Application of Laser and Cryogenic Surface Treatment for the Evolution of Surface Morphology in Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Fabrication
2.2. Description of Research Sites
2.2.1. Dry Ice Blasting Method
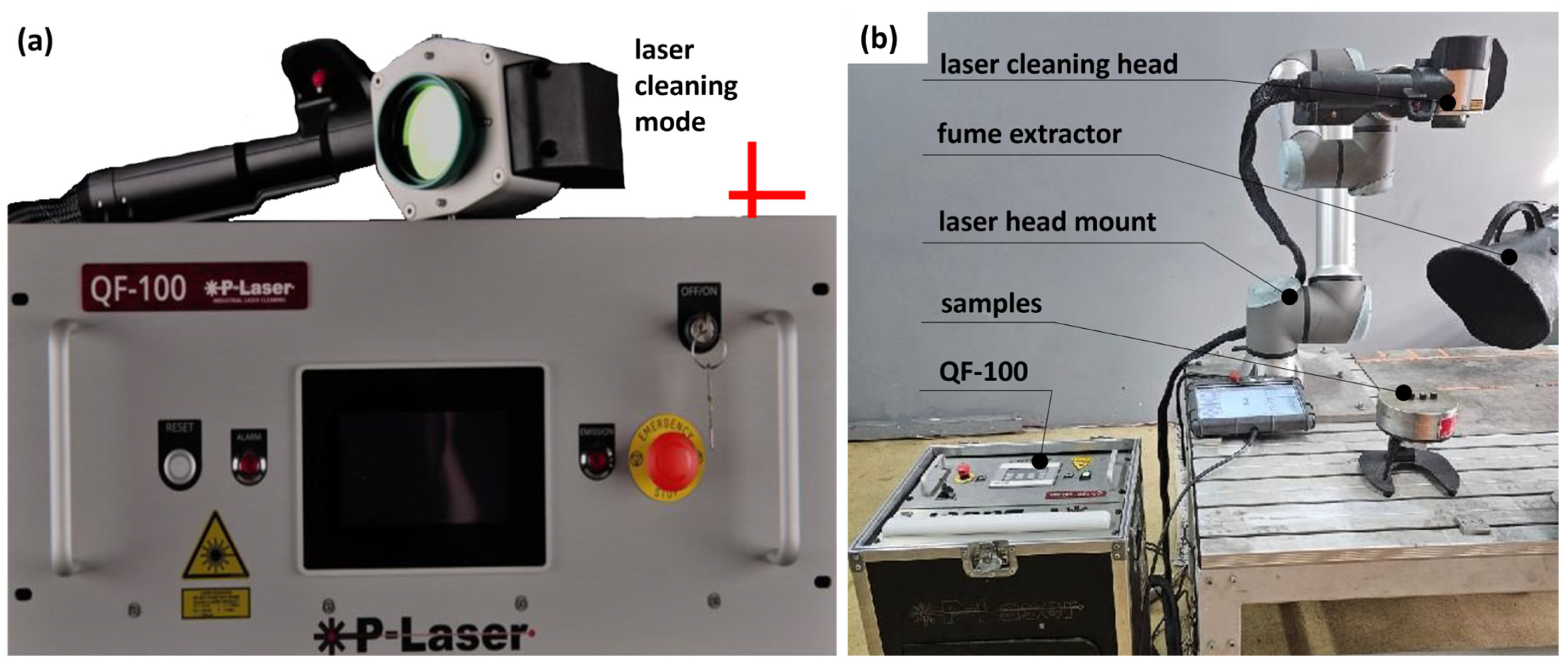
2.2.2. Laser Treatment Method
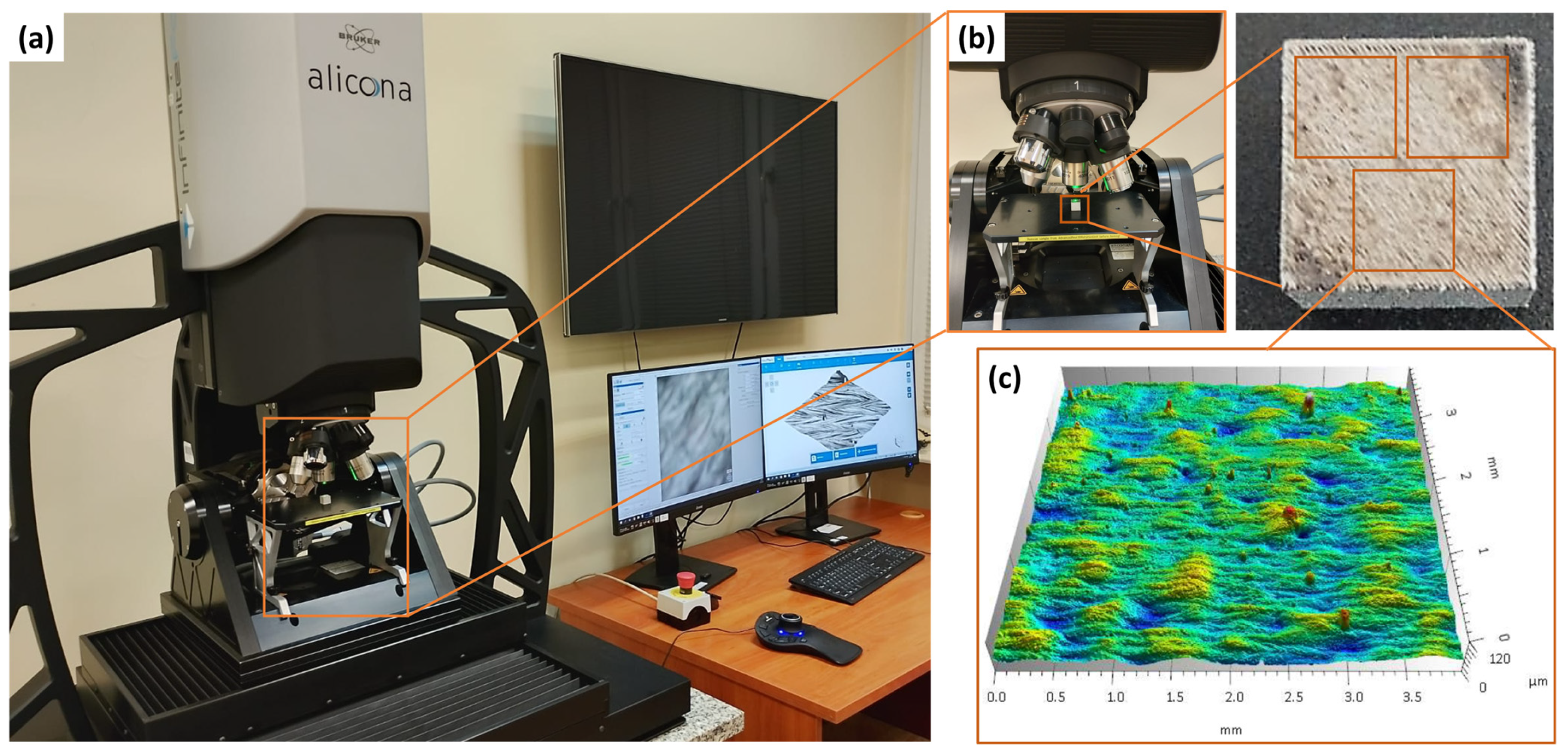
2.3. Evaluation of Surface Morphology and Roughness
3. Results and Discussion
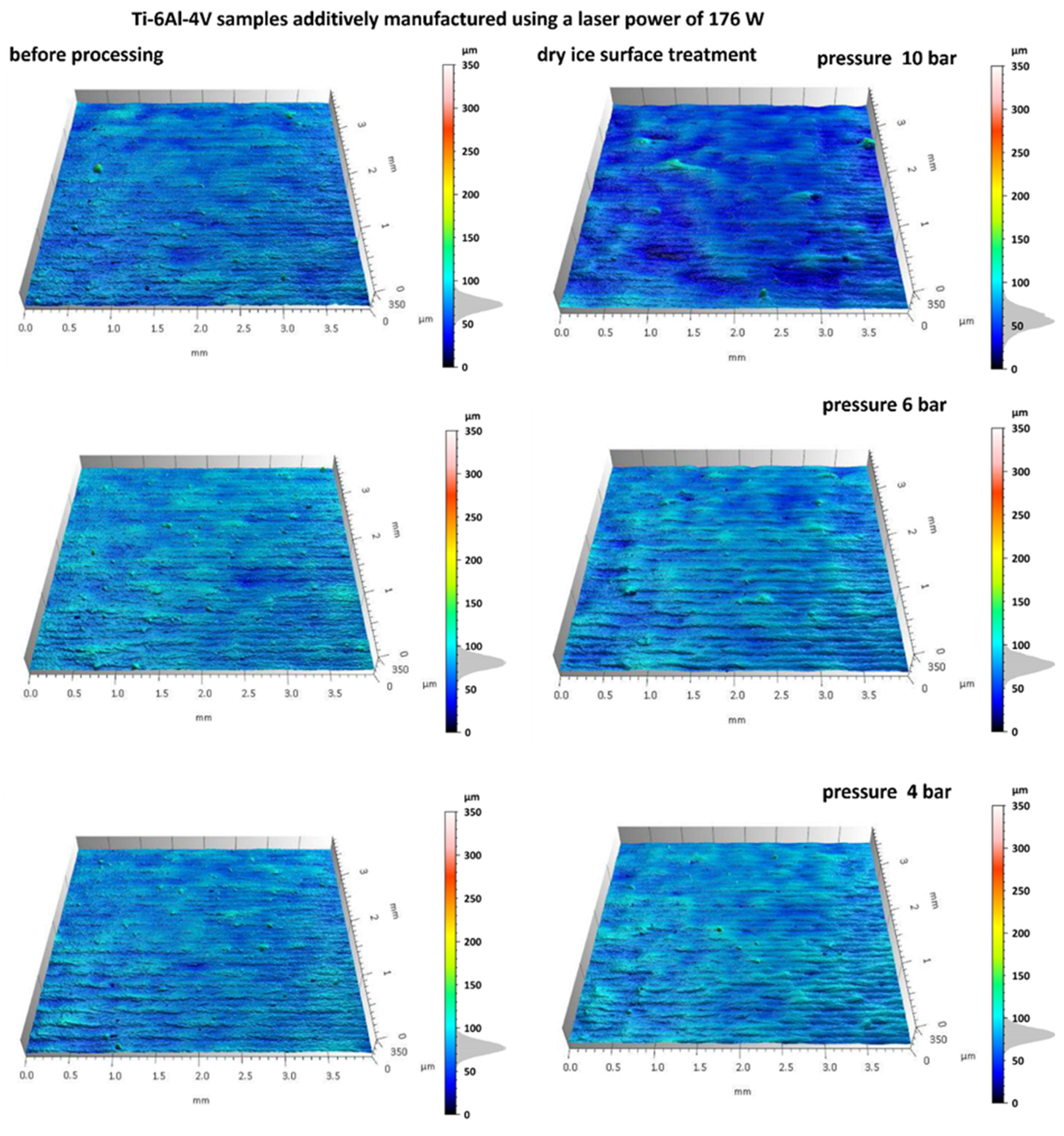
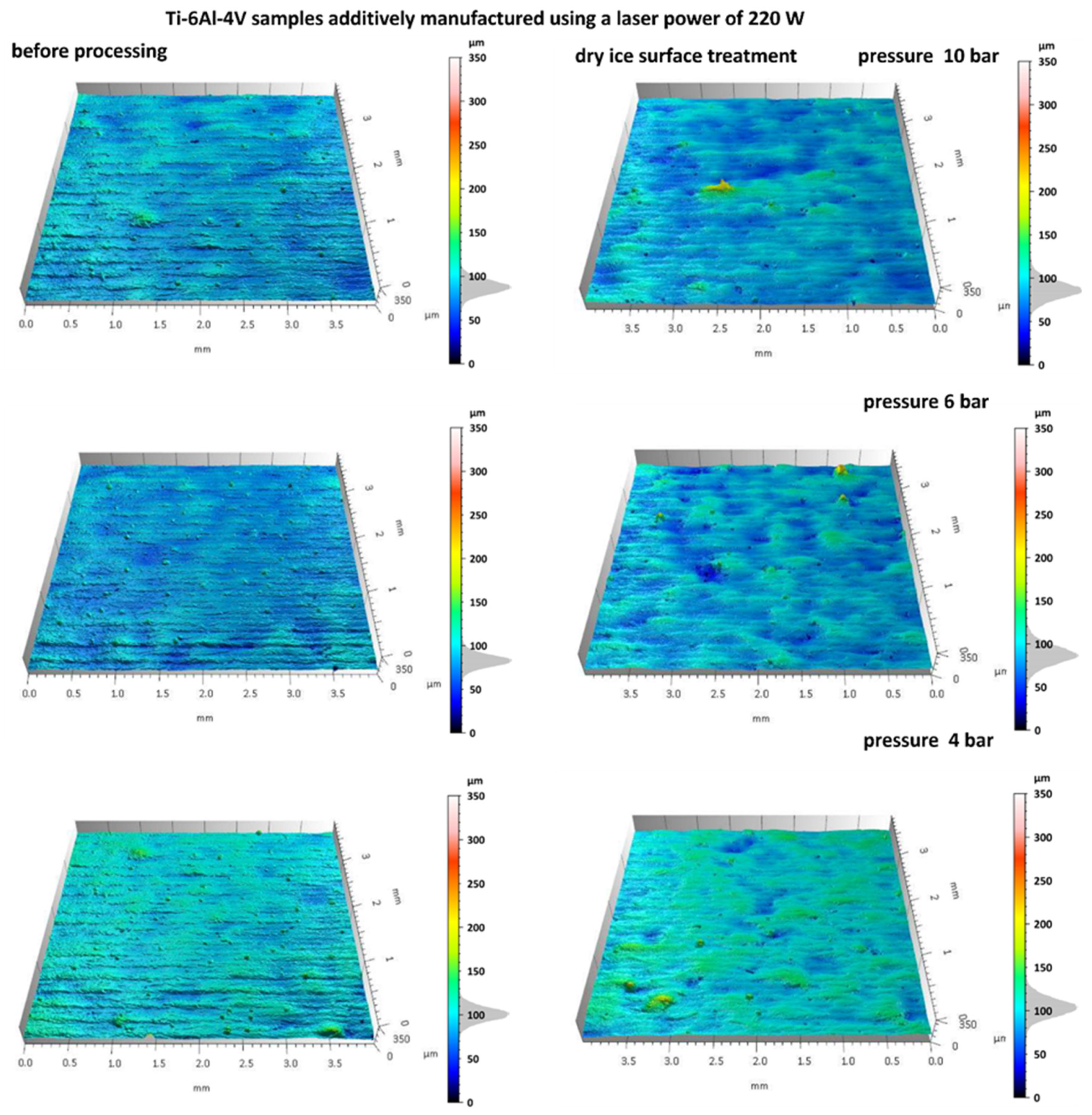
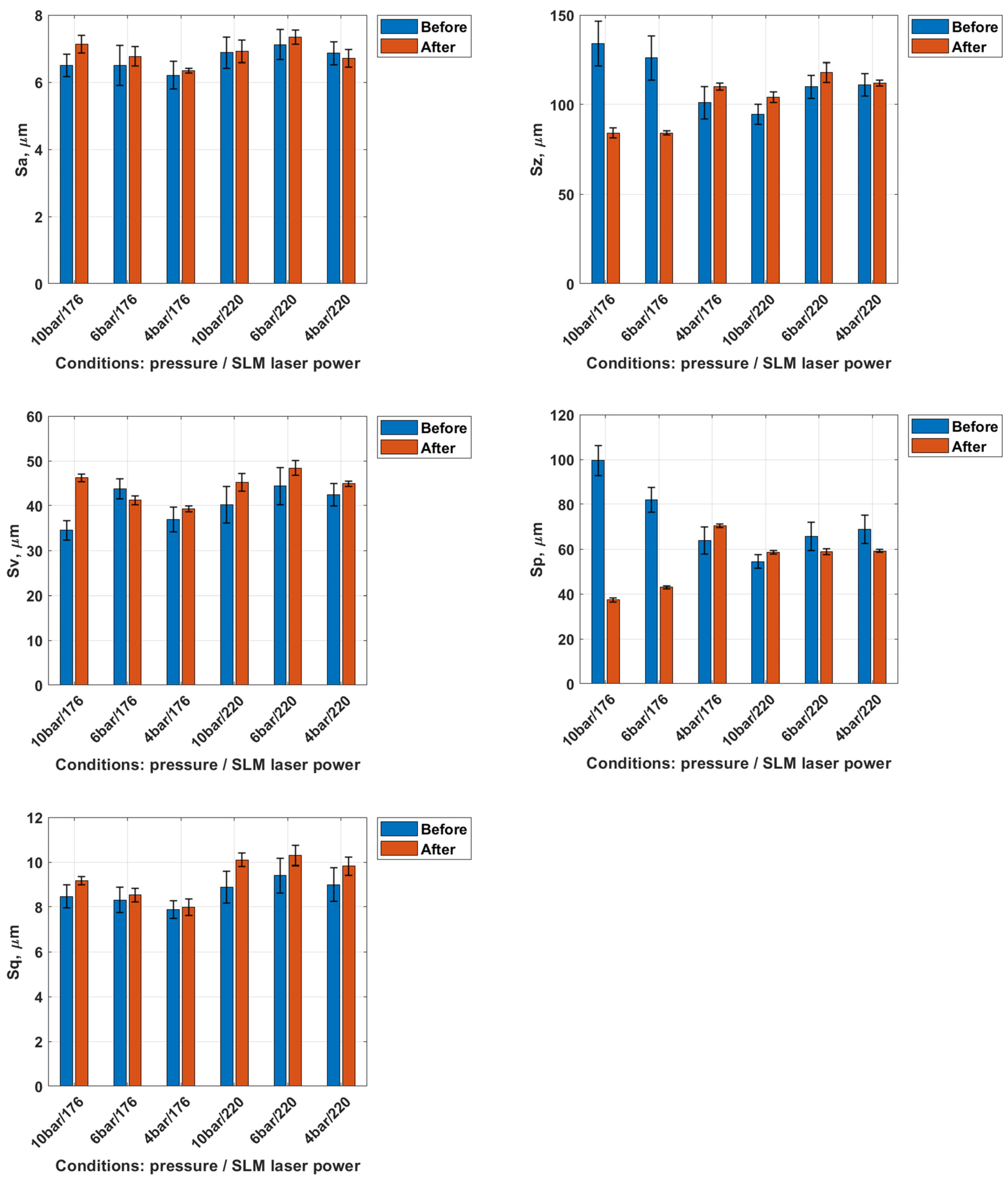
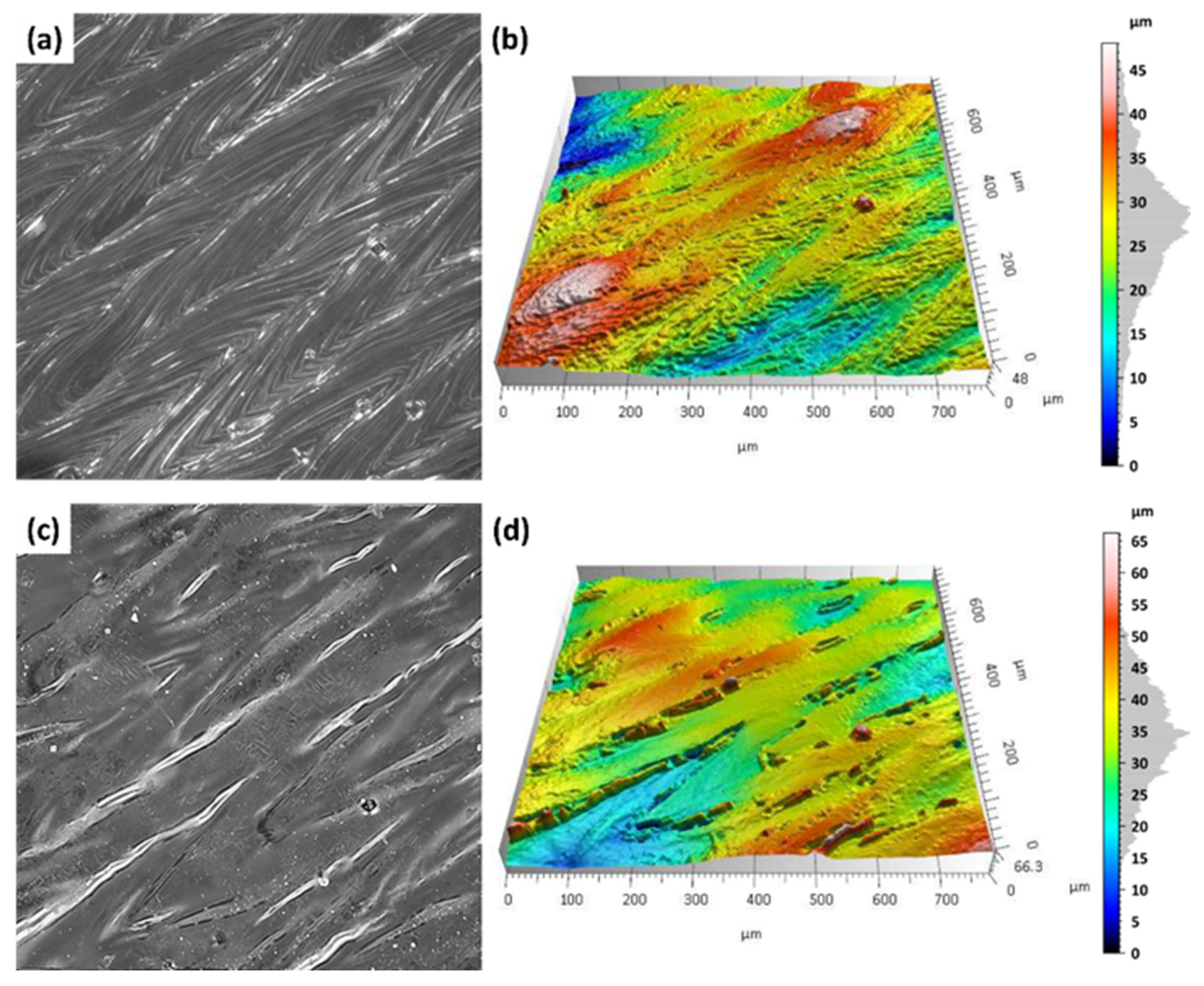
3.1. Analysis of Surface Topography After Dry Ice Blasting Method
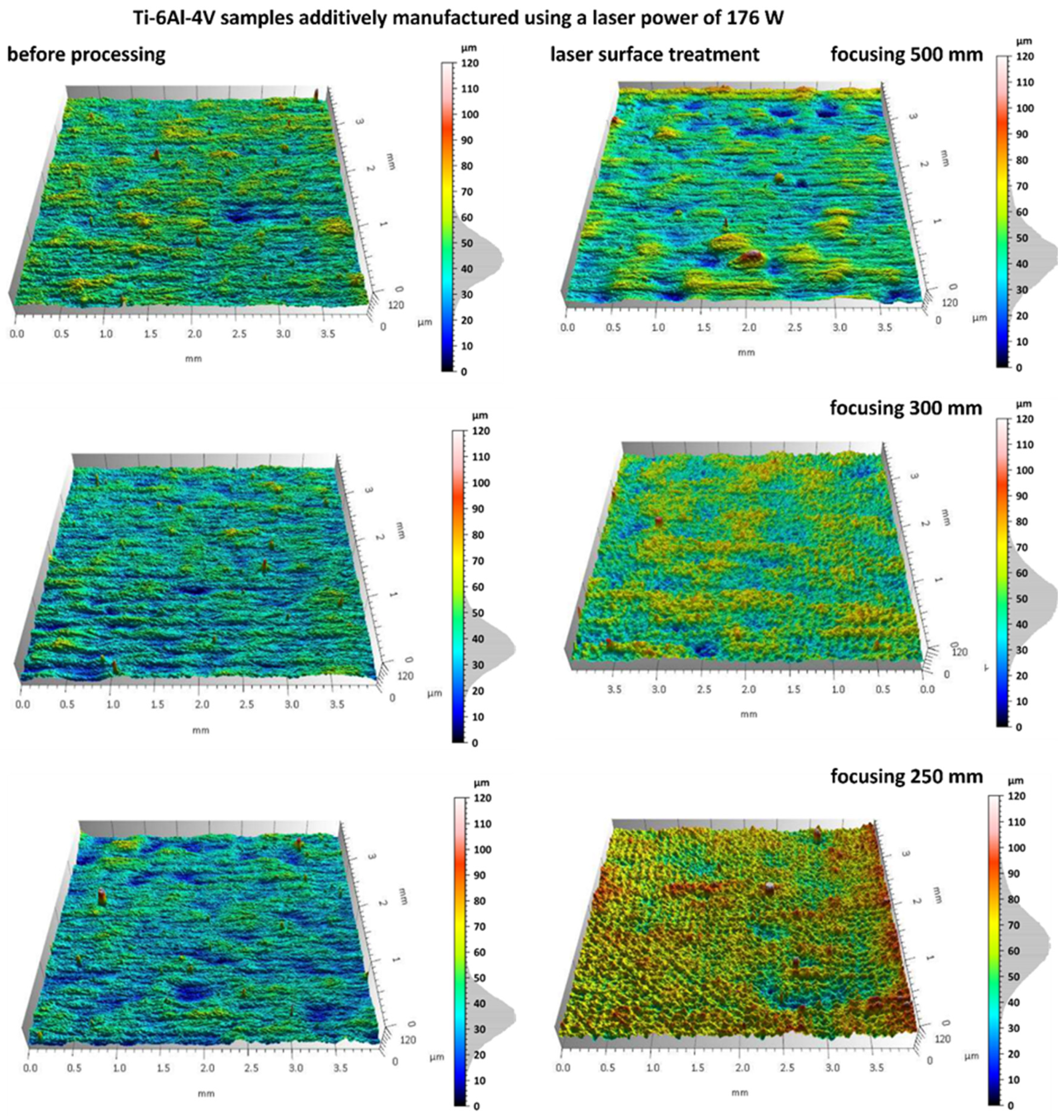
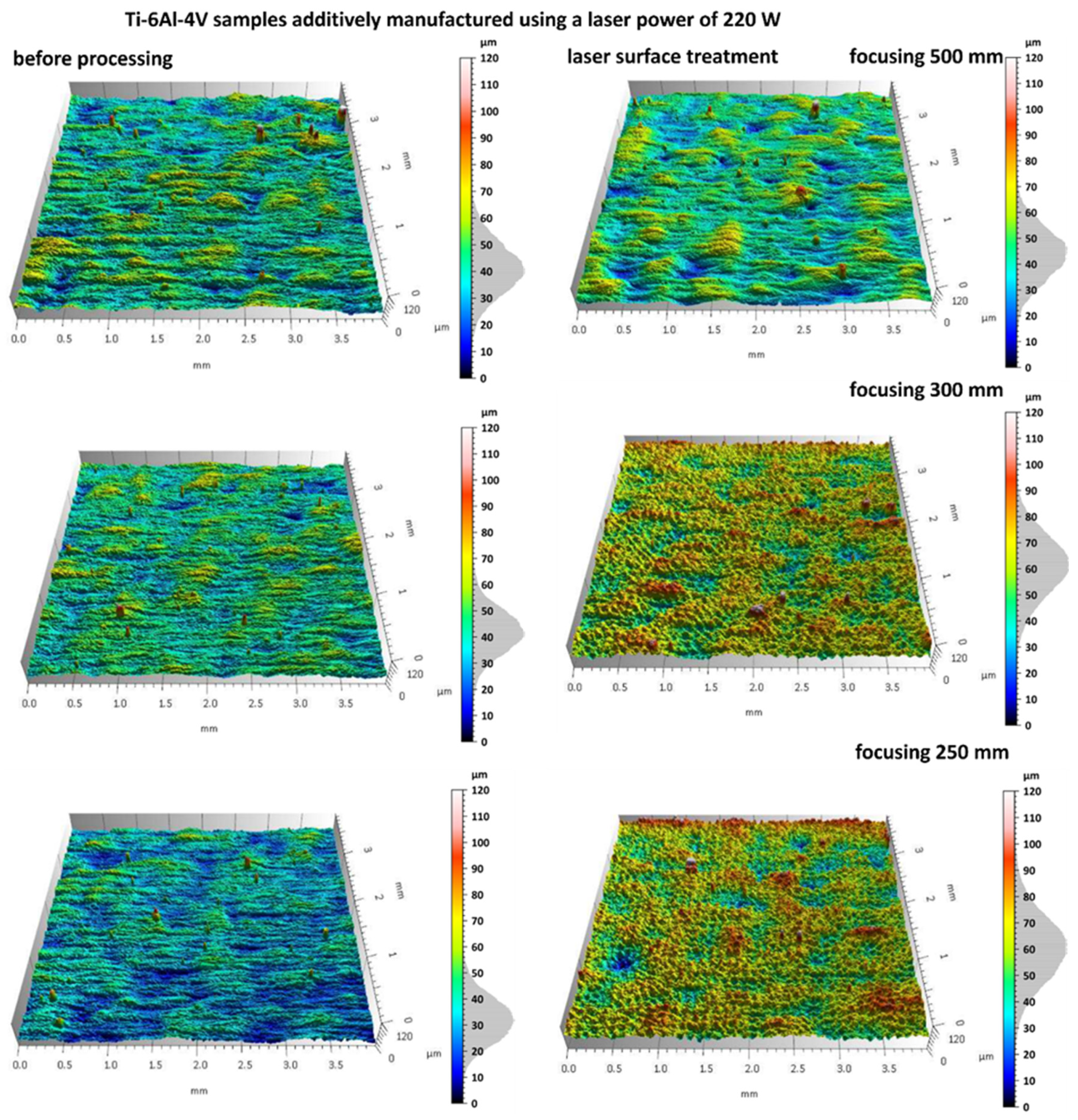
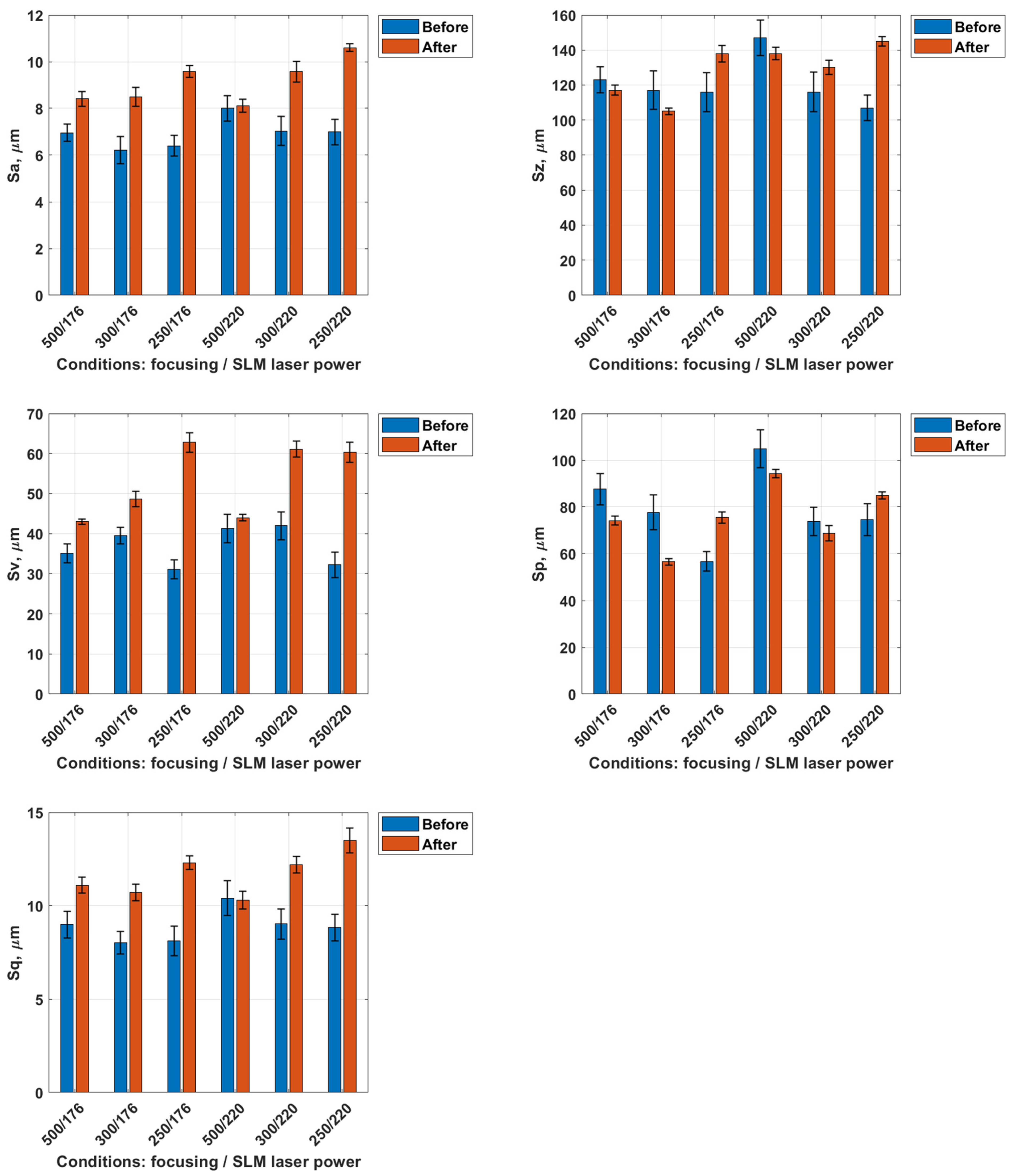
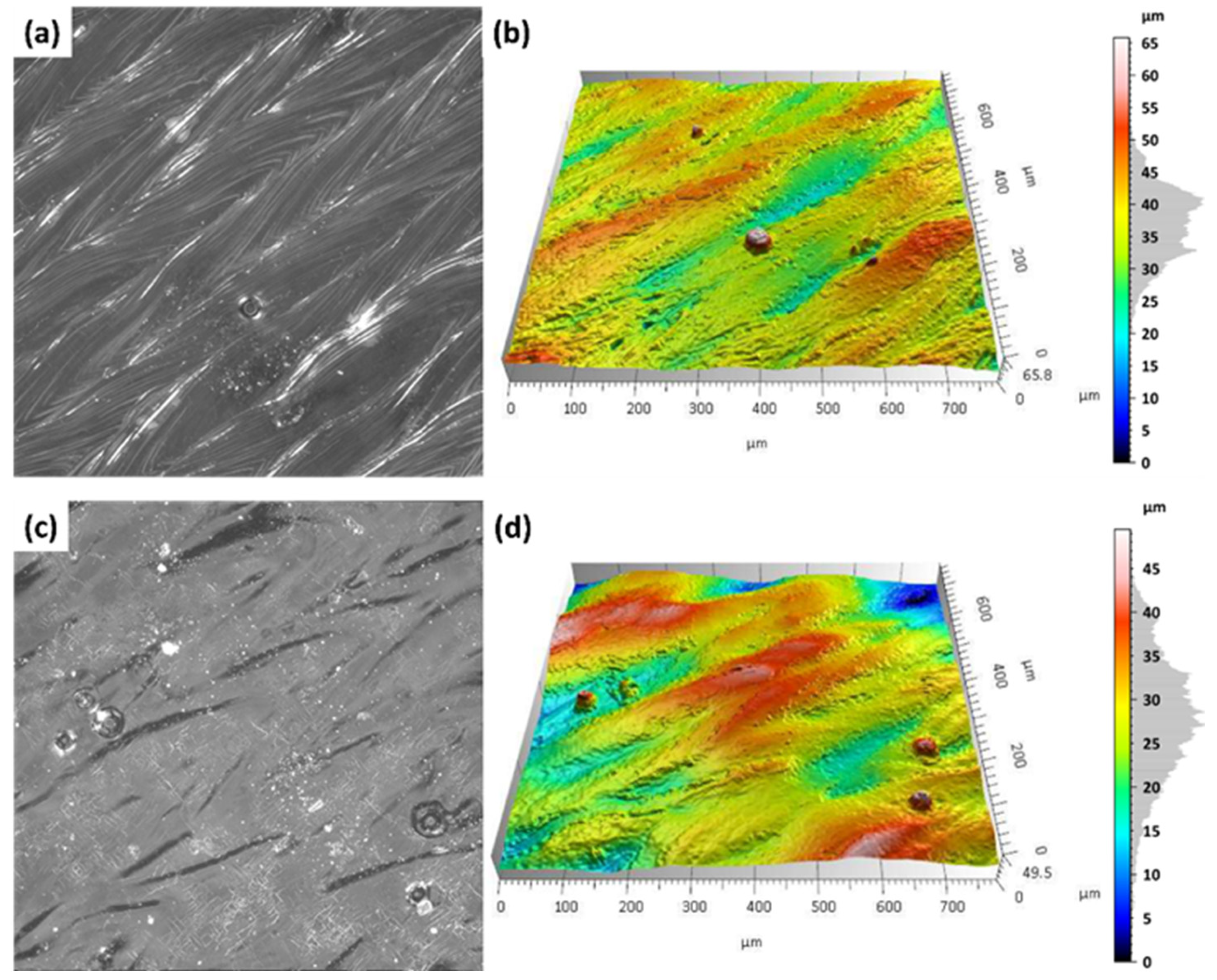
3.2. Analysis of Surface Topography After Laser Treatment
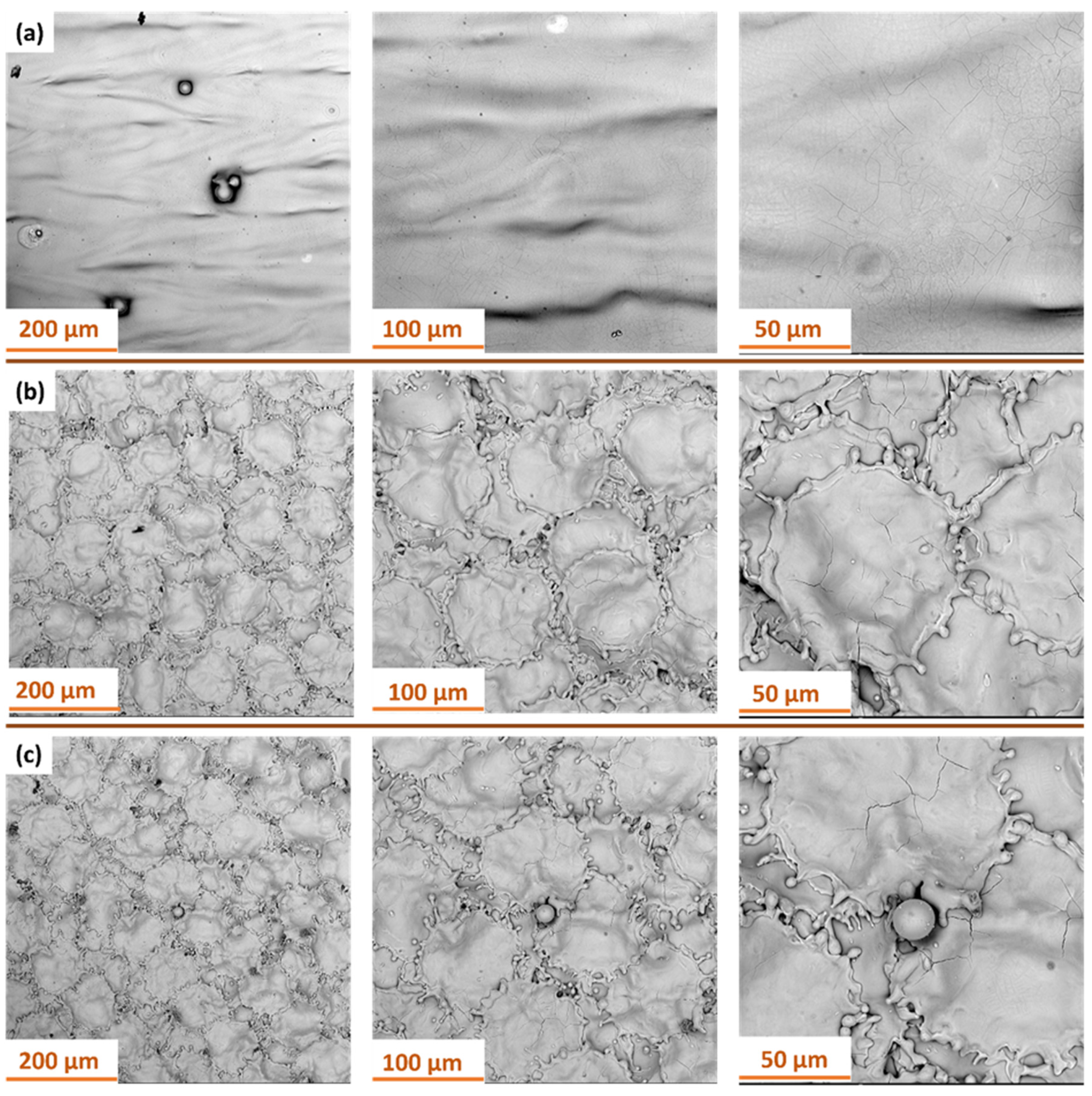
3.3. Analysis of Surface Morphology
4. Conclusions
- Cryogenic dry ice blasting effectively removed residual powder and oxide films from as-built SLM surfaces. For instance, in samples fabricated with the S_176 strategy and treated at 10 bar, the Sp parameter dropped from 99.5 µm to 37.4 µm, indicating significant peak removal. Concurrently, Sv increased from 34.5 µm to 46.2 µm, exposing deeper valleys, while Sz decreased from 134 µm to 84.2 µm, reflecting a reduced overall profile height. Moderate increases in Sa (from 6.5 to 7.13 µm) and Sq (from 8.47 to 9.17 µm) were consistent with selective top-layer removal.
- The best surface cleaning effects were achieved with dry ice at 10 bar and CO2 flow of 50 kg/h, resulting in surfaces with minimal residual contamination and visibly improved cleanliness.
