Construction of a Gradient Nanostructure for Enhanced Surface Properties in 38CrMoAl Steel via Ultrasonic Severe Surface Rolling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
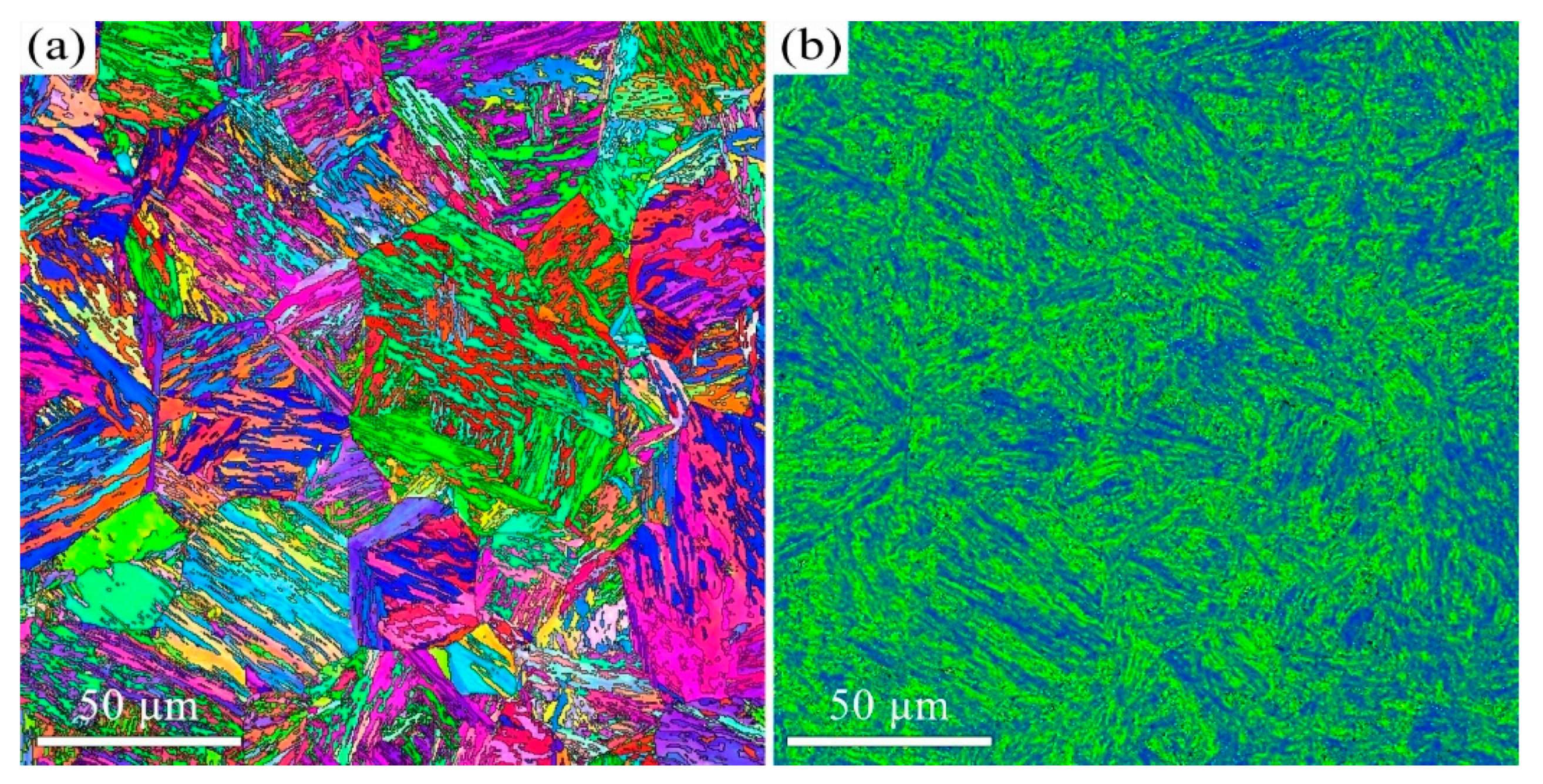
