Equilibrium-Based Finite Element Analysis of the Reissner–Mindlin Plate Bending Problem
Abstract
1. Introduction
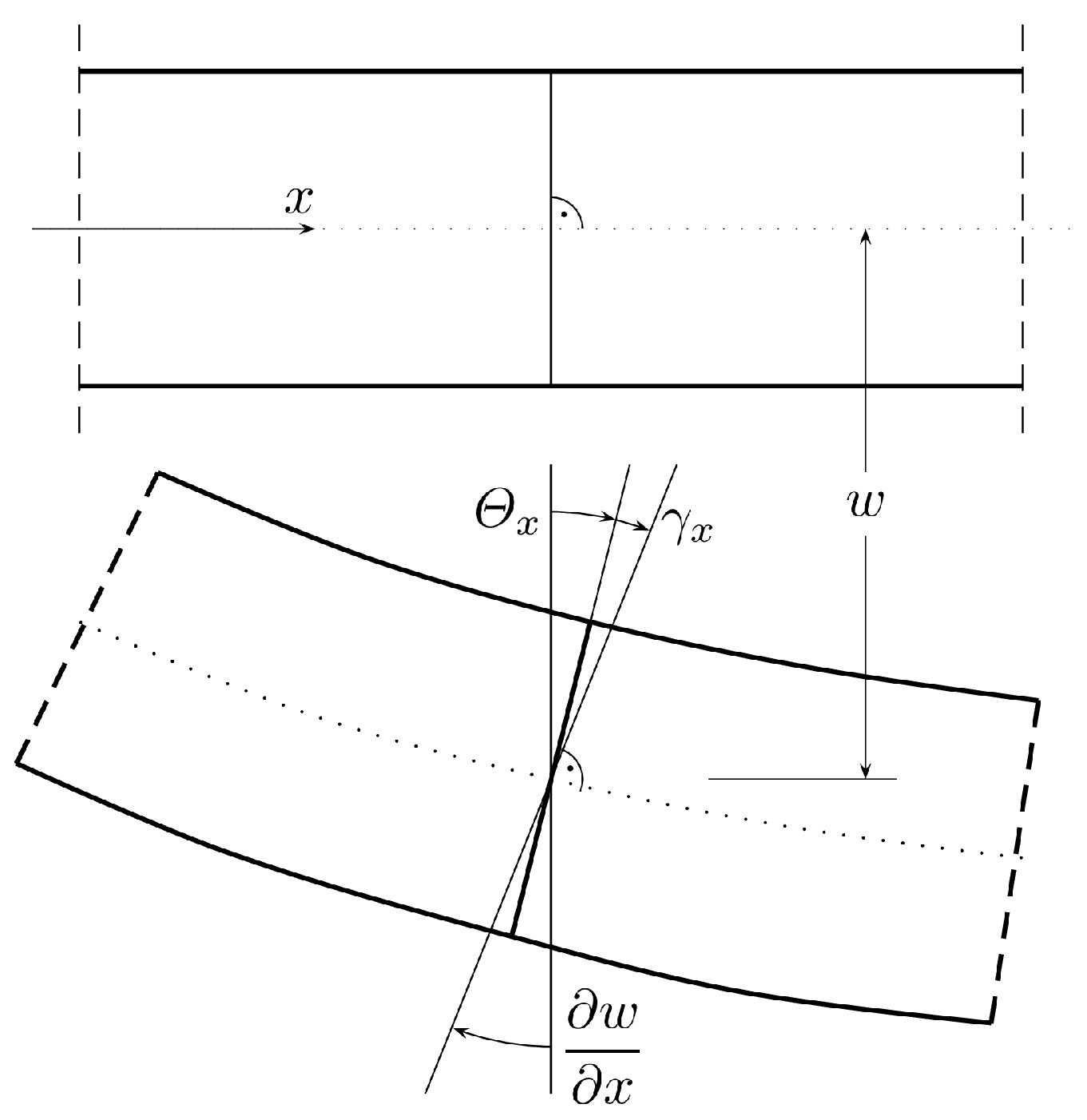
2. Formulation of the Reissner–Mindlin Plate Bending Problem
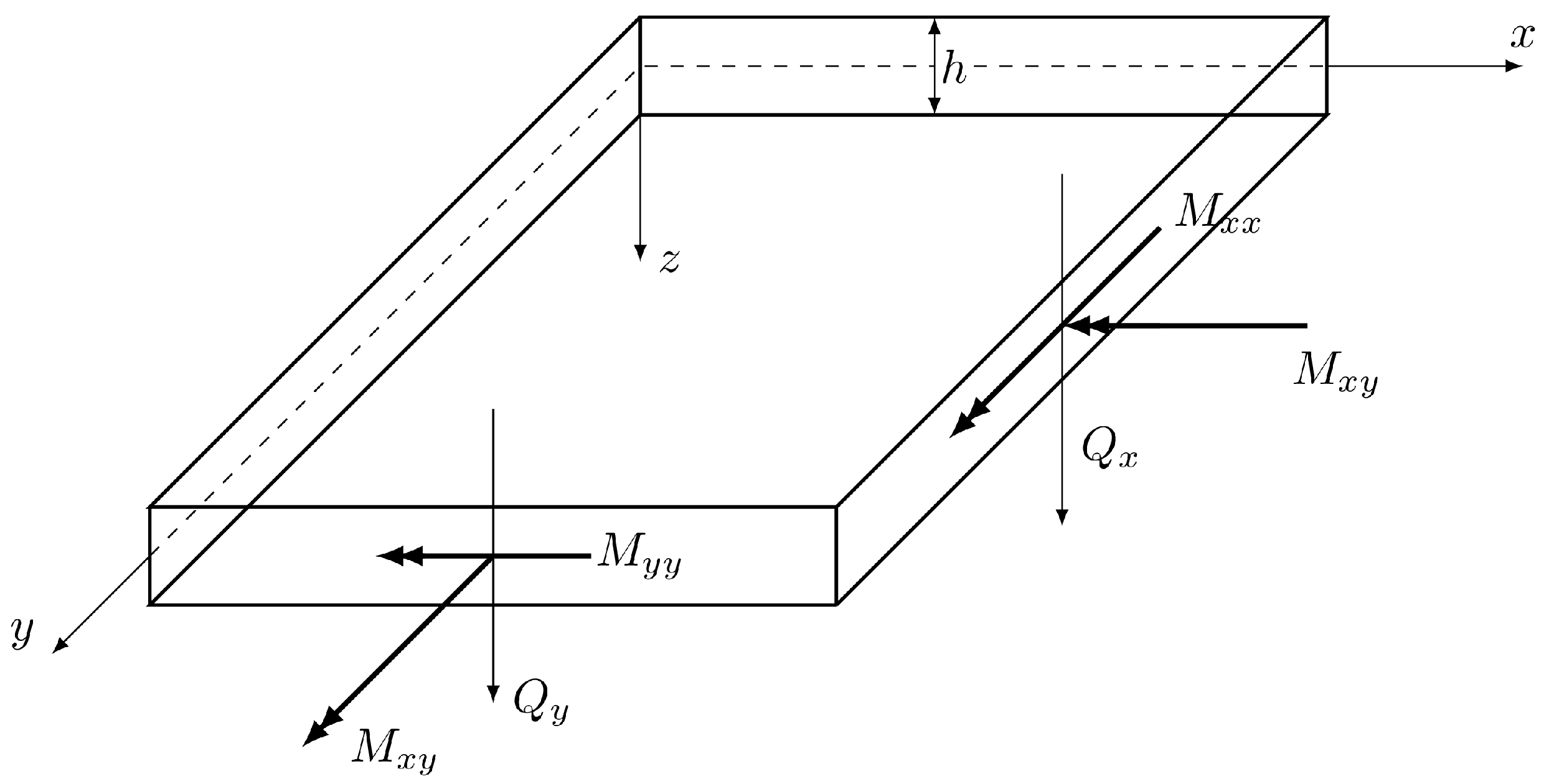
2.1. Construction of the Statically Admissible Stress Field
2.2. Stress-Based Variational Formulation of the Problem
2.3. Displacement-Based Formulation of the Problem
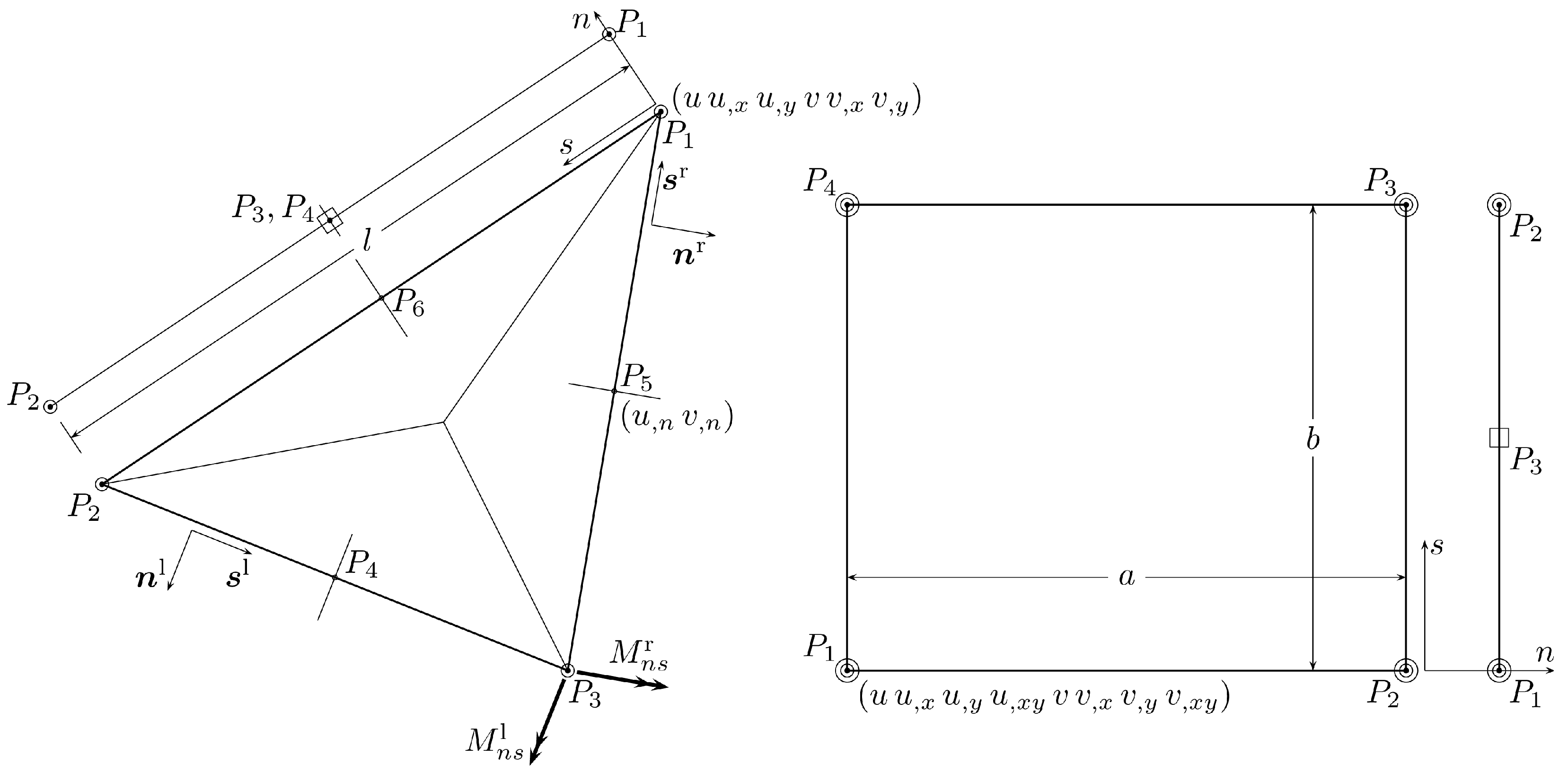
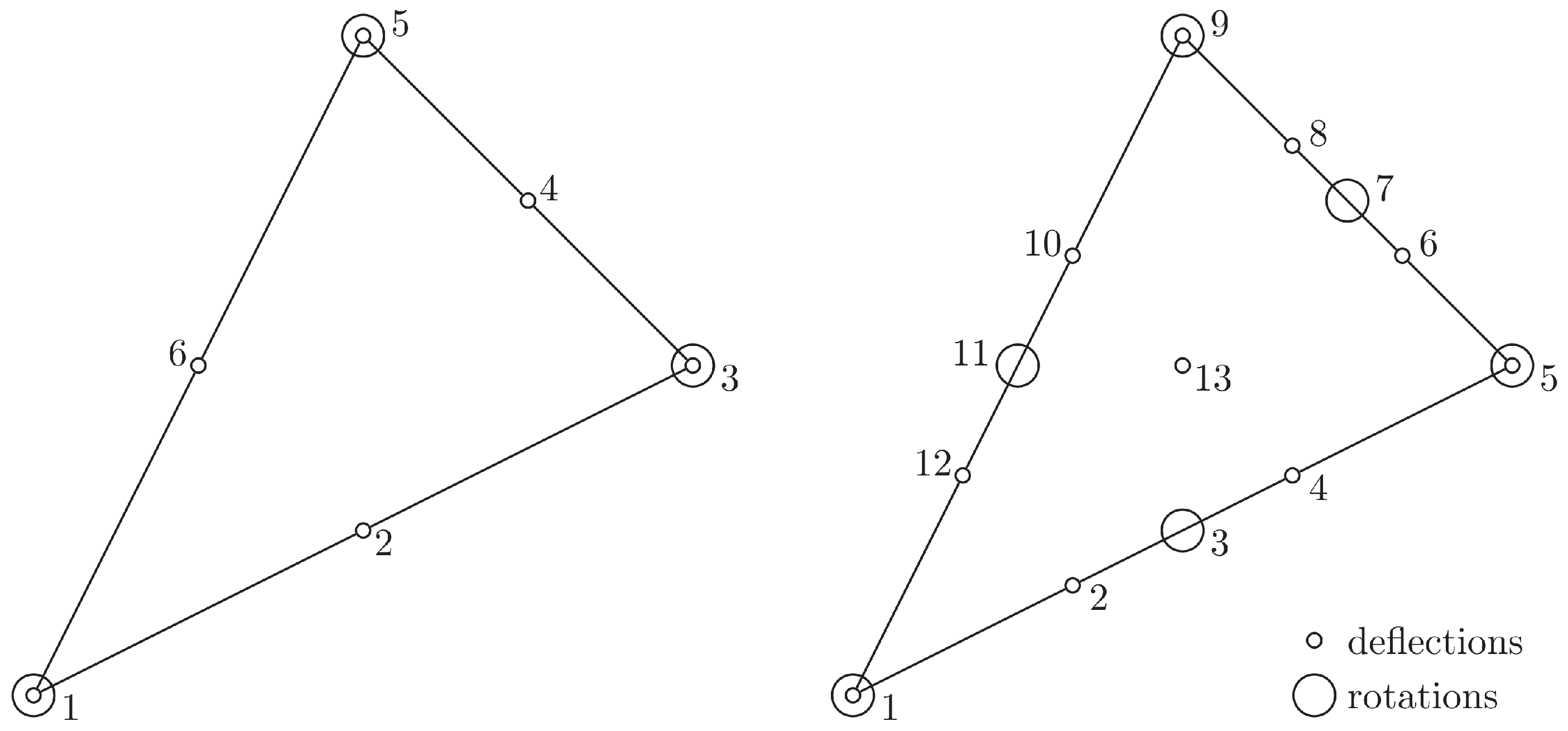
3. Stress-Based FE Approximation
3.1. Equilibrium of Corner Nodes
3.2. Enforcing the Boundary Conditions
4. Displacement-Based FE Approximation
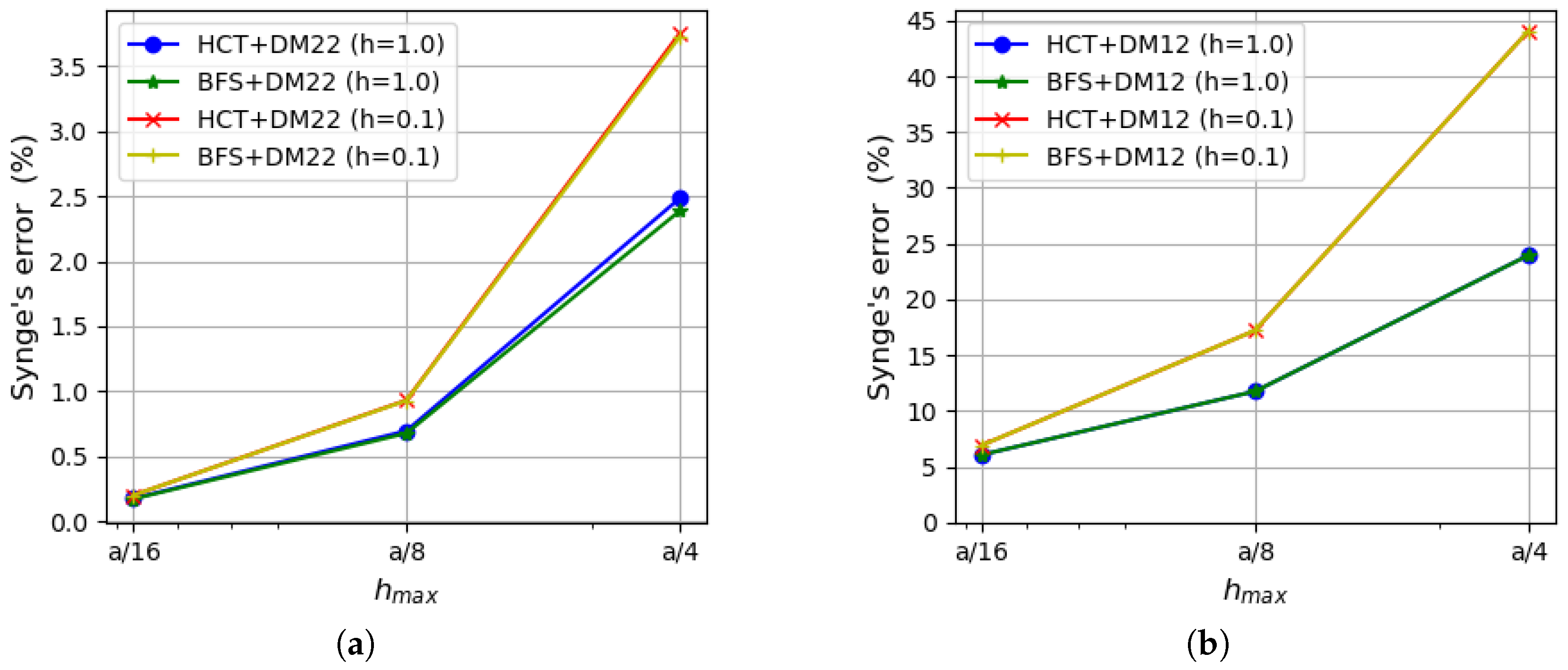
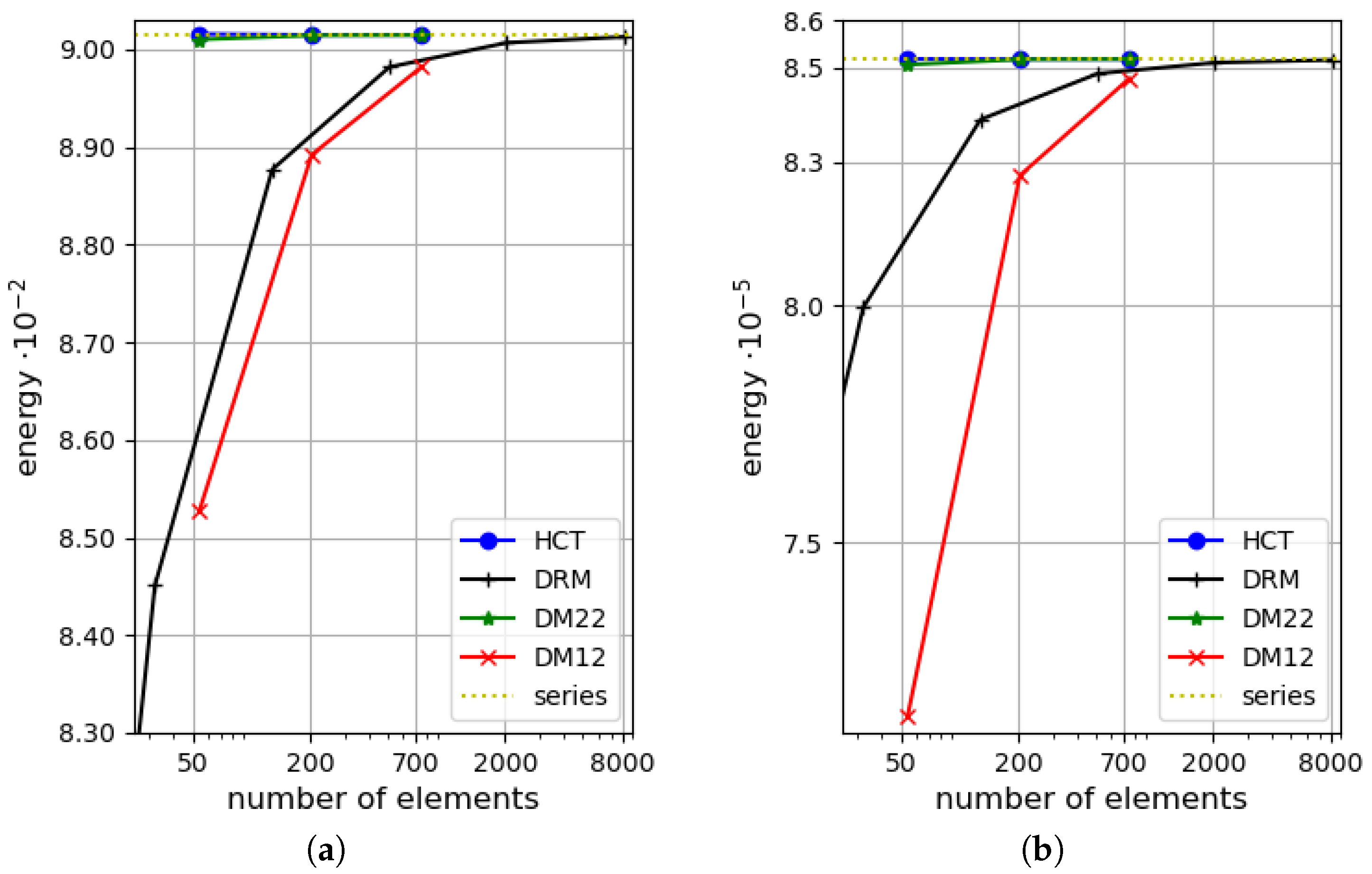
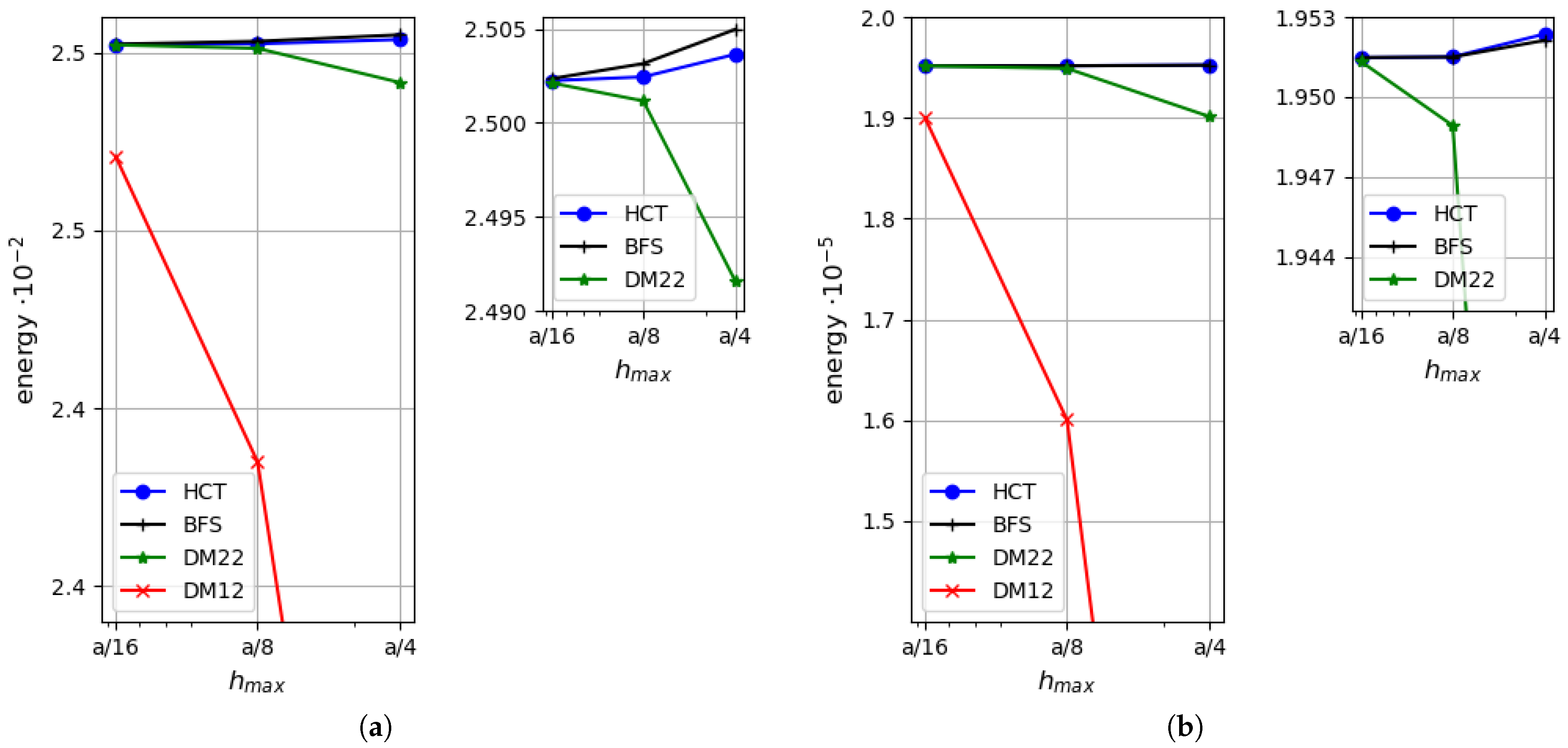
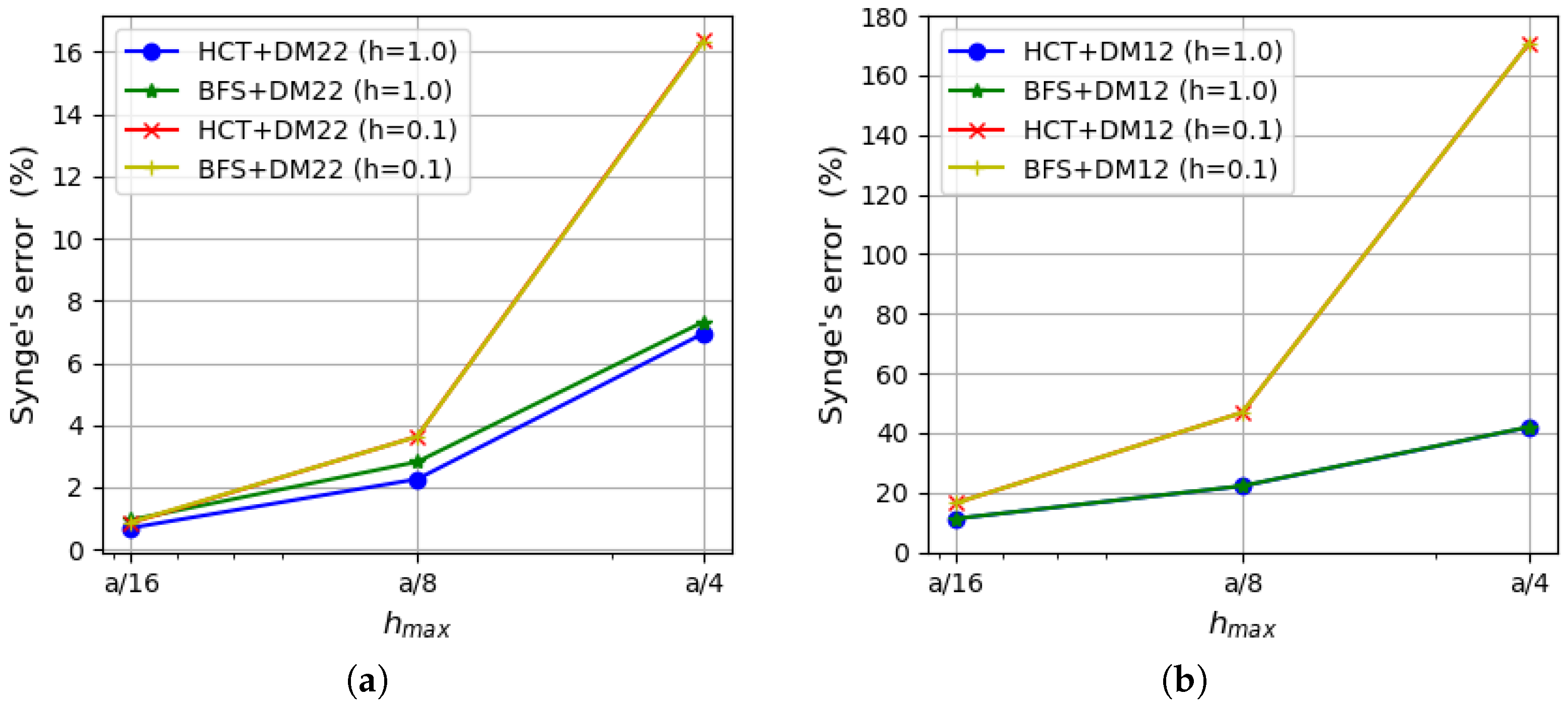
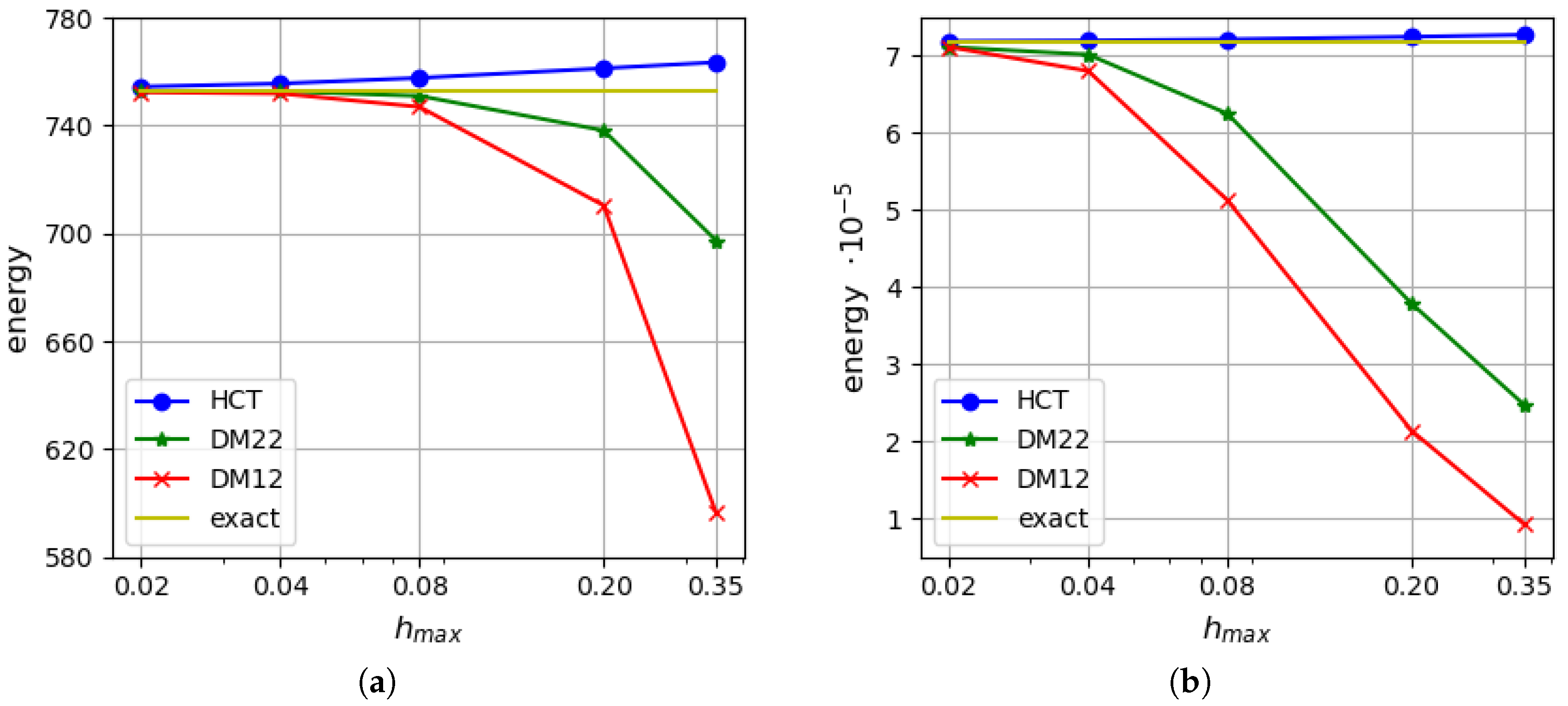
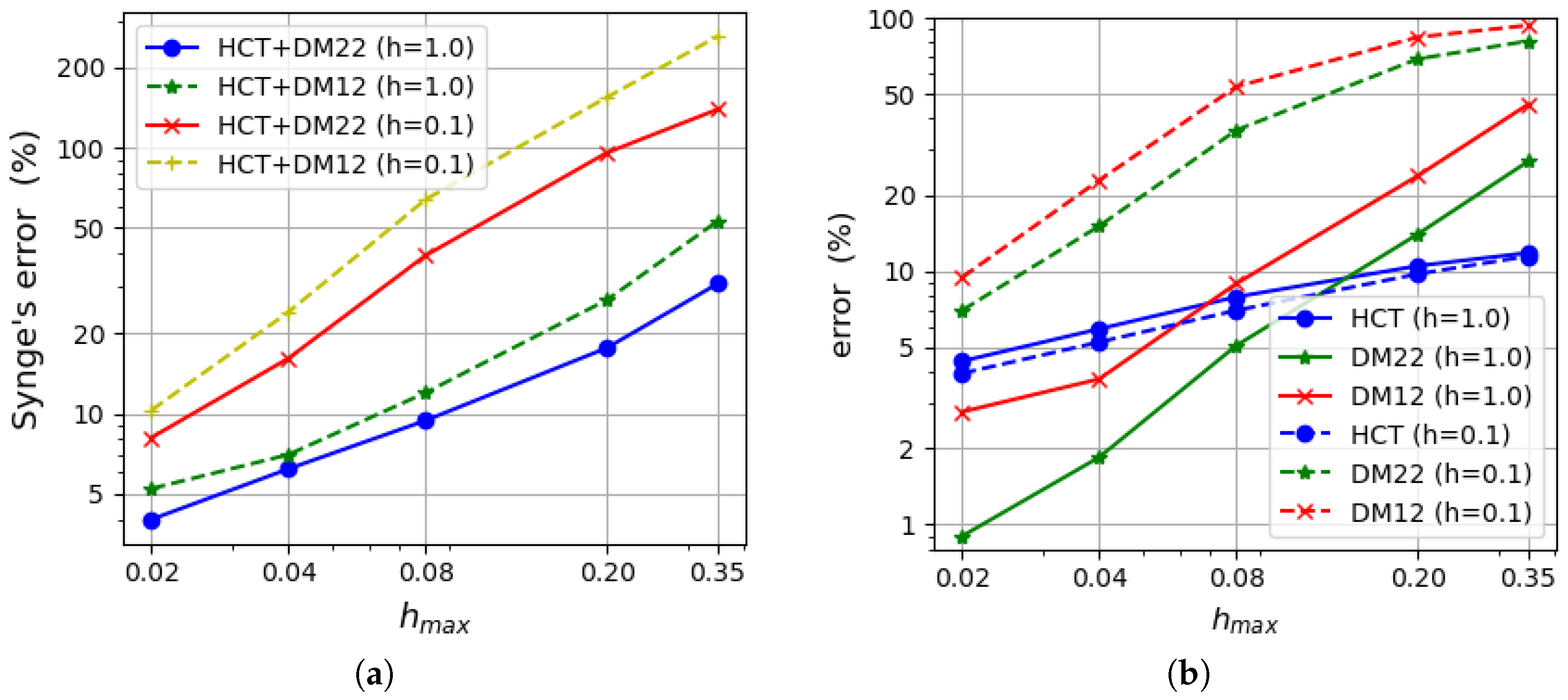
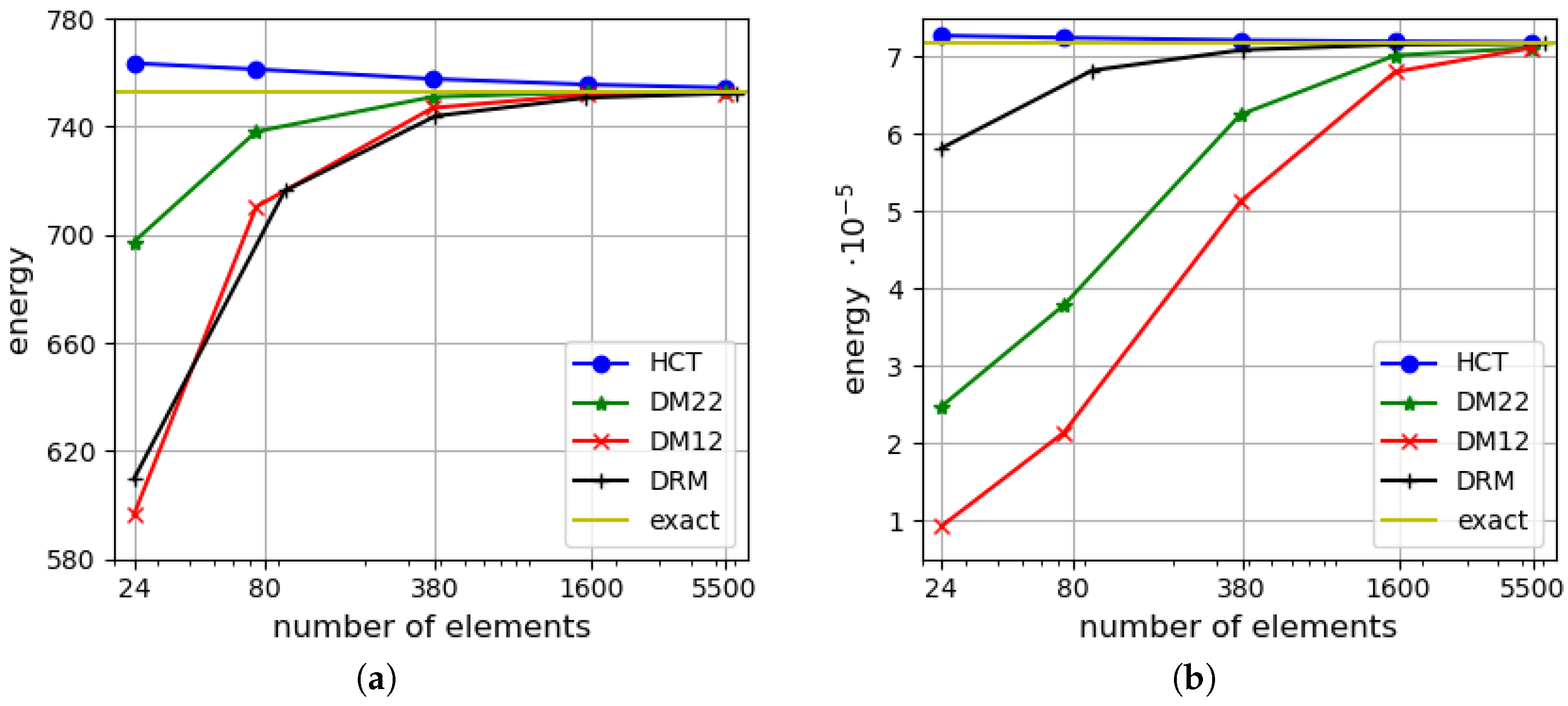
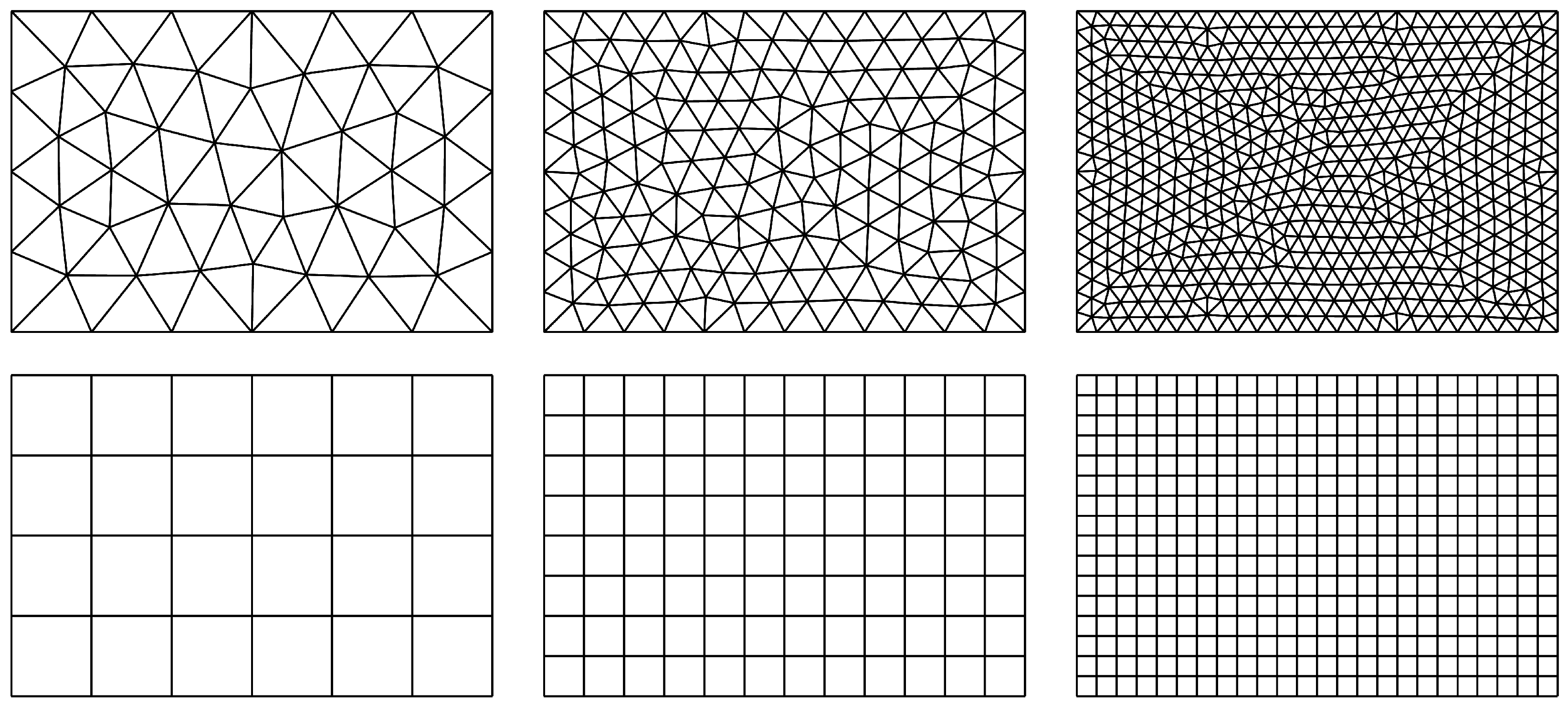
5. Numerical Examples
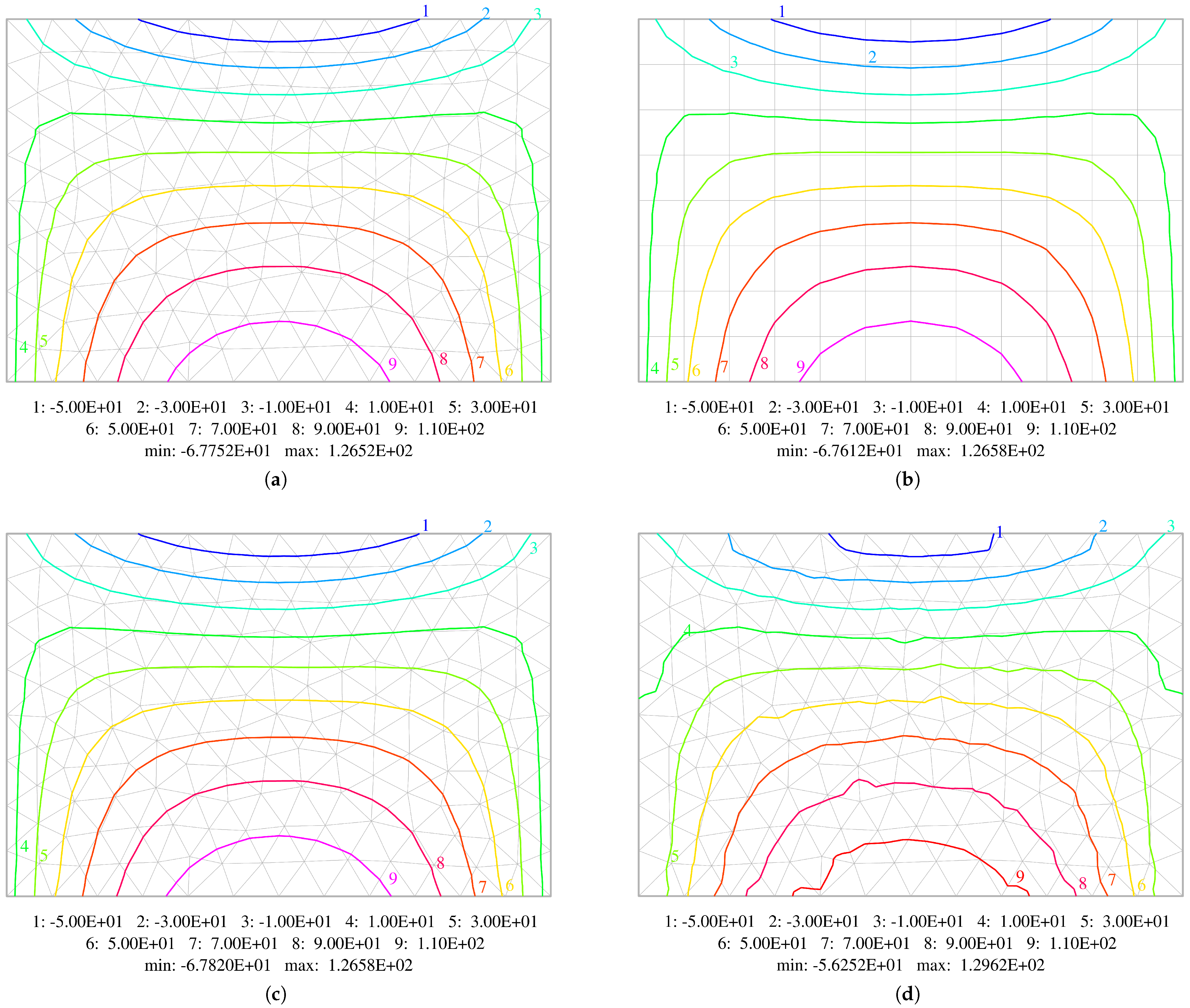
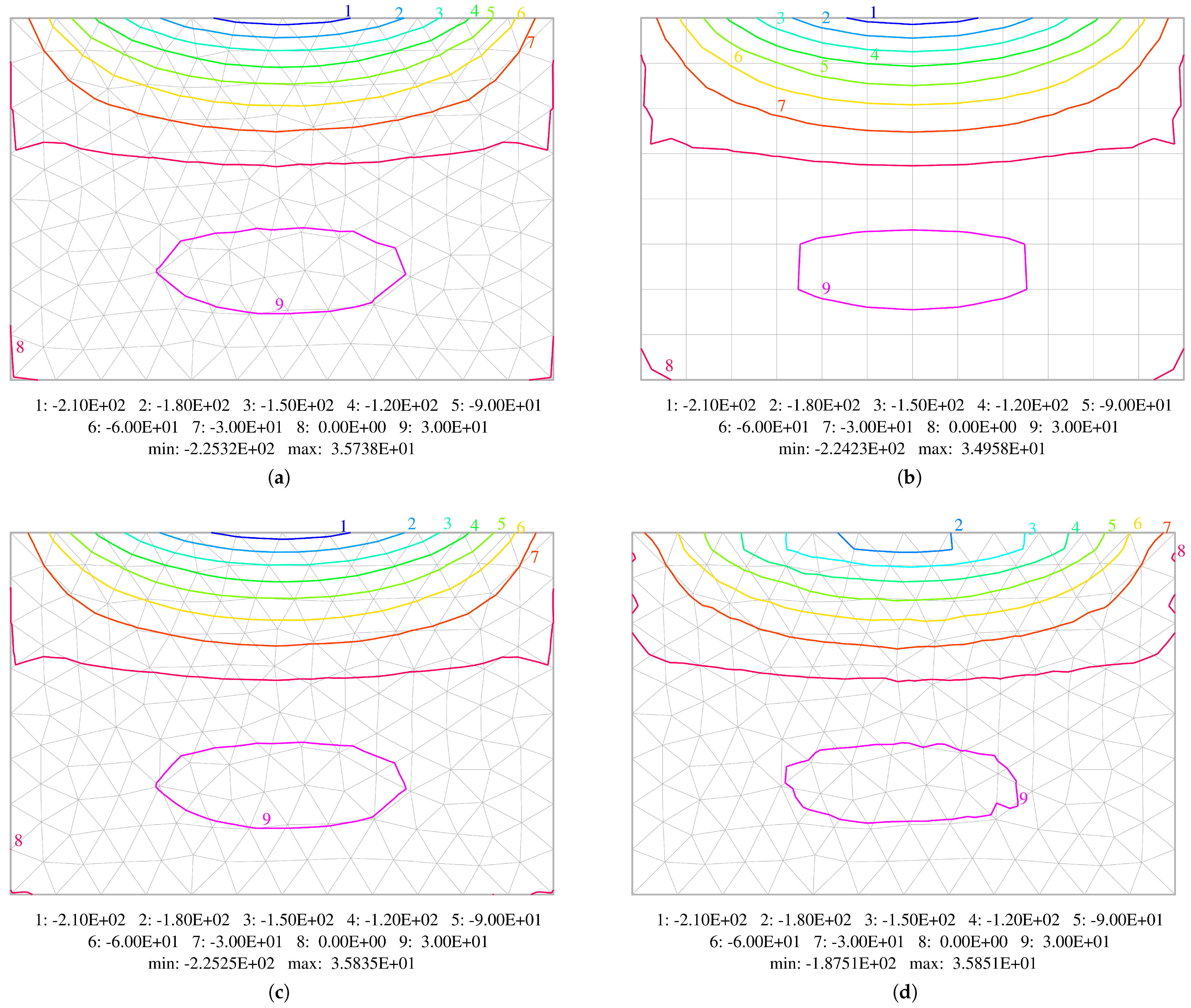
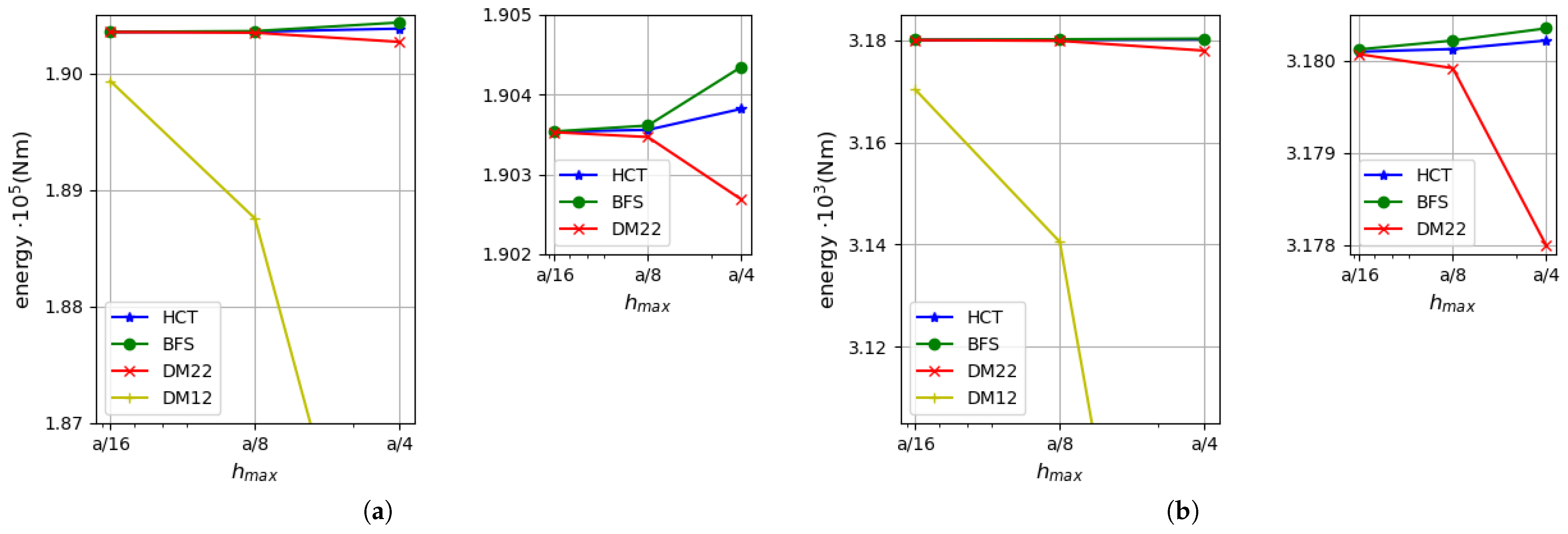
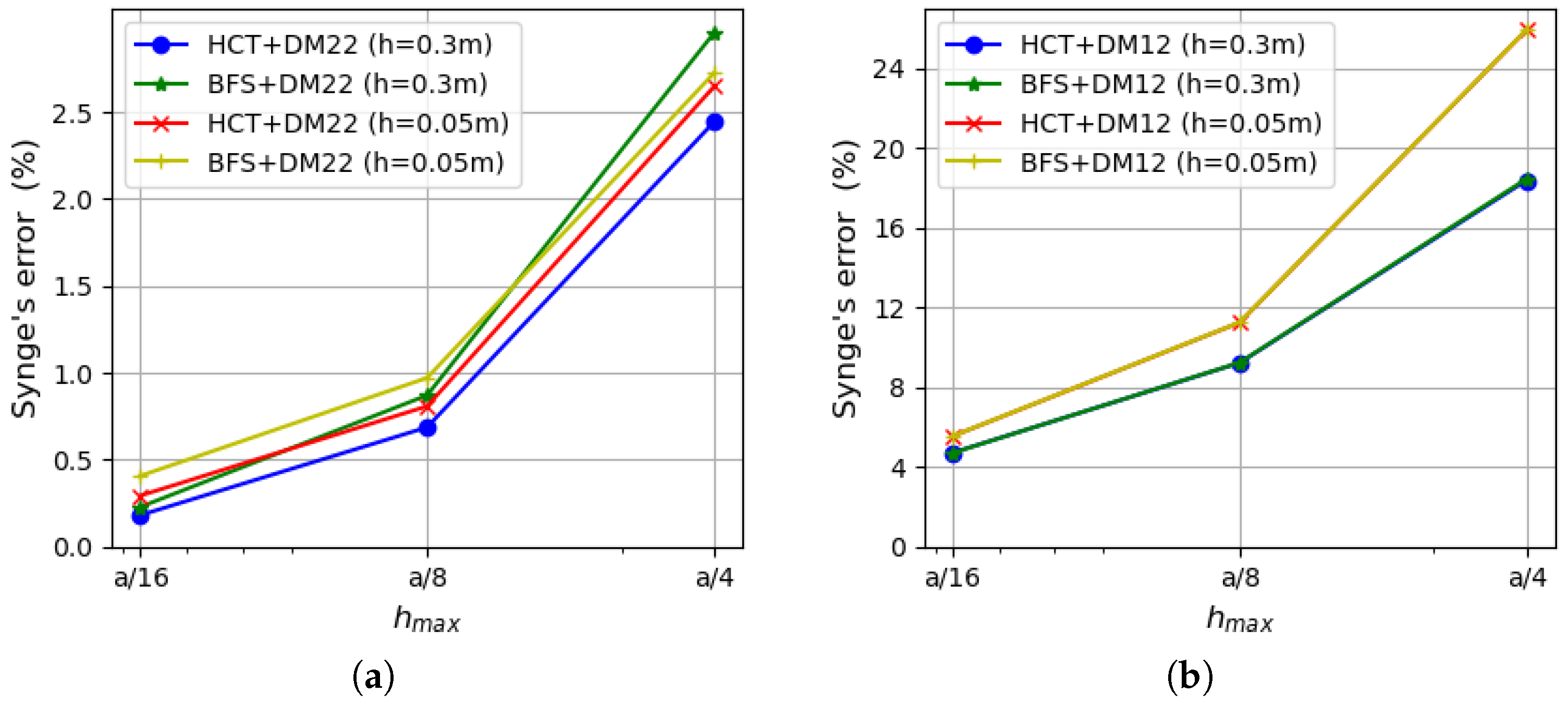
5.1. Uniformly Loaded Square Plates
5.2. Uniformly Loaded Simply Supported Circular Plate
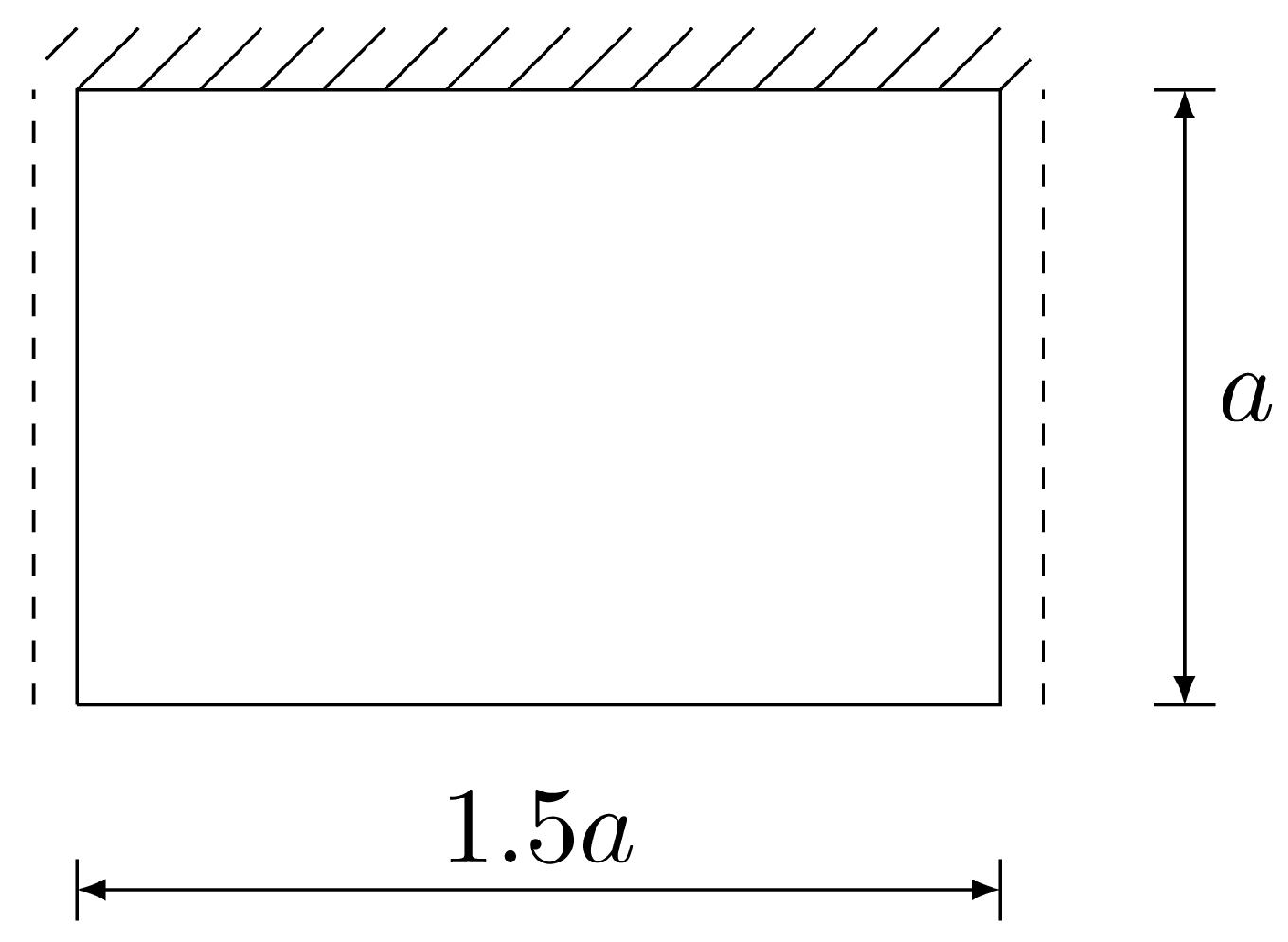
