Dynamic Compressive Mechanical Behavior of a Novel Three-Dimensional Re-Entrant Honeycomb (3D-RH) Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Models
2.1. Architecture Design
2.2. Theoretical Analysis
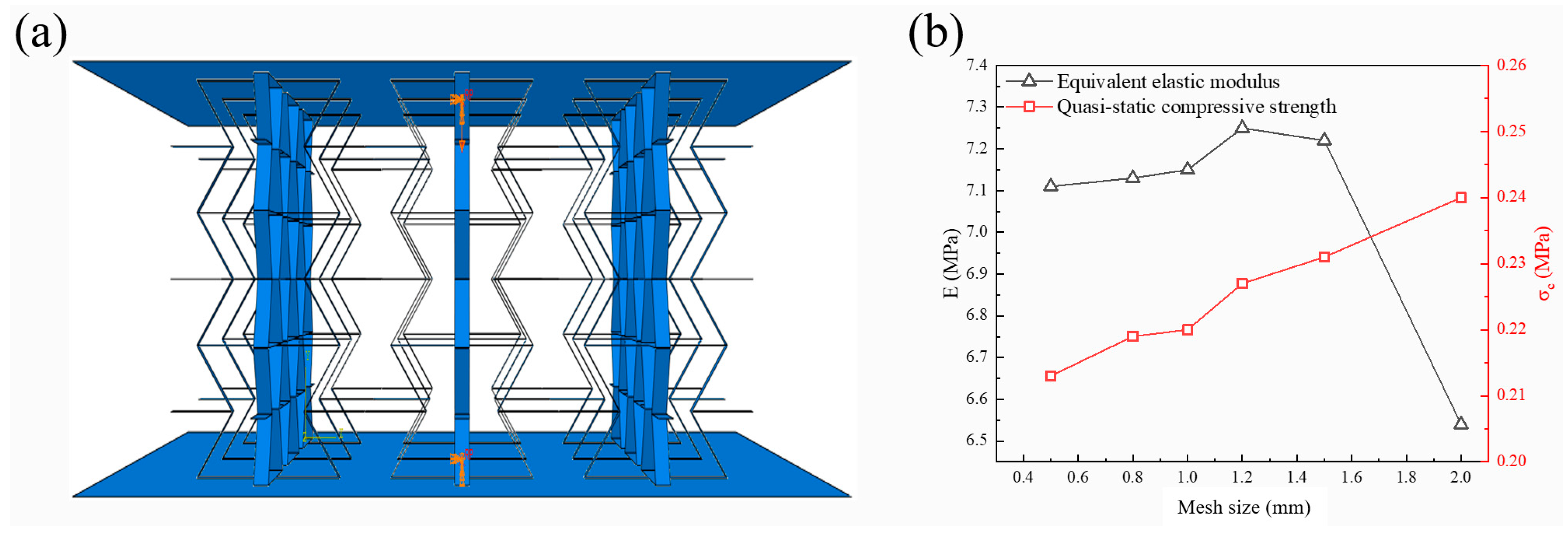
2.3. Computational Model
3. Validation of Numerical and Theoretical Results
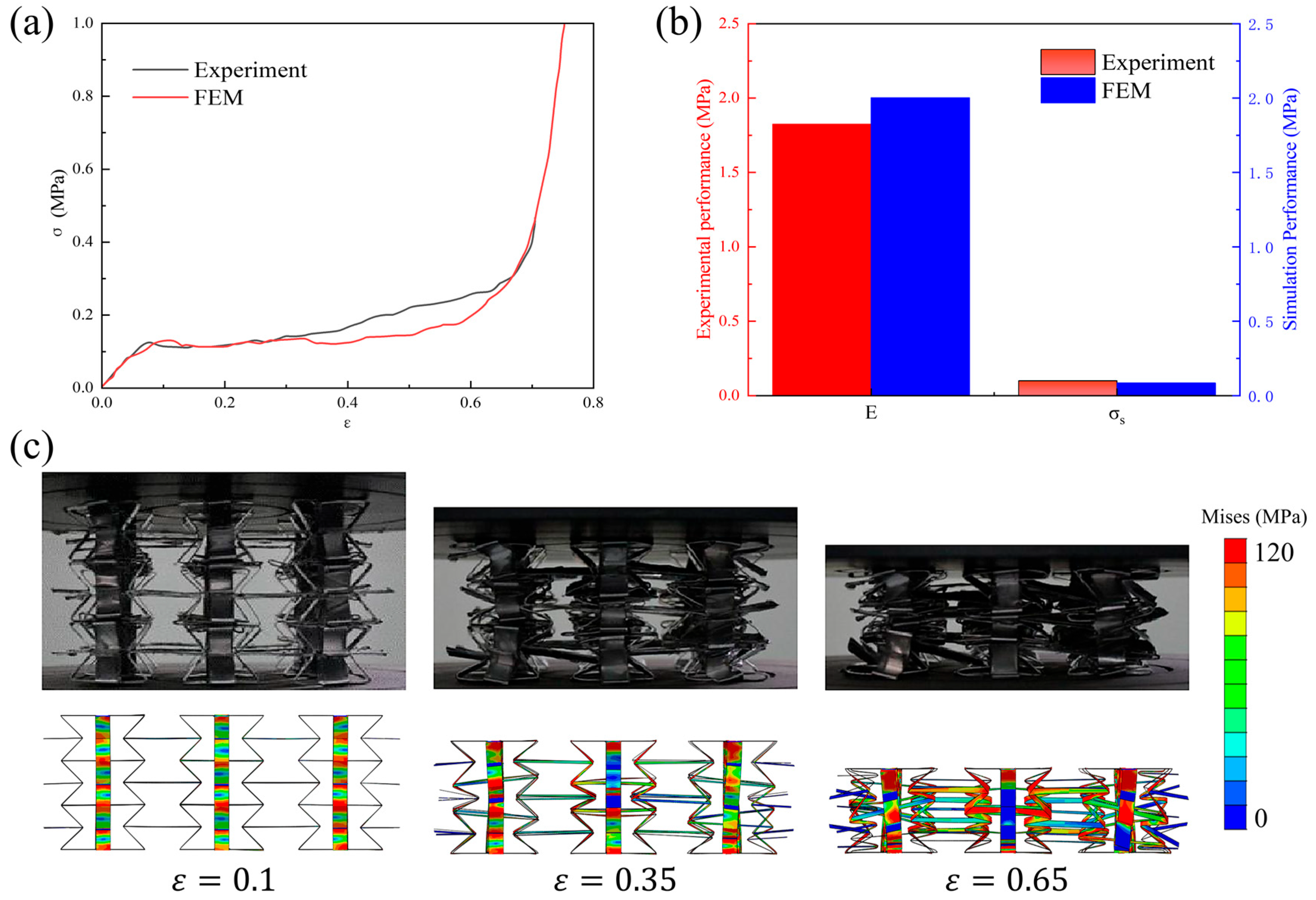
3.1. Validation of Finite Element Model
