Investigation of the Microstructure and High-Temperature Performance of Laser-Clad Ni50(AlNbTiV)50-xY2O3 Complex-Concentrated Alloy Composite Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
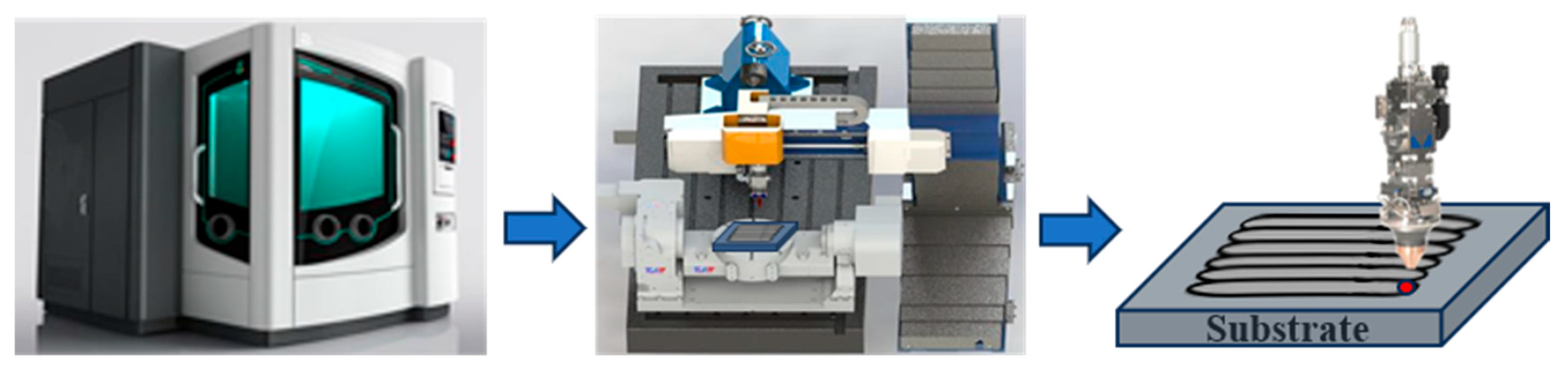
2.1. Experimental Equipment and Sample Preparation
2.2. Microstructure and Phase Composition Test
2.3. High-Temperature Oxidation Test
2.4. Thermal Shock Test
2.5. Mechanical Properties Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Composition
