High-Efficiency PDLC Smart Films Enabled by Crosslinking Agent Optimization and MoS2 Nanosheets for Energy-Saving Windows
Highlights
- The structure of the PDLC network is greatly influenced by the alkyl chains of the polymer monomers.
- By introducing MoS2 nanosheets, the PDLC film has a low drive voltage (23 V) and high CR (135).
- The MoS2/PDLC films can reduce the temperature by about 5 °C compared with the conventional films
- The E-O properties of PDLC film can be improved by adjusting the structure of the polymer molecules.
- Appropriate amounts of nanoparticles can optimize the E-O properties of PDLC film.
- MoS2 can enhance the heat insulation performance of PDLC film.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of MoS2 Nanosheets
2.2. Preparation of PDLC Film
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Crosslinker Chain Length and Monomer Chain Length on the Electro-Optical Properties of Thin Films
3.2. Characterization of MoS2 Nanosheets
3.3. Effects of MoS2 Nanosheets on Film Morphology and Electro-Optical Properties
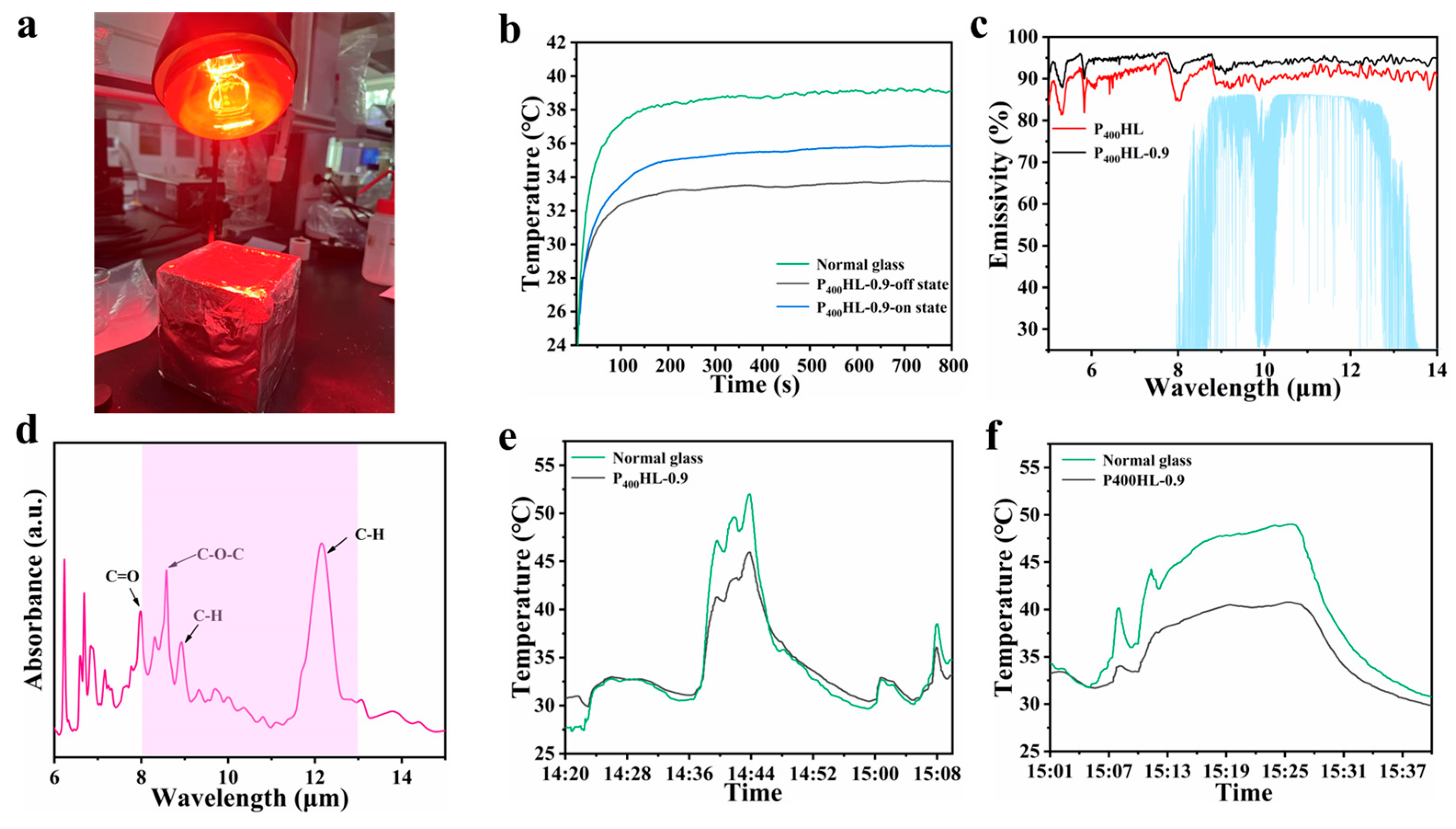
3.4. Analysis of Optical and Thermal Management Properties of Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D. Preparation of Progressive Driving Bilayer Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystals Possessing a PDLC-PVA-PDLC Structure. Molecules 2024, 29, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, D.; Luan, Y.; Wang, L. Preparation and Characterization of Bilayer Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystals Doped with Gd2O3 Nanoparticles and Rhodamine B Base Fluorescent Dye. Molecules 2024, 29, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; He, Z.; Gao, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Luan, Y. Preparation of polymer dispersed liquid crystal doped with bilayer nanofiber membranes and phase-change microcapsule coating for