Branched Hyaluronic Acid for Reduced Viscosity and Enhanced Moisturization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
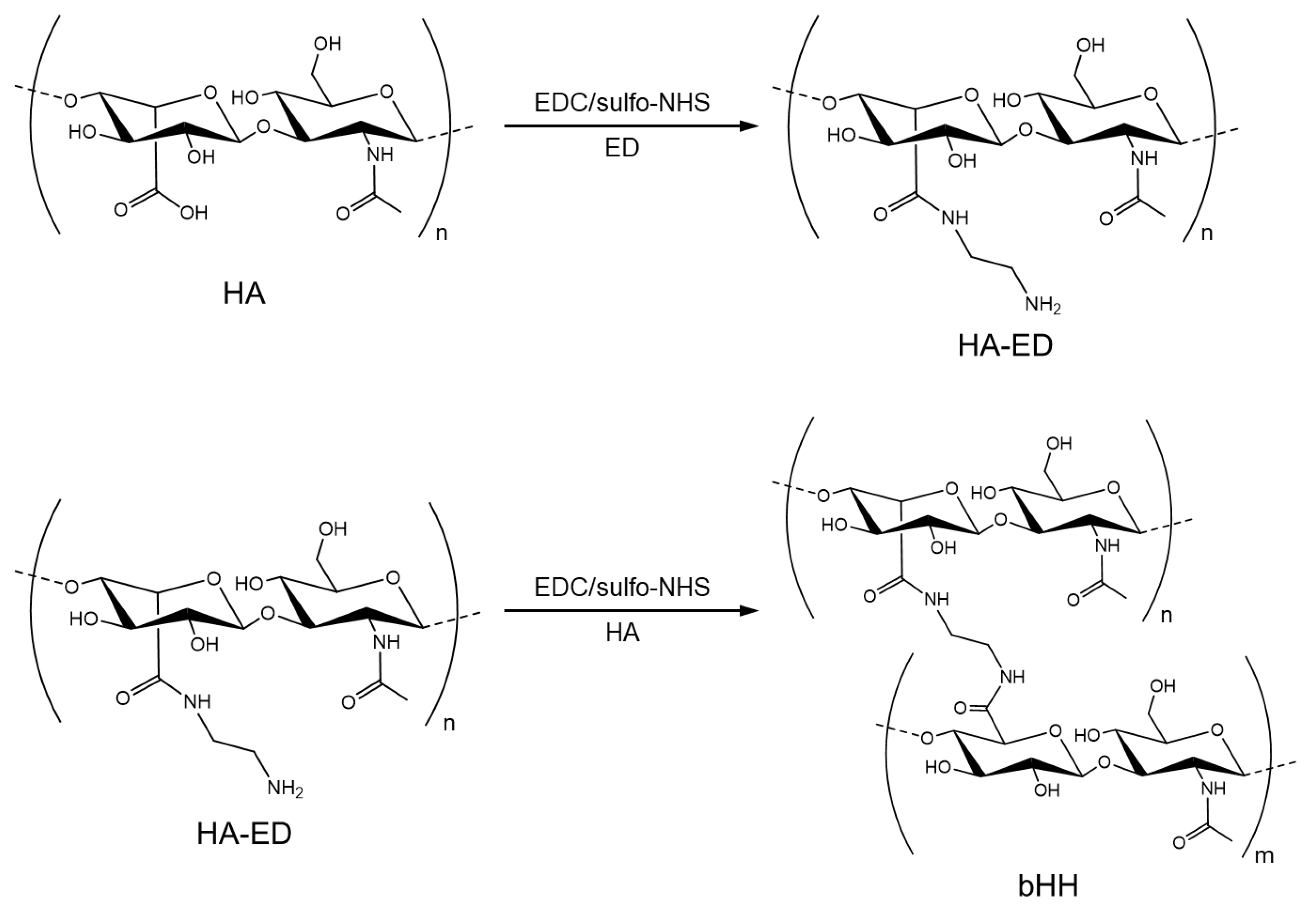
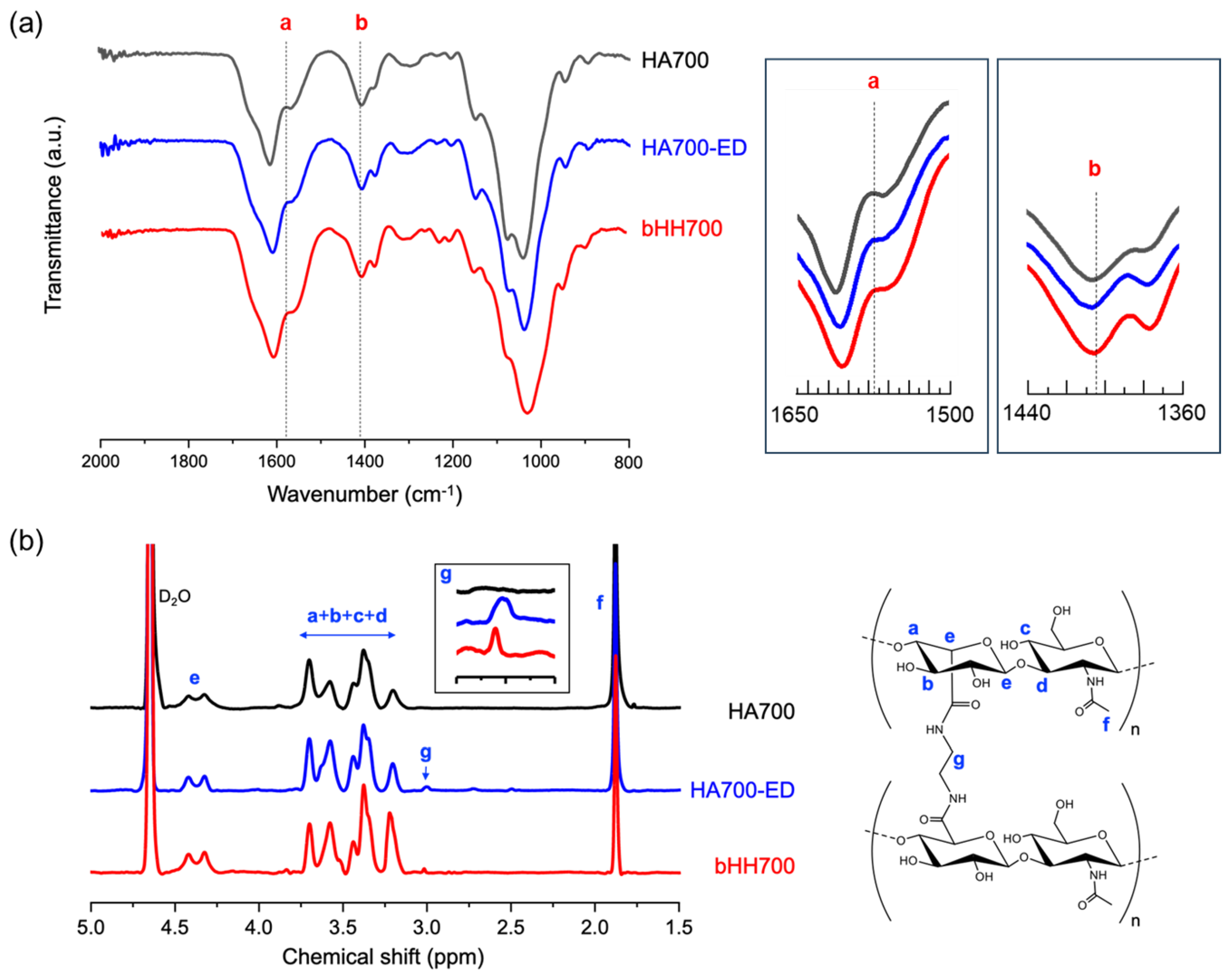
2.1. Synthesis of bHH
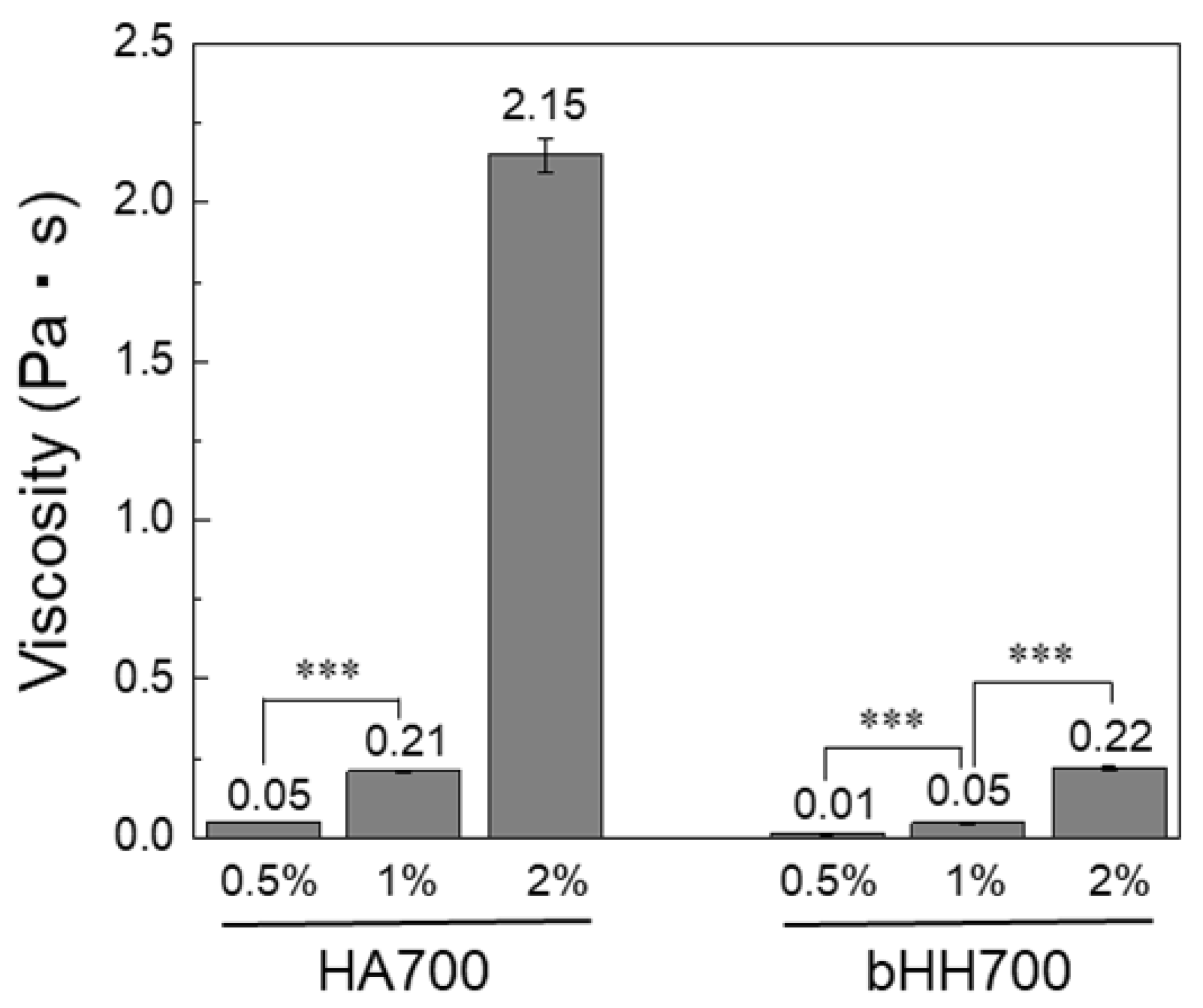
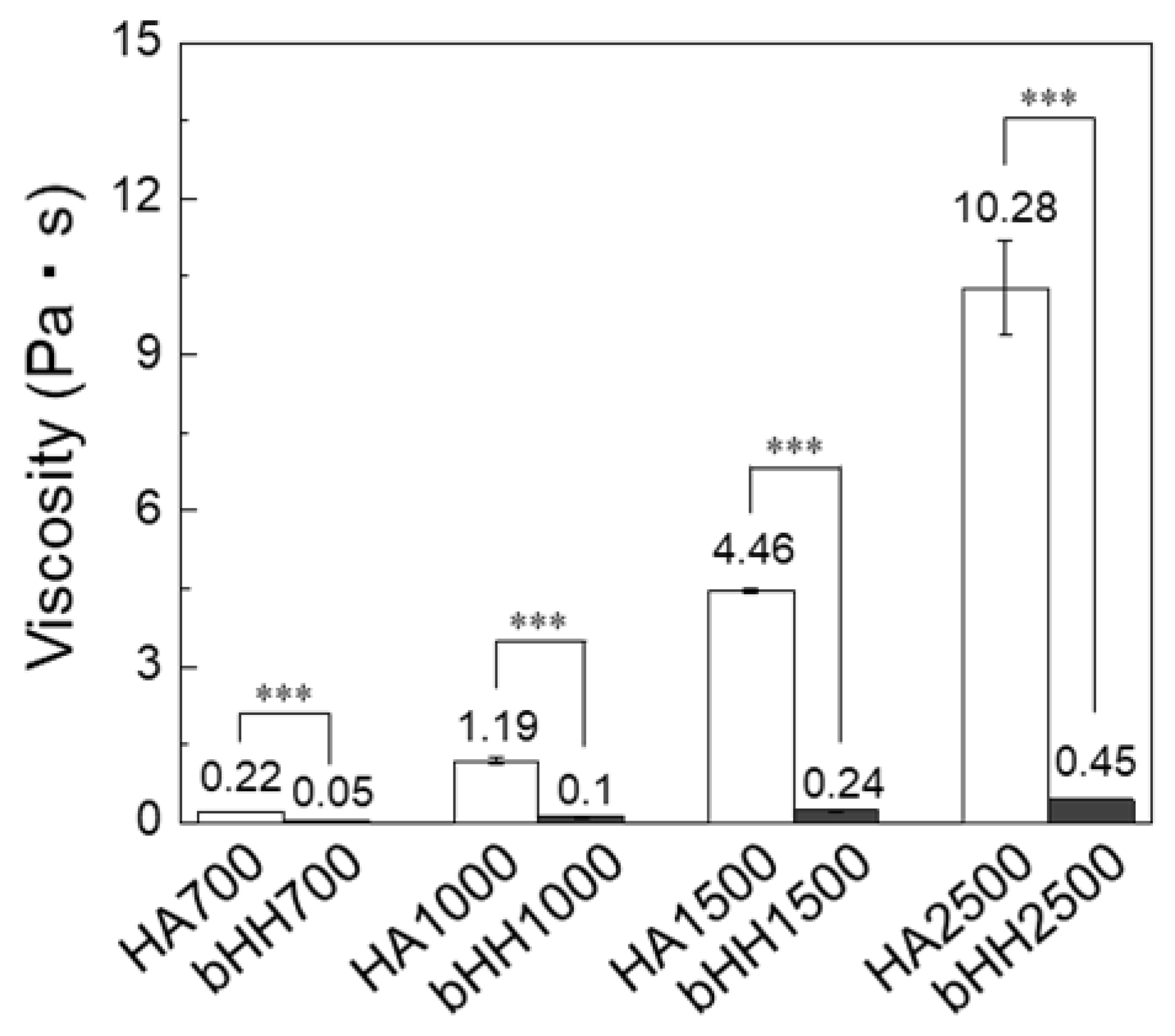
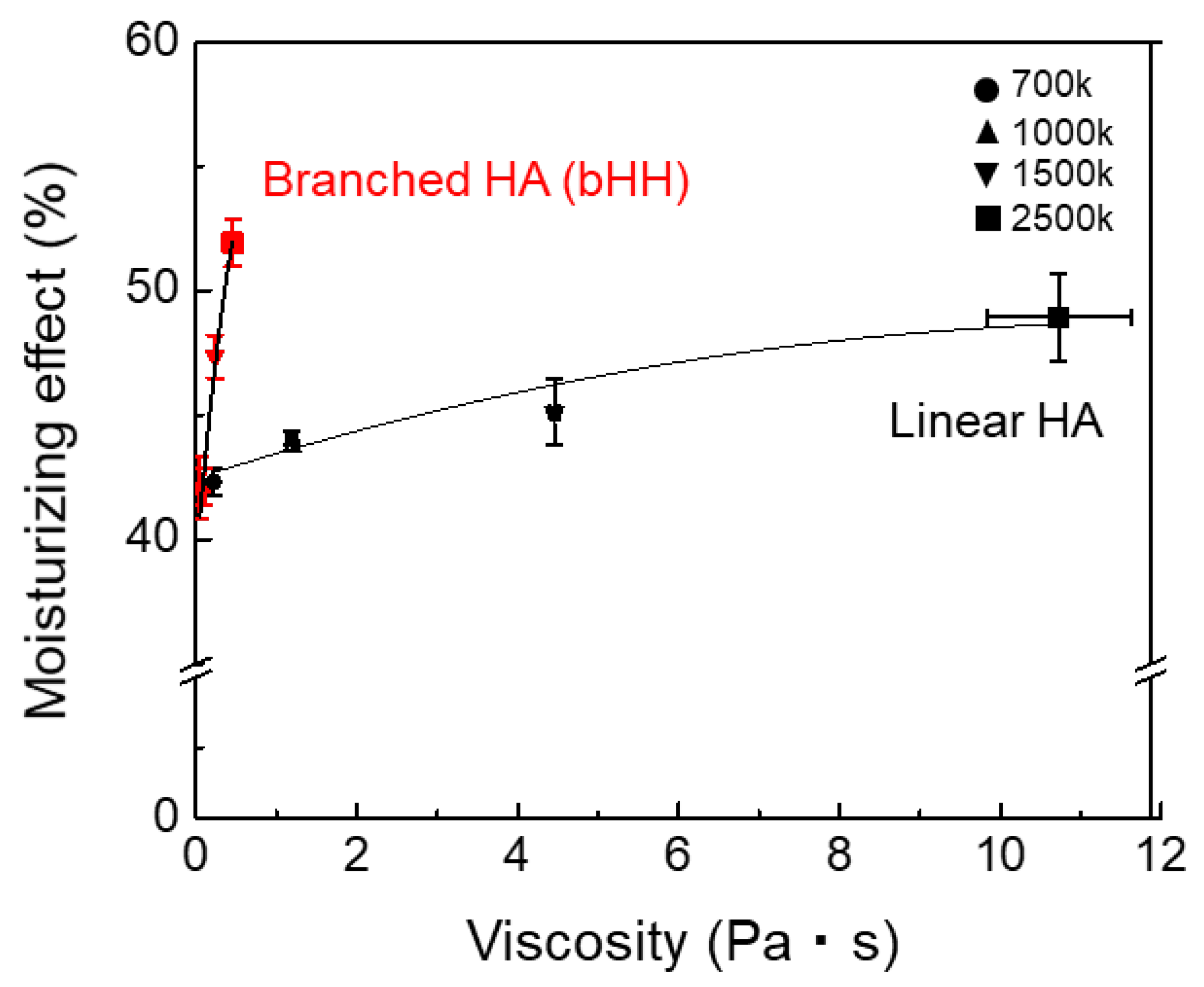
2.2. Rheological Properties of bHH
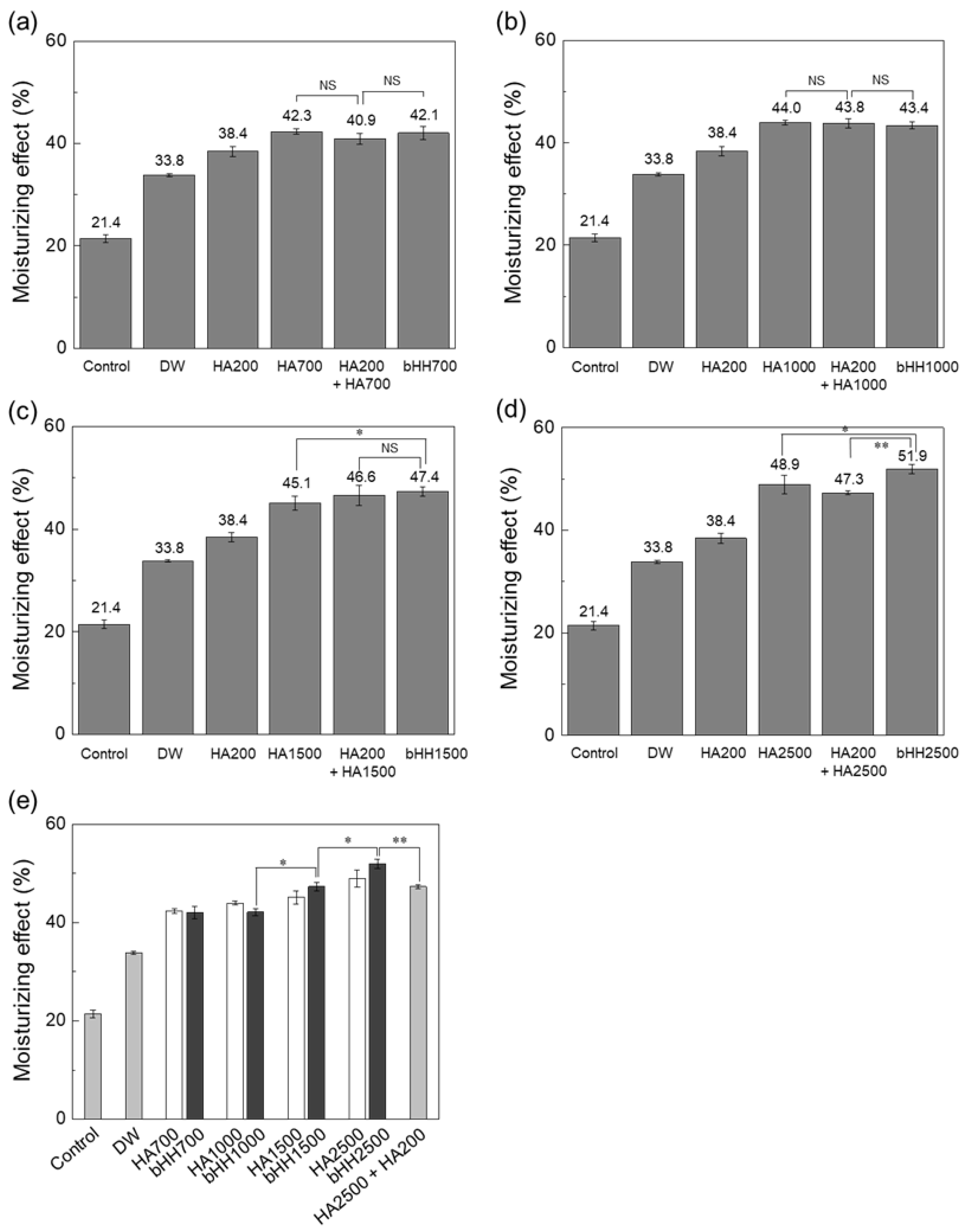
2.3. Moisturizing Effect (Ex Vivo)
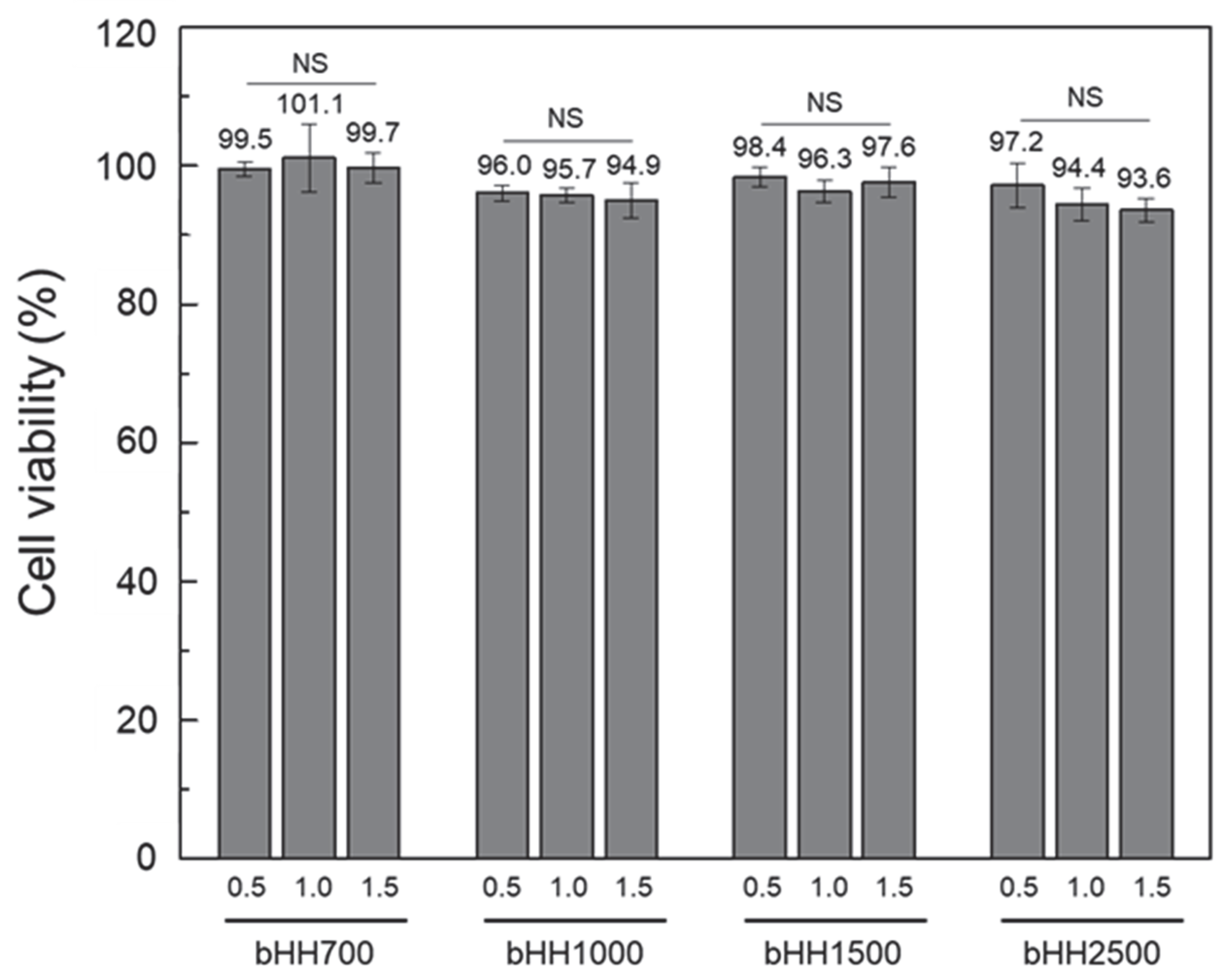
2.4. Cytotoxicity of bHH
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of bHH
4.3. Characterization of bHH
4.4. Cell Viability Evaluation
4.5. Viscosity Measurement
4.6. Water Retention Test (Ex Vivo)
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vishal, M.T.; Kiran, C.R.; Vansika; Ashlesha, S.B.; Sneha, S.B.; Rutuj, R.W. Review on Moisturizers. Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Commun. Technol. 2025, 5, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawazi, S.M.; Ann, J.; Othman, N.; Khan, J.; Alolayan, S.O.; Al Thagfan, S.S.; Kaleemullah, M. A Review of Moisturizers; History, Preparation, Characterization and Applications. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, V.; Mohapatra, S. A brief review on declarative concepts of pharmaceutical characteristics, classification, mechanisms, preparation, formulation and evaluation studies of moisturizing cream. Nano Med. Mater. 2024, 4, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Lee, P.