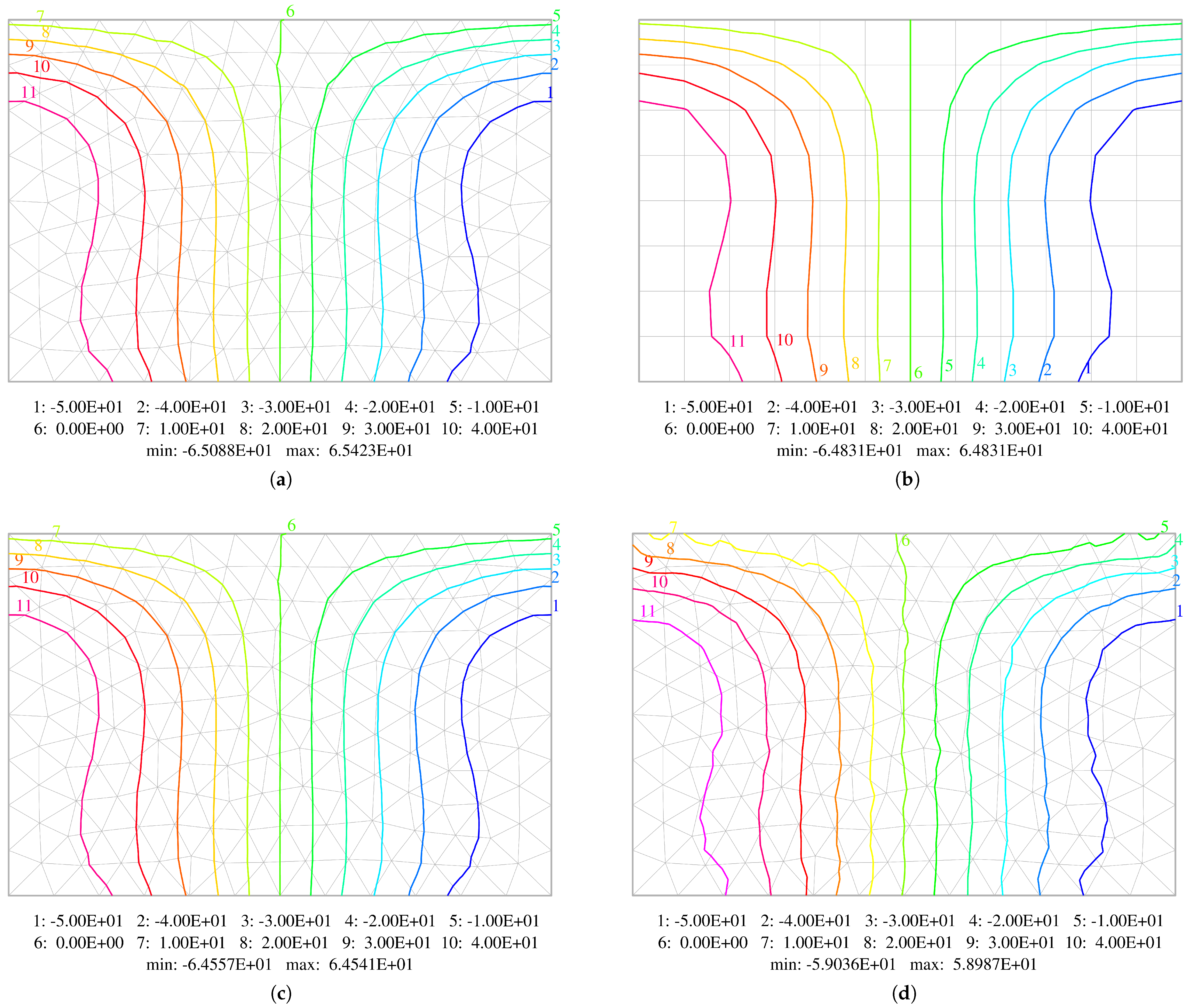
5.3. Uniformly Loaded Rectangular Plate
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fung, Y.C.; Tong, P. Classical and Computational Solid Mechanics; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 805–822. [Google Scholar]
- Oñate, E. Structural Analysis with the Finite Element Method. Linear Statics: Volume 2: Beams, Plates and Shells, Lecture Notes on Numerical Methods in Engineering and Sciences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 291–381. [Google Scholar]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Too, J.M. Reduced integration technique in general analysis of plates and shells. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1971, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.J.R.; Cohen, M. The “Heterosis” Finite Element for Plate Bending. Comput. Struct. 1978, 9, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathe, K.J.; Dvorkin, E.N. Short communication a four-node plate bending element based on Mindlin/Reissner plate theory and a mixed interpolation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1985, 21, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergan, P.G.; Wang, X. Quadrilateral plate bending elements with shear deformations. Comput. Struct. 