The Effect of Graphene Oxide Deposition, Shot Peening, and Hybrid Graphening on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of 30HGSA Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- BM: 30HGSA steel in the base material;
- BM + GO: 30HGSA steel with a deposited graphene oxide layer;
- BM + SP: 30HGSA steel after surface shot peening;
- BM + GO + SP: 30HGSA steel with a deposited graphene oxide layer that was then subjected to surface shot peening.
2.1. Object of Research
2.1.1. 30HGSA Steel
2.1.2. Dispersed Aqueous Suspension of Graphene Oxide
2.2. Sample Preparation Methodology
2.2.1. Methodology for Surface Deposition of Graphene Oxide Layer
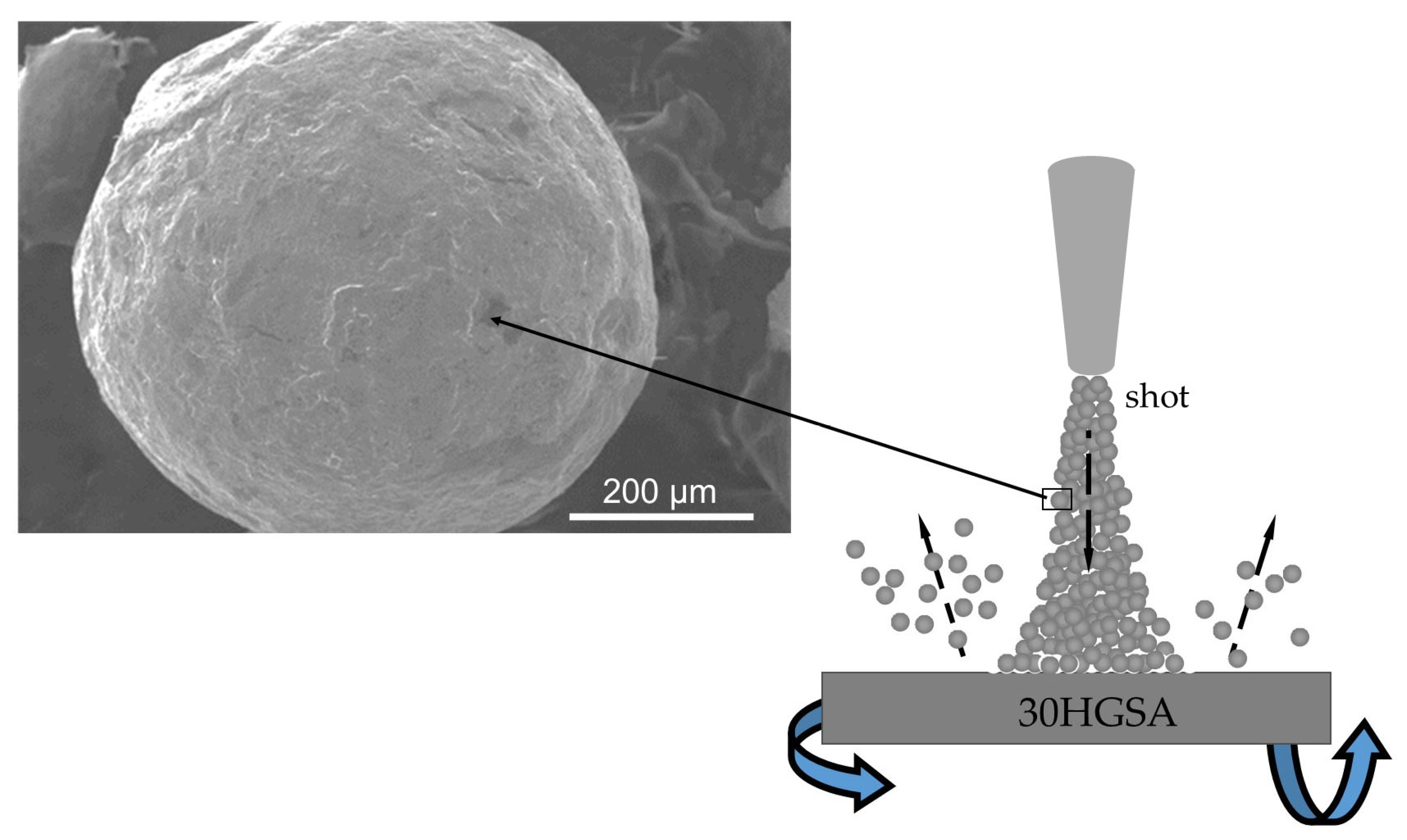
2.2.2. Surface Shot Peening Methodology
2.2.3. Hybrid Graphening Process Methodology
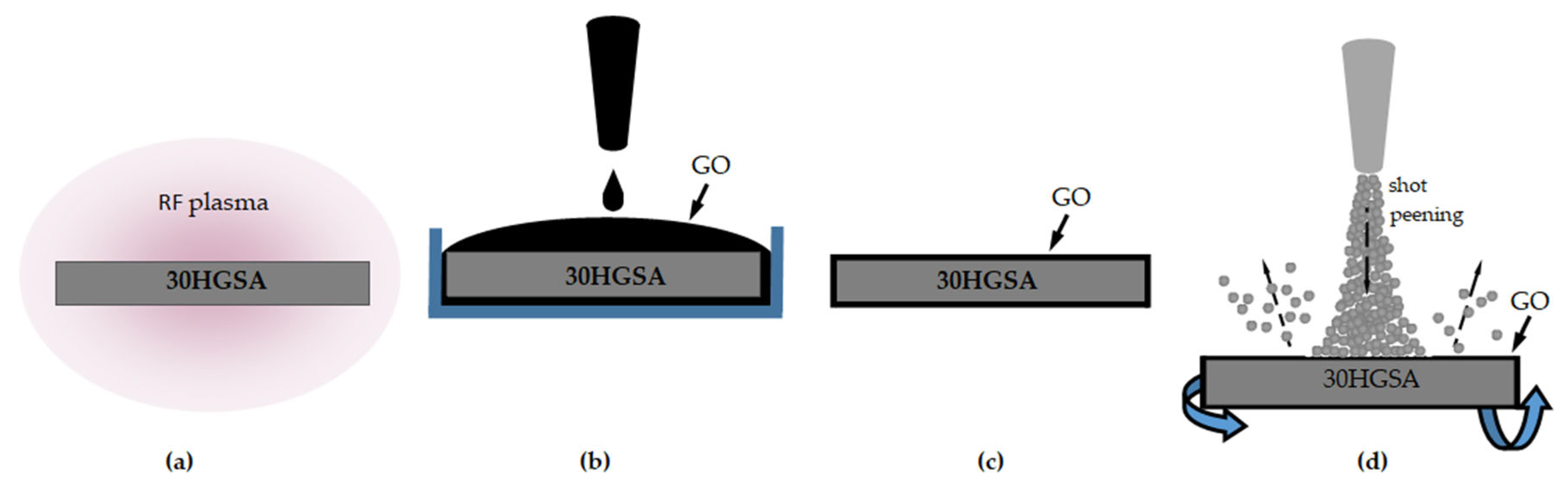
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Structural Analysis
2.3.2. Research Methodology for X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3.3. Research Methodology for Microhardness
2.3.4. Research Methodology for Surface Roughness
2.3.5. Research Methodology for Electrochemical Corrosion
