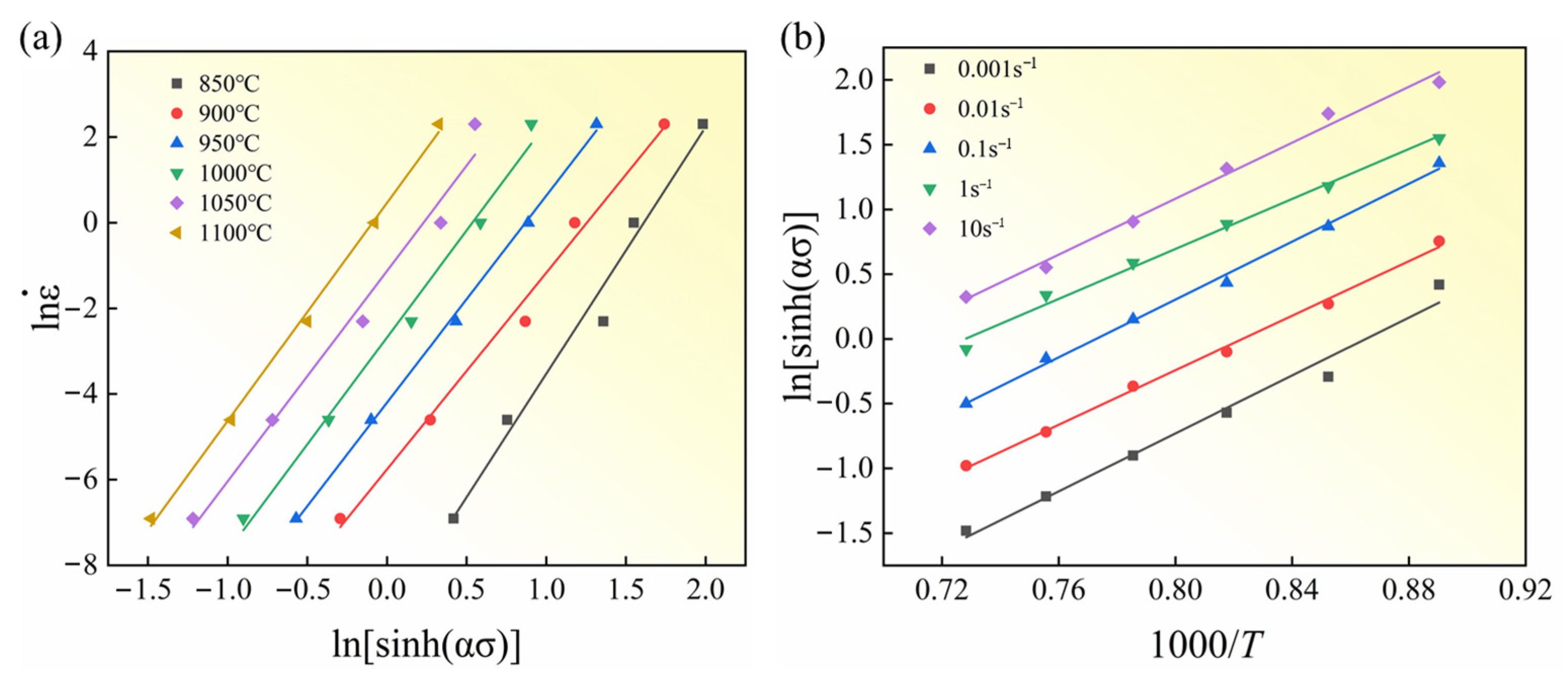
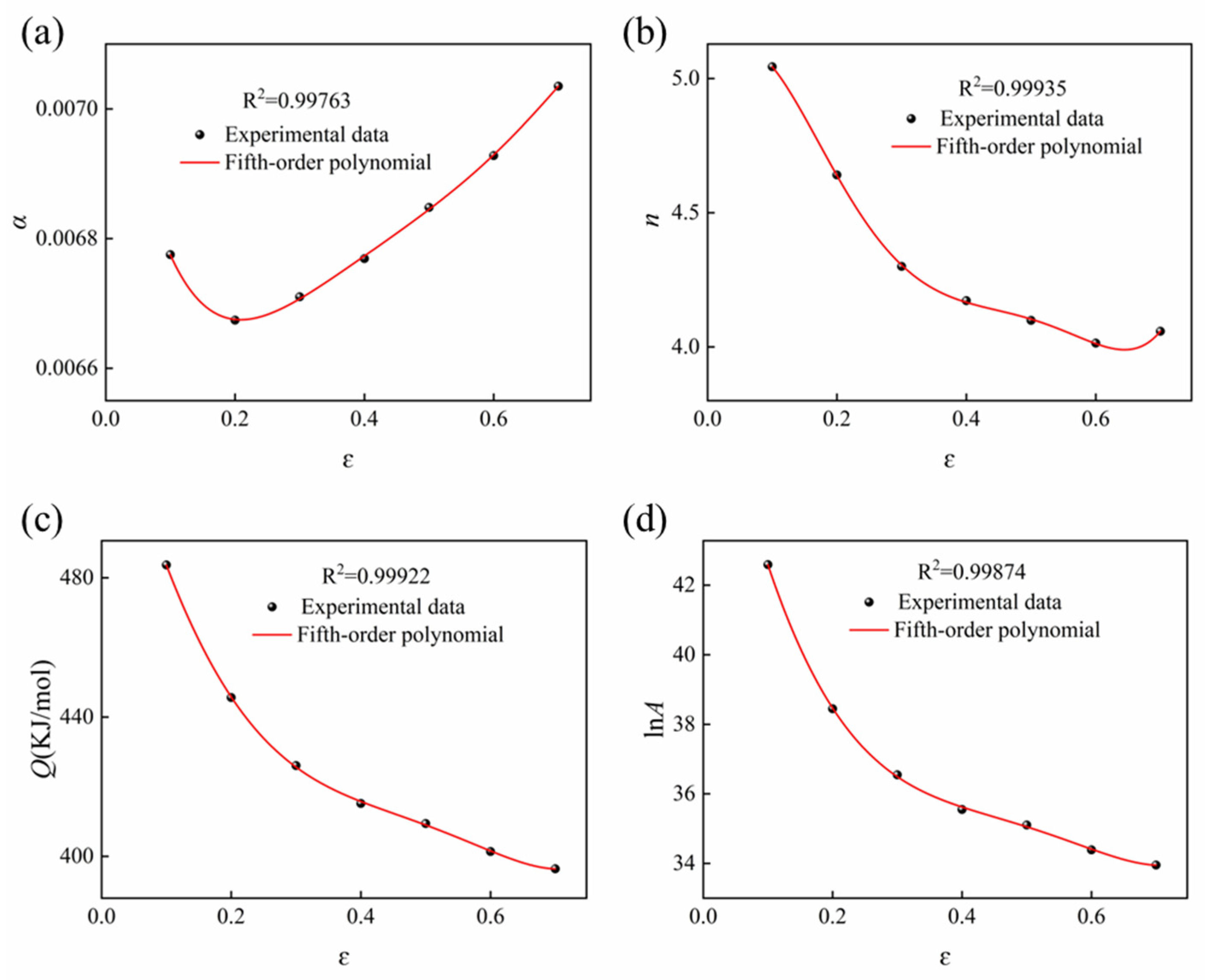
3.2. Constitutive Modeling
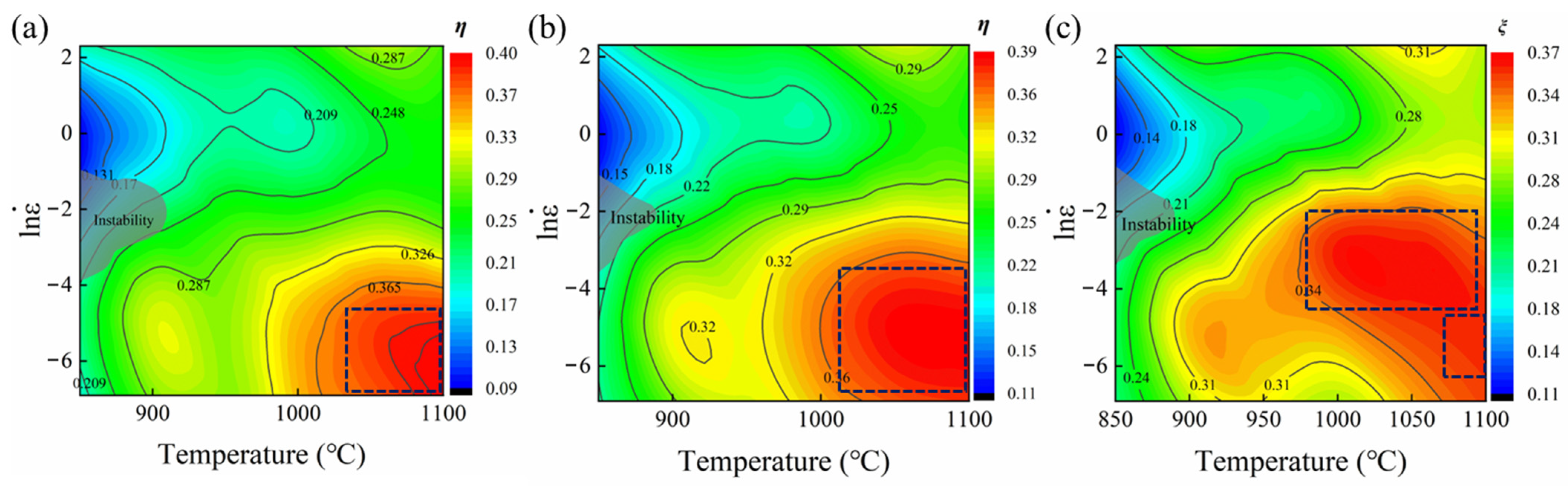
3.3. Hot Processing Map
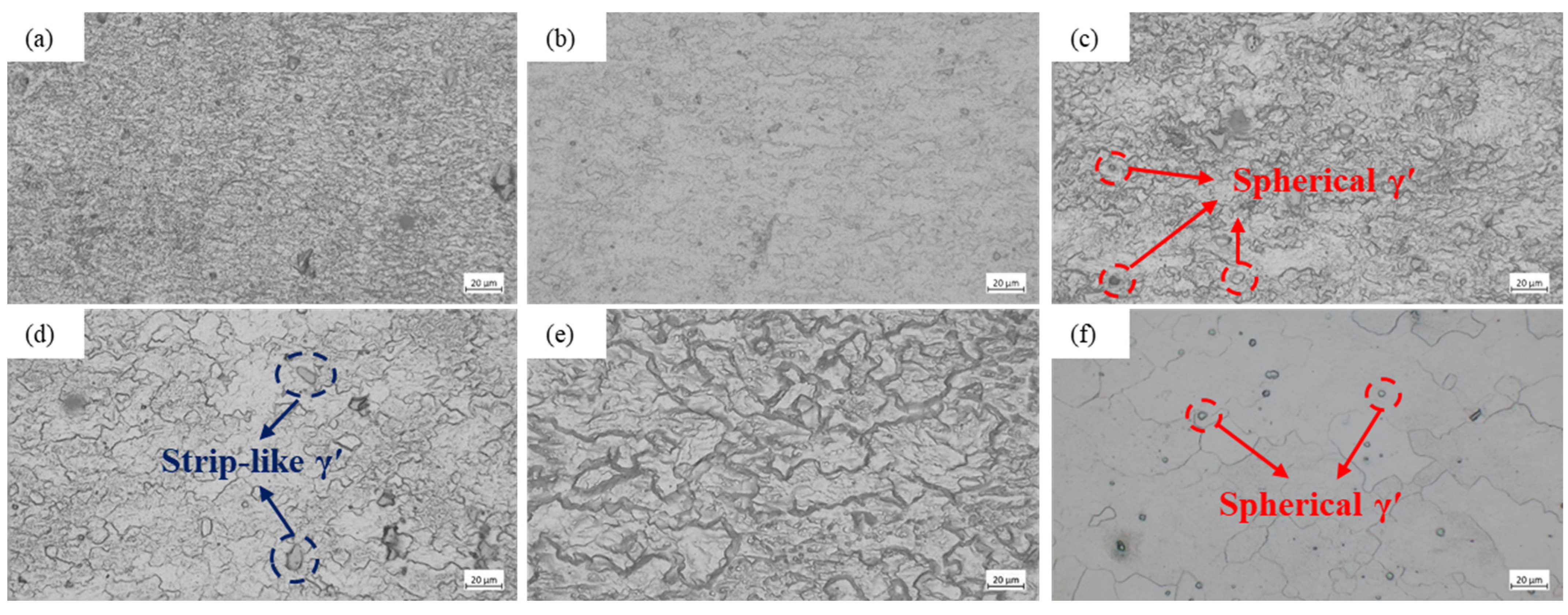
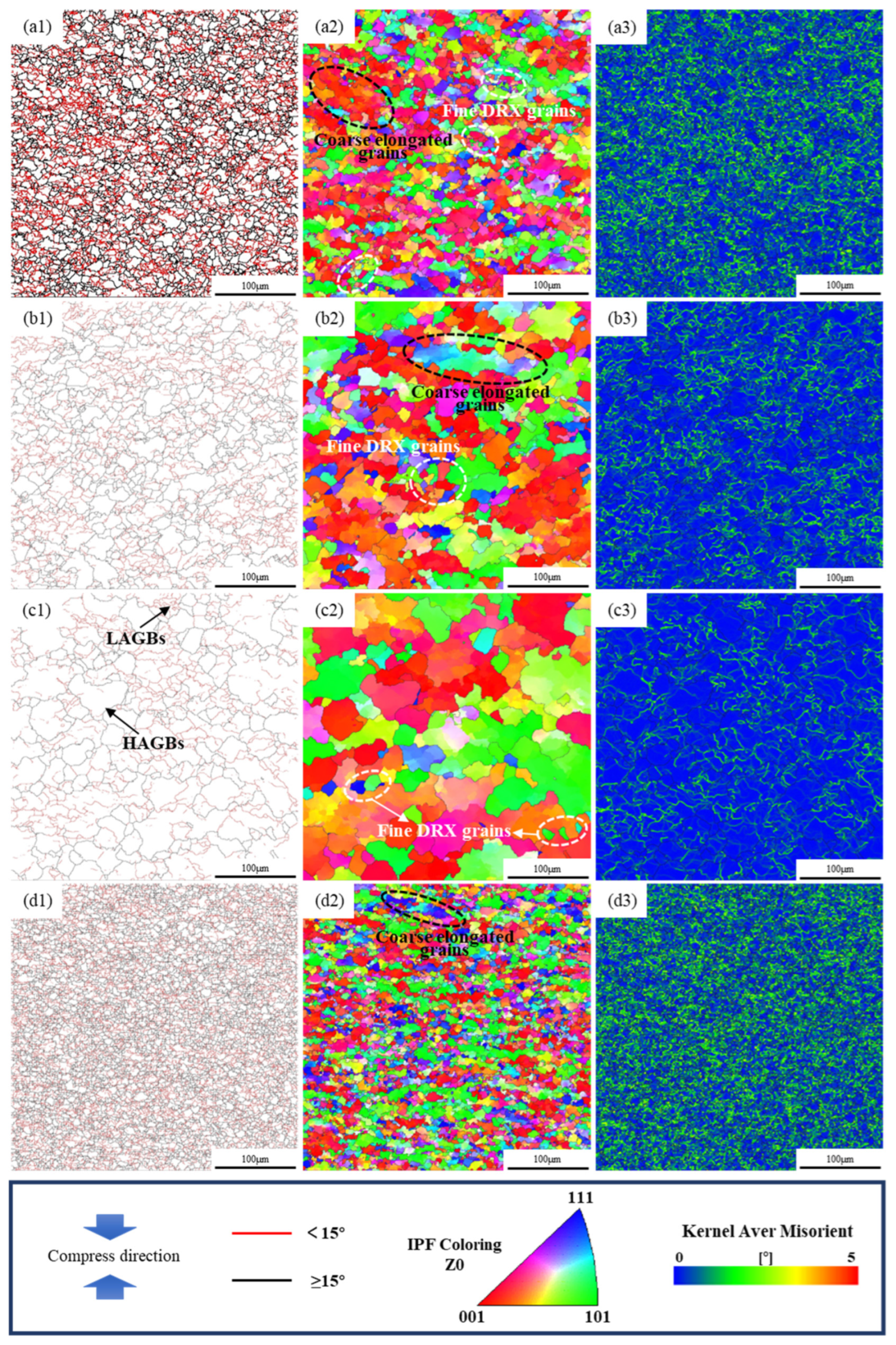
3.4. Microstructural Evolution Analysis
3.4.1. Metallographic Analysis
3.4.2. EBSD Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The peak stress of the GH2132 alloy was found to decrease significantly with increasing deformation temperature, while exhibiting a pronounced increase with rising strain rate under identical temperature conditions.
