Tailoring Magnetic Properties and Power Loss in Low-Temperature Sintered NiCuZn Ferrites with BMLS-CaTiO3/BaTiO3 Composite Additives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of BMLS Glass
2.3. Fabrication of NiCuZn with Added BMLS-CaTiO3/BaTiO3 Composites
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- NiCuZn ferrites incorporating BMLS-CaTiO3/BaTiO3 as composite additives were successfully prepared at a low sintering temperature of 925 °C, and all samples exhibited a pure spinel phase structure.
- (2)
- The microstructure evolution with the CaTiO3/BaTiO3 content (x) was systematically revealed. As x increased from 0.00 to 0.15 wt%, the average grain size exhibited a continuous reduction. Notably, the grain size uniformity initially improved, reaching an optimum at x = 0.05 wt%, before deteriorating at higher concentrations (x ≥ 0.08 wt%) due to excessive inhibition of grain growth.
- (3)
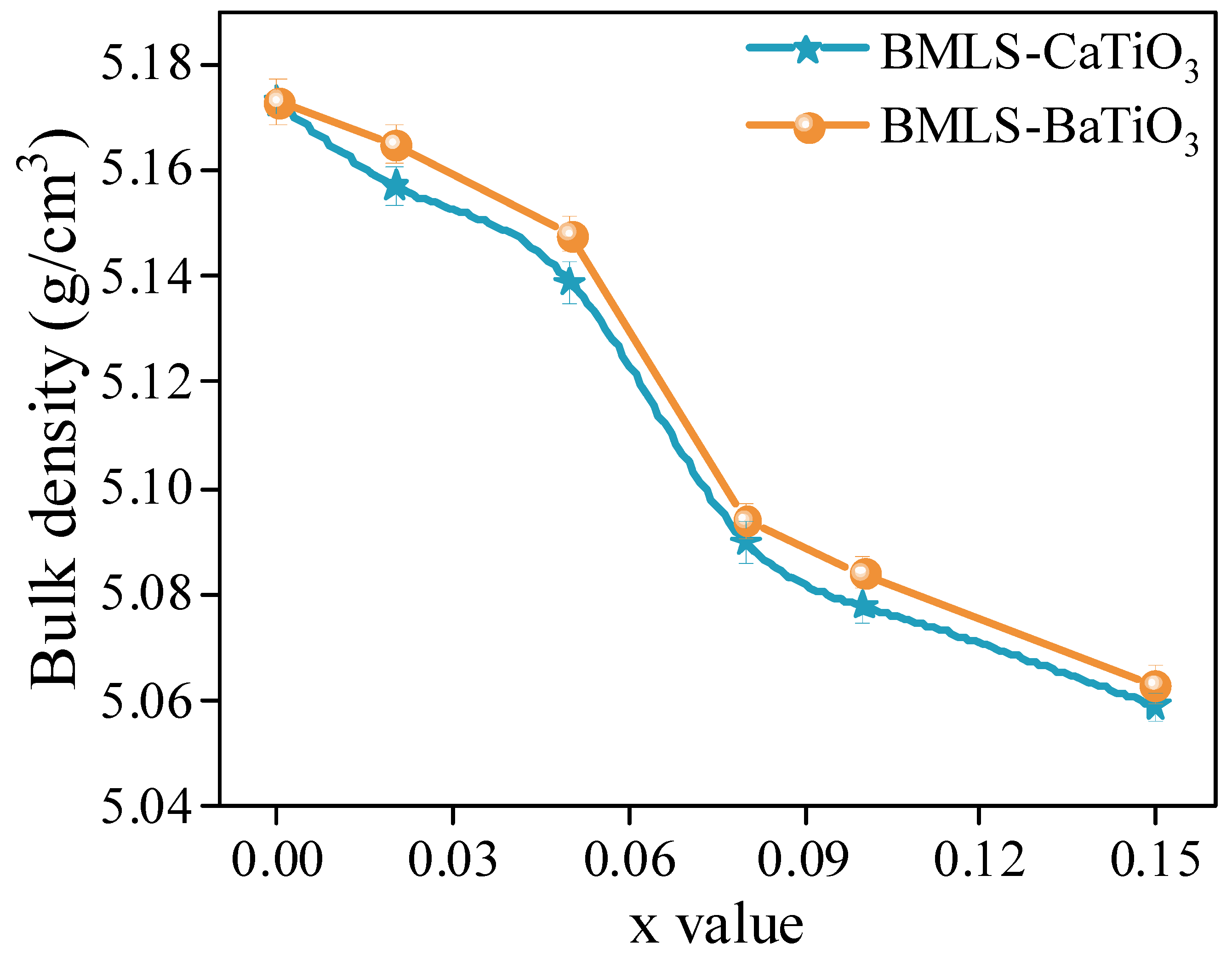
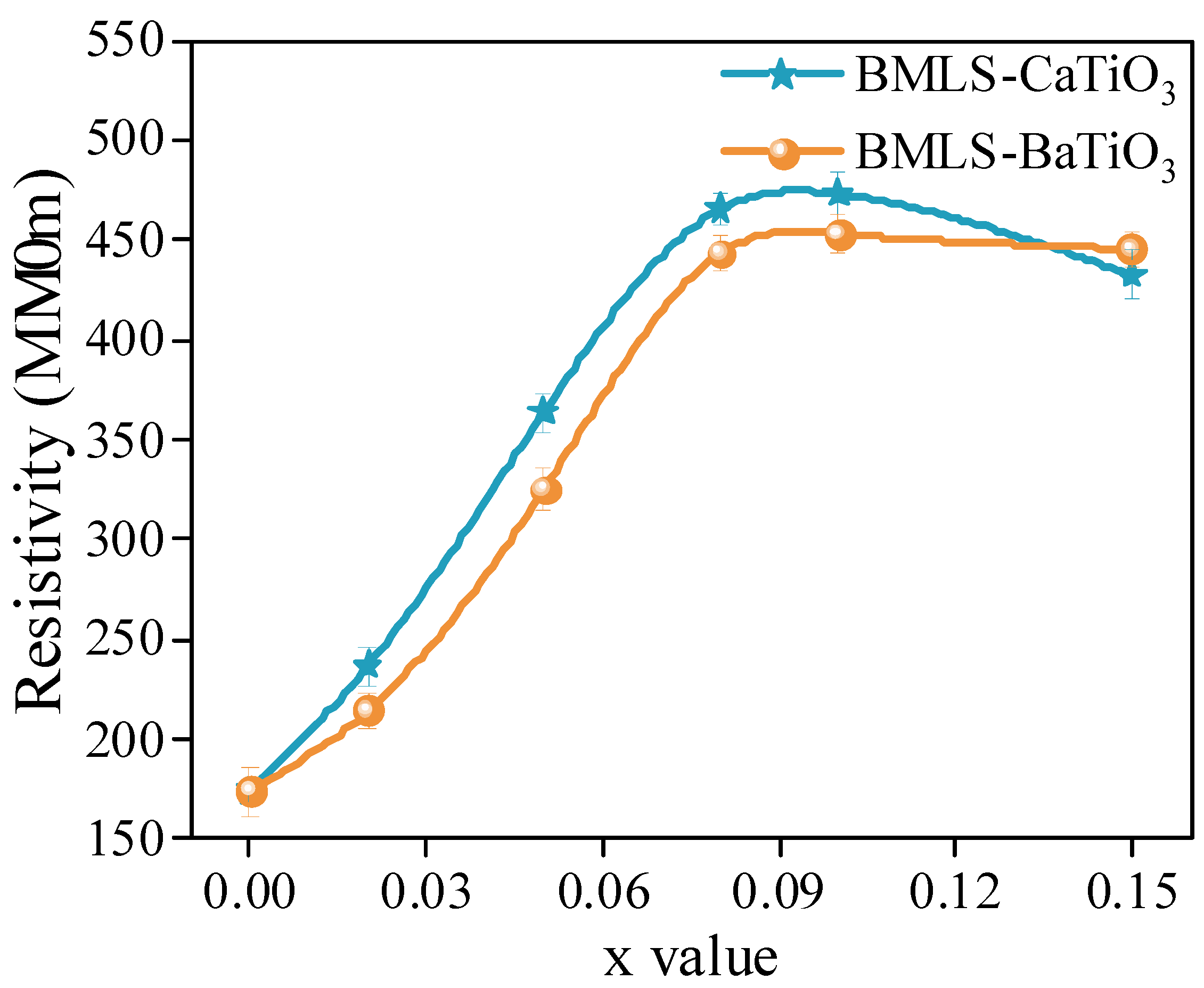
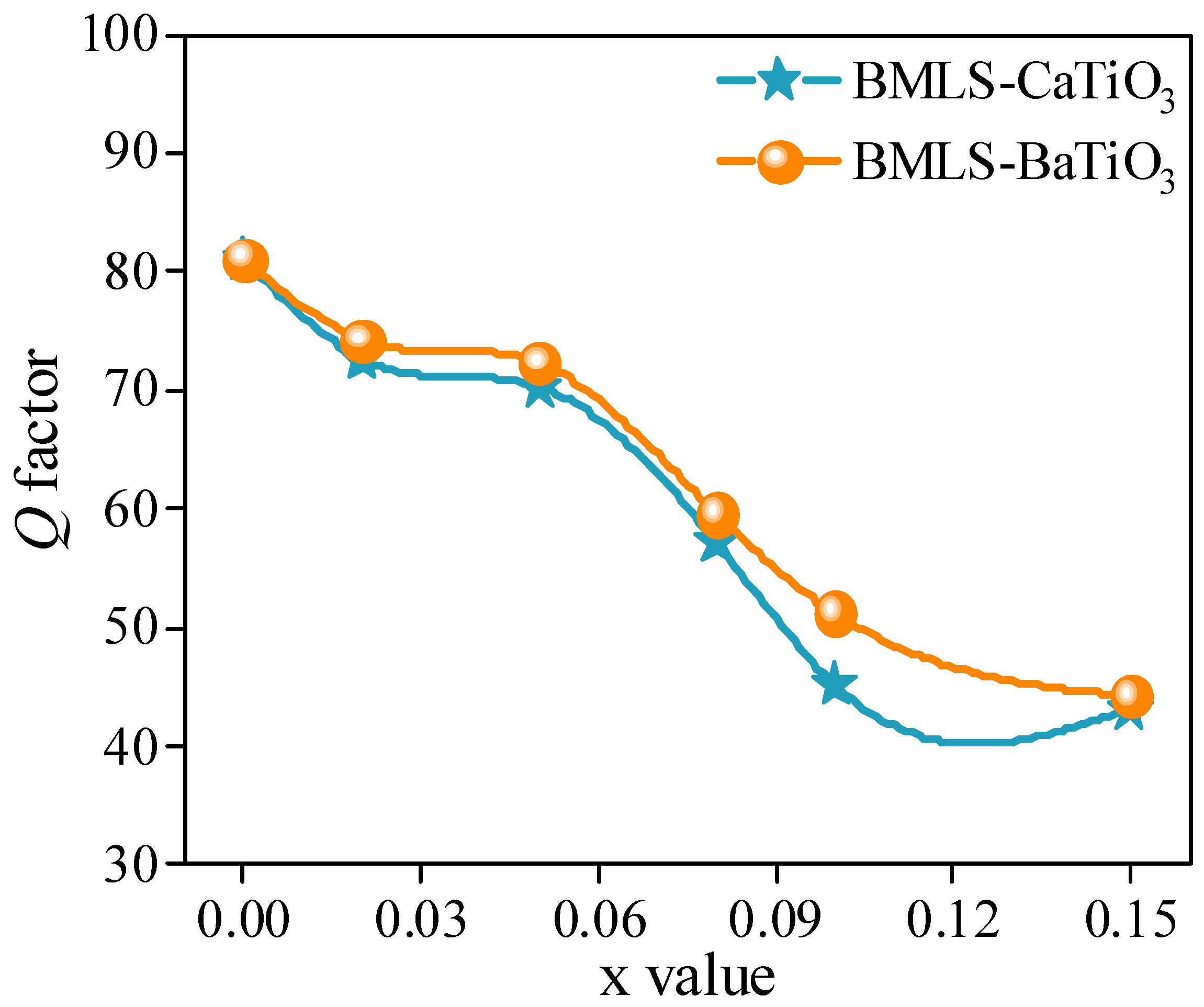
- As the content of CaTiO3 or BaTiO3 increased, the density, complex permeability, and Q factor consistently decreased. The resistivity, however, showed a non-monotonic dependence on x, reaching a maximum at x = 0.10 wt%. This trend is attributed to two competing effects: the initial increase is due to the increased number of high-resistivity grain boundaries and the segregation of insulating CaTiO3/BaTiO3 phases, which impede electron transport. The subsequent decrease at x = 0.15 wt% is likely caused by the excessive porosity and degraded densification, which can create defective paths and outweigh the benefits of grain refinement.