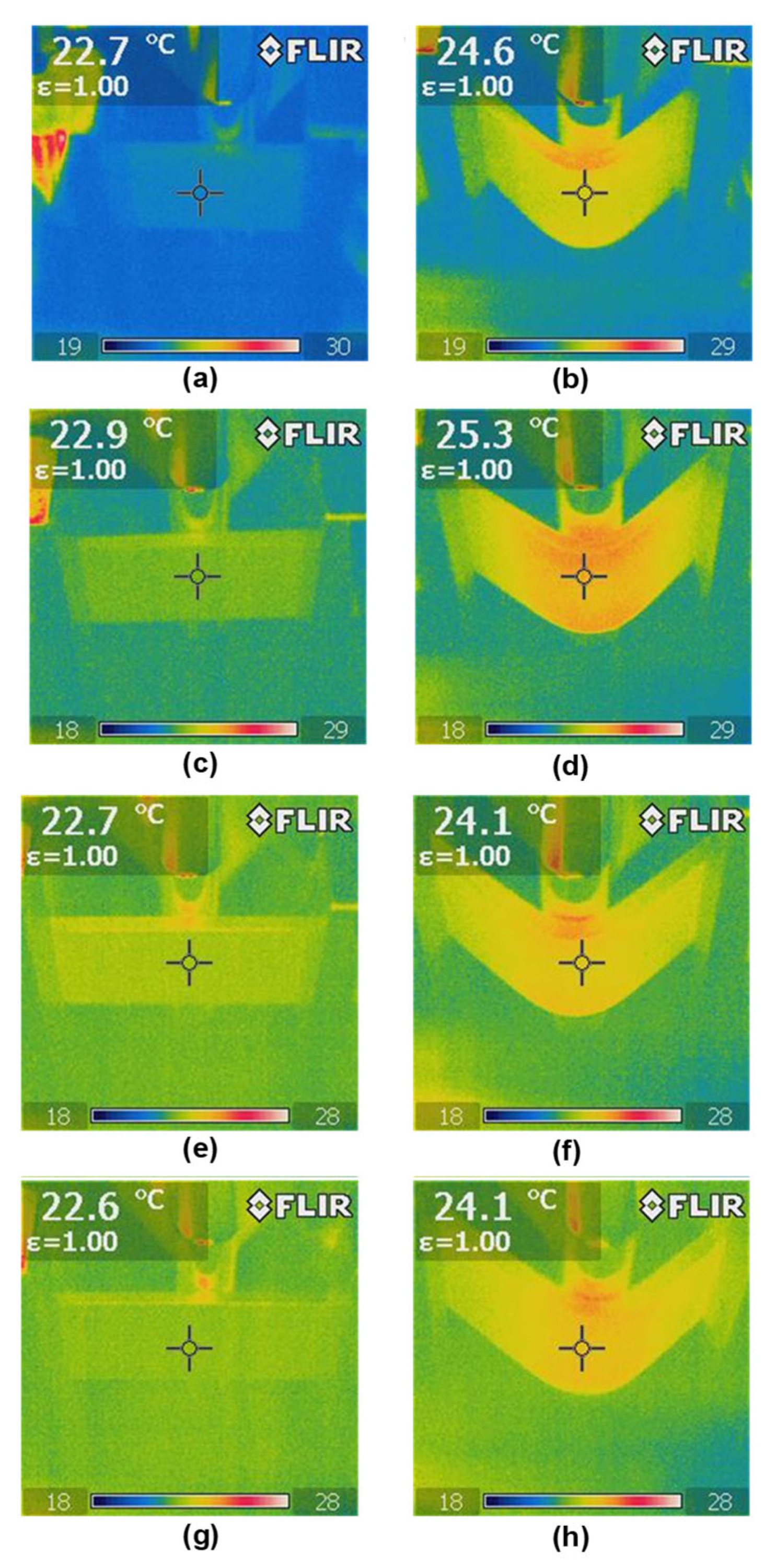
2.3.6. Research Methodology for Ageing and Thermal Shock
2.3.7. Research Methodology for Residual Stress
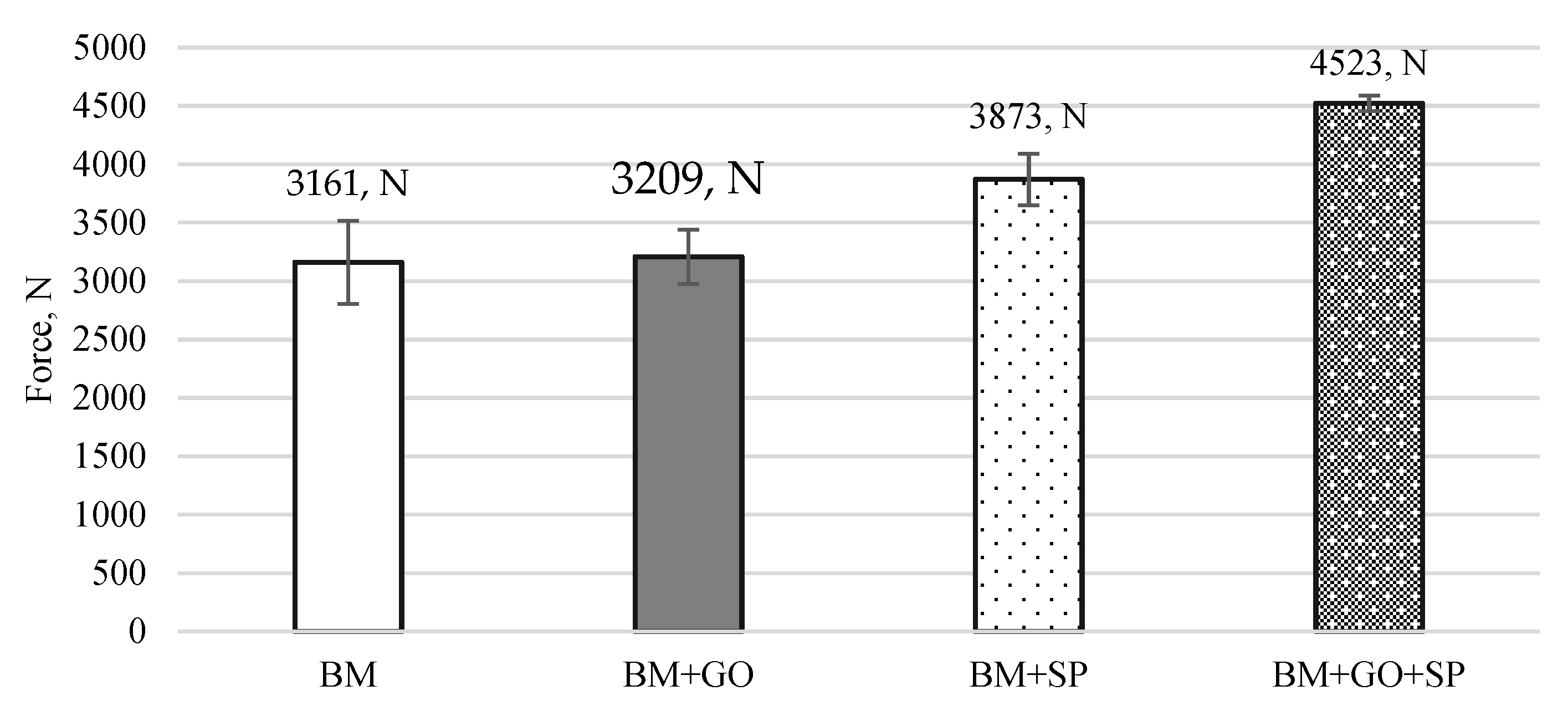
2.3.8. Research Methodology for Three-Point Bending
3. Research Results
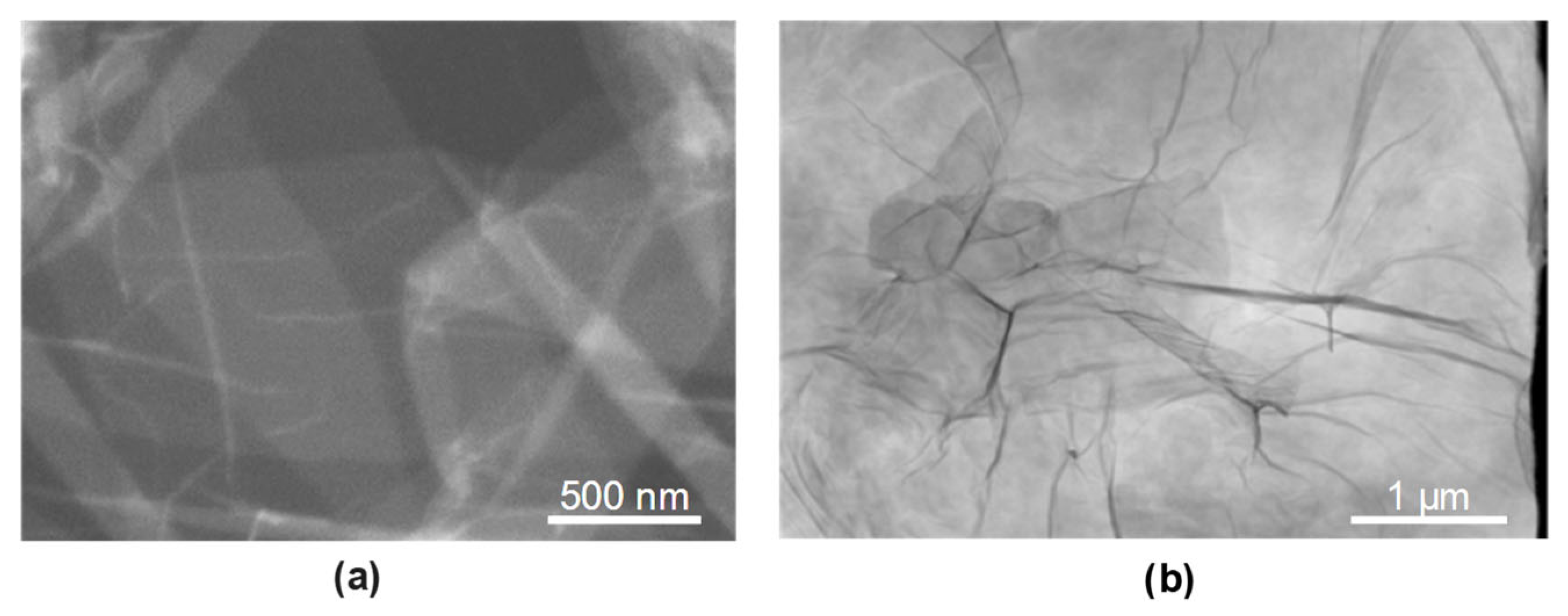
3.1. Structural Analysis GO
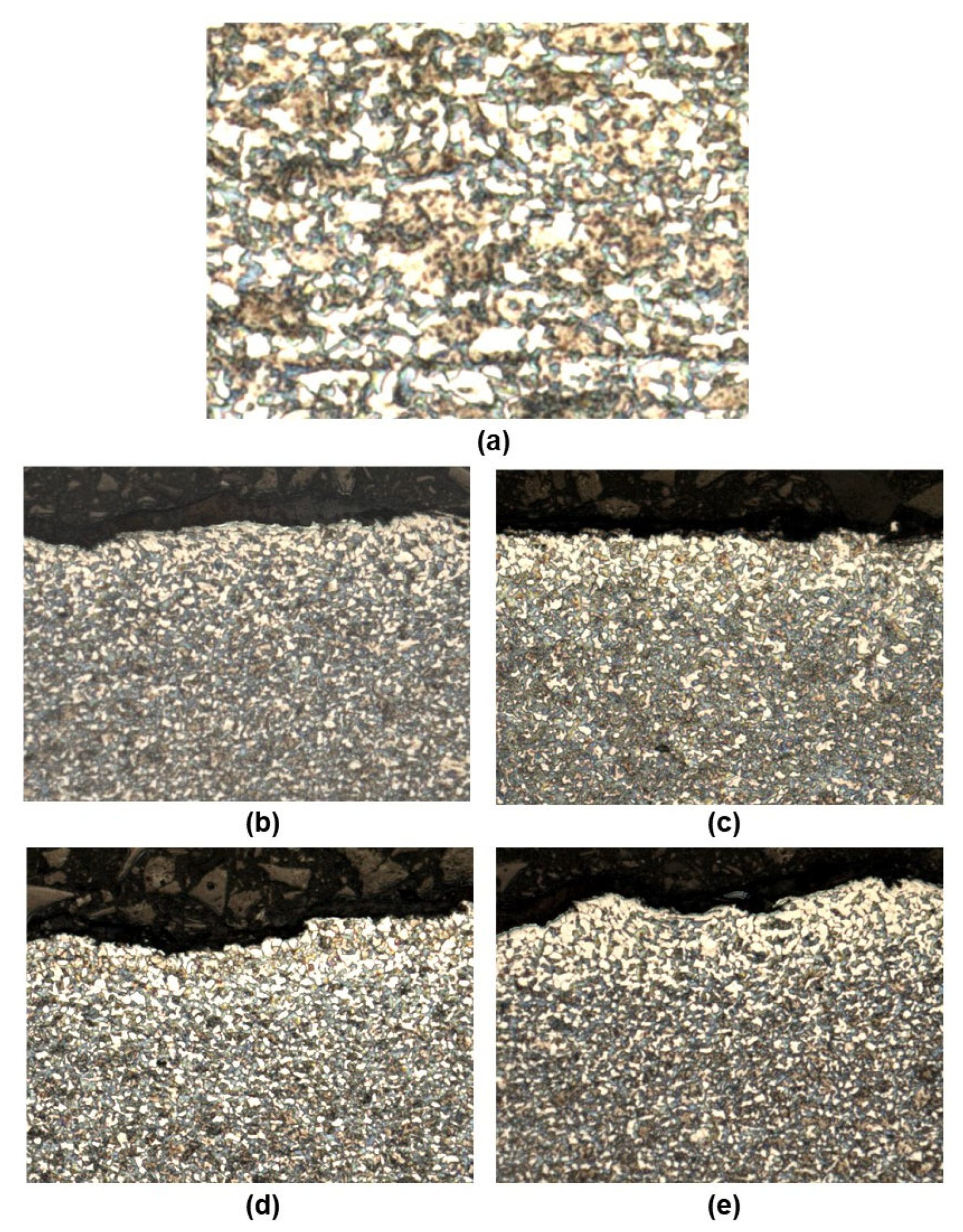
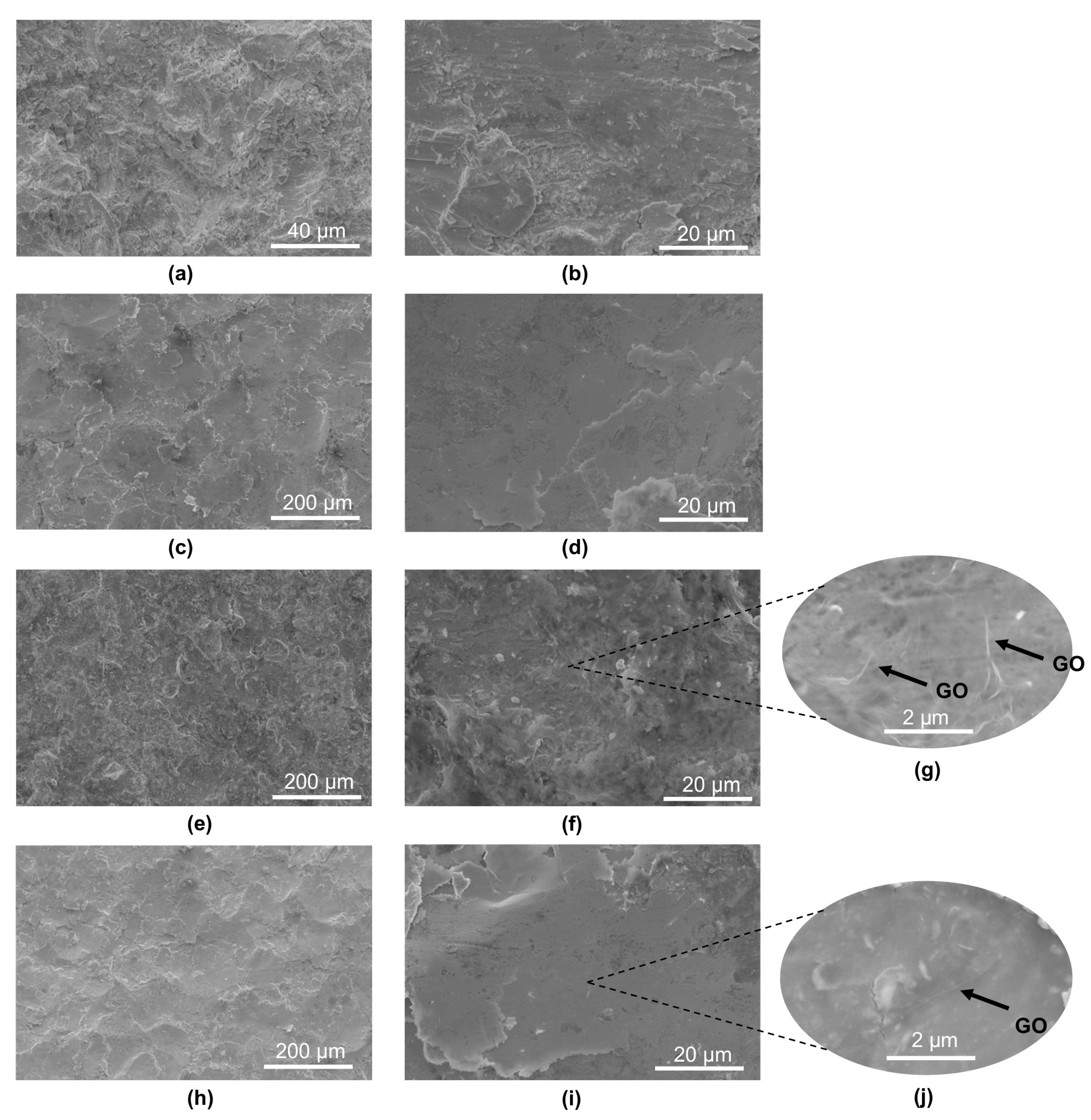
3.2. Structural Analysis 30HGSA Steel
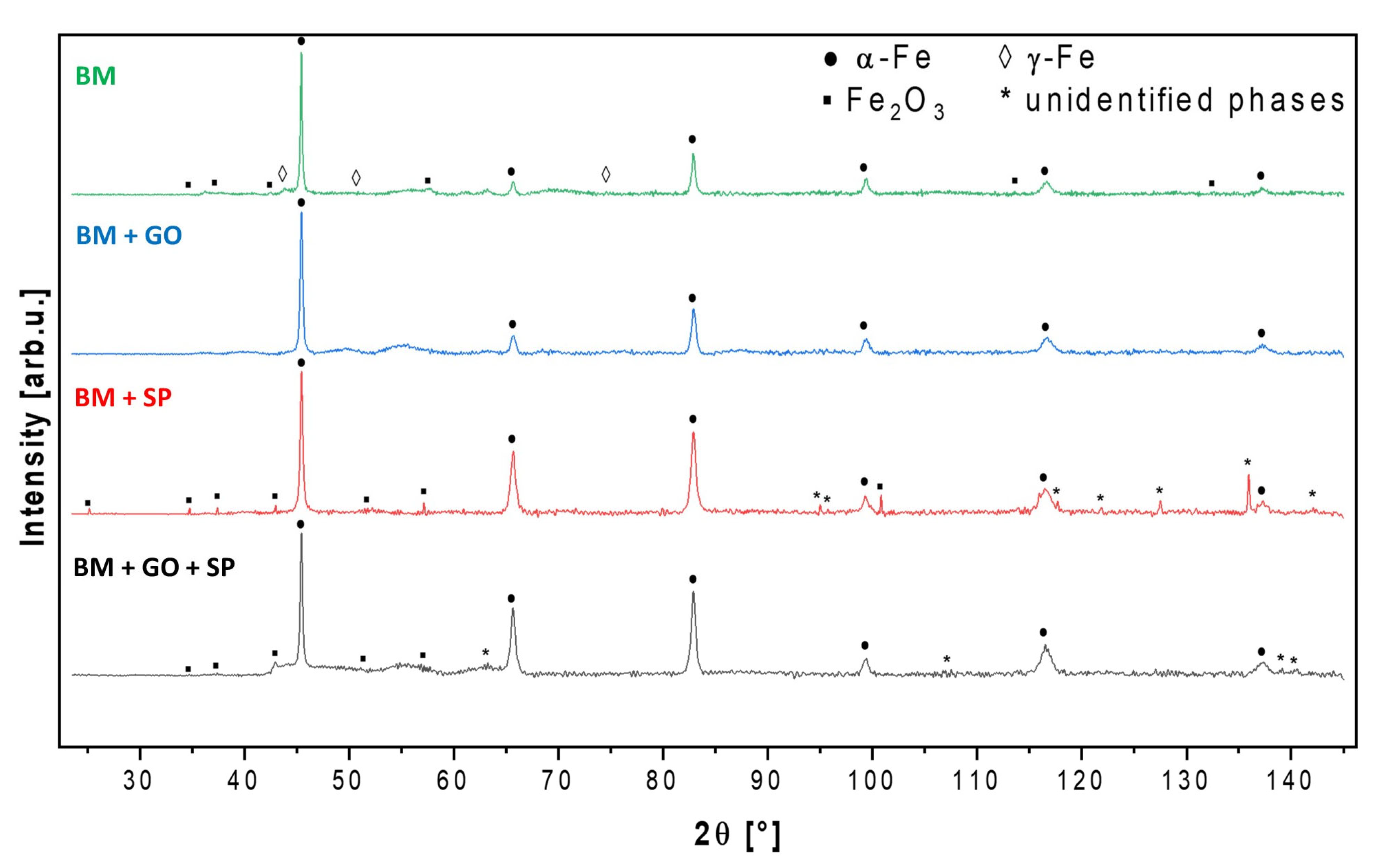
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction
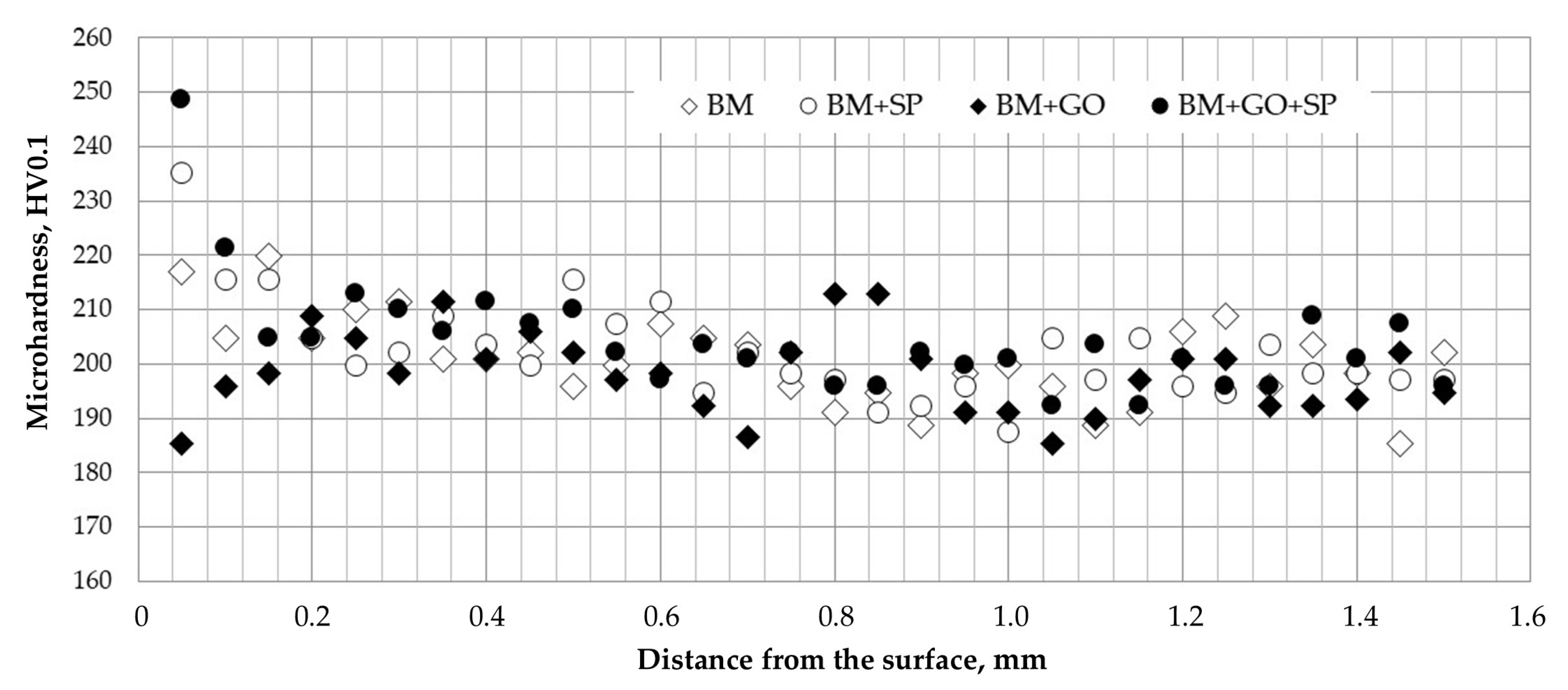
