More Trustworthy Prediction of Elastic Modulus of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using MCBE and TabPFN
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- It represents the first integration of a foundation model (TabPFN) into the field of RAC mechanics, enabling knowledge transfer between data science and materials engineering; and
- (2)
- It introduces a bias-aware data calibration framework (MCBE) that complements the model’s Bayesian learning with explicit bias quantification and correction.
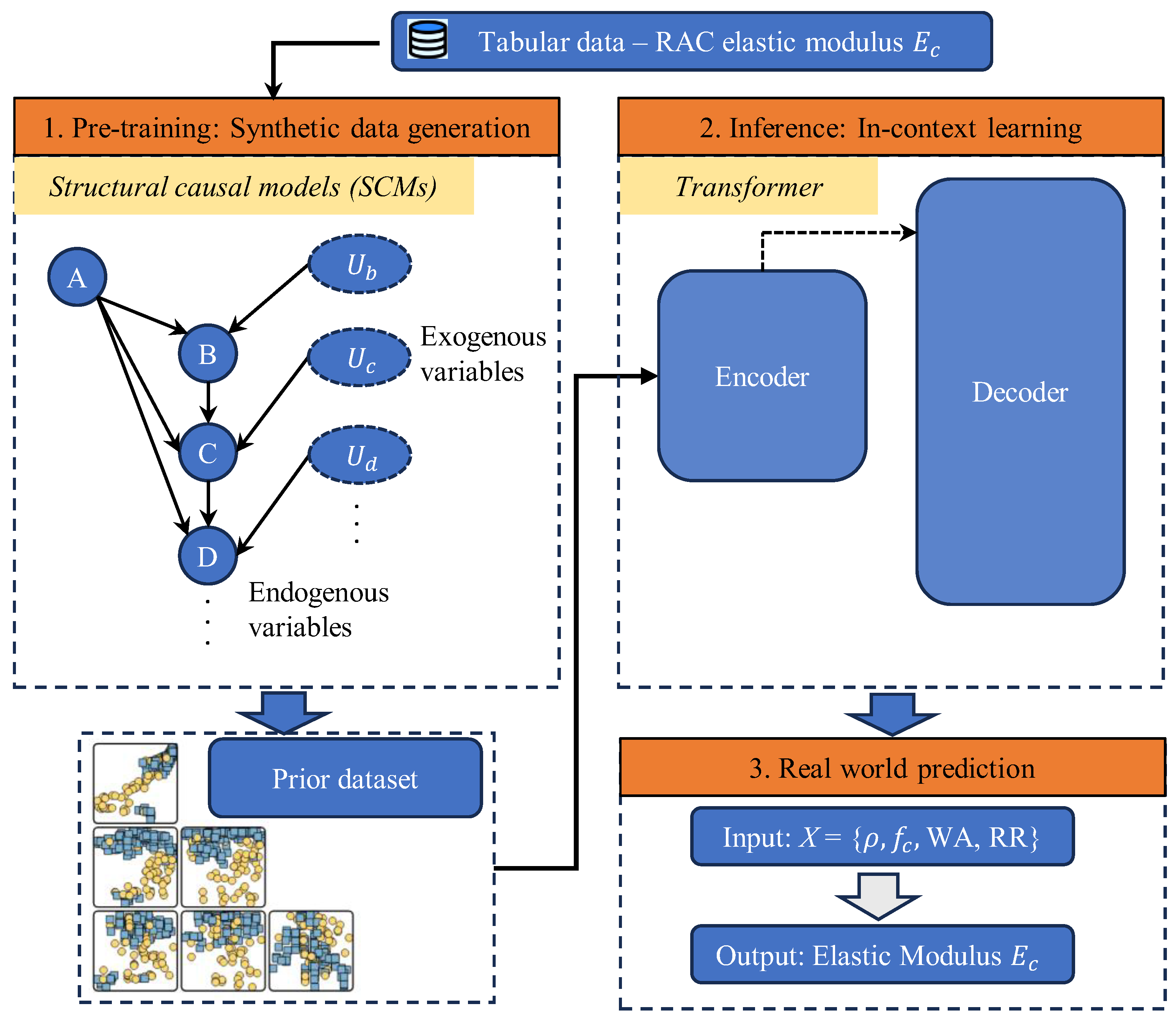
2. Methodology
2.1. Tabular Prior-Data Fitted Network
2.2. Artificial Neural Networks
2.3. Random Forest
2.4. Extreme Gradient Boosting
2.5. Gradient Boosted Decision Trees
2.6. Support Vector Machines
3. Experimental Database and Data Processing
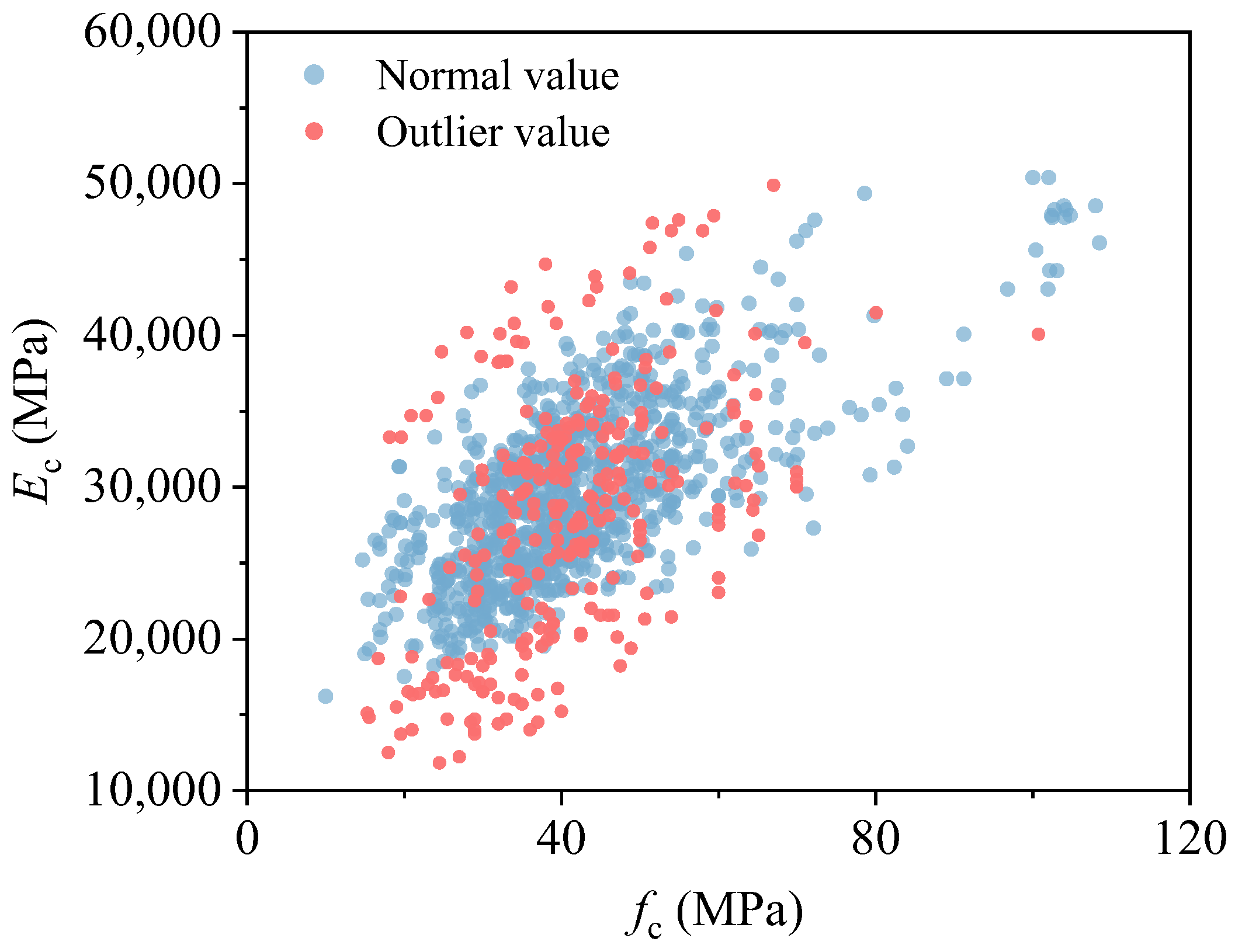
3.1. Outlier Analyses
3.2. Dataset Characterization
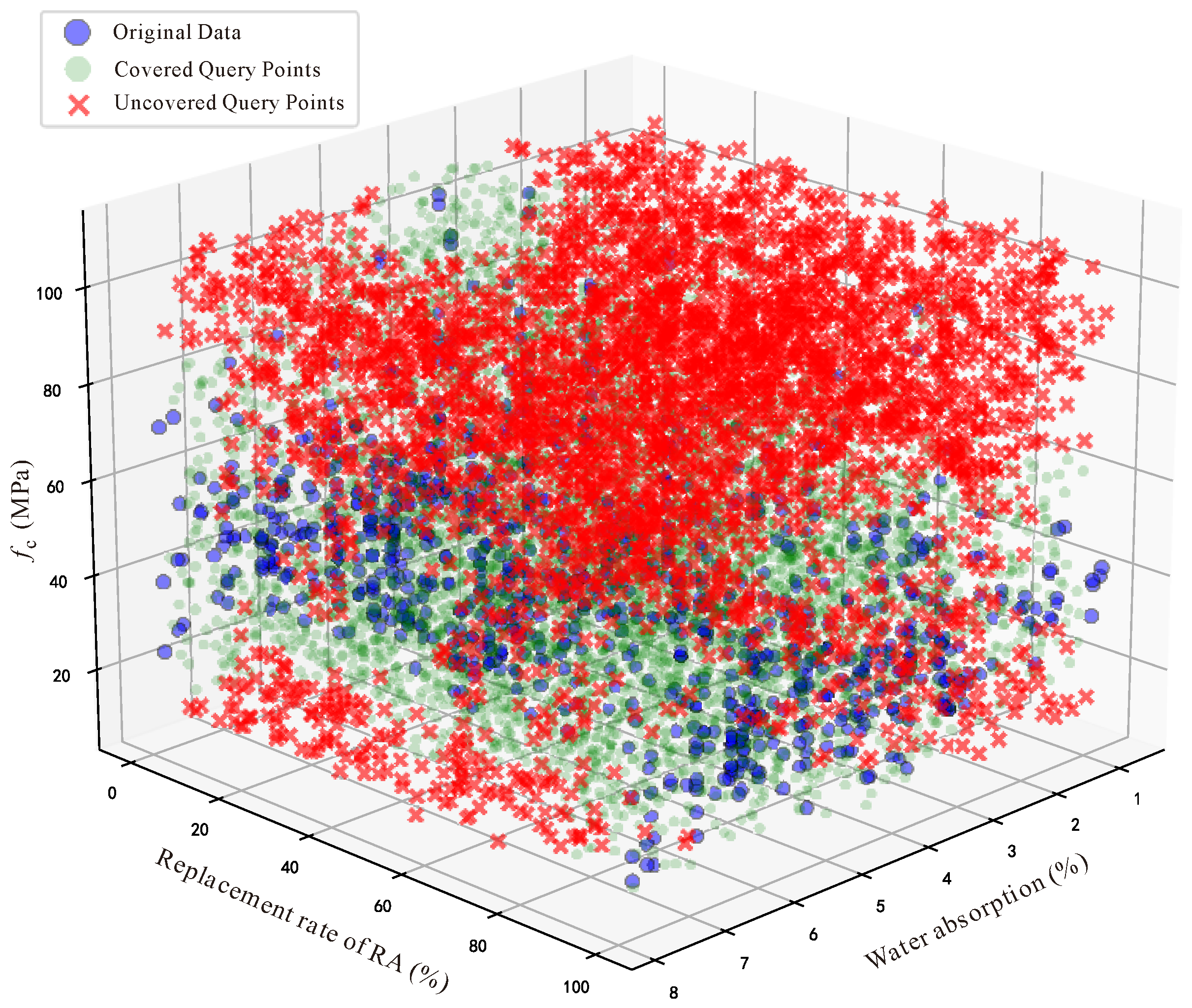
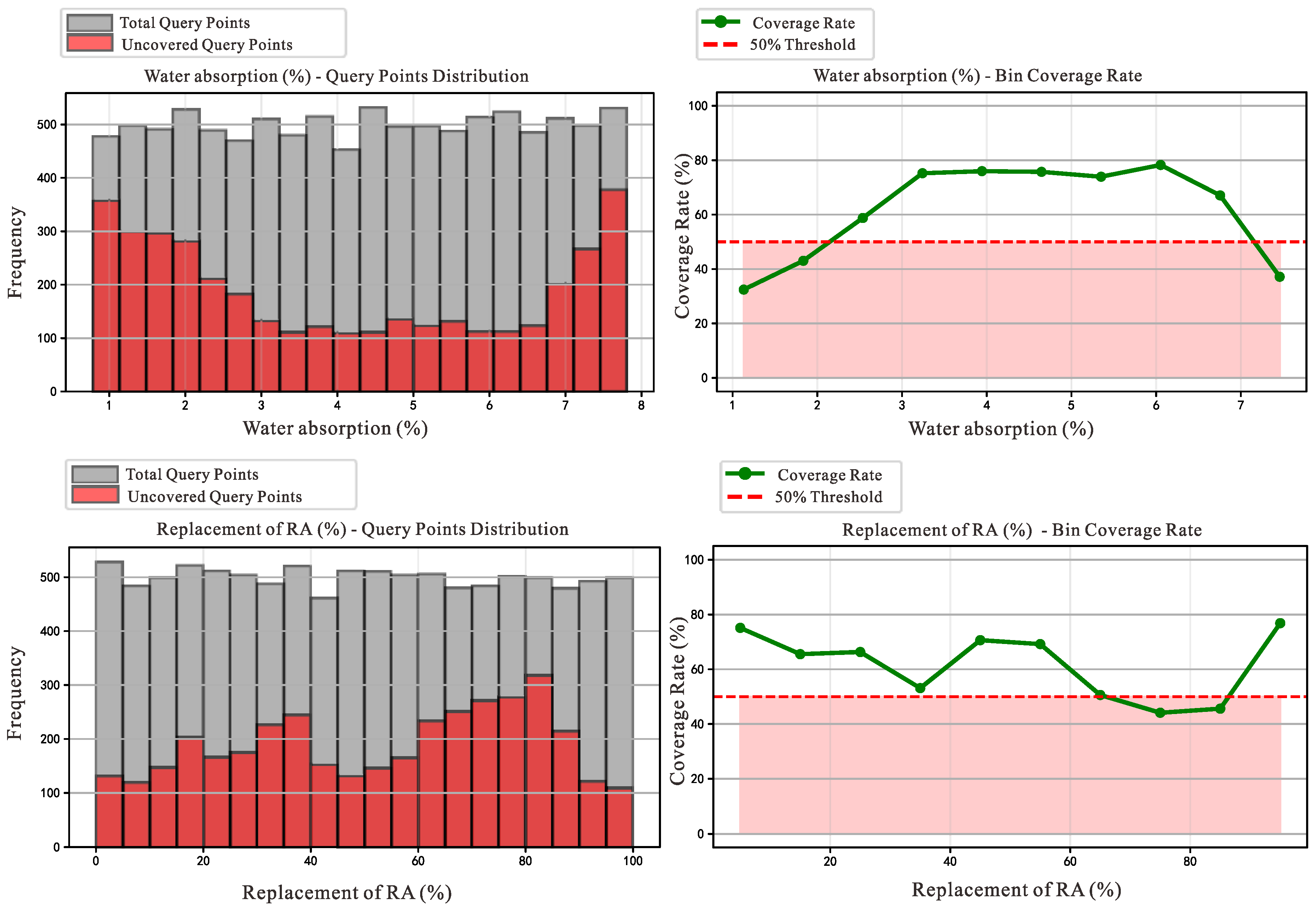
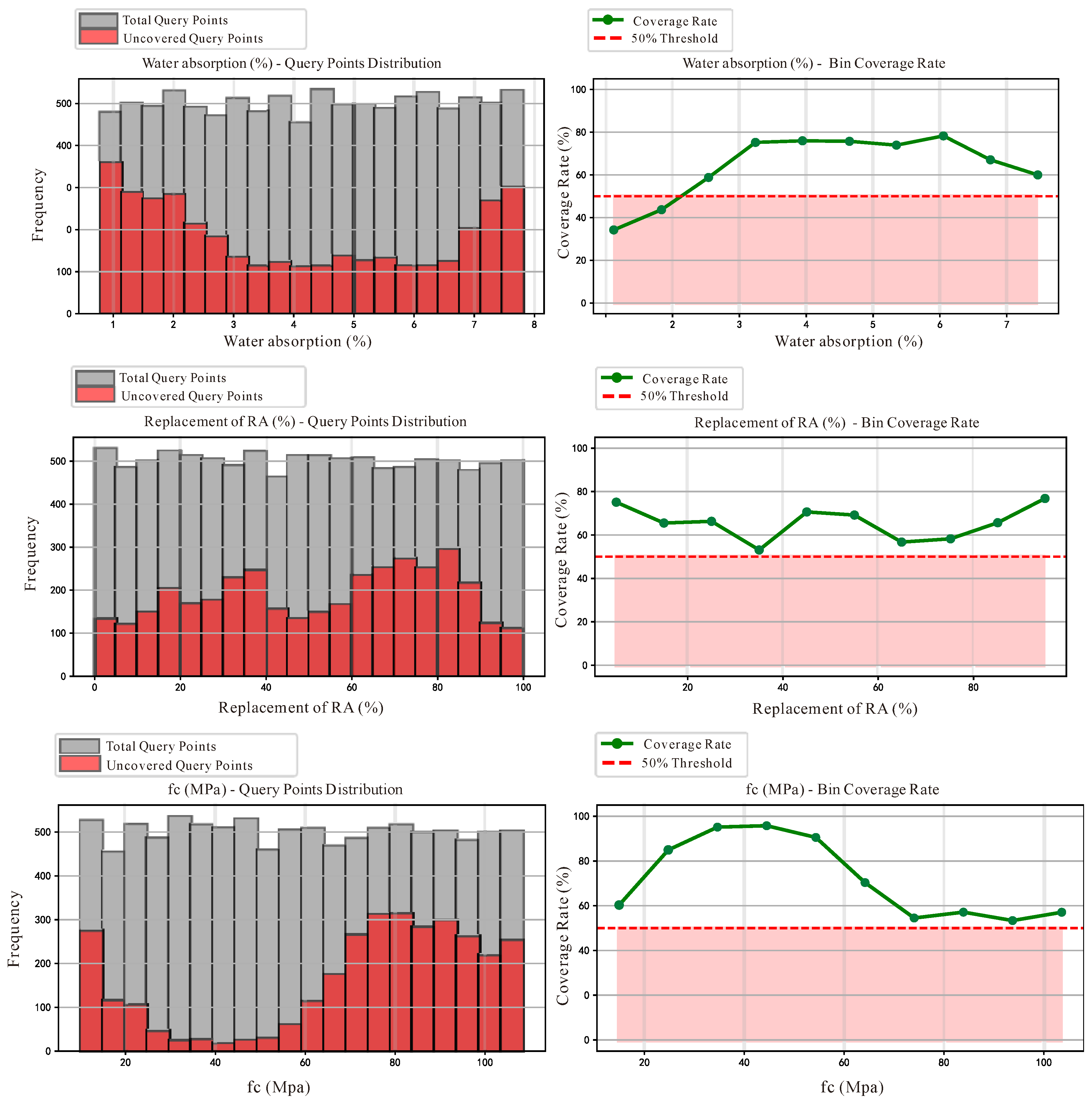
3.3. Bias Analysis of the Dataset
3.4. Bias Removal and Data Preprocessing
4. Results and Discussion
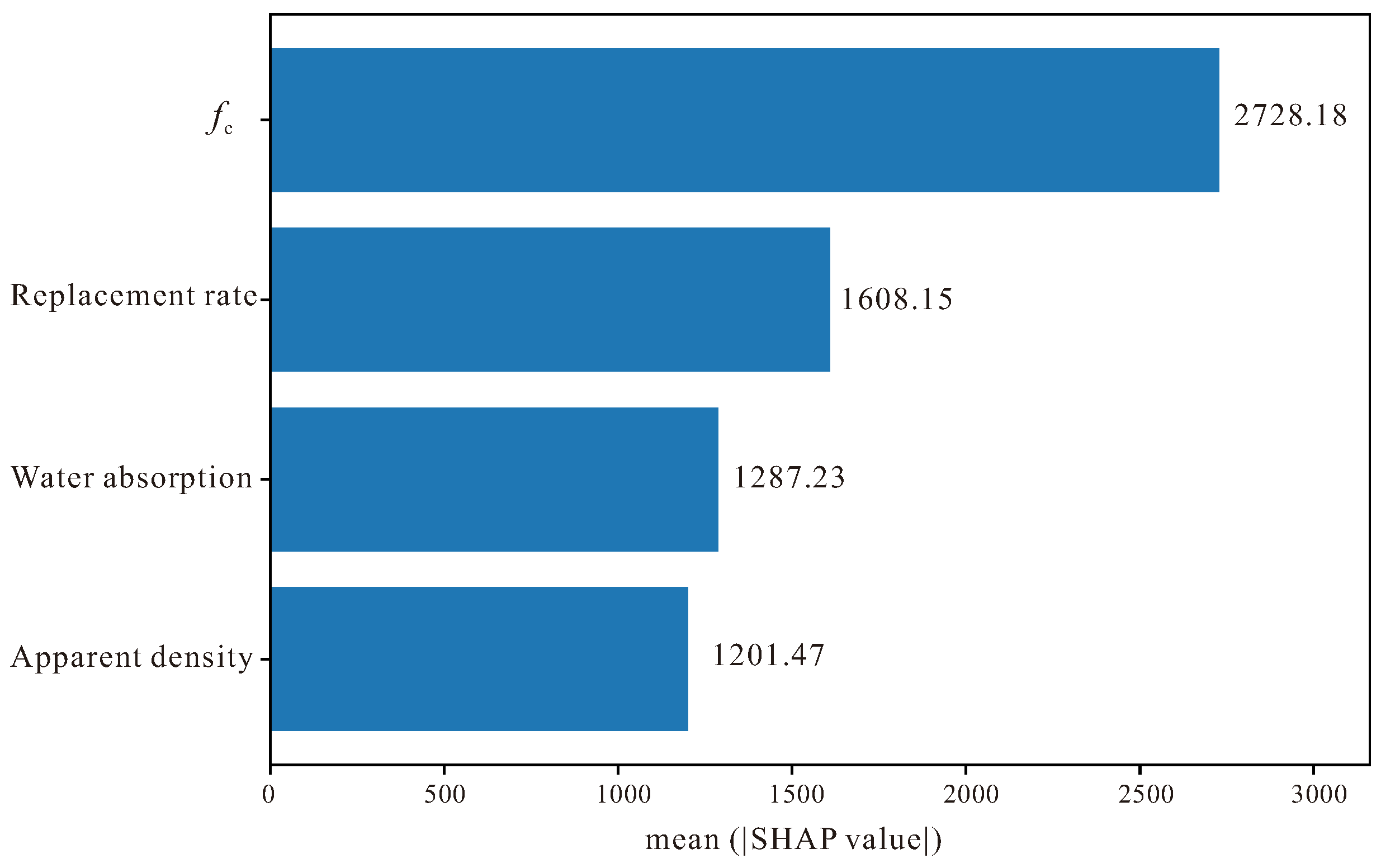
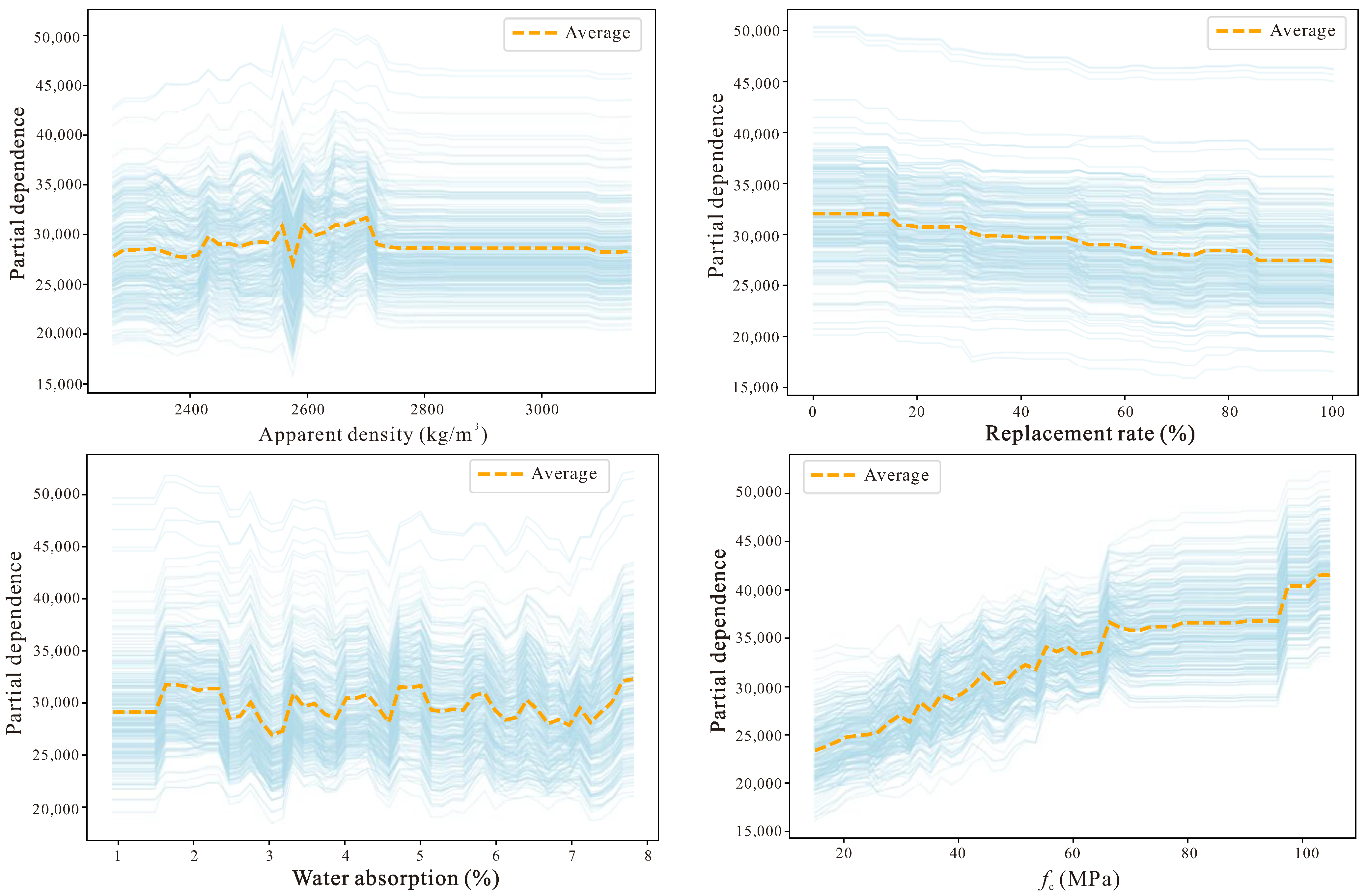
5. Shapley Additive Explanations
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- This work represents the first application of a transformer-based foundation model to RAC. Leveraging pre-training on millions of Bayesians and causal inference tasks, TabPFN performs one-shot Bayesian prediction on small and heterogeneous tabular datasets. It eliminates the need for task-specific retraining or hyperparameter tuning, enabling robust inference even under data scarcity. This establishes a transferable learning framework that can generalize across varying experimental and regional data distributions;
- (2)
- MCBE analysis revealed substantial representational gaps—particularly within the high-strength RAC domain—where traditional models suffered accuracy drops exceeding 25%. Through targeted data augmentation guided by MCBE metrics, these biases were significantly mitigated, leading to uniform performance across all strength ranges. The synergy between TabPFN’s prior-informed generalization and MCBE’s bias quantification yielded a bias-aware predictive model capable of maintaining accuracy in previously underrepresented data domains.
- (3)
- Compared with five benchmark machine learning algorithms (ANN, SVM, RF, GBDT, and XGBoost), TabPFN achieved the highest predictive performance (R2 = 0.912, RMSE = 1.65 GPa) with minimal computational cost. Predictions were generated in a single forward pass, reducing training time by several orders of magnitude. The model’s stability across heterogeneous datasets confirms its robustness and transferability, enabling consistent results across diverse experimental settings without dataset-specific calibration.
- (4)
- SHAP-based analysis verified that compressive strength dominates Ec prediction, followed by the influence of aggregate quality indicators such as replacement ratio and water absorption. These patterns are mechanically consistent with established theories of stiffness degradation in recycled aggregate systems, confirming that the TabPFN framework maintains not only predictive accuracy but also physical interpretability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trivedi, S.S.; Snehal, K.; Das, B.; Barbhuiya, S. A Comprehensive Review towards Sustainable Approaches on the Processing and Treatment of Construction and Demolition Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 132125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, M.; Di Maio, F.; Sprecher, B.; Yang, X.; Tukker, A. An Overview of the Waste Hierarchy Framework for Analyzing the Circularity in Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Li, J. Construction and Demolition Waste Management: China’s Lessons. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschen-Schimek, J.; Kasper, T.; Huber-Humer, M. Critical Review of the Recovery Rates of Construction and Demolition Waste in the European Union–An Analysis of Influencing Factors in Selected EU Countries. Waste Manag. 2023, 167, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayhan, D.S.A.; Bhuiyan, I.U. Review of Construction and Demolition Waste Management Tools and Frameworks with the Classification, Causes, and Impacts of the Waste. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2024, 6, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabirifar, K.; Mojtahedi, M.; Wang, C.; Tam, V.W. Construction and Demolition Waste Management Contributing Factors Coupled with Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle Strategies for Effective Waste Management: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, J. A Review of Life Cycle Assessment of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinković, S.; Radonjanin, V.; Malešev, M.; Ignjatović, I. Comparative Environmental Assessment of Natural and Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yan, L.; Fu, Q.; Kasal, B. A Comprehensive Review on Recycled Aggregate and Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 171, 105565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; De Brito, J.; Dhir, R.K. Availability and Processing of Recycled Aggregates within the Construction and Demolition Supply Chain: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, A.; Mostaani, A.; Gebremariam, A.T.; Di Maio, F.; Rem, P. Feasibility of Utilizing Recycled Coarse Aggregates in Commercial Concrete Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 474, 143578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, K.; Ding, T.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X. Fundamental Issues towards Unified Design Theory of Recycled and Natural Aggregate Concrete Components. Engineering 2023, 29, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remišová, E.; Deckỳ, M.; Mikolaš, M.; Hájek, M.; Kovalčík, L.; Mečár, M. Design of Road Pavement Using Recycled Aggregate. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 44, 022016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.; Soomro, M.; Evangelista, A.C.J. A Review of Recycled Aggregate in Concrete Applications (2000–2017). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Zhu, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, B. An Evaluation of the Recycled Aggregate Characteristics and the Recycled Aggregate Concrete Mechanical Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Huang, X. An Overview of Study on Recycled Aggregate Concrete in China (1996–2011). Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 31, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Bao, J.; Gu, F.; Lu, J.; Ma, Z.; Hou, S.; Duan, Z. Determining the Importance of Recycled Aggregate Characteristics Affecting the Elastic Modulus of Concrete by Modeled Recycled Aggregate Concrete: Experiment and Numerical Simulation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 162, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hao, H.; de Brito, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, J. Discussion of the Implementation of Water Compensation Methods for Recycled Aggregate Concrete: A Critical Review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 161, 106080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Setién, J.; Polanco, J.A.; Alaejos, P.; De Juan, M.S. Durability of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, C.; Guan, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y.; Ling, T.-C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Durability of Recycled Aggregate Concrete–A Review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 89, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbakkaloglu, T.; Gholampour, A.; Xie, T. Mechanical and Durability Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete: Effect of Recycled Aggregate Properties and Content. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04017275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, S.; Eggimann, M.; Wagner, E.; Mróz, R.; Deja, J. Performance of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Based on a New Concrete Recycling Technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Geng, Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.-Y. Probabilistic Model for Compressive Strength of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Accounting for Uncertainty of Recycled Aggregates from Different Sources. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 479, 141485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cao, D.; Dang, H.; Ding, B. Comparison of Recycled Aggregate Treatment Methods on the Performance for Recycled Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.; West, J.S.; Tighe, S.L. Effect of Recycled Concrete Coarse Aggregate from Multiple Sources on the Hardened Properties of Concrete with Equivalent Compressive Strength. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Poon, C. Effect of the Quality of Parent Concrete on the Properties of High Performance Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Poon, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, T.; Geng, Y.; Ye, T.; Li, L. Fundamental Behaviour of Recycled Aggregate Concrete–Overview I: Strength and Deformation. Mag. Concr. Res. 2022, 74, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxeberria, M.; Vázquez, E.; Marí, A.; Barra, M. Influence of Amount of Recycled Coarse Aggregates and Production Process on Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.; Zhu, W.; Howind, T.; de Rojas, M.I.S.; Frías, M. Influence of Mixed Recycled Aggregate on the Physical–Mechanical Properties of Recycled Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 68, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Shui, Z.; Lam, L.; Fok, H.; Kou, S. Influence of Moisture States of Natural and Recycled Aggregates on the Slump and Compressive Strength of Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxeberria, M.; Marí, A.R.; Vázquez, E. Recycled Aggregate Concrete as Structural Material. Mater. Struct. 2007, 40, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; De Brito, J.; Dhir, R. Tensile Strength Behaviour of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 83, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayarre, F.L.; Perez, C.L.-C.; Lopez, M.A.S.; Cabo, A.D. The Effect of Curing Conditions on the Compressive Strength of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.; Wang, K.; Tam, C.M. Assessing Relationships among Properties of Demolished Concrete, Recycled Aggregate and Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using Regression Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.-Z.; Li, J.-B.; Zhang, C. On Relationships between the Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete: An Overview. Mater. Struct. 2006, 39, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.H.; Poon, C.S. Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Made with Recycled Aggregates with Different Amounts of Old Adhered Mortars. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casuccio, M.; Torrijos, M.; Giaccio, G.; Zerbino, R. Failure Mechanism of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.C. Recycling of Demolished Concrete and Masonry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, A. Properties of Concrete Made with Recycled Aggregate from Partially Hydrated Old Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verian, K.P.; Ashraf, W.; Cao, Y. Properties of Recycled Concrete Aggregate and Their Influence in New Concrete Production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 133, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Influence of Quality of Recycled Aggregates on the Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concretes: An Overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Ji, Y.; Xing, Z. Mechanical Performance of Recycled Aggregate Concrete in Green Civil Engineering. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, A.I.; Yang, J.; Dirar, S. Enhancing the Performance of Recycled Aggregate Concrete with Microsilica. Int. J. Struct. Civ. Eng. Res. 2015, 4, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, G.; Miren, E. Experimental Analysis of Properties of High Performance Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.K.; Satomi, T.; Takahashi, H. Improvement of Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Basing on a New Combination Method between Recycled Aggregate and Natural Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardeh, G.; Ghorbel, E.; Gomart, H. Mix Design and Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concretes: Applicability of Eurocode 2. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2015, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, B.S.; Dawi, A.H. Sustainable Normal and High Strength Recycled Aggregate Concretes Using Crushed Tested Cylinders as Coarse Aggregates. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2017, 7, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, V.; Evangelista, L.; De Brito, J. The Effect of Multi-Recycling on the Mechanical Performance of Coarse Recycled Aggregates Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-K.; Kim, G.-Y.; Eu, H.-M.; Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, C.-M. The Effect of Recycled Aggregate Produced by the New Crushing Device with Multi-Turn Wings and Guide Plate on the Mechanical Properties and Carbonation Resistance of Concrete. J. Korean Recycl. Constr. Resour. Inst. 2021, 9, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, N.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. The Influence of Curing Conditions on the Mechanical Performance of Concrete Made with Recycled Concrete Waste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Lehman, D.E.; Geng, Y.; Kuder, K. Time-Dependent Drying Shrinkage Model for Concrete with Coarse and Fine Recycled Aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 105, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Siddique, A.; Khayat, K.; Huang, J.; Kumar, A. An Ensemble Machine Learning Approach for Prediction and Optimization of Modulus of Elasticity of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 244, 118271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.M.S.; Munir, M.J.; Wu, Y.-F.; Lin, X.; Ashiq, S.Z. Development of Unified Elastic Modulus Model of Natural and Recycled Aggregate Concrete for Structural Applications. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A.; Olek, J.; Glinicki, M.A. Predicting Modulus Elasticity of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using M5′ Model Tree Algorithm. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.-H.; Kou, S.-C.; Poon, C.-S. Using Artificial Neural Networks for Predicting the Elastic Modulus of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.-J.; Liu, S.-Y.; Chao, W.-L. A Closer Look at Tabpfn v2: Strength, Limitation, and Extension. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.17361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, N.; Müller, S.; Purucker, L.; Krishnakumar, A.; Körfer, M.; Hoo, S.B.; Schirrmeister, R.T.; Hutter, F. Accurate Predictions on Small Data with a Tabular Foundation Model. Nature 2025, 637, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, N.; Müller, S.; Eggensperger, K.; Hutter, F. Tabpfn: A Transformer That Solves Small Tabular Classification Problems in a Second. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.01848. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Yu, R.; Ge, X.; Fu, J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S. Tabular Prior-Data Fitted Network for Urban Air Temperature Inference and High Temperature Risk Assessment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 128, 106484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arezoumandi, M.; Smith, A.; Volz, J.S.; Khayat, K.H. An Experimental Study on Flexural Strength of Reinforced Concrete Beams with 100% Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Eng. Struct. 2015, 88, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilbas, H.; Şimşek, M.; Çakır, Ö. An Investigation on Mechanical and Physical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) with and without Silica Fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 61, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Teranishi, K.; Nakagome, A.; Kishimoto, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Narikawa, M. Application of Recycled Coarse Aggregate by Mixture to Concrete Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickel, D.; Tighe, S.; West, J.S. Assessing Benefits of Pre-Soaked Recycled Concrete Aggregate on Variably Cured Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.; Zhan, B.; Poon, C.S. Assessment of Mechanical Properties of Concrete Incorporating Carbonated Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 65, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaad, J.; Daou, Y. Behavior of Structural Polymer-Modified Concrete Containing Recycled Aggregates. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 874–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Yun, H.-D.; Park, W.-S.; Jang, Y.-I. Bond Strength Prediction for Deformed Steel Rebar Embedded in Recycled Coarse Aggregate Concrete. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Ye, S.