3.2. High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior
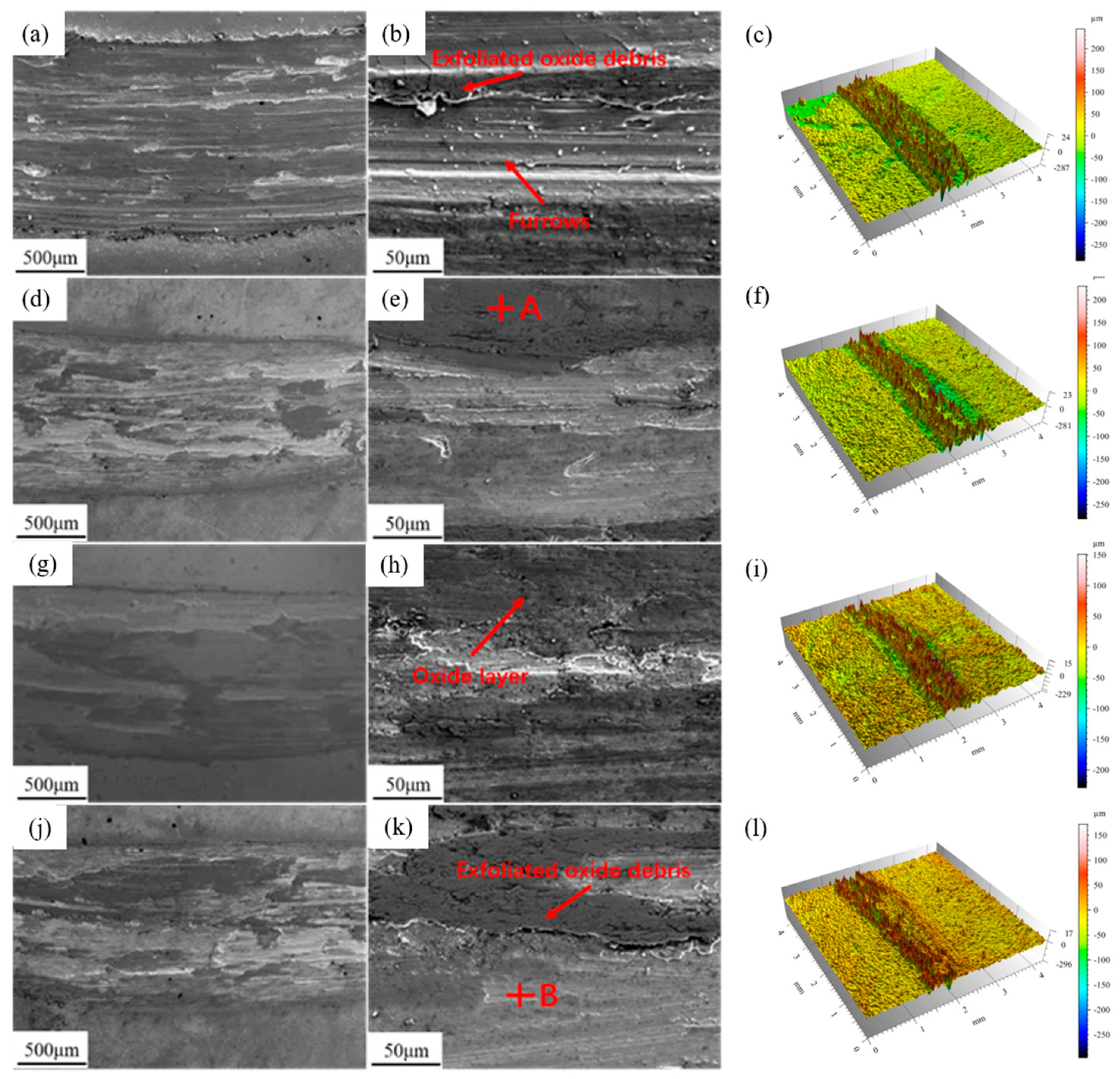
3.3. Thermal Shock Performance
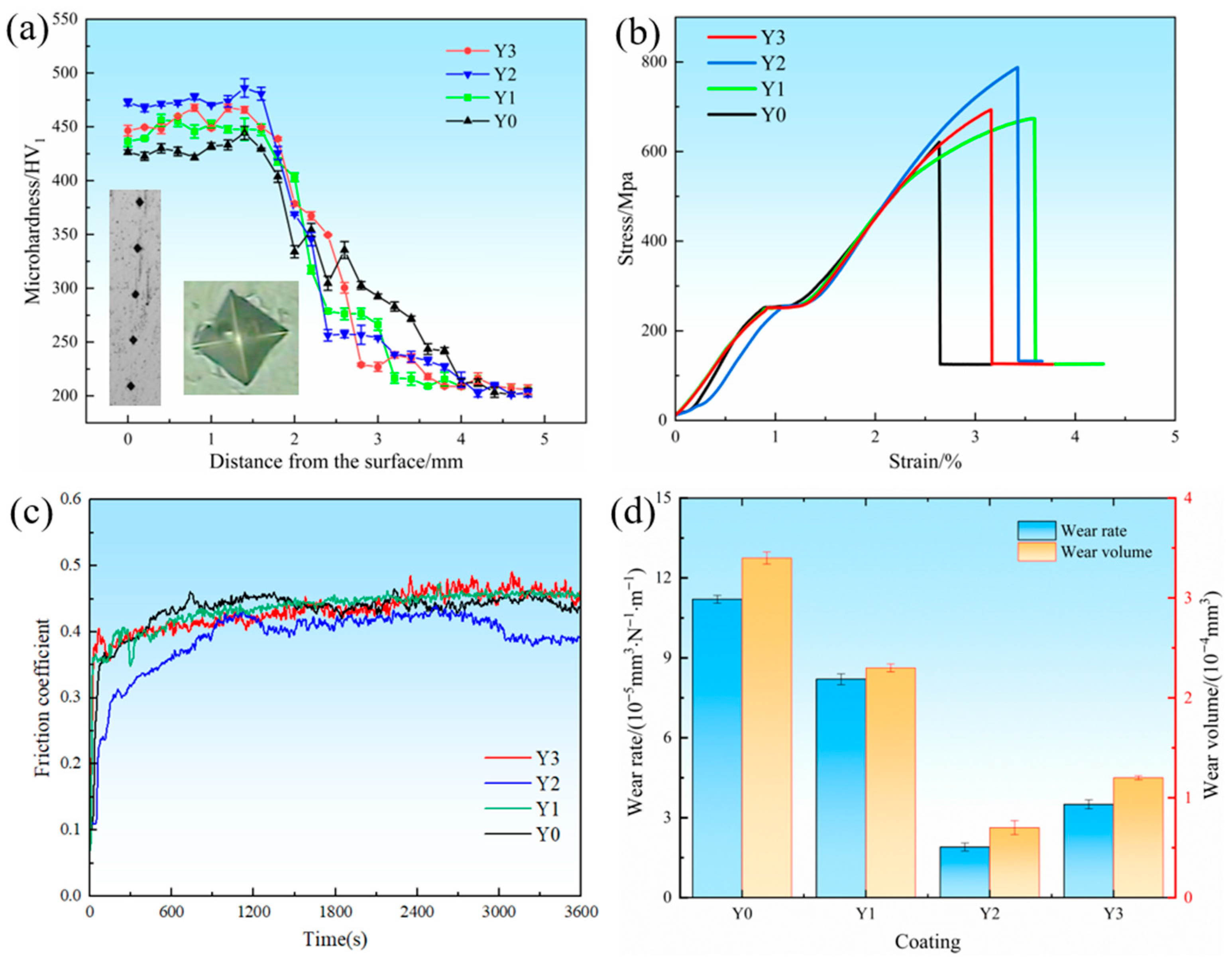
3.4. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Adding an appropriate proportion of Y2O3 to the complex concentrated alloy can refine the grains, but excessive addition leads to a slowdown in the molten pool cooling rate, resulting in larger grains and increased precipitation of lamellar structures in the interdendritic regions.
