Effect of Thickness on Color Stability of Gingiva-Colored Composite Resins Applied to 3D-Printed Resin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
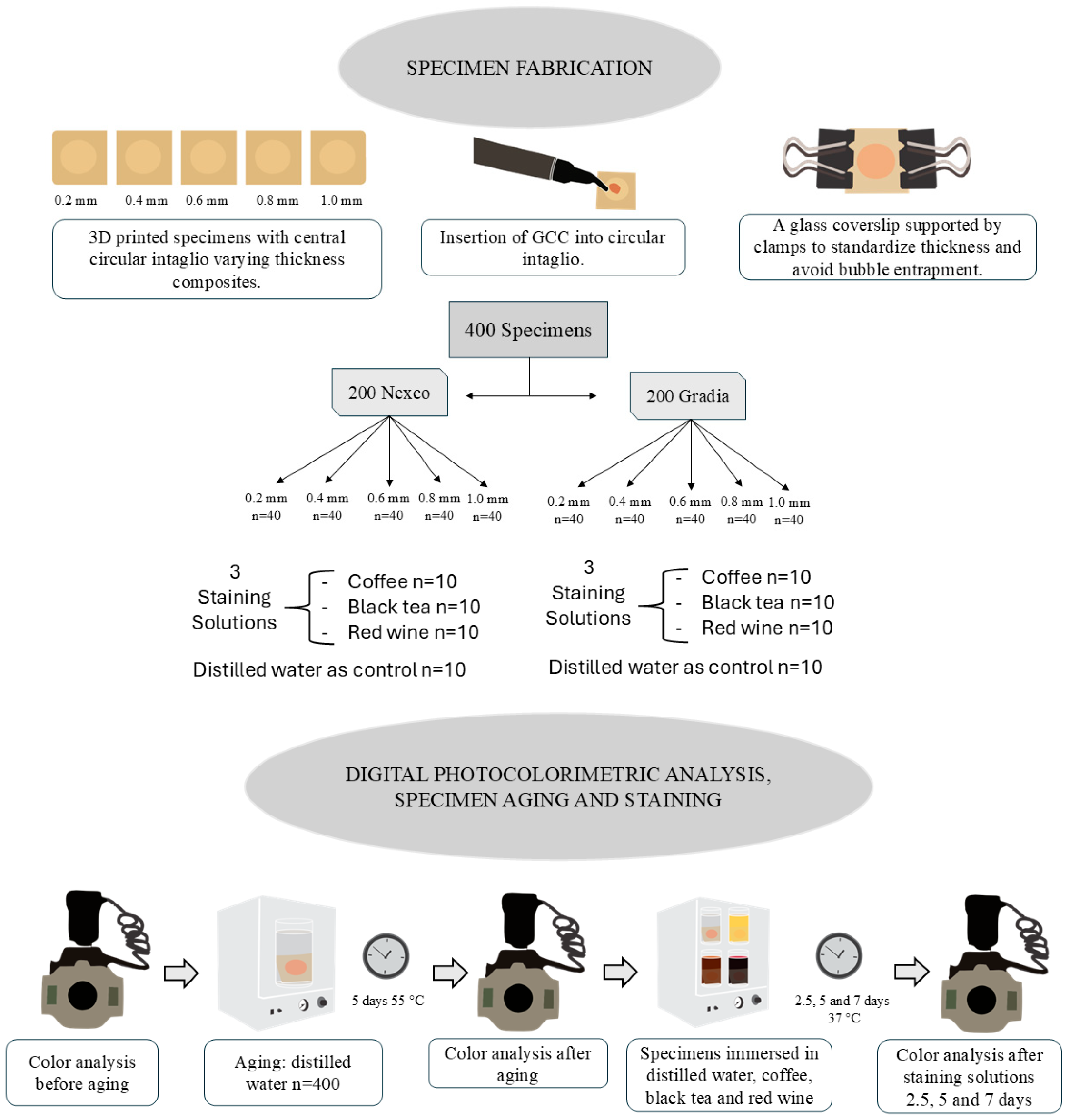
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Staining Solutions
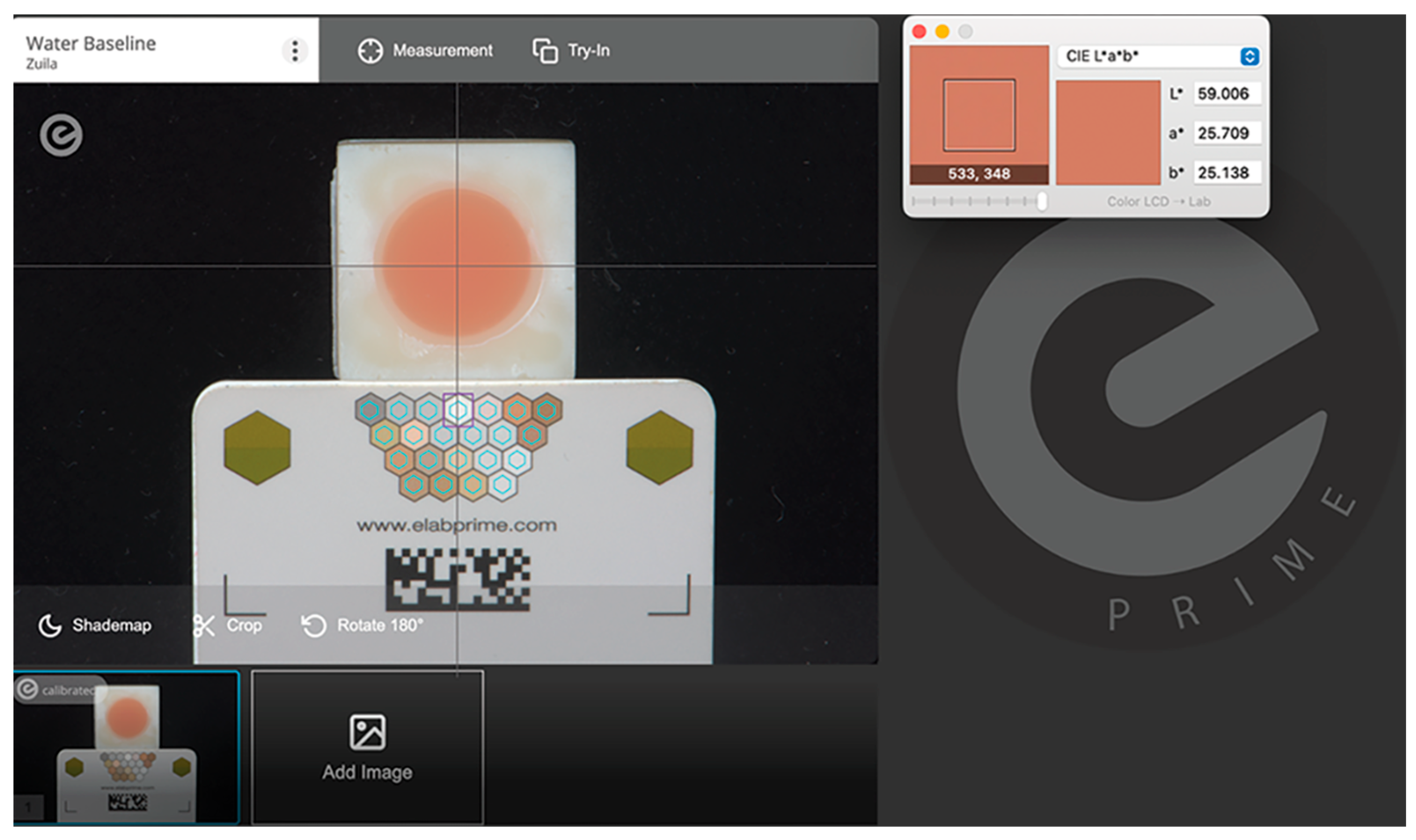
2.3. Digital Photocolorimetric Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
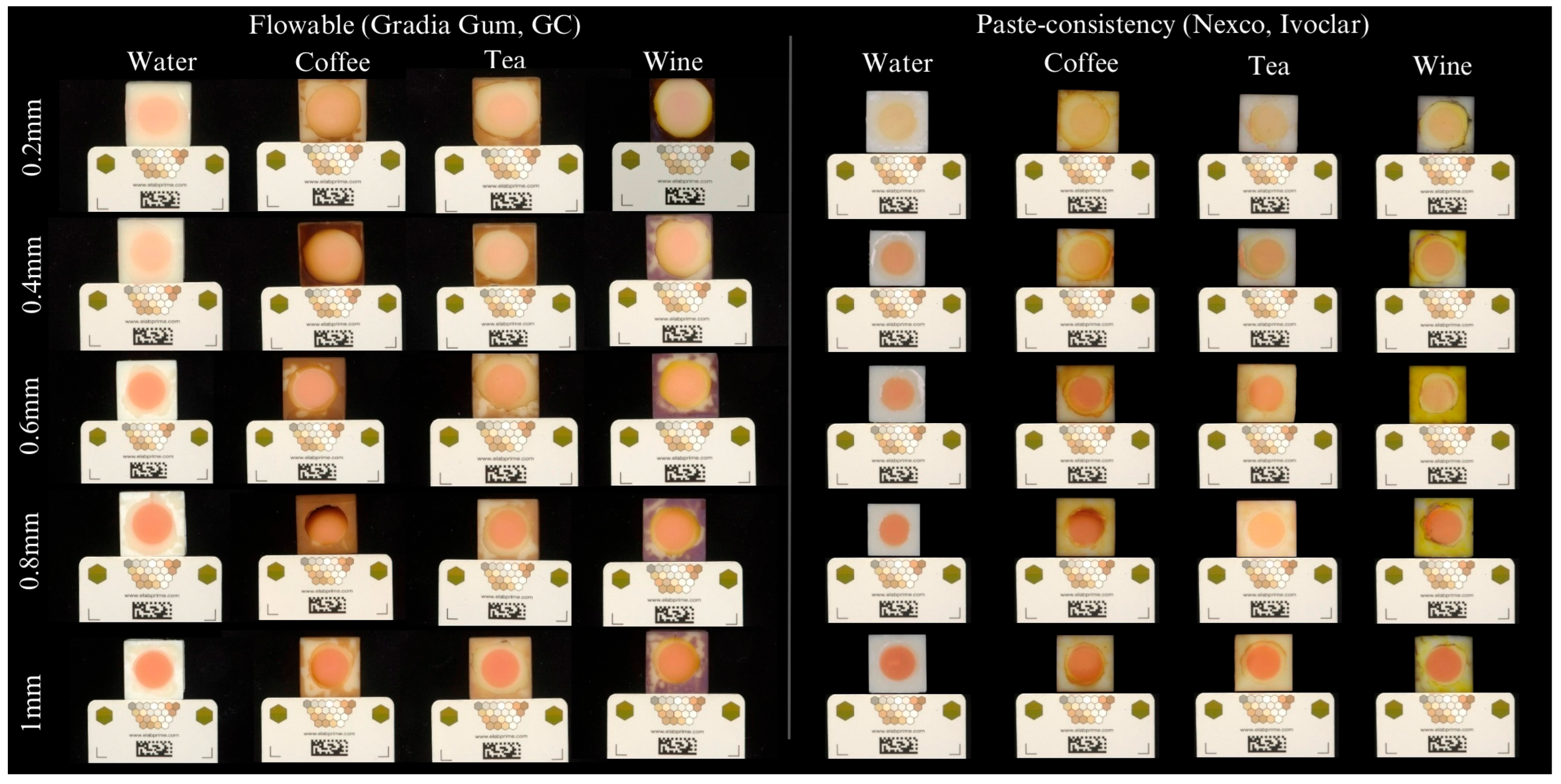
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waldemarin, R.F.; Terra, P.C.; Pinto, L.R.; Faot, F.; Camacho, G.B. Color Change in Acrylic Resin Processed in Three Ways After Immersion in Water, Cola, Coffee, Mate and Wine. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2013, 26, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, R.M.S.; Conterno, B.; Arrais, C.A.G.; Sugio, C.Y.C.; Urban, V.M.; Neppelenbroek, K.H. Porosity, Water Sorption and Solubility of Denture Base Acrylic Resins Polymerized Conventionally or in Microwave. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2018, 26, e20170383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Palaskar, J.N.; Mittal, S. Comparative Evaluation of Surface Porosities in Conventional Heat Polymerized Acrylic Resin Cured by Water Bath and Microwave Energy with Microwavable Acrylic Resin Cured by Microwave Energy. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2013, 4, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolone, G.; Pavan, F.; Guglielmi, P.C.; Scotti, N.; Cantatore, G.; Vichi, A. In Vitro Procedures for Color Stability Evaluation of Dental Resin-based Composites Exposed to Smoke: A Scoping Review. Dent. Mater. J. 2022, 41, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Noort, R. The Future of Dental Devices is Digital. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandurino, M.; Cortili, S.; Coccoluto, L.; Greco, K.; Cantatore, G.; Gherlone, E.F.; Vichi, A.; Paolone, G. Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed vs. Subtractively Manufactured Composite Resins for Permanent Restorations: A Systematic Review. Materials 2025, 18, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive Manufacturing (3D printing): A Review of Materials, Methods, Applications and Challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.W.; Kim, N.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.H. Technique for Fabricating Individualized Dentures with a Gingiva-Shade Composite Resin. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubochi, K.; Komine, F.; Fushiki, R.; Yagawa, S.; Mori, S.; Matsumura, H. Shear Bond Strength of a Denture Base Acrylic Resin and Gingiva-Colored Indirect Composite Material to Zirconia Ceramics. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Reyes, C.; Perez, M.M.; Tejada-Casado, M.; Ruiz-Lopez, J.; Lucena, C. Color Stability and Degree of Conversion of Gingiva-Colored Resin-Based Composites. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2023, 35, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, A.; Dimitriadi, M.; Zinelis, S.; Sarafianou, A.; Eliades, G. Surface Characteristics and Color Stability of Gingiva-Colored Resin Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideridou, I.; Tserki, V.; Papanastasiou, G. Study of Water Sorption, Solubility and Modulus of Elasticity of Light-Cured Dimethacrylate-Based Dental Resins. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamszadeh, S.; Sheikh-Al-Eslamian, S.M.; Hasani, E.; Abrandabadi, A.N.; Panahandeh, N. Color Stability of the Bulk-Fill Composite Resins with Different Thickness in Response to Coffee/Water Immersion. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 7186140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, C.; Campillo, M.; Aref, J. Color Stability of Ten Resin-Based Restorative Materials. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2012, 24, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashayar, G.; Bain, P.A.; Salari, S.; Dozic, A.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Feilzer, A.J. Perceptibility and Acceptability Thresholds for Colour Differences in Dentistry. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Peter, A.; Pietrobon, N.; Hammerle, C.H. Visual and Spectrophotometric Shade Analysis of Human Teeth. J. Dent. Res. 2002, 81, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, M.A.; Sim, C.P.C.; Nunn, M.E.; Zeng, L.L.; Hamza, T.A.; Wee, A.G. Validation of Two Clinical Color Measuring Instruments for Use in Dental Research. J. Dent. 2022, 125, 104223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, R.; Burrow, M.F.; Tyas, M. Influence of Food-Simulating Solutions and Surface Finish on Susceptibility to Staining of Aesthetic Restorative Materials. J. Dent. 2005, 33, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, A.U.; Yilmaz, F.; Kulunk, T.; Guler, E.; Kurt, S. Effects of Different Drinks on Stainability of Resin Composite Provisional Restorative Materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 94, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, S.; Tapia, J.; Bazos, P. eLABor_aid: A New Approach to Digital Shade Management. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2017, 12, 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Philippi, A.G.; Sabatini, G.P.; Freitas, M.S.; Oshima, S.N.; Tango, R.N.; Goncalves, T. Clinical Tooth Color Matching: In Vivo Comparisons of Digital Photocolorimetric and Spectrophotometric Analyses. Oper. Dent. 2023, 48, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavangar, M.; Bagheri, R.; Kwon, T.Y.; Mese, A.; Manton, D.J. Influence of Beverages and Surface Roughness on the Color Change of Resin Composites. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9, e12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.S.; Labruna Moreira, A.D.; de Albuquerque, P.P.; de Menezes, L.R.; Pfeifer, C.S.; Schneider, L.F. Effect of Monomer Type on the CC Degree of Conversion, Water Sorption and Solubility, and Color Stability of Model Dental Composites. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, P.; Lu, H.; Okte, Z.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Powers, J.M. Effects of Staining and Bleaching on Color Change of Dental Composite Resins. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2006, 95, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Polo, C.; Portillo Munoz, M.; Lorenzo Luengo, M.C.; Vicente, P.; Galindo, P.; Martin Casado, A.M. Comparison of the CIELab and CIEDE2000 Color Difference Formulas. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Materials | Manufacturer | Batch Nº | Composition * |
|---|---|---|---|