3.2. Validation of Theoretical Model
4. Results and Discussion
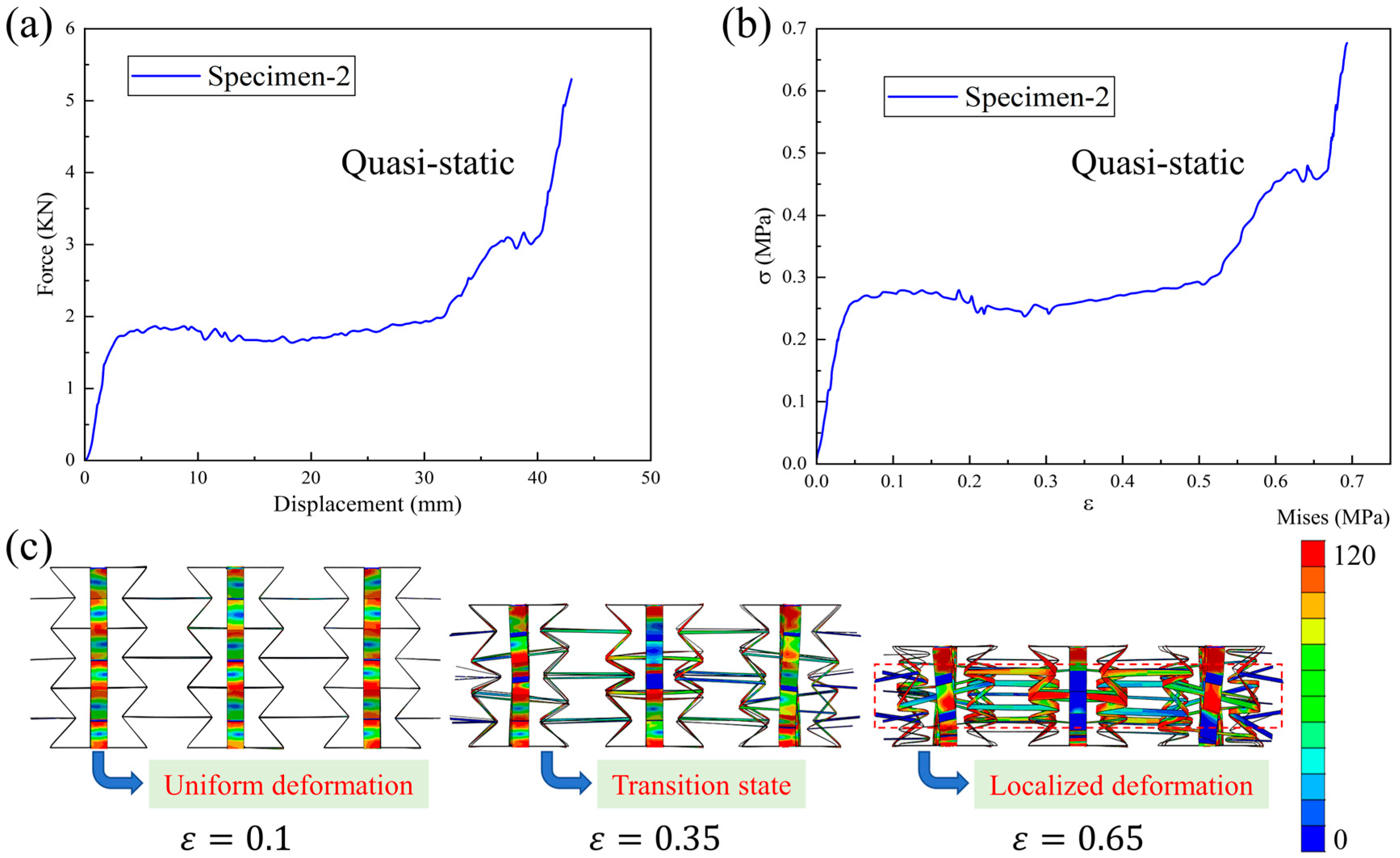
4.1. Quasi-Static Compression Behavior
4.1.1. Mechanical Behavior
4.1.2. Effect of Geometric Parameter
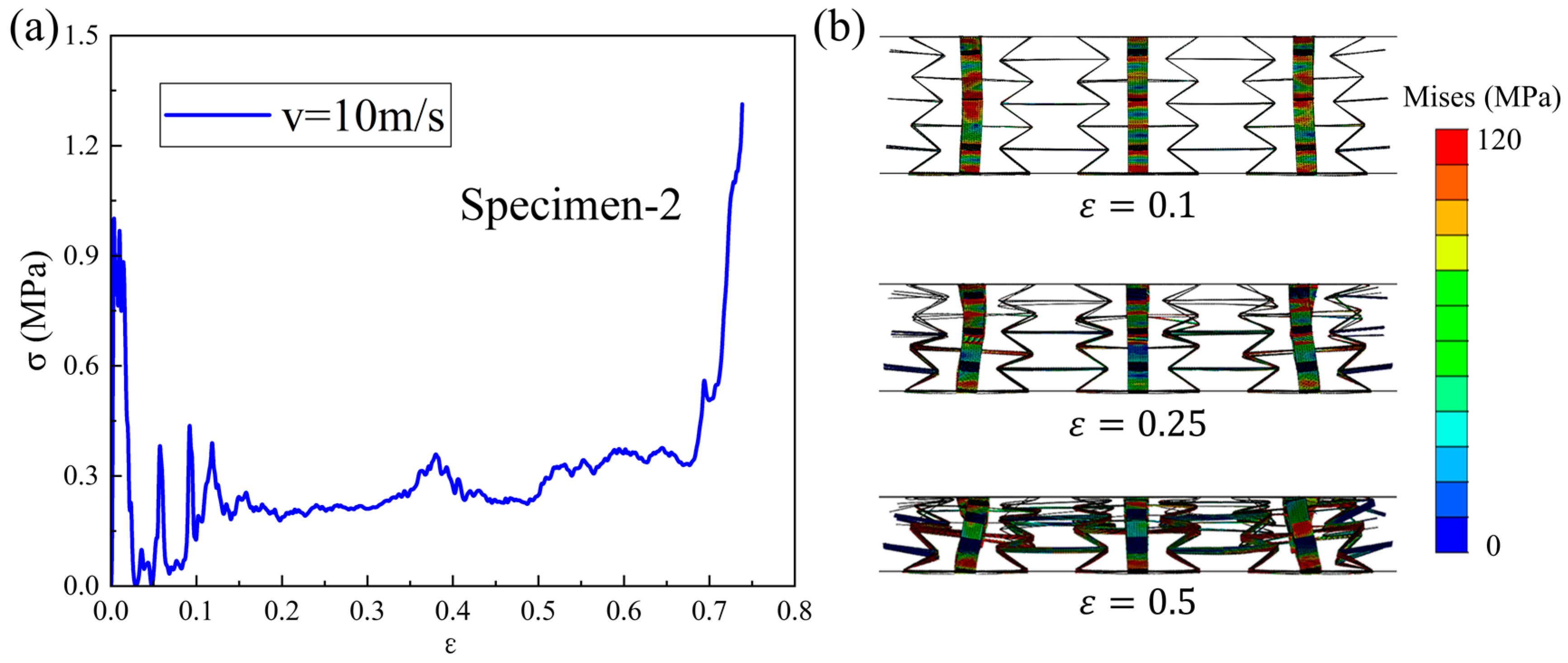
4.2. Dynamic Compression Behavior
4.2.1. Effect of Loading Velocity
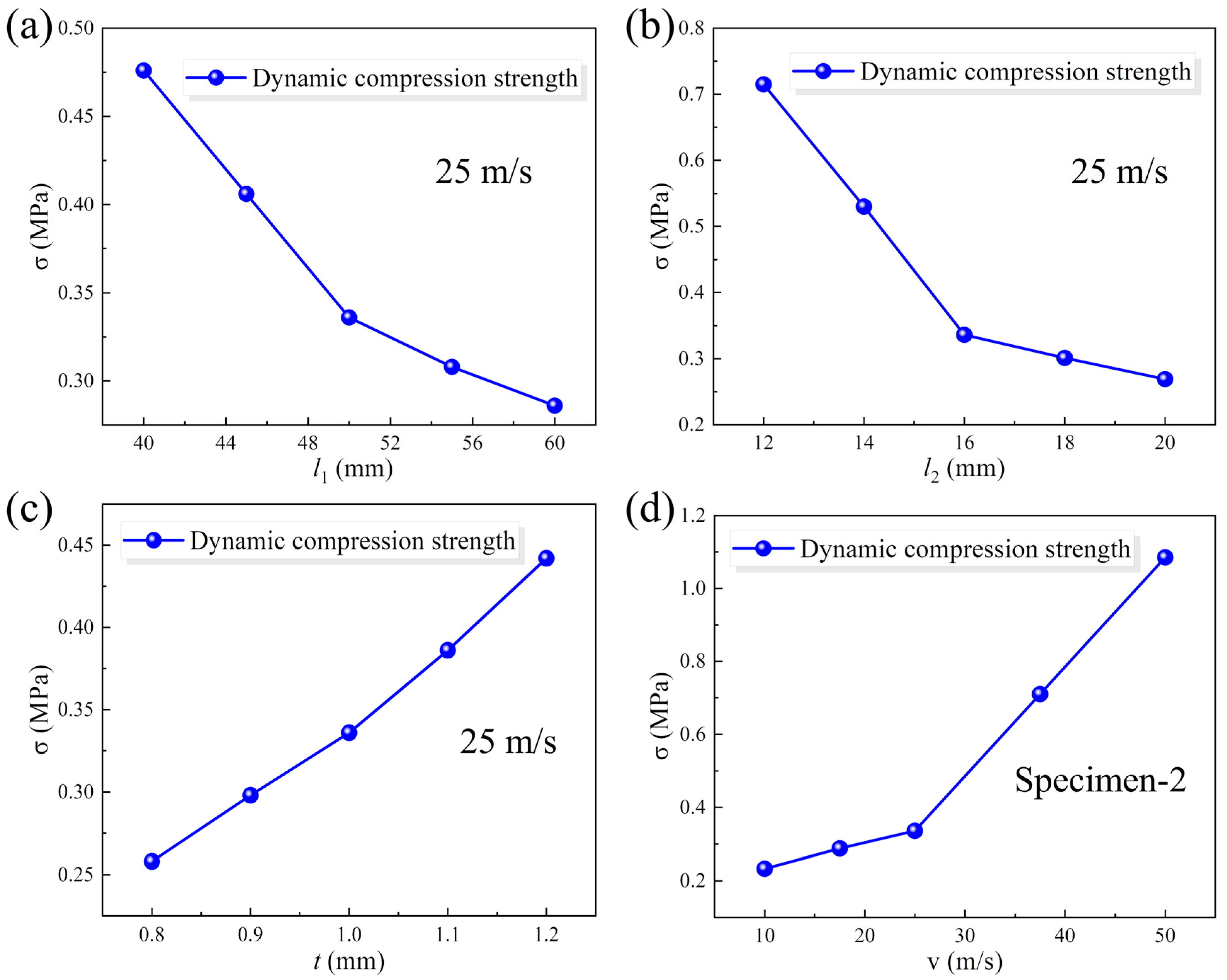
4.2.2. Parametric Analysis
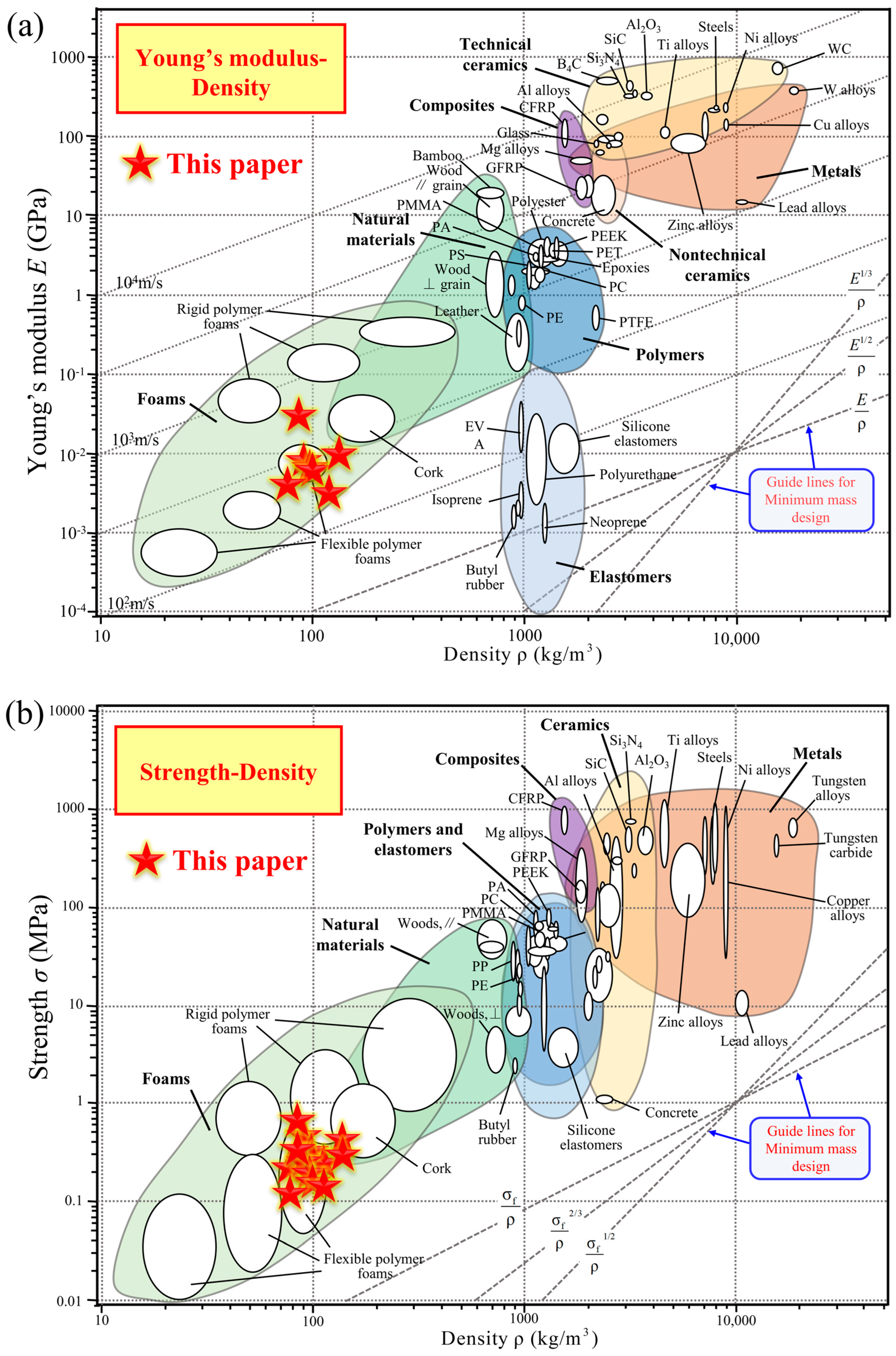
4.3. Comparison with Competing Configurations
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The quasi-static compressive performance curve of the 3D-RH pattern is a typical bending-dominated deformation behavior. The typical performance characteristics of cellular materials can be observed: an initial elastic deformation region, intermediate plateau stress segment, and final densification stage. The corresponding compression modulus and plateau stress both exhibit a decreasing trend as the horizontal cell wall length or oblique cell wall length increases. However, they will increase with the increase in cell wall thickness.
- (2)
- The dynamic compressive performance curve of the 3D-RH pattern exhibits an initial peak stress followed by an oscillating plateau stress and a rapid rising stress. The dynamic compression strength exhibits a decreasing trend as the horizontal cell wall length or oblique cell wall length increases, while it increases with the increase in cell wall thickness. In addition, the dynamic mechanical properties of the 3D-RH structural pattern exhibit an apparent strain rate effect. When the loading velocity increases from 10 m/s to 50 m/s, the dynamic compression plateau stress can increase from 0.233 MPa to 1.085 MPa.