enhanced infrared modulation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhao, Y.; He, Z.; Gao, H.; Du, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Luan, Y. Dye-assisted bicomponent spun nanofibers toward PDLC electro-optical properties modulation and controlled patterning display. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 38, 102260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhong, Z.; Gao, H.; Du, X.; Zhao, Y.; He, Z.; Cao, H.; Yang, Z. PDLC flexible films with multiple fluorescence and voltage modulated modes and intelligent coding for applications in anti-counterfeiting and transparent displays. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Ma, Z.R.; Ma, A.Z.; He, Z.M.; Miao, Z.C. The effect of doping sulphhydryl-functionalised silica with different diameters on the electro-optical properties of PDLC. Liq. Cryst. 2024, 51, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Malik, P. New graphene oxide doped polymer dispersed liquid crystal nanocomposites targeted to eco-friendly and energy-efficient smart windows. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 410, 125565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchegolkov, A.V.; Jang, S.-H.; Shchegolkov, A.V.; Rodionov, Y.V.; Sukhova, A.O.; Lipkin, M.S. A Brief Overview of Electrochromic Materials and Related Devices: A Nanostructured Materials Perspective. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Zhang, Z.W.; He, L.X.; Shi, Y.J.; Gao, Y.Z.; Yu, M.N.; Yang, H. Liquid crystal/polymer composites for energy-efficient smart windows with a wide working temperature range and low off-axis haze. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 178, 107976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booten, C.; Rao, P.; Rapp, V.; Jackson, R.; Prasher, R. Theoretical minimum thermal load in buildings. Joule 2021, 5, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.C.; Peng, J.Q.; Tan, Y.T.; Li, C.C.