Unraveling Anomalous Eutectic Formation in Ni-Sn Alloys During Directional Solidification with Transition Variable Speed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructural Morphology of Ni-Sn Alloys Under Different Drawing Speeds
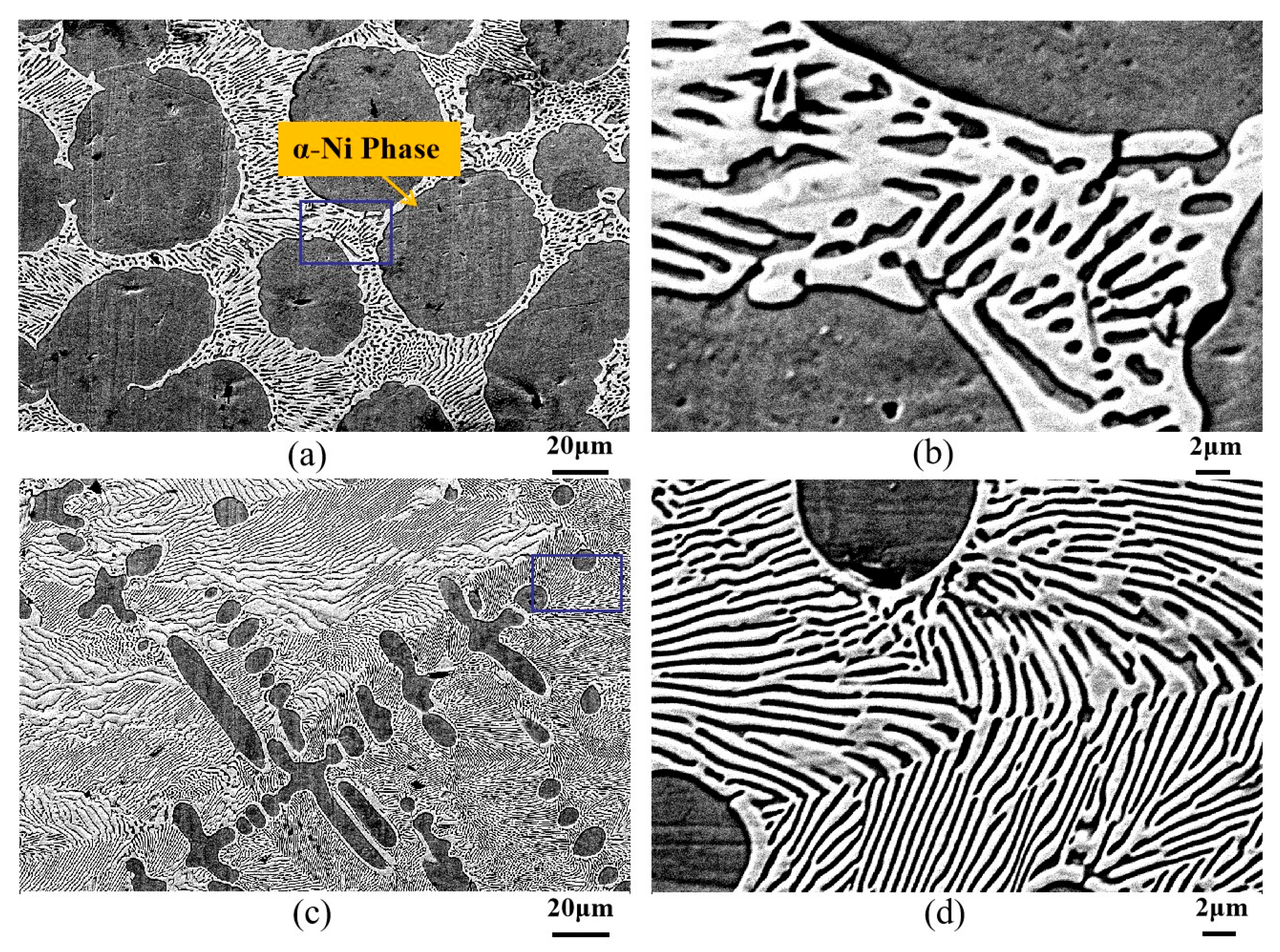
3.1.1. Ni-30 wt.%Sn Hypoeutectic Alloy
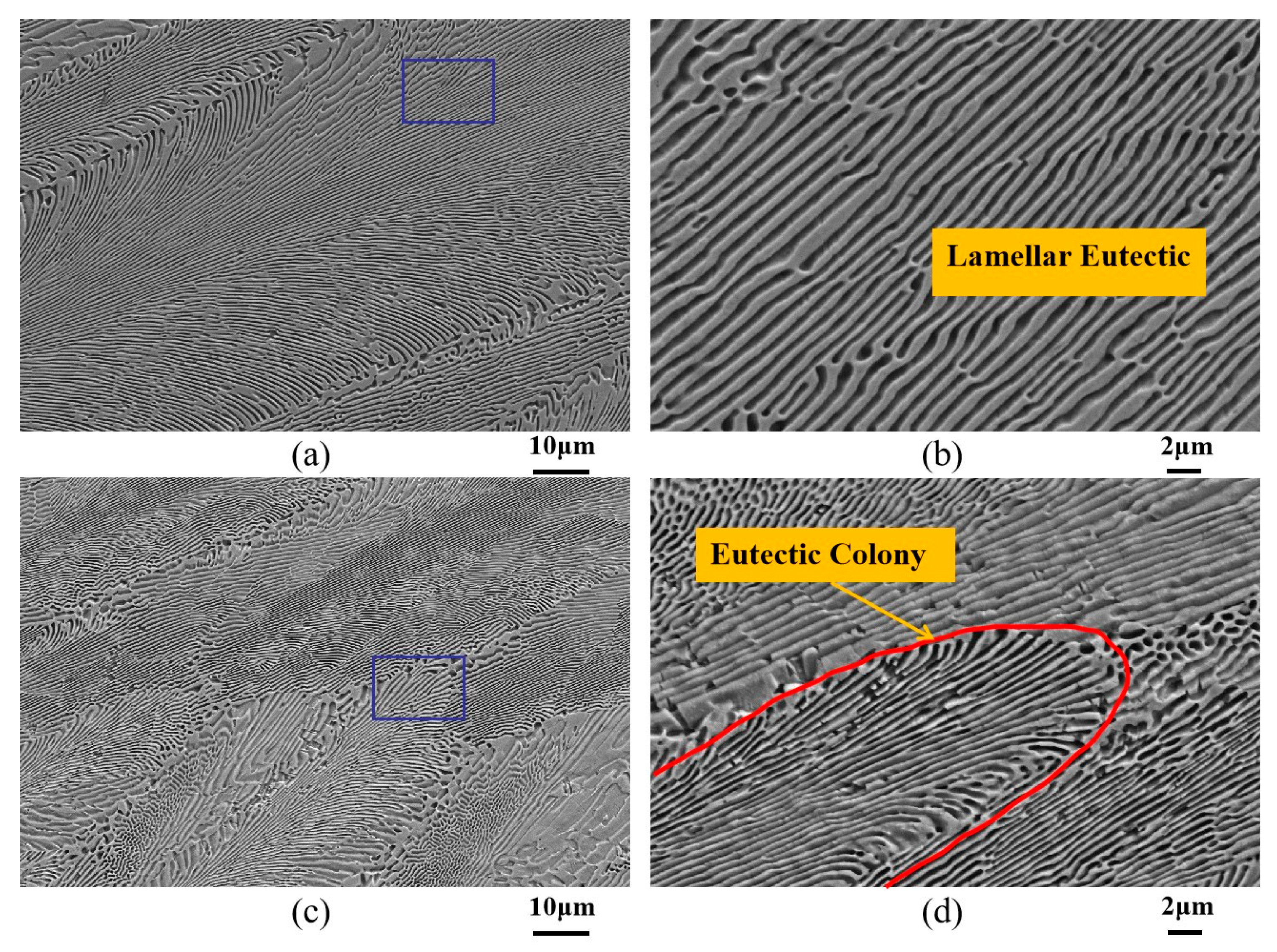
3.1.2. Ni-32.5 wt.%Sn Eutectic Alloy
3.1.3. Ni-33 wt.%Sn Hypereutectic Alloy
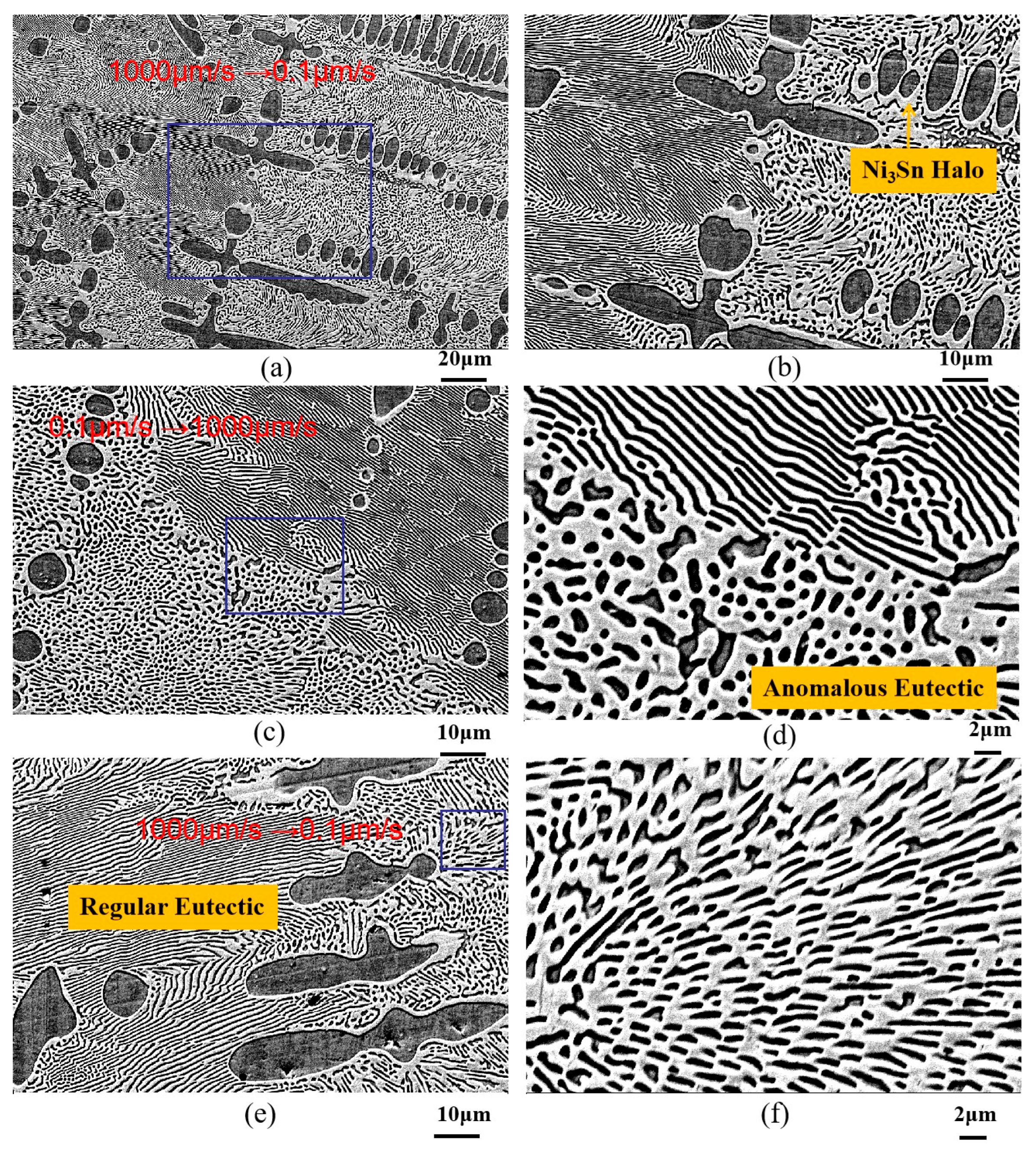
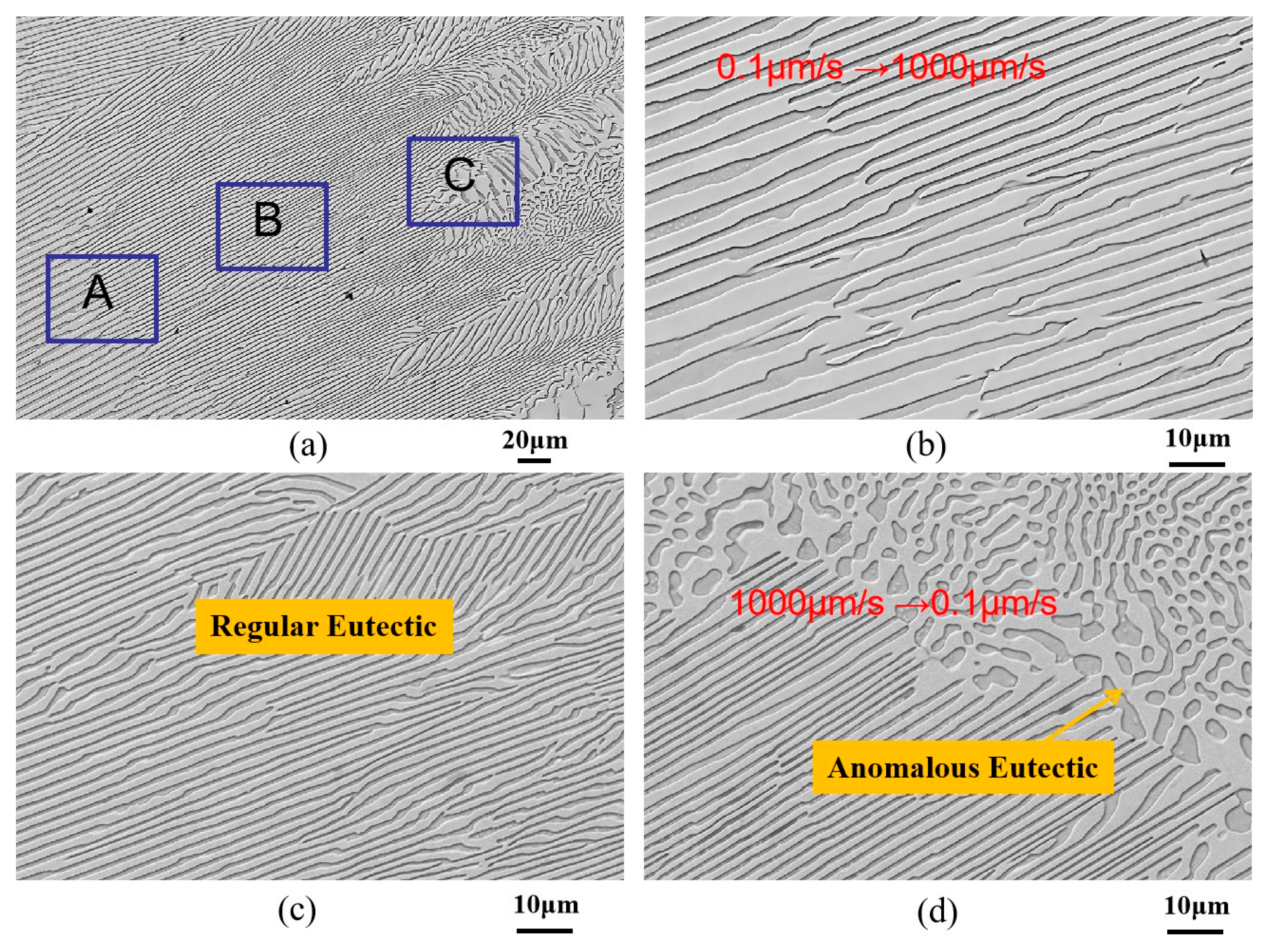
3.2. Effect of Transition Variable Speeds on Ni-Sn Eutectic Microstructural Morphology
3.2.1. Microstructural Morphology at the Transition Interface in Ni-30 wt.%Sn Hypoeutectic Alloy
3.2.2. Microstructural Morphology at the Transition Interface in Ni-32.5 wt.%Sn Eutectic Alloy
3.2.3. Microstructural Morphology at Transition Interfaces in Ni-33 wt.%Sn Hypereutectic Alloy
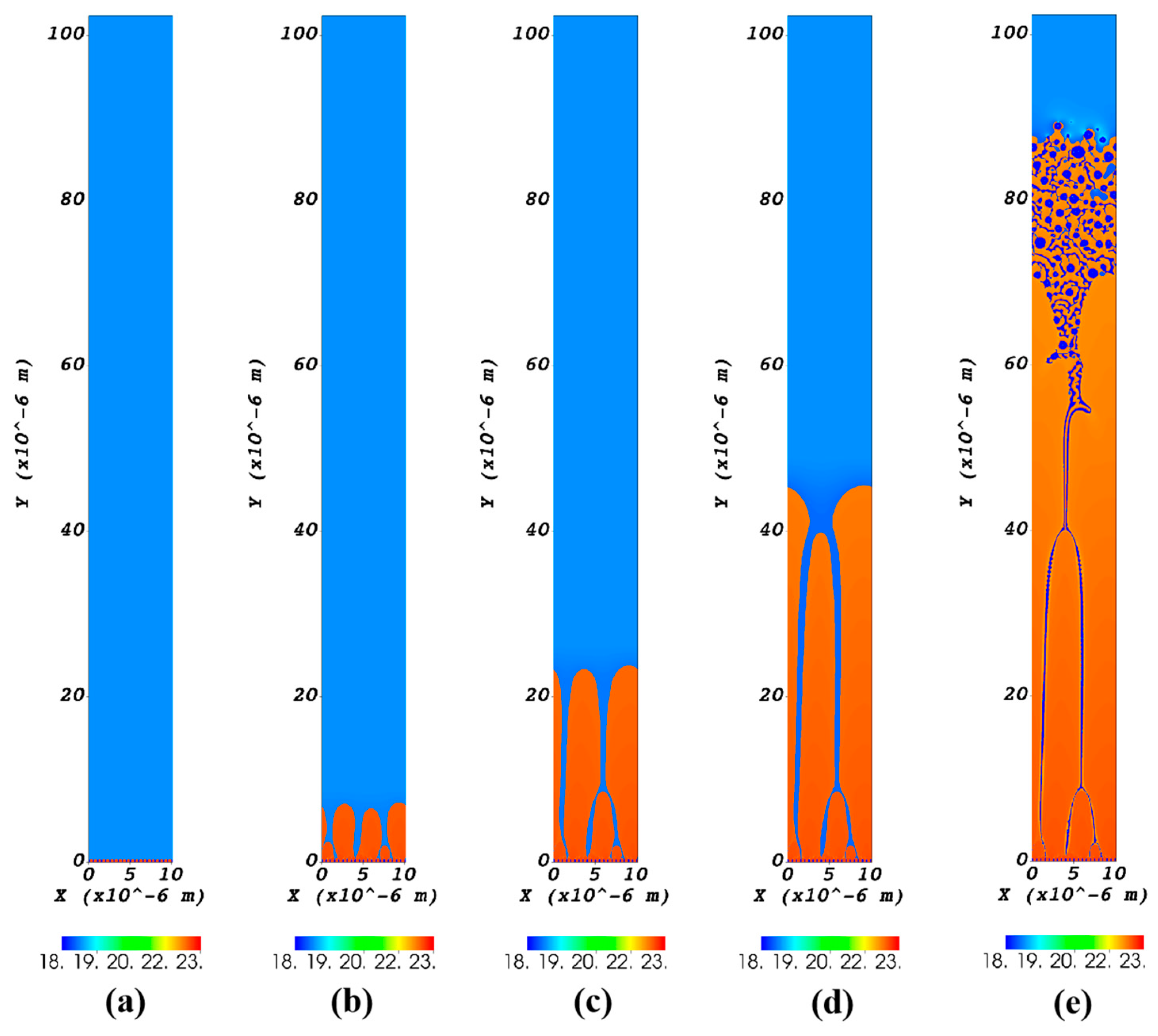
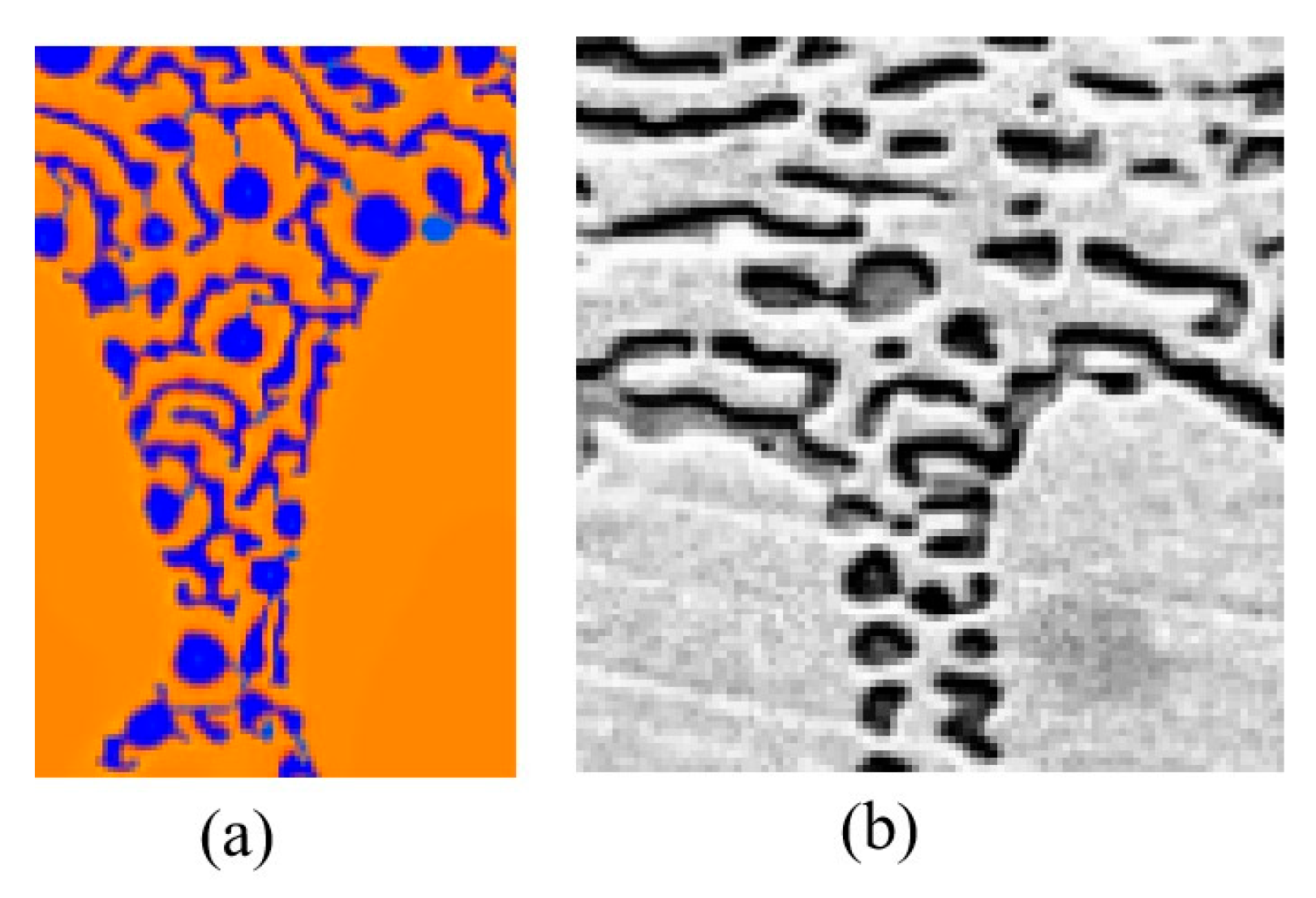
3.3. CA Simulation of Ni-Sn Eutectic Microstructural Evolution During Directional Solidification
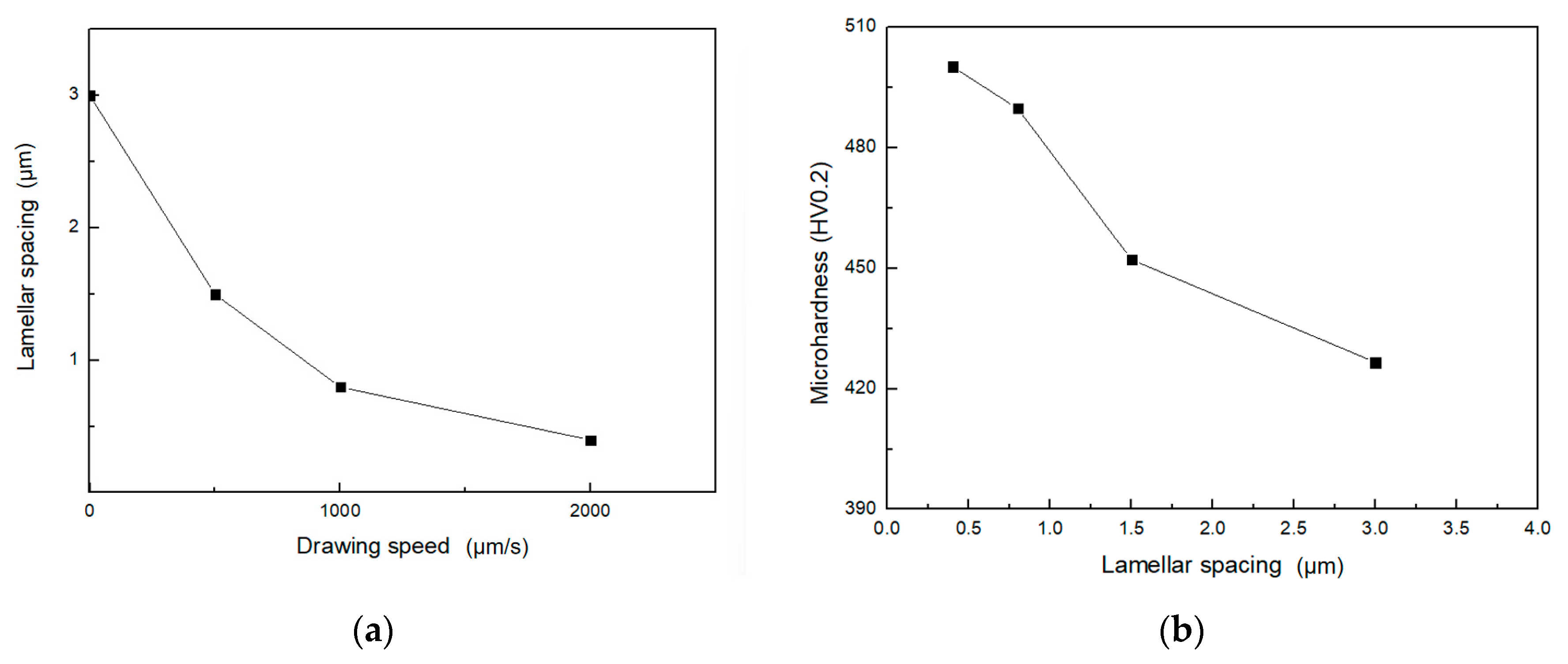
3.4. The Relationship Among Growth Rate, Eutectic Microstructure, and Microhardness of Directionally Solidified Ni-Sn Alloys
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The novelty of the velocity-jump methodology includes being able to achieve different growth conditions by varying speed in the same sample and more accurately comparing the structures under different conditions; enabling the study of dynamic change processes, such as the transformation mechanism of morphology during speed variation; precisely controlling parameters to investigate critical conditions for lamellar/rod–anomalous eutectic transition (ΔV = 1000 μm/s); and potentially observing unsteady-state growth behaviors, which enriches the theory of eutectic growth.
- (2)
- The CA simulations revealed that rapid jumps in growth velocity destabilize the regular lamellar eutectic. This instability facilitates the epitaxial Ni3Sn phase and independent α-Ni nucleation, ultimately forming the anomalous eutectic structure. The α-Ni phase and the Ni3Sn phase exhibit decoupled growth to form anomalous eutectic. The CA simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental findings from Bridgman directional solidification.