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, S.L.; Huang, B.W.; Dai, F.J.; Chau, C.F.; Chen, C.S.; Lin, Y.S. Moisture retention of glycerin solutions with various concentrations: A comparative study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquero-Casals, J.; Morgado-Carrasco, D.; Granger, C.; Trullàs, C.; Jesús-Silva, A.; Krutmann, J. Urea in Dermatology: A Review of its Emollient, Moisturizing, Keratolytic, Skin Barrier Enhancing and Antimicrobial Properties. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yin, S.; Lu, X.; Fu, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S. Research on the Correlation Between Skin Elasticity Evaluation Parameters and Age. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draelos, Z.D.; Nelson, D.B. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of an Emollient-Rich Moisturizer Developed to Address Three Critical Elements of Natural Moisturization. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e70085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncan, A.M.; Moisă, D.G.; Santini, A.; Morgovan, C.; Rus, L.-L.; Vonica-Țincu, A.L.; Loghin, F. Advantages of Hyaluronic Acid and Its Combination with Other Bioactive Ingredients in Cosmeceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholamali, I.; Vu, T.T.; Jo, S.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Lim, K.T. Exploring the Progress of Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels: Synthesis, Characteristics, and Wide-Ranging Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, F.; Bahrulolum, H.; Talebi, M.; Karimi, M.; Bozorgchami, N.; Ghale, R.A.; Zafar, S.; Aghighi, Y.; Asiaei, E.; Tabandeh, F. Advances and principles of hyaluronic acid production, extraction, purification, and its applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 312, 143839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, B.; Tang, X.; Mao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Cui, S.; Chen, W. Absorption, metabolism, and