- (2)
- In the high-temperature oxidation and thermal shock tests, the addition of 0.6 wt.% Y3 coating exhibits the optimal high-temperature stability. This is attributed to the higher density of lamellar precipitate phases rich in Nb and Ti between the dendrites in Y3, which possess lower oxygen diffusion coefficients and free energy.
- (3)
- In the mechanical property test, the addition of 0.4 wt.% of the Y2 coating significantly improved hardness, tensile properties, and wear resistance through the fine-grain strengthening mechanism. The addition of excessive Y2O3 will increase the dilution rate of the substrate, and the lamellar precipitated phase will increase, resulting in a decrease in microhardness and tensile properties. Due to the decrease in hardness, during the cyclic load-friction process of applying pressure, the oxide film is more likely to fall off, which will instead reduce the strength of the coating.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clare, A.; Oyelola, O.; Folkes, J.; Farayibi, P. Laser cladding for railway repair and preventative maintenance. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, B.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Zhao, J. The effects of in-situ synthesized TiC on the performance improvement of nickel-based composite coatings for rail repair. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 28628–28640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.B.; Liu, Y.F.; Luo, Y.S.; Meng, Y. Microstructure and tribological performance of Ni60-based composite coatings on Ti6Al4V alloy with different Ti3SiC2 ceramic additions by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 28996–29010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, O.; Popoola, P.; Sadiku, R.; Okanlawon, D.; Akinlabi, E.T.; Akinlabi, S.A. Advanced materials for laser surface cladding: Processing, manufacturing, challenges and future prospects. In Photoenergy and Thin Film Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 563–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liao, Z.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Cai, M.W.; Wei, X.S.; Li, J.; Shen, J. A review on coatings deposited by extreme high-speed laser cladding: Processes, materials, and properties. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 164, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Mi, G.; Chen, L.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, P.; Shao, X.; Wang, C. Research on microstructures and properties of Inconel 625 coatings obtained by laser cladding with wire. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 715, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Q. Research progress and prospect of laser cladding technology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2419, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, B.; Lindner, T.; Kaur, S.; Tapia Cabrera, J.E.; Hanisch, N.; Schwarz, H.; Lampke, T. Development of CoCr0.65FeNi-BSiC as a self-fluxing high-entropy alloy for thermal spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazamer, N.; Muntean, R.; Vălean, P.C.; Pascal, D.T.; Mărginean, G.; Șerban, V.A. Comparison of Ni-based self-fluxing remelted coatings for wear and corrosion applications. Materials 2021, 14, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilinykh, N.; Krivorigova, A.; Gelchinski, B.; Ilinykh, S.; Kovalev, L. Thermodynamic modeling of composition and properties of self-fluxing materials based on the nickel. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 329, 02026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Yang, Y.; Hu, G.; Lu, X.; Li, J. Thermal expansion control of composite coatings on 42CrMo by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 397, 125983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; He, X.; Gao, L.; Su, G.; Xu, C.; Xu, N. Study on crack behavior of laser cladding ceramic-metal composite coating with high content of WC. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17460–17470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Park, H.; Yoo, J.; Lee, C.; Woo, W.; Park, S. Residual stress and crack initiation in laser clad composite layer with Co-based alloy and WC + NiCr. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, J. New studies on wear and corrosion behavior of laser cladding FeNiCoCrMox high entropy alloy coating: The role of Mo. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 102, 105721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Thind, A.S.; Ren, G.; Mishra, R.; Flores, K.M. Microstructure and properties of NbVZr refractory complex concentrated alloys. Acta Mater. 2021, 213, 116919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yamaguchi, T. High-temperature oxidation performance of laser-cladded amorphous TiNiSiCrCoAl high-entropy alloy coating on Ti-6Al-4V surface. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 433, 128123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; He, L.; Ye, X.; Ouyang, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X. Microstructure and elevated temperature wear behavior of laser-cladded AlCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy coating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Yu, X.; Li, J. Synthesis and characterization of refractory TiZrNbWMo high-entropy alloy coating by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 311, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hu, H.; Li, L.; Yan, H.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Li, J. Effects of ultrasonic surface rolling process on the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Ni50(AlNbTiV)50 high-entropy alloy laser cladding layer. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 47, 113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T. Influence of Y2O3 addition on the microstructure of TiC reinforced Ti-based composite coating prepared by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2022, 189, 111962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hao, H.; Gao, Q.; Cao, Y.-B.; Han, R.-H.; Qi, H.-B. Strengthening mechanism and high-temperature properties of H13+ WC/Y2O3 laser-cladding coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Wen, B.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Ren, S. Effect of La2O3 addition on wear properties of Ni60a/SiC coating using laser-cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 148, 107640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sui, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, C. Laser metal