Thermoregulatory Performance and Thermal Comfort Analysis of Phase-Change Fiber Seamless Knitted Fabrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Yarn Selection
2.1.2. Fabric Structure Design
2.1.3. Establishment of the Sample Scheme
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. DSC Testing and Analysis
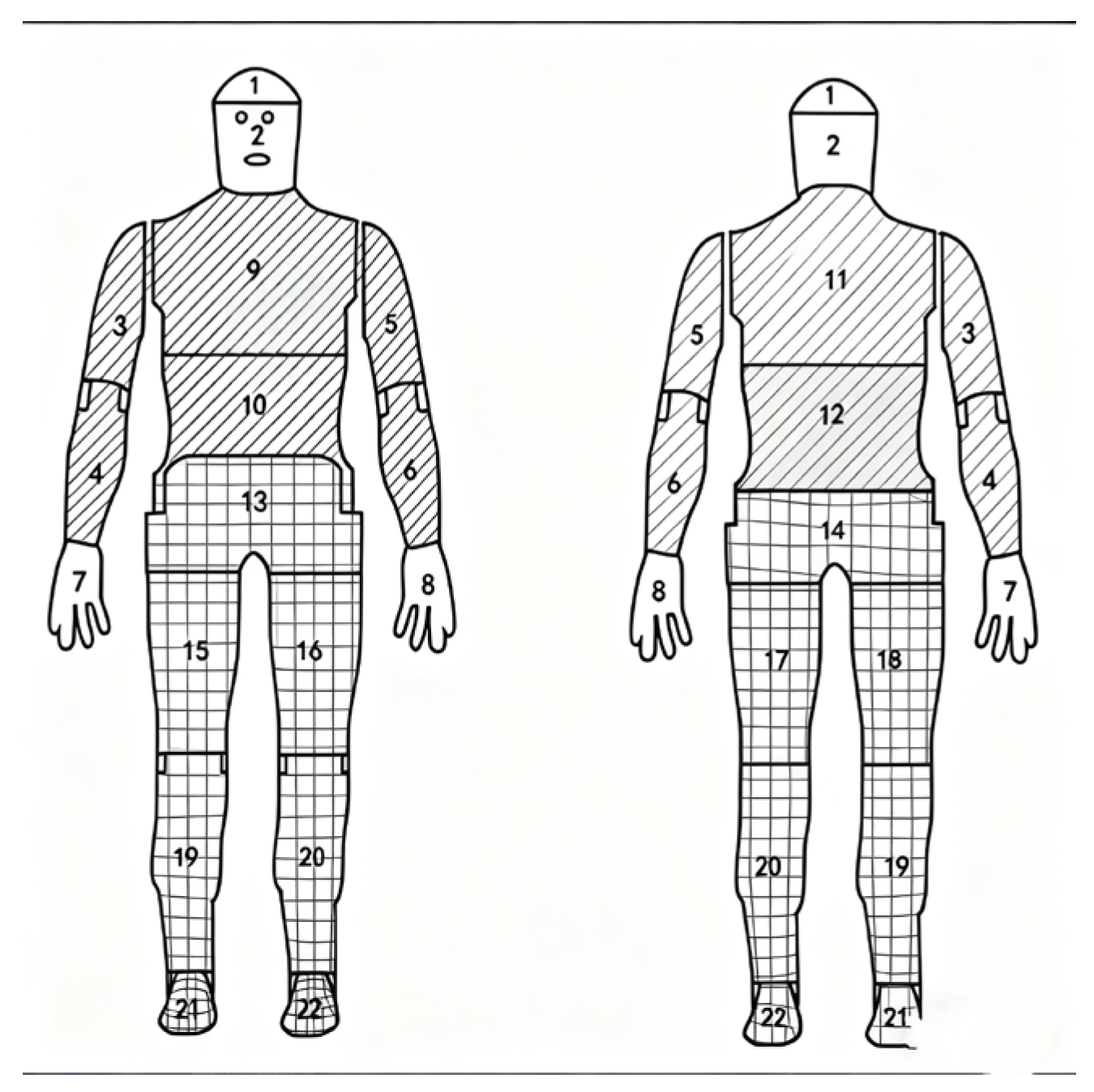
2.2.2. Thermal Resistance and Thermal Comfort Performance Testing Based on a Thermal Manikin