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Long, Y. Liquid thermoresponsive smart window derived from hydrogel. Joule 2020, 4, 2458–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Yu, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Guo, R.; Cao, H.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhu, S. Effects on thermos-optical properties of the composition of a polymer-stabilised liquid crystal with a smectic A-chiral nematic phase transition. Liq. Cryst. 2008, 35, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, H.; Gotoh, T.; Nakata, T.; Hasegawa, E. Homeotropic reverse-mode polymer-liquid crystal device. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 1962–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunning, T.J.; Natarajan, L.V.; Tondiglia, V.P.; Sutherland, R.L. Holographic polymer-dispersed liquid crystals (H-PDLCs). Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2000, 30, 83–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, J.W.; Golemme, A.; West, J.L.; Whitehead, J.B.; Wu, B.G. Polymer dispersed liquid crystals for display application. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1988, 165, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.T.; Lee, P.Y.; Qasim, M.M.; Liu, C.K.; Cheng, W.F.; Wilkinson, T.D. Electrically switchable and permanently stable light scattering modes by dynamic fingerprint chiral textures. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 10483–10493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, M.A.; Liu, I.B.; Luo, Y.; Serra, F.; Bade, N.D.; Kim, H.N.; Xia, Y.; Yang, S.; Kamien, R.D.; Stebe, K.J. Smectic gardening on curved landscapes. Langmuir 2015, 31, 11135–11142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Pivnenko, M.; Chu, D.P.; Cockburn, A.; O’Neill, W. Uniform and fast switching of window-size smectic A liquid crystal panels utilising the field gradient generated at the fringes of patterned electrodes. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Cao, H.; Song, P.; Yang, C.; Yang, H.; Hu, G.H. Preparation and electro-optical properties of polymer dispersed liquid crystal films with relatively low liquid crystal content. Polym. Advan. Technol. 2013, 24, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.H.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhou, L.; Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Yang, D.K.; Yang, H. Effects of rigid structures containing (meth)acrylate monomers and crosslinking agents with different chain length on the morphology and electro-optical properties of polymer-dispersed liquid crystal films. J. Mod. Optic. 2020, 67, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Hu, W. Effects of Multi-Fluorinated Liquid Crystals with High Refractive Index on the Electro-Optical Properties of Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystals. Materials 2025, 18, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, I.; Kiruthika, S.; Ganesha, M.K.; Baral, M.; Kumar, A.; Vimala, S.; Madhuri, P.L.; Nair, G.G.; Prasad, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; et al. ITO-free large area PDLC smart windows: A cost-effective fabrication using spray coated SnO2 on an invisible Al mesh. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 23157–23168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelle, B.P.; Hynd, A.; Gustavsen, A.; Arasteh, D.; Goudey, H.; Hart, R. Fenestration of Today and Tomorrow: A State-of-the-Art Review and Future Research Opportunities. Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C. 2012, 96, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nundy, S.; Mesloub, A.; Alsolami, B.M.; Ghosh, A. Electrically actuated visible and near-infrared regulating switchable smart window for energy positive building: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 2, 126854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Hong, H.; Choi, W.; Akhtar, I.; Rehman, M.A.; Seo, Y. Acrylate-assisted fractal nanostructured polymer dispersed liquid crystal droplet based vibrant colored smart-windows. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12645–12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaligh, H.H.; Liew, K.; Han, Y.; Abukhdeir, N.M.; Goldthorpe, I.A. Silver nanowire transparent electrodes for liquid crystal-based smart windows. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 132, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ma, H.; Han, C.; Hu, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. A novel light diffuser based on the combined morphology of polymer networks and polymer balls in a polymer dispersed liquid crystals film. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21690–21698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; He, T.; Gong, X.; Geng, P.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of alkyl chain length of monomer and dye-doped type on the electro-optical properties of polymer-dispersed liquid crystal films prepared by nucleophile-initiated thiol-ene click reaction. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Ding, H.; Li, F.; Yu, H.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H. Effects of functionality of thiol monomer on electro-optical properties of polymer-dispersed liquid crystal films. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, S.; Saeed, M.; Zhou, L.; Gao, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Xiao, J.; Gao, Y. Effects of the methacrylate monomers with different end groups on the morphologies, electro-optical and mechanical properties of polymer dispersed liquid crystals composite films. Liq. Cryst. 