1984, 19, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.; Kerh, T.; Lin, C. A conforming quadrilateral plate bending element with shear deformations. Comput. Struct. 1995, 56, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowski, R.; Taczała, M.; Kleiber, M. A 16-node locking-free Mindlin plate resting on two-parameter elastic foundation—Static and eigenvalue analysis. Comput. Assist. Methods Eng. Sci. 2015, 22, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruttmann, F.; Wagner, W. A stabilized one-point integrated quadrilateral Reissner–Mindlin plate element. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2004, 61, 2273–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Wong, S.C. Mixed formulation finite elements for Mindlin theory plate bending. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1982, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikis, G.; Klinkel, S. Two-field formulations for isogeometric Reissner–Mindlin plates and shells with global and local condensation. Comput. Mech. 2022, 69, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batoz, J.L.; Katili, I. On a simple triangular Reissner/Mindlin plate element based on incompatible modes and discrete constraints. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1992, 35, 1603–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheel, M.A. A finite volume method for analysing the bending deformation of thick and thin plates. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1997, 147, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noormohammadi, N.; Boroomand, B. A boundary method using equilibrated basis functions for bending analysis of in-plane heterogeneous thick plates. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2020, 91, 487–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, A.T.; von Hertzen, R.; Reddy, J.N.; Romanoff, J. Shear deformable plate elements based on exact elasticity solution. Comput. Struct. 2018, 200, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.D. Two hybrid elements for analysis of thick, thin and sandwich plates. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1972, 5, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunder, E.A.W.; Moitinho de Almeida, J.P. A triangular hybrid equilibrium plate element of general degree. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2005, 63, 315–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwell, R.V. On the analogues relating flexure and extention of flat plates. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 1950, 3, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunder, E.A.W.; Izzuddin, B.A. Equilibrium and Displacement Elements for the Design of Plates and Shells. Eng. Comput. Mech. 2019, 172, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ma, X.; Xili, J.; Chen, W. Higher-order hybrid stress triangular Mindlin plate element. Comput. Mech. 2016, 58, 911–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunder, E.A.W.; Moitinho de Almeida, J.P. Equilibrium Finite Element Formulations, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Maunder, E.A.W.; Moitinho de Almeida, J.P. Recovery of strong equilibrium from displacement-based finite element models of Reissner–Mindlin plates. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2018, 114, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, S.; Shang, Y. Developments of Mindlin-Reissner Plate Elements. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 456740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątkiewicz, P.; Więckowski, Z. Statically admissible finite element solution of the thin plate bending problem with a posteriori error estimation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2019, 121, 1977–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, R.W.; Tocher, J.L. Finite element stiffness matrices for analysis of plate bending. In Proceedings of the Conference on Matrix Methods in Structural Mechanics, Dayton, OH, USA, 26–28 October 1965; pp. 515–545. [Google Scholar]
- Więckowski, Z.; Youn, S.K.; Moon, B.S. Stress-based finite element analysis of plane plasticity problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1985, 44, 1505–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L. The Finite Element Method for Solid and Structural Mechanics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, T.J.R. The Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element Analysis; Dover Publications: Garden City, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Häggblad, B.; Bathe, K.-J. Specifications of boundary conditions for Reissner/Mindlin plate bending finite elements. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1990, 30, 981–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synge, J.L. The Hypercircle in Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, S.; Woinowsky-Krieger, S. Theory of Plate and Shells, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, D.N.; Falk, R.S. Asymptotic analysis of the boundary layer for the Reissner–Mindlin plate model. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1996, 27, 486–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraeijs De Veubeke, B.; Zienkiewicz, O.C. Strain-energy bounds in finite-element analysis by slab analogy. J. Strain Anal. 1967, 2, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, F.K.; Fox, R.L.; Schmit, L.A. The generation of interelement compatible stiffness and mass matrices by the use of interpolation formulas. In Proceedings of the Conference on Matrix Methods in Structural Mechanics, Dayton, OH, USA, 26–28 October 1965; pp. 397–443. [Google Scholar]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Papadopoulos, P.; Oñate, E. Plate bending elements with discrete constraints: New triangular elements. Comput. Struct. 1990, 35, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, P.; Šalkauskas, K. Surfaces generated by moving least squares method. Math. Comput. 1981, 37, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Hard Conditions | Soft Conditions | |
|---|---|---|
| Clamped edge: | , , | , , |
| Simply supported edge: | , , | , , |
| Free edge: | , , | , , |
| Mesh | h = 0.3 m | h = 0.05 m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT | BFS | DM22 | DM12 | HCT | BFS | DM22 | DM12 | |
| a/4 | 1.4209 | 1.4187 | 1.4213 | 1.4547 | 1.2753 | 1.2767 | 1.2800 | 1.2967 |
| a/8 | 1.4139 | 1.4134 | 1.4142 | 1.4525 | 1.2652 | 1.2658 | 1.2658 | 1.2962 |
| a/16 | 1.4126 | 1.4124 | 1.4126 | 1.4371 | 1.2626 | 1.2627 | 1.2620 | 1.2833 |
