Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Swelling: Integrating Constitutive Models with Sparse Experimental Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Governing Equations of Hydrogel Swelling
2.2. Physics-Informed Neural Network Framework
3. Results and Discussion
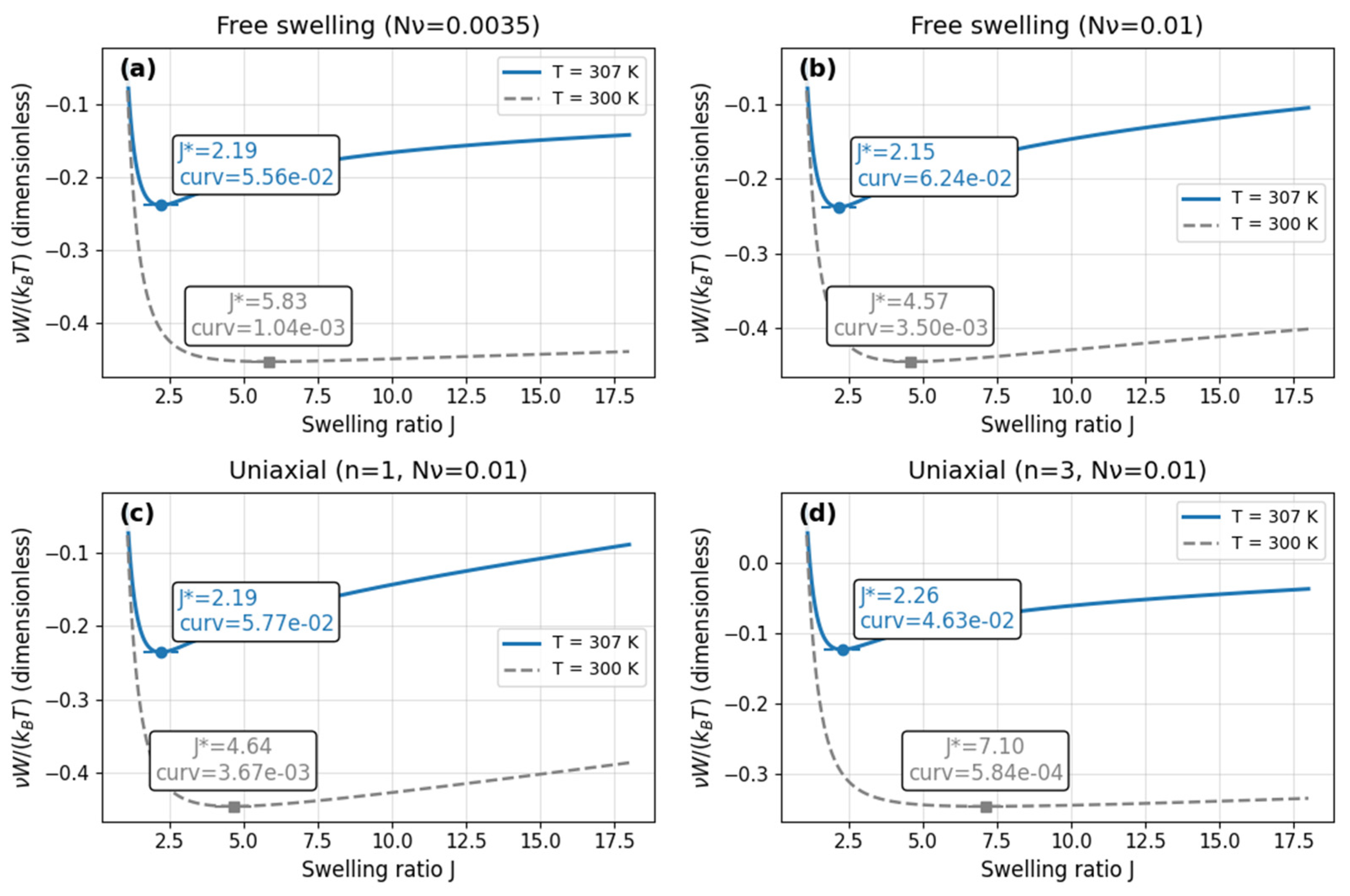
3.1. Energy Landscapes
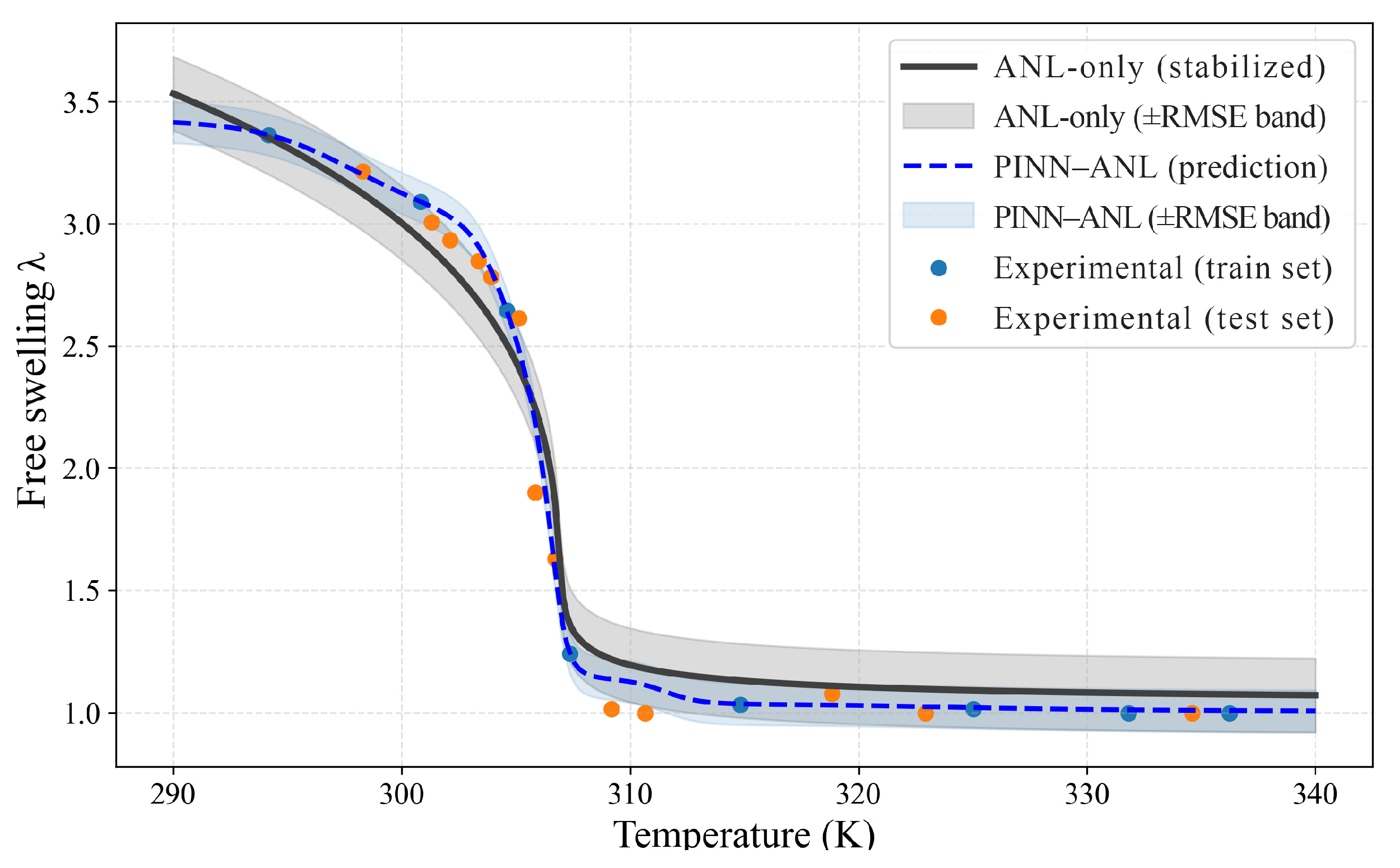
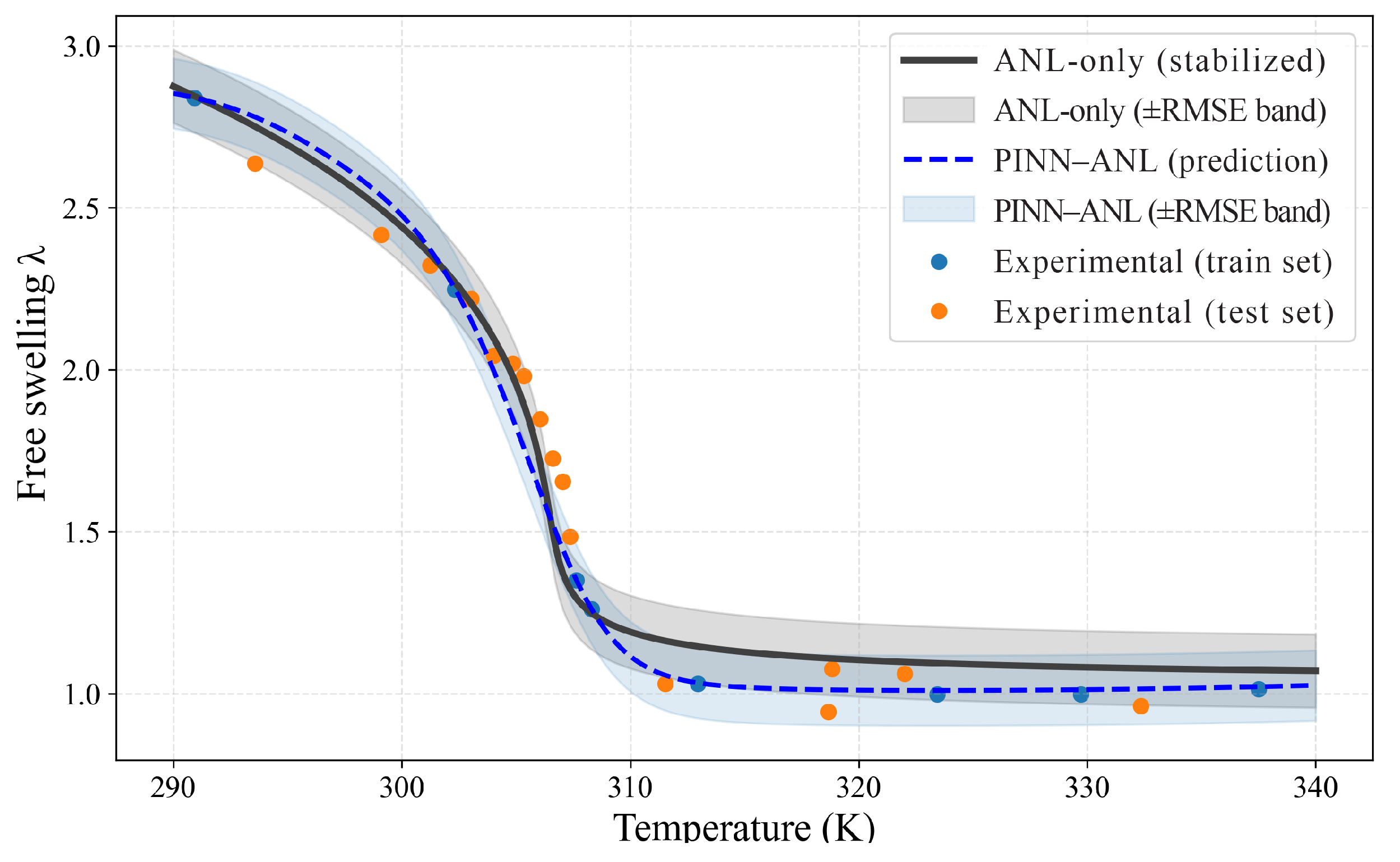
3.2. Free Swelling
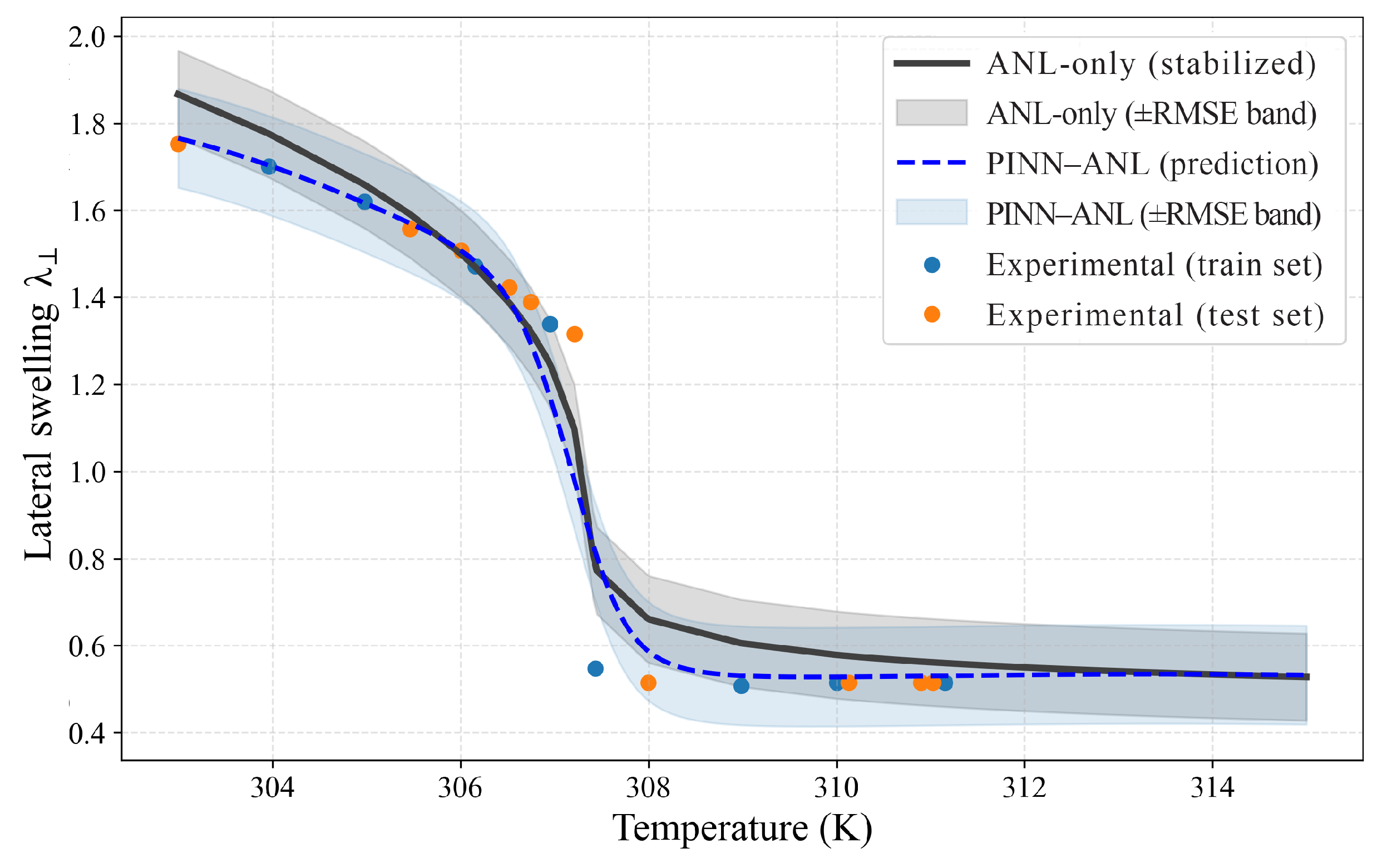
3.3. Constrained Swelling
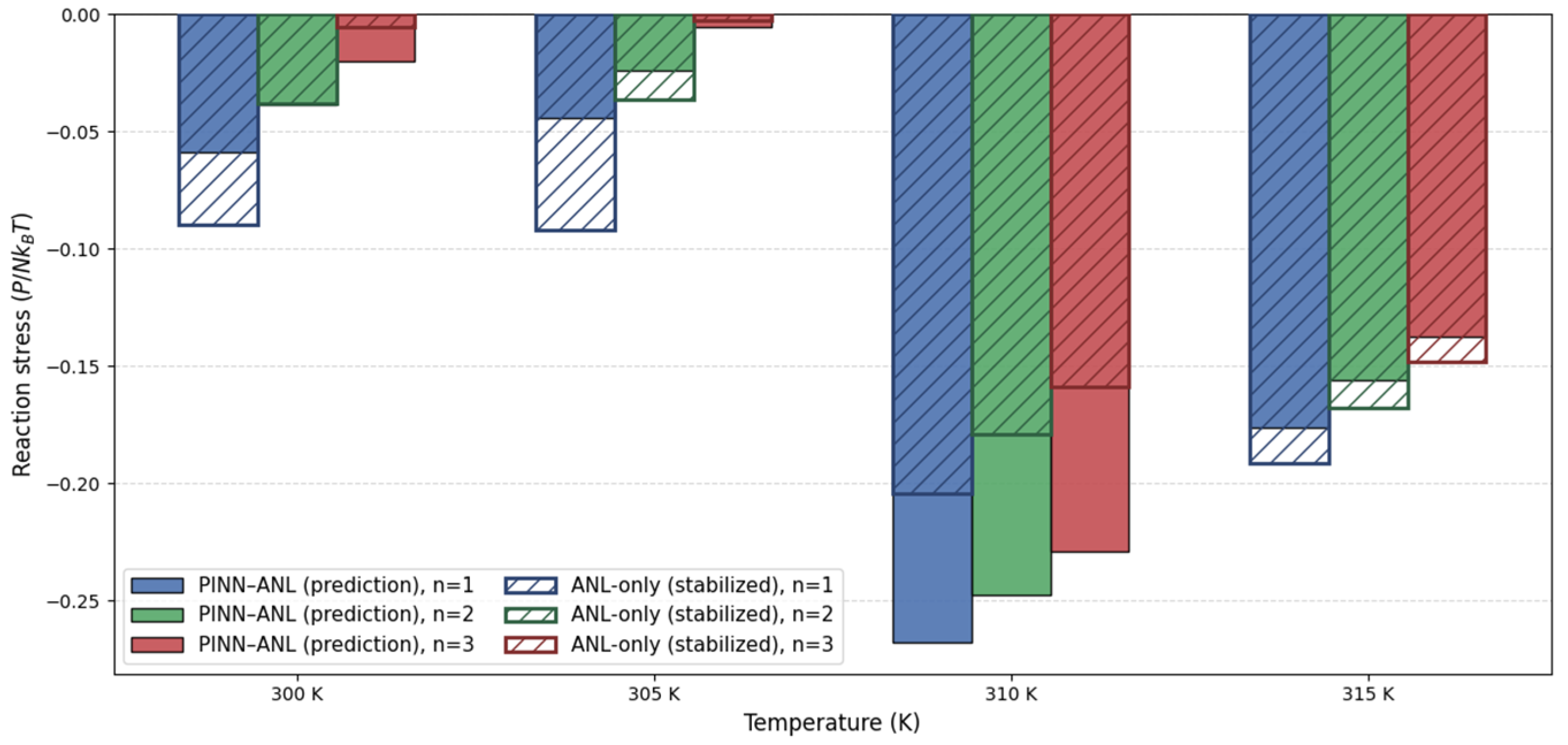
3.4. Reaction Stress Under Uniaxial Constraint
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PINN | Physics-informed neural network |
| ANL | Analytical (stabilized reference model) |
| GCT | Gel collapse temperature |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
| Dimensionless crosslink density (number of chains per reference volume × solvent molar volume) | |
| * | Equilibrium swelling ratio |
| Stretch ratio | |
| Constraint multiplier in uniaxial swelling | |
| Thermal energy (Boltzmann constant × temperature) | |
| ±RMSE band | Prediction interval based on one root mean square error |
References
- Kato, N.; Sakai, Y.; Shibata, S. Wide-Range Control of Deswelling Time for Thermosensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Gel Treated by Freeze-Drying. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 961–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, E.; Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H. Upper or lower critical solution temperature, or both? Studies on cationic copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3074–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavagnacco, L.; Zaccarelli, E.; Chiessi, E. Modeling Solution Behavior of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): A Comparison between Water Models. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 3778–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, Y.; Inui, T.; Namioka, R.; Uchihashi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Suzuki, D. Clarification of Surface Deswelling of Thermoresponsive Microgels by Electrophoresis. Langmuir 2022, 38, 16084–16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Yang, J.; Song, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, B.; Yang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. A motion-responsive injectable lubricative hydrogel for efficient Achilles tendon adhesion prevention. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 30, 101458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nie, C.; Wang, Z.; Lan, F.; Wan, L.; Li, A.; Zheng, P.; Zhu, W.; Pan, Q. A spatial confinement biological heterogeneous cascade nanozyme composite hydrogel combined with nitric oxide gas therapy for enhanced treatment of psoriasis and diabetic wound. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, R.; Wang, Q. Bioinspired Flexible Kevlar/Hydrogel Composites with Antipuncture and Strain-Sensing Properties for Personal Protective Equipment. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 2024, 16, 45473–45486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Zeng, B.; Deng, Z.; Shao, L. “Double-sided protector” Janus hydrogels for skin and mucosal wound repair: Applications, mechanisms, and prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Song, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, J.-L.; Li, J. Injectable Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Formed by Alginate-g-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) That Releases Doxorubicin-Encapsulated Micelles as a Smart Drug Delivery System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35673–35682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.J.; Rajendran, R.R.; Mohanto, S.; Agarwal, U.; Panda, K.; Dhotre, K.; Manne, R.; Deepak, A.; Zafar, A.; Yasir, M.; et al. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Gels 2022, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Gosecka, M.; Bodaghi, M.; Crespy, D.; Youssef, G.; Dodda, J.M.; Wong, S.H.D.; Imran, A.B.; Gosecki, M.; Jobdeedamrong, A.; et al. Engineering multifunctional dynamic hydrogel for biomedical and tissue regenerative applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Tang, X.S.; Margel, S. Superparamagnetic Amine-Functionalized Maghemite Nanoparticles as a Thixotropy Promoter for Hydrogels and Magnetic Field-Driven Diffusion-Controlled Drug Release. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 5272–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Xu, X.; Zhu, J.; Bai, B.; Wang, Q.; Shi, W.; Li, J. Humidity capture and solar-driven water collection behaviors of alginate-g-PNIPAm-based hydrogel. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cai, T.; Shao, C.; Xiao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, Y. MXene-Based Responsive Hydrogels and Applications in Wound Healing. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202402073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, D.; Yu, H. A Cellulose Ionogel with Rubber-Like Stretchability for Low-Grade Heat Harvesting. Research 2024, 7, 0533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Akther, N.; Duan, X.; Peng, S.; Onggowarsito, C.; Mao, S.; Fu, Q.; Kolev, S.D. Recent Development of Atmospheric Water Harvesting Materials: A Review. ACS Mater. Au 2022, 2, 576–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Sakikawa, N.; Miyata, T. Thermo-responsive gels that absorb moisture and ooze water. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Q.; Gao, K.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Z.-Z. Super-Hygroscopic Calcium Chloride/Graphene Oxide/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Gels for Spontaneous Harvesting of Atmospheric Water and Solar-Driven Water Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 33881–33891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari-Sedeh, M.; Baghani, M. pH-Sensitive Hydrogel Bilayers: Investigation on Transient Swelling-Induced Bending through Analytical and FEM Approaches. Gels 2023, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Cappelleri, D.J. Responsive Hydrogel-Based Modular Microrobots for Multi-Functional Micromanipulation. Small 2024, 20, 2404311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Díaz, A.; Vázquez, A.S.; Vázquez, E. Hydrogels in Soft Robotics: Past, Present, and Future. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 20817–20826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-Z.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Wang, F.