Microstructural Mechanisms of Concrete Degradation Under Different Coal Gangue Sand Replacement Ratios
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Establishing a unified energy–force-chain–crack coupling framework to evaluate the global, synergistic evolution of meso-scale parameters with replacement ratio;
- (2)
- Elucidating the intrinsic link between the structural stability of the force-chain network and internal energy reallocation—specifically, the shift from strain-energy-dominated storage to frictional/damping-dominated dissipation—as the driver of macroscopic brittle transition;
- (3)
- Providing direct experimental support via SEM for numerically revealed ITZ mechanisms (e.g., transformation from a dense “three-phase” to a porous “two-phase” structure), achieving cross-scale correspondence between micro-morphology and meso-mechanics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Macroscopic Experimental Program
2.1.1. Preparation of Concrete with Coal Gangue Manufactured Sand
2.1.2. Curing of Specimens
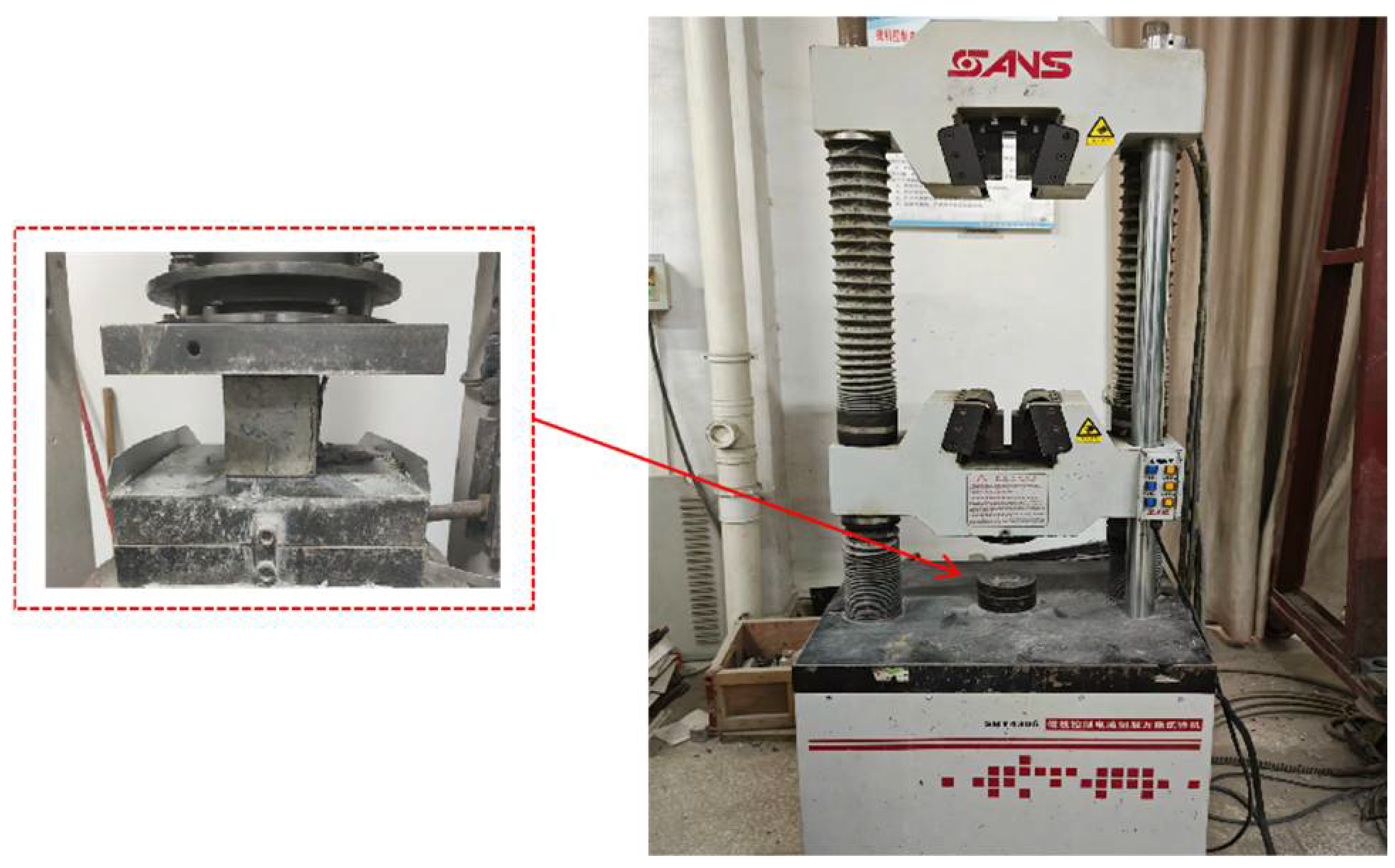
2.1.3. Compressive Strength Test on Cubes
2.2. Two-Dimensional DEM Modeling and Parameter Calibration of CGS Concrete
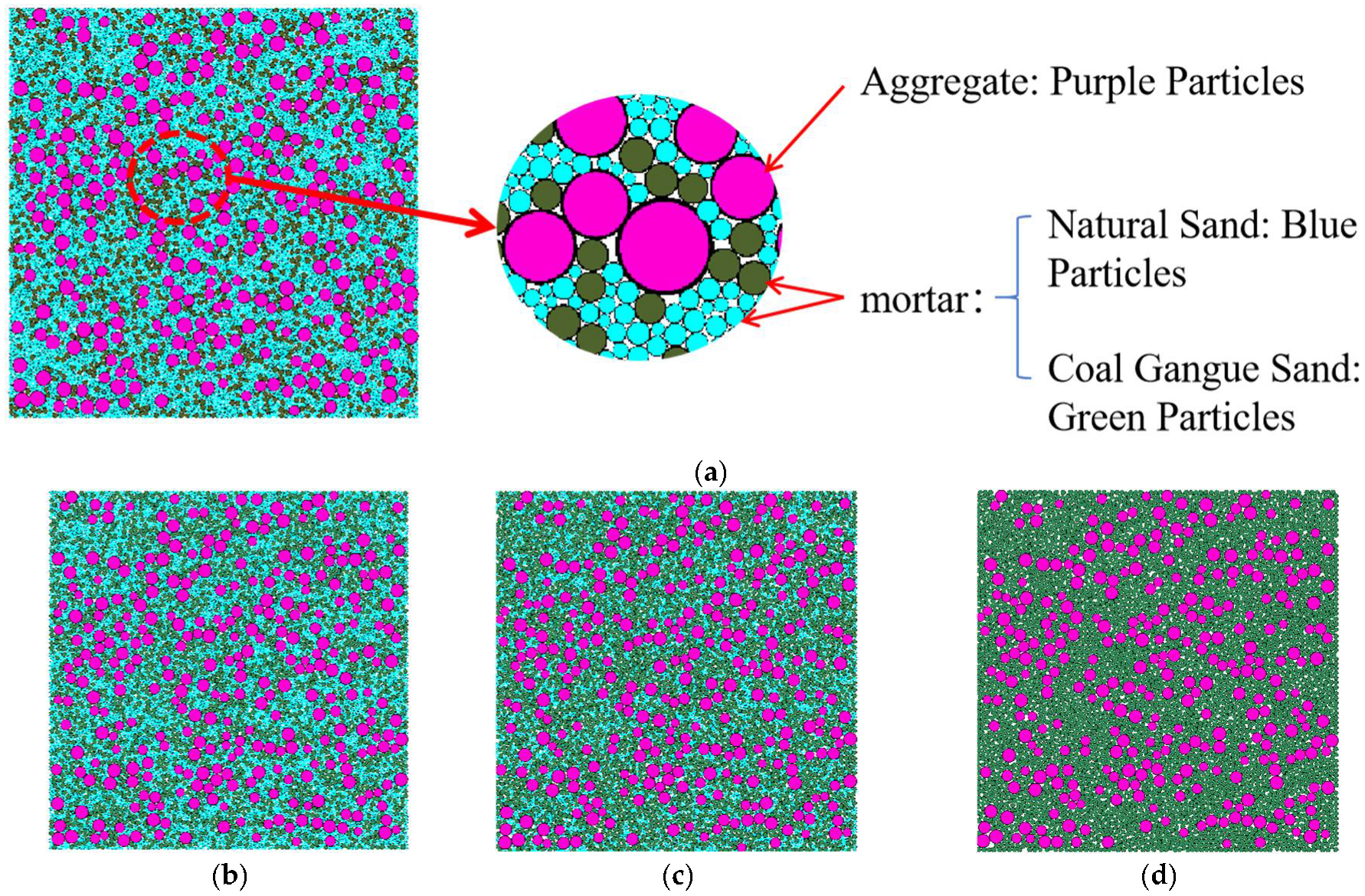
2.2.1. Construction of the 2D DEM Model
2.2.2. PFC2D-Based Discrete Element Simulation
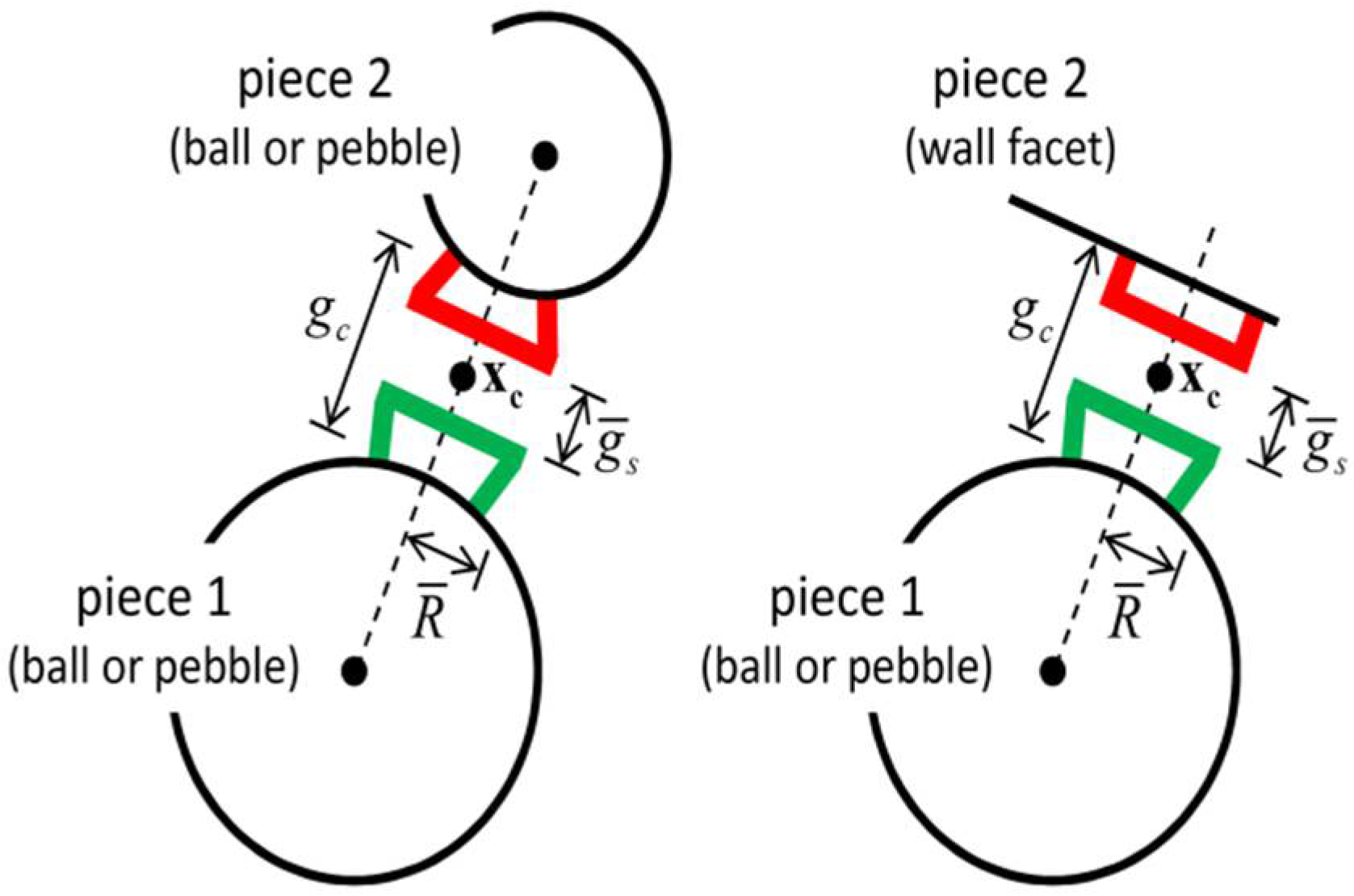
- (1)
- Updates of contact force and moment
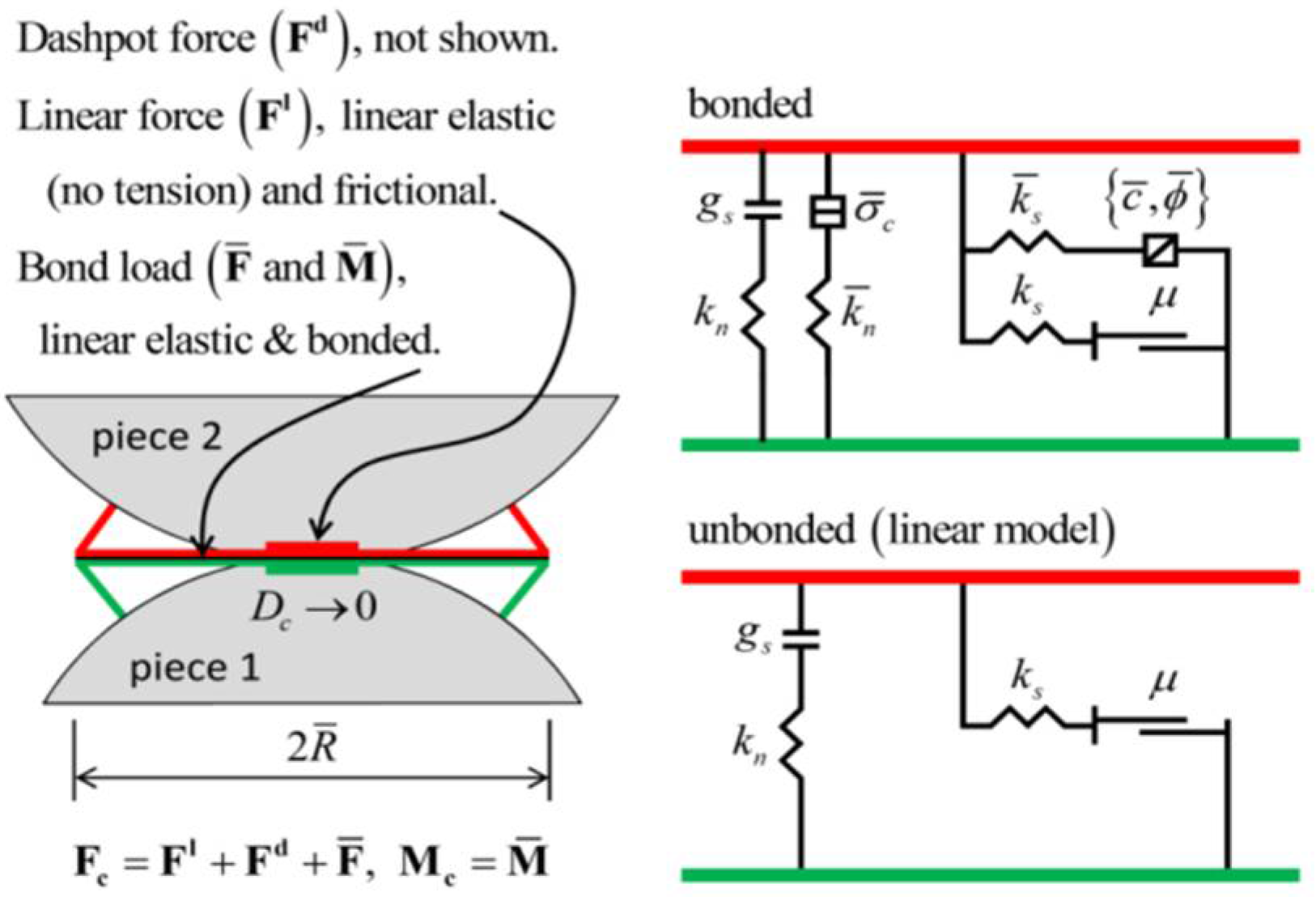
- (2)
- Bond formation and failure criterion
- (3)
- Parameters and applicability
- (4)
- Unified constitutive model and calibration
- (5)
- Definition, classification, and counting of microcracks
2.2.3. Parameter Calibration of the Model
2.2.4. PFC2D-Based Numerical Simulation Scheme
3. Results
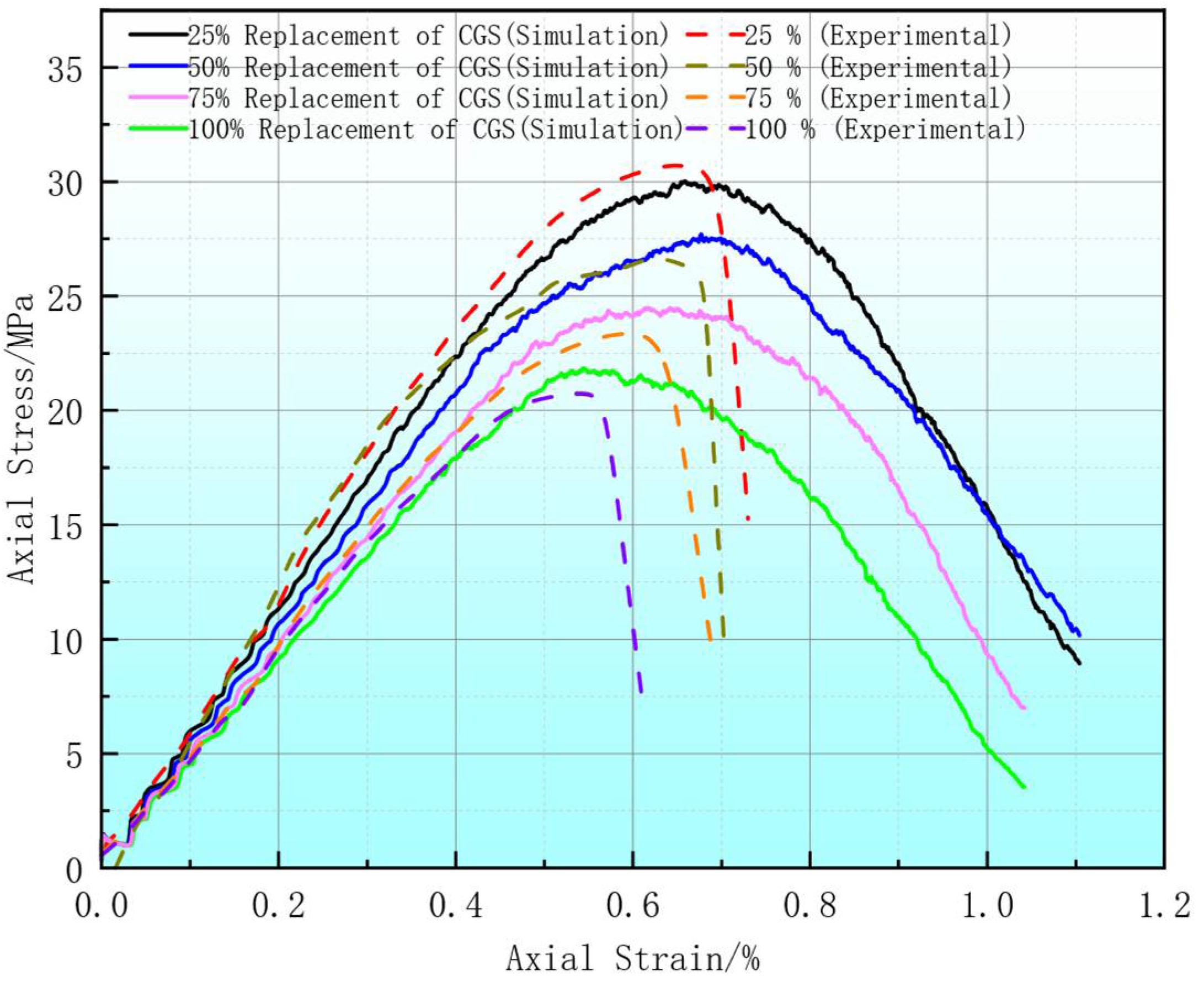
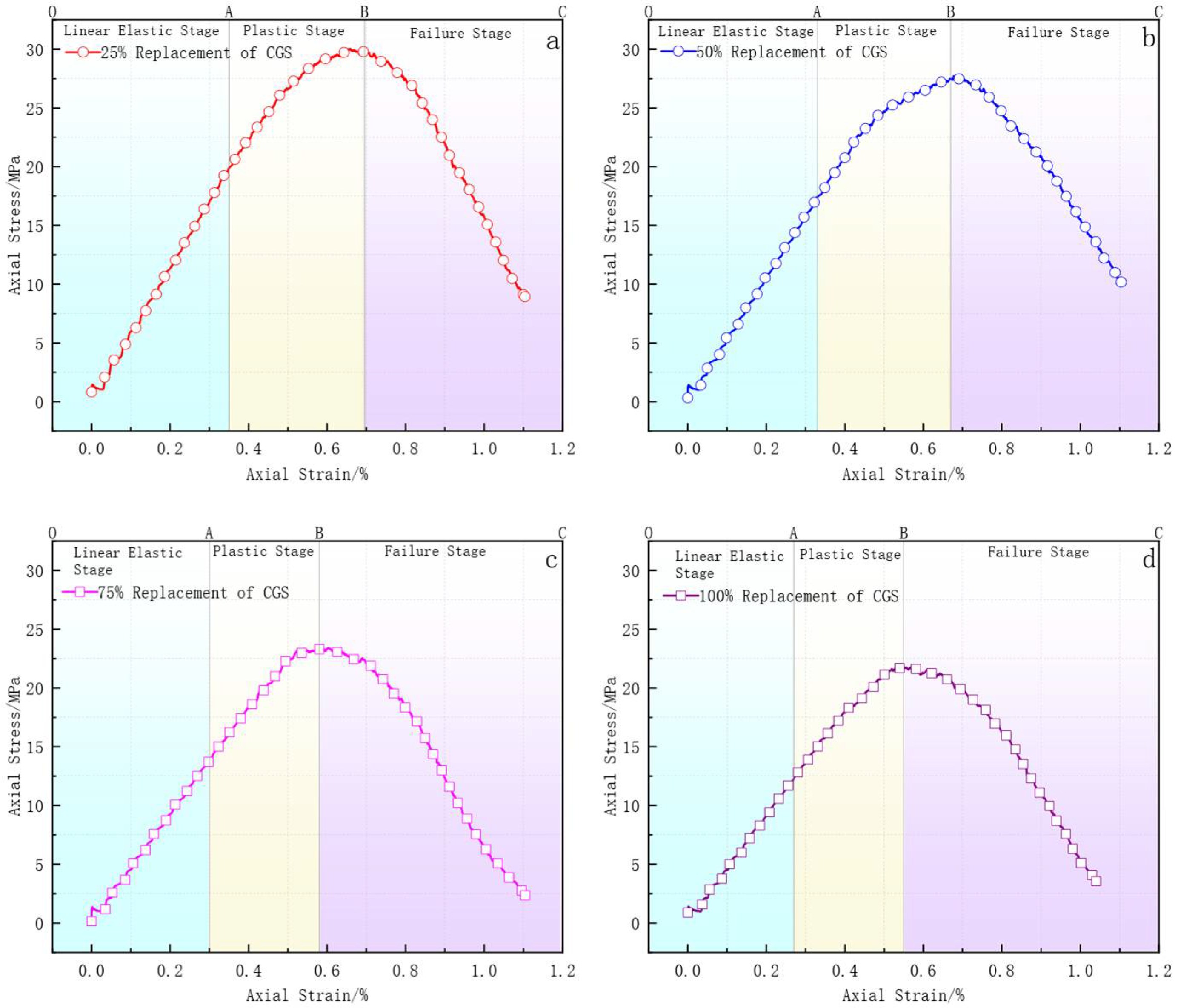
3.1. Analysis of Peak Stress and Strain
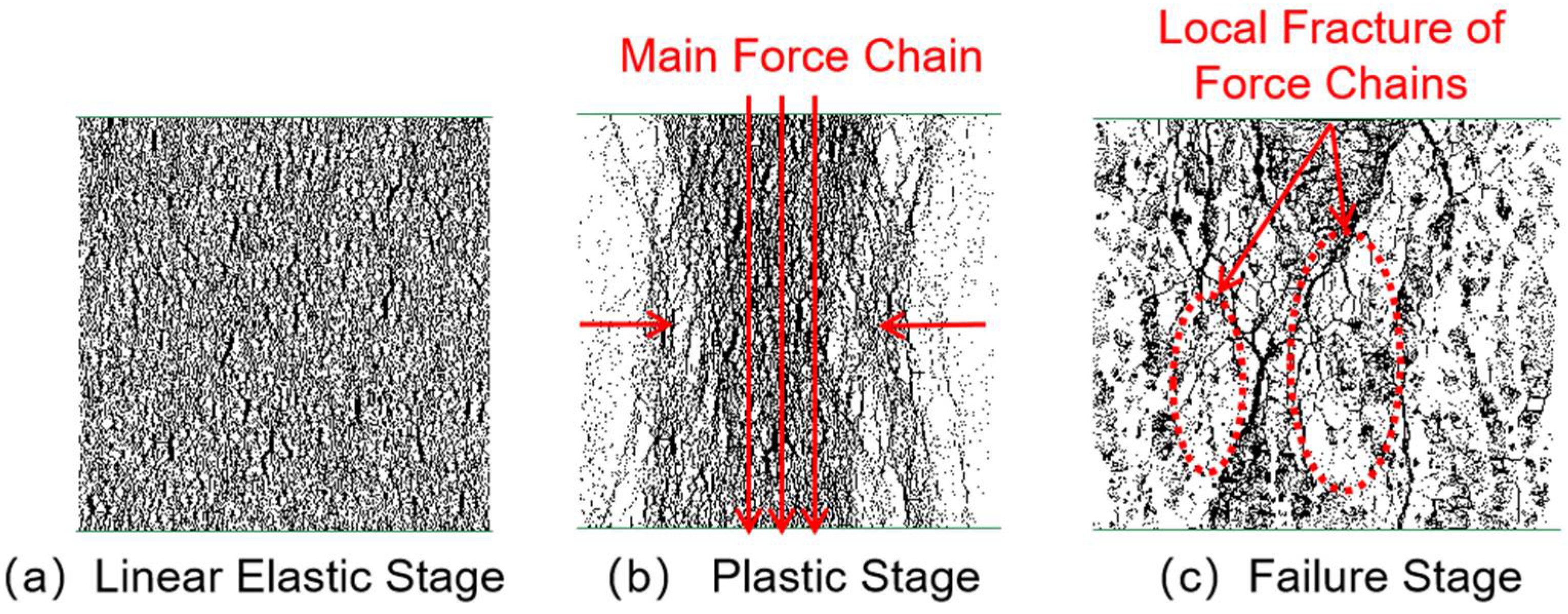
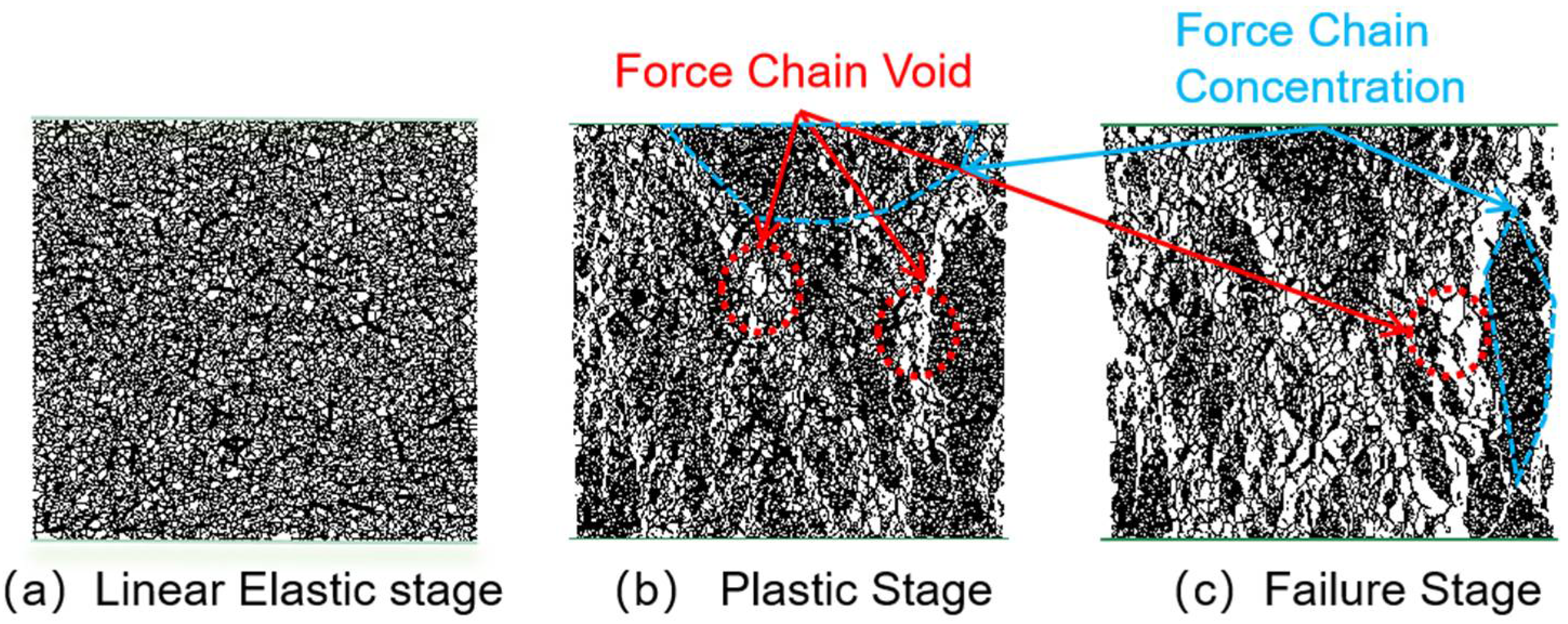
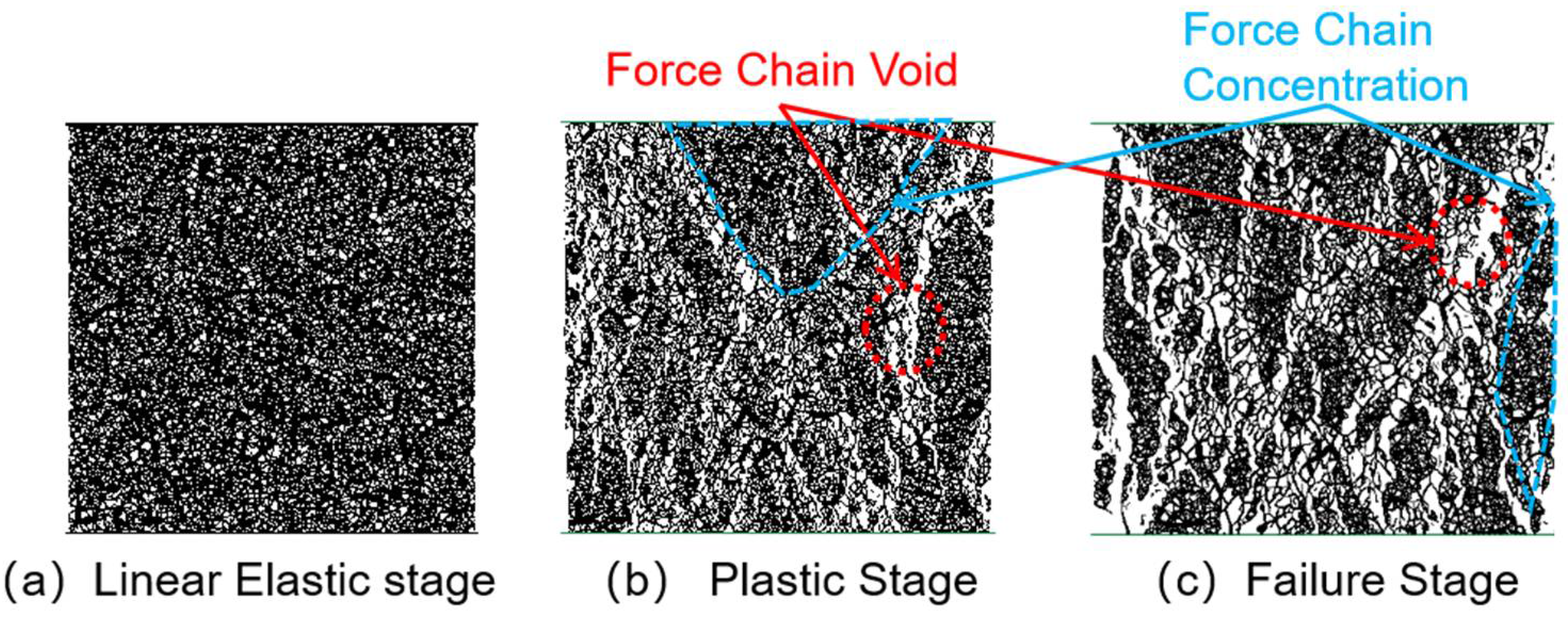
3.2. Force Chain Analysis
3.3. Crack Analysis
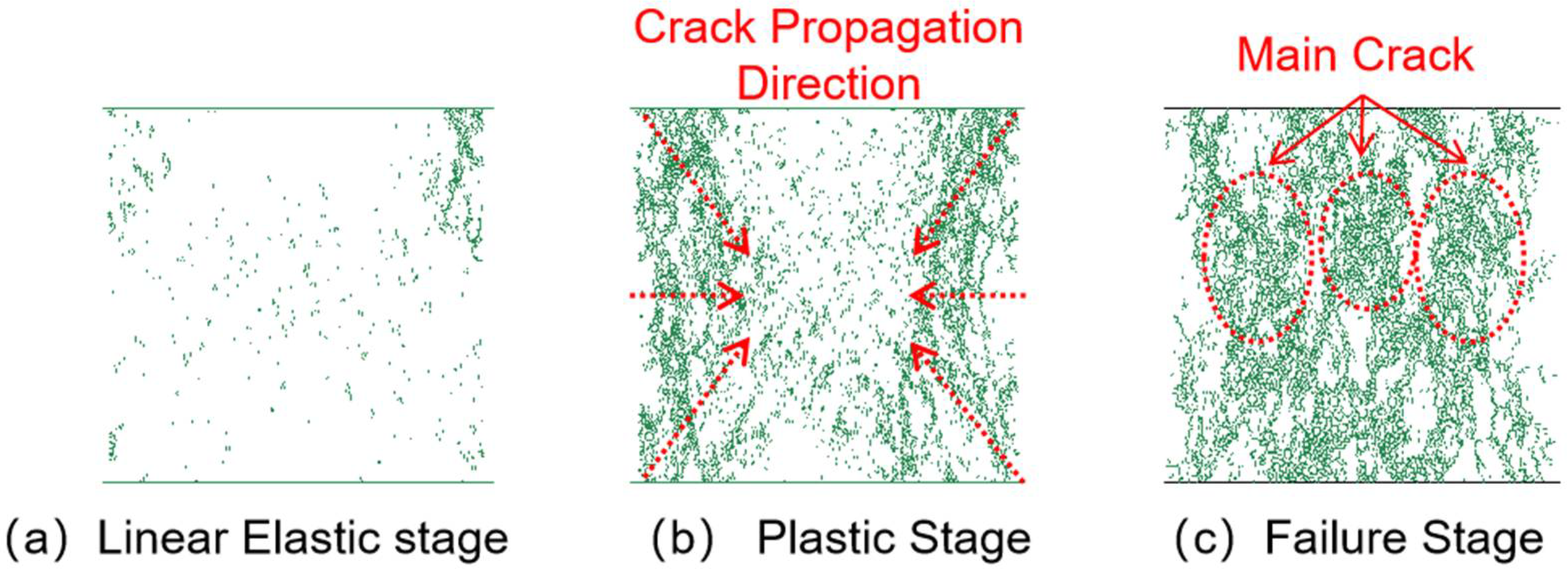
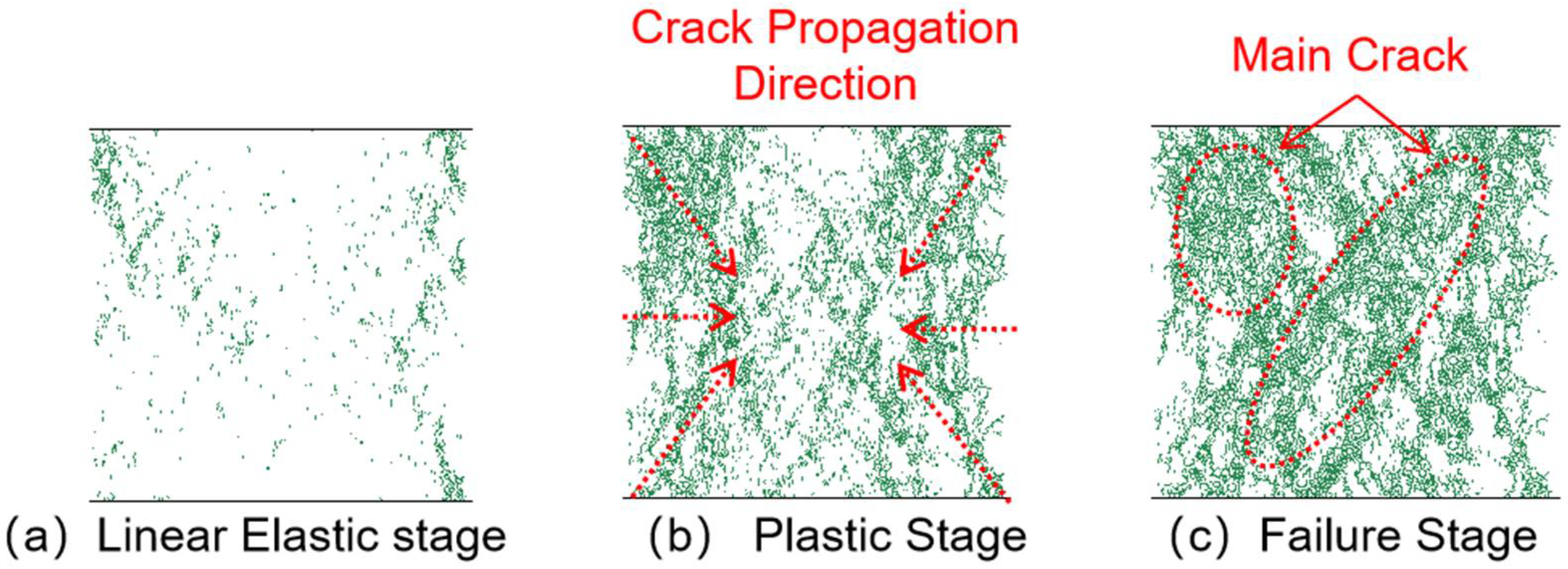
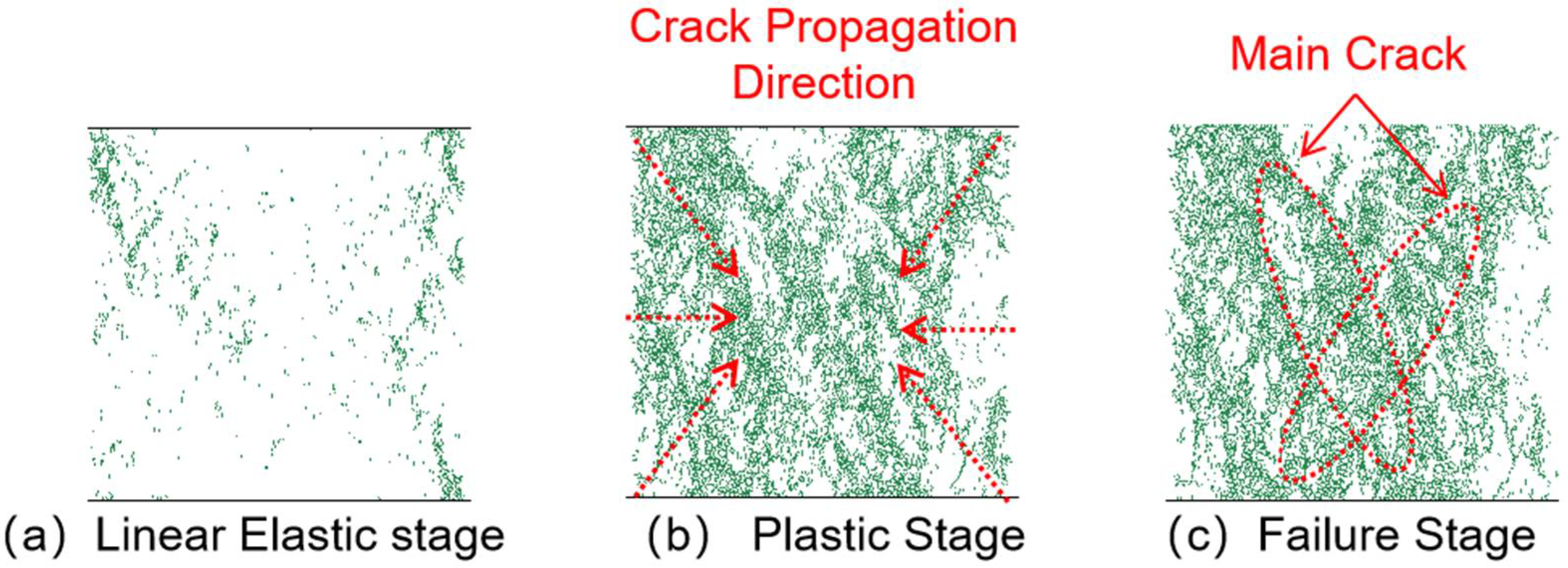
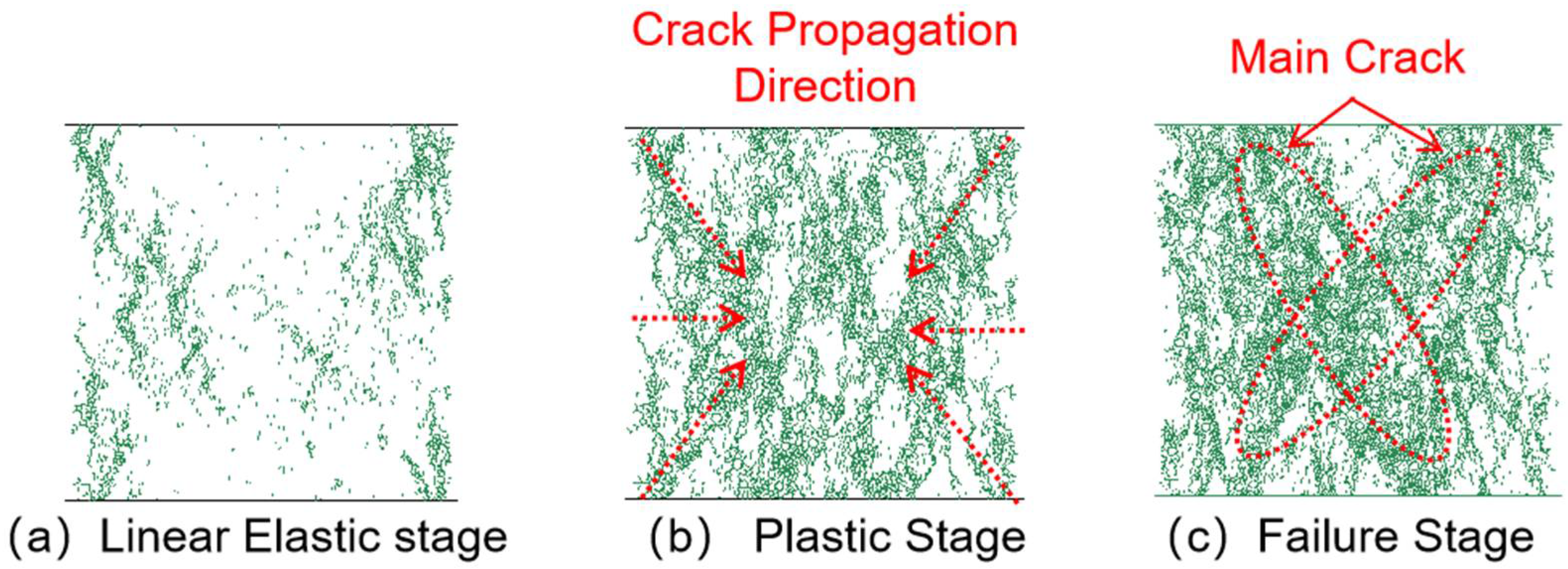