3.4. Microhardness Testing
3.5. Structural Roughness
3.6. Residual Stresses
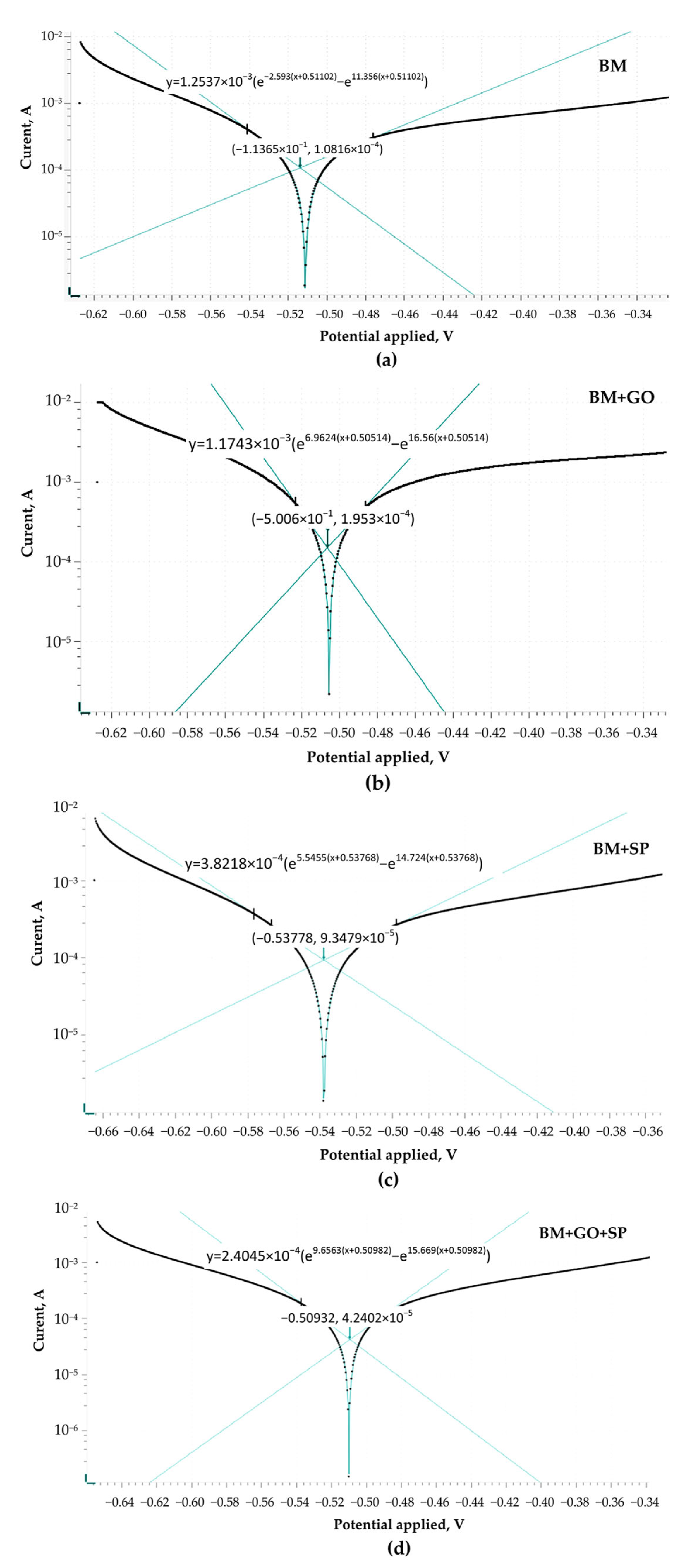
3.7. Electrochemical Corrosion
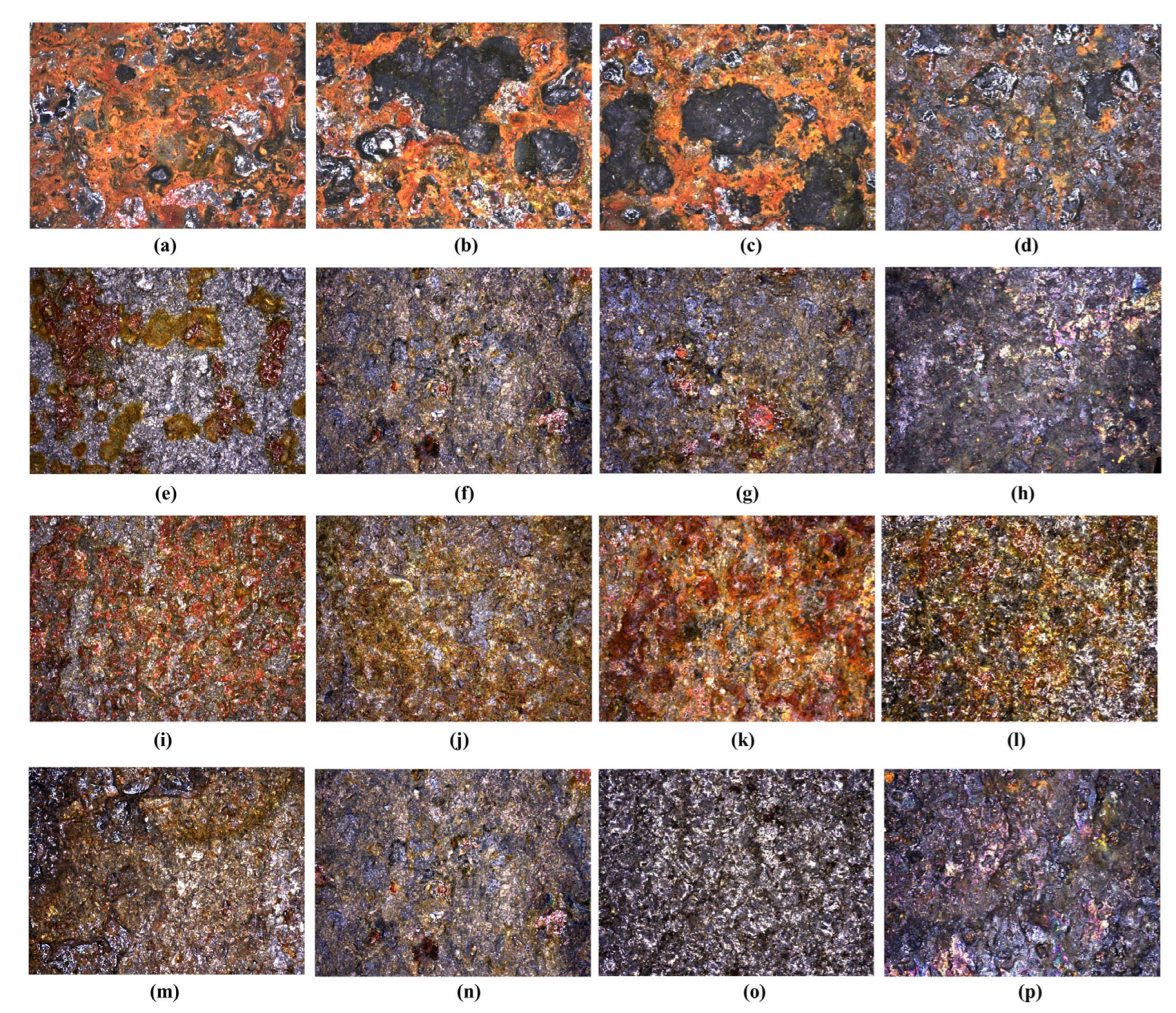
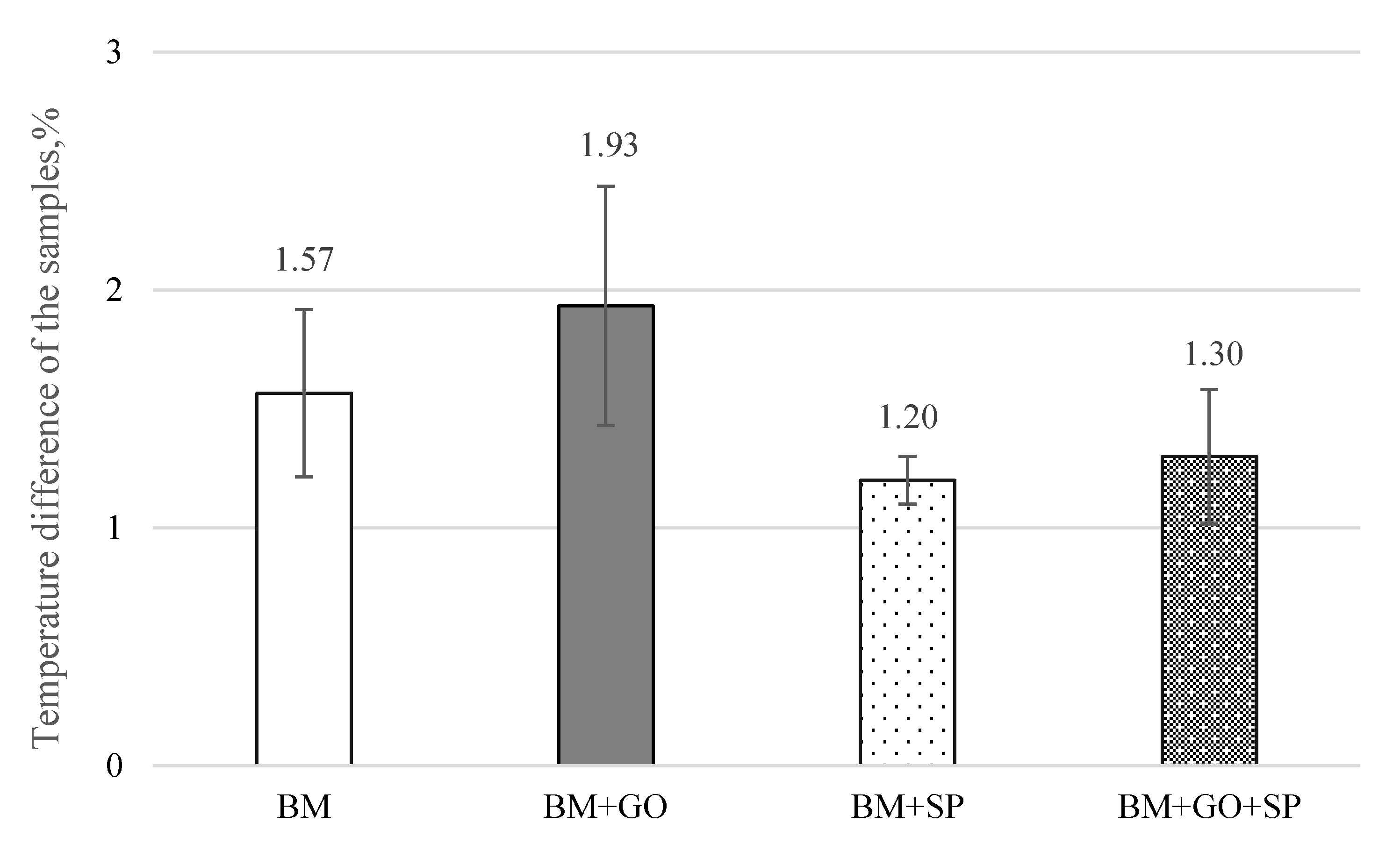
3.8. Ageing and Thermal Shock Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Structural studies using an optical microscope and XRD revealed the presence of ferrite (α-Fe) and trace amounts of austenitic steel (γ-Fe).
- The surface of the base material (30HGSA steel), despite having undergone quenching and tempering, was