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, Y. Carbonated Recycled Coarse Aggregate and Uniaxial Compressive Stress-Strain Relation of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, S.; Singh, B.; Bhargava, P. Characterization of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. In Advances in Structural Engineering: Materials, Volume Three; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1813–1822. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.-C.; Yun, H.-D. Compressive Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Columns with Recycled Aggregate under Uniaxial Loading. Eng. Struct. 2012, 41, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, S. Compressive Stress-Strain Relation of Recycled Aggregate Concrete under Cyclic Loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, B.; Martínez, F. Concretes with Aggregates from Demolition Waste and Silica Fume. Mater. Mech. Prop. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.P.; Fu, T.; Cabrera, A.G.; Morales, M.; Ideker, J.H.; Isgor, O.B. Cracking Susceptibility of Concrete Made with Coarse Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaack, A.M.; Kurama, Y.C. Creep and Shrinkage of Normal-Strength Concrete with Recycled Concrete Aggregates. ACI Mater. J. 2015, 112, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Creep Behaviour of Concrete Using Recycled Coarse Aggregates Obtained from Source Concrete with Different Strengths. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 128, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y. Creep Model of Concrete with Recycled Coarse and Fine Aggregates That Accounts for Creep Development Trend Difference between Recycled and Natural Aggregate Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 103, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xuan, D.; Sojobi, A.O.; Liu, S.; Chu, S.; Poon, C.S. Development of Nano-Silica Treatment Methods to Enhance Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 118, 103963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakır, Ö.; Dilbas, H. Durability Properties of Treated Recycled Aggregate Concrete: Effect of Optimized Ball Mill Method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, M.G.; Barbudo, A.; Agrela, F.; Galvín, A.P.; Jiménez, J.R. Effect of Cement Addition on the Properties of Recycled Concretes to Reach Control Concretes Strengths. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 79, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xiao, J.; Tam, V.W. Effect of Old Attached Mortar on the Creep of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Struct. Concr. 2014, 15, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, W.M.; Elbaz, K.; Yang, J.; Thomas, B.S.; Shen, X.; Li, L.; Du, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, L. Effect of Pozzolan Slurries on Recycled Aggregate Concrete: Mechanical and Durability Performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 121940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.-H.; Jeong, J.-Y. Effect of Recycled Coarse Aggregate on Compressive Strength and Mechanical Properties of Concrete. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2016, 28, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fonteboa, B.; Martinez-Abella, F.; Eiras-Lopez, J.; Seara-Paz, S. Effect of Recycled Coarse Aggregate on Damage of Recycled Concrete. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wu, W.; Wu, K. Effect of Recycled Coarse Aggregates Enhanced by CO2 on the Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 431, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachouh, N.; El-Hassan, H.; El-Maaddawy, T. Effect of Steel Fibers on the Performance of Concrete Made with Recycled Concrete Aggregates and Dune Sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 213, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, X.