- (3)
- In this work, as the drawing speed increased, the lamellar spacing decreased, while the microhardness increased and followed the Hall–Petch relationship. The microhardness of anomalous eutectic is lower than lamellar/rod-like eutectic. However, anomalous eutectic exhibits a better plastic deformation capacity through structural modulation in high entropy alloy [47], which is beneficial to design multi-component alloys with superior properties. Regarding the lamellar–rod transition mechanism of eutectic, some scholars have adopted transparent system simulation and in situ observation technology [5], and this method can also be used to investigate the formation mechanism of anomalous eutectic in future work.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chao, P.; Aramanda, S.K.; Xiao, X.; Bottin-Rousseau, S.B.; Akamatsu, S.; Shahani, A.J. From Irregular to Regular Eutectic Growth in the Al-Al3Ni system: In Situ Observations During Directional Solidification. Acta Mater. 2024, 280, 120314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhai, W.; Li, H.; Wang, J.Y.; Wei, B. Ultrasounds induced eutectic structure transition and associated mechanical property enhancement of FeCoCrNi2.1Al high entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2023, 252, 118900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, S.; Xing, H. Formation of Seaweed Morphology and Enhancing Mechanical Properties of an A356 Alloy by Directional Solidification. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wu, S.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, H.; Song, K.; Wang, T.; Xing, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Yang, L. Microstructural Refinement and Anomalous Eutectic Structure Induced by Containerless Solidification for High-Entropy Fe–Co–Ni–Si–B Alloys. Intermetallics 2020, 122, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, S.; Sabine, B.R.; Silvère, A. Lamella-Rod Pattern Transition and Confinement Effects During Eutectic Growth. Acta Mater. 2023, 242, 118425. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Zhang, Z.R.; Shan, G.B.; Zhang, W.X.; Liu, F. Mechanisms of Eutectic Lamellar Destabilization upon Rapid Solidification of an Undercooled Ag-39.9 at.% Cu Eutectic Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, G.; Quaglia, A.; Battezzati, L. Banded Regular/Anomalous Eutectic in Rapidly Solidified Co-61.8 at.% Si. Scr. Mater. 2019, 168, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, R.; Magnin, P.; Kurz, W. Theory of eutectic growth under rapid solidification conditions. Acta Metall. 1987, 35, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, A.M.; Clopet, C.R. On the Origin of Anomalous Eutectic Growth From Undercooled Melts: Why Re-melting is not a Plausible Explanation. Acta Mater. 2018, 145, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Lü, X.; Hua, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Revealing the nucleation and growth modes upon rapid solidification of undercooled Co-24 at.% Sn eutectic alloy by the crystallographic orientation relations. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1004, 175806. [Google Scholar]
- Soodabeh, A.; Jeffrey, E.S. Multiple origins of anomalous eutectic microstructure in rapidly solidified Mg-Al alloy. Materialia 2020, 9, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kuribayashi, K. Nucleation-controlled microstructures and anomalous eutectic formation in undercooled Co-Sn and Ni-Si eutectic melts. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34A, 2999–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Lü, X.; Hua, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Crystallographic evidences for twin-assisted eutectic growth in undercooled Ni-18.7 at.% Sn eutectic melts. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 135, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Wang, K.; Shan, G.B.; Zhang, Z.R.; Zhang, W.X.; Liu, F. Modeling Remelting Induced Destabilization of Lamellar Eutectic Structure in an Undercooled Ni-18.7 at.% Sn Eutectic Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Baker, E.B.; Matson, D.M.; Kolbe, M.; Chuang, A.C.P.; Ren, Y. In Situ and Ex Situ Studies of Anomalous Eutectic Formation in Undercooled Ni–Sn Alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 197, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiao, Z. Microstructure Evolution upon Directional Solidification Process of Nb-Si Based Ultrahigh Temperature Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1033, 181246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qi, Z.; Peng, H.; Hou, R.