functions of hyaluronic acid and its therapeutic prospects in combination with microorganisms: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chylińska, N.; Maciejczyk, M. Hyaluronic Acid and Skin: Its Role in Aging and Wound-Healing Processes. Gels 2025, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekaev, N.N.; Borzykh, O.B.; Medvedev, G.V.; Pushkin, D.V.; Petrova, M.M.; Petrov, A.V.; Dmitrenko, D.V.; Karpova, E.I.; Demina, O.M.; Shnayder, N.A. The Role of Extracellular Matrix in Skin Wound Healing. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, N.; Chang, Y.-y.J.; Lobianco, F.A.; Hodgkinson, T.; Browne, S. Hyaluronic acid as a versatile building block for the development of biofunctional hydrogels: In vitro models and preclinical innovations. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanaktsidou, E.; Kammona, O.; Kiparissides, C. Recent Developments in Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels for Cartilage Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.P.; Suresh, S.; Zennifer, A.; Sethuraman, S.; Sundaramurthi, D. Hyaluronic Acid as Bioink and Hydrogel Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 3134–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopov, A.; Drobintseva, A.; Kvetnoy, I.; Gazitaeva, Z.; Sidorina, A. Effect of a hyaluronic acid-based mesotherapeutic injectable on the gene expression of CLOCK and Klotho proteins, and environmentally induced oxidative stress in human skin cells. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, B.; Correia, P.; Gonçalves Junior, J.E.; Sant’Anna, B.; Kerob, D. Benefits of topical hyaluronic acid for skin quality and signs of skin aging: From literature review to clinical evidence. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Shih, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Chen, X. Dose-Dependent Effects of Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Through Intradermal Injection on Female Facial Photoaging: A Prospective Study. Aesthetic Surg. J. Open Forum 2025, 7, ojaf046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez-Martin, P.; Soto-Fernandez, C.; Romero-Rueda, J.; Cabañas, J.; Torrent, A.; Castells, G.; Martinez-Puig, D. A Novel Hyaluronic Acid Matrix Ingredient with Regenerative, Anti-Aging and Antioxidant Capacity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iaconisi, G.N.; Lunetti, P.; Gallo, N.; Cappello, A.R.; Fiermonte, G.; Dolce, V.; Capobianco, L. Hyaluronic Acid: A Powerful Biomolecule with Wide-Ranging Applications—A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncan, A.M.; Morgovan, C.; Rus, L.-L.; Loghin, F. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Anti-Ageing Cream Based on Hyaluronic Acid and Other Innovative Cosmetic Actives. Polymers 2023, 15, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mráček, A.; Gřundělová, L.; Minařík, A.; Veríssimo, L.M.P.; Barros, M.C.F.; Ribeiro, A.C.F. Characterization at 25 °C of Sodium Hyaluronate in Aqueous Solutions Obtained by Transport Techniques. Molecules 2015, 20, 5812–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tollenaere, M.; Meunier, M.; Lapierre, L.; Chapuis, E.; Guilleret, A.; Harrison, I.; Jean, T.; Rannou, A.; Scandolera, A.; Reynaud, R. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid vectorised with clay provides long-term hydration and reduces skin brightness. Ski. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valachová, K.; Hassan, M.E.; Šoltés, L. Hyaluronan: Sources, Structure, Features and Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Li, A.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, W. Branched Polymers: Synthesis and Application. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 830–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.H.; Biron, J.A.; Wilson, A.; Nelson, D.B. Efficacy and tolerability of a hyaluronic acid-based serum and a peptide-rich cream for the face and neck in subjects with photodamaged skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3458–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siquier-Dameto, G.; Boadas-Vaello, P.; Verdú, E. Intradermal Treatment with a Hyaluronic Acid Complex Supplemented with Amino Acids and Antioxidant Vitamins Improves Cutaneous Hydration and Viscoelasticity in Healthy Subjects. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Ángeles, G.; Nešporová, K.; Ambrožová, G.; Kubala, L.; Velebný, V. An Effective Translation: The Development of Hyaluronan-Based Medical Products from the Physicochemical, and Preclinical Aspects. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanparast, T.; Ayatollahi, A.; Samadi, A.; Sabzvari, A.; Kafi, H.; Firooz, A. Safety and Efficacy of a “High and Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid Hybrid Complex” Injection for Face Rejuvenation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e70117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dovedytis, M.; Liu, Z.J.; Bartlett, S. Hyaluronic acid and its biomedical applications: A review. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, K.C.; Campos, M.G.N.; Mei, L.H.I. Hyaluronic acid electrospinning: Challenges, applications in wound dressings and new perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 173, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhaščik, M.; Kováčik, A.; Huerta-Ángeles, G. Recent Advances of Hyaluronan for Skin Delivery: From Structure to Fabrication Strategies and Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Halaseh, L.K.; Tarawneh, S.K.; Al-Jawabri, N.A.; Al-Qdah, W.K.; Abu-Hajleh, M.N.; Al-Samydai, A.M.; Ahmed, M.A. A review of the cosmetic use and potentially therapeutic importance of hyaluronic acid. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, K.Y. Three-dimensional bioprinting of polysaccharide-based self-healing hydrogels with dual cross-linking. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2022, 110, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Woo, E.K.; Lee, K.Y. Ionically cross-linkable hyaluronate-based hydrogels for injectable cell delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 196, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Seo, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, K.Y. Regulation of the Viscoelastic Properties of Hyaluronate–Alginate Hybrid Hydrogel as an Injectable for Chondrocyte Delivery. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 15567–15575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, A.K.R.; Relleve, L.S.; Silos, A.P. Gel Properties of Carboxymethyl Hyaluronic Acid/Polyacrylic Acid Hydrogels Prepared by Electron Beam Irradiation. Mater. Proc. 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, M.K.; Yahya, M.; Noor, I.M.; Singh, P. Structural, electrochemical, and dielectric studies of phytagel and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tricyanomethanide-based bio-polymer electrolytes. Zast. Mater. 