- Laser treatment induced surface changes dependent on focal length. At a 500 mm focal length, thermal effects were moderate—Sp decreased by ~15% and Sq increased by only 10–15%, indicating controlled surface smoothing with minimal remelting.
- In contrast, reducing the focal length to 250 mm led to a 20–40% increase in Sp and Sv, suggesting intensified thermal gradients, local remelting, and potential microcrack formation.
- Compared to mechanical or chemical cleaning, dry ice blasting offers a non-contact, environmentally friendly solution for titanium alloys, preserving microstructure while effectively removing surface contaminants.
- Dry ice improves surface cleanliness and uniformity, even if roughness increases slightly. Laser treatment allows targeted morphology control, with its impact tunable by focal length. These results emphasize the importance of process optimization in relation to intended application requirements, especially for aerospace and biomedical components, where surface precision, cleanliness, and integrity are essential.
- Further research should address the influence of these surface treatments on mechanical and electrochemical performance, including fatigue resistance and corrosion behavior of SLM Ti-6Al-4V, to validate their suitability in demanding operational environments.
- Overall, cleaning effectiveness is closely tied to physical mechanisms involved: dry ice relies on mechanical and cryogenic interaction, while laser processing is governed by photothermal energy absorption and localized melting dynamics.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveria Campos, F.; Araujo, A.C.; Munhoz, A.L.J.; Kapoor, S.G. The influence of additive manufacturing on the micromilling machinability of Ti6Al4V: A comparison of SLM and commercial workpieces. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 60, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Miu, L.; Luo, Y. Titanium alloys for biomedical applications: A review on additive manufacturing process and surface modification technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 137, 3215–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hernández, C.; García-Cabezón, C.; González-Diez, F.; Ampudia, M.; Juanes-Gusano, D.; Rodriguez-Cabello, J.C.; Martín-Pedrosa, F. Effect of processing on microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion and biocompatibility of additive manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V orthopaedic implants. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szada-Borzyszkowska, M.; Laskowska, D.; Bałasz, B.; Szada-Borzyszkowski, W. Hydrojet Surface Treatment of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Produced by Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2025, 18, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genna, S.; Rubino, G. Laser Finishing of Ti6Al4V Additive Manufactured Parts by Electron Beam Melting. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balyakin, A.V.; Shvetcov, A.N.; Zhuchenko, E.I. Chemical polishing of samples obtained by selective laser melting from titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. MATEC Web. Conf. 2018, 224, 01031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H.; Chieko, K. Improving effects of cavitation peening, using a pulsed laser or a cavitating jet, and shot peening on the fatigue properties of additively manufactured titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 451, 129047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Zuo, D. Surface and property characterization of selective laser-melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy after laser polishing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 128, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, E.; Genna, S.; Menna, E.; Rubino, G.; Salmi, A.; Trovalusci, F. Surface Finishing of Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy: A Comparison between Abrasive Fluidized Bed and Laser Finishing. Materials 2021, 14, 5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, D. Effect of post-processing methods on the surface quality of Ti6Al4V fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1126749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuniewski, W.; Walczak, M.; Szala, M. Effects of Shot Peening and Electropolishing Treatment on the Properties of Additively and Conventionally Manufactured Ti6Al4V Alloy: A Review. Materials 2024, 17, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zuo, D. Laser polishing of additive manufactured Ti6Al4V alloy: A review. Opt. Eng. 2021, 60, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizzul, L.; Sorgato, M.; Bertolini, R.; Ghiotti, A.; Bruschi, S. Surface finish of additively manufactured Ti6Al4V workpieces after ball end milling. Procedia CIRP 2021, 102, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregoli, C.; Mohajerani, S.; Fiocchi, J.; Mehrpouya, M.; Elahinia, M.; Tuissi, A.; Vergani, L.M.; Biffi, C.A. Impact of Surface Finishing on Ti6Al4V Voronoi Additively Manufactured Structures: Morphology, Dimensional Deviation, and Mechanical Behavior. Materials 2024, 17, 4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Pramanik, A.; Basak, A.K.; Dong, Y.; Prakash, C.; Debnath, S.; Shankar, S.; Jawahir, I.S.; Dixit, S.; Buddhi, D. A critical review on additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 4641–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, E.; Bagherifard, S.; Bandini, M.; Guagliano, M. Surface