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, G. Lamellar Orientation Modulation of Fe-Al Alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 939, 148523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, H. Investigation on Nonequilibrium Crystallization of Highly Undercooled Cu–Ni–Co Alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jia, L.; Kong, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. Eutectic Evolution of Directionally Solidified Nb-Si Based Ultrahigh Temperature Alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 71, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.Y.; Jung, I.Y.; Choi, B.G.; Shin, J.H.; Jo, C.Y.; Lee, J.H. Effects of Chemical Composition and Solidification Rate on the Solidification Behavior of High-Cr White Irons. Metals 2024, 14, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Lai, Y.; Deng, L.; Su, H. Microstructure and Fracture Toughness of the Bridgman Directionally Solidified Fe-Al-Ta Eutectic at Different Solidification Rates. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, J. Microstructural Evolution in Directional Solidification of Nb-doped Co-Sn/Ni-Sn Eutectic Alloys. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, K.N.; Wischi, M.; Rodrigues, J.F.Q.; Starck, L.F.; Sangali, M.C.; Caram, R. Directional Solidification of the Al0.8CrFeNi2.2 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 8874–8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. Quantitative Cellular Automaton Model and Simulations of Dendritic and Anomalous Eutectic Growth. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 156, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clopet, C.R.; Cochrane, R.F.; Mullis, A.M. Spasmodic Growth During the Rapid Solidification of Undercooled Ag-Cu Eutectic Melts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 031906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. Regular eutectic and anomalous eutectic growth behavior in laser remelting of Ni-30wt.