- (4)
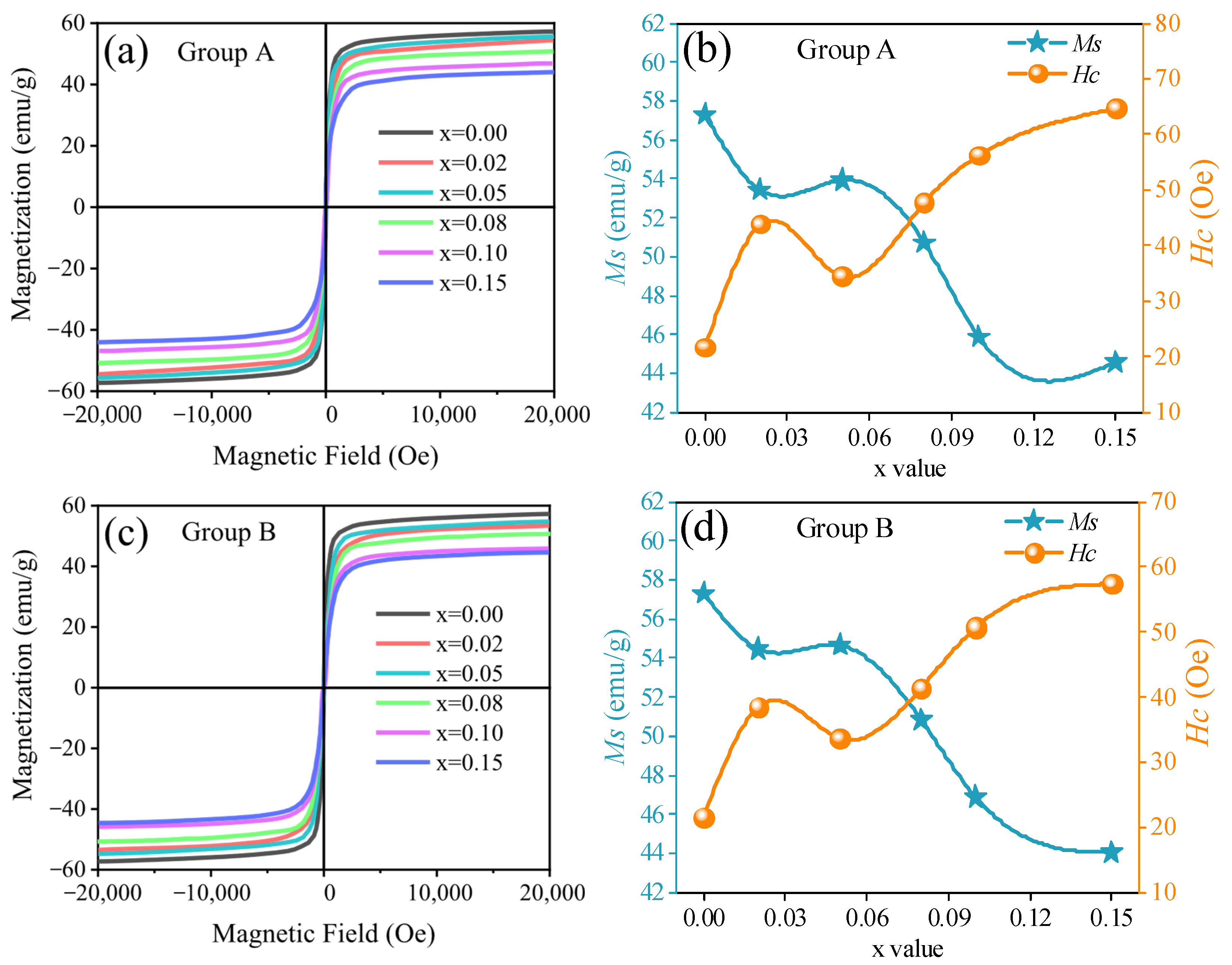
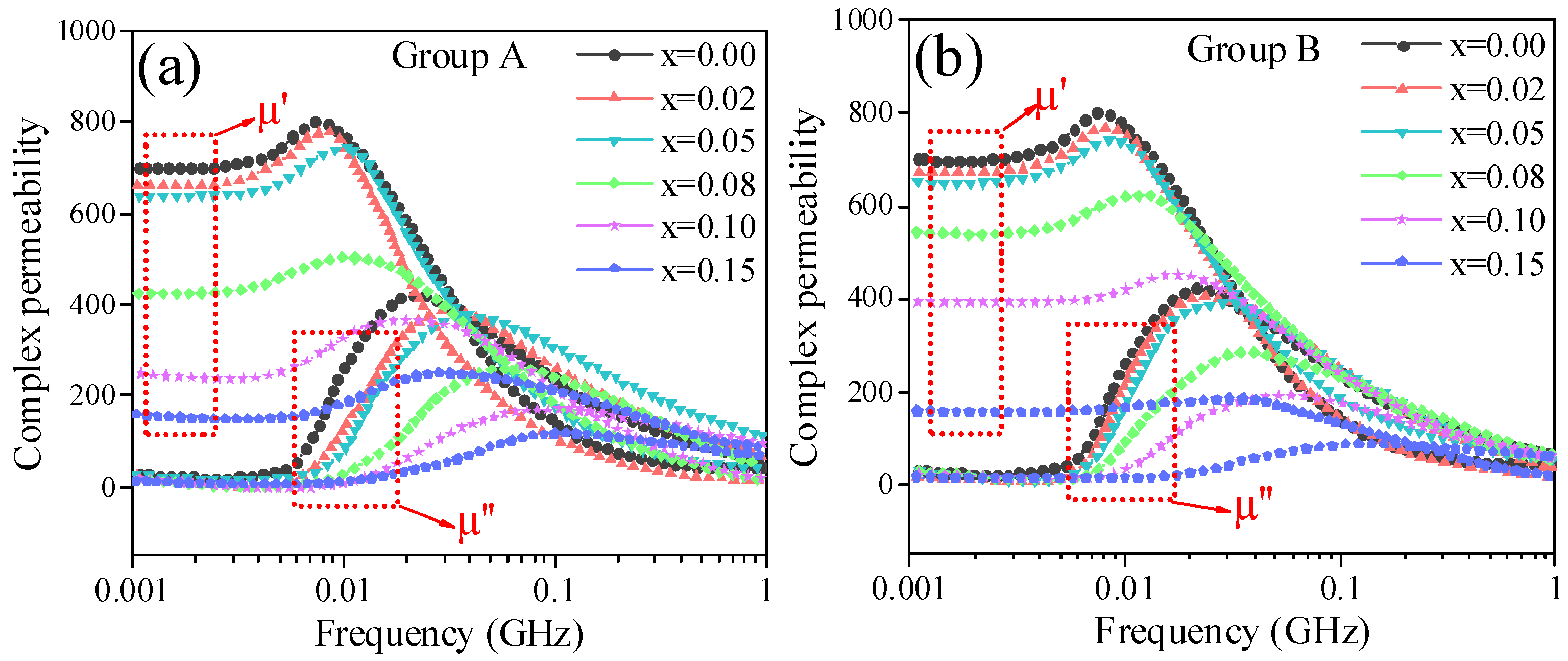
- With increasing CaTiO3/BaTiO3 content, Ms and permeability followed a general declining trend, while the Hc exhibited a continuous increase. The sample at x = 0.05 wt% represents an optimal compromise within this trend (Ms > 53.9 emu/g, permeability > 636), where the positive effect of enhanced grain uniformity partially counteracts the negative impacts of magnetic dilution, crystallite size reduction, and density decrease.