post-treatments for metal additive manufacturing: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y. Effects of Post-processing on the Surface Finish, Porosity, Residual Stresses, and Fatigue Performance of Additive Manufactured Metals: A Review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 6407–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zou, Y.; Lim, C.V.S.; Wu, X. Review of laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) fabricated Ti-6Al-4V: Process, post-process treatment, microstructure, and property. Light Adv. Manuf. 2021, 2, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavari, M.; Imani, A.; Setavoraphan, A.; Schaller, R.F.; Asselin, E. Electron beam surface remelting enhanced corrosion resistance of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V as a potential in-situ re-finishing technique. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentinčič, J.; Koroth, J.E.; Zeidler, H. Advancements in surface finish for additive manufacturing of metal parts: A comprehensive review of plasma electrolytic polishing (PEP). Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2024, 19, e2364222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambo, A.M.; Younas, M.; Njuguna, J. Insights into Machining Techniques for Additively Manufactured Ti6Al4V Alloy: A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máša, V.; Horňák, D.; Petrilák, D. Industrial use of dry ice blasting in surface cleaning. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Bosch, A.; Santamarina-Campos, V.; Colomina-Subiela, A.; Carabal-Montagud, M.-Á. Cryogenics as an Advanced Method of Cleaning Cultural Heritage: Challenges and Solutions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; He, N.; Zhao, W.; Khan, A.M.; Xiang, H.; Gupta, M.K.; Iqbal, A.J. A novel low-pressure hybrid dry ice blasting system for improving the tribological and machining characteristics of AISI-52100 tool steel. Manuf. Process. 