%Sn alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 126, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Gao, J.; Liao, H.; Fenineche, N.; Coddet, C. Selective laser melting of elemental powder blends for fabrication of homogeneous bulk material of near-eutectic Ni-Sn composition. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena, G.; Bugelnig, K.; Sket, F.; Milenkovic, S.; Rödler, G.; Weisheit, A.; Gussone, J.; Haubrich, J.; Barriobero-Vila, P.; Pusztai, T.; et al. Ultrafine Fe-Fe2Ti eutectics by directed energy deposition: Insights into microstructure formation based on experimental techniques and phase field modelling. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 33, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Huang, W. Cellular Automaton Simulation of the Growth of Anomalous Eutectic during Laser Remelting Process. Materials. 2018, 11, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.; Fisher, D.J.; Rappaz, M. Fundamentals of Solidification, 5th ed.; Trans Tech Publications: Aedermannsdorf, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 57–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Liu, L. Solidification Microstructures of the Undercooled Co-24at%Sn Eutectic Alloy Containing 0.5at%Mn. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, I.; Ueyama, S.; Ohnaka, I. Effects of Mn and Co Addition on Morphology of Unidirectionally Solidified FeSi2 Eutectic Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 208, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y. Eutectic growth from cellular to dendritic form in the undercooled Ag-Cu eutectic alloy melt. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Tian, Y.; Liu, S.; Lv, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q. Microstructure Development in Eutectic Al-Fe Alloy During Directional Solidification under High Magnetic Fields at Different Growth Velocities. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 16134–16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y. High Undercooling and Rapid Solidification of Ni-32.5%Sn Eutectic Alloy. Acta Metall. Mater. 1991, 39, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, K.A.; Hunt, J.D. Lamellar and Rod Eutectic Growth. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME. 1966, 236, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, J. Halo Formation in Solidification of Off-eutectic Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2025, 56A, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.Y.; Li, J.F.; Yang, L.; Liu, L.J. Solidification Behavior and Microstructure of Ag–Cu Eutectic Alloy at Different Sub-Rapid Cooling Rates. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 311, 128521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karma, A. Beyond Steady-State Lamellar Eutectic Growth. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, W.D.; Fen, J. History dependent selection of primary cellular dendritic spacing during unidirectional solidification in aluminum alloys. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.J.; Wei, X.X.; Ferry, M.; Li, J.F. Investigation of the Origin of Anomalous Eutectic Formation by Remelting Thin-Gauge Samples of an Ag-Cu Eutectic Alloy. Scr. Mater. 2020, 174, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Feng, W.J.; Xiao, J.Z.; Gan, Z.H.; Yi, H.Y.; Cui, K. Non-equilibrium solidification of bulk undercooled Ni-P eutectic alloys. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 256, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiao, D.; Dong, S.; Peng, P.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X. Analysis on phase selection and microstructure evolution in directionally solidified Zn-Al-Mg-Ce alloy. China Foundry 2023, 20, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trived, R.; Kurz, W. Modeling of solidification microstructures in concentrated solutions and intermetallic systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1990, 21, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischi, M.; Campo, K.N.; Starck, L.F.; Fonseca, E.B.; Lopes, É.S.N.; Caram, R. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of the directionally solidified AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Cao, Y.; Huang, W. Microstructure evolution in laser surface remelting of Ni–33wt.