2024, 65, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namjoo, A.; Hassani, A.; Amini, H.; Nazaryabrbekoh, F.; Saghati, S.; Saadatlou, M.; Khoshfetrat, A.; Didar Khosrowshahi, N.; Rahbarghazi, R. Multiprotein collagen/keratin hydrogel promoted myogenesis and angiogenesis of injured skeletal muscles in a mouse model. BMC Biotechnol. 2024, 24, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malytskyi, V.; Moreau, J.; Callewaert, M.; Henoumont, C.; Cadiou, C.; Feuillie, C.; Laurent, S.; Molinari, M.; Chuburu, F. Synthesis and Characterization of Conjugated Hyaluronic Acids. Application to Stability Studies of Chitosan-Hyaluronic Acid Nanogels Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer. Gels 2022, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, Q. Applications and delivery mechanisms of hyaluronic acid used for topical/transdermal delivery—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukić, M.; Pantelić, I.; Savić, S.D. Towards Optimal pH of the Skin and Topical Formulations: From the Current State of the Art to Tailored Products. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, C.; Xia, Y.; Jin, L. Advances in hyaluronic acid: Bioactivity, complexed biomaterials and biological application: A review. Asian J. Surg. 2025, 48, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, M.; Gmyrek, D.; Żurawska, M.; Trusek, A. Hyaluronic Acid: Production Strategies, Gel-Forming Properties, and Advances in Drug Delivery Systems. Gels 2025, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meloni, M.; De Servi, B.; Carriero, F.; Simon O’Brien, E.; Houamel, D.; Deruelle, P.; Castagné, V. Demonstrating the principal mechanism of action of medical devices intended for vaginal use on reconstructed human vaginal epithelium: The case of two hyaluronic acid-containing devices. Front. Drug Saf. Regul. 