2022, 80, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.A.; Greem, G. Dry Ice Cleaning of Electrical Equipment. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE IAS Pulp and Paper Industry Conference (PPIC), Spokane, WA, USA, 11–15 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzido, A.; Krawczyk, P. Abrasive Technologies with Dry Ice as a Blasting Medium—Review. Energies 2023, 16, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amon, S.; Jobst, A.; Merklein, M.; Hanenkamp, N. Influence of dry ice blasting process properties on surface roughness and residual stresses of machined and additive manufactured workpieces. Procedia CIRP 2022, 108, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Shi, W. Titanium Alloy Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing for Medical Applications: Obtaining, Characterization and Application—Review. Metals 2023, 13, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowska, D.; Bałasz, B.; Zawadka, W. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of As-Built Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-7Nb Alloys Produced by Selective Laser Melting Technology. Materials 2024, 17, 4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 25178-2:2021; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Areal—Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 1660-61; Geometrical product specification (GPS)—Filtration—Part 61: Linear areal filters—Gaussian Filters, International Standard. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Yang, J.; Schlenger, L.M.; Nasab, M.H.; Van Petegem, S.; Marone, F.; Logé, R.E.; Leinenbach, C. Experimental quantification of inward Marangoni convection and its impact on keyhole threshold in laser powder bed fusion of stainless steel. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 84, 104092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Lojen, G.; Hudak, R.; Rajtukova, V.; Brajlih, T.; Kokol, V.; Drstvenšek, I. As-fabricated surface morphologies of Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different laser processing parameters in selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 33, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Strategy Symbol | |
|---|---|---|
| S_176 | S_220 | |
| Laser power, P [W] | 176 | 220 |
| Scanning speed, Ss [mm/s] | 880 | 1100 |
| Hatching distance, Hd [mm] | 0.1 | |
| Layer thickness, Lt [mm] | 0.03 | |
| Volumetric energy density, Ev [J/mm3] | 67 | |
| Ti | Al | V | Fe | O | C | N | H | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | Balance | 6.00 | 4.00 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.13 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.012 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| CO2 mass flow rate, [kg/h] | 0–72 |
| CO2 granulate diameter, [mm] | 10 (max) |
| Granulate container capacity, [kg] | <20 |
| Working air pressure, [bar] | 0.3–0.5 |
| Power supply, [V] | 200–240 |
| Process Number | CO2 Mass Flow Rate, [kg/h] | Working Air Pressure, [bar] | Working Nozzle Diameter, [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 10 | 7 |
| 2 | 40 | 6 | |
| 3 | 30 | 4 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Laser wavelength, [nm] | 1064 |
| Laser focal length, [mm] | 250, 300, 500 |
| Diameter of the scanned area, [mm] | 50 |
| Laser pulse frequency, [kHz] | 100 |
| Pulse energy, [mJ] | 1 |