2021, 48, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Peng, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L. Liquid-Crystal Biosensor Based on Nickel-Nanosphere-Induced Homeotropic Alignment for the Amplified Detection of Thrombin. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 23418–23422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, V.; Raina, K. Studies on inter-dependency of electrooptic characteristics of orange azo and blue anthraquinone dichroic dye doped polymer dispersed liquid crystals. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 251, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.J.; Yoon, D.Y. Electro-optical characteristics of dye-doped polymer dispersed liquid crystals. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaila-Maximean, D. Effective Permittivity of a Multi-Phase System: Nanoparticle-Doped Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystal Films. Molecules 2021, 26, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, C.S.; Jo, S. Spray Deposition of Ag Nanowire-Graphene Oxide Hybrid Electrodes for Flexible Polymer–Dispersed Liquid Crystal Displays. Materials 2018, 11, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kang, D.; Nguyen, V.; Nasir, N.; Hong, H.; Kim, M.; Nguyen, D.C.; Lee, Y.; Lee, N.; Seo, Y. Application of Titanium-Carbide MXene-Based Transparent Conducting Electrodes in Flexible Smart Windows. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 40976–40985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Singh, S.P.; Biradar, A.M.; Choudhary, A.; Sreenivas, K. Enhanced electro-optical properties in gold nanoparticles doped ferroelectric liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 023120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Zhang, L.N.; Xu, J.J.; He, X.; Yuan, B.H.; Chen, C.; Zou, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.Z.; Yu, M.N.; et al. A novel dual-functional flexible