- (3)
- Based on the performance comparison in the Ashby maps, the 3D-RH structure proposed in this paper has an acceptable quasi-static and dynamic compressive modulus and compressive strength, and is within the region of foams, demonstrating its potential attractive application prospects in the innovative development of lightweight, high-specific-stiffness, and high-specific-strength structural materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F. Cellular Solids (Structure and Properties)||Preface to the Second Edition; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, S.; Zhu, S.; Li, T. Metamaterials:From fundamental physics to intelligent design. Interdiscip. Mater. 2023, 2, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Wang, E.D.; Yang, H.; Zhai, W. Mechanical characterization and constitutive modeling of additively-manufactured polymeric materials and lattice structures. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2024, 189, 105711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Koh, J.J.; Lim, G.J.; Zhang, D.; Xiong, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Duan, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Direct ink writing of programmable functional silicone-based composites for 4D printing applications. Interdiscip. Mater. 2022, 1, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, L.R.; Das, S.; Greer, J.R. Strong, lightweight, and recoverable three-dimensional ceramic nanolattices. Science 2014, 345, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Cao, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Lei, H.; Fang, D. Design of self-supporting lattices for additive manufacturing. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2021, 148, 104298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.W.; Fu, J.Z.; Yao, X.H.; He, Y. Triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) porous structures: From multi-scale design, precise additive manufacturing to multidisciplinary applications. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2022, 4, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; He, M.X.; Zhao, J.L.; Kam, C.T.; Ding, Q.; Lee, H.P. The ABH-based lattice structure for load bearing and vibration suppression. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 252, 108378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morciano, M.; Alberghini, M.; Fasano, M.; Almiento, M.; Calignano, F.; Manfredi, D.; Asinari, P.; Chiavazzo, E. 3D printed lattice metal structures for enhanced heat transfer in latent heat storage systems. J. Energy Storage 2023, 65, 107350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Chen, L. Negative Poisson’s Ratio in Modern Functional Materials. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8079–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, W.T.; Dong, Y.; Pramanik, A.; Selvan, M.C.P.; Zhang, Z.X.; Ramakrishna, S. Additive manufacturing of re-entrant structures: Well-tailored structures, unique properties, modelling approaches and real applications. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 78, 103829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khazraji, M.S. Review on impact, crushing response and applications of re-entrant core sandwich structures. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2024, 96, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Jiang, F.; Yang, S. Advanced honeycomb designs for improving mechanical properties: A review. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 227, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Tiwari, G. Crushing behavior of honeycomb structure: A review. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2019, 24, 555–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Su, Y.T.; Shi, J. In-plane impact resistance enhancement with a graded cell-wall angle design for auxetic metamaterials. Compos. Struct. 2020, 247, 112451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; He, Z.C.; Li, K.X.; Li, E.; Cheng, A.G.; Xu, B. In-plane crashworthiness of re-entrant hierarchical honeycombs with negative Poisson’s ratio. Compos. Struct. 2019, 229, 111415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.T.; Wu, X.; Shi, J. A novel 3D printable multimaterial auxetic metamaterial with reinforced structure: Improved stiffness and retained auxetic behavior. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 29, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.X.; Yu, H.B.; Hu, W.X.; He, C.W.; Wu, W.W.; Ma, Y.B. Bandgap and wave attenuation mechanisms of innovative reentrant and anti-chiral hybrid auxetic metastructure. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2019, 28, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Qiang, L.; Fu, J.; Li, Q.; Hui, D. Dynamic crash responses of bio-inspired aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP panels. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2017, 121, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.E.; Alderson, A. Auxetic materials: Functional materials and structures from lateral thinking! Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.L.; Qin, S.A. In-plane energy absorption characteristics and mechanical properties of novel re-entrant honeycombs. Compos. Struct. 2023, 313, 116951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Zhong, R.C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wu, H.; Fu, M.H. Mechanical properties of re-entrant chiral anisotropic honeycomb. Eng. Struct. 2023, 291, 116431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Li, J.H.; Wu, B.S.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.M. Enhanced mechanical properties of re-entrant auxetic honeycomb with self-similar inclusion. Compos. Struct. 2024, 331, 117921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Lou, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, J.; Wu, T.; Qin, Q. On in-plane crushing behavior of a combined re-entrant double-arrow honeycomb. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 194, 111303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.A.; Deng, C.; Ojo, O.; Akinrinlola, B.; Kozub, J.; Wu, N. Design and modeling of a novel three dimensional auxetic reentrant honeycomb structure for energy absorption. Compos. Struct. 