% Sn alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.X.; Chang, J.; Wang, W.L.; Zhu, X.N.; Lin, M.J.; Wei, B. Eutectic growth kinetics and microscopic mechanical properties of rapidly solidified CoCrFeNiMo0.8 high entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2022, 237, 118149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Fei, J. Effects of Interaction Between Sn-Rich and Pb-Rich Phases on the Mechanical Properties of Sn-Pb Eutectic Solder Alloy at Cryogenic Temperature. J. Electron. Mater. 2025, 54, 2368–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Impurity Elements | Fe | Cu | Co | Pb | Zn | Cr | Mg | Al | Bal. | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured values (mg/kg) | 8.4 | 3.3 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 5.3 | 2.9 | 3.6 | 5.2 | <12.0 | 44.3 |
| Standard requirements (<mg/kg) | 50 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 30 | 50 | <100 | <100 |
| Impurity Elements | Fe | Cu | Pb | Sb | As | Bi | Zn | Bal. | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured values (mg/kg) | 10.2 | 4.9 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 6.2 | <15.3 | 52.1 |
| Standard requirements (<mg/kg) | 50 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 30 | <100 | <100 |
| Composition | Ni-30 wt.%Sn Ingot | Ni-32.5 wt.%Sn Ingot | Ni-33 wt.%Sn Ingot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni (wt.%) | 69.11 | 67.66 | 66.38 |
| Sn (wt.%) | 30.89 | 32.24 | 33.62 |
| Segment Number | Starting Speed (μm/s) | Termination Speed (μm/s) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 5 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 2000.0 | 1 |
| 3 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 5 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 2000.0 | 3 |
| 5 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 5 |
| 6 | 0.1 | 2000.0 | 5 |
| 7 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 5 |
| 8 | 0.1 | 2000.0 | 7 |
| 9 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 20 |
| Segment Number | Starting Speed (μm/s) | Termination Speed (μm/s) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 25 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 1000.0 | 10 |
| 3 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 5 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 1000.0 | 20 |