dimming film for smart window applications: Energy saving and self-cleaning performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 488, 150601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; He, X.; Zhang, L.N.; Xu, J.; Yuan, B.H.; Chen, C.; Zou, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.Z.; Yu, M.N.; et al. A novel low-voltage fast-response electrically controlled dimming film based on fluorinated PDLC for smart window applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, H.L.; Lan, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Ultrafast Switchable Passive Radiative Cooling Smart Windows with Synergistic Optical Modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 33, 2301319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Yi, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, T.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, T.; Cai, Y. Self-cleaning and spectrally selective coating on cotton fabric for passive daytime radiative cooling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Shi, L.; Hu, X.; Chen, M.; Wu, L. A structural polymer for highly efficient all-day passive radiative cooling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
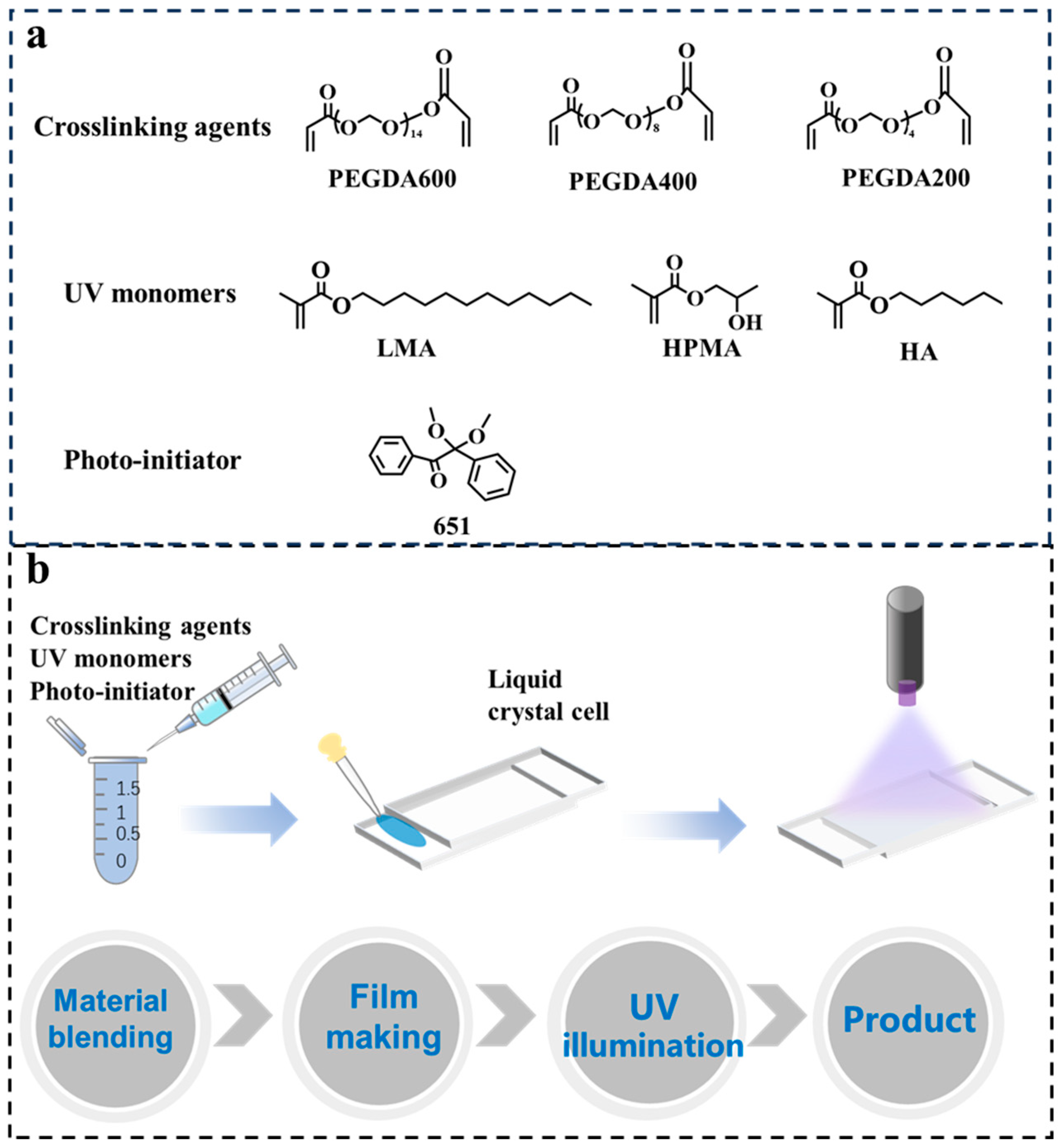
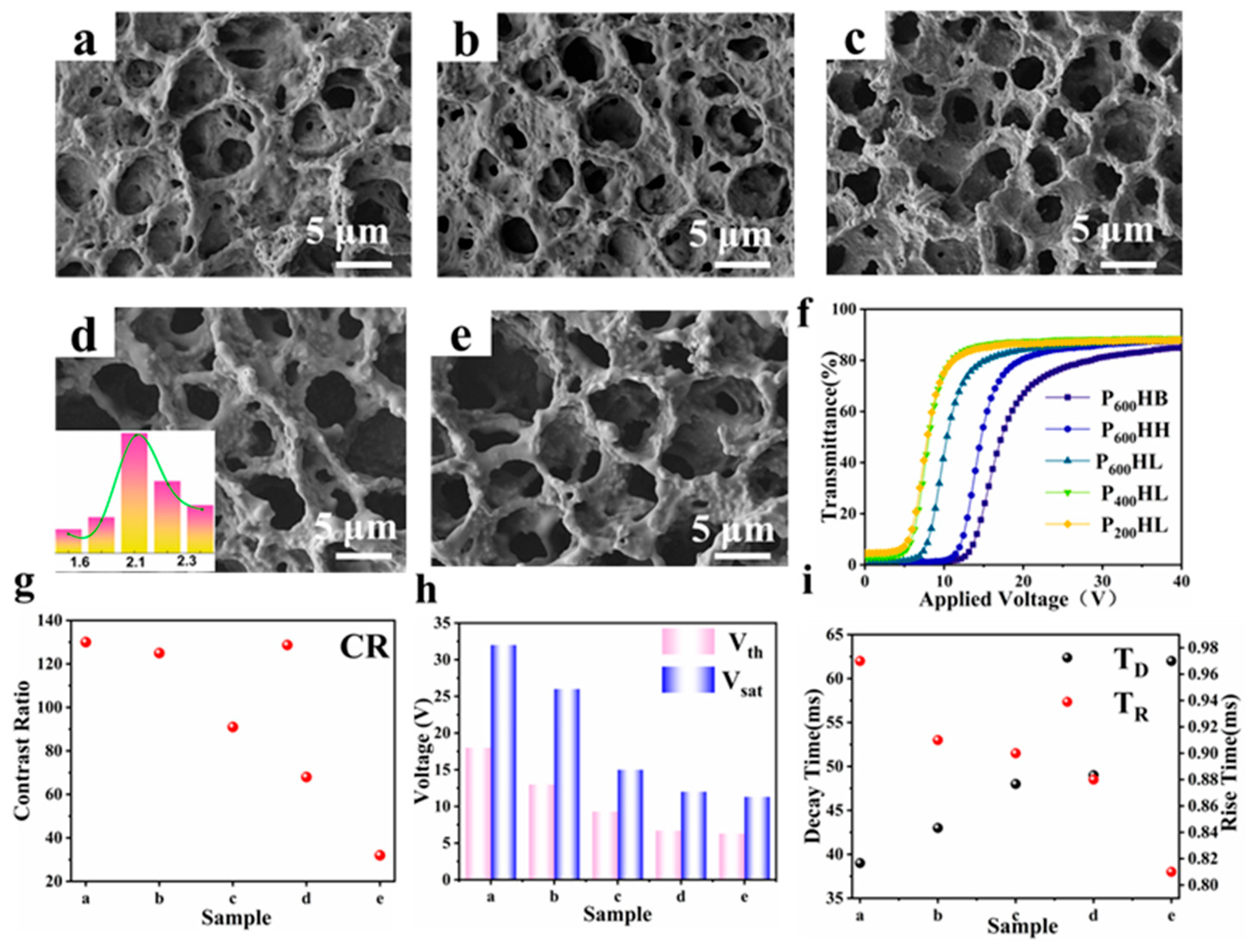

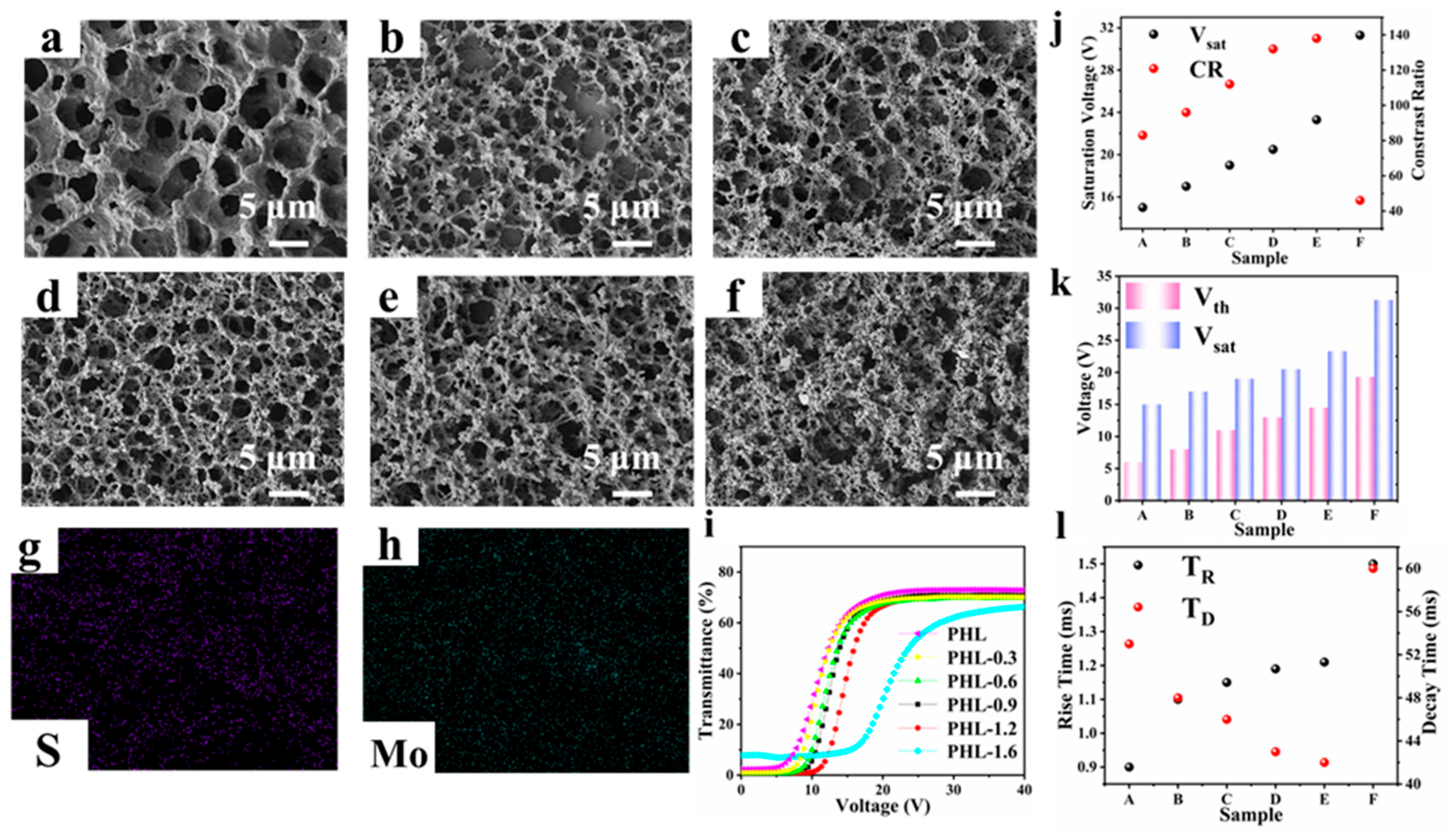
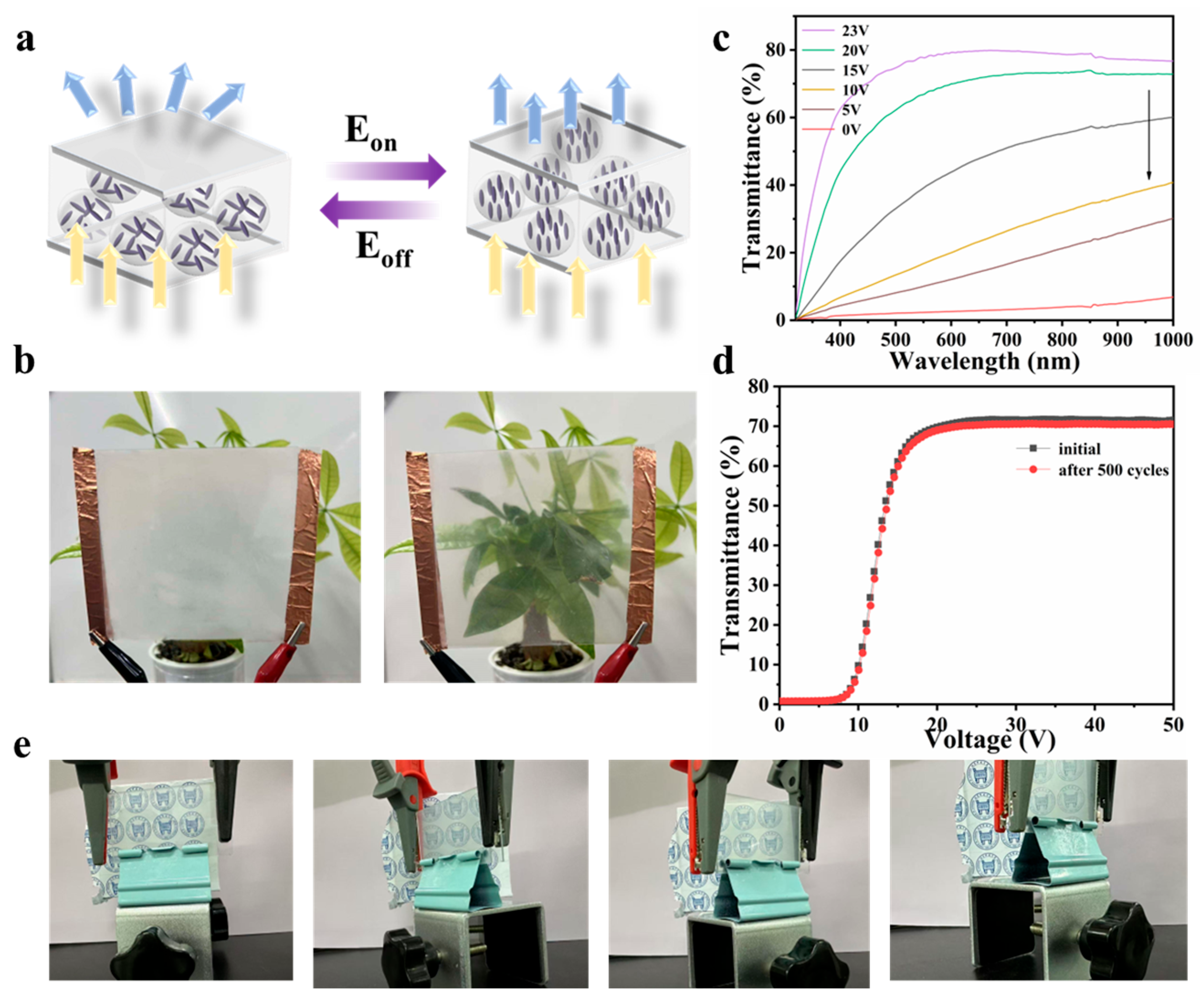
| Sample | Composition | (wt. %) |
|---|---|---|
| Group 1: Effects of crosslinker chain length and monomer chain length on the electro-optical properties of films | ||
| a | PEGDA600/HPMA/BA/LC | 6.0/6.0/18.0/70 |
| b | PEGDA600/HPMA/HA/LC | 6.0/6.0/18.0/70 |
| c | PEGDA600/HPMA/LMA/LC | 6.0/6.0/18.0/70 |
| d | PEGDA400/HPMA/LMA/LC | 6.0/6.0/18.0/70 |
| e | PEGDA200/HPMA/LMA/LC | 6.0/6.0/18.0/70 |
| Group 2: Effects of MoS2 nanosheets on film morphology and electro-optical properties | ||
| A | PEGDA400/HPMA/LMA/MoS2/LC | 6.0/6.0/18.0/0/70 |
