Surface Texture, Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Titanium Nitride-Based Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure and Surface Texture Results
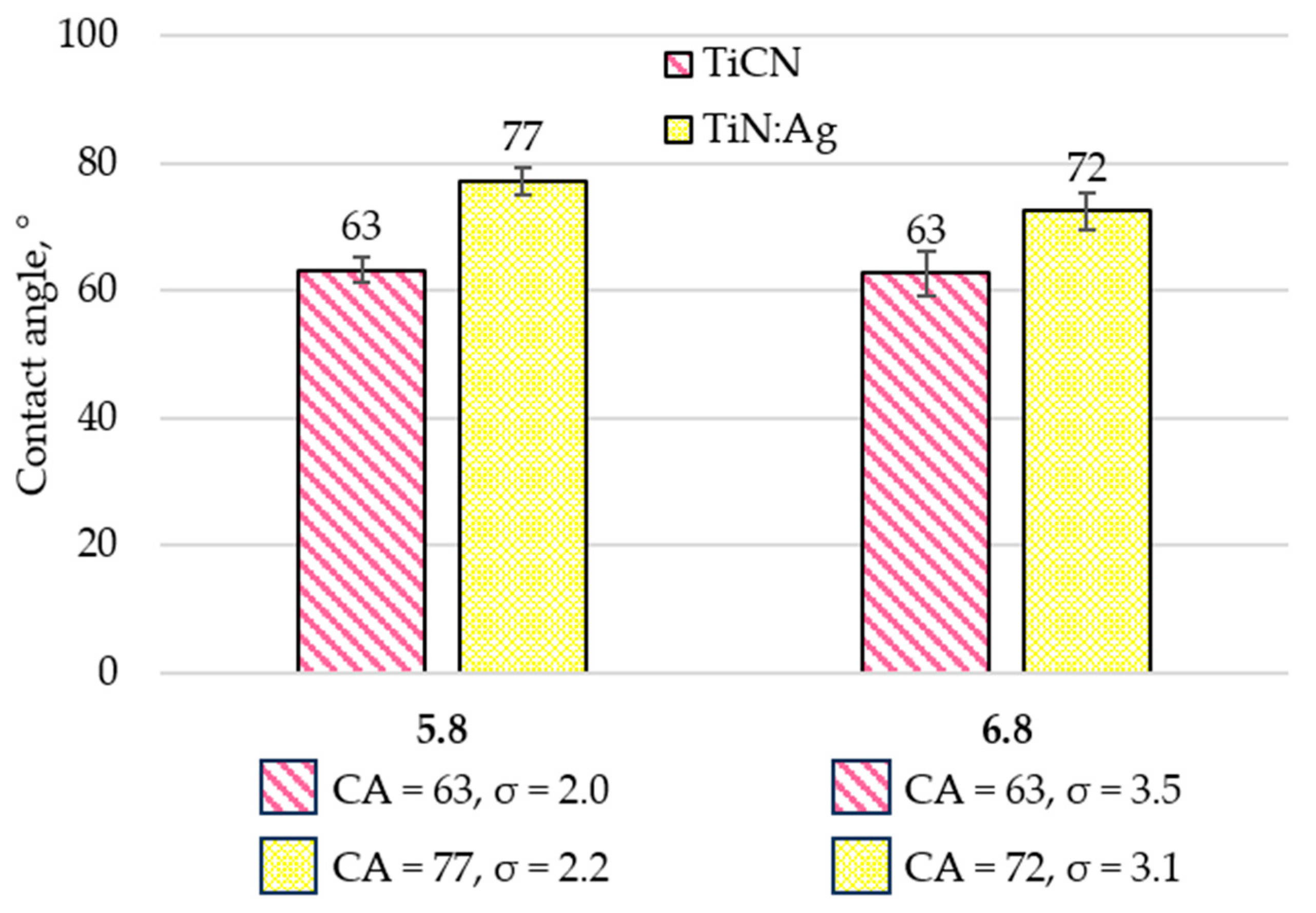
3.2. Contact Angle
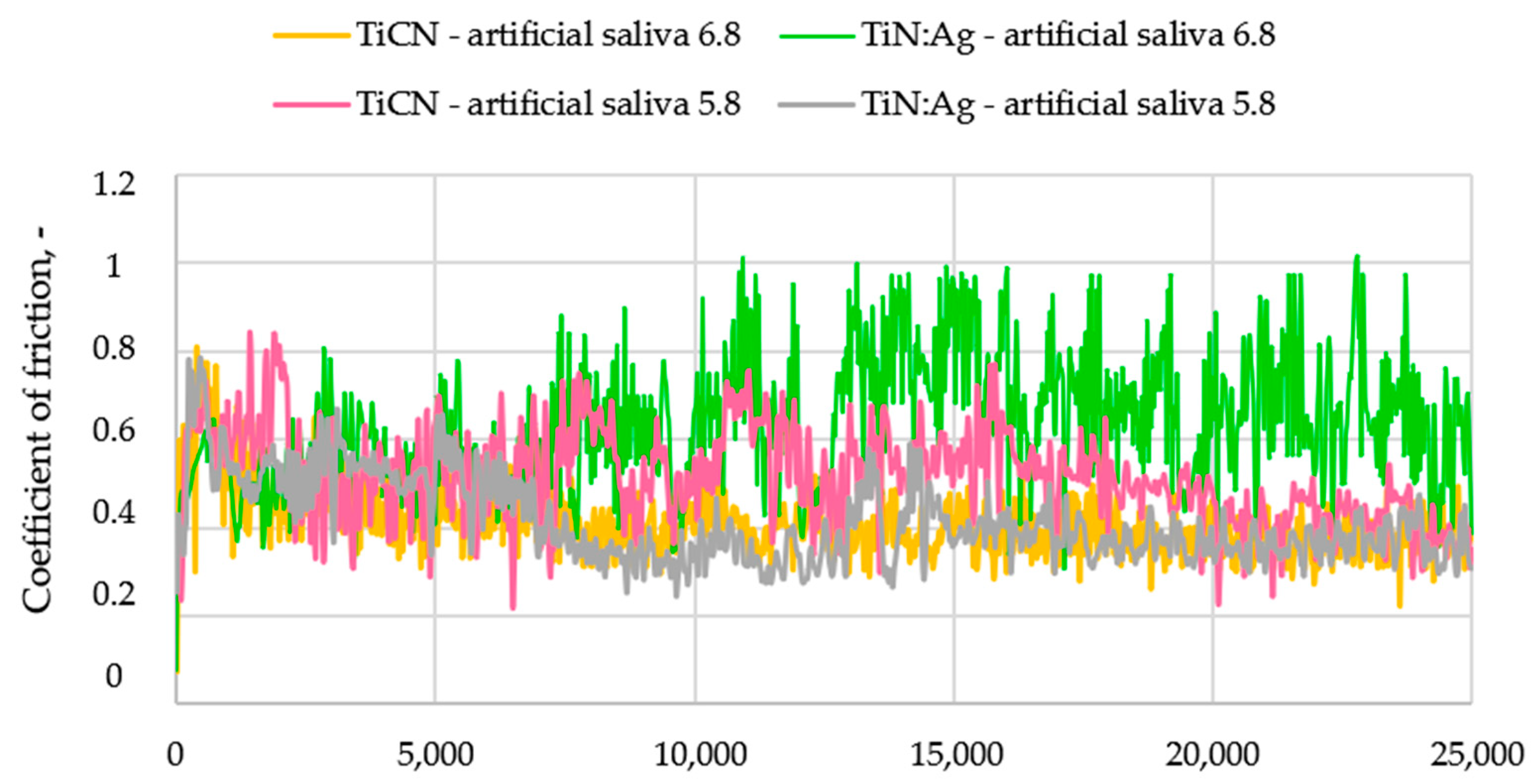
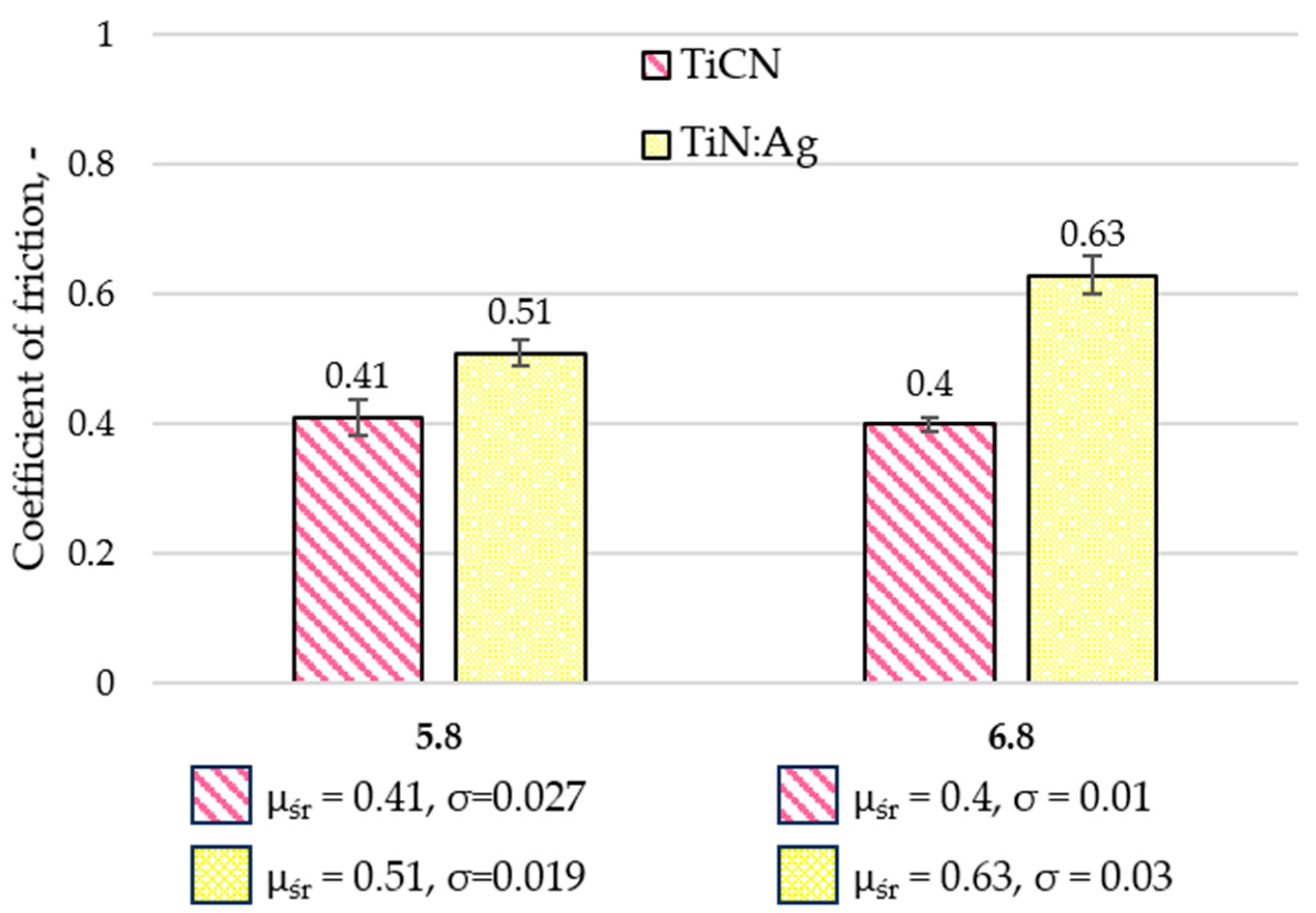
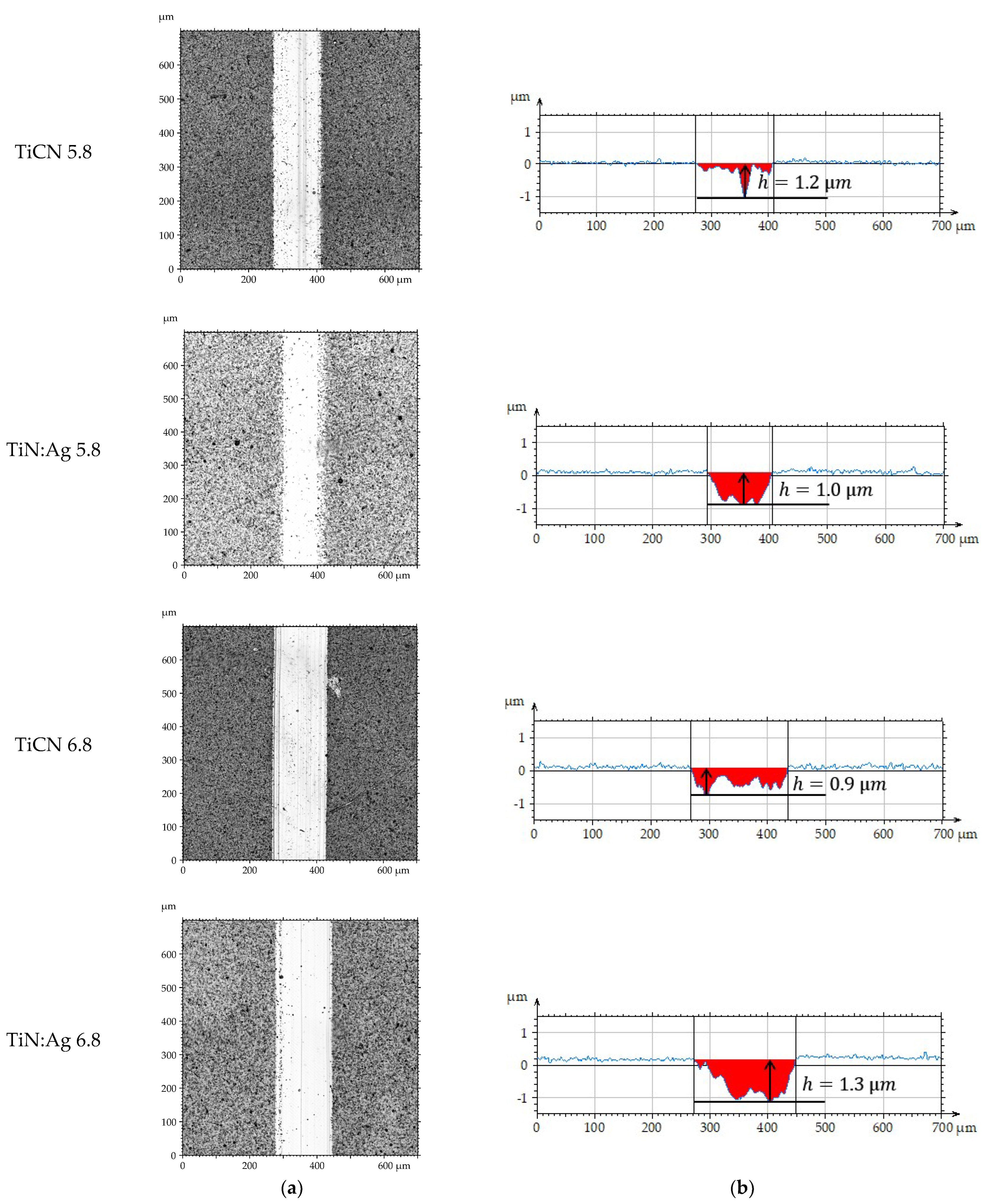
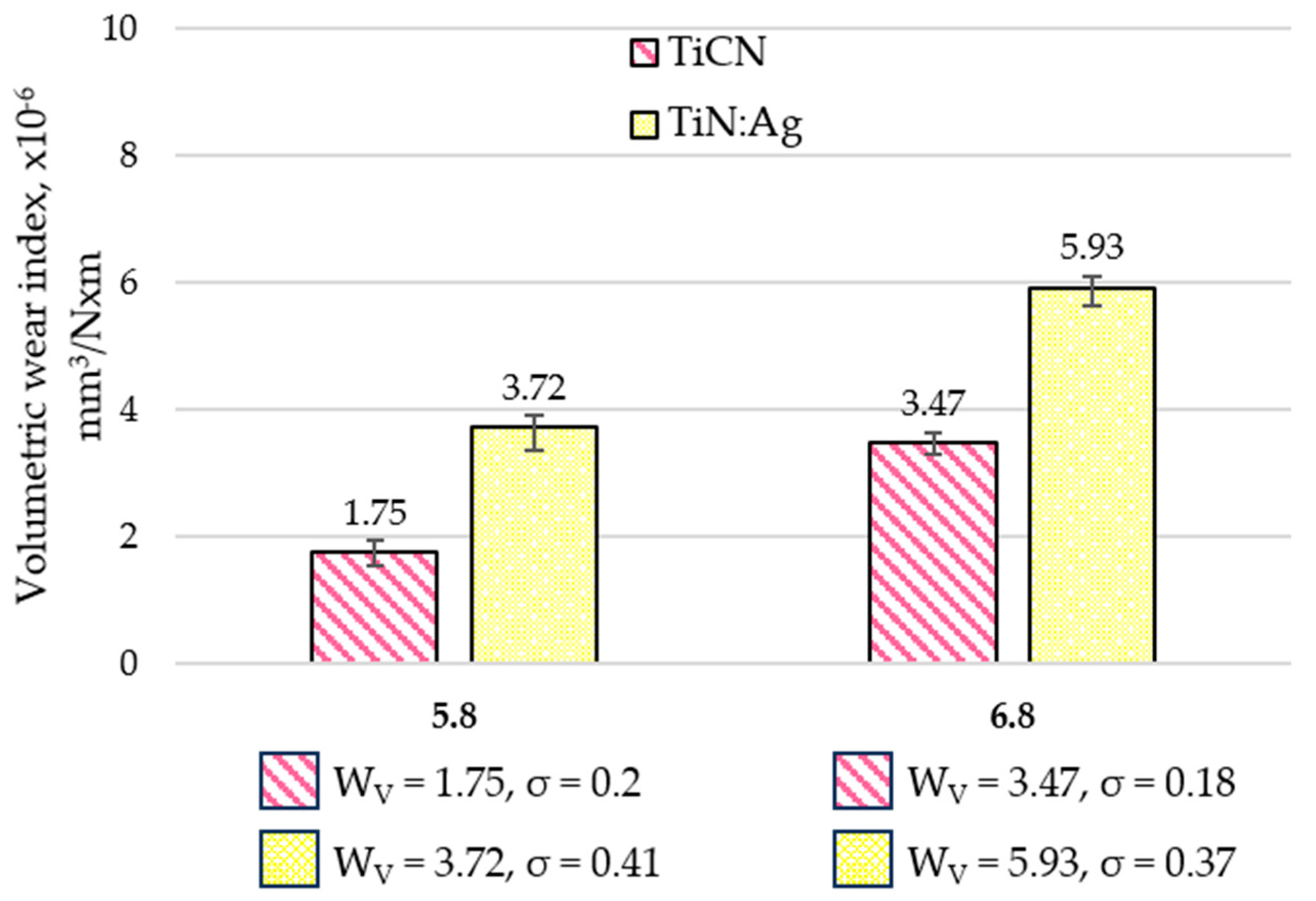
3.3. Tribological Properties and Assessment of Surface Geometric Structure After Tribological Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kochar, S.P.; Reche, A.; Paul, P. The Etiology and Management of Dental Implant Failure: A Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtis, S.G.; Sotiriadou, S.; Voliotis, S.; Challas, A. Private Practice Results of Dental Implants. Part I: Survival and Evaluation of Risk Factors—Part II: Surgical and Prosthetic Complications. Implant Dent. 2004, 13, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, C.; Costa, R.C.; Sukotjo, C.; Takoudis, C.G.; Mathew, M.T.; Barão, V.A.R. Progression of Bio-Tribocorrosion in Implant Dentistry. Front. Mech. Eng. Sec. Tribol. 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.F.A.; Oliveira, F.; Carvalho, I.; Piedade, A.P.; Carvalho, S. Influence of albumin on the tribological behavior of Ag-Ti (C, N) thin films for orthopedic implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 34, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viteri, V.S.; Barandika, M.G.; Gopegui, U.R.; Bayón, R.; Zubizarreta, C.; Fernández, X.; Igartua, A.; Agullo-Rueda, F. Characterization of Ti-C-N coatings deposited on Ti6Al4V for biomedical applications. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 117, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, M.; Piotrowska, K. Characterisation of TiCN Coatings for Biomedical Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, H.A.; Choudhury, D.; Nine, M.J.; Osman, N.A.A. Effects of surface coating on reducing friction and wear of orthopaedic implants. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2014, 15, 014402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onisi, M.; Kondo, W. Establishing an Environment for Growth of Aciduric Bacteria in the Oral Cavity. J. Dent. Res. 1956, 35, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzotti, G.; Adachi, T.; Gasparutti, I.; Vincini, G.; Zhu, W.; Boffelli, M.; Rondinella, A.; Marin, E.; Ichioka, H.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Vibrational Monitor of Early Demineralization in Tooth Enamel after in Vitro Exposure to Phosphoridic Liquid. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.J. Dental Calculus: Recent Insights into Occurrence, Formation, Prevention, Removal and Oral Health Effects of Supragingival and Subgingival Deposits. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1997, 105, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N. Microbial Ecosystem in the Oral Cavity: Metabolic Diversity in an Ecological Niche and Its Relationship with Oral Diseases. Int. Congr. Ser. 2005, 1284, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arivazhagan, A.; Mani, K.; Kamarajan, B.P.; Saai Aashique, A.G.S.; Vijayaragavan, S.; Riju, A.A.; Rajeshkumar, G. Mechanical and biocompatibility studies on additively manufactured Ti6Al4V porous structures infiltrated with hydroxyapatite for implant applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, E.; Lanzutti, A. Biomedical Applications of Titanium Alloys: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2023, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, M.M.; Wu, X.; Alnazzawi, A.; Watson, J.; Watts, D. Surface characteristics and biocompatibility of cranioplasty titanium implants following different surface treatments. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydar, H.J.; Al-Deen, H.J.; Abidali, A.K.; Mahmoud, A.A. Improved performance of Ti6Al4V alloy in Biomedical applications-Review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1973, 012146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikova, T.; Hashim, D.P.; Mintcheva, N. Morphology and Structure of TiO2 Nanotube/Carbon Nanostructure Coatings on Titanium Surfaces for Potential Biomedical Application. Materials 2024, 17, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Cao, H. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Laser-Clad Ni60/WC Composite Coating. Materials 2024, 17, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozimina, D.; Piotrowska, K.; Madej, M.; Granek, A. The influence of ion implantation on the properties of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy in biotribological systems. Tribologia 2020, 292, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, M.M.; Ch Murthy, T.S.R.; Paul, B.; Sahu, A.K.; Sankar, M.R. Experimental investigation on dry sliding wear characteristics of additive manufactured titanium alloy features with various carbide balls. Tribol. Int. 2026, 213, 111029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, Z.; Kundan, N.; Dey, A. Corrosion and wear characterization of Ti6-Al-4 V alloy: Experimental analysis and performance evaluation. Tribol. Int. 2024, 197, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, C.N.; Oshida, Y.; Cavalcanti Lima, J.H.; Muller, C.A. Relationship between surface properties (roughness, wettability and morphology) of titanium and dental implant removal torque. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 1, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, J.; Liu, G.; Guo, F.; Xu, J.; Chen, M. Enhanced tribological properties and cyto-biocompatibility of dental Ti6Al4V alloy via laser surface texturing. Technology 2024, 33, 4105–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 25178-2:2021; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Areal, Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Dzierwa, A.; Pawlus, P.; Zelasko, W. The Influence of Disc Surface Topography after Vapor Blasting on Wear of Sliding Pairs under Dry Sliding Conditions. Coatings 2020, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Song, Q.; Wan, Y.; Chen, L. Surface Characterization and Tribological Performance of Anodizing Micro-Textured Aluminum-Silicon Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X. Effects of Surface Roughness Parameters on Tribological Performance for Micro-textured Eutectic Aluminum–Silicon Alloy. J. Tribol. 2020, 142, 021702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.H.; Sow, P.K.; Zahiri, B.; Mérida, W. Assessment and Interpretation of Surface Wettability Based on Sessile Droplet Contact Angle Measurement: Challenges and Opportunities. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A.; Volpe, C.D.; Siboni, S.; Amirfazli, A.; Drelich, J.W. Contact angles and wettability: Towards common and accurate terminology. Surf. Innov. 2017, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokińska-Miszczuk, J.; Piotrowska, K.; Paulo, M.; Madej, M. Composite Materials Used for Dental Fillings. Materials 2024, 17, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, G. Influence of surface roughness on contact angle hysteresis and spreading work. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2020, 298, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyan, B.D.; Lotz, E.M.; Schwartz, Z. Roughness and Hydrophilicity as Osteogenic Biomimetic Surface Properties. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartoretto, S.C.; Alves, A.T.N.N.; Resende, R.F.B.; Calasans-Maia, J.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Calasans-Maia, M.D. Early osseointegration driven by the surface chemistry and wettability of dental implants. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2015, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumgardner, J.D.; Wiser, R.; Elder, S.H.; Jouett, R.; Yang, Y.; Ong, J.L. Contact angle, protein adsorption and osteoblast precursor cell attachment to chitosan coatings bonded to titanium. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2003, 14, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kot, M.; Rakowski, W.; Major, Ł.; Lackner, J. Examination of the fracture toughness and wear resistance of multilayer coatings. Tribologia 2014, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowska, K. Influence of Selected Surface Layers on the Performance Properties of the Titanium Alloy Ti13Nb13Zr in Biotribological Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Kielce University of Technology, Kielce, Poland, 2023. [Google Scholar]



| Coatings | Manufacturer | Deposition Technique | View |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiCN | Oerlikon Balzers, Montcada i Reixac, Spain | s3p |  |
| TiN:Ag | Oerlikon Balzers, Brügg bei Biel, Switzerland | arc |  |
| Methodology and Section Number | Measurement Instruments | Research Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| 3.1. Microstructure and surface texture before tribological test | Phenom XL (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) DCM8 non-contact profilometer (Leica, Heerbrugg, Switzerland) | sample shape: disc, Ø 18 mm, method: SED magnification: ×5000 sample shape: disc, Ø 18 mm, method and lens: confocal, ×20 measurement area: 0.65 mm × 0.85 mm |
| 3.2. Wettability | Attension Theta Flex (Biolin Scientific, Tietäjäntie, Finland) | method: sessile drop method, liquid: artificial saliva 5.8 and 6.8 drop volume: 5 µL |
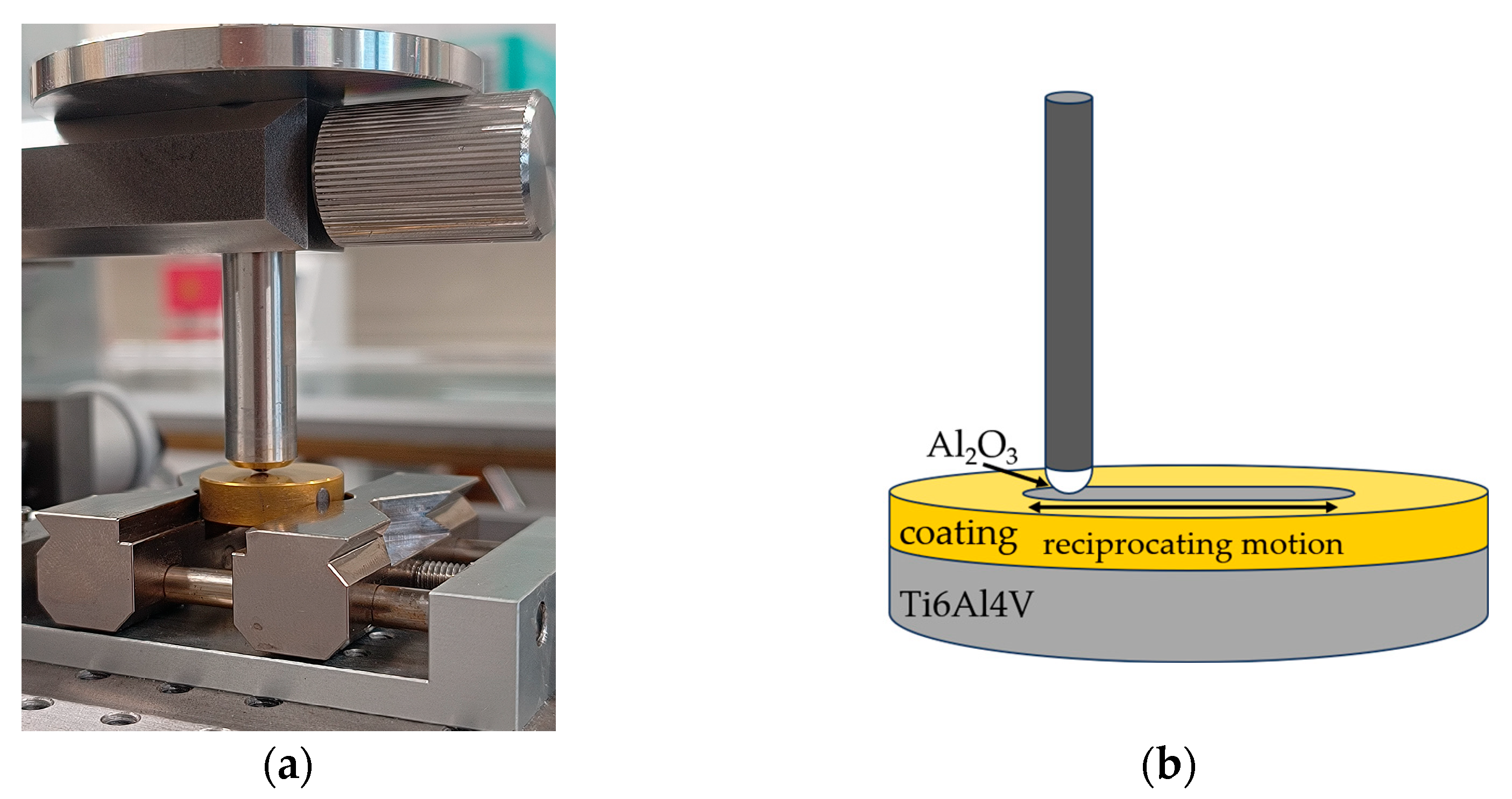
| 3.3. Tribological Properties and Assessment of Surface Geometric Structure After Tribological Tests | TRB3 tribometer (Anton Paar, Baden, Switzerland) | sample shape: disc, Ø 18 mm, motion: reciprocating, load and cycle: 1 N, 25,000 amplitude and frequency: 10 mm, 1 Hz countersample: Al2O3 ball, diameter 6 mm lubrication: artificial saliva 5.8 and 6.8 |
| DCM8 non-contact profilometer (Leica, Heerbrugg, Switzerland) | sample shape: disc, Ø 18 mm, method and lens: confocal, ×20 measurement area: 0.7 mm × 0.7 mm |
| Sa | Sq | Sv | Sp | Ssk | Sku | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µm | - | |||||
| TiCN | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 25.7 |
| TiN:Ag | 0.2 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 8.6 | 3.7 | 56.9 |
| Sk | Spk | Svk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| µm | |||
| TiCN | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.18 |
| TiN:Ag | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piotrowska, K.; Madej, M. Surface Texture, Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Titanium Nitride-Based Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18215010
Piotrowska K, Madej M. Surface Texture, Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Titanium Nitride-Based Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(21):5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18215010
Chicago/Turabian StylePiotrowska, Katarzyna, and Monika Madej. 2025. "Surface Texture, Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Titanium Nitride-Based Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy" Materials 18, no. 21: 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18215010
APA StylePiotrowska, K., & Madej, M. (2025). Surface Texture, Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Titanium Nitride-Based Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy. Materials, 18(21), 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18215010