2024, 4, 1445519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mola, A.; Landi, M.R.; Massa, A.; D’Amora, U.; Guarino, V. Hyaluronic Acid in Biomedical Fields: New Trends from Chemistry to Biomaterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggett, S.; Lyles, E.; Schlesinger, T. Update on Low-Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid in Dermatology: A Scoping Review. EMJ Dermatol. 2024, 12, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaqbeh, H.; Al-Ghzawi, B.; Baniamer, F. Exploring the Formulation and Approaches of Injectable Hydrogels Utilizing Hyaluronic Acid in Biomedical Uses. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.J.; Lee, I.Y.; Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.-c.; Lee, K.Y. Branched Hyaluronic Acid for Reduced Viscosity and Enhanced Moisturization. Materials 2025, 18, 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214882
Lee HJ, Lee IY, Choi Y, Lee Y-c, Lee KY. Branched Hyaluronic Acid for Reduced Viscosity and Enhanced Moisturization. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214882
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyun Ji, In Young Lee, Yongseok Choi, Yun-chan Lee, and Kuen Yong Lee. 2025. "Branched Hyaluronic Acid for Reduced Viscosity and Enhanced Moisturization" Materials 18, no. 21: 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214882
APA StyleLee, H. J., Lee, I. Y., Choi, Y., Lee, Y.-c., & Lee, K. Y. (2025). Branched Hyaluronic Acid for Reduced Viscosity and Enhanced Moisturization. Materials, 18(21), 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214882