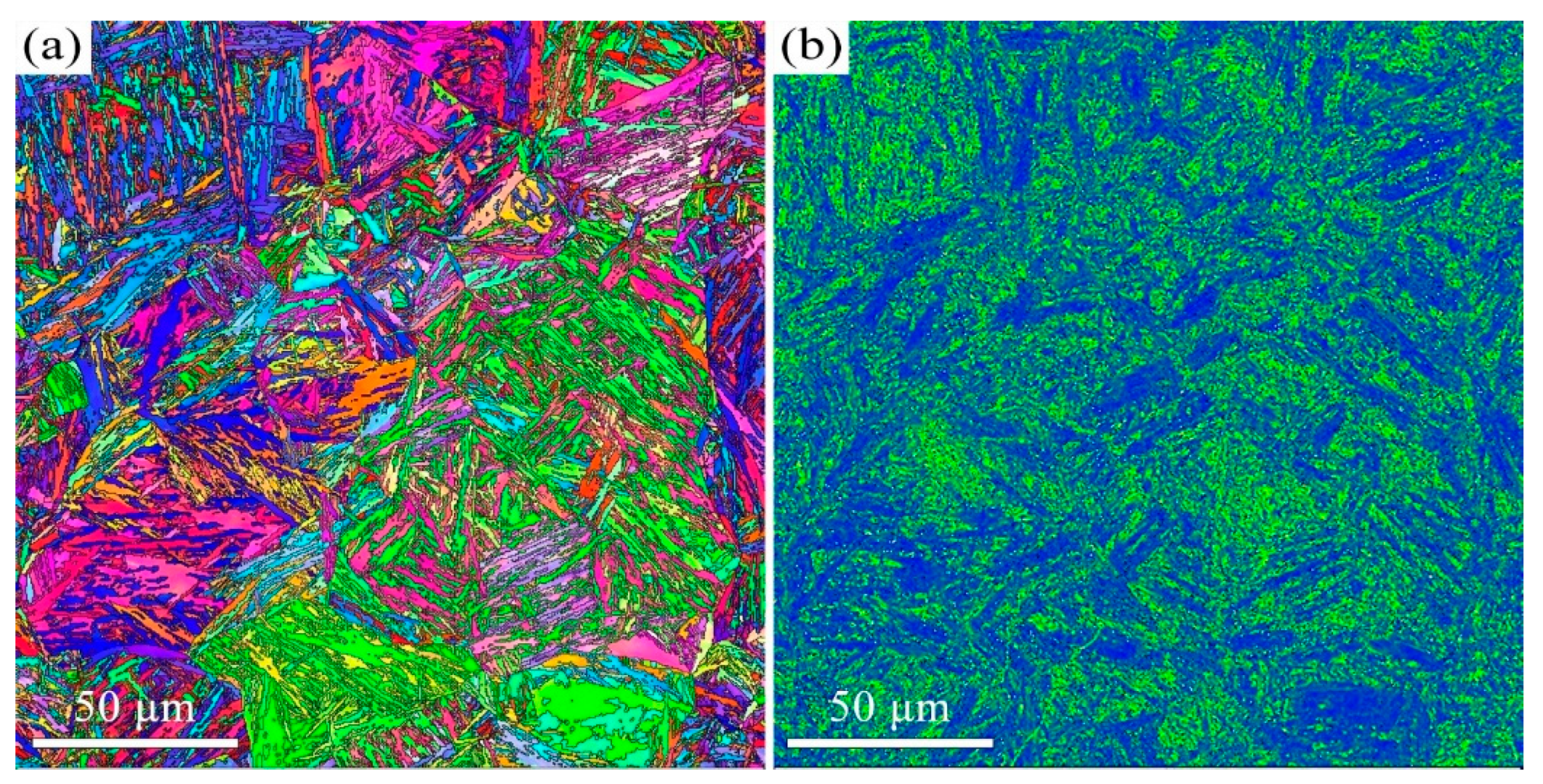
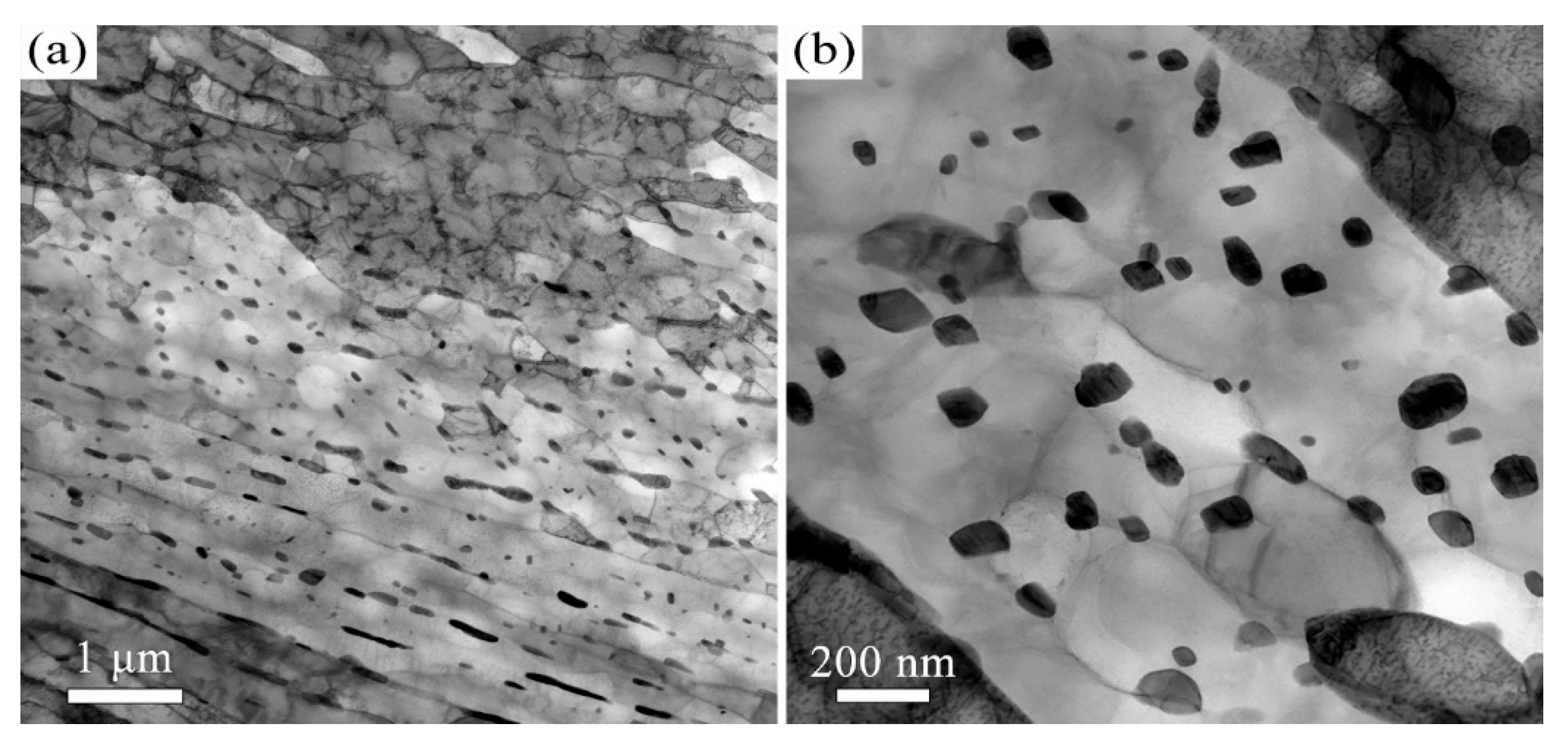
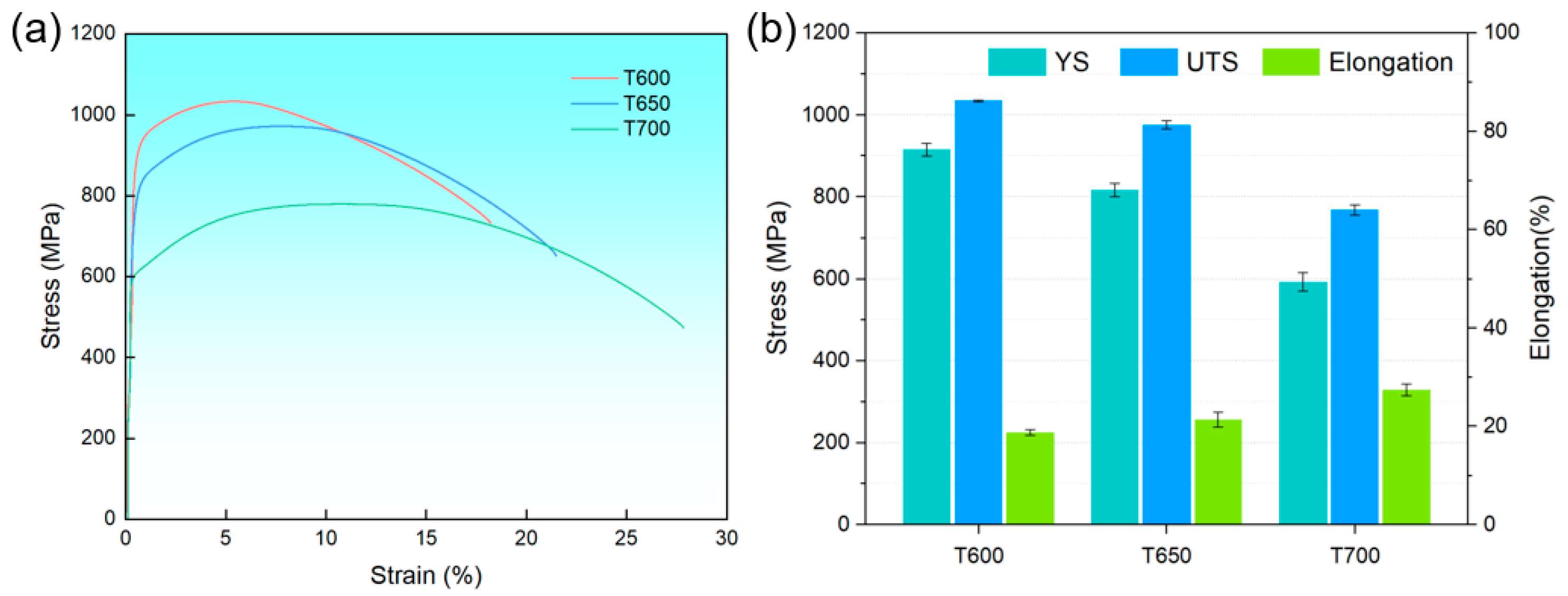
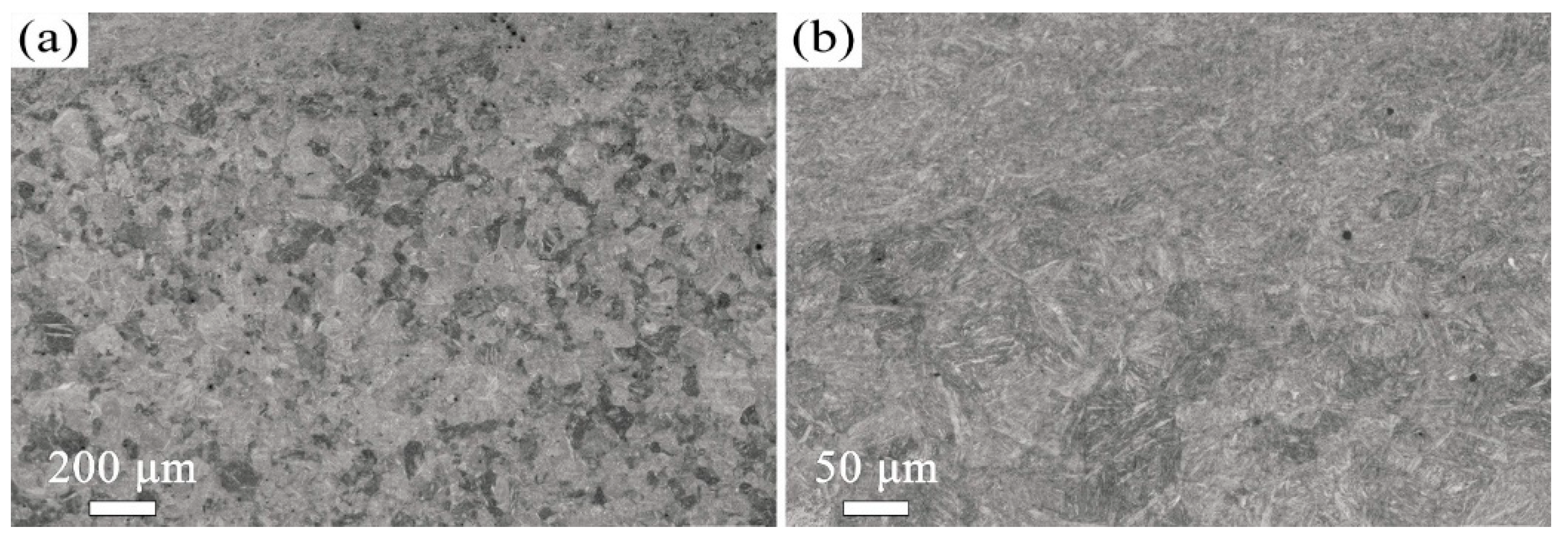
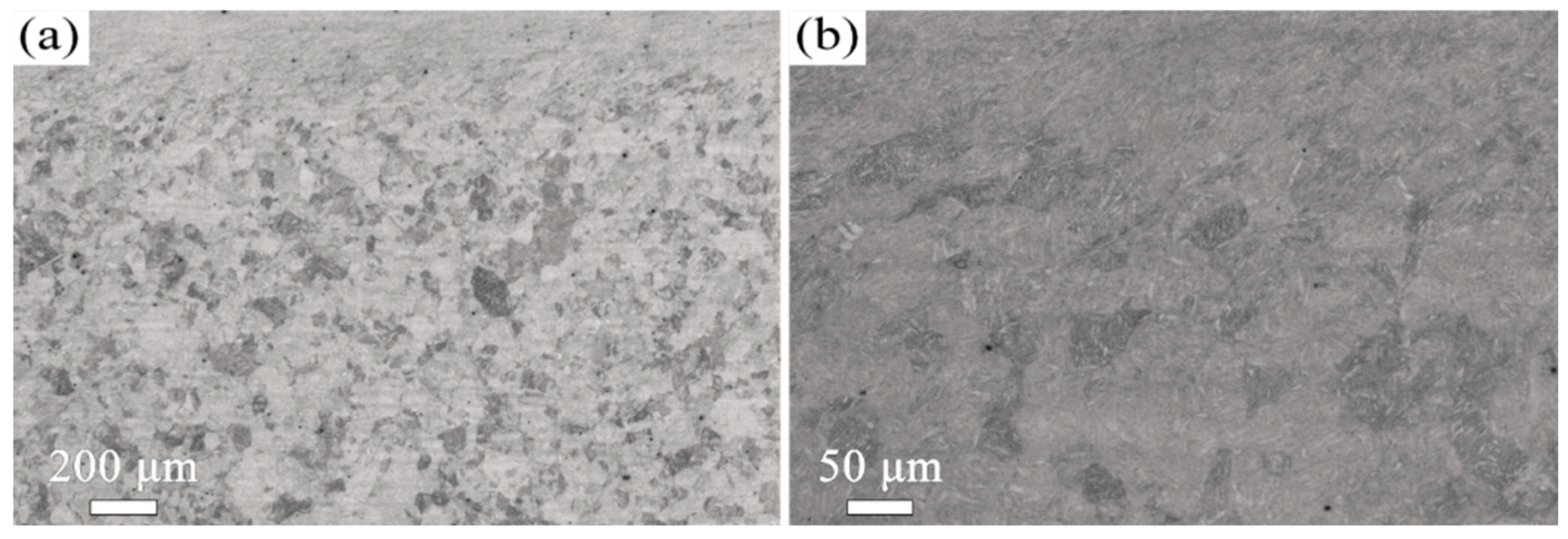