| Power supply, [V] | 230 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Optical zoom (light mode) | 27×–160× |
| SEM magnification (electron optics) | From 160× up to 350,000× |
| Resolution, nm | ≤6 SED, ≤8 BSD |
| Digital image magnification | Up to 12× |
| Beam accelerating voltage | 5 to 20 kV |
| Maximum sample width | 25 mm (optionally 32 mm) |
| Maximum sample height | 35 mm (optionally up to 100 mm) |
| Electron source lifespan (CeB6) | Up to 1500 h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laskowska, D.; Szada-Borzyszkowska, M.; Bałasz, B.; Szada-Borzyszkowski, W.; Bukała, I. Application of Laser and Cryogenic Surface Treatment for the Evolution of Surface Morphology in Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Samples. Materials 2025, 18, 5315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235315
Laskowska D, Szada-Borzyszkowska M, Bałasz B, Szada-Borzyszkowski W, Bukała I. Application of Laser and Cryogenic Surface Treatment for the Evolution of Surface Morphology in Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Samples. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaskowska, Dorota, Monika Szada-Borzyszkowska, Błażej Bałasz, Wiesław Szada-Borzyszkowski, and Izabela Bukała. 2025. "Application of Laser and Cryogenic Surface Treatment for the Evolution of Surface Morphology in Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Samples" Materials 18, no. 23: 5315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235315
APA StyleLaskowska, D., Szada-Borzyszkowska, M., Bałasz, B., Szada-Borzyszkowski, W., & Bukała, I. (2025). Application of Laser and Cryogenic Surface Treatment for the Evolution of Surface Morphology in Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Samples. Materials, 18(23), 5315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235315