deposited steel alloys with uniform microstructures and improved properties prepared by addition of small amounts of dispersed Y2O3 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 806, 140827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yu, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Ward, R.M. Effects of Y2O3 nanoparticles on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of IN738LC manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Corros. Sci. 2020, 171, 108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yu, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, F.; Xu, Z.; Han, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ward, R.M.; Zhu, Q. Y2O3 nanoparticles decorated IN738LC superalloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion: Cracking inhibition, microstructures and mechanical properties. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2022, 230, 109555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalan, F.C.; Sobrinho, A.S.D.S.; Nishihora, R.K.; Santos, S.F.; Martins, G.V.; Cardoso, K.R. Effect of Nb and Ti additions on microstructure, hardness and wear properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Yuasa, T.; Sato, H.; Okubo, S.; Fujimaki, K. Grain refinement of stainless steel by strontium oxide heterogeneous nucleation site particles during laser-based powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 308, 117700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chan, K.; Yang, X.S. Maintaining Grain Boundary Segregation-Induced Strengthening Effect in Extremely Fine Nanograined Metals. Nano Lett. 2025, 25, 5493–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Guo, W.; Yang, Y. Effect of thermal growth oxide composition and morphology on local stresses in thermal barrier coatings. Materials 2022, 15, 8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Cai, H.N. Comprehensive effects of TGO growth on the stress characteristic and delamination mechanism in lamellar structured thermal barrier coatings. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2220–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, T.; Yamasaki, T.; Kushimoto, K.; Kano, J.; Omata, T. Enhanced Proton Transport in Nb-Doped Rutile TiO2, A Highly Useful Class of Proton-Conducting Mixed Ionic Electronic Conductors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 30757–30767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, B.; Nitzsche, M.; Bredow, T. Energetic Order of Nb2O5 and Ta2O5 Polymorphs. Phys. Status Solidi B 2022, 259, 2200052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Peng, X.; Lü, W.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, J. Ultra-high temperature oxidation resistant refractory high entropy alloys fabricated by laser melting deposition: Al concentration regulation and oxidation mechanism. Corros. Sci. 2023, 224, 111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, F.Y.; Tung, S.W.; Ouyang, F.Y. High temperature oxidation behavior of high entropy alloy Al4Co3Cr25Cu10Fe25Ni33 in oxygen-containing atmospheres. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wu, M.; He, R.; Gong, Y.; Miao, X. Effect of CeO2 addition on grain refinement and mechanical properties of stellite-6 coating fabricated by laser cladding. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 2621–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Hu, J. Effect of SiC/nano--CeO2 on wear resistance and microstructures of Ti3Al/γ--Ni matrix laser--cladded composite coating on Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Surf. Interface Anal. 2012, 44, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, X.; Guan, Y.; Jin, G.; Zheng, W.; Su, W.; Wan, S.; Shi, Z. Effects of Cr content on microstructure and tribological properties of laser cladding Ti-based coatings. Tribol. Int. 2023, 187, 108744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wei, P.; Yue, L.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, B.; Bai, P.; Meng, Y.; Tian, Y. Differences in adhesive wear mechanisms of soft/hard materials caused by varying loads during the friction process. Tribol. Int. 2025, 214, 111157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, A.; Yuan, W.; Gao, Z. Contribution of hardness and work hardening to the wear resistance of Pt-based metallic surfaces revealed by nanoscale reciprocating sliding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 614, 156178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