Clothing Thermal Resistance Testing and Analysis
PMV Testing and Analysis
PMV Experimental Calculation Method
Data Analysis Methods
3. Results and Analysis
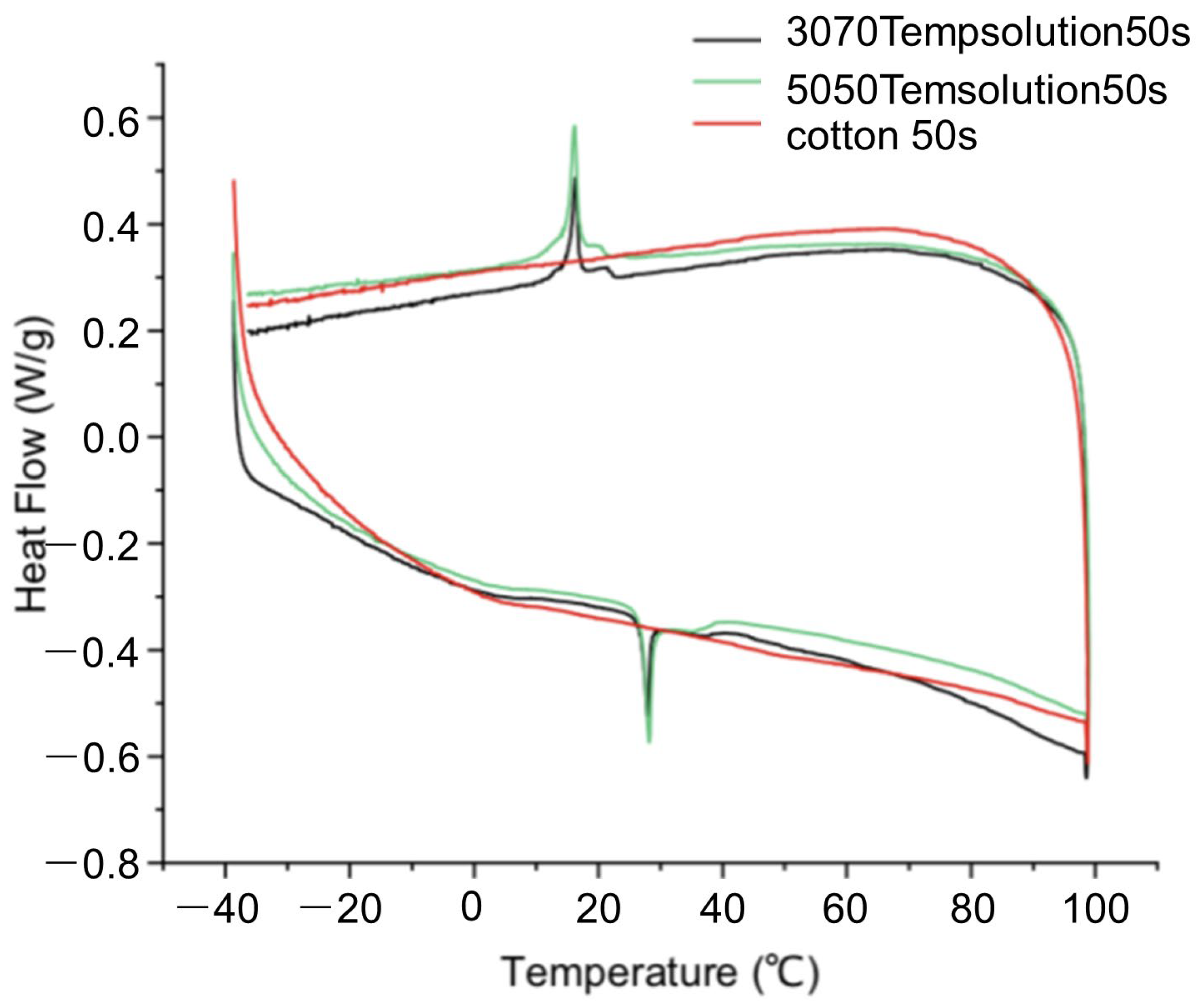
3.1. DSC Experimental Results and Analysis
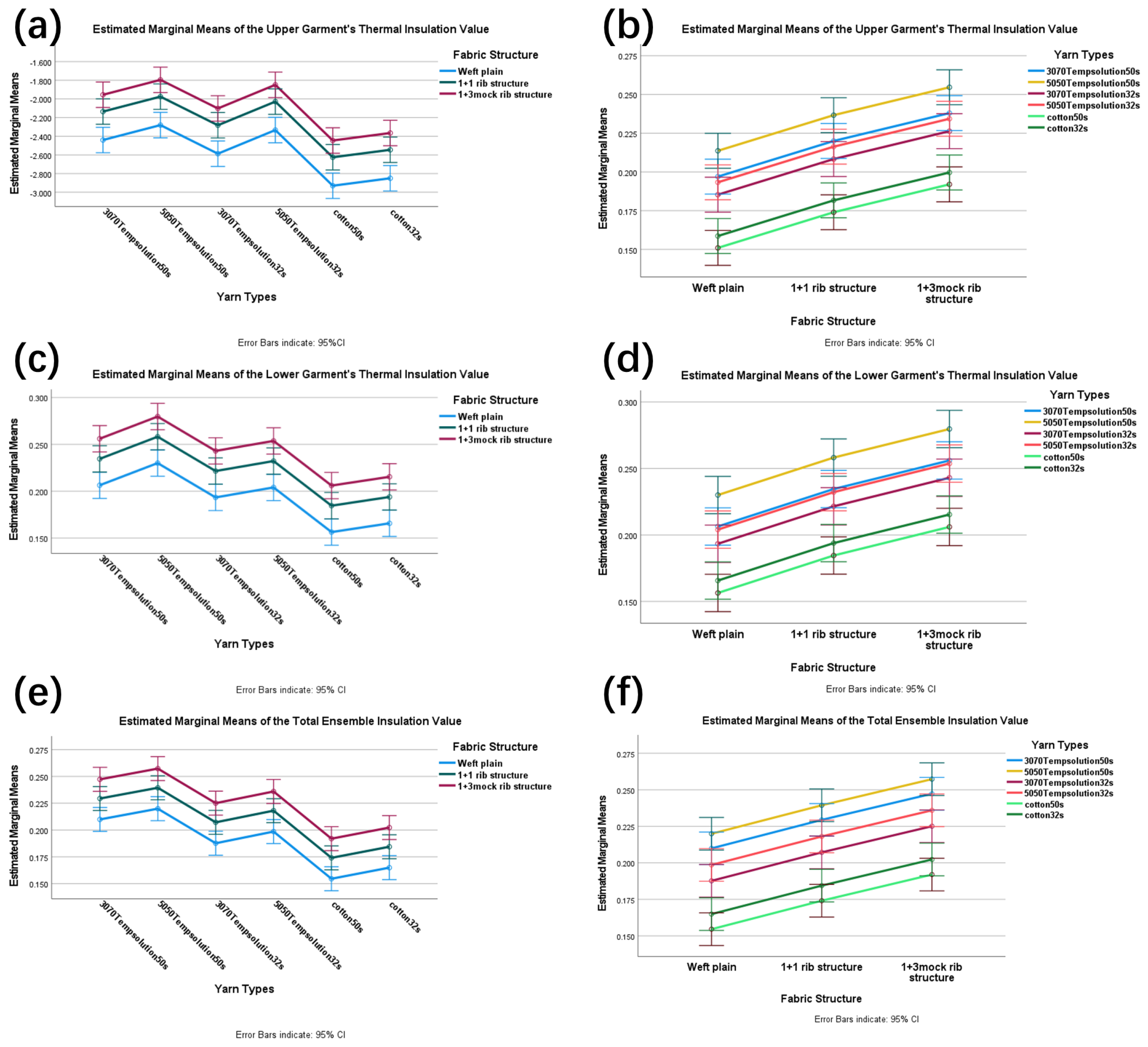
3.2. Thermal Resistance Experimental Results and Analysis
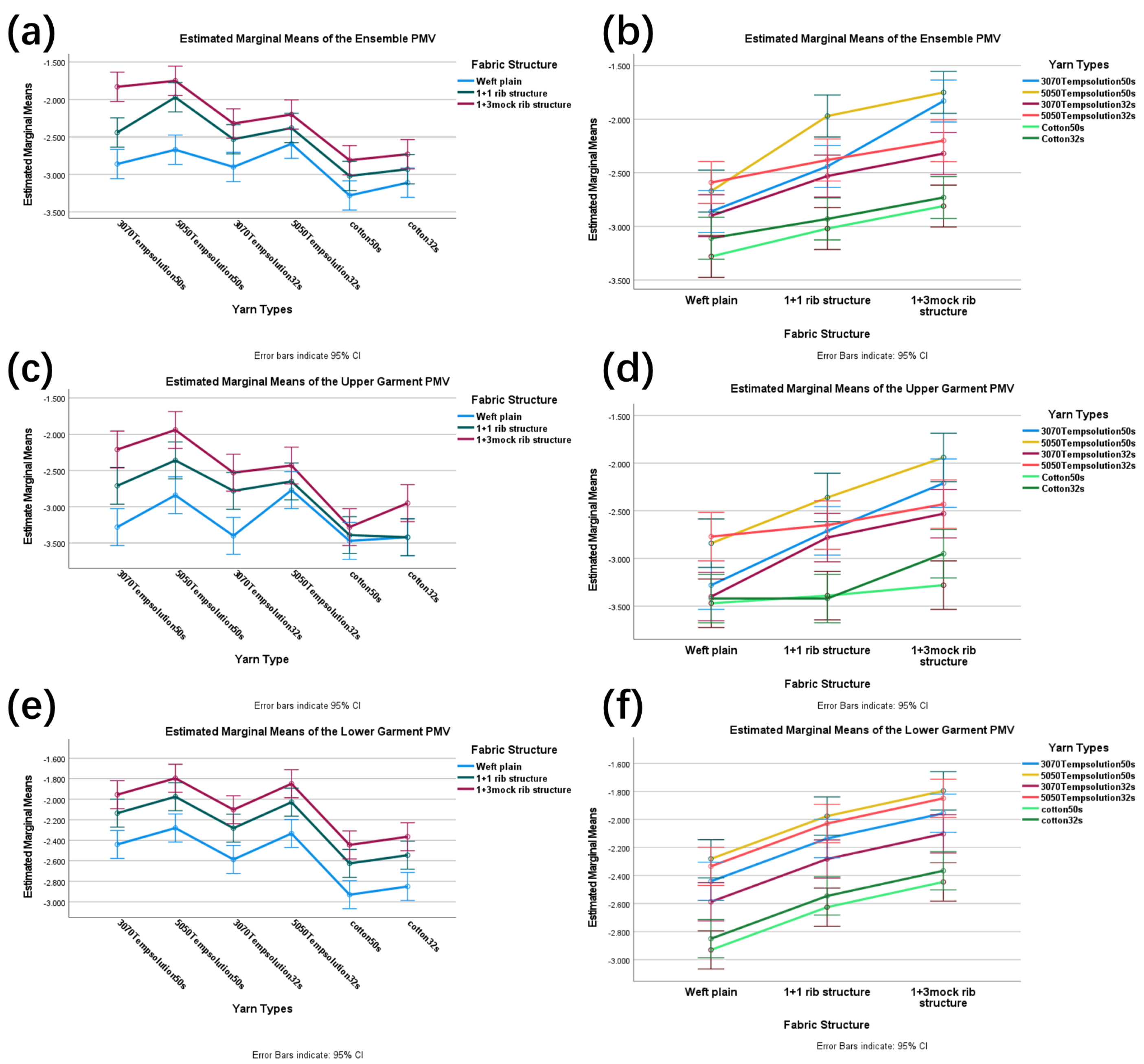
3.3. PMV Test Results and Analysis
3.4. Discussion and Analysis
3.4.1. Interpretation of the Mechanisms Underlying the Findings
3.4.2. Limitations and Future Prospects
- (1)
- DSC testing was conducted only on 50 s yarn; future studies should include comprehensive characterization of all yarn counts. The DSC results revealed significant supercooling in the phase-change material, indicating inherent initial energy loss in practical thermal energy cycling efficiency. Since only one thermal cycle was performed without laundering tests, the long-term cycling stability of the material requires further verification.
- (2)
- The experiments were conducted solely under standard 22 °C conditions without testing in colder environments. The practical effectiveness in colder climates may be diminished, necessitating future performance evaluations under broader temperature ranges.