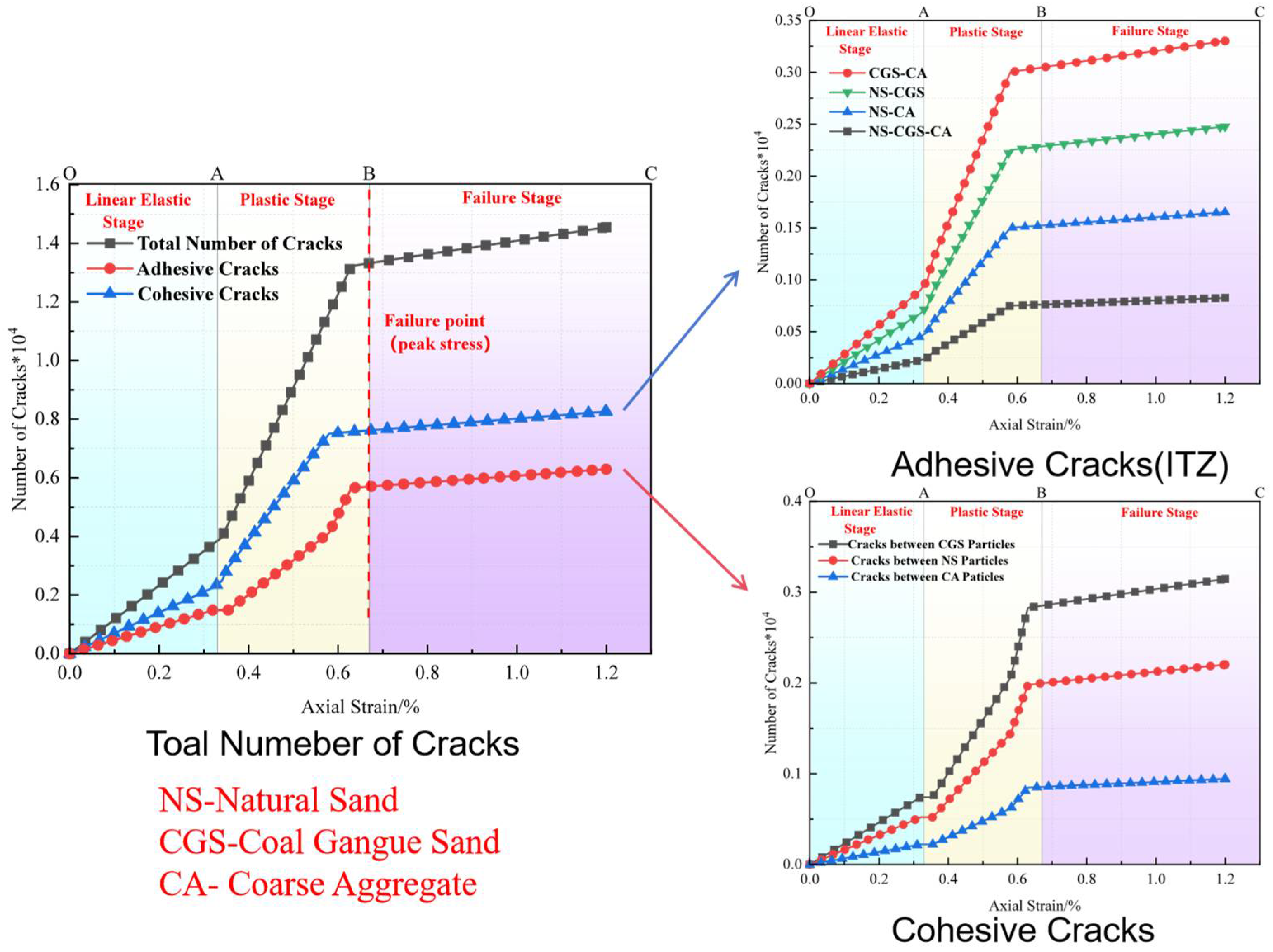
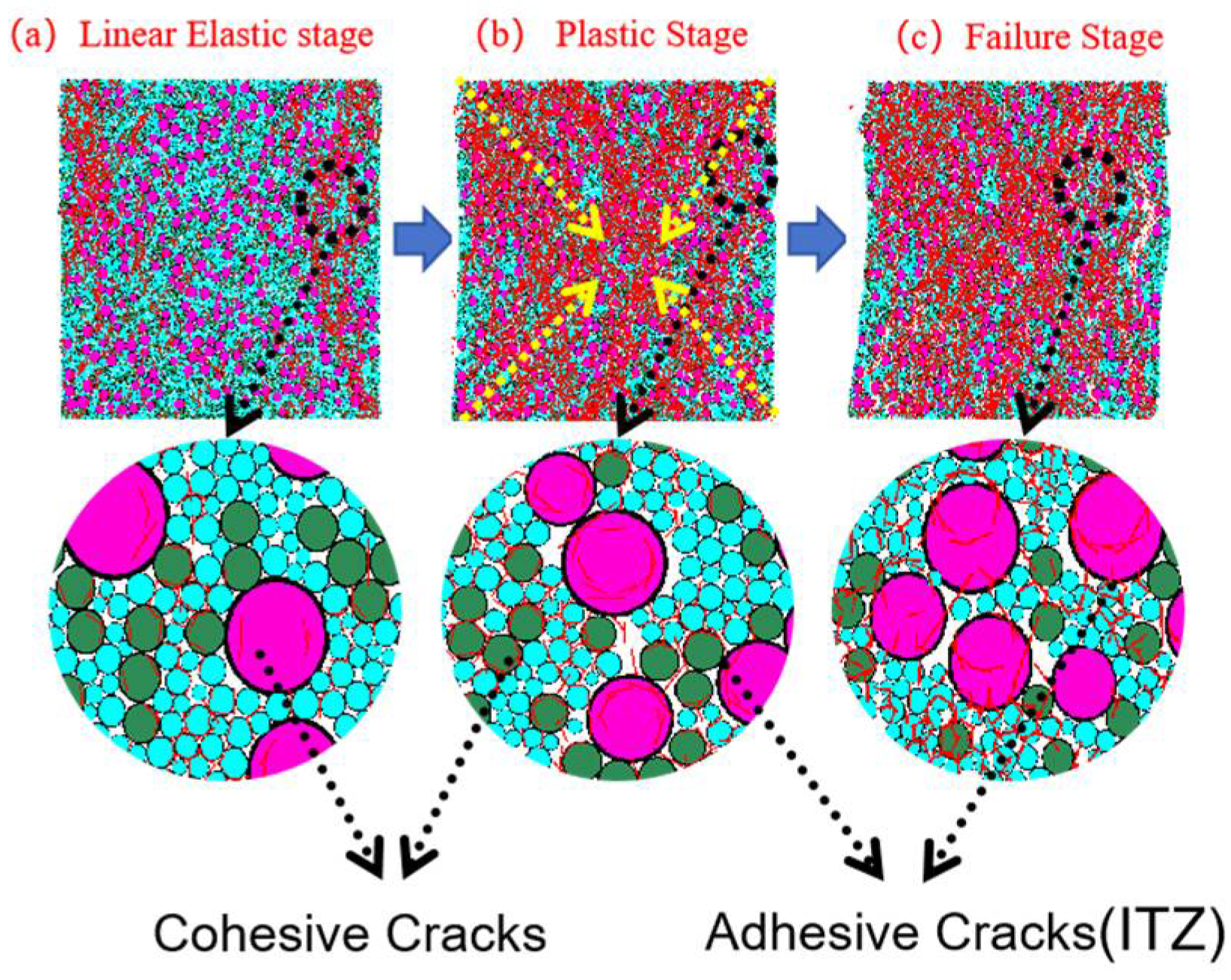
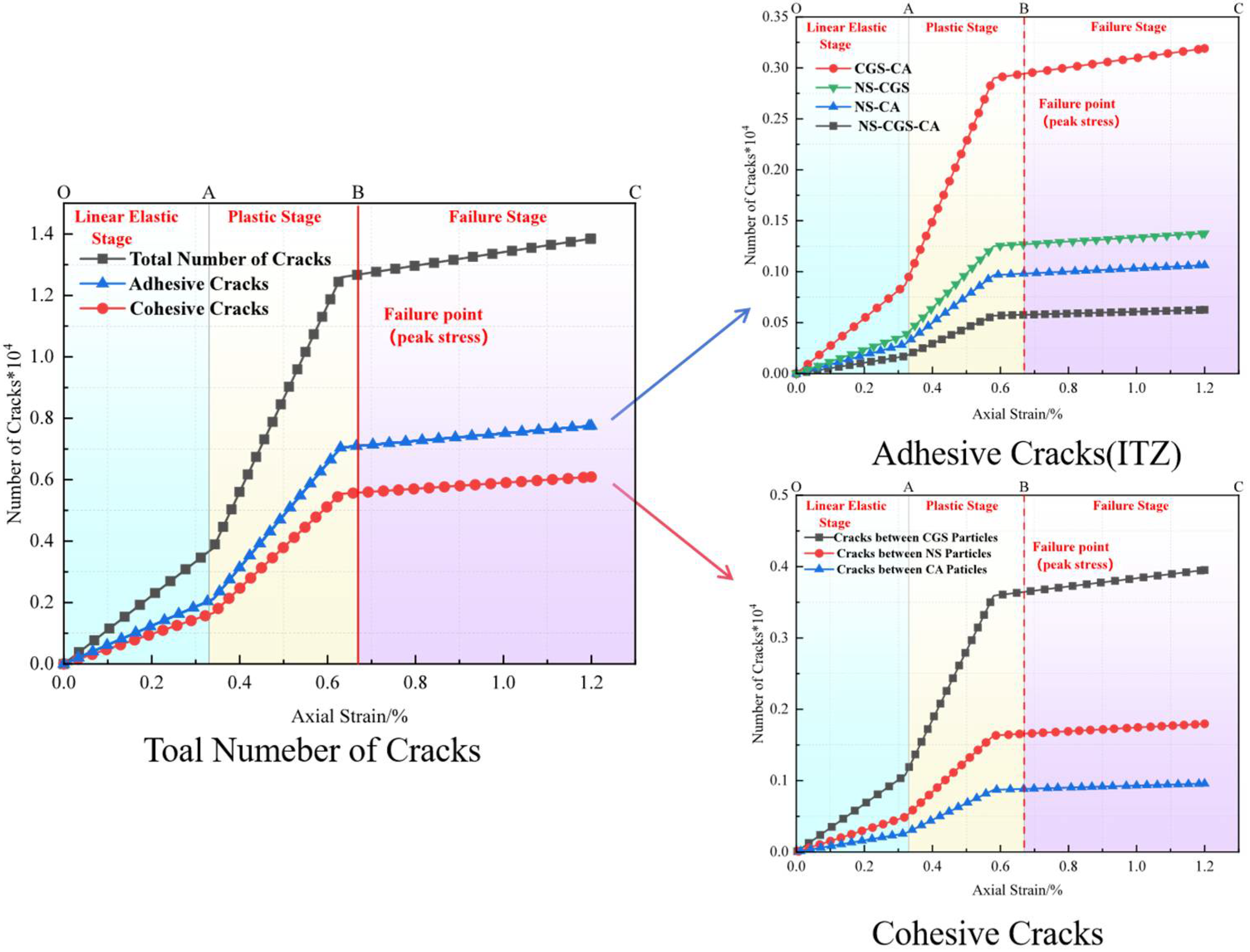
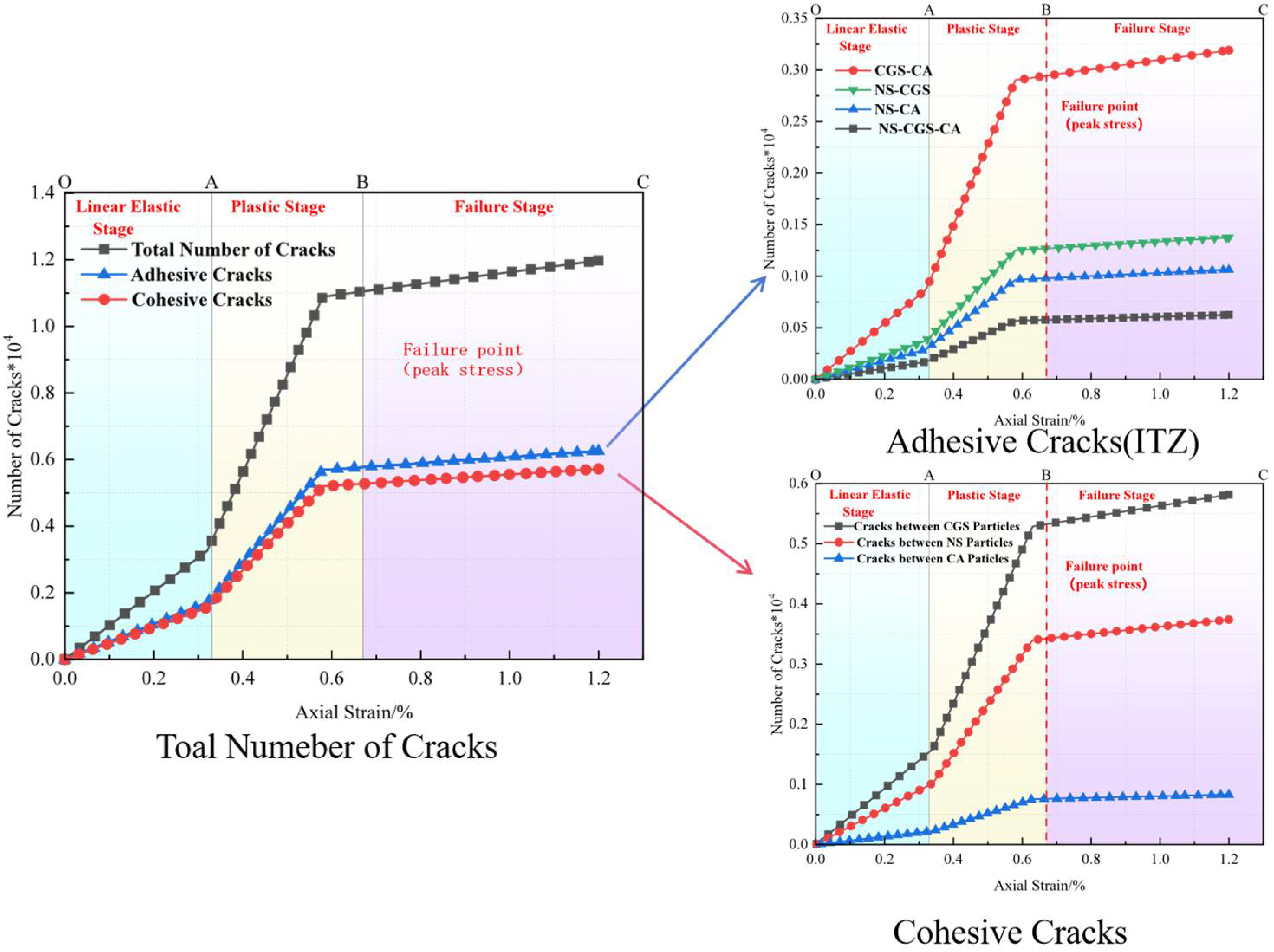
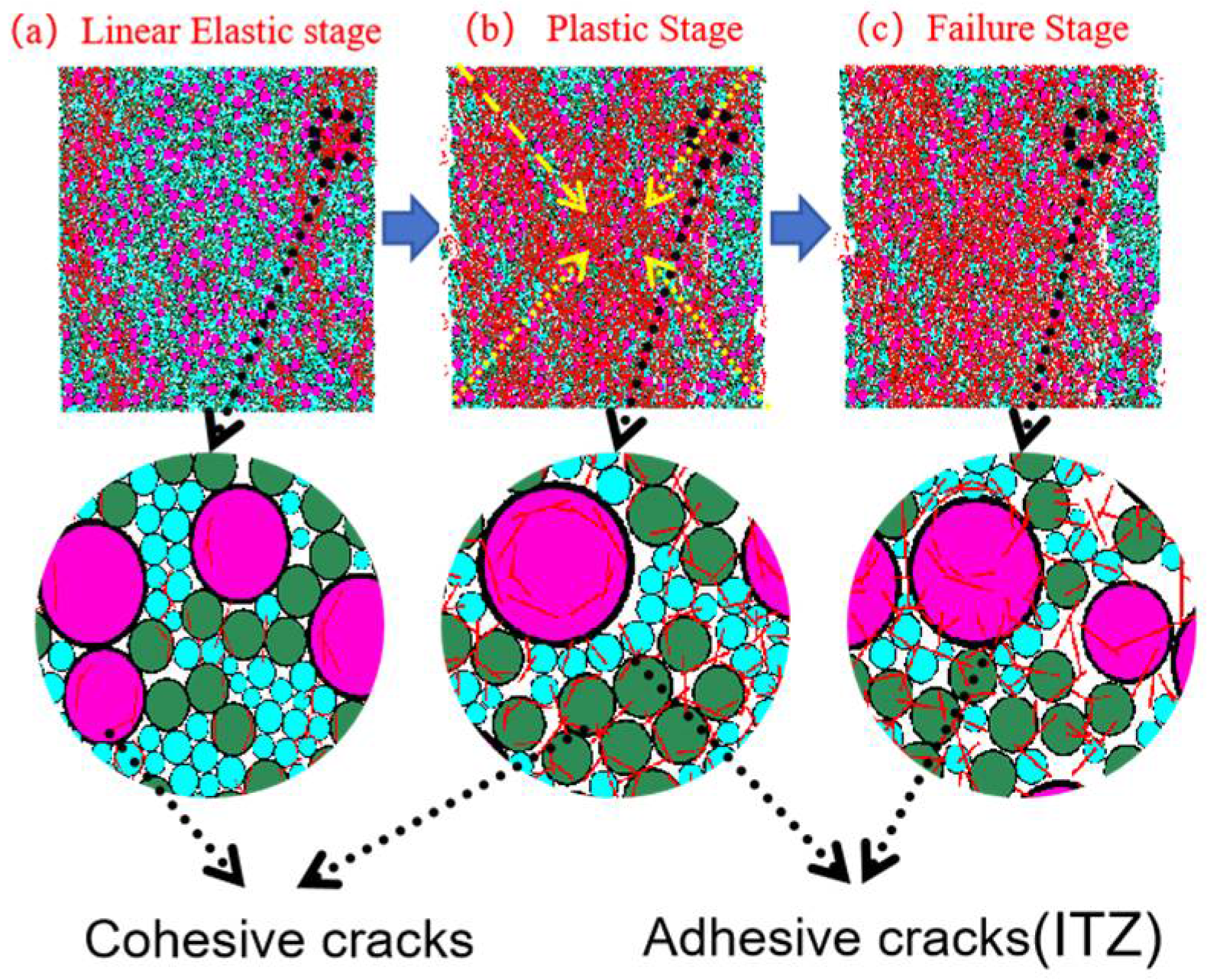
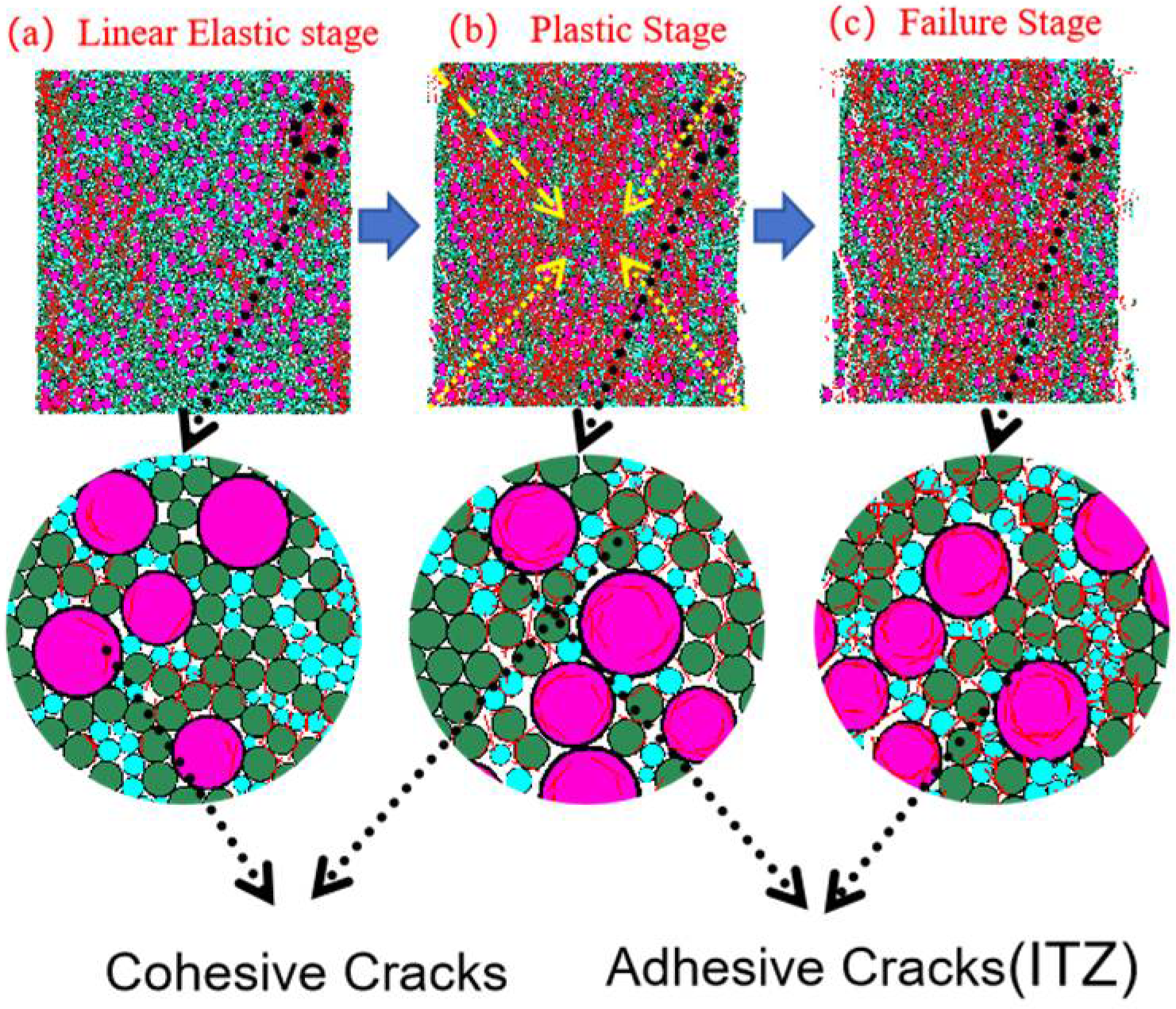
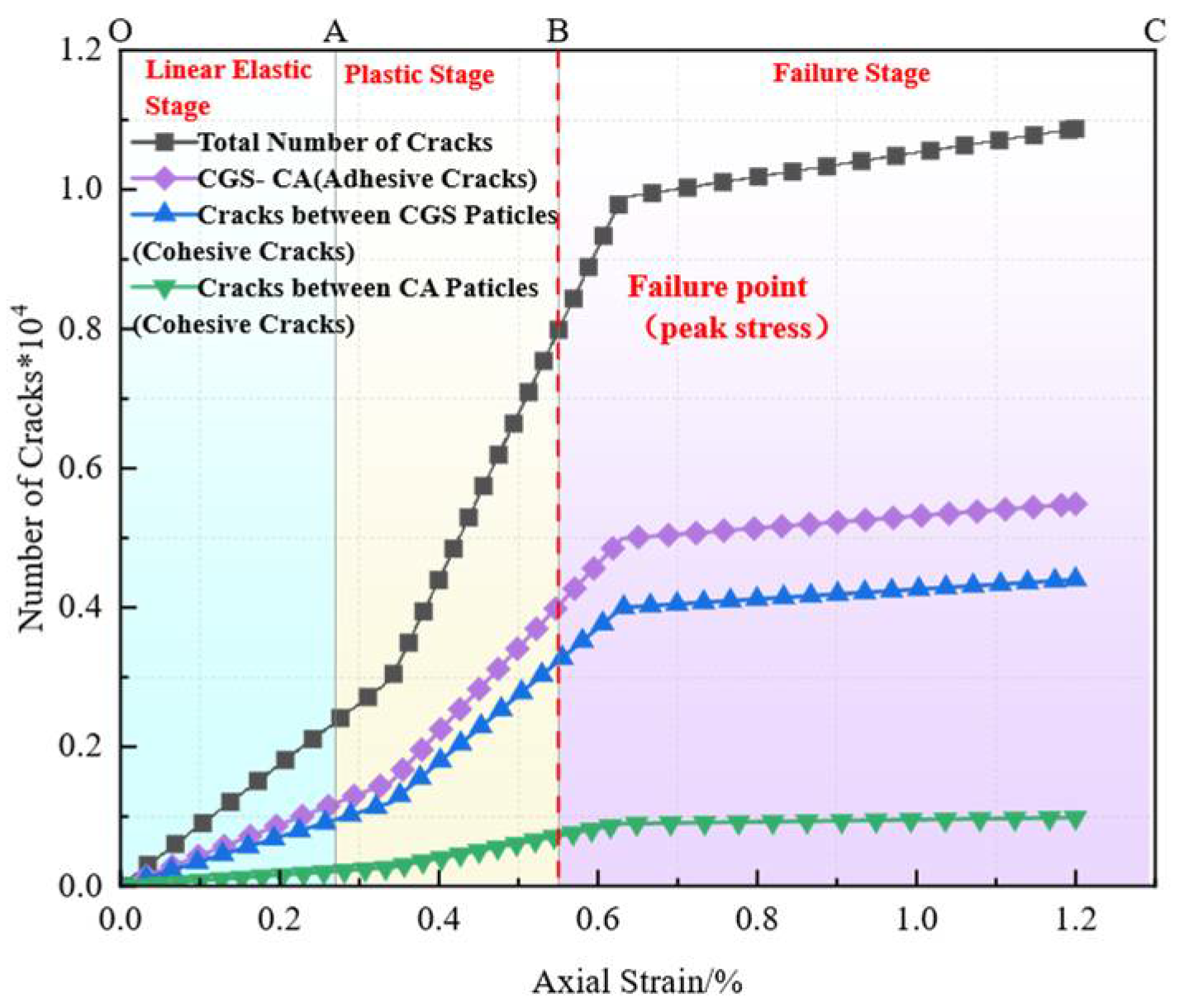
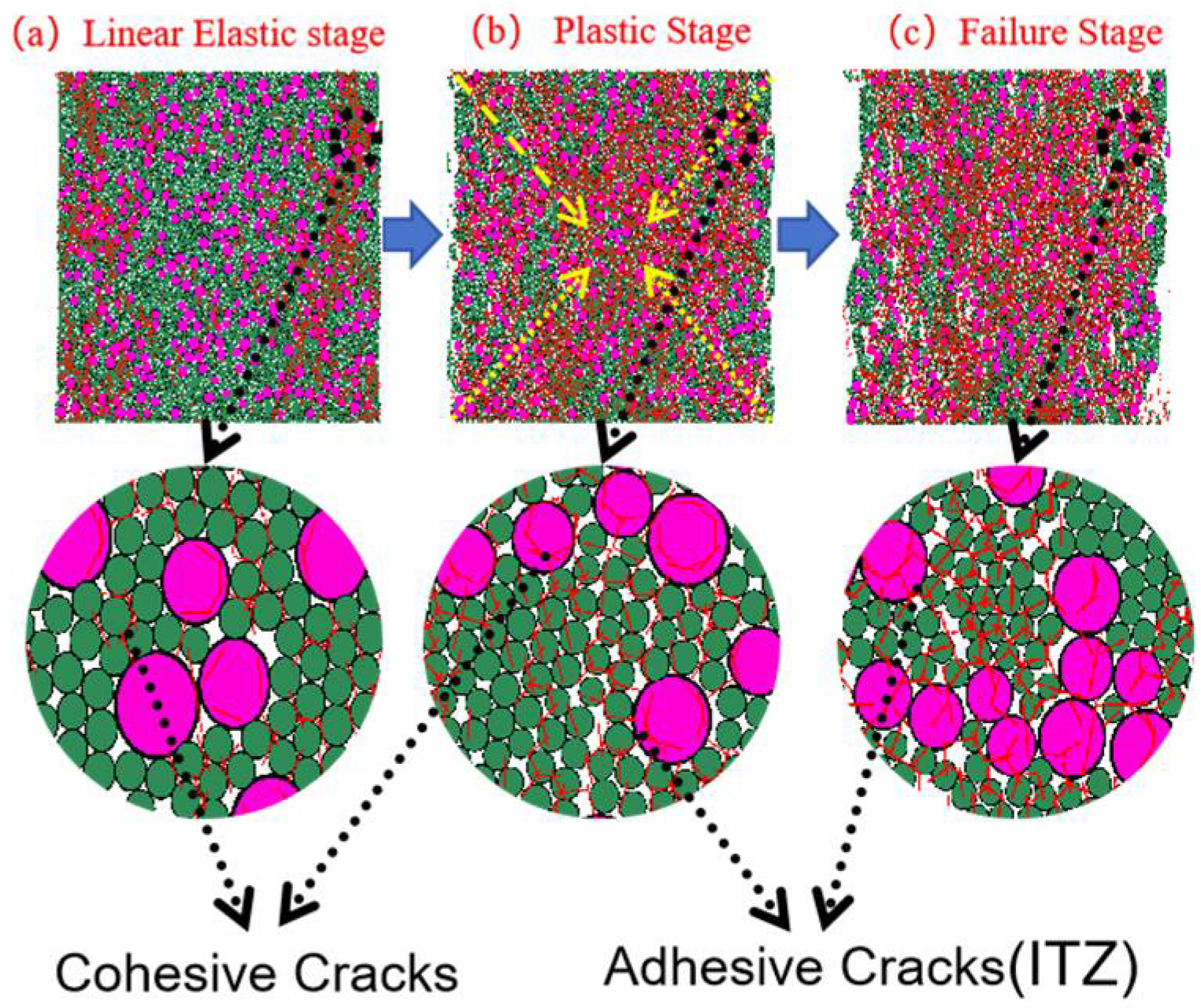
3.3.1. Crack Propagation Analysis
3.3.2. Analysis of Particle-Contact Cracks
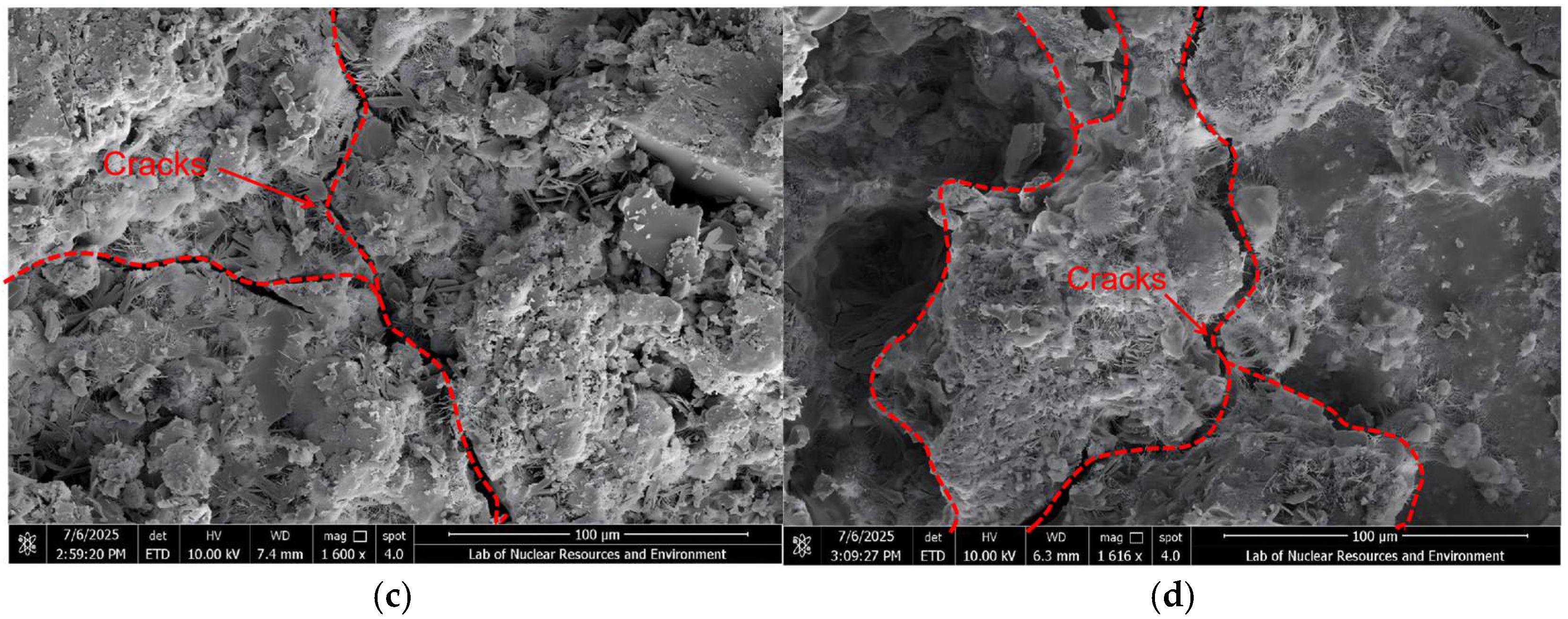
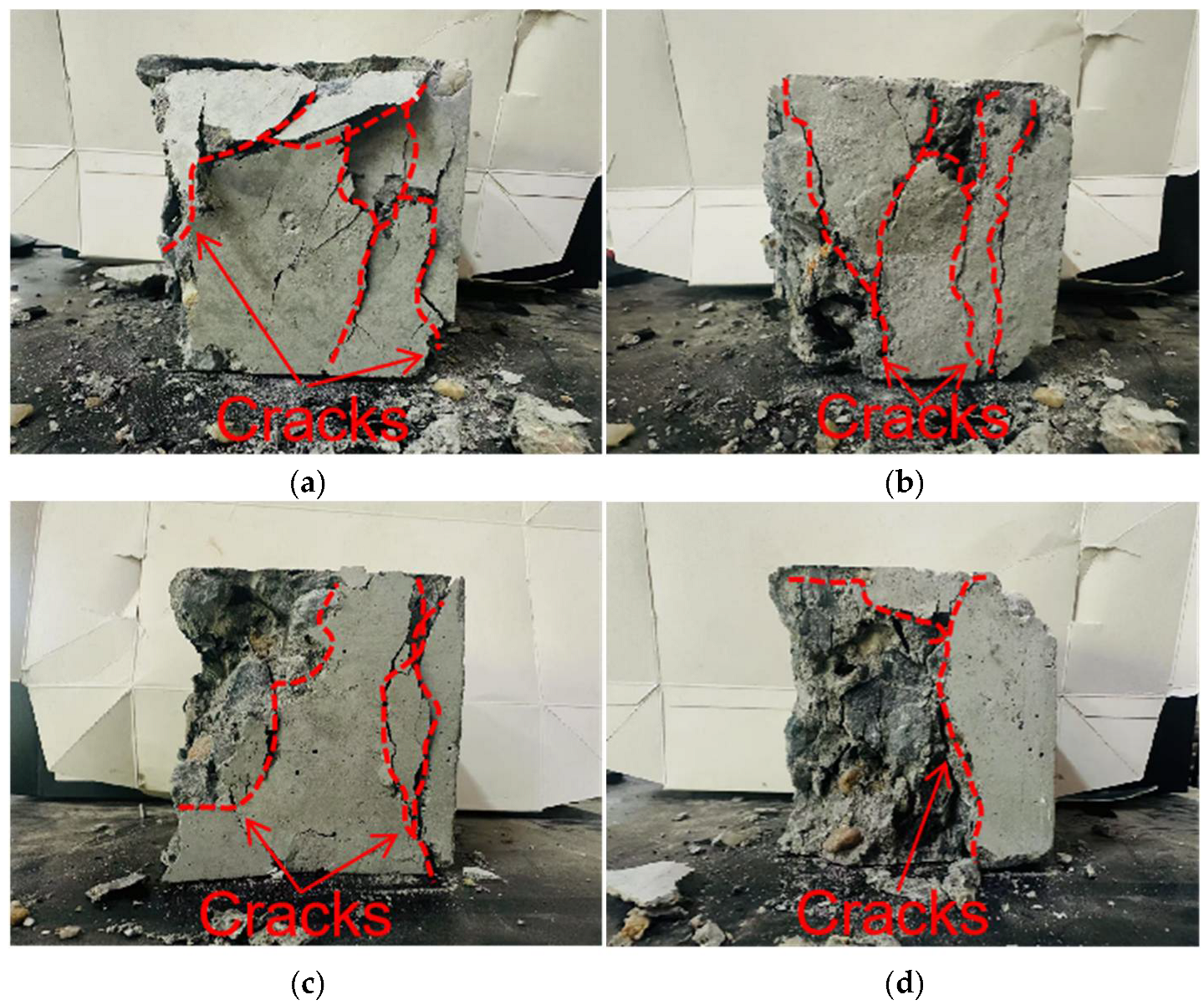
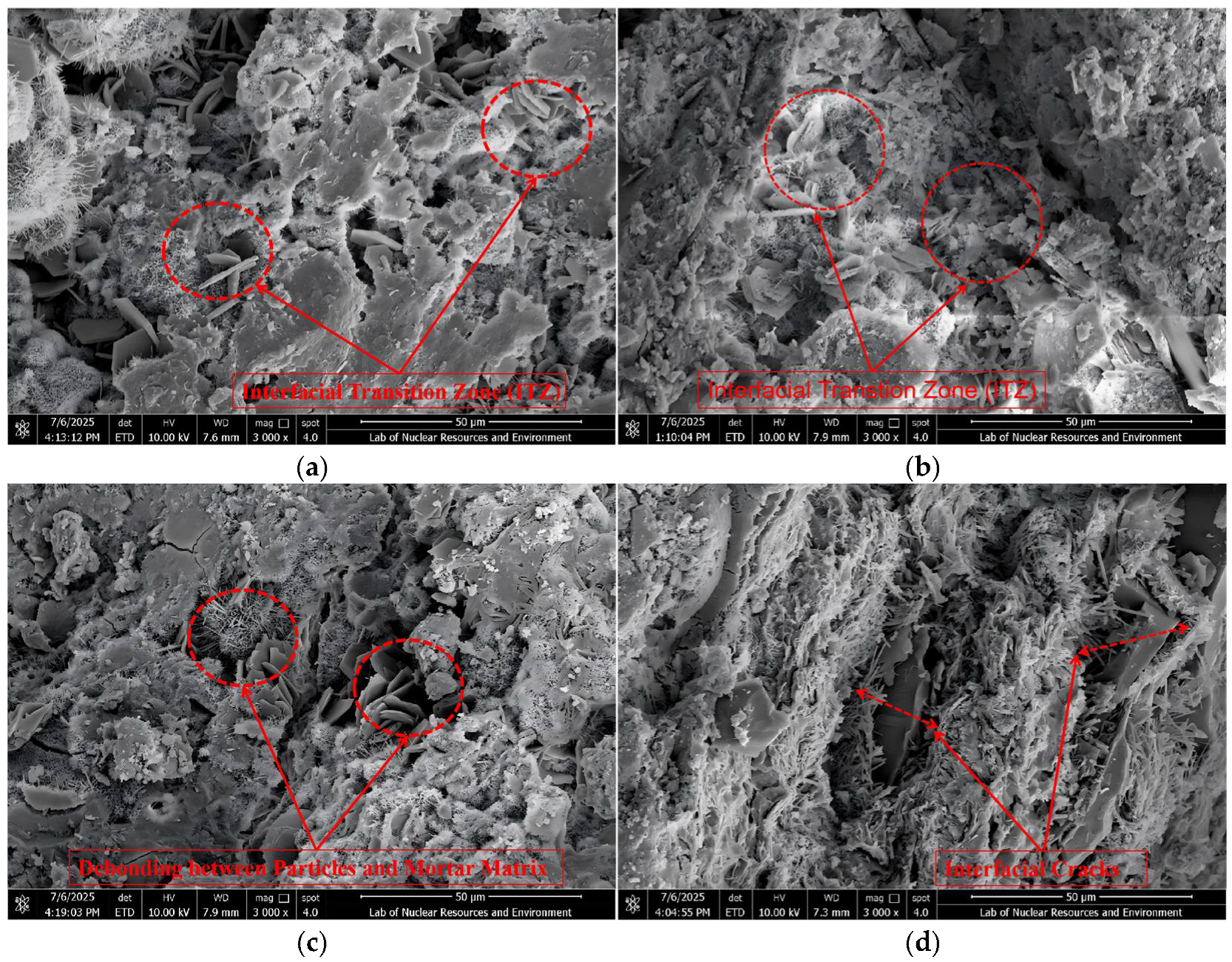
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
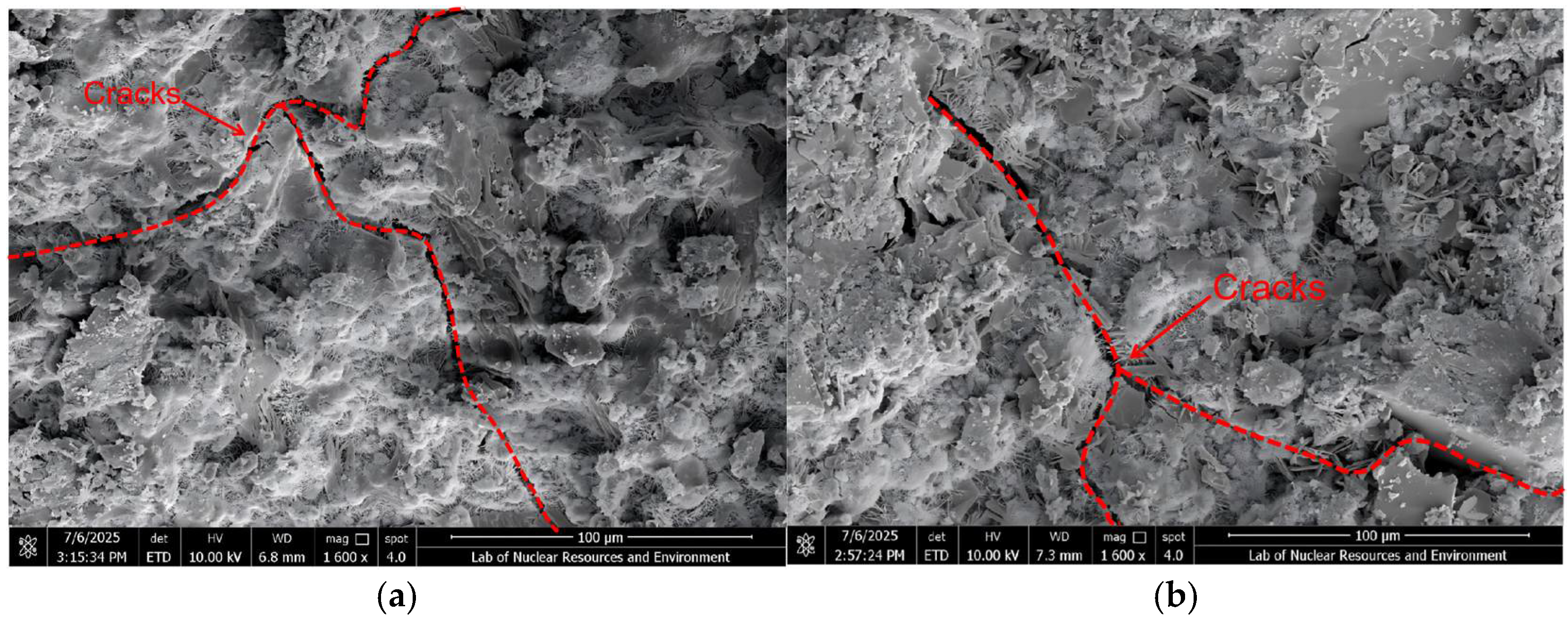
3.4.1. ITZ Classification Criteria and SEM Observations
3.4.2. Correlation Between SEM Observations and DEM Simulations
3.5. Energy Evolution Analysis
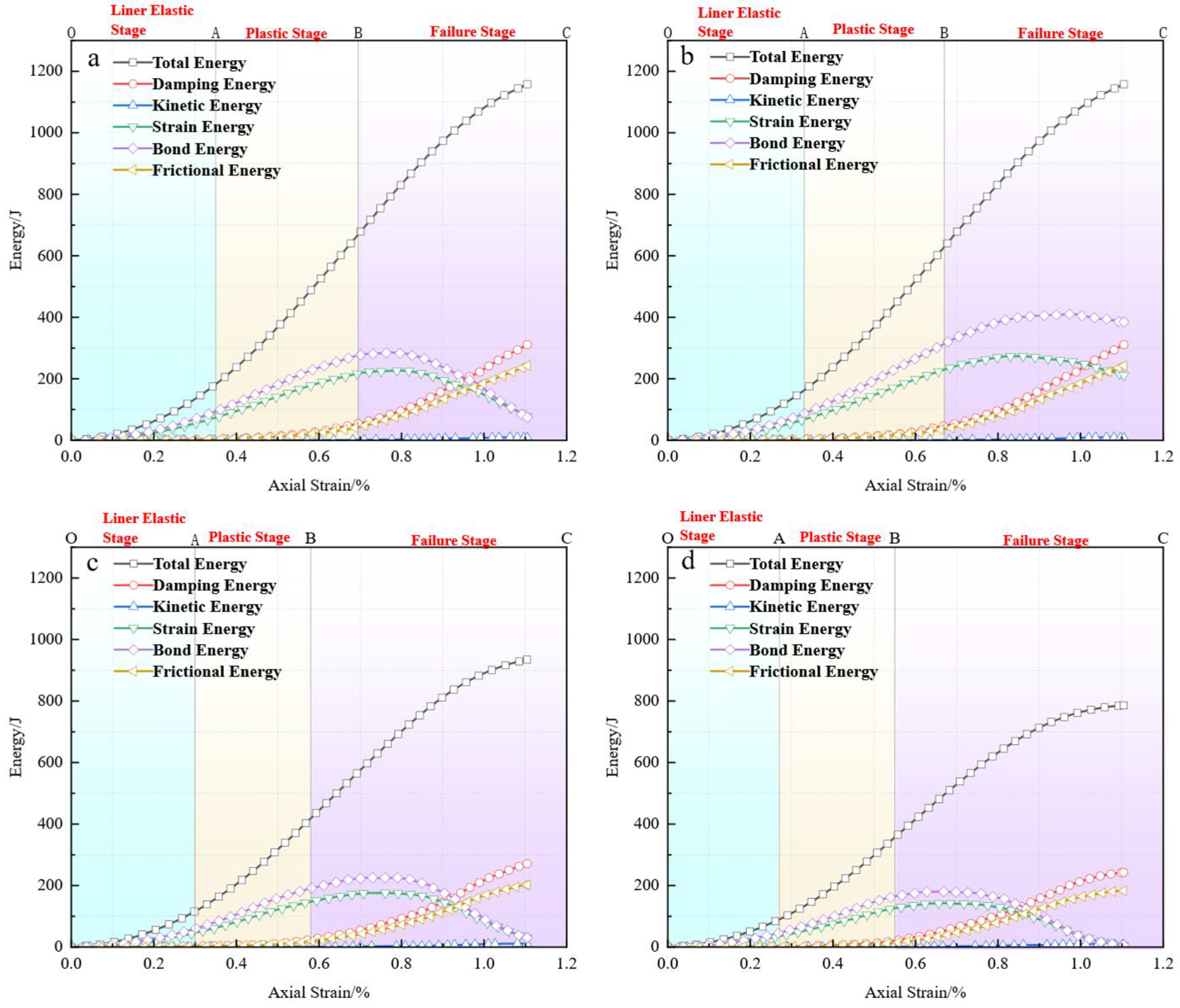
3.5.1. Energy Evolution Patterns Under Different Replacement Ratios
3.5.2. Relationship Between Energy Evolution and Performance Degradation Mechanisms
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations of the Study
4.2. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, H.; Kang, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Q.; Shen, R.; Shu, Z. Research of the workability, mechanical and hydration mechanism of coal gangue–construction solid waste backfilling materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Liao, L.; Lv, G. Environmental hazards and comprehensive utilization of solid waste coal gangue. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2024, 34, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, S. Research progress on the comprehensive utilization of coal gangue. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, L.; Gao, Y.; Guo, H.; Che, Y.; Fu, H. Research progress of concrete preparation based on solid waste properties of coal gangue. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Low-carbon utilization of coal gangue under the carbon neutralization strategy: A short review. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Liu, K.; Sun, D. Research progress of resourceful and efficient utilization of coal gangue in the field of building materials. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Hou, M.; Nasr, A.