2022, 280, 114882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Ding, C.Y.; Ji, X.; Mu, J.H.; Wang, X.F.; Xue, Y.Y. Fabrication, microstructure and mechanical properties of a 3D re-entrant anti-trichiral honeycomb structure with excellent auxeticity and mechanical performance. J. Mater. Res. Technol.-JMRT 2024, 32, 841–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.G.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Luo, C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Hao, J.; Xie, Y.M.; Ren, X. Bending performance of 3D re-entrant and hexagonal metamaterials. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 188, 110829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Remennikov, A.; Pei, L.Z.; Yang, S.; Yu, Z.H.; Ngo, T.D. Impact and close-in blast response of auxetic honeycomb-cored sandwich panels: Experimental tests and numerical simulations. Compos. Struct. 2017, 180, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Li, Q.M. Dynamic compressive behaviour of cellular materials: A review of phenomenon, mechanism and modelling. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2018, 112, 74–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
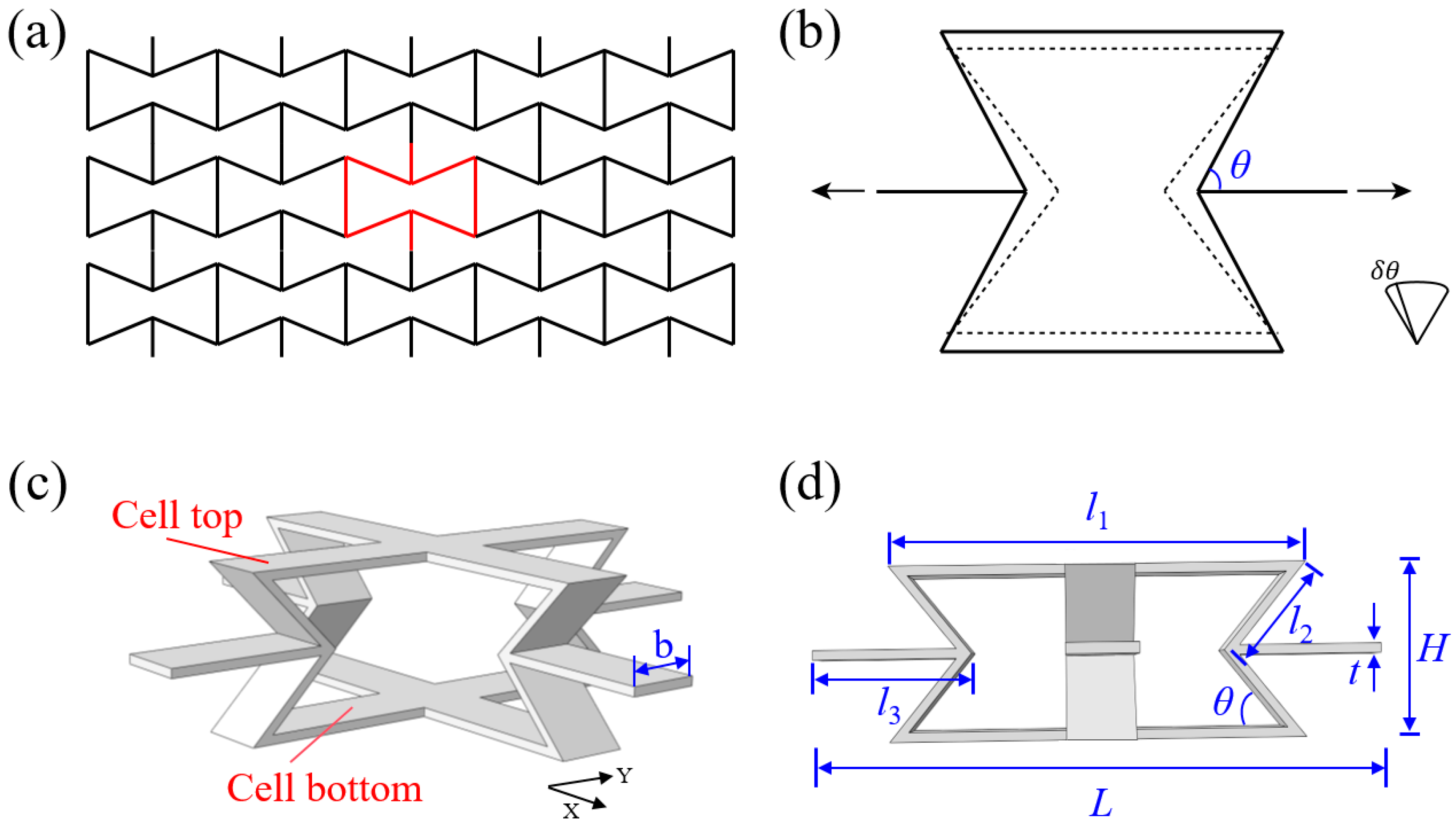
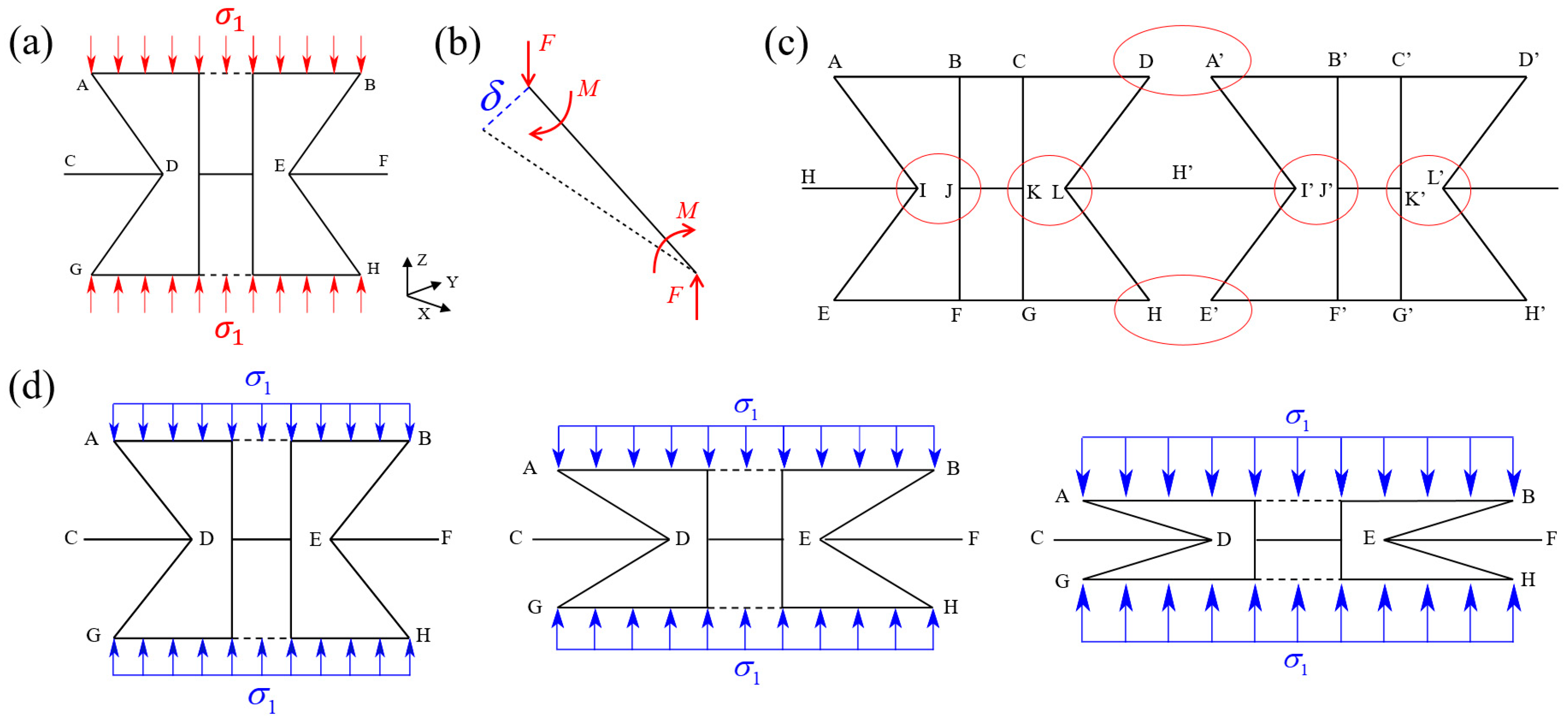




| Specimen | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (°) | (mm) | Relative Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen-1 | 40 | 16 | 27.87 | 1 | 36.42 | 8 | 0.033 |
| Specimen-2 | 50 | 16 | 22.87 | 1 | 36.42 | 0.035 | |
| Specimen-3 | 60 | 16 | 17.87 | 1 | 36.42 | 0.036 | |
| Specimen-4 | 50 | 12 | 17.33 | 1 | 52.34 | 0.030 | |
| Specimen-5 | 50 | 20 | 27.60 | 1 | 28.36 | 0.039 | |
| Specimen-6 | 50 | 16 | 22.80 | 0.8 | 36.87 | 0.027 | |
| Specimen-7 | 50 | 16 | 22.95 | 1.2 | 35.98 | 0.042 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, X.; Qi, L.; Shi, Y.; Xing, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Bai, W.; Cao, X.; He, C. Dynamic Compressive Mechanical Behavior of a Novel Three-Dimensional Re-Entrant Honeycomb (3D-RH) Structure. Materials 2025, 18, 5234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225234
Du X, Qi L, Shi Y, Xing L, Wang G, Zhang H, Bai W, Cao X, He C. Dynamic Compressive Mechanical Behavior of a Novel Three-Dimensional Re-Entrant Honeycomb (3D-RH) Structure. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225234
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Xiyan, Lun Qi, Yulong Shi, Lei Xing, Gang Wang, Haibo Zhang, Wenting Bai, Xiaofei Cao, and Chunwang He. 2025. "Dynamic Compressive Mechanical Behavior of a Novel Three-Dimensional Re-Entrant Honeycomb (3D-RH) Structure" Materials 18, no. 22: 5234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225234
APA StyleDu, X., Qi, L., Shi, Y., Xing, L., Wang, G., Zhang, H., Bai, W., Cao, X., & He, C. (2025). Dynamic Compressive Mechanical Behavior of a Novel Three-Dimensional Re-Entrant Honeycomb (3D-RH) Structure. Materials, 18(22), 5234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225234