3.1. The Influence of Tempering Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
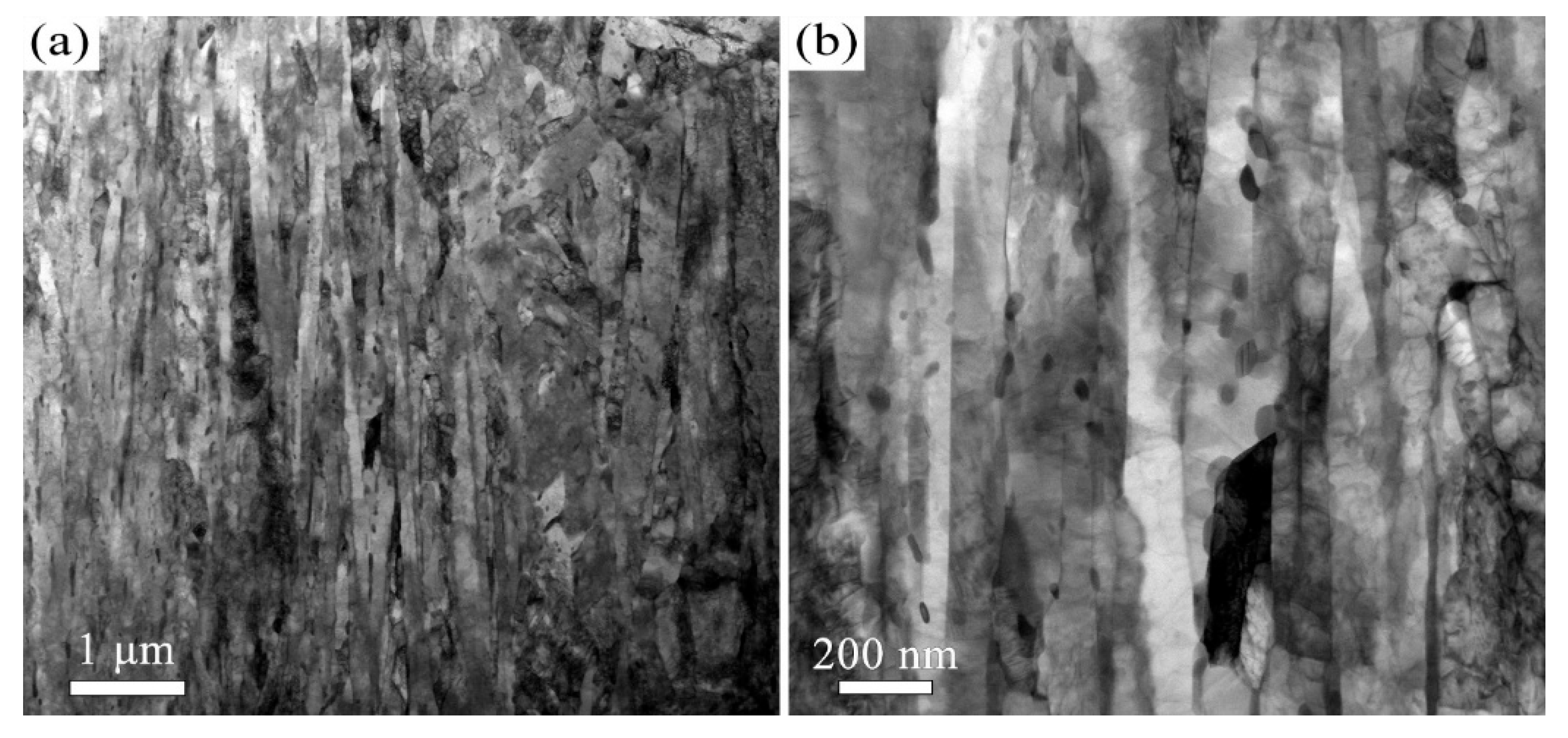
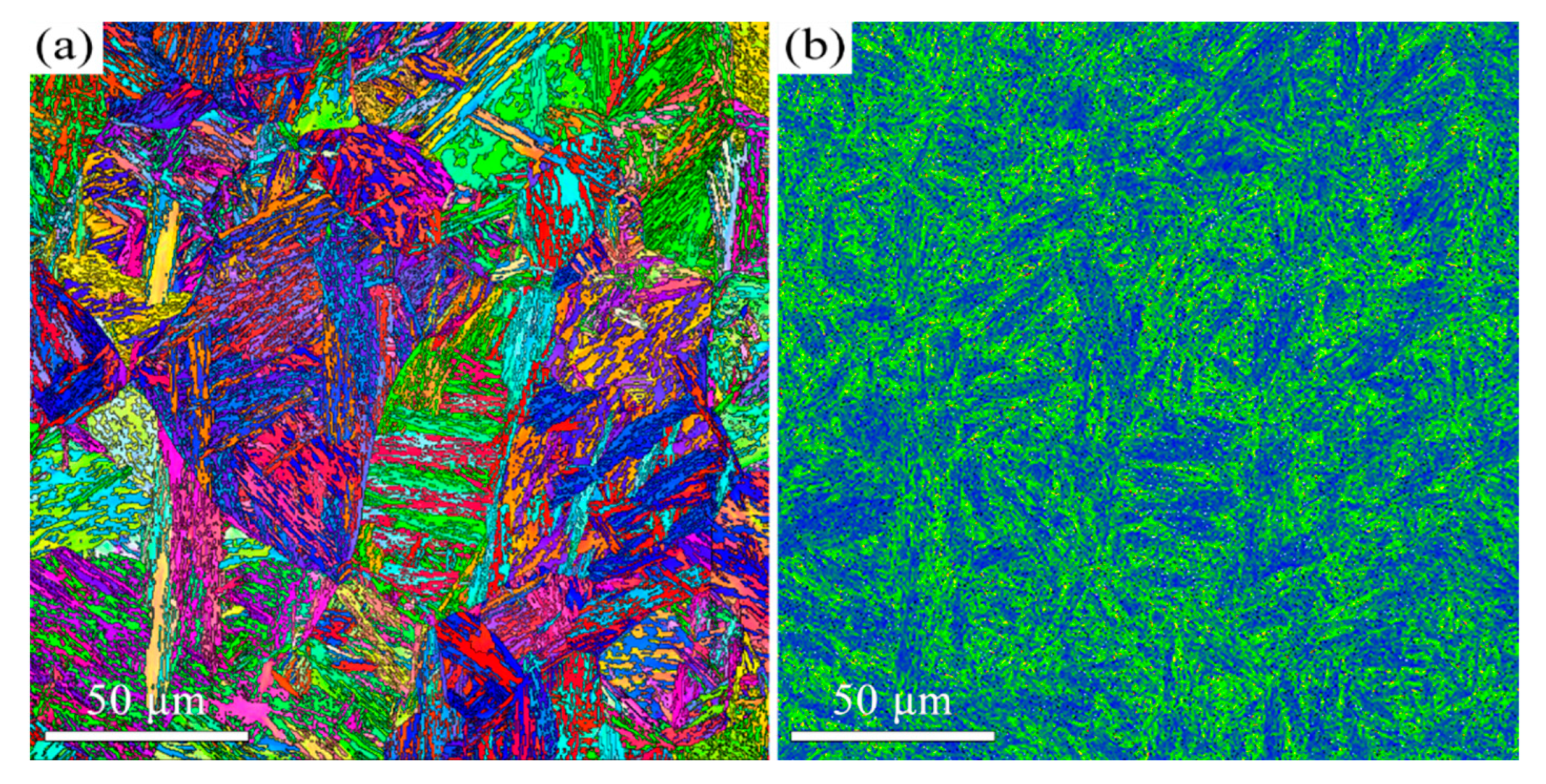
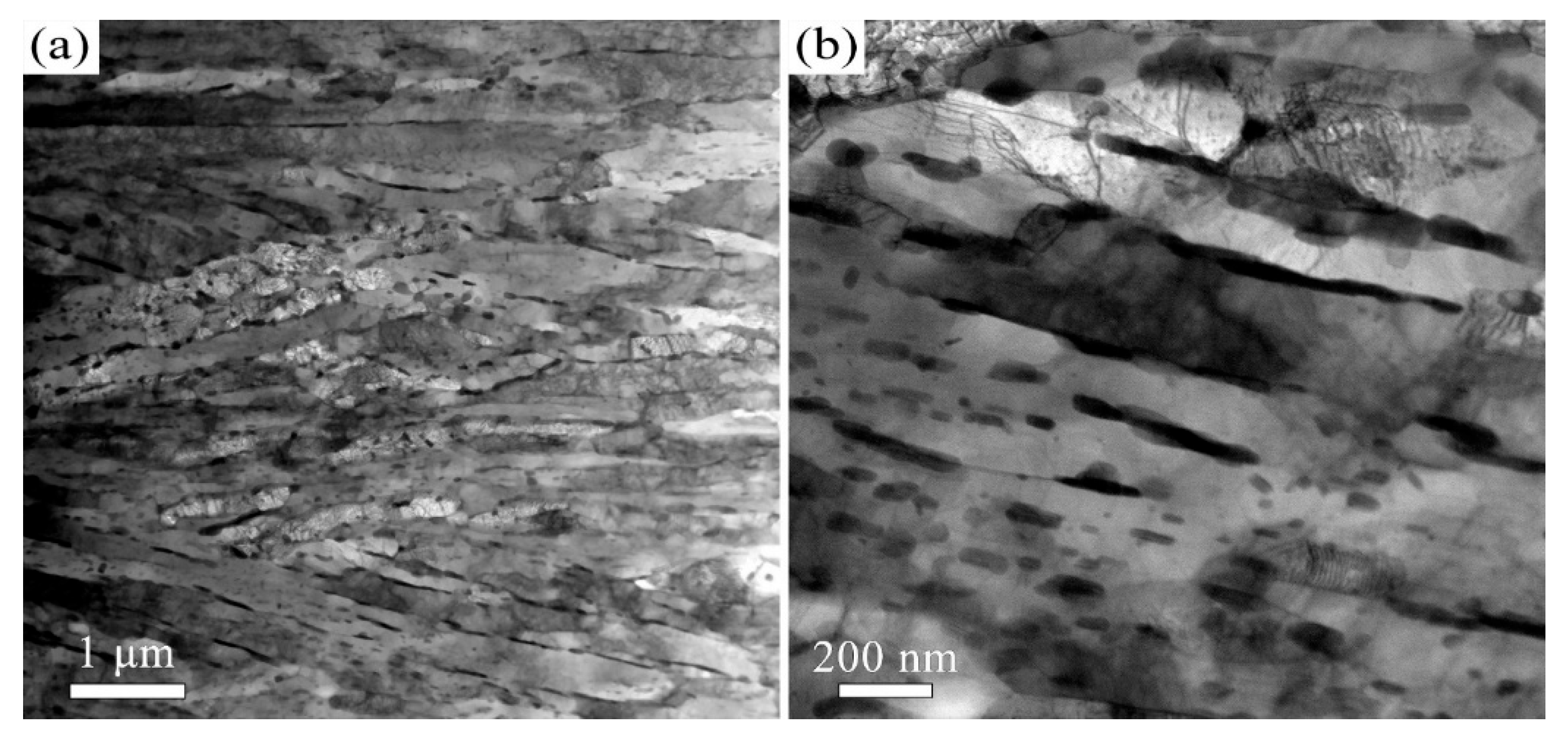
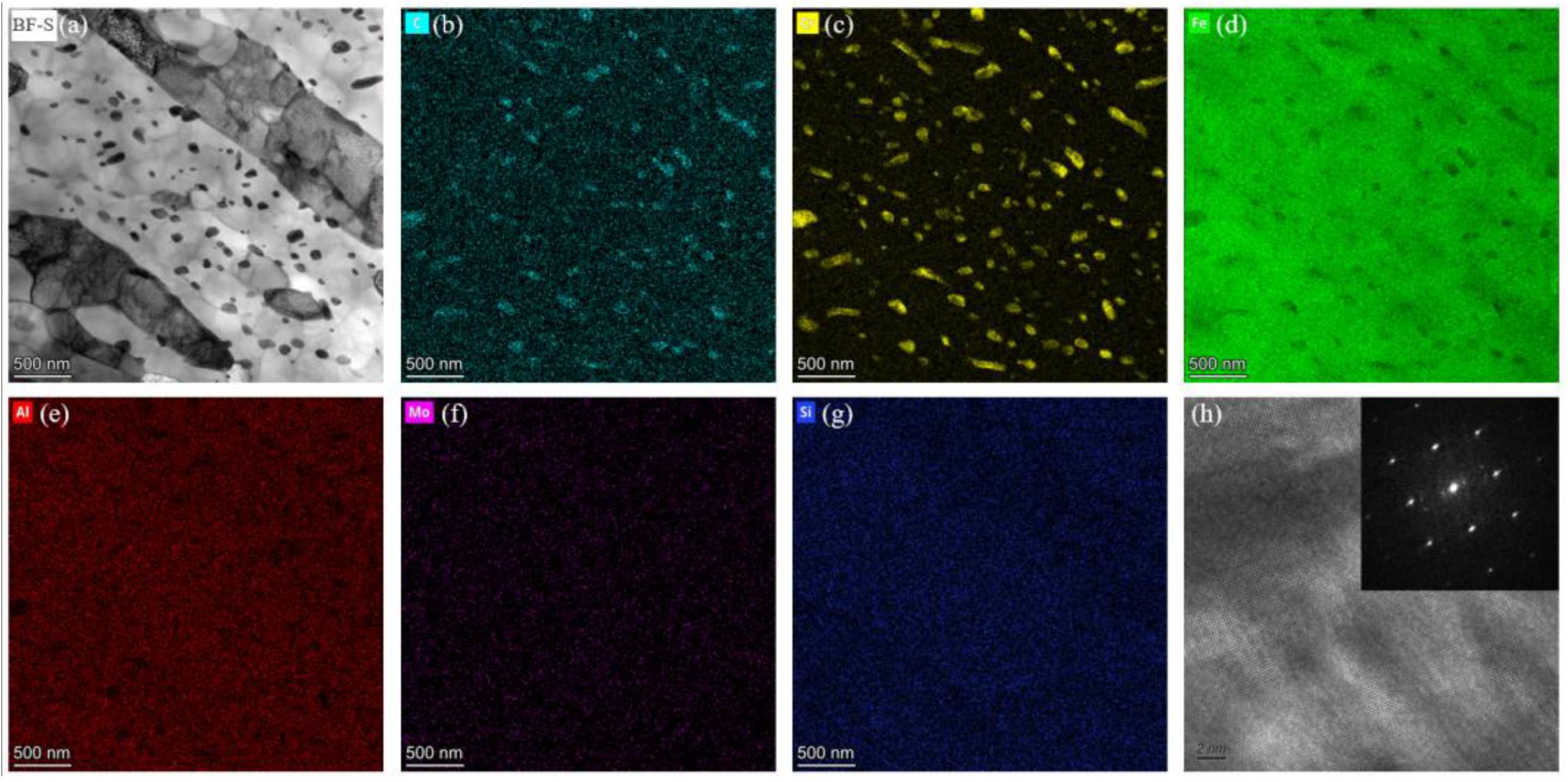