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, H. Clarifying the role of aggregate characteristics in the rheological and mechanical properties of coal gangue aggregate concrete with a packing perspective. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 111, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, G.; Guo, L.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, K. Utilization of coal gangue as coarse aggregates in structural concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Guan, X. Multitechnique investigation of concrete with coal gangue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wen, Q.; Gao, S.; Tang, J. Comparative study on mechanical and environmental properties of coal gangue sand concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L. Application of coal gangue as a coarse aggregate in green concrete production: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Xu, W.; May, B.M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Experimental study on the micro-mechanism and compressive strength of concrete with calcined coal gangue coarse aggregate. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y. Influence and Mechanism of Coal Gangue Sand on the Properties and Microstructure of Shotcrete Mortar. Materials 2025, 18, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jia, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, M. Effect of hydration process on properties and microstructure of coal gangue admixture concrete. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 3520–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiouta-Mitra, P.; Svourakis, K.; Nomikos, P. Particle flow numerical study of size effect on uniaxial compressive strength of natural building stone. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2024, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gao, N.; Ji, K.; Stewart, L.; Arson, C. DEM analysis on the role of aggregates on concrete strength. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 119, 103290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Xing, C.; Hu, J.; Li, S.; Dai, M. Investigation into the force chain transmission mechanism of asphalt mixture under indirect tensile mode. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owayo, A.A.; Teng, F.C.; Chen, W.C. DEM simulation of crack evolution in cement-based materials under inclined shear test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.J.; Wu, Z.X.; Wen, Z.J.; Cheng, Z.S.; Zhu, R. Mesoscale analysis of the effect of interfacial transition zone on compressive damage of concrete based on discrete element method. Materials 2022, 15, 8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Jia, S.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Z. Discrete element modelling of damage evolution of concrete considering meso-structure of ITZ. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2024, 139, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xing, S.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, X.; Xie, L.; Xie, C. Preparing shotcrete materials applied to roadways using gangue solid wastes–influences of mix proportions on mechanical properties. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, C.; Mao, L.; Han, Z.; Chen, L.; Zou, H.; Li, L.; Yu, P.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y. Study on the effect of activated coal gangue on the mechanical and hydration properties of cement. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1186055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, X.; Zhu, M. The influence of fly ash content on ITZ microstructure of coal gangue concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Huang, D.; Zhang, L.; Song, Q.; Gao, G.; Huo, D. Study on mechanical properties and size effect of coal gangue concrete at mesoscale. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 360, 129551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xia, J.; Xia, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Study on the mechanical behavior and micro-mechanism of concrete with coal gangue fine and coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitka, M.; Tejchman, J. Modelling of concrete behaviour in uniaxial compression and tension with DEM. Granul. Matter 2015, 17, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Liao, L.; Wang, C. Numerical study of the effect