| 5 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 5 |
| 6 | 0.1 | 1000.0 | 30 |
| 7 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 30 |
| Drawing Speed (μm/s) | Average Spacing of Lamellar Eutectic (μm) | Average Width of Primary Ni3Sn Phase (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 3 | 28 |
| 500 | 1.5 | 20 |
| 1000 | 0.5 | 7 |
| Composition of Alloy | Drawing Speed (μm/s) | Spacing of Lamellar Eutectic (μm) | Vickers Microhardness (HV 0.2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-30 wt.%Sn hypoeutectic | 0.1 | 1.78~2.12 | 436.9 |
| Ni-30 wt.%Sn hypoeutectic | 1000 | 0.76~0.81 | 470.5 |
| Ni-32.5 wt.%Sn eutectic | 1000 | 0.87~0.91 | 473.2 |
| Ni-32.5 wt.%Sn eutectic | 2000 | 0.41~0.47 | 500.2 |
| Ni-33 wt.%Sn hypereutectic | 0.1 | 2.45~3.02 | 426.6 |
| Ni-33 wt.%Sn hypereutectic | 500 | 1.39~1.51 | 452.2 |
| Ni-33 wt.%Sn hypereutectic | 1000 | 0.54~0.78 | 489.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Song, L.; Wei, L.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Jia, L.; Li, M.; Zhu, D. Unraveling Anomalous Eutectic Formation in Ni-Sn Alloys During Directional Solidification with Transition Variable Speed. Materials 2025, 18, 4933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214933
Cao Y, Cheng H, Song L, Wei L, Shi L, Li J, Jia L, Li M, Zhu D. Unraveling Anomalous Eutectic Formation in Ni-Sn Alloys During Directional Solidification with Transition Variable Speed. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214933
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yongqing, Huanhuan Cheng, Lianmei Song, Lei Wei, Lei Shi, Jiakang Li, Lixiao Jia, Miaoling Li, and Derong Zhu. 2025. "Unraveling Anomalous Eutectic Formation in Ni-Sn Alloys During Directional Solidification with Transition Variable Speed" Materials 18, no. 21: 4933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214933
APA StyleCao, Y., Cheng, H., Song, L., Wei, L., Shi, L., Li, J., Jia, L., Li, M., & Zhu, D. (2025). Unraveling Anomalous Eutectic Formation in Ni-Sn Alloys During Directional Solidification with Transition Variable Speed. Materials, 18(21), 4933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214933