- (3)
- For thermal resistance (ensemble/upper garment/lower garment) and PMV (lower garment), the interaction effects showed large effect sizes (η2p > 0.14) but failed to reach statistical significance (p > 0.05). This discrepancy may stem from the limited sample size (n = 3), which, although conforming to conventional textile testing standards, might have constrained the detection of subtle differences. Future studies should increase the sample size to enhance statistical power.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Min, S.Q.; Zhan, T.H.; Niu, F.Z.; Miao, J.; Xu, B. Multi-inspired Janus fabrics with asymmetric coolmax patterns for rapid sweat diffusion and effective sweat-shedding. Colloid. Surface A 2024, 686, 133300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.J.; Dou, G.J.; Hu, Y.H.; Sun, Y.H.; Chen, Z.T. Phase Change Material (PCM) Microcapsules for Thermal Energy Storage. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 9490873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, H.; Batool, M.; Osorio, F.J.B.; Isaza-Ruiz, M.; Xu, X.H.; Vignarooban, K.; Phelan, P.; Inamuddin; Kannan, A.M. Recent developments in phase change materials for energy storage applications: A review. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 129, 491–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Liu, L.K.; Alva, G.; Jia, Y.T.; Fang, G.Y. Synthesis and properties of microencapsulated octadecane with silica shell as shape-stabilized thermal energy storage materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 160, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, B.K.; Sistla, V.S. Inorganic salt hydrate for thermal energy storage application: A review. Energy Storage 2021, 3, e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Khan, A.; Sun, D.M.; Ashraf, M.; Rehman, A.; Safdar, F.; Basit, A.; Maqsood, H.S. Phase change materials, their synthesis and application in textiles-a review. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkayalar, S.; Alay-Aksoy, S. Developing of thermoregulating cotton fabric by incorporating of the poly(methyl methacrylate-co-methacrylamide)/fatty alcohol latent heat storing nanocapsules. J. Text. Inst. 2022, 113, 2585–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.J.; Cheng, X.L.; Wang, X.; Du, P.X.; Liu, C.Z.; Rao, Z.H. Supercooling regulation and thermal property optimization of erythritol as phase change material for thermal energy storage. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 105000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Qian, Y.Q.; Wang, G.X.; Wei, Y.; Guo, S.W. Ultrafast and continuous synthesis of phase change nanocapsules using salt-accelerated microwave-assisted polymerization. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. Temperature control and low infrared emissivity double-shell phase change microcapsules and their application in infrared stealth fabric. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 159, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.L.; Jing, H.R.; Zou, M.J. Preparation and preliminary evaluation of chitosan composite KGF-2 mutant thermal sensitive dressing. Mil. Med. Sci. 2018, 42, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Ke, Y.; Wang, H.F. Design and evaluation of cooling workwear for miners in hot underground mines using PCMs with different temperatures. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2022, 28, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, D.G.; Kandasubramanian, B. A review on Polymeric-Based Phase Change Material for Thermo-Regulating Fabric Application. Polym. Rev. 2020, 60, 389–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Tong, N.N.; Song, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.M. Preparation and Characterization of Phase Change Polyester Fiber. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2022, 228, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Qin, M.L. Experimental Study of a Novel Kapok-Fibre Phase Change Energy Storage Fabric. Fresen Environ. Bull. 2022, 31, 5742–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3418-21; Standard Test Method for Transition Temperatures and Enthalpies of Fusion and Crystallization of Polymers by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- G.T. 1335.1-2008; Standard Sizing Systems for Garments—Men. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- ISO 15831:2004; Clothing—Physiological Effects—Measurement of Thermal Insulation by Means of a Thermal Manikin. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- ISO 7730:2005; Ergonomics of the Thermal Environment-Analytical Determination and Interpretation of Thermal Comfort Using Calculation of the PMV and PPD Indices and Local Thermal Comfort Criteria. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Giro-Paloma, J.; Konuklu, Y.; Fernández, A.I. Preparation and exhaustive characterization of paraffin or palmitic acid microcapsules as novel phase change material. Sol. Energy 2015, 112, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, S.; Kilinc, N. Thermal Comfort Properties of 100% Cashmere Knitted Fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2024, 25, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Jamshaid, H.; Yosfani, S.H.S.; Hussain, U.; Nadeem, M.; Petru, M.; Tichy, M.; Muller, M. Thermo physiological comfort of single jersey knitted fabric derivatives. Fash. Text. 2021, 8, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, J.; Mazari, A.; Akcagun, E.; Havelka, A.; Kus, Z. Analysis of thermal properties, water vapor resistance and radiant heat transmission through different combinations of firefighter protective clothing. Ind. Textila 2018, 69, 458–465. [Google Scholar]
| Yarn Type | Yarn Blend Ratio | Yarn Count |
|---|---|---|
| 3070 TempSolution yarn 50 s | 30% PCM Viscose + 70% Cotton | 11.81 tex (50 s) |
| 3070 TempSolution yarn 32 s | 30% PCM Viscose + 70% Cotton | 18.45 tex (32 s) |
| 5050 TempSolution yarn 50 s | 50% PCM Viscose + 50% Cotton | 11.81 tex (50 s) |
| 5050 TempSolution yarn 32 s | 50% PCM Viscose + 50% Cotton | 18.45 tex (32 s) |
| Cotton Yarn 50 s | 100%Cotton | 11.81 tex (50 s) |
| Cotton Yarn 32 s | 100% Cotton | 18.45 tex (32 s) |
| Sample Number | A (Yarn Type) | B (Fabric Structure) |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | 3070TempSolution yarn 50 s | Weft plain |
| 2# | 3070 TempSolution yarn 50 s | 1 + 1 rib structure |
| 3# | 3070 TempSolution yarn 50 s | 1 + 3 mock rib structure |
| 4# | 5050 TempSolution yarn 50 s | Weft plain |
| 5# | 5050 TempSolution yarn 50 s | 1 + 1 rib structure |
| 6# | 5050 TempSolution yarn 50 s | 1 + 3 mock rib structure. |
| 7# | 3070 TempSolution yarn 32 s | Weft plain |
| 8# | 3070 TempSolution yarn 32 s | 1 + 1 rib structure |
| 9# | 3070 TempSolution yarn 32 s | 1 + 3 mock rib structure |
| 10# | 5050 TempSolution yarn 32 s | Weft plain |
| 11# | 5050 TempSolution yarn 32 s | 1 + 1 rib structure |
| 12# | 5050 TempSolution yarn 32 s | 1 + 3 mock rib structure |
| 13# | Cotton Yarn 50 s | Weft plain |
| 14# | Cotton Yarn 50 s | 1 + 1 rib structure |
| 15# | Cotton Yarn 50 s | 1 + 3 mock rib structure |
| 16# | Cotton Yarn 32 s | Weft plain |
| 17# | Cotton Yarn 32 s | 1 + 1 rib structure |
| 18# | Cotton Yarn 32 s | 1 + 3 mock rib structure |
| PMV Value | − | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Thermal Sensation | Very Cold | cold | Slightly Cool | Neutral | Slightly Warm | Warm | hot |