| P Pro Resin | Institut Straumann AG | 231,568 | Acrylic resin, urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA), diacrylate, phosphine oxide, diphenyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) (TPO) |
| Gradia Plus Gum | GC Europe (Louvain, Belgium) | 2,201,261 | Urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA) (25−50%), dimethacrylate component (5−10%), dimethacrylate (1−5%), trimethacrylate (1−5%) UV-light absorber (1−5%) |
| SR Nexco Paste | Ivoclar AG (Schaan, Liechtenstein) | Z047PF | DMA (17–19 wt%); copolymer and silicon dioxide (82–83 wt%), stabilizers, catalysts, pigments, 10–100-nm inorganic fillers (64–65 wt%) |
| 2.5 Days | 5 Days | 7 Days | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | Water | Wine | Coffee | Tea | Water | Wine | Coffee | Tea | Water | Wine | Coffee | Tea |
| 0.2 | 1.65 ± 1.03 Aa | 2.54 ± 1.09 ABab* | 3.72 ± 2.27 Ab* | 2.38 ± 1.66 Aab | 2.00 ± 1.38 Aa | 3.66 ± 2.16 Aab** | 5.61 ± 3.37 Ab** | 2.70 ± 1.17 Aa | 2.23 ± 0.97 Aa | 4.36 ± 2.43 Aa** | 6.78 ± 4.042 Ab*** | 2.94 ± 0.82 ABa |
| 0.4 | 1.17 ± 0.86 Aa* | 2.03 ± 1.03 Aab | 4.09 ± 0.30 Abc* | 6.09 ± 0.98 Bc* | 1.77 ± 0.93 Aa* | 2.81 ± 1.33 Aab | 6.15 ± 1.17 Ac** | 4.02 ± 0.96 Abc** | 2.93 ± 1.35 Aa** | 2.80 ± 1.59 Aa | 7.32 ± 0.816 Ab*** | 3.09 ± 1.03 ABa*** |
| 0.6 | 2.62 ± 1.02 Aa | 4.42 ± 3.57 ABa | 5.25 ± 2.12 ABa* | 4.31 ± 4.55 ABa* | 3.13 ± 0.95 Aa | 4.44 ± 3.40 Aa | 5.63 ± 2.55 Aa*,** | 3.23 ± 2.43 Aa*,** | 2.90 ± 0.72 Aa | 3.86 ± 3.99 Aab | 6.23 ± 3.048 Ab** | 5.23 ± 5.27 Bab** |
| 0.8 | 1.94 ± 0.43 Aa | 4.79 ± 4.19 Bb*,** | 7.91 ± 1.98 Bc* | 2.63 ± 0.56 Aab | 2.50 ± 0.63 Aa | 4.96 ± 4.10 Aa* | 7.95 ± 2.87 Ab* | 2.49 ± 0.73 Aa | 2.49 ± 0.77 Aa | 3.99 ± 4.80 Aa** | 10.37 ± 2.849 Bb** | 2.13 ± 0.67 Aa |