- (5)
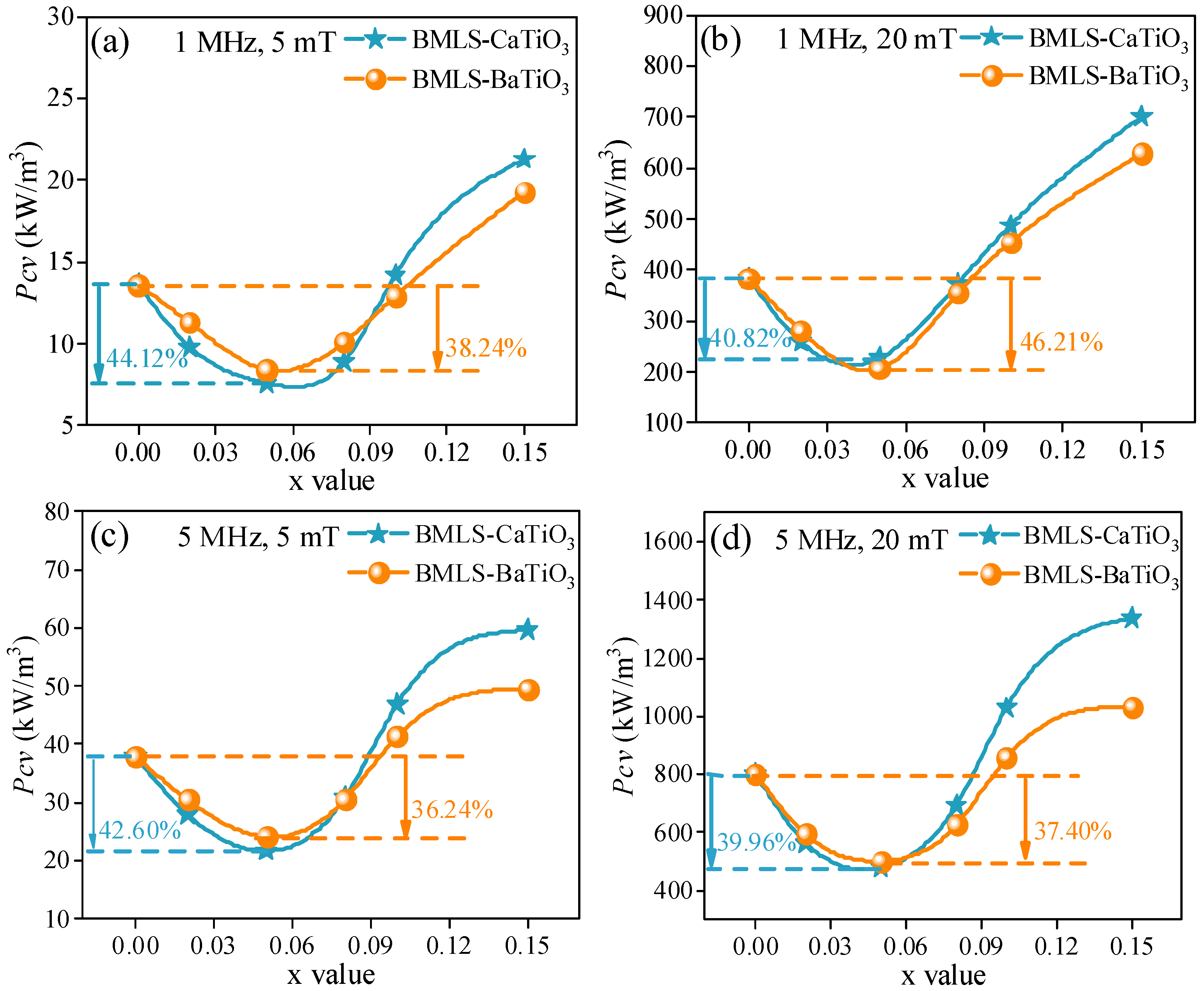
- As the content of CaTiO3 or BaTiO3 increased, the total power loss of the samples first decreased and then increased. The lowest power loss was achieved at x = 0.05, with a reduction exceeding 35.00% across various magnetic induction levels and frequencies. This reason is mainly due to increased resistivity, which significantly lowers eddy current loss. However, when x exceeds 0.05, the sharp decrease in complex permeability contributes to a substantial increase in hysteresis loss, ultimately raising the total power loss despite the continued increase in resistivity.