| Yarn Raw Materials | Phase Transition Process | Phase Transition Temperature Range/°C | Peak Temperature/°C | Enthalpy Value/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3070TempSolution 50 s | Heating Process | 21.77~31.66 | 27.89 | 2.973 |
| 3070TempSolution 50 s | Cooling Process | 23.37~9.02 | 16.27 | 1.677 |
| 5050TempSolution 50 s | Heating Process | 20.18~39.73 | 28.15 | 4.132 |
| Cooling Process | 23.58~3.71 | 16.17 | 3.828 |
| Sample Garment Number | Upper Garment/(m2·K/W) | Lower Garment/(m2·K/W) | Set/(m2·K/W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B01 | 0.191 ± 0.010 | 0.198 ± 0.009 | 0.193 ± 0.028 |
| B02 | 0.215 ± 0.013 | 0.227 ± 0.010 | 0.217 ± 0.019 |
| B03 | 0.249 ± 0.012 | 0.272 ± 0.010 | 0.259 ± 0.011 |
| B04 | 0.203 ± 0.018 | 0.214 ± 0.011 | 0.206 ± 0.018 |
| B05 | 0.240 ± 0.012 | 0.266 ± 0.015 | 0.241 ± 0.005 |
| B06 | 0.262 ± 0.048 | 0.288 ± 0.011 | 0.267 ± 0.015 |
| B07 | 0.190 ± 0.006 | 0.199 ± 0.013 | 0.192 ± 0.009 |
| B08 | 0.207 ± 0.010 | 0.220 ± 0.021 | 0.209 ± 0.009 |
| B09 | 0.223 ± 0.008 | 0.239 ± 0.012 | 0.226 ± 0.018 |
| B10 | 0.198 ± 0.008 | 0.210 ± 0.017 | 0.200 ± 0.014 |
| B11 | 0.222 ± 0.016 | 0.235 ± 0.011 | 0.223 ± 0.014 |
| B12 | 0.224 ± 0.022 | 0.245 ± 0.017 | 0.230 ± 0.019 |
| B13 | 0.151 ± 0.009 | 0.163 ± 0.012 | 0.155 ± 0.007 |
| B14 | 0.174 ± 0.011 | 0.186 ± 0.026 | 0.175 ± 0.013 |
| B15 | 0.192 ± 0.010 | 0.198 ± 0.013 | 0.192 ± 0.004 |
| B16 | 0.166 ± 0.016 | 0.172 ± 0.010 | 0.167 ± 0.008 |
| B17 | 0.179 ± 0.012 | 0.191 ± 0.016 | 0.186 ± 0.009 |
| B18 | 0.195 ± 0.010 | 0.212 ± 0.012 | 0.198 ± 0.010 |
| Sample Garment Number | Upper Garment PMV | Lower Garment PMV | Set PMV |
|---|---|---|---|
| B01 | −3.28 ± 0.093 | −2.51 ± 0.168 | −2.86 ± 0.104 |
| B02 | −2.71 ± 0.085 | −2.18 ± 0.131 | −2.44 ± 0.086 |
| B03 | −2.21 ± 0.092 | −1.83 ± 0.088 | −1.83 ± 0.049 |
| B04 | −2.84 ± 0.104 | −2.39 ± 0.048 | −2.67 ± 0.120 |
| B05 | −2.36 ± 0.208 | −1.91 ± 0.115 | −1.97 ± 0.078 |
| B06 | −1.94 ± 0.198 | −1.75 ± 0.069 | −1.75 ± 0.088 |
| B07 | −3.40 ± 0.139 | −2.64 ± 0.110 | −2.9 ± 0.163 |
| B08 | −2.78 ± 0.110 | −2.21 ± 0.201 | −2.53 ± 0.071 |
| B09 | −2.53 ± 0.096 | −2.12 ± 0.194 | −2.32 ± 0.089 |
| B10 | −2.77 ± 0.101 | −2.25 ± 0.249 | −2.59 ± 0.127 |
| B11 | −2.65 ± 0.145 | −2.02 ± 0.197 | −2.38 ± 0.139 |
| B12 | −2.43 ± 0.092 | −1.94 ± 0.208 | −2.20 ± 0.155 |
| B13 | −3.47 ± 0.232 | −2.85 ± 0.203 | −3.28 ± 0.198 |
| B14 | −3.39 ± 0.122 | −2.69 ± 0.100 | −3.02 ± 0.074 |
| B15 | −3.28 ± 0.163 | −2.46 ± 0.139 | −2.81 ± 0.114 |
| B16 | −3.42 ± 0.237 | −2.77 ± 0.094 | −3.11 ± 0.081 |
| B17 | −3.42 ± 0.302 | −2.58 ± 0.112 | −2.93 ± 0.068 |
| B18 | −2.95 ± 0.298 | −2.41 ± 0.181 | −2.73 ± 0.098 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, J.; Chang, L.; Fei, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, M. Thermoregulatory Performance and Thermal Comfort Analysis of Phase-Change Fiber Seamless Knitted Fabrics. Materials 2025, 18, 5317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235317
Cheng J, Chang L, Fei J, Jin Z, Zhao M. Thermoregulatory Performance and Thermal Comfort Analysis of Phase-Change Fiber Seamless Knitted Fabrics. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235317
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Jingfeng, Lu Chang, Jiahui Fei, Zimin Jin, and Mingtao Zhao. 2025. "Thermoregulatory Performance and Thermal Comfort Analysis of Phase-Change Fiber Seamless Knitted Fabrics" Materials 18, no. 23: 5317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235317
APA StyleCheng, J., Chang, L., Fei, J., Jin, Z., & Zhao, M. (2025). Thermoregulatory Performance and Thermal Comfort Analysis of Phase-Change Fiber Seamless Knitted Fabrics. Materials, 18(23), 5317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235317