of ITZ on failure behaviour of concrete using particle element modelling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 170, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Mahajan, M.M. Performance-based simulation of pervious concrete using discrete element method. Gradevinar 2020, 72, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Li, W.; Zhao, M.; Tam, V.W. Numerical discrete-element method investigation on failure process of recycled aggregate concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04018353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Pan, X.; Niu, Y.; Du, L. Concrete failure simulation method based on discrete element method. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 139, 106505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J. Study on the basic mechanical properties and discrete element method simulation of permeable concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Meng, Q.; Mei, Q.; Wu, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Dynamic response characteristics of coral reef sand concrete under impact loading. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Tang, C.; Meng, L.; Yu, Y.; Wei, K. A deep insight into the micro-mechanical properties of mortar through a multi-phase model. Buildings 2024, 14, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14684-2022; Sand for construction. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese)
- Lavanya, M.R.; Bathusha, M.I.; Sugumaran, B. A review on use of municipal solid waste ash in concrete. Indian Concr. J. 2014, 88, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Li, W.; Dong, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Ni, G. Mechanical and Durability Properties of Concrete Prepared with Coal Gangue: A Review. Buildings 2025, 15, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50081-2019; Standard for test methods of concrete structures. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Xu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Jin, S.; Han, Z.; Liang, C.; Zhu, H. Study on polyurethane elastomer modification for improving low-temperature resistance of high-capacity polyurethane elastomeric bearing for bridges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 347, 128625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Si, R.; Wu, J. A review on early-age cracking of concrete: Causes and control. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.L.; Wang, L.; Ghannam, M.; Guan, M.; Luo, J. Prediction of concrete compressive strength based on early-age effective conductivity measurement. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 101998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, S.B.; Barai, S.V.; Ojha, P.N.; Kumar, R. Experimental investigation for the determination of stress-strain relationship for sintered flyash lightweight aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Z. A review of the interfacial transition zones in concrete: Identification, physical characteristics, and mechanical properties. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 300, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Properties and microstructure of an interfacial transition zone enhanced by silica fume in concrete prepared with coal gangue as an aggregate. ACS Omega 2023, 9, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korouzhdeh, T.; Eskandari-Naddaf, H.; Kazemi, R. The ITZ microstructure, thickness, porosity and its relation with compressive and flexural strength of cement mortar; influence of cement fineness and water/cement ratio. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2022, 16, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaie, V.; Rad, M.M. Multi-objective genetic algorithm calibration of colored self-compacting concrete using DEM: An integrated parallel approach. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, T.; Luo, T.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, K.; Ma, W. Study on the deterioration of concrete under dry–wet cycle and sulfate attack. Materials 2020, 13, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, D.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Pei, X.; Min, K.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, E.; et al. Numerical Simulation of the Effect of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on the Axial Compression Strength of Rubber Concrete. Materials 2023, 16, 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Sang, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y. Electrical characterization of interfacial transition zone in concrete during freeze-thaw process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 425, 135960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

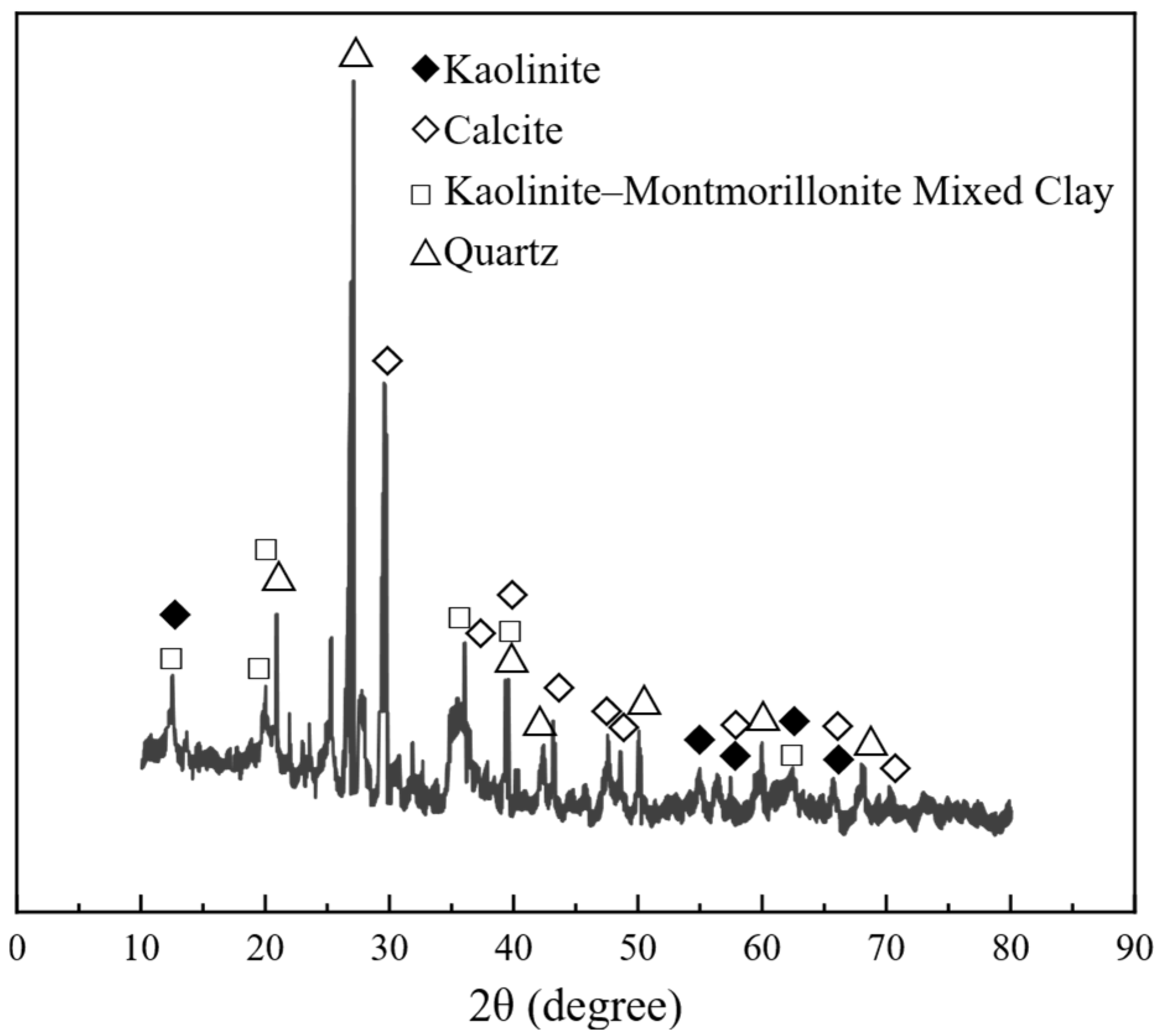




| Apparent Density (kg/m3) | Bulk Density (kg/m3) | Void Ratio (%) | Stone Powder Content (%) | Clay Lump Content (%) | Crushing Index (%) | Fineness Modulus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2700 | 1620 | 40 | 14.8 | 0.2 | 21 | 2.65 |
| Mix ID | Cement (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | Coarse Aggregate (kg/m3) | Fine Aggregate (kg/m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stone | Sand | CGS | |||
| J1 | 400 | 180 | 1120 | 510 | 170 |
| J2 | 400 | 180 | 1120 | 340 | 340 |
| J3 | 400 | 180 | 1120 | 170 | 510 |
| J4 | 400 | 180 | 1120 | 0 | 680 |
| Mix ID | Age | /MPa | 95% CI | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1 | 1 d | 13.530.35 | [12.66–14.41] | 3 |
| J1 | 3 d | 19.630.53 | [18.31–20.95] | 3 |
| J1 | 7 d | 25.660.65 | [24.04–27.27] | 3 |
| J1 | 28 d | 30.740.65 | [29.40–32.08] | 3 |
| J2 | 1 d | 0.2 | [13.05–14.0] | 3 |
| J2 | 3 d | 0.41 | [15.57–17.58] | 3 |
| J2 | 7 d | 23.260.98 | [20.82–25.71] | 3 |
| J2 | 28 d | 26.710.72 | [24.92–28.5] | 3 |
| J3 | 1 d | 0.1 | [10.92–11.42] | 3 |
| J3 | 3 d | 13.510.32 | [12.73–14.30] | 3 |
| J3 | 7 d | 0.24 | [19.35–20.53] | 3 |
| J3 | 28 d | 0.68 | [22.14–25.52] | 3 |
| J4 | 1 d | 0.37 | [9.44–11.28] | 3 |
| J4 | 3 d | 0.56 | [9.68–12.47] | 3 |
| J4 | 7 d | 15.670.49 | [14.45–16.90] | 3 |
| J4 | 28 d | 0.7 | [19.12–22.57] | 3 |
| Mix ID | Age | Mean ± SD/% | 95% CI | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1 | 1 d | 0.578 ± 0.008 | [0.565, 0.597] | 3 |
| J1 | 3 d | 0.591 ± 0.003 | [0.584, 0.598] | 3 |
| J1 | 7 d | 0.624 ± 0.006 | [0.611, 0.639] | 3 |
| J1 | 28 d | 0.673 ± 0.005 | [0.661, 0.685] | 3 |
| J2 | 1 d | 0.563 ± 0.008 | [0.543, 0.584] | 3 |
| J2 | 3 d | 0.576 ± 0.005 | [0.563, 0.589] | 3 |
| J2 | 7 d | 0.618 ± 0.01 | [0.593, 0.643] | 3 |