also subjected to sandblasting. This was confirmed by surface elemental analysis of the samples. The sandblasting process was not indicated in the material specification provided by the steel manufacturer.
- The surface roughness of the base material samples was Ra = 9.05 µm. It slightly decreased after the GO coating process to Ra = 8.87 µm and increased after shot peening to Ra = 12.40 µm for BM + SP samples and Ra = 11.55 µm for BM + GO + SP samples.
- Shot peening and hybrid graphening resulted in an increase in compressive residual stresses. For BM + SP samples, the increase was σx by 158% and σy by 165%; for BM + GO + SP samples, the increase was σx by 127% and σy by 152%, relative to the stress state in the base material.
- The maximum force required for three-point bending increased by 43% after hybrid graphening for BM + GO + SP samples compared to the base material (BM).
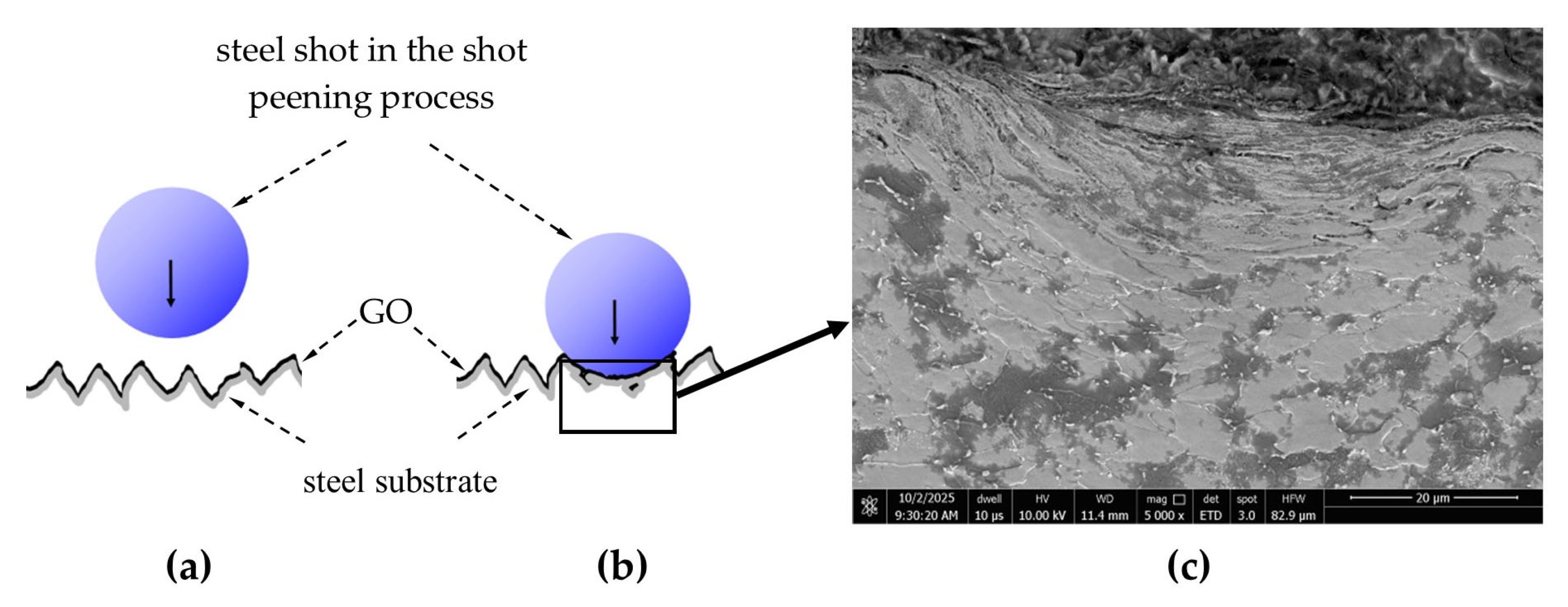
- Surface topography analysis of BM + GO samples revealed uniform and durable graphene oxide coverage, which contributed to the reduction in surface roughness as a result of plasma cleaning prior to deposition.