- (6)
- This study demonstrates that the microstructure and electromagnetic properties of low-temperature-sintered NiCuZn ferrites can be effectively tailored by the BMLS-Ca/BaTiO3 composite additives. The evolution of these parameters with x offers a clear guideline for material selection based on application needs: compositions with x ≤ 0.05 wt% are optimal for applications requiring high permeability and low power loss (e.g., high-efficiency inductors), whereas compositions with higher x values (e.g., 0.10 wt%), which exhibit peak resistivity, might be better suited for RF and microwave device applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almessiere, M.A.; Slimani, Y.; Trukhanov, A.V.; Korkmaz, A.D.; Guner, S.; Akhtar, S.; Shirsath, S.E.; Baykal, A.; Ercan, I. Effect of Nd-Y co-substitution on structural, magnetic, optical and microwave properties of NiCuZn nanospinel ferrites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 11278–11290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X.; Xiang, X. High-permeability and high-Curie temperature NiCuZn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 283, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Xu, F.; Liao, Y.; Liu, C.; Su, H. Low-temperature sintering synthesis and electromagnetic properties of NiCuZn/BaTiO3 composite materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 788, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X.; Jing, Y.; Zhong, Z. Dielectric and magnetic properties of low-temperature fired NiCuZn–BaTiO3 composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2763–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almessiere, M.A.; Slimani, Y.; Attia, H.; Sheikh, S.I.M.; Sadaqat, A.; Vakhitov, M.G.; Klygach, D.S.; Sertkol, M.; Baykal, A.; Trukhanov, A.V. Alterations in the magnetic and electrodynamic properties of hard-soft Sr0.5Ba0.5Eu0.01Fe12O19/NixCuyZnwFe2O4 nanocomposites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 1416–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Jin, L.; Cheng, L.; Jia, L.; Zhang, D.; Liao, Y. Synthesis and magnetic properties of low-temperature sintered, LMZBS glass-doped dense NiCuZn ferrites. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 19011–19016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.F.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.Y.; Wu, L.N.; Luo, R.; Wei, B.; Wang, T. Probing the influence of V2O5 and SBZKN composite additives on the magnetic characteristics and power loss of low-temperature sintered NiCuZn ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 988, 174184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, K.; Sadhana, K.; Liu, H.; Maramu, N.; Himanandini, G. Improved microwave absorption properties of TiO2 and Ni0.53Cu0.12Zn0.35Fe2O4 nanocomposites potential for microwave devices. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 681, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzali, H.; Saida, F.; Marzouki, A.; Megriche, A.; Baillon, F.; Espitalier, F.; Mgaidi, A. Structural and magnetic properties of nano-sized NiCuZn ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method with ultrasound irradiation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 419, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, G.; Gan, G.W.; Rao, Y.H. Effects of Bi2O3-MnO2 additives on tunable microstructure and magnetic properties of low temperature co-fired NiCuZn ferrite ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 12325–12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Shen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced electromagnetic properties of low-temperature sintered NiCuZn ferrites by doping with Bi2O3. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 20315–20323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, G.; Jin, L.; Li, J.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. Synthesis of V2O5-Doped and low-sintered NiCuZn ferrite with uniform grains and enhanced magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 10652–10657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, X.; Dong, S.; Zheng, H.; Hu, J.; Zheng, L. Microstructure and electromagnetic properties of low-temperature sintered NiCuZn ferrite by co-doped Bi2O3 and Co2O3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Yao, H. Soft magnetic, gyromagnetic, and microstructural properties of BBSZ-Nb2O5 doped NiCuZn ferrites for LTCC applications. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 8653–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Jing, Y.; Su, H. Microstructure, magnetic, and power loss characteristics of low-sintered NiCuZn ferrites with La2O3-Bi2O3 additives. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 106, 7523–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Su, H.; Tang, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jing, Y. Effects of Bi2O3 addition on power loss characteristics of low-temperature-fired NiCuZn ferrites. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16005–16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Jing, Y.; Su, H. Effect of Bi2O3 and Co2O3 co-doping on power loss characteristics of low-temperature-fired NiCuZn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 555, 169368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Xu, F.; Wang, G.; Gao, F.; Su, H. Nb5+ ion substitution assisted the magnetic and gyromagnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrite for high frequency LTCC devices. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 12490–12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Kong, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z. Investigation on the micro-structure and magnetic properties of LMZBS-Bi2O3 doped low-temperature sintered NiCuZn ferrites. Mater. Res. Express 2023, 10, 046101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Gui, Z. Effects of MnO2 on the electromagnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrites prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 233, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Bai, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Jin, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, M. Synergistic effect of V2O5 and Bi2O3 on the grain boundary structure of high-frequency NiCuZn ferrite ceramics. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Yi, S.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, J.; Bai, G. High-frequency MnZn soft magnetic ferrite by engineering grain boundaries with multiple-ion doping. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 79, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.D.; Patange, S.M.; Dighe, P.M.; Shaikh, S.F.; Rana, A.u.H.S.; Pandit, B.; Jadhav, S.S. Tuning the structural, optical and magnetic properties of NiCuZn (Ni0.4Cu0.3Zn0.3Fe2O4) spinel ferrites by Nb2O5 additive. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 27039–27050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.M.; Liu, X.P.; Gao, P.Z.; He, L.T.; Li, J.W. Effects of Ni2+ concentration on the composition, structure, magnetic properties, and DC-bias superposition characteristics of NiCuZn ferrites. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 11228–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.X.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.W. Magnetic and dielectric properties of low-temperature sintered NiCuZn/CaTiO3 composite dual-performance materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 910, 164906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znidarsic, A.; Drofenik, M. High-resistivity grain boundaries in CaO-doped MnZn ferrites for high-frequency power application. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Low temperature firing of Li0.43Zn0.27Ti0.13Fe2.17O4 ferrites with enhanced magnetic properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 98, 2556–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, C.; Xiao, S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H. Effects of solid-state reaction temperature on the activation energy and DC-bias superposition of NiCuZn ferrites based on master sintering curve. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2016, 115, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, B.; Toksha, B.; Shirsath, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Tonde, S.; Chishty, S. Microstructure, magnetic, and dielectric interplay in NiCuZn ferrite with rare earth doping for magneto-dielectric applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 537, 168229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Chen, T.; Shen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, K.; Sun, M.; Yu, Y.; Fan, L.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Q.; et al. Magnetic and dielectric properties of NiCuZn ferrite with optimized Cu content and sintered by a two-step process. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 898, 162906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Zaag, P.J.; Van Der Valk, P.J.; Rekveldt, M.T. A domain size effect in the magnetic hysteresis of NiZn-ferrites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 2927–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Rao, Y.; Wang, G.; Gan, G. Bi3+ doping adjusted microstructure, magnetic, and dielectric properties of nickel zinc ferrite ceramics for high frequency LTCC antennas. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 25697–25704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrin, S.; Khan, S.; Matin, M.; Khan, M.; Hossain, A.K.M.A.; Rahaman, M.M. Synthesis and deciphering the effects of sintering temperature on structural, elastic, dielectric, electric and magnetic properties of magnetic Ni0.25Cu0.13Zn0.62Fe2O4 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 10722–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murbe, J.; Topfer, J. Ni-Cu-Zn Ferrites for low temperature firing: II. Effects of powder morphology and Bi2O3 addition on microstructure and permeability. J. Electroceram. 