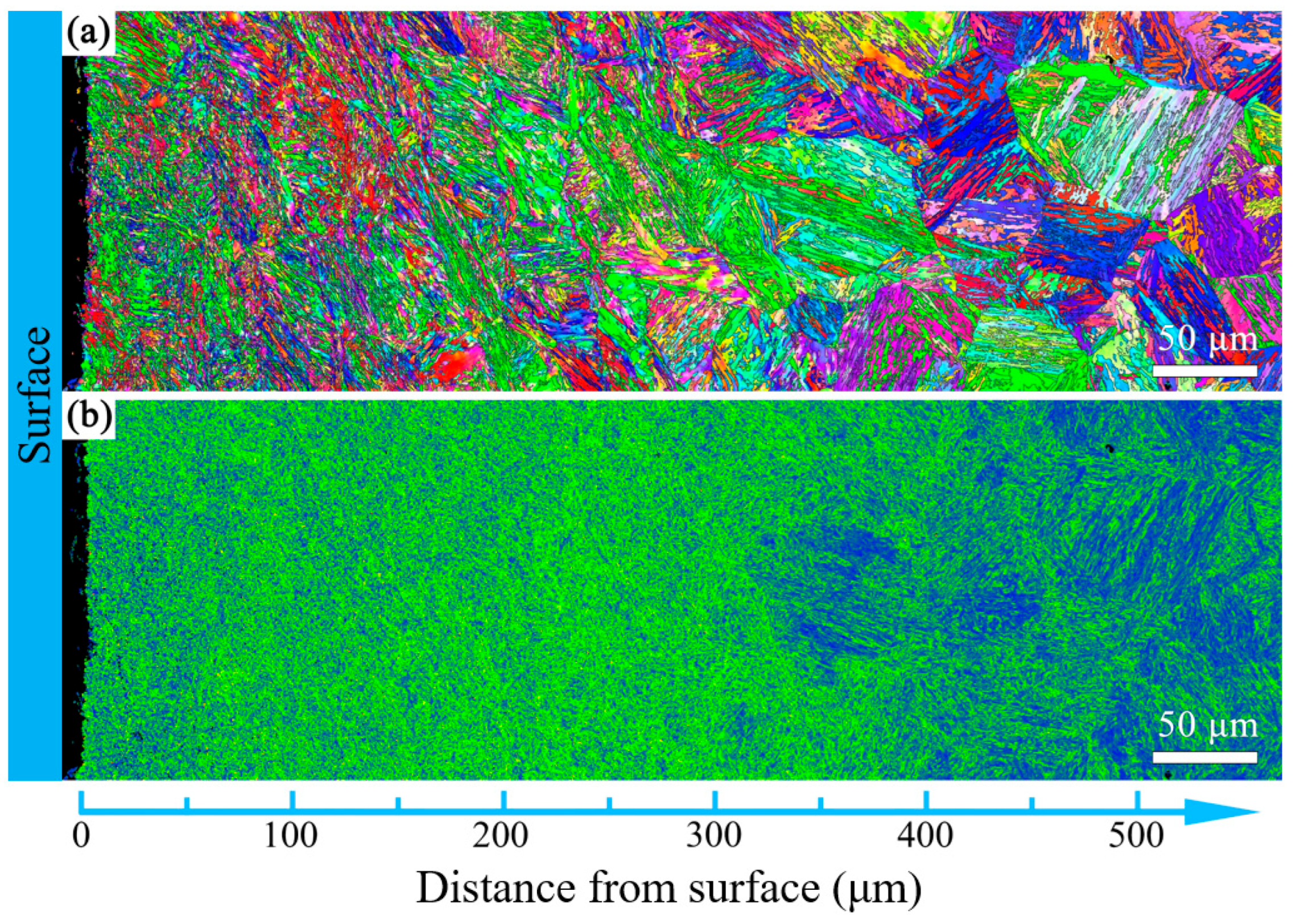
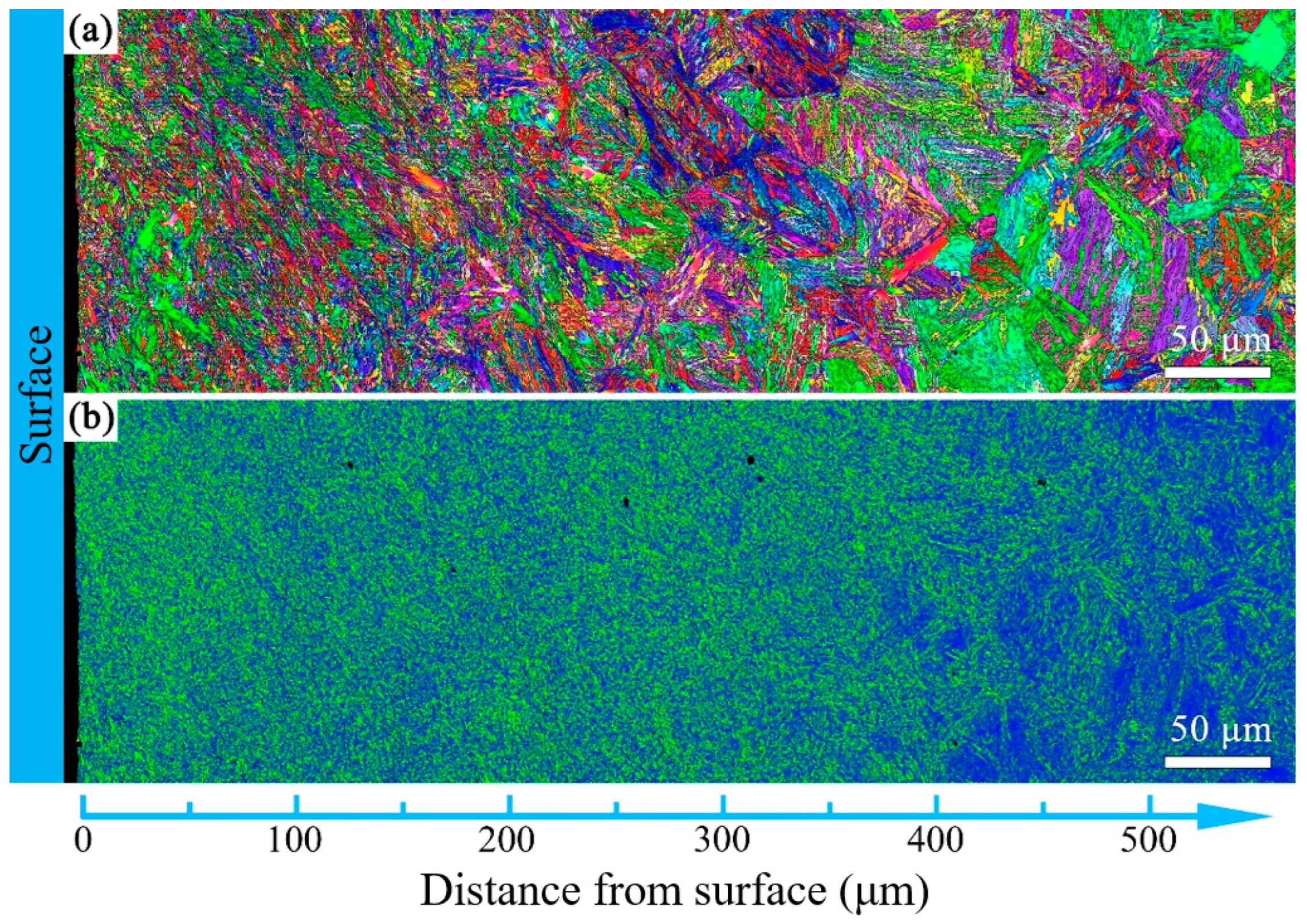
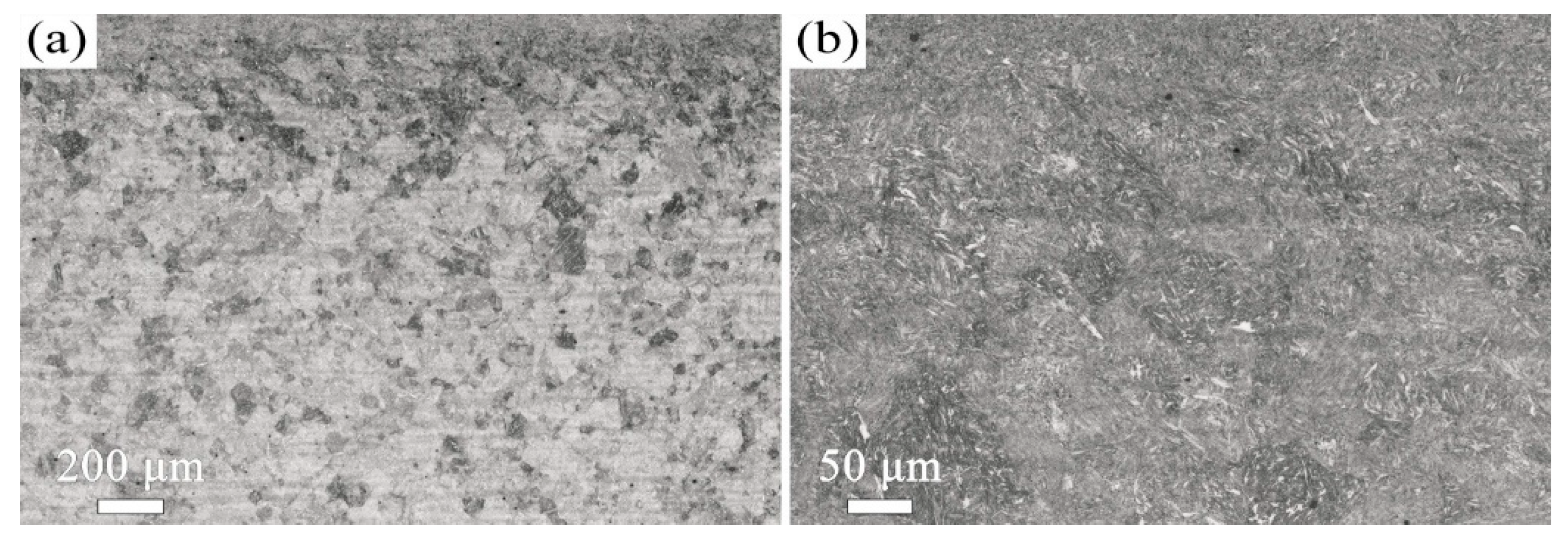
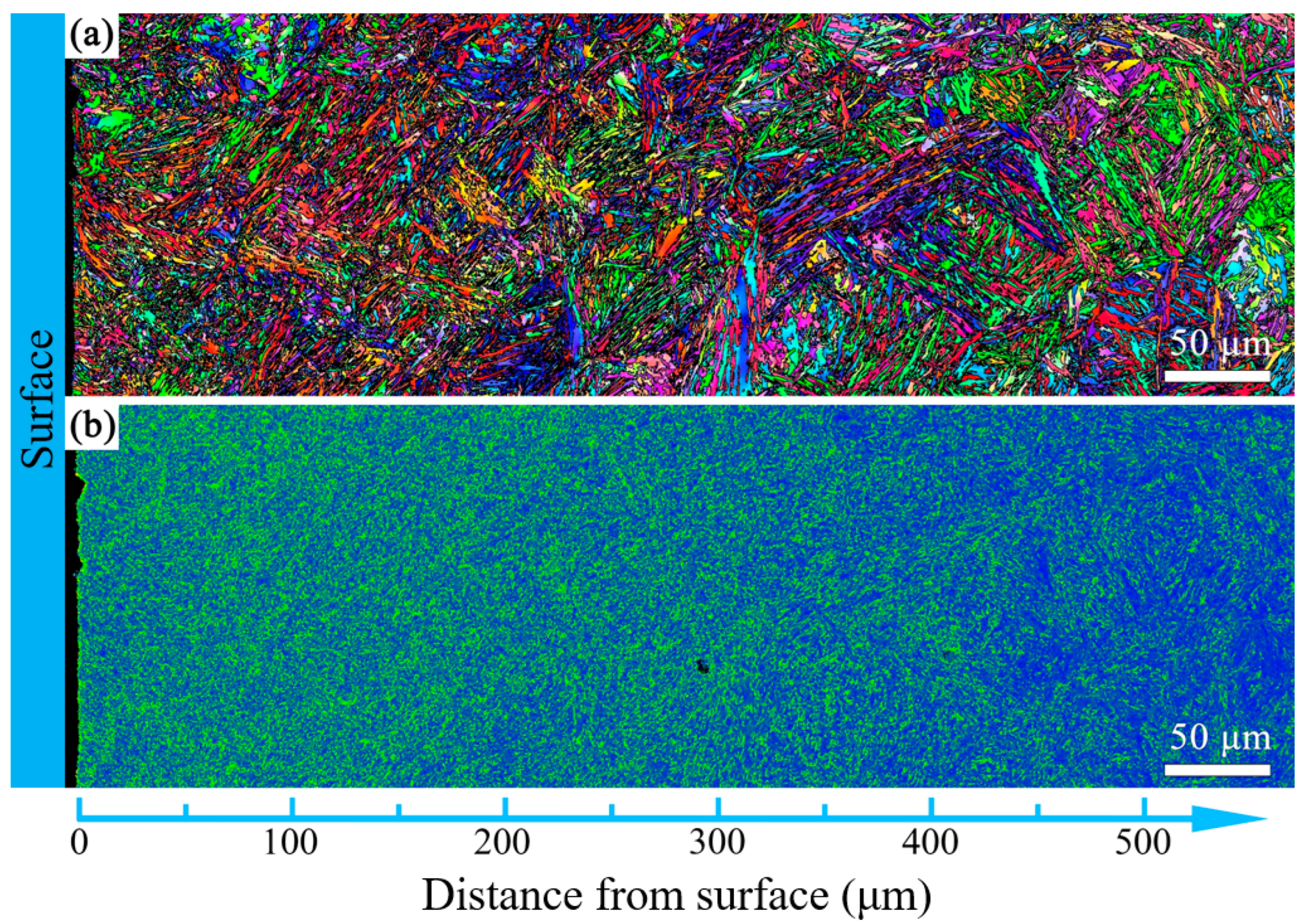
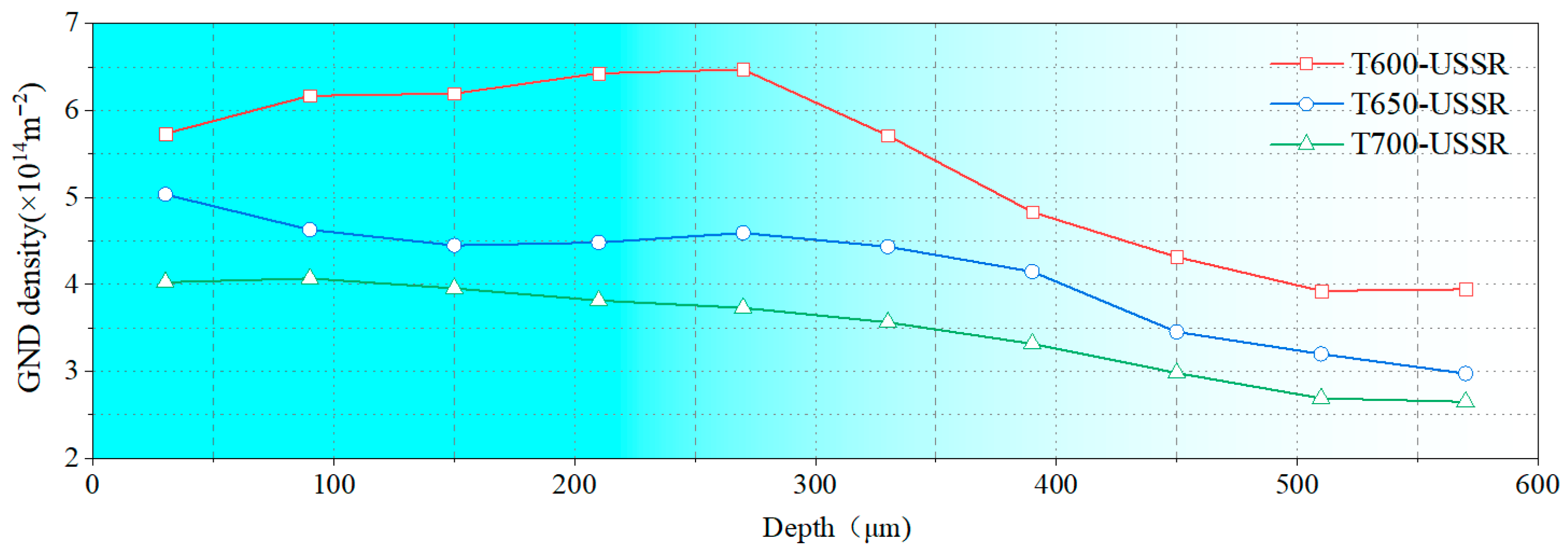