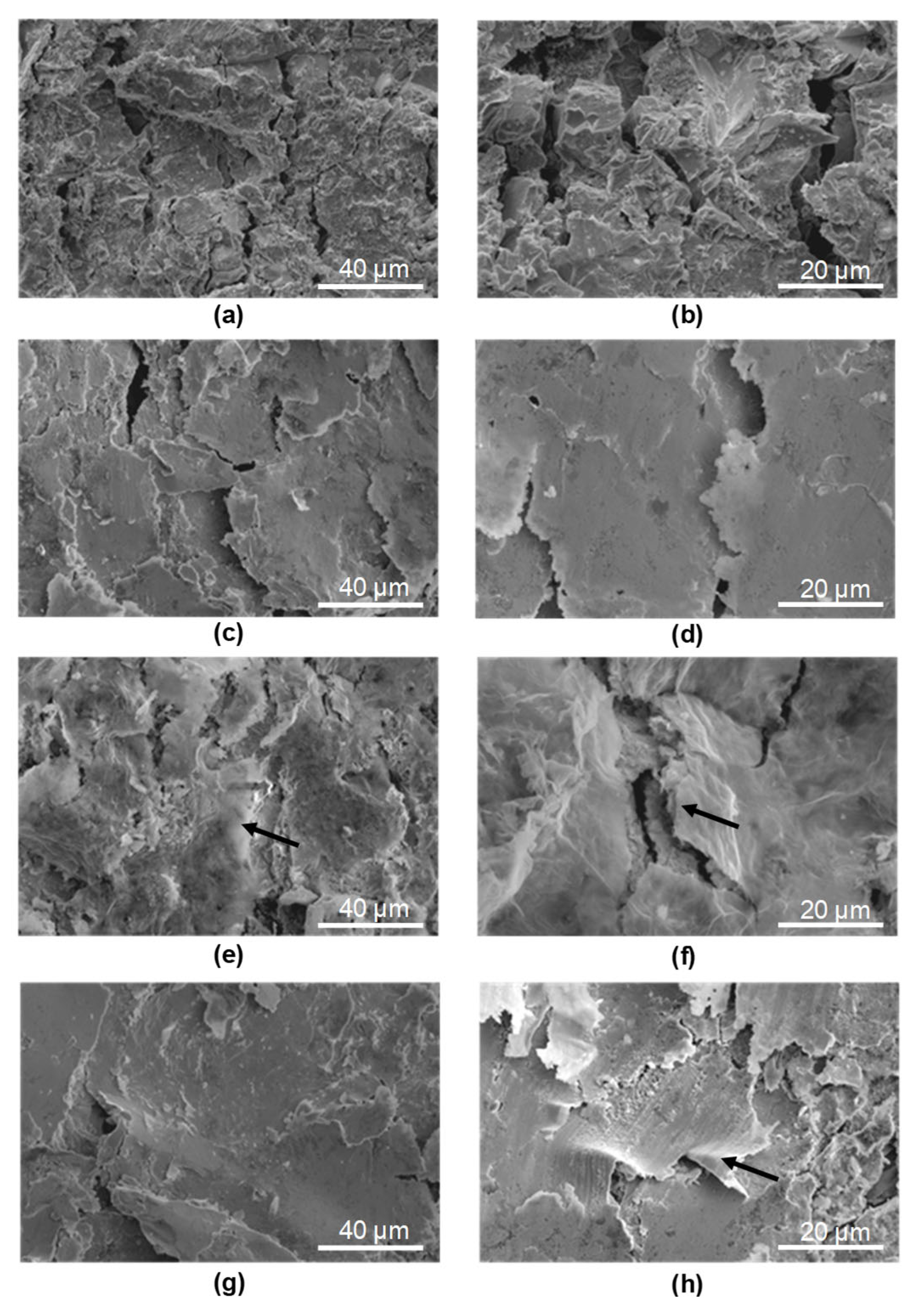
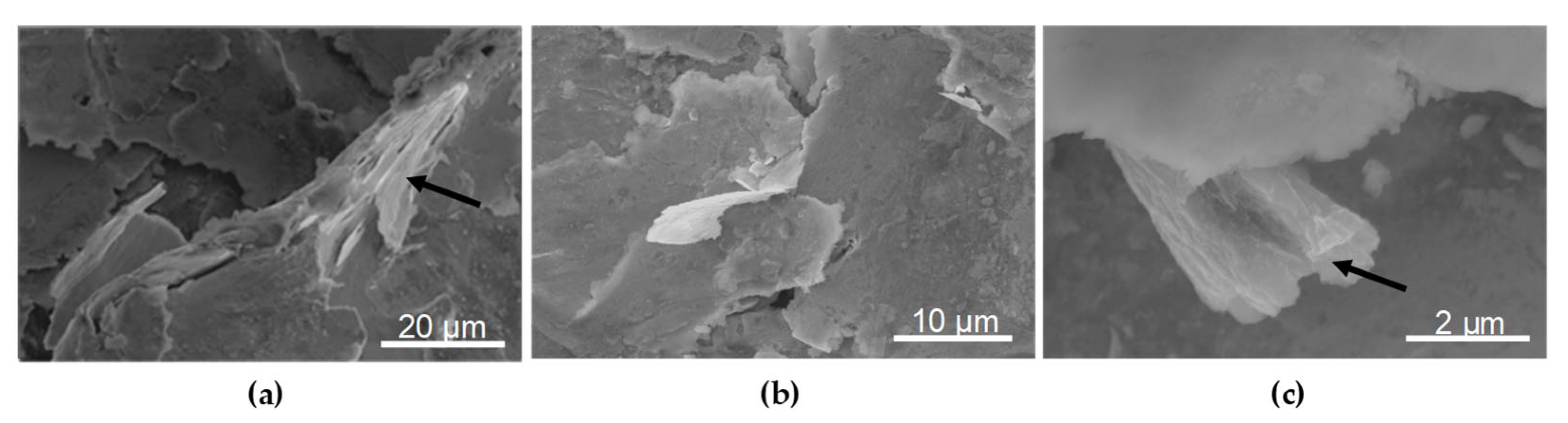
- Examination of hybrid graphening samples (BM + GO + SP) after three-point bending revealed the presence of graphene oxide flakes embedded within the shot peening surface layer at the points of maximum deflection.
- Based on the conducted observations of the effects of GO and shot peening, a mechanism for hybrid graphening was proposed [7]. This mechanism is based on the entrapment of GO flakes within plastically deformed surface irregularities created by the impact of shot particles during the peening process.