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of Coral, Recycled and Natural Coarse Aggregates on the Mechanical Properties of Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 192, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.K.; Satomi, T.; Takahashi, H. Enhancement of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Properties by a New Treatment Method. GEOMATE J. 2018, 14, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, G.; Savva, P.; Petrou, M.F. Enhancing Mechanical and Durability Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Sosa, I.; Setién, J.; Polanco, J.A.; Cimentada, A.I. Evaluation of the Fatigue Behavior of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.; De Brito, J.; Chastre, C.; Evangelista, L. Experimental Investigation on the Variability of the Main Mechanical Properties of Concrete Produced with Coarse Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Ren, Q. Experimental Research on Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Multimedia Technology, Hangzhou, China, 26–28 July 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1539–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Duan, M.L. Experimental Research on Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete under Uniaxial Loading. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 671, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, T.-S.; Lee, M.-S. Experimental Study on Tensile Creep of Coarse Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2015, 9, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadati, S.; Khayat, K.H. Field Performance of Concrete Pavement Incorporating Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.H.-K.; Kim, W.; Kwak, Y.-K.; Hong, S.-G. Flexural Testing of Reinforced Concrete Beams with Recycled Concrete Aggregates. ACI Struct. J. 2014, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakradhara Rao, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Barai, S. Influence of Field Recycled Coarse Aggregate on Properties of Concrete. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.C.; Poon, C.S.; Chan, D. Influence of Fly Ash as Cement Replacement on the Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2007, 19, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Influence of Service Time of Recycled Coarse Aggregate on the Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Mater. Struct. 2019, 52, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; De Brito, J.; Barra, M. Influence of the Pre-Saturation of Recycled Coarse Concrete Aggregates on Concrete Properties. Mag. Concr. Res. 2011, 63, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Influence of the Use of Recycled Concrete Aggregates from Different Sources on Structural Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, R.; Amirthavalli, R.R.; Karan, L. Influence of Treatment Methods on the Strength and Performance Characteristics of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.-H.; Chung, H.-S.; Ashour, A. Influence of Type and Replacement Level of Recycled Aggregates on Concrete Properties. ACI Mater. J. 2008, 105, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier, V.; Ortega, J.M.; Muñoz, P.; Tarela, E.; Moriconi, G. Influence of Waste Brick Powder in the Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Liu, B.; Ye, B.; Xiang, P. Mechanical Behavior and Constitutive Relationship of the Three Types of Recycled Coarse Aggregate Concrete Based on Standard Classification. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 22, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.; De Brito, J.; Pontes, J.; Evangelista, L. Mechanical Performance of Concrete Made with Aggregates from Construction and Demolition Waste Recycling Plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier, V.; Ortega, J.M.; Tarela, E.; Muñoz, P.; Henríquez-Jara, B.I.; Moriconi, G. Mechanical Performance of Eco-Friendly Concretes with Volcanic Powder and Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A.E.B.; Schalch, V.; Dal Molin, D.C.C.; Ribeiro, J.L.D. Mechanical Properties Modeling of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.-C.; Poon, C.-S. Mechanical Properties of 5-Year-Old Concrete Prepared with Recycled Aggregates Obtained from Three Different Sources. Mag. Concr. Res. 2008, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lee, H. Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Proportioned with Modified Equivalent Mortar Volume Method for Paving Applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y. Mechanical Properties of Sea Sand Recycled Aggregate Concrete under Axial Compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Ramli, M. Mechanical Strength and Drying Shrinkage Properties of Concrete Containing Treated Coarse Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Performance of Concrete Made with Aggregates Recycled from Precasting Industry Waste: Influence of the Crushing Process. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 3965–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbachiya, M.; Meddah, M.S.; Ouchagour, Y. Performance of Portland/Silica Fume Cement Concrete Produced with Recycled Concrete Aggregate. ACI Mater. J. 2012, 109, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Soberón, J.M. Porosity of Recycled Concrete with Substitution of Recycled Concrete Aggregate: An Experimental Study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; Correia, J.; De Brito, J. Post-Fire Residual Mechanical Properties of Concrete Made with Recycled Concrete Coarse Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Ravindrarajah, R.; Tam, C. Properties of Concrete Made with Crushed Concrete as Coarse Aggregate. Mag. Concr. Res. 1985, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengaram, U.J.; Salam, A.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Jaafar, F.F.; Saad, H.B. Properties of High-Workability Concrete with Recycled Concrete Aggregate. Mater. Res. 2011, 14, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, M.; Vvl, K.R.; Lakshmy, P. Recycled Aggregate Concrete for Transportation Infrastructure. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 104, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folino, P.; Xargay, H. Recycled Aggregate Concrete–Mechanical Behavior under Uniaxial and Triaxial Compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.V.P.; Allawi, A.; Albayati, A.; Cao, T.N.; El-Zohairy, A.; Nguyen, Y.T.H. Recycled Concrete Aggregate for Medium-Quality Structural Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddah, M.S.; Al-Harthy, A.; Ismail, A.M. Recycled Concrete Aggregates and Their Influences on Performances of Low and Normal Strength Concretes. Buildings 2020, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, C.; Di Maio, A. Recycled Concrete Exposed to High Temperatures. Mag. Concr. Res. 2006, 58, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, C.J.; Di Maio, A.A. Recycled Concrete Made with Different Natural Coarse Aggregates Exposed to High Temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, C.J.; Di Maio, A.A. Recycled Concretes Made with Waste Ready-Mix Concrete as Coarse Aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, H. Residual Compressive Response of Concrete Produced with Both Coarse and Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates after Thermal Exposure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 244, 118397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Thaickavil, N.N.; Wilson, P. Strength and Durability of Concrete Containing Recycled Concrete Aggregates. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 19, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belén, G.-F.; Fernando, M.-A.; Diego, C.L.; Sindy, S.-P. Stress–Strain Relationship in Axial Compression for Concrete Using Recycled Saturated Coarse Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, V. Structural Concrete Prepared with Coarse Recycled Concrete Aggregate: From Investigation to Design. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2011, 2011, 283984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, D.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L. Structural Concrete with Simultaneous Incorporation of Fine and Coarse Recycled Concrete Aggregates: Mechanical, Durability and Long-Term Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.; Sarsam, K.; Hussien, M. The Influence of Recycled Concrete Aggregate on the Properties of Concrete. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 162, 02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Time-Dependent and Long-Term Mechanical Properties of Concretes Incorporating Different Grades of Coarse Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Eng. Struct. 2018, 157, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.J.; West, J.S.; Tighe, S.L. Towards the Classification of Recycled Concrete Aggregates: Influence of Fundamental Aggregate Properties on Recycled Concrete Performance. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2014, 3, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, L.; Francesconi, L. Ultrasonic Test on Recycled Concrete: Relationship among Ultrasonic Waves Velocity, Compressive Strength and Elastic Modulus. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 894, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-J.; Yen, T.; Chen, K.-H. Use of Building Rubbles as Recycled Aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, K.; Akbarnezhad, A. Variability of Stress-Strain Relationship for Recycled Aggregate Concrete under Uniaxial Compression Loading. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiti, A. A Critical Overview of Outlier Detection Methods. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2020, 38, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, V.; Austin, J. A Survey of Outlier Detection Methodologies. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2004, 22, 85–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bao, Y. Effect of Dataset Representation Bias on Generalizability of Machine Learning Models in Predicting Flexural Properties of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) Beams. Eng. Struct. 2025, 326, 119508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Corominas, A.; Etxeberria, M. Effects of Using Recycled Concrete Aggregates on the Shrinkage of High Performance Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.C.; Poon, C.S.; Chan, D. Influence of Fly Ash as a Cement Addition on the Hardened Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Mater. Struct. 2008, 41, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbudo, A.; De Brito, J.; Evangelista, L.; Bravo, M.; Agrela, F. Influence of Water-Reducing Admixtures on the Mechanical Performance of Recycled Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 59, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| k | Bias | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 3 | 0.510 |
| 0.1 | 3 | 0.483 |
| 0.05 | 3 | 0.512 |
| 0.01 | 3 | 0.479 |
| 0.01 | 5 | 0.495 |
| Interval Range | Total Number of Query Points | Number of Covered Points | Coverage Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [0.78, 1.48] | 977 | 317 | 32.4 |
| [1.48, 2.19] | 1020 | 439 | 43.0 |
| [2.19, 2.89] | 961 | 565 | 58.8 |
| [2.89, 3.59] | 993 | 747 | 75.2 |
| [3.59, 4.29] | 970 | 737 | 76.0 |
| [4.29, 5.00] | 1026 | 777 | 75.7 |
| [5.00, 5.70] | 986 | 729 | 73.9 |
| [5.70, 6.40] | 1040 | 814 | 78.3 |
| [6.40, 7.11] | 1002 | 672 | 67.1 |
| [7.11, 7.81] | 1025 | 381 | 37.2 |
| Interval Range | Total Number of Query Points | Number of Covered Points | Coverage Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [0, 10] | 1013 | 761 | 75.1 |
| [10, 20] | 1021 | 669 | 65.5 |
| [20, 30] | 1018 | 675 | 66.3 |
| [30, 40] | 1011 | 537 | 53.1 |
| [40, 50] | 974 | 688 | 70.6 |
| [50, 60] | 1016 | 703 | 69.2 |
| [60, 70] | 988 | 500 | 50.6 |
| [70, 80] | 986 | 435 | 44.1 |
| [80, 90] | 980 | 447 | 45.6 |
| [90, 100] | 993 | 763 | 76.8 |
| Interval Range | Total Number of Query Points | Number of Covered Points | Coverage Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [10.00, 19.85] | 980 | 389 | 60.3 |
| [19.85, 29.70] | 1003 | 151 | 84.9 |
| [29.70, 39.55] | 1051 | 51 | 95.1 |
| [39.55, 49.40] | 1039 | 44 | 95.8 |
| [49.40, 59.26] | 962 | 91 | 90.5 |
| [59.26, 69.11] | 975 | 289 | 70.4 |
| [69.11, 78.96] | 993 | 606 | 39.0 |
| [78.96, 88.81] | 1014 | 828 | 18.3 |
| [88.81, 98.66] | 982 | 728 | 25.9 |
| [98.66, 108.51] | 1001 | 645 | 35.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, W.-T.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Zhao, X.-Y. More Trustworthy Prediction of Elastic Modulus of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using MCBE and TabPFN. Materials 2025, 18, 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225221
Lu W-T, Wang Z-Z, Zhao X-Y. More Trustworthy Prediction of Elastic Modulus of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using MCBE and TabPFN. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225221
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Wei-Tian, Ze-Zhao Wang, and Xin-Yu Zhao. 2025. "More Trustworthy Prediction of Elastic Modulus of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using MCBE and TabPFN" Materials 18, no. 22: 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225221
APA StyleLu, W.-T., Wang, Z.-Z., & Zhao, X.-Y. (2025). More Trustworthy Prediction of Elastic Modulus of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using MCBE and TabPFN. Materials, 18(22), 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225221