2006, 16, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Rahaman, M.D.; Khan, M.N.I.; Hossain, A.K.M.A. Synthesis, structural, morphological, electrical and magnetic properties of (1-x) [Ni0.35Cu0.15Zn0.50Mn0.05Fe1.95O4] + (x) [Rice husk ash] composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 112, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Jin, L.; Rao, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, F.; et al. Densification and magnetic properties of NiCuZn low-sintering temperature ferrites with Bi2O3-Nb2O5 composite additives. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 776, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Luo, Q.; Jing, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X. Effects of calcination temperature and flux doping on the microstructure and magnetic properties of low-temperature-fired NiCuZn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 469, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Seifert, D.; Topfer, J. Phase formation and saturation magnetization of La-Zn-substituted M-type strontium ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 508, 166887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, M.L.S.; Kong, L.B.; Li, Z.W.; Lin, G.Q.; Gan, Y.B. Development of magneto-dielectric materials based on Li-ferrite ceramics: I. Densification behavior and microstructure development. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 459, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X.; Jing, Y. Influence of microstructure on permeability dispersion and power loss of NiZn ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 093903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
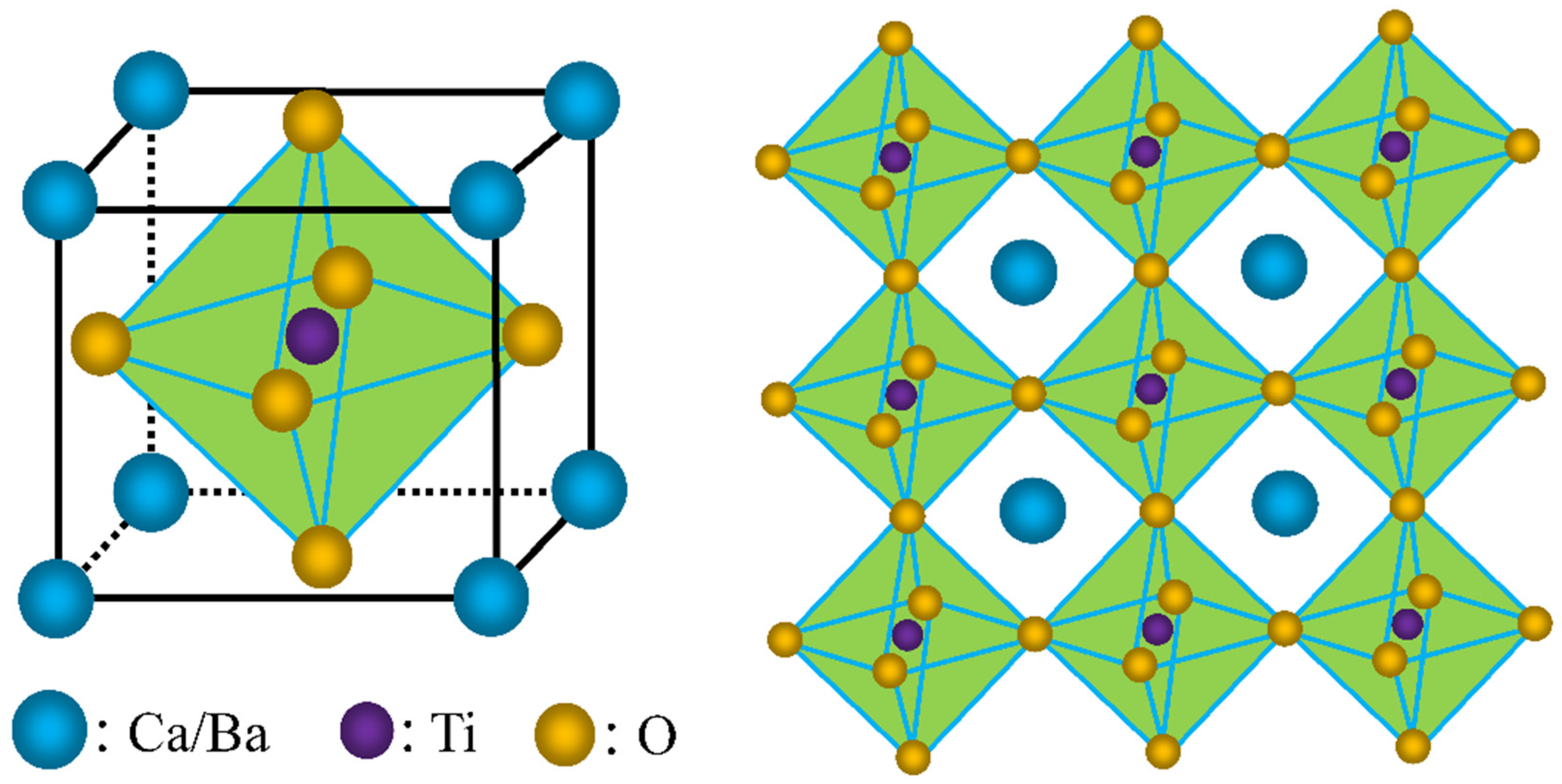
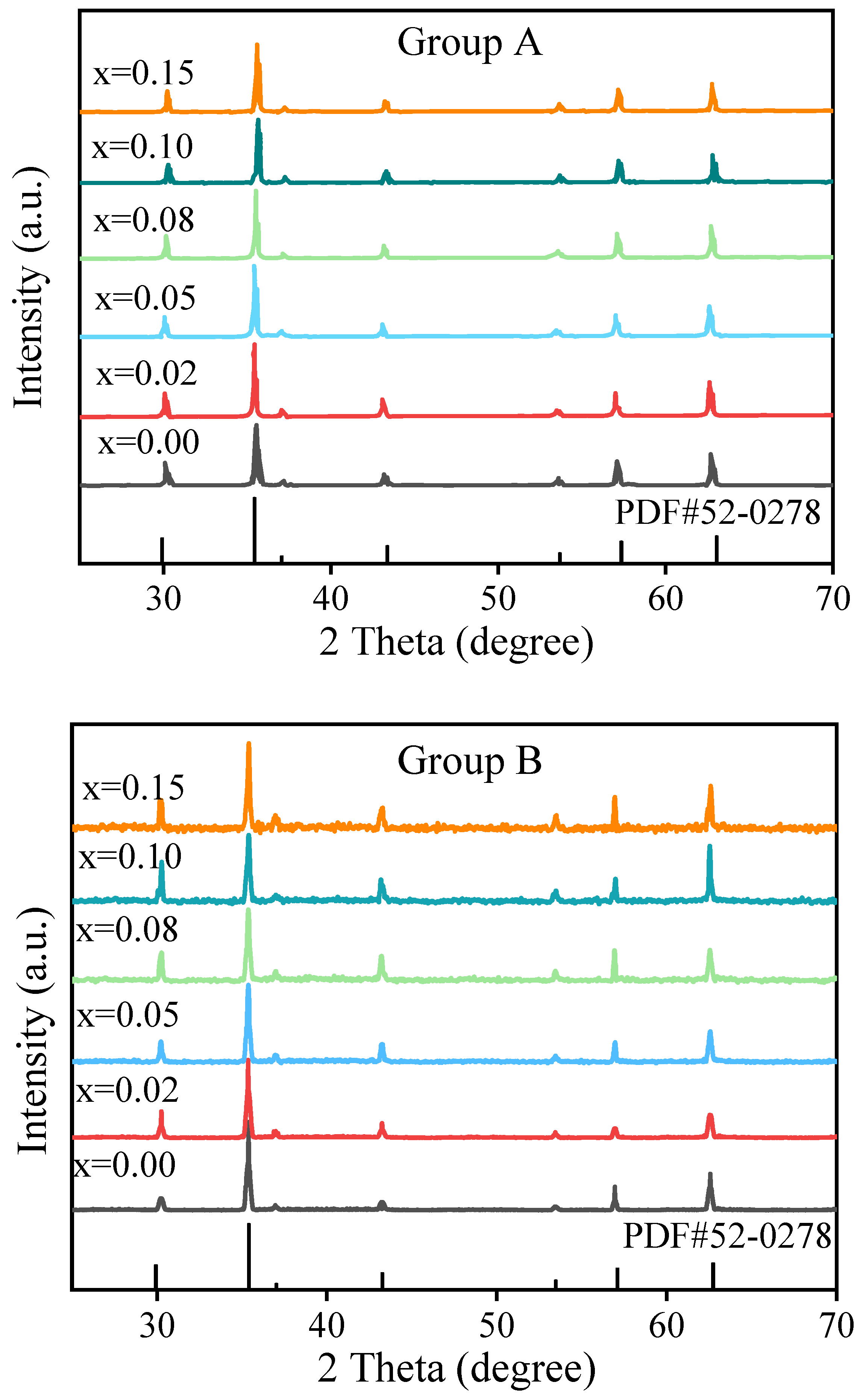
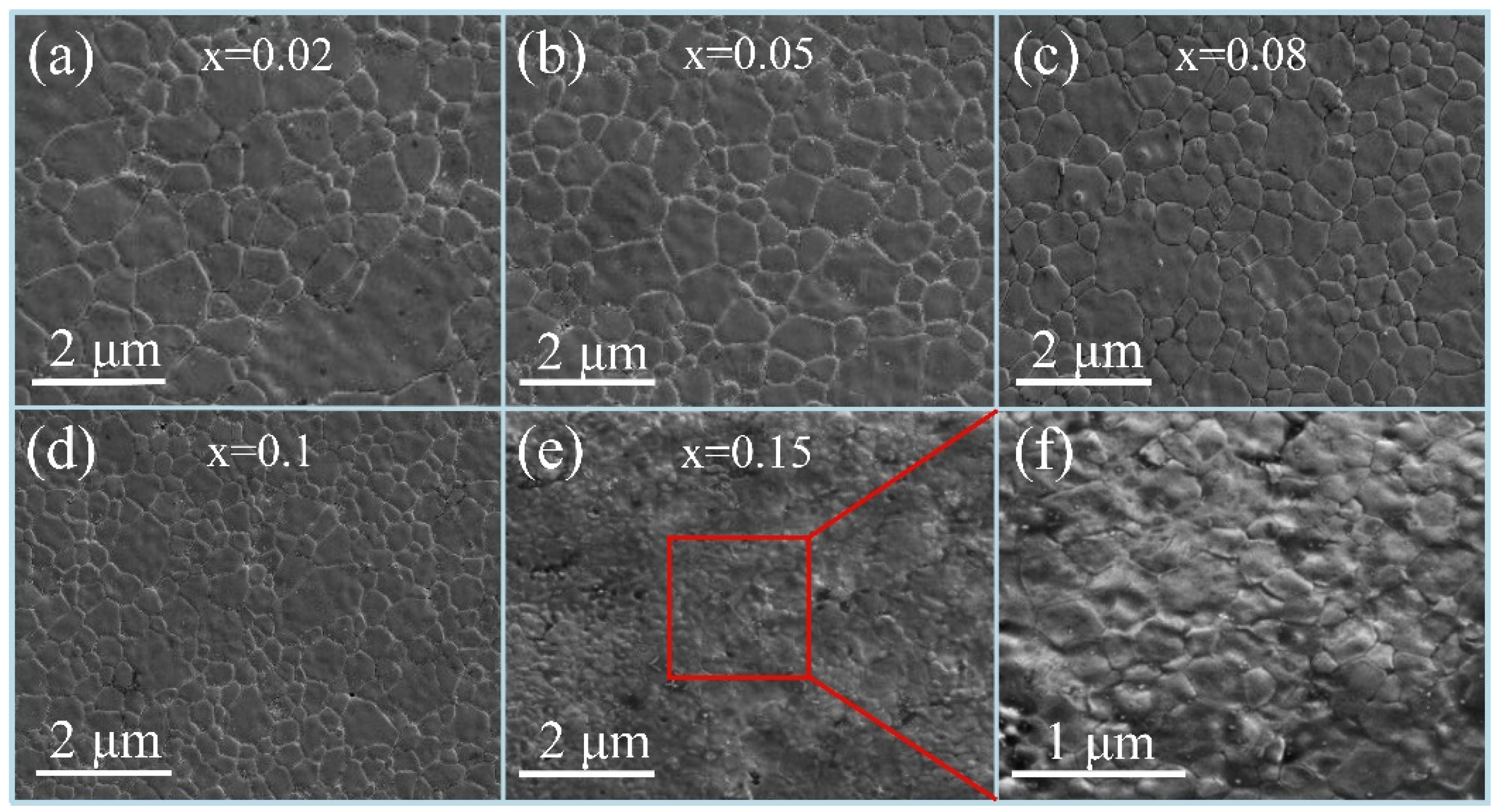
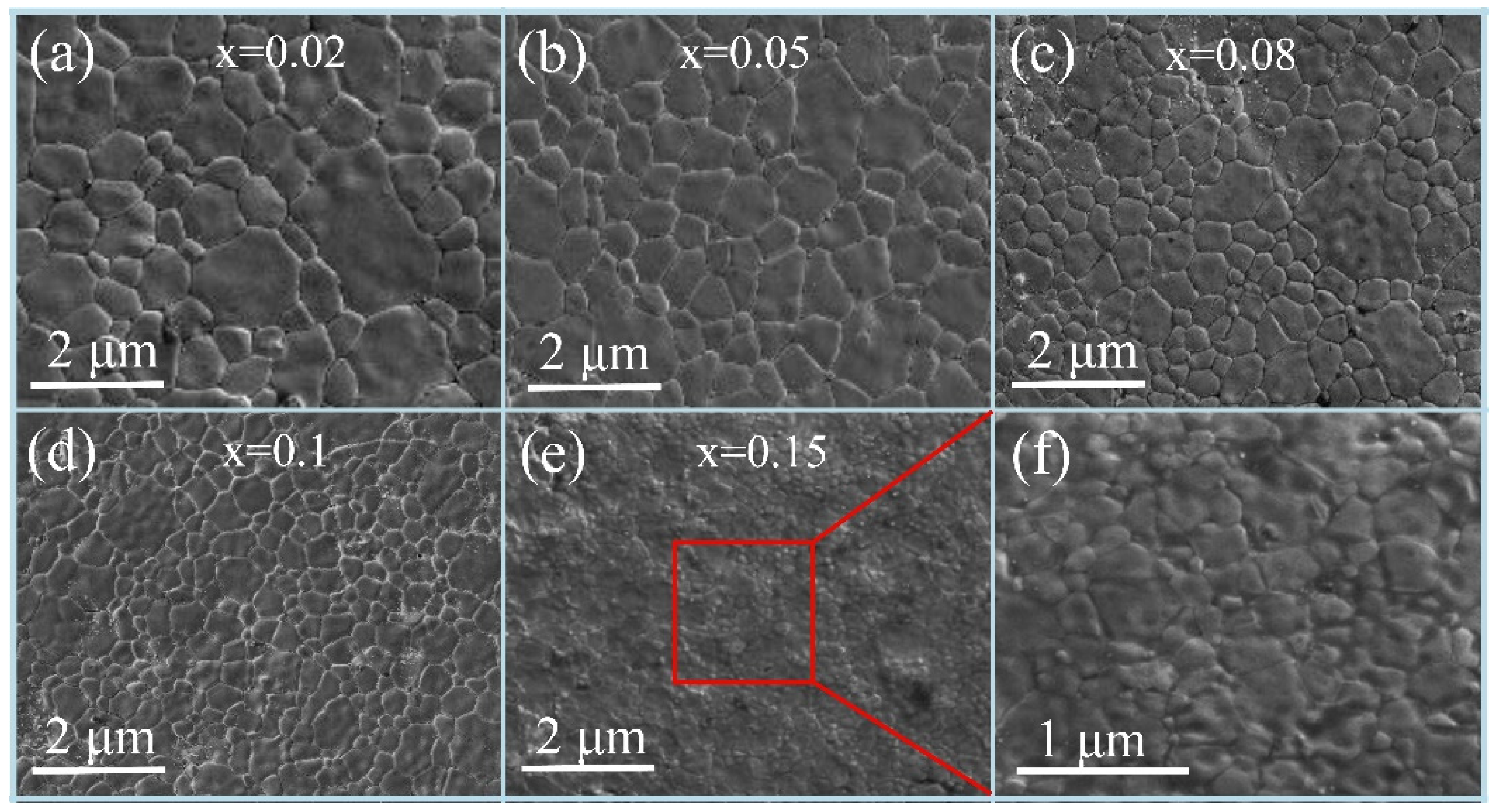

| Item | Density (g/cm3, 25 °C) | Melting Point (°C) | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaTiO3 | 4.1 | 1975 | 135.94 |
| BaTiO3 | 6.08 | 1625 | 233.19 |
| Additive contents | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaTiO3 | a (Å) | 8.4148 | 8.4143 | 8.4129 | 8.4113 | 8.4091 |
| ε (×10−4) | 1.19 | 2.85 | 4.75 | 5.94 | 8.37 | |
| t (nm) | 47.38 | 44.63 | 42.36 | 38.67 | 28.28 | |
| BaTiO3 | a (Å) | 8.4149 | 8.4145 | 8.4134 | 8.4121 | 8.4095 |
| ε (×10−4) | 2.26 | 3.30 | 4.95 | 6.49 | 9.50 | |
| t (nm) | 48.07 | 45.03 | 42.16 | 39.68 | 30.38 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Cao, Z.; Cui, L.; Chang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, L.; Ge, X. Tailoring Magnetic Properties and Power Loss in Low-Temperature Sintered NiCuZn Ferrites with BMLS-CaTiO3/BaTiO3 Composite Additives. Materials 2025, 18, 5202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225202
Chen C, Cao Z, Cui L, Chang F, Xiao Y, Wu L, Ge X. Tailoring Magnetic Properties and Power Loss in Low-Temperature Sintered NiCuZn Ferrites with BMLS-CaTiO3/BaTiO3 Composite Additives. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225202
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chuan, Zhengfeng Cao, Lei Cui, Fangyuan Chang, Yan Xiao, Lining Wu, and Xiangyu Ge. 2025. "Tailoring Magnetic Properties and Power Loss in Low-Temperature Sintered NiCuZn Ferrites with BMLS-CaTiO3/BaTiO3 Composite Additives" Materials 18, no. 22: 5202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225202
APA StyleChen, C., Cao, Z., Cui, L., Chang, F., Xiao, Y., Wu, L., & Ge, X. (2025). Tailoring Magnetic Properties and Power Loss in Low-Temperature Sintered NiCuZn Ferrites with BMLS-CaTiO3/BaTiO3 Composite Additives. Materials, 18(22), 5202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225202