- (2)
- An average activation energy of 446.213 kJ/mol was obtained for the deformation of the GH2132 superalloy within the deformation temperature range of 850–1100 °C and strain rate range of 0.001–10 s−1. The R2 and AARE values of the Arrhenius constitutive model are 0.9916 and 3.86%, respectively.
- (3)
- The hot processing map of the GH2132 superalloy was constructed, and based on the Prasad flow instability criterion, the safe processing domain was identified within the deformation temperature range of 1000–1100 °C and strain rate range of 0.001–0.01 s−1.
- (4)
- Microstructural analysis confirmed that the dynamic softening mechanism of the GH2132 superalloy transitions from dynamic recovery to complete dynamic recrystallization with increasing temperature and decreasing strain rate. High temperatures and low strain rates promote full recrystallization and the formation of equiaxed grains, whereas higher strain rates favor the development of refined substructures and partially recrystallized microstructures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Qin, X.; Zhou, L. Microstructure, thermal stability and tensile properties of a Ni–Fe–Cr based superalloy with different Fe contents. Intermetallics 2023, 153, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Dong, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, Y. High-temperature oxidation behavior of Ni-Cr-W and Ni-Cr-Fe superalloys: A comparative study at 1000 °C. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1025, 180271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R. Corrosion aspects of Ni–Cr–Fe based and Ni–Cu based steam generator tube materials. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 393, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Gao, Y.; Gu, Y. Effects of long term thermal exposure on microstructure and mechanical property evolution of a new wrought Ni–Fe based superalloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 105, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh Babu, M.; Anandan, V.; Dinesh Babu, M. Analysis of turning on A286 alloy with different environmental conditions. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2024, 39, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.; Rong, L. Precipitate evolution and mechanical properties of Si-modified A286 alloy aged at 510 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 899, 146478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Li, H.; He, J.; Weng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Peng, J.; Zhu, M. Fretting wear behavior of GH2132 superalloy at different temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2025, 204, 110502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Machining performance of high energy die-sinking electrical discharge machining on GH2132. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2020, 35, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Huang, L.; Xu, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, W.; Tu, Q.; Pei, L.; Luo, J. Microstructure evolution and strengthening mechanisms of GH2132 bolts manufactured by electromagnetic induction heating-local forging. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 46, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaedi, Z.; Motallebi, R.; Mirzadeh, H. A review of hot deformation behavior and constitutive models to predict flow stress of high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-M.; Huang, L.; Li, C.-L.; Hui, S.-X.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, M.-J.; Guo, S.-Q.; Li, J.-J. Research progress on hot deformation behavior of high-strength β titanium alloy: Flow behavior and constitutive model. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 1434–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zhu, J. Constitutive modeling of hot deformation behavior of AlCrFeNi multi-component alloy. Vacuum 2022, 201, 111059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.; Zhang, R.; Cui, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X. Solidification segregation behavior and homogenization process of a difficult-to-deform Superalloy used at 850 °C. Crystals 2023, 13, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Gao, Z.; Liu, D. Continuous dynamic recrystallization nucleation mechanism and annealing twin evolution with respect to grain growth in a nickel-based superalloy. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zan, B.; Cai, J.; Wang, K.; Chen, X. Evolution of hot processing map and microstructure of as-forged nickel-based superalloy during hot deformation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 7638–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; He, Y.; Jia, H.; Li, B.; Fang, G. State-of-the-art review of the simulation of dynamic recrystallization. Metals 2024, 14, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qu, J. Hot deformation behavior and process parameters optimization of GH4738 nickel-based superalloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 7990–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, P.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhan, M. Microstructural evolution and mechanical behaviour in the hot deformation of GH3128 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Qi, Q.; Gong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.; Zhou, F.; Li, X. Research on hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution mechanism of GH4169 superalloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Tan, Y.; Bai, R.; Ning, L.; You, X.; Cui, C.; Li, P. Deformation and recrystallization behavior of the new Ni-Co based superalloy ingot material prepared by electron beam smelting layered solidification. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 934, 167880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Duan, R.; Hou, X.; Wang, C.; Lian, X.; Huang, S. Effect of Stabilization Treatment on the Microstructural Evolution and Tensile Properties of GH4706 Superalloy. Materials 2025, 18, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Qian, X.; Sun, K.; Xu, S.; Pan, R.; Miao, J.; Zeng, Y. The dynamic recrystallization and elevated-temperature work hardening behavior of Mg-Y-Sn alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1024, 180097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Hot deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization mechanism of Cu-Ni-Co-Si alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, W.; Hao, Z.; Zhan, C. Work hardening mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulation in cutting Ni–Fe–Cr series of Ni-based alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 153331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ding, H.; Zhao, W.; Huang, M.; Wei, D.; Jiang, Z. Modelling of the hot deformation behaviour of a titanium alloy using constitutive equations and artificial neural network. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 92, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, F. Hot deformation behavior and constitutive modeling of fine grained Inconel 718 superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 741, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, C.M.; McTegart, W.J. On the mechanism of hot deformation. Acta Metall. 1966, 14, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Lang, M.; Shi, L.; Li, M.; Zhou, T.; Bao, C.; Yang, M. Study on hot deformation behavior of homogenized Mg-8.5 Gd-4.5 Y-0.8 Zn-0.4 Zr alloy using a combination of strain-compensated Arrhenius constitutive model and finite element simulation method. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Sun, L.; Teng, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J. Constitutive model and microstructure evolution of Ti65 titanium alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Xiao, B.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K. Constitutive flow behavior and hot workability of powder metallurgy processed 20 vol.% SiCP/2024Al composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7865–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; He, X.; Tang, Z.; Dong, W.; Liu, Z.; Bao, H. Hot deformation behavior and hot working window of a solid solution strengthened Ni–Cr–Fe-based superalloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y. Processing maps: A status report. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.; Seshacharyulu, T. Processing maps for hot working of titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, S.N.; Nageswara Rao, B.; Kashyap, B. Instability criteria for hot deformation of materials. Int. Mater. Rev. 2000, 45, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, L.; Zhao, M.; Guo, S.; Su, Y.; Li, J. Characterization of hot workability of Ti-6Cr-5Mo-5V-4Al alloy based on hot processing map and microstructure evolution. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 905, 164161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Qian, C.; Huang, S.; Xiao, H. Investigation of deformation behavior, microstructure evolution, and hot processing map of a new near-α Ti alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ouyang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chu, C. Hot deformation behaviors and dynamic softening mechanism of 6% Si high-silicon austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 4263–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Song, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zong, Y. Hot deformation behavior and processing maps of BG801 bearing steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 3725–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Han, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Cao, X. Dynamic recrystallization behavior of single-phase BCC structure AlFeCoNiMo0. 2 high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 4376–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Yuan, H.; Guo, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M. Microstructure evolution and recrystallization temperature change of cold-rolled Fe–19Mn–0.6 C twinning-induced plasticity steel during annealing. Metals 2021, 11, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, H.; Abbasi, S.; Momeni, A.; Taheri, A.K. On the constitutive modeling and microstructural evolution of hot compressed A286 iron-base superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 564, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Kang, J.; Li, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, D.; Su, R.; You, B. Influence of Initial Elemental Microsegregation Severity in Controlling Dynamic Recrystallization Heterogeneity during Hot Deformation of High-Recycled-Ratio GH4169 Superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 945, 149012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Tang, Z.; He, X.; Jia, L.; Li, G.; He, J.; Wang, X. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of a novel as-forged Ni-based superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1024, 180195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.; Cao, L.; Liao, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q. Hot deformation and dynamic recrystallization in Al-Mg-Si alloy. Mater. Charact. 2021, 173, 110976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krbaťa, M.; Eckert, M.; Križan, D.; Barényi, I.; Mikušová, I. Hot deformation process analysis and modelling of X153CrMoV12 steel. Metals 2019, 9, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

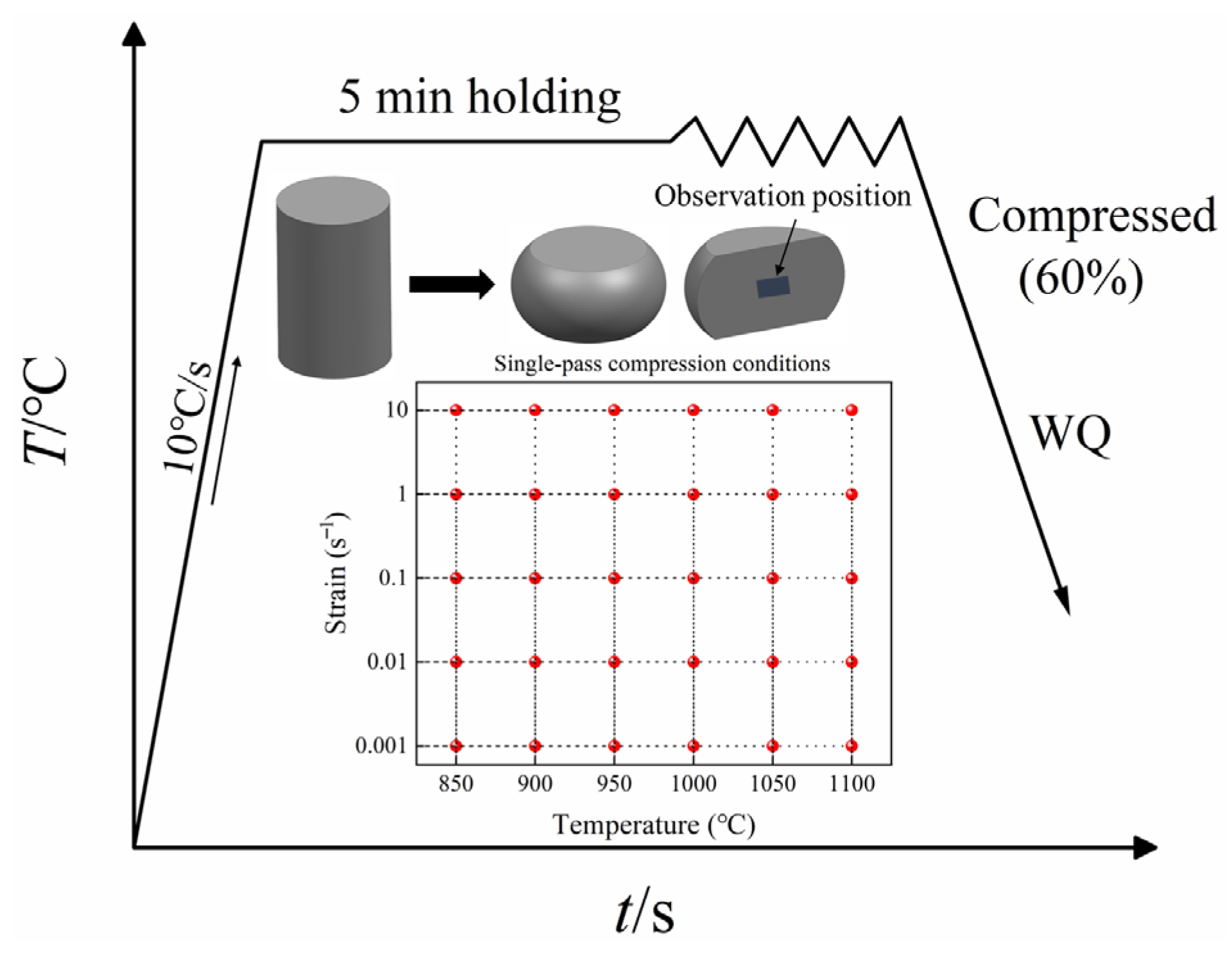





| Ni | Cr | Ti | Mn | Mo | V | Al | C | Si | B | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26.85 | 15.71 | 1.96 | 1.24 | 1.04 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.027 | 0.08 | 0.0092 | 0.004 | 0.002 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Cheng, P.; Wang, D.; Shao, C.; Cheng, L. Hot Deformation Behavior via Isothermal Compression and Constitutive Model of GH2132 Superalloy. Materials 2025, 18, 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245650
Sun Y, Cheng P, Wang D, Shao C, Cheng L. Hot Deformation Behavior via Isothermal Compression and Constitutive Model of GH2132 Superalloy. Materials. 2025; 18(24):5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245650
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yue, Peng Cheng, Decheng Wang, Chenxi Shao, and Lu Cheng. 2025. "Hot Deformation Behavior via Isothermal Compression and Constitutive Model of GH2132 Superalloy" Materials 18, no. 24: 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245650
APA StyleSun, Y., Cheng, P., Wang, D., Shao, C., & Cheng, L. (2025). Hot Deformation Behavior via Isothermal Compression and Constitutive Model of GH2132 Superalloy. Materials, 18(24), 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245650