| 1.0 | 1.79 ± 1.13 Aa* | 2.70 ± 2.84 ABab* | 5.62 ± 3.47 ABc* | 4.63 ± 2.72 ABbc* | 2.93 ± 1.00 Aa** | 3.36 ± 2.25Aab*,** | 5.48 ± 1.92Ab* | 4.40 ± 2.40 Aab* | 2.39 ± 1.24 Aa*,** | 3.76 ± 3.33 Aa** | 6.62 ± 2.73 Ab** | 2.47 ± 1.39 ABa** |
| 2.5 Days | 5 Days | 7 Days | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | Water | Wine | Coffee | Tea | Water | Wine | Coffee | Tea | Water | Wine | Coffee | Tea |
| 0.2 | 2.14 ± 0.77 Aa | 2.67 ± 0.83 Aa | 3.79 ± 1.79 ABa | 3.69 ± 0.68 Aa* | 2.42 ± 1.78 Aa | 2.81 ± 0.91 Aa | 3.34 ± 2.44 Aab | 5.03 ± 1.00 ABCb*,** | 2.48 ± 1.13 ABa | 2.85 ± 0.98 Aa | 4.33 ± 2.51 Aab | 5.48 ± 0.52 ABb** |
| 0.4 | 2.30 ± 0.90 Aa | 2.79 ± 0.64 Aa* | 3.01 ± 1.49 Aab | 4.84 ± 2.01 Ab* | 3.08 ± 1.18 Aa | 3.98 ± 1.22 Aa*,** | 4.11 ± 1.59 Aa | 6.69 ± 2.66 Ab** | 3.45 ± 2.55 Ba | 4.94 ± 2.50 Bab** | 3.62 ± 2.20 Aa | 6.24 ± 2.67 Bb** |
| 0.6 | 1.93 ± 0.54 Aa | 3.65 ± 2.32 Ab | 3.87 ± 2.06 ABab | 3.57 ± 1.50 Aab | 1.61 ± 0.68 Aa | 3.43 ± 1.75 Aab | 3.84 ± 1.94 Ab | 4.56 ± 0.72 BCb | 1.29 ± 0.44 Aa | 4.47 ± 2.38 ABb | 5.15 ± 2.62 Ab | 4.78 ± 1.10 ABb |
| 0.8 | 1.88 ± 1.174 Aa | 5.59 ± 2.69 Bb* | 5.34 ± 2.03 Bb* | 10.28 ± 2.04 Bc* | 2.18 ± 1.07 Aa | 3.19 ± 1.28 Aa** | 4.04 ± 2.21 Aa** | 6.14 ± 1.21 ABb** | 2.20 ± 1.44 ABa | 4.15 ± 2.06 Aba*,** | 3.28 ± 1.92 Aa** | 6.80 ± 2.55 Bb** |
| 1.0 | 2.64 ± 1.4 Aa | 5.46 ± 2.67 Bb* | 4.06 ± 1.90 ABab | 4.11 ± 1.15 Aab | 2.00 ± 1.08 Aa | 3.43 ± 1.42 Aa** | 2.98 ± 2.17 Aa | 3.47 ± 0.70 Ca | 1.74 ± 0.75 ABa | 3.00 ± 1.69 ABab** | 3.22 ± 1.78 Aab | 4.15 ± 0.74 Ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drummond, L.d.R.B.; Reginaldo, I.; Duarte, L.; Wanghon, Z.M.L.