-J.; Chung, T.-S. Thermosensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) Hydrogels with Expanded Network Structures and Improved Oscillating Swelling−Deswelling Properties. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Fast and opposite temperature responsivity in release behavior of cocontinuous hydrogel composites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 104, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetting, M.C.; Peters, J.T.; Steichen, S.D.; Peppas, N.A. Stimulus-responsive hydrogels: Theory, modern advances, and applications. Mater Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2015, 93, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L. Recent advancements in hydrogels as novel tissue engineering scaffolds for dental pulp regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Zheng, J.; Fan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, Y. Multifunctional DNA hydrogels with light-triggered gas-therapy and controlled G-Exos release for infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 52, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Fu, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, R.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, J. Smart hydrogel: A new platform for cancer therapy. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 340, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osváth, Z.; Tóth, T.; Iván, B. Sustained Drug Release by Thermoresponsive Sol–Gel Hybrid Hydrogels of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide-co-3-(Trimethoxysilyl)Propyl Methacrylate) Copolymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1600724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Suo, Z. A theory of coupled diffusion and large deformation in polymeric gels. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Suo, Z. Mechanics and chemical thermodynamics of phase transition in temperature-sensitive hydrogels. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2011, 59, 2259–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri, H.; Baghani, M.; Naghdabadi, R. Inhomogeneous and homogeneous swelling behavior of temperature-sensitive poly-(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 27, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Anitescu, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Rabczuk, T. Transfer learning enhanced physics informed neural network for phase-field modeling of fracture. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2020, 106, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, J.; Kong, X.; Deng, L. Multi-level physics informed deep learning for solving partial differential equations in computational structural mechanics. Commun. Eng. 2024, 3, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Zhang, E.; Bazilevs, Y.; Srivastava, V. Modeling finite-strain plasticity using physics-informed neural network and assessment of the network performance. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2023, 172, 105177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.; Cho, M.; Chung, H.; Kim, D.-N. Data-driven nonparametric identification of material behavior based on physics-informed neural network with full-field data. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 418, 116569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jin, H. Identifying constitutive parameters for complex hyperelastic materials using physics-informed neural networks. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 5915–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, C.M.; Long, K.N.; Kramer, S.L.B. Calibrating constitutive models with full-field data via physics informed neural networks. Strain 2023, 59, e12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.A.; Askari-Sedeh, M.; Zolfagharian, A.; Baghani, M. Enhancing hydrogel predictive modeling: An augmented neural network approach for swelling dynamics in pH-responsive hydrogels. Appl. Math. Mech. 2025, 46, 1787–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karniadakis, G.E.; Kevrekidis, I.G.; Lu, L.; Perdikaris, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, L. Physics-informed machine learning. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 422–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Sanda, K.; Omori, Y. Phase transition in strongly stretched polymer gels. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 5179–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Ishii, T. Phase coexistence of neutral polymer gels under mechanical constraint. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.S.; Oh, J.S.; Choi, H.S.; Bae, Y.C. Effect of Cross-Linking Density on Swelling Behavior of NIPA Gel Particles. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 7328–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtin, M.E.; Fried, E.; Anand, L. The Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Continua; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gwinner, J. Non-linear elastic deformations. Acta Appl. Math. 1988, 11, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, S.A.; Anand, L. A coupled theory of fluid permeation and large deformations for elastomeric materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2010, 58, 1879–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroze, F.; Nies, E.; Berghmans, H. Phase transitions in the system poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/water and swelling behaviour of the corresponding networks. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 554, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yoshikawa, S.; Bai, G. Shrinking pattern and phase transition velocity of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari-Sedeh, M.; Faraji, M.; Baniardalan, M.; Choi, E.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Baghani, M. Physics-Informed Neural Network Modeling of Inflating Dielectric Elastomer Tubes for Energy Harvesting Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keener, J.P.; Sircar, S.; Fogelson, A.L. Influence of the standard free energy on swelling kinetics of gels. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin Soft Matter. Phys. 2011, 83, 041802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriyev, M.S.; Chang, Y.-W.; Goldbart, P.M.; Fernández-Nieves, A. Swelling thermodynamics and phase transitions of polymer gels. Nano Futures 2019, 3, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tanaka, T. Phase Transitions of Gels. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 1992, 22, 243–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Quantity | Free Swelling | Uniaxial Swelling | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature-independent component of χ | |||
| Temperature-dependent component of χ | |||
| Volume-fraction dependent component of χ | |||
| Temperature-dependent component of χ via volume fraction | |||
| Reference stretch | Baseline longitudinal stretch used in uniaxial swelling |
| Loss-Term Weight 1 | Free Swelling | Uniaxial Swelling | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physics residual weight | Contribution of equilibrium residuals | ||
| Monotonicity penalty weight | Penalizes non-contractile response with temperature | ||
| Value prior weight | Regularizes deviation from baseline stretch outside GCT | ||
| Slope prior weight | inside GCT) | Regularizes slope relative to baseline outside GCT | |
| Data loss weight (final target) | (ramped) | (ramped) | Weight applied to Huber misfit against experiments |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takmili, S.A.; Choi, E.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Baghani, M. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Swelling: Integrating Constitutive Models with Sparse Experimental Data. Materials 2025, 18, 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235401
Takmili SA, Choi E, Ostadrahimi A, Baghani M. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Swelling: Integrating Constitutive Models with Sparse Experimental Data. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235401
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakmili, Seyed Amirmasoud, Eunsoo Choi, Alireza Ostadrahimi, and Mostafa Baghani. 2025. "Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Swelling: Integrating Constitutive Models with Sparse Experimental Data" Materials 18, no. 23: 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235401
APA StyleTakmili, S. A., Choi, E., Ostadrahimi, A., & Baghani, M. (2025). Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Swelling: Integrating Constitutive Models with Sparse Experimental Data. Materials, 18(23), 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235401