- The surface images after thermal shocks and ageing confirm that the application of the SP + GO combination enhances the material’s resistance to environmental conditions acting on its surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mason, H. Graphene 101: Forms, Properties and Applications; Gardner Business Media: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, S.A.; Galhena, D.T.L. Trajectory of Graphene-Based Aerospace Applications; Versarien PLC: Gloucestershire, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Alemour, B. A Review of Using Conductive Composite Materials in Solving Lightning Strike and Ice Accumulation Problems in Aviation. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manag. 2019, 11, e1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D. Functional NiAl-graphene oxide composite as a model coating for aerospace component repair. Carbon 2016, 105, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, G.; Suo, T. Impact Dynamics for Advanced Aerospace Materials and Structures. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2023, 36, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakonieczny, A. Dynamiczna Powierzchniowa Obróbka Plastyczna; Instytut Mechaniki Precyzyjnej: Warsaw, Poland, 2002. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Nasiłowska, B. Tlenek Grafenu—Badania Wpływu na Właściwości Funkcjonalne Materiałów; WAT: Warsaw, Poland, 2023; ISBN 978-83-7938-398-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sasikumar, K.S.K.; Dineshkumar, K.; Deeban, K.; Sambathkumar, M.; Saravanan, N. Effect of shot peening on surface properties of Al7075 hybrid aluminum metal matrix composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 2792–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, B.; Bi, S.; Zhang, P.; Tian, Q.; Yu, Z. Exploring salt-mist corrosion resistance of GPTMS functionalized graphene oxide reinforced epoxy resin composite coating on shot peening Ti-15333 titanium alloy. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 44, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Vaezi, M.R.; Rashidi, A.; Bagherzadeh, M.R. Distinctive roles of silane coupling agents on the corrosion inhibition performance of graphene oxide in epoxy coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 111, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrollahi, S.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Yari, H.; Ramezanzadeh, M.; Mahdavian, M. Synthesis of polyaniline-modified graphene oxide for obtaining a high performance epoxy nanocomposite film with excellent UV blocking/anti-oxidant/anti-corrosion capabilities. Compos B Eng. 2019, 173, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, S. Characterization on Aluminum Alloy 7050 Metal Matrix Composite Reinforced with Graphene Nanoparticles. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 30, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Rathi, K.; Pal, K. Synthesis, characterization of graphene oxide wrapped silicon carbide for excellent mechanical and damping performance for aerospace application. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 740, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Mišković-Stanković, V. A Review of the Corrosion Behaviour of Graphene Coatings on Metal Surfaces Obtained by Chemical Vapour Deposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 021505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yan, F.; Yan, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Ma, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Graphene-based anticorrosion coatings for steel: Fundamental mechanism, recent progress and future perspectives. Prog. Org. Coat. 2025, 200, 108966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xue, Q. Corrosion mechanism of graphene coating with different defect levels. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.R.; Chen, J.; Zhu, M.Y.; Zhang, F.J.; Hu, Q.F.; Oh, W.C. Research on anti-corrosion graphene coatings with promising properties. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2024, 61, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasai, D.; Tuberquia, J.C.; Harl, R.R.; Jennings, G.K.; Bolotin, K.I.; Coating, C.-I.; Nano, A.C. Graphene: Corrosion-Inhibiting Coating. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, G.J.; Zhao, K. Defects mediated corrosion in graphene coating layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017, 9, 11902–11908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, M.; Akita, K.; Itano, Y.; Imafuku, M.; Ohya, S. X-ray diffraction study on microstructures of shot/laser-peened AISI316 stainless steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 443, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Jiang, C.H.; Ji, V. Effect of prestress state on surface layer characteristic of S30432 austenitic stainless steel in shot peening process. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Jiang, C.H.; Ji, V. Surface mechanical properties of S30432 austenitic steel after shot peening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 9559–9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Jiang, C.H.; Ji, V. Uniformity of residual stress distribution on the surface of S30432 austenitic stainless steel by different shot peening processes. Mater. Lett. 2013, 99, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakuwa, O.; Soyama, H. Suppression of hydrogen-assisted fatigue crack growth in austenitic stainless steel by cavitation peening. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 5268–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O. A comprehensive investigation on the effects of laser and shot peening on fatigue crack growth in friction stir welded AA2195 joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2009, 31, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moridi, S.M.; Guagliano, A.; Ghidini, M.; Boniardi, A. The effect of nitriding, severe shot peening and their combination on the fatigue behavior and microstructure of a low-alloy steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 62, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiłowska, B.; Bogdanowicz, Z.; Mierczyk, Z. Sposób Grafenowania Hybrydowego z Wykorzystaniem Zabiegu Kulowania. Polish Patent P.438715, 25 Novermber 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiłowska, B.; Bogdanowicz, Z.; Hińcza, K.; Mierczyk, Z.; Góźdź, S.; Djas, M.; Kowiorski, K.; Bombalska, A.; Kowalik, A. Graphene Oxide Aerosol Deposition and its Influence on Cancer Cells. Prelim. Results Mater. 2020, 13, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakonieczny, A.; Kamowicz, S.; Mońka, G.; Kozlowsky, W.; Lamprecht, E. Sposób Dynamicznej, Powierzchniowej Obróbki Plastycznej Przedmiotów i Urządzenie do Dynamicznej, Powierzchniowej Obróbki Plastycznej Przedmiotów. Polish Patent P.376544, 8 Auguest 2024. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 7438:2016; Metallic Materials—Bend Test. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.


| Elemental Composition | C | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [%] | 0.31 | 0.99 | 0.017 | 0.0007 | 0.87 | 0.24 | 0.19 |
| Ra | Rq | Rz | Rp | Rv | Rt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µm | ||||||
| Surface of the base material (BM) | 9.053 | 11.464 | 52.461 | 34.775 | 33.068 | 67.843 |
| Surface of the GO-coated sample (BM + GO) | 8.871 | 11.436 | 44.826 | 30.740 | 41.223 | 71.963 |
| Surface of the shot peening sample (BM + SP) | 12.406 | 15.542 | 62.514 | 32.894 | 48.133 | 81.027 |
| Surface of the hybrid graphening sample (BM + GO + SP) | 11.556 | 14.094 | 61.884 | 32.387 | 39.850 | 72.237 |
| Sample | Ecorr. (V) | jcorr. (×10−4 A/cm2) | Polarization Resistance (kΩ) | Corrosion Rate (mm/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM | −0.51365 | 1.0361 | 91.019 | 2.4079 |
| BM + SP | −0.53778 | 0.38998 | 129.09 | 0.90746 |
| BM + GO | −0.50606 | 0.9705 | 36.202 | 2.2583 |
| BM + GO + SP | −0.50932 | 0.19872 | 164.22 | 0.46241 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stabryn, S.; Nasiłowska, B.; Szczepaniak, R.; Mucha, M.; Mońka, G.; Rygier, T.; Chrzanowski, W.; Chrunik, M.; Olejnik, P.; Kutwin, M.; et al. The Effect of Graphene Oxide Deposition, Shot Peening, and Hybrid Graphening on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of 30HGSA Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 4853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214853
Stabryn S, Nasiłowska B, Szczepaniak R, Mucha M, Mońka G, Rygier T, Chrzanowski W, Chrunik M, Olejnik P, Kutwin M, et al. The Effect of Graphene Oxide Deposition, Shot Peening, and Hybrid Graphening on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of 30HGSA Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214853
Chicago/Turabian StyleStabryn, Sebastian, Barbara Nasiłowska, Robert Szczepaniak, Mateusz Mucha, Grzegorz Mońka, Tomasz Rygier, Wojciech Chrzanowski, Maciej Chrunik, Piotr Olejnik, Marta Kutwin, and et al. 2025. "The Effect of Graphene Oxide Deposition, Shot Peening, and Hybrid Graphening on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of 30HGSA Steel" Materials 18, no. 21: 4853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214853
APA StyleStabryn, S., Nasiłowska, B., Szczepaniak, R., Mucha, M., Mońka, G., Rygier, T., Chrzanowski, W., Chrunik, M., Olejnik, P., Kutwin, M., & Bogdanowicz, Z. (2025). The Effect of Graphene Oxide Deposition, Shot Peening, and Hybrid Graphening on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of 30HGSA Steel. Materials, 18(21), 4853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214853