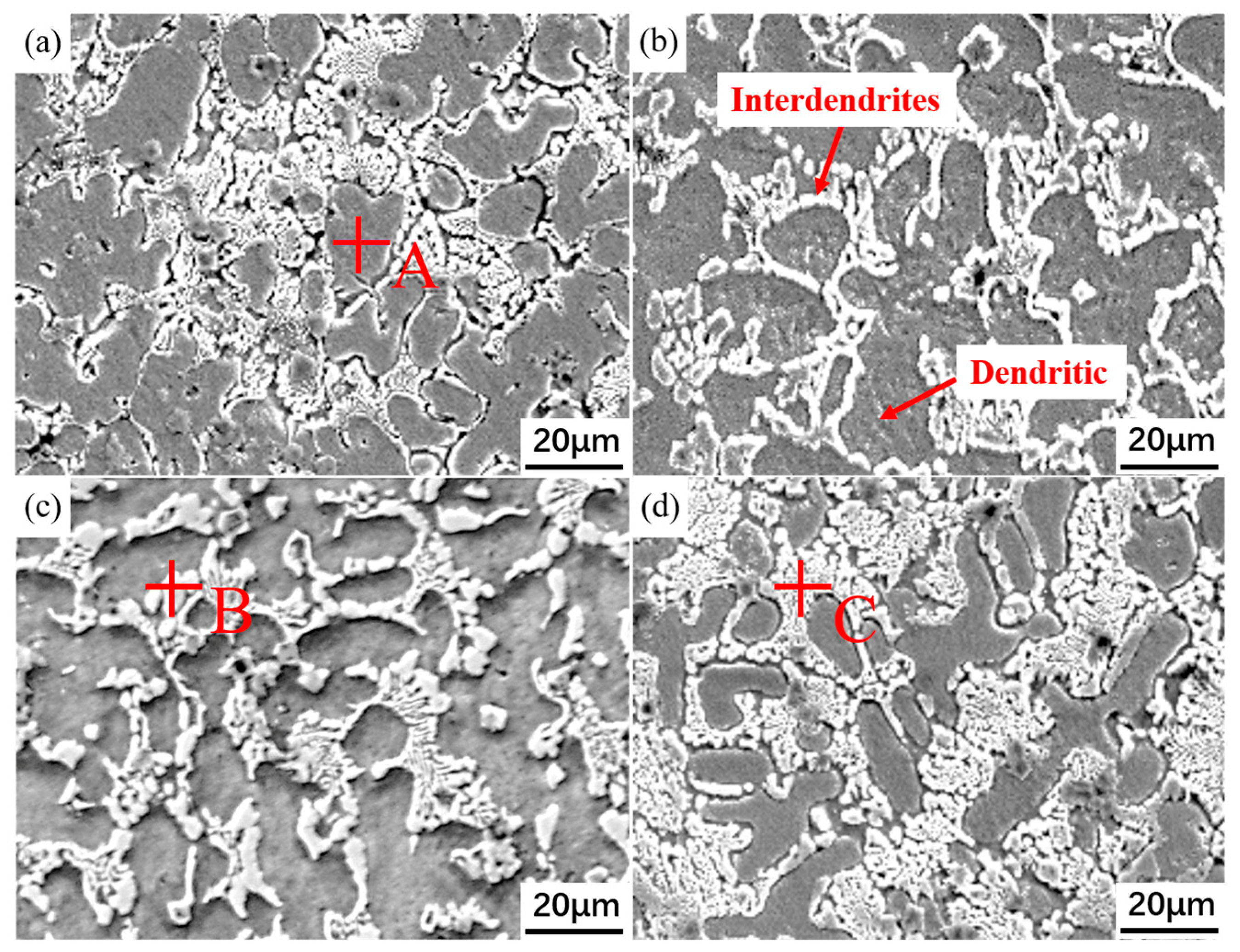
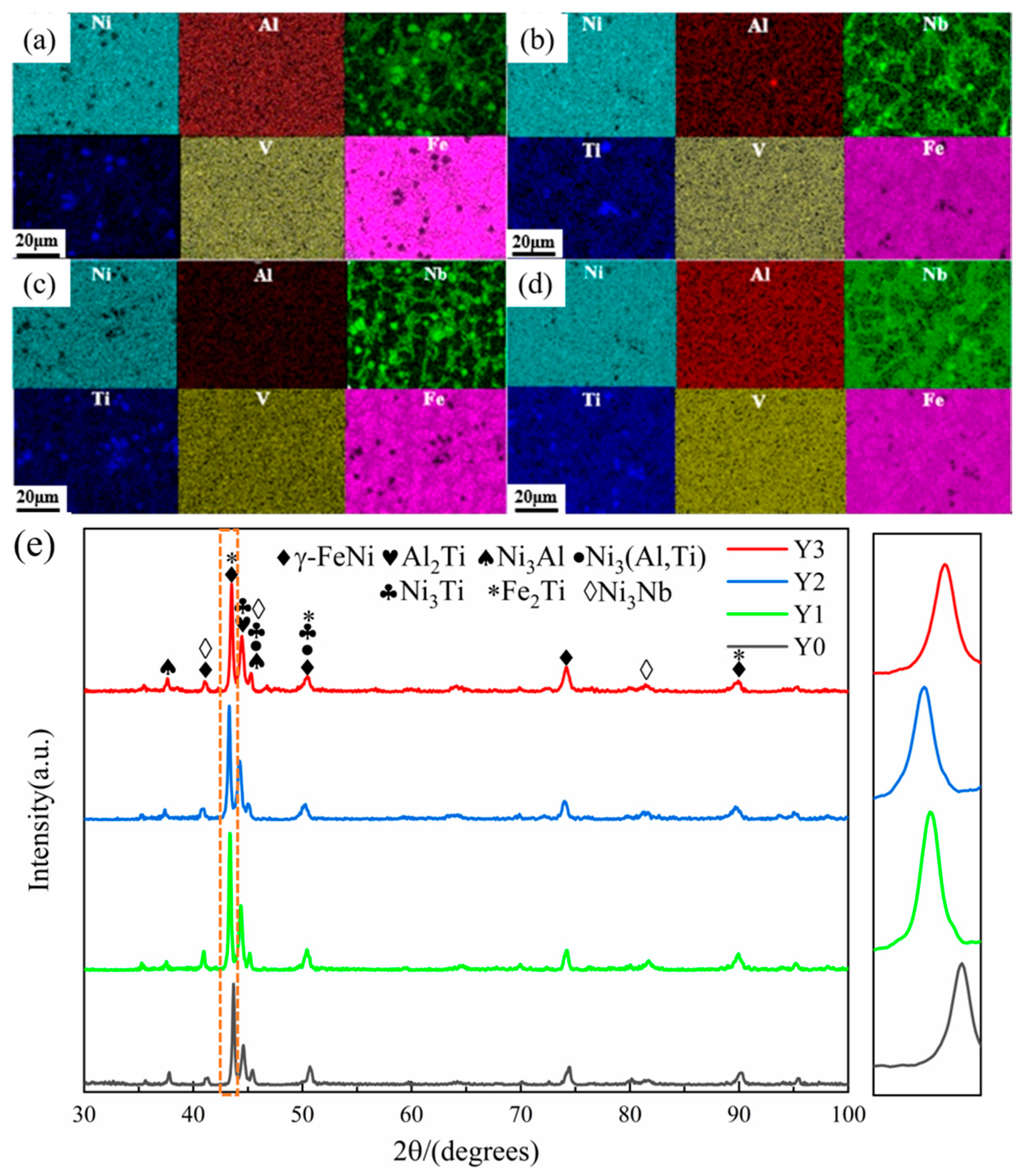


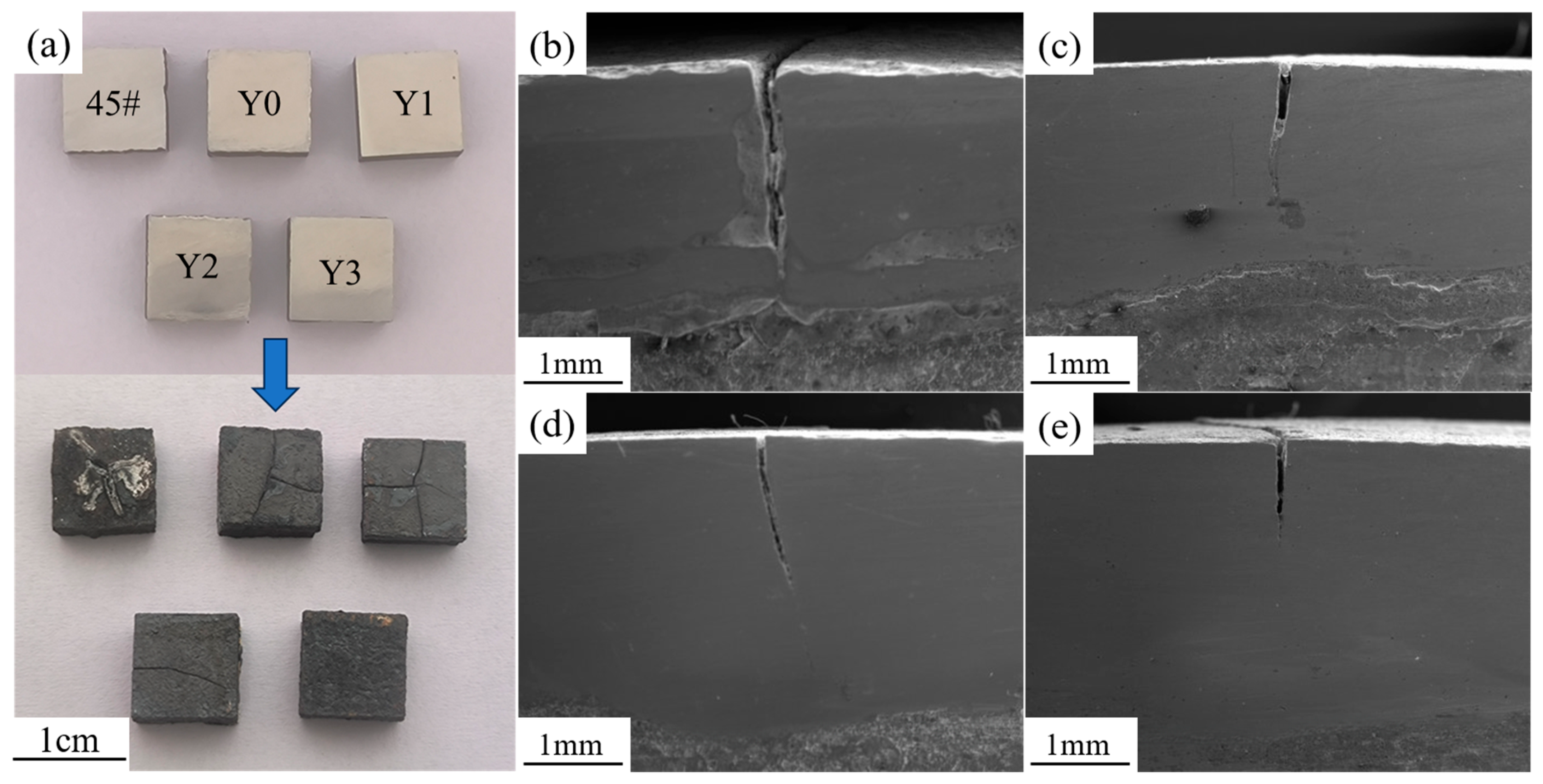
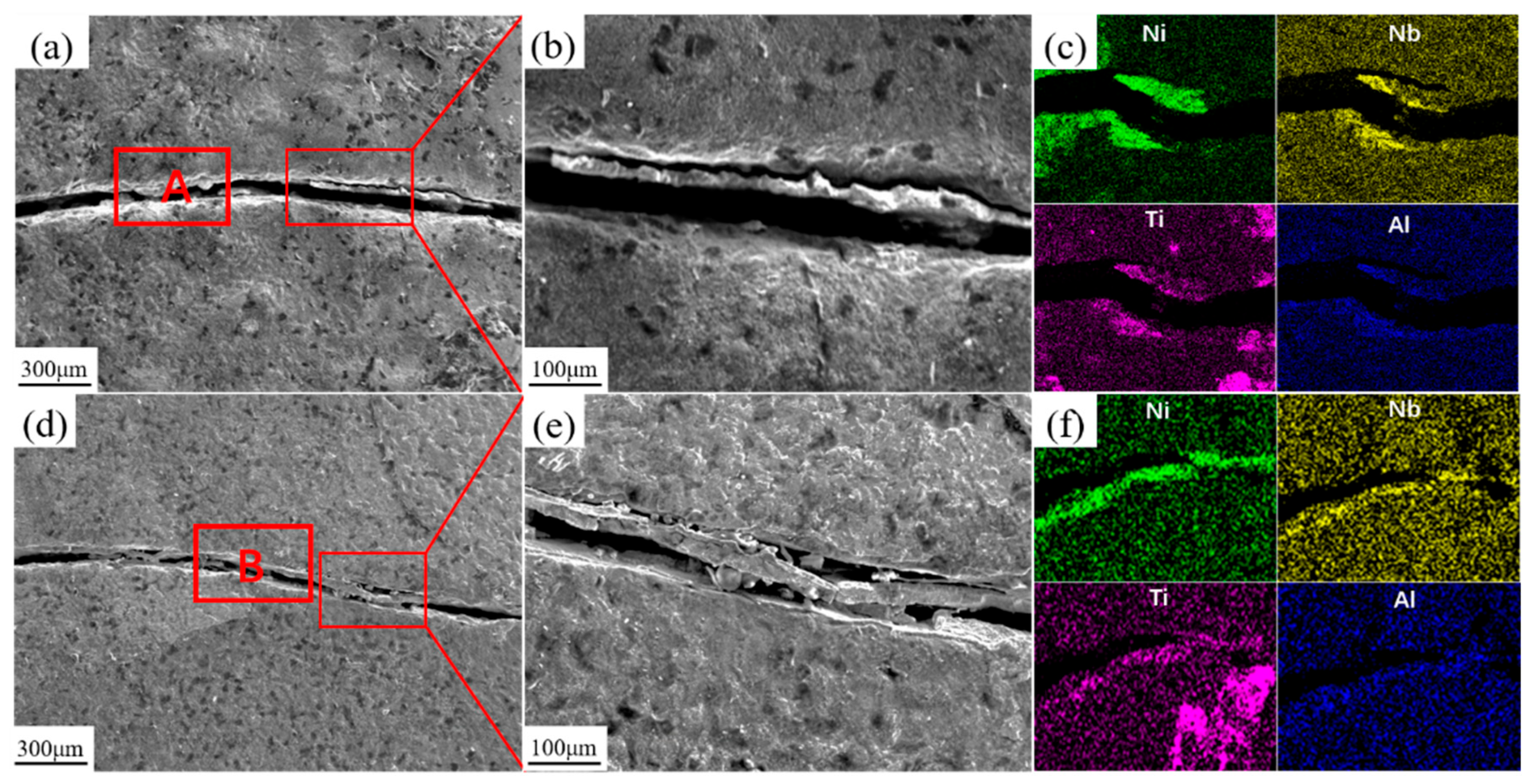
| Elements | Ni | Al | Nb | V | Ti | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 24.89 ± 1.24 | 2.31 ± 0.12 | 2.94 ± 0.15 | 5.71 ± 0.29 | 2.30 ± 0.12 | 61.8 ± 3.09 |
| B | 18.9 ± 0.95 | 1.50 ± 0.08 | 22.7 ± 1.14 | 3.95 ± 0.20 | 6.41 ± 0.32 | 46.4 ± 2.32 |
| C | 20.8 ± 1.04 | 1.76 ± 0.09 | 20.0 ± 1.00 | 4.25 ± 0.21 | 5.20 ± 0.26 | 47.8 ± 2.39 |
| Elements | Ni | Al | Nb | V | Ti | Fe | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 22.47 ± 1.12 | 3.18 ± 0.16 | 10.63 ± 0.53 | 5.52 ± 0.28 | 6.13 ± 0.31 | 19.90 ± 1.00 | 32.17 ± 1.61 |
| B | 26.33 ± 1.32 | 1.42 ± 0.07 | 12.74 ± 0.64 | 7.34 ± 0.37 | 8.30 ± 0.42 | 24.81 ± 1.24 | 19.06 ± 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yan, H.; Huang, W. Investigation of the Microstructure and High-Temperature Performance of Laser-Clad Ni50(AlNbTiV)50-xY2O3 Complex-Concentrated Alloy Composite Coatings. Materials 2025, 18, 5303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235303
Huang W, Wang H, Li C, Li L, Yan H, Huang W. Investigation of the Microstructure and High-Temperature Performance of Laser-Clad Ni50(AlNbTiV)50-xY2O3 Complex-Concentrated Alloy Composite Coatings. Materials. 2025; 18(23):5303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235303
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wen, Huaji Wang, Chunlei Li, Lei Li, Huan Yan, and Wenyi Huang. 2025. "Investigation of the Microstructure and High-Temperature Performance of Laser-Clad Ni50(AlNbTiV)50-xY2O3 Complex-Concentrated Alloy Composite Coatings" Materials 18, no. 23: 5303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235303
APA StyleHuang, W., Wang, H., Li, C., Li, L., Yan, H., & Huang, W. (2025). Investigation of the Microstructure and High-Temperature Performance of Laser-Clad Ni50(AlNbTiV)50-xY2O3 Complex-Concentrated Alloy Composite Coatings. Materials, 18(23), 5303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18235303