| J2 | 28 d | 0.655 ± 0.009 | [0.634, 0.676] | 3 |
| J3 | 1 d | 0.544 ± 0.005 | [0.533, 0.555] | 3 |
| J3 | 3 d | 0.546 ± 0.01 | [0.522, 0.571] | 3 |
| J3 | 7 d | 0.576 ± 0.007 | [0.559, 0.594] | 3 |
| J3 | 28 d | 0.616 ± 0.004 | [0.605, 0.627] | 3 |
| J4 | 1 d | 0.524 ± 0.007 | [0.508, 0.54] | 3 |
| J4 | 3 d | 0.544 ± 0.007 | [0.527, 0.561] | 3 |
| J4 | 7 d | 0.564 ± 0.003 | [0.557, 0.570] | 3 |
| J4 | 28 d | 0.584 ± 0.007 | [0.566, 0.601] | 3 |
| Macroscopic Parameters | Microscopic Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Parameters | PB Model | ||||||||
| E/ GPa | R1/ mm | Ρ/ kg·m−3 | Ec/ GPa | tanΦt | Ec/ GPa | σc/ MPa | σb MPa | ||
| Coarse Aggregate | 35.5 | 10–16 | 2350 | 7.2 | 0.5 | 3.6 | 28 | 2.7 | |
| Cement Mortar | Natural Sand | 35 | 0–4 | 2400 | 6.8 | 0.45 | 3.2 | 30 | 2.5 |
| Coal Gangue Sand | 25 | 0–4 | 2250 | 6.0 | 0.4 | 2.8 | 26 | 1.8 | |
| ID | Specimen Dimensions (Width × Height) /mm | Coal Gangue Sand Mix Ratio | Particle Size Range /mm | Loading Rate /mm·s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 100 × 100 | 25% | 3.5~4.75 | 0.01 |
| B | 100 × 100 | 50% | 3.5~4.75 | |
| C | 100 × 100 | 75% | 3.5~4.75 | |
| D | 100 × 100 | 100% | 3.5~4.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Zha, W.; Xu, T.; Ji, C.; Li, Y. Microstructural Mechanisms of Concrete Degradation Under Different Coal Gangue Sand Replacement Ratios. Materials 2025, 18, 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204787
Cai Y, Zha W, Xu T, Ji C, Li Y. Microstructural Mechanisms of Concrete Degradation Under Different Coal Gangue Sand Replacement Ratios. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204787
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yukai, Wenhua Zha, Tao Xu, Chao Ji, and Yaozong Li. 2025. "Microstructural Mechanisms of Concrete Degradation Under Different Coal Gangue Sand Replacement Ratios" Materials 18, no. 20: 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204787
APA StyleCai, Y., Zha, W., Xu, T., Ji, C., & Li, Y. (2025). Microstructural Mechanisms of Concrete Degradation Under Different Coal Gangue Sand Replacement Ratios. Materials, 18(20), 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204787