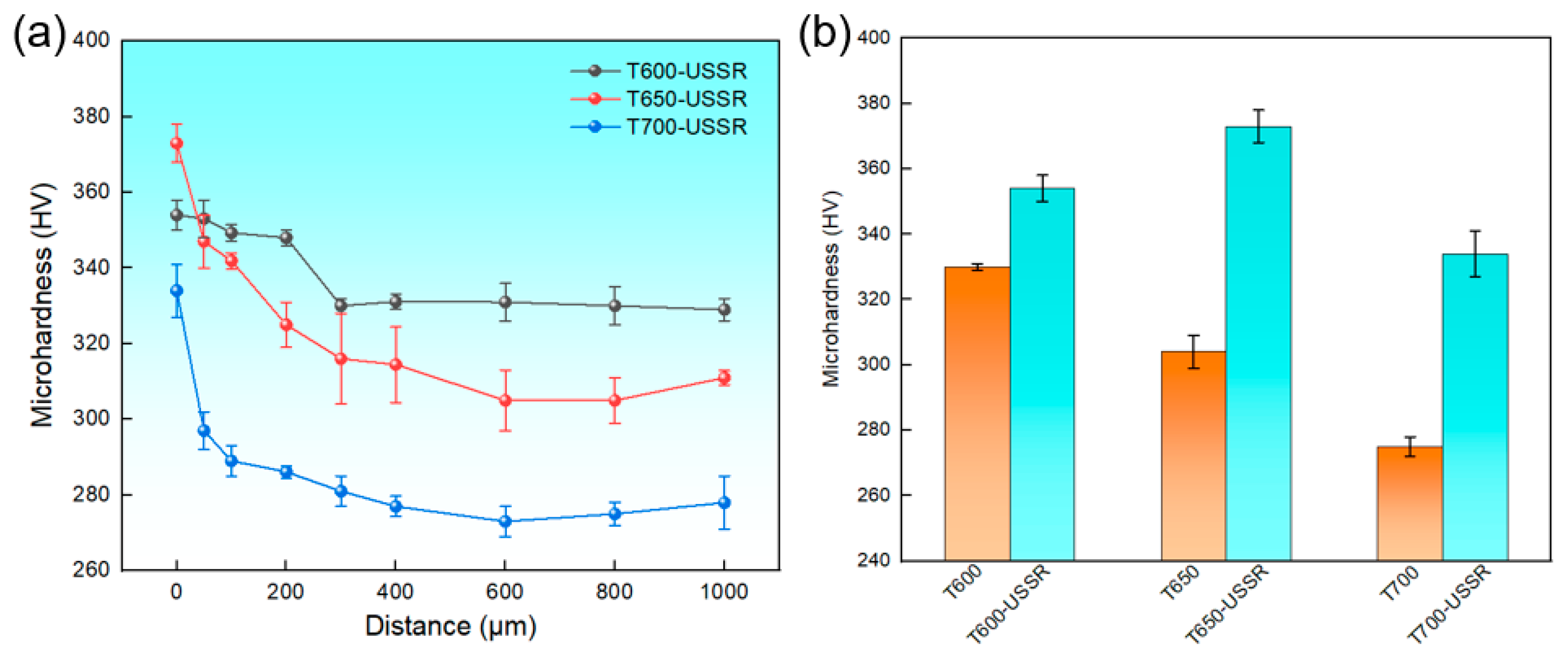
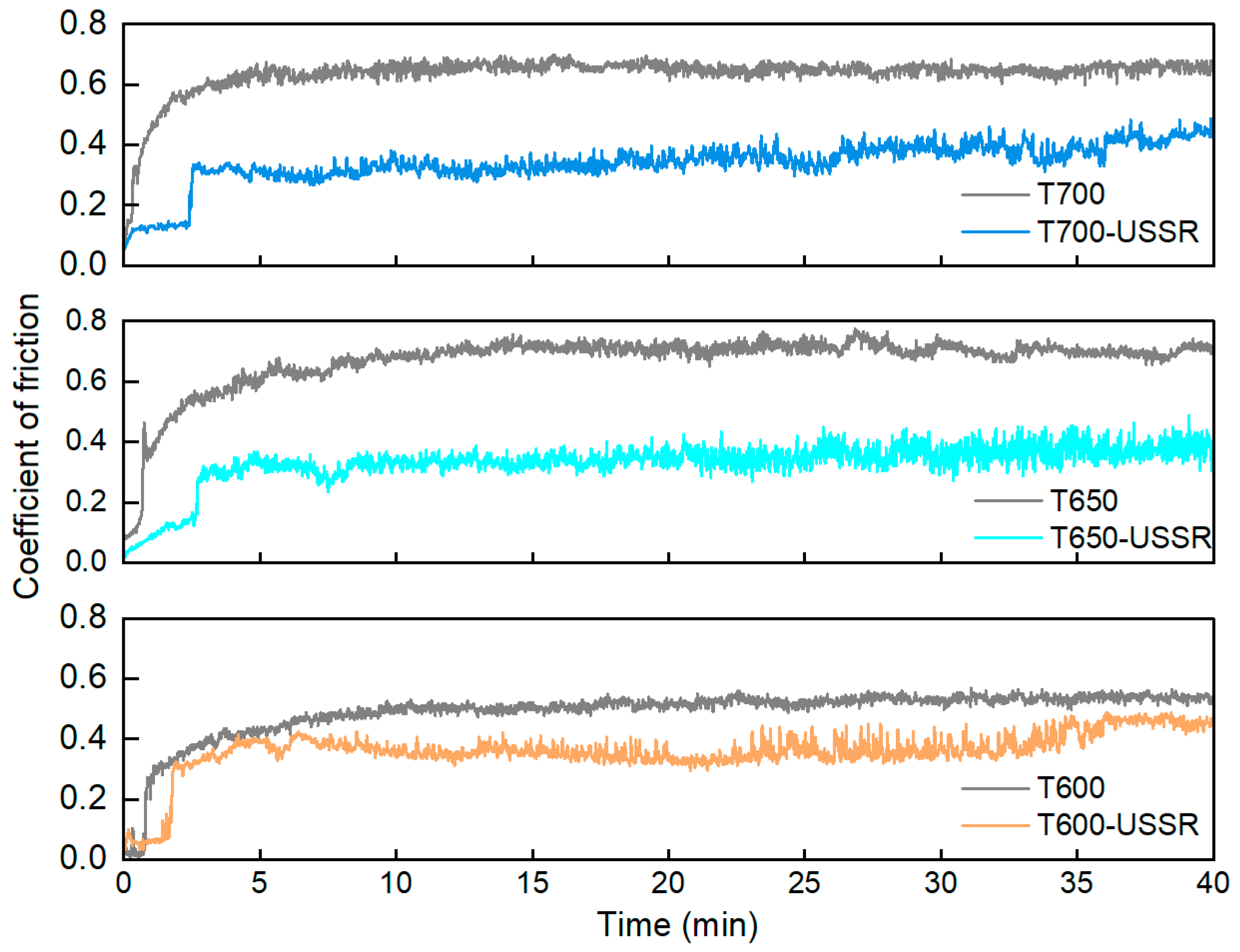
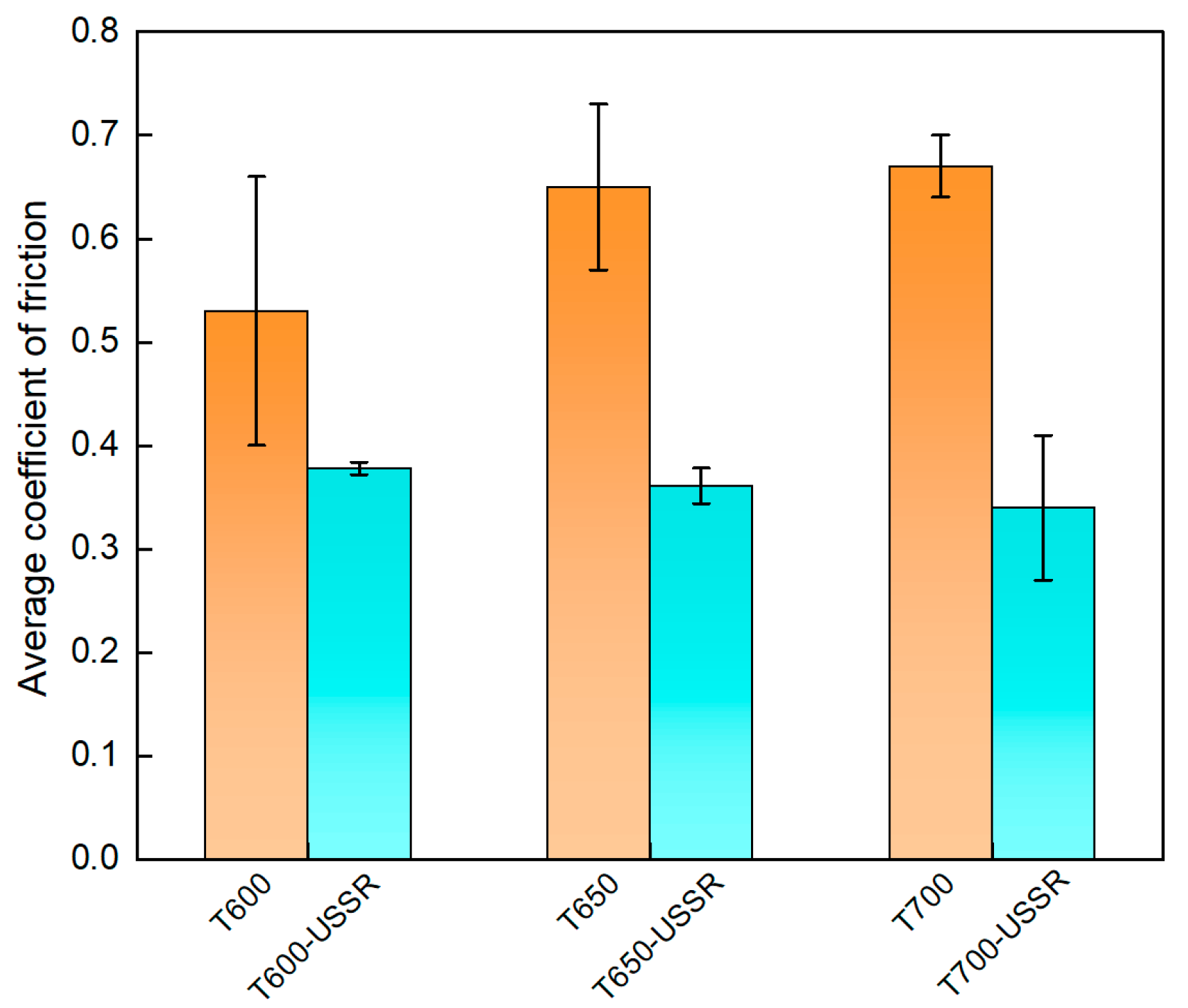
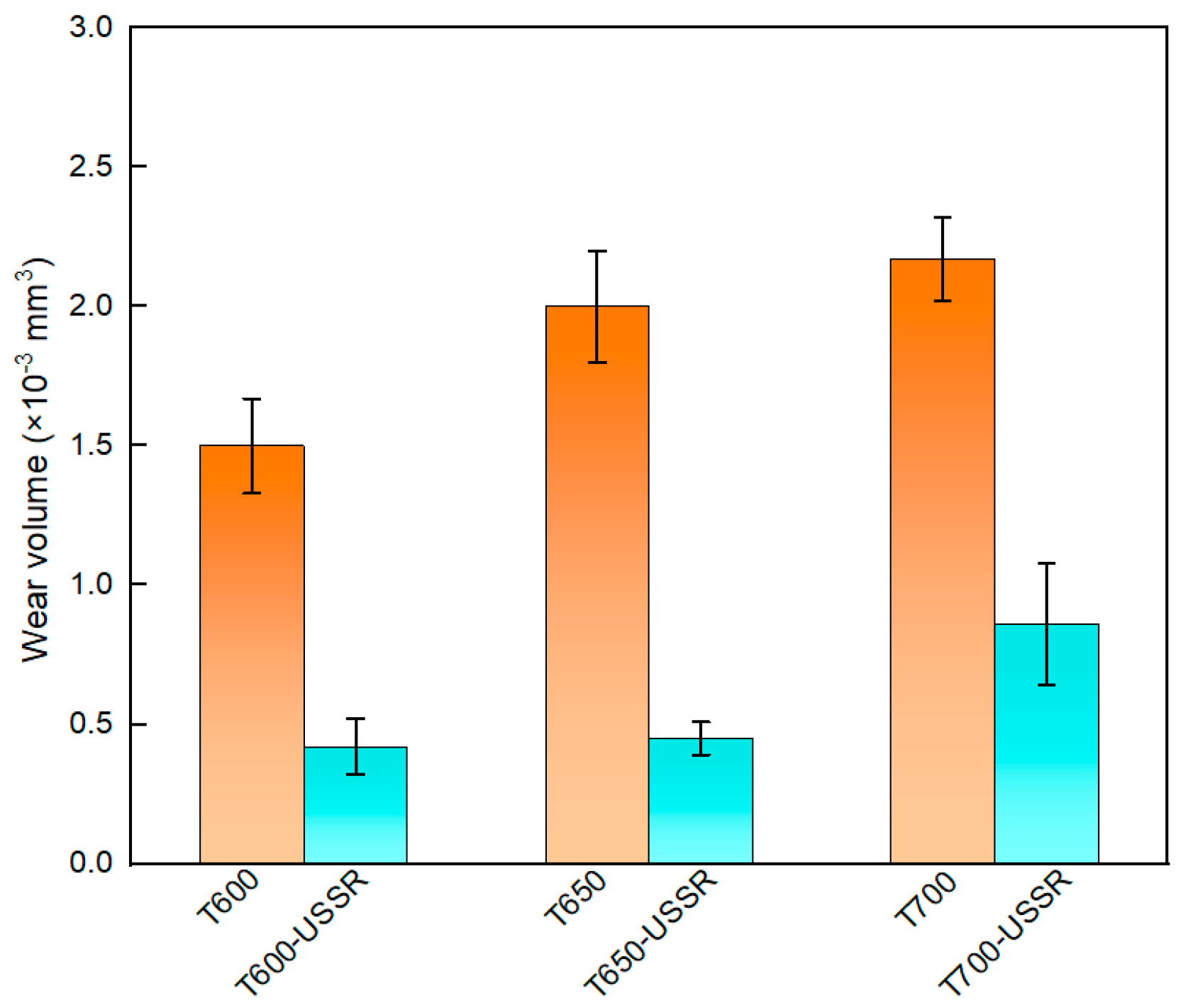
3.2. The Influence of USSR Processing on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The microstructure of the 38CrMoAl steel evolves from tempered martensite with fine carbides at 600 °C to a ferrite matrix with coarse carbides at 700 °C. This microstructural transition leads to a decrease in yield strength (from 915 ± 16 MPa to 815 ± 16 MPa) but an increase in elongation (from 18.7 ± 0.6 to 27.3 ± 1.2%). An excellent combination of strength and ductility is achieved in the samples tempered at 600 °C and 650 °C.