| B | PEGDA400/HPMA/LMA/MoS2/LC | 6.0/6.0/17.7/0.3/70 |
| C | PEGDA400/HPMA/LMA/MoS2/LC | 6.0/10.0/17.4/0.6/70 |
| D | PEGDA400/HPMA/LMA/MoS2/LC | 6.0/10.0/17.1/0.9/70 |
| E | PEGDA400/HPMA/LMA/MoS2/LC | 6.0/10.0/16.8/1.2/70 |
| F | PEGDA400/HPMA/LMA/MoS2/LC | 6.0/10.0/16.4/1.6/70 |
| Transmittance | 0 V | 5 V | 10 V | 15 V | 20 V | 23 V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tlum (%) | 1.86 | 2.66 | 14.54 | 36.67 | 54.43 | 75.83 |
| Tsol (%) | 3.86 | 19.43 | 39.31 | 55.36 | 58.46 | 67.78 |
| ΔTlum (%) | - | 0.80 | 12.68 | 34.81 | 52.57 | 73.97 |
| ΔTsol (%) | - | 15.57 | 35.45 | 51.50 | 54.60 | 63.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, T.; Jing, F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, M.; Yang, H. High-Efficiency PDLC Smart Films Enabled by Crosslinking Agent Optimization and MoS2 Nanosheets for Energy-Saving Windows. Materials 2025, 18, 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225139
Yu T, Jing F, Shi Y, Yang Z, Xu J, Zhang Z, Yu M, Yang H. High-Efficiency PDLC Smart Films Enabled by Crosslinking Agent Optimization and MoS2 Nanosheets for Energy-Saving Windows. Materials. 2025; 18(22):5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225139
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Tao, Fuman Jing, Yingjie Shi, Zhou Yang, Jianjun Xu, Zuowei Zhang, Meina Yu, and Huai Yang. 2025. "High-Efficiency PDLC Smart Films Enabled by Crosslinking Agent Optimization and MoS2 Nanosheets for Energy-Saving Windows" Materials 18, no. 22: 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225139
APA StyleYu, T., Jing, F., Shi, Y., Yang, Z., Xu, J., Zhang, Z., Yu, M., & Yang, H. (2025). High-Efficiency PDLC Smart Films Enabled by Crosslinking Agent Optimization and MoS2 Nanosheets for Energy-Saving Windows. Materials, 18(22), 5139. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18225139







