Preparation of Highly Uniform Silica Microspheres Recycled from Silicone Rubber and Their Application as Fillers in Epoxy Resin-Based Insulating Materials
Highlights
- What are the main findings?
- A stepwise pyrolysis and electrophoretic fractionation route converts waste silicone rubber into uniform SiO2 microspheres.
- Stepwise pyrolysis and electrophoretic fractionation enabled particle size control.
- Recycled SiO2 achieved comparable dielectric enhancement to commercial fillers.
- What is the implication of the main finding?
- Provides a high-value, waste-to-resource solution for non-degradable silicone rubber from power systems.
- Demonstrates the technical and economic feasibility of closed-loop recycling in the electrical industry.
- Contributes to sustainable material cycles and greener production in high-voltage insulation.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
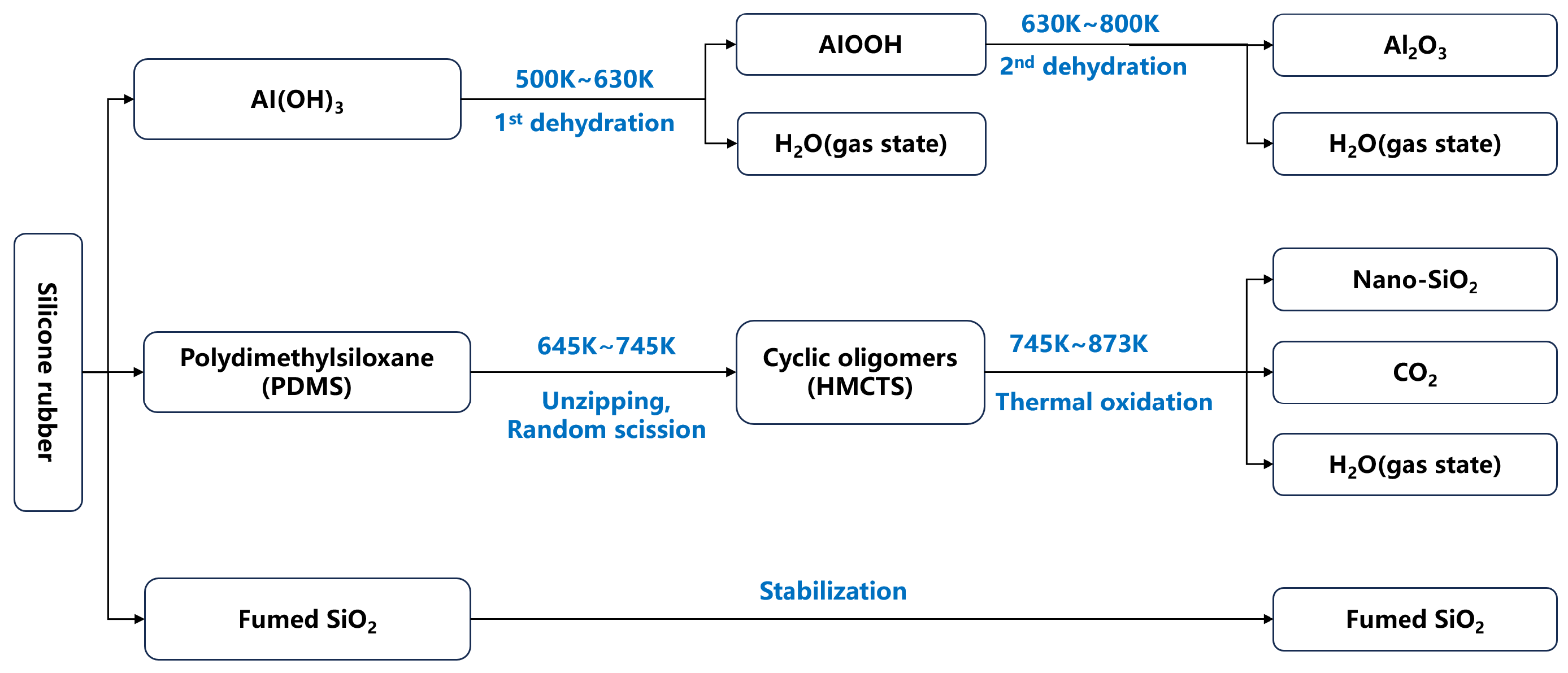
2.2. Chemical Mechanism of SiO2 Formation from Silicone Rubber
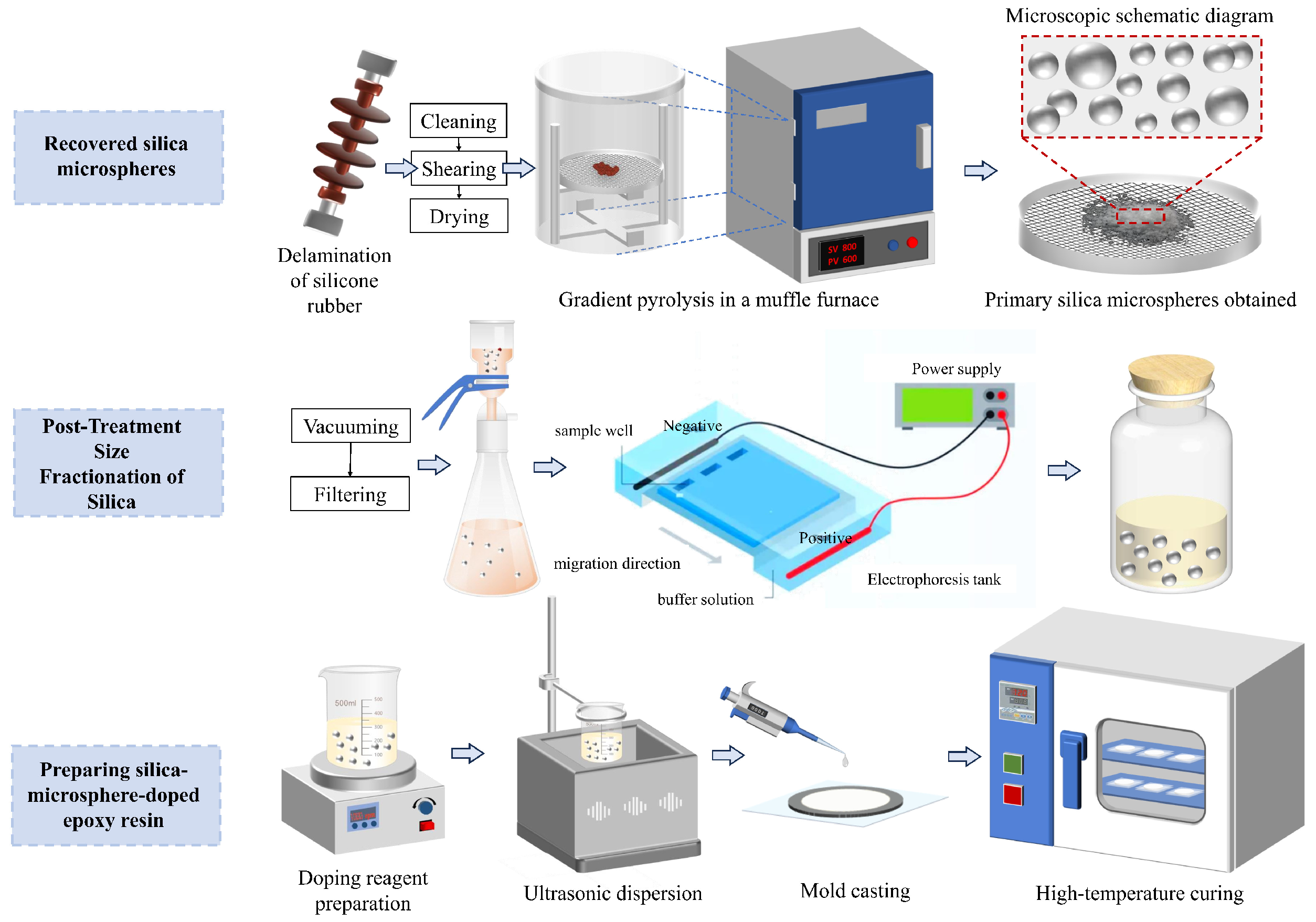
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.3.1. Pretreatment
2.3.2. Stepwise Pyrolysis
2.3.3. Glass Fiber Membrane Filtration
2.3.4. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis-Based Fractionation
2.3.5. Preparation of SiO2/EP Composites
2.4. Characterization Techniques
2.4.1. Microstructural Surface Morphology Analysis
2.4.2. Particle Size Distribution Analysis (DLS)
- D10 represents the particle size below which 10% of the particles are contained, reflecting the lower boundary of fine particles in the sample.
- D50, also known as the median diameter, indicates the particle size below which 50% of the particles are distributed and serves as a representative characteristic diameter.
- D90 refers to the particle size below which 90% of the particles fall, typically used to describe the upper boundary of coarse particles.
2.4.3. Gel Imaging System
2.4.4. Breakdown Voltage Test
2.4.5. Dielectric Property Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
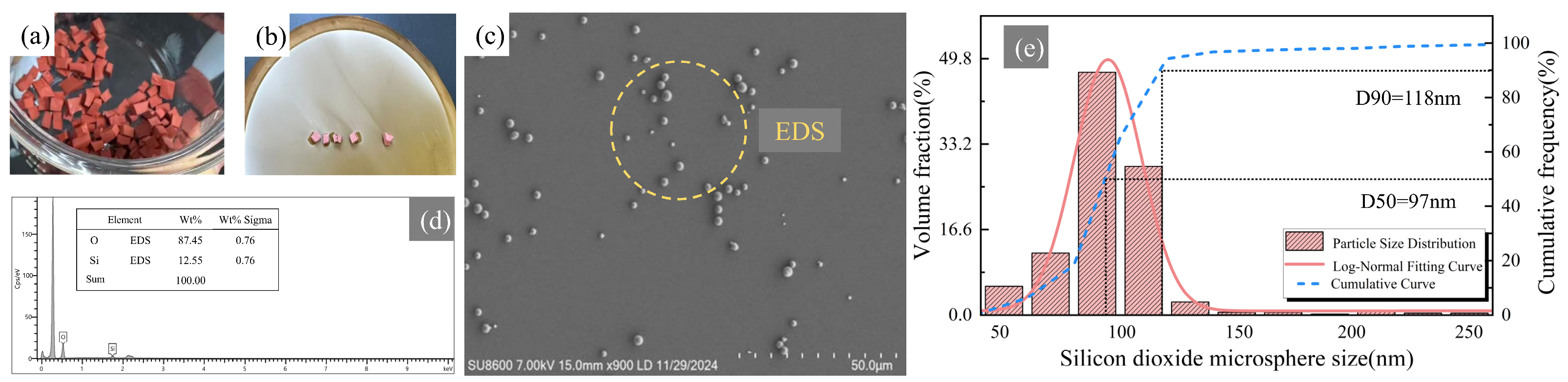
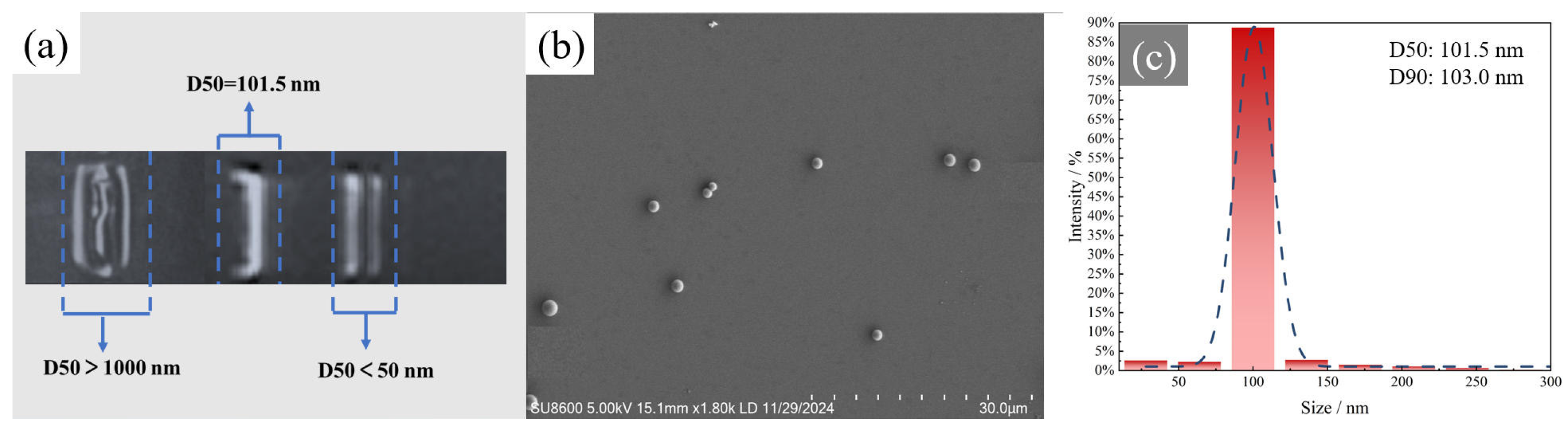
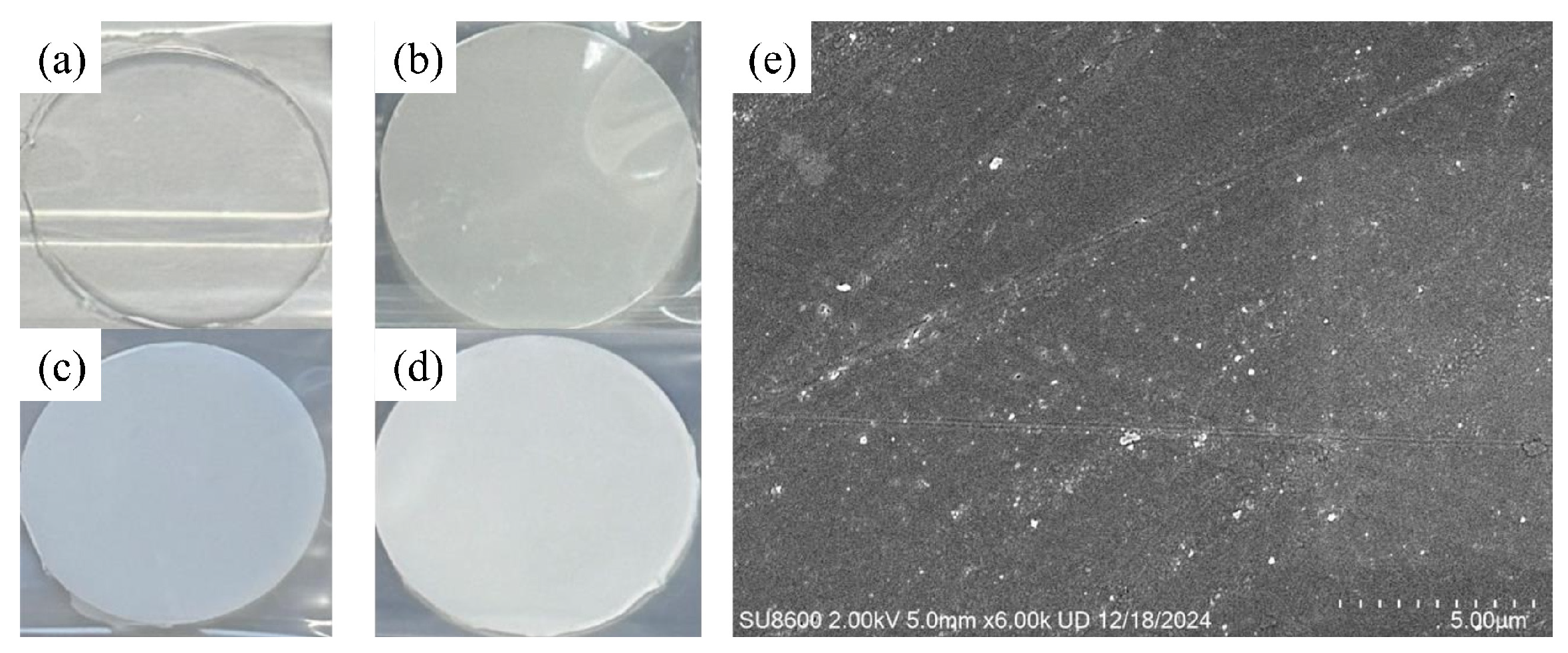
3.1. Microstructural Characterization of Recycled SiO2 Microspheres
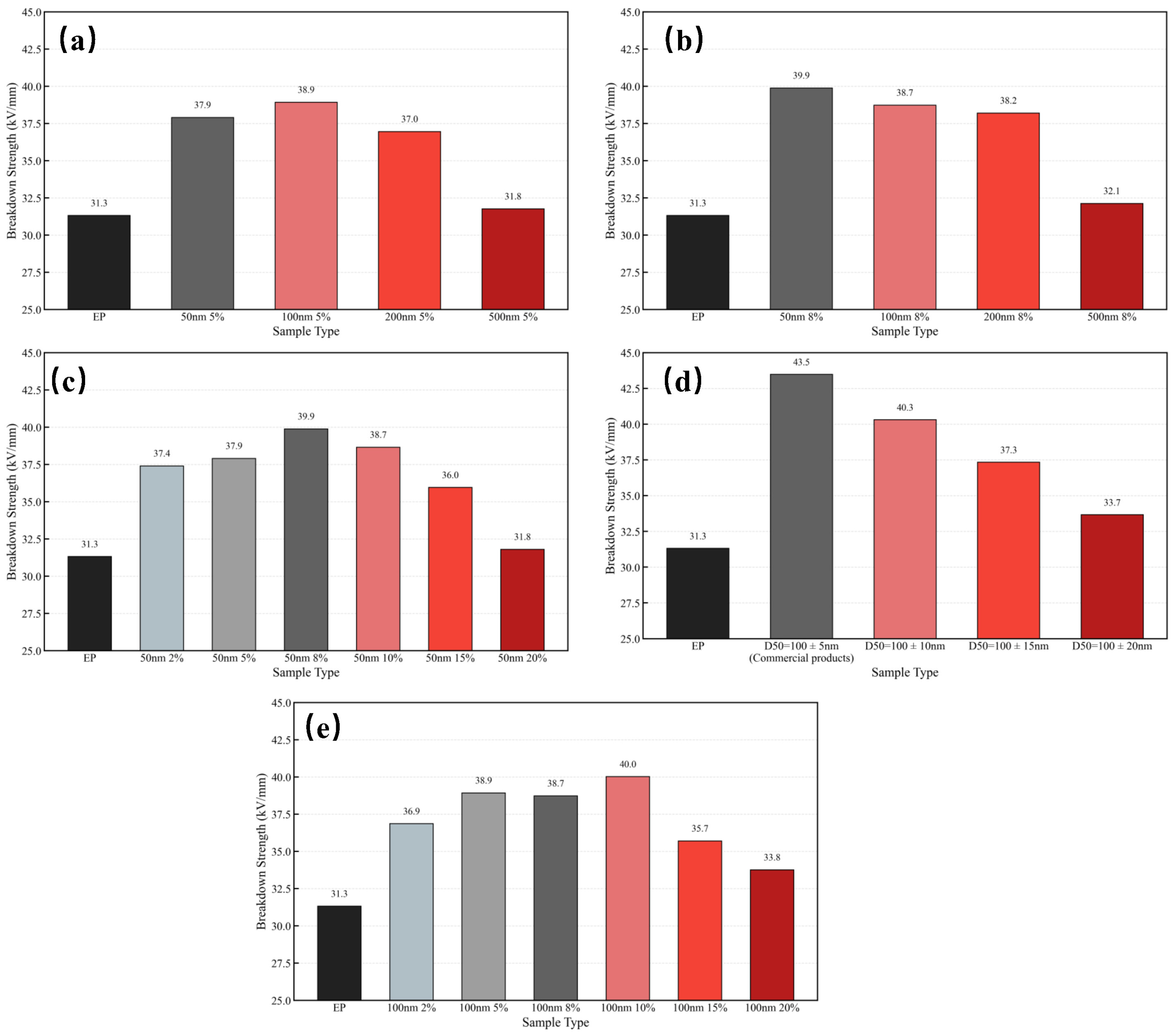
3.2. Breakdown Strength of SiO2/EP Composites
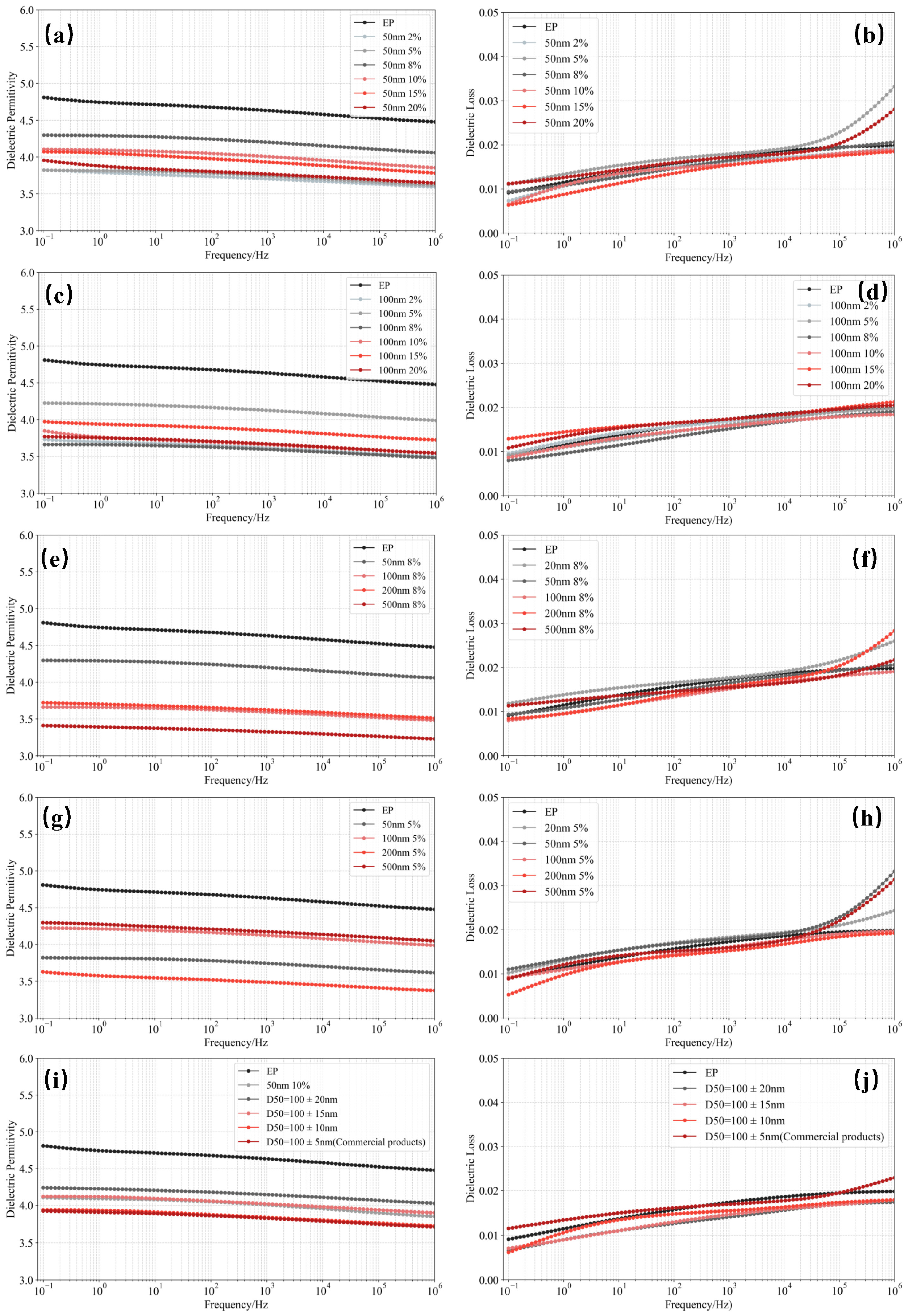
3.3. Dielectric Properties of SiO2/EP Composites
4. Conclusions
- Combined recovery + post-treatment route—By integrating stepwise pyrolysis with agarose gel electrophoresis, high-uniformity silica (SiO2) microspheres were successfully recovered from decommissioned composite insulator silicone rubber. The resulting microspheres exhibited regular smooth spherical morphology, achieved a uniformity of up to 90%, and their diameters were controllably tuned within the 50–500 nm range.
- Insulation performance enhancement in epoxy composites—The recycled SiO2 microspheres were incorporated into epoxy resin to prepare SiO2/EP composites with improved insulating properties. When the filler loading was optimized to 8–10 vol% and the particle size was either 50 nm or 100 nm, the breakdown strength increased from 31.3 kV/mm to 40 kV/mm, a rise of 27.5%. At the same time, at a given frequency, both dielectric constant and dielectric loss were reduced; the dielectric constant decreased by 8–21%, while the dielectric loss experienced only a modest increase at high frequencies.
- Comparable performance to commercial high-precision silica—Through comparative analysis of recycled and commercial nanosilica fillers in epoxy resin, the recycled SiO2 microspheres from silicone rubber demonstrated essentially equivalent capability in enhancing breakdown strength and improving dielectric properties. This confirms the feasibility of achieving high-value, economically beneficial recycling of silicone rubber from retired composite insulators.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, H.; Dong, R.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, W.; Qin, G.; Zhuang, Q.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, Z.; Zhang, Z. Resource Treatment and Green Recycling Application of Decommissioned Composite Insulators in Power Grids; State Grid Henan Electric Power Research Institute; Henan University of Technology; Henan Enpai Hi-Tech Group Co., Ltd.; Zhengzhou Xianghe Electric Equipment Co., Ltd.; Ningbo Institute of Technology, Zhejiang University; State Grid Kaifeng Power Supply Company: Zhengzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Hu, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Feasibility study on overall recycling and reuse of 220 kV decommissioned composite insulator core rods. Trans. China Electrotechnol. Soc. 2024, 39, 3433–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, D.; Yao, D. Analysis and prospect of China’s power system development for carbon peak and carbon neutrality targets. Proc. CSEE 2021, 41, 6245–6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Sun, K. New mission and challenges of distribution systems for carbon peak and carbon neutrality. Proc. CSEE 2022, 42, 6931–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Dong, W.; Lie, J.; Yang, M.; Cui, M.; Yang, D.; Yu, Q.; Liang, Y. Study on the resource utilization of decommissioned composite insulators. New Chem. Mater. 2019, 47, 240–241, 245. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, S. Rapid development of silicone rubber composite insulators in China. High Volt. Eng. 2016, 42, 2888–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, C. Effect of SiO Surface Modification on the Filler-Reinforced Interfaces in SiO-Filled Functional Styrene Butadiene Rubber Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, N.; Cao, L.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Highly Integrated Polysulfone/Polyacrylonitrile/Polyamide-6 Air Filter for Multilevel Physical Sieving Airborne Particles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29062–29072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D. Monomer Recovery and Nano-Silica Separation From Biodegraded Waste Silicone Rubber Shed of Composite Insulator. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 863731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabirova, A.; Florica, C.F.; Pisig, F.; Syed, A.; Buttner, U.; Li, X.; Nunes, S.P. Nanoporous Membrane Fabrication by Nanoimprint Lithography for Nanoparticle Sieving. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, O.; Mace, C.R.; Martinez, R.V.; Kumar, A.A.; Nie, Z.; Patton, M.R.; Whitesides, G.M. Separation of Nanoparticles in Aqueous Multiphase Systems through Centrifugation. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4060–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Liao, R.; Wang, T. Synthesis of High-purity Mesoporous Nanosilica Microspheres from Retired Composite Insulators Based on Orthogonal Experiment. High Volt. 2022, 7, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, D.; Wille, K. Stabilizing Dispersed Colloidal Nanosilica Exposed to an Ultra-High Performance Concrete Environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Sun, A.; Chu, C.; Yu, M.; Ma, S.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, J.; Xu, G. A Novel Silica Nanowire-Silica Composite Aerogels Dried at Ambient Pressure. Mater. Des. 2017, 115, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, M.R.; Pircheraghi, G.; Alinoori, A. Sustainable SBR/Silica Nanocomposites Prepared Using High-Quality Recycled Nanosilica from Lead-Acid Battery Separators. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xie, C.; Luo, S.; Gou, B.; Xu, H.; Zeng, L. The Influence Mechanism of Nanoparticles on the Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Resin. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19648–19656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Cui, J.; Ohki, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Tao, K. Dielectric and Relaxation Properties of Composites of Epoxy Resin and Hyperbranched-Polyester-Treated Nanosilica. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 30669–30677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, G.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Z. Dielectric and Thermal Properties of Epoxy Resins with TiO2 Nanowires. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 17871–17880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Fang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, L.; Liao, R. Study on the Non-Destructive Evaluation of Overall Particle Dispersion within Nanocomposites by Nonlinear Ultrasonic and Its Applicability. Powder Technol. 2025, 456, 120815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, L. Terahertz-Based Method for Accurate Characterization of Early Water Absorption Properties of Epoxy Resins and Rapid Detection of Water Absorption. Polymers 2021, 13, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Property | Recycled SiO2 (This Work) | Commercial SiO2 (100 nm) | Improvement/Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size | 50–500 nm (controlled) | 100 ± 5 nm | Comparable |
| Uniformity (D90–D10)/D50 | <5% after electrophoresis | 8–12% | Recycled microspheres have higher monodispersity |
| Sphericity | High | High | Similar |
| Breakdown strength (kV/mm) | 40 kV/mm at 10 vol% | 41–42 kV/mm | Nearly identical |
| Dielectric constant reduction | 8–21% | 10–23% | Comparable |
| Dielectric loss | stable | stable | Similar |
| Production cost | 50 CNY/kg | 1500–500,000 CNY/kg | Recycled microspheres are 30–10,000× cheaper |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Cheng, L.; Xu, W.; Liao, R. Preparation of Highly Uniform Silica Microspheres Recycled from Silicone Rubber and Their Application as Fillers in Epoxy Resin-Based Insulating Materials. Materials 2025, 18, 5647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245647
Chen Z, Cheng L, Xu W, Liao R. Preparation of Highly Uniform Silica Microspheres Recycled from Silicone Rubber and Their Application as Fillers in Epoxy Resin-Based Insulating Materials. Materials. 2025; 18(24):5647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245647
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhiling, Li Cheng, Wenlong Xu, and Ruijin Liao. 2025. "Preparation of Highly Uniform Silica Microspheres Recycled from Silicone Rubber and Their Application as Fillers in Epoxy Resin-Based Insulating Materials" Materials 18, no. 24: 5647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245647
APA StyleChen, Z., Cheng, L., Xu, W., & Liao, R. (2025). Preparation of Highly Uniform Silica Microspheres Recycled from Silicone Rubber and Their Application as Fillers in Epoxy Resin-Based Insulating Materials. Materials, 18(24), 5647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18245647