| Mesh | h = 0.3 m | h = 0.05 m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT | BFS | DM22 | DM12 | HCT | BFS | DM22 | DM12 | |
| a/4 | −5.7174 | −5.5222 | −5.6741 | −3.9544 | −6.7870 | −6.7078 | −6.8105 | −4.2447 |
| a/8 | −5.8558 | −5.7913 | −5.8529 | −4.9958 | −6.7752 | −6.7612 | −6.7820 | −5.6252 |
| a/16 | −5.8858 | −5.8718 | −5.8962 | −5.4176 | −6.7735 | −6.7685 | −6.7650 | −6.1566 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Więckowski, Z.; Świątkiewicz, P. Equilibrium-Based Finite Element Analysis of the Reissner–Mindlin Plate Bending Problem. Materials 2025, 18, 4969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214969
Więckowski Z, Świątkiewicz P. Equilibrium-Based Finite Element Analysis of the Reissner–Mindlin Plate Bending Problem. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214969
Chicago/Turabian StyleWięckowski, Zdzisław, and Paulina Świątkiewicz. 2025. "Equilibrium-Based Finite Element Analysis of the Reissner–Mindlin Plate Bending Problem" Materials 18, no. 21: 4969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214969
APA StyleWięckowski, Z., & Świątkiewicz, P. (2025). Equilibrium-Based Finite Element Analysis of the Reissner–Mindlin Plate Bending Problem. Materials, 18(21), 4969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214969