- (2)
- Following USSR processing, all tempered samples develop a defect-free gradient nanostructured surface layer, evidenced by progressively coarser martensite/ferrite grains and reduced dislocation density with depth, alongside a smooth surface (Ra 0.17 μm). The thickness of this layer expands with increasing tempering temperature, from 300 μm at 600 °C to 400 μm at 700 °C.
- (3)
- After USSR processing, the samples tempered at 600 °C, 650 °C, and 700 °C exhibit a notable increase in surface hardness, reaching 354 ± 4 HV, 373 ± 5 HV, and 334 ± 7 HV, respectively—corresponding to improvements of 7.3%, 22.7%, and 21.5% over their unprocessed counterparts. Their wear volume decreases significantly by approximately 73%, 78%, and 60% for each tempering condition, respectively. Notably, the wear volumes of the samples tempered at 600 °C and 650 °C are comparable and substantially lower than that of the sample tempered at 700 °C. USSR treatment also leads to a reduction in the coefficient of friction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, W.; Zhou, R.; Vivegananthan, P.; See Wu, M.; Gao, H.; Zhou, K. Recent Progress in Gradient-Structured Metals and Alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 140, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H. Mechanical Properties and Deformation Mechanisms of Gradient Nanostructured Metals and Alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, G. Research Progress of Heterogeneous Structure Magnesium Alloys: A Review. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2024, 2, 2147–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Meyers, M.A.; Ritchie, R.O. Structural Architectures with Toughening Mechanisms in Nature: A Review of the Materials Science of Type-I Collagenous Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 425–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Tao, N.R. Martensitic Transformation Dominated Tensile Plastic Deformation of Nanograins in a Gradient Nanostructured 316L Stainless Steel. Acta Mater. 2023, 248, 118780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Cao, C.; Yang, J.; Hua, M.; Cai, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhong, F. Research on Multi-Scale Failure Mechanism of Gradient Nanostructured 316L Steel Under Strain-Controlled Fatigue at 650 °C. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 177, 107970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y. Strengthening Mechanism of Abnormally Enhanced Fatigue Ductility of Gradient Nanostructured 316L Stainless Steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 186, 108415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Qu, C.; Zhong, H.; Duan, C.; Li, X.; Qu, S. Quantitative Mechanism of Abnormal Hardening Behavior of Ti6Al4V Alloy Strengthened by Ultrasonic Surface Rolling. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 494, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X. Effect of High-Frequency Dynamic Characteristics in the Ultrasonic Surface Rolling Process On the Surface Properties. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 327, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, K.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C. Effects of Ultrasonic Surface Rolling Processing and Subsequent Recovery Treatment On the Wear Resistance of AZ91D Mg Alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Huang, C.X.; Wang, M.S.; Li, Y.S.; Zhu, Y.T. Quantifying the Synergetic Strengthening in Gradient Material. Scr. Mater. 2018, 150, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhu, Y.T. Gradient Structured Copper by Rotationally Accelerated Shot Peening. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.P.; Babu, P.D.; Gautam, J.; Rai, A.K.; Paul, C.P. Synergistic Integration of Laser Shock Peening and Heat Treatment for Refined Microstructure and Enhanced Mechanical Properties in Additively Manufactured 17–4PH Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 328, 118395. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Fang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Huang, K. Gradient Microstructure and Prominent Performance of Wire-Arc Directed Energy Deposited Magnesium Alloy Via Laser Shock Peening. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2023, 188, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Wan, W.; Liu, H.; Zhou, W.; Ye, Y.; Ren, X. Combination of Annealing and Laser Shock Peening for Tailoring Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Directed Energy Deposited CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 61, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Sun, J.; Song, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S.; Han, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, J. Achieving Gradient Heterogeneous Structure in Mg Alloy for Excellent Strength-Ductility Synergy. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2023, 11, 2392–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Fu, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, B.; Xu, S.; Huang, P.; Cheng, J.; Han, Y.; Han, J.; et al. Tuning Strength-Ductility Combination On Selective Laser Melted 316L Stainless Steel through Gradient Heterogeneous Structure. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 48, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sun, J.; Han, J.; Wu, G. Gradient Age-Precipitation Behavior Induced by Gradient Nano-Grain in Mg–Gd–Ag–Zr Alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2025, 32, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, J.; Fu, Y.; Xu, B.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, G. Preparing Thick Gradient Surface Layer in Cu-Zn Alloy Via Ultrasonic Severe Surface Rolling for Strength-Ductility Balance. Materials 2022, 15, 7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Deng, B.; Zhong, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J. Effect of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment On Corrosion Behavior of 316 Stainless Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2009, 16, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Deng, C. Fatigue Behaviors of Ultrasonic Surface Rolling Processed AISI 1045: The Role of Residual Stress and Gradient Microstructure. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 178, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T3077-2015; Alloy Structural Steels. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Zhang, H.; Qin, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, J.; Hou, X.; Doll, G.L.; Dong, Y.; Ye, C. Low-Temperature Nitriding of Nanocrystalline Inconel 718 Alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 330, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.P.; Tao, N.R.; Wang, Z.B.; Lu, J.; Lu, K. Nitriding Iron at Lower Temperatures. Science 2003, 299, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Suslov, S.; Vellore, A.; Ren, Z.; Amanov, A.; Pyun, Y.; Martini, A.; Dong, Y.; Ye, C. Surface Nanocrystallization by Ultrasonic Nano-Crystal Surface Modification and its Effect On Gas Nitriding of Ti6Al4V Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.P.; Han, Z.; Wang, L.M.; Lu, J.; Lu, K. Low-Temperature Nitriding of 38CrMoAl Steel with a Nanostructured Surface Layer Induced by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 4957–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E92-17; Standard Test Methods for Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTMG 133-05; Standard Test Method for Linearly Reciprocating Ball-on-Flat Sliding Wear. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Wang, C.; Luo, K.; Wang, J.; Lu, J. Carbide-Facilitated Nanocrystallization of Martensitic Laths and Carbide Deformation in AISI 420 Stainless Steel During Laser Shock Peening. Int. J. Plast. 2022, 150, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, C.; Huang, D.; Sun, J.; Zhao, J. Unveiling the Deformation Mechanism of High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Steel with Gradient Dislocation-Cell Structure. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2025, 38, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, A.; Miyamoto, G.; Morito, S.; Nakamura, A.; Moronaga, T.; Kitano, H.; Gutierrez-Urrutia, I.; Hara, T.; Tsuzaki, K. Substructure and Crystallography of Lath Martensite in as-Quenched Interstitial-Free Steel and Low-Carbon Steel. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, C.; Huang, D.; Zhao, J. Improving the Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Additively Manufactured 316L Stainless Steel via Ultrasonic Severe Surface Rolling. China Surf. Eng. 2025, 38, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. Gradient Dual-Phase Structure Design in Brass: A New Strategy for Balancing Mechanical and Tribological Properties. Metals 2025, 15, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Zha, Y.; Zhang, T.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Cao, C.; Huang, D.; Sun, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, J. Construction of a Gradient Nanostructure for Enhanced Surface Properties in 38CrMoAl Steel via Ultrasonic Severe Surface Rolling. Materials 2025, 18, 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235308
Han J, Zha Y, Zhang T, Shi H, Zhang X, Cao C, Huang D, Sun J, Zhang B, Zhao J. Construction of a Gradient Nanostructure for Enhanced Surface Properties in 38CrMoAl Steel via Ultrasonic Severe Surface Rolling. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235308
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jing, Yongzheng Zha, Tao Zhang, Haiyong Shi, Xingyue Zhang, Chao Cao, Di Huang, Jiapeng Sun, Bin Zhang, and Jiyun Zhao. 2025. "Construction of a Gradient Nanostructure for Enhanced Surface Properties in 38CrMoAl Steel via Ultrasonic Severe Surface Rolling" Materials 18, no. 23: 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235308
APA StyleHan, J., Zha, Y., Zhang, T., Shi, H., Zhang, X., Cao, C., Huang, D., Sun, J., Zhang, B., & Zhao, J. (2025). Construction of a Gradient Nanostructure for Enhanced Surface Properties in 38CrMoAl Steel via Ultrasonic Severe Surface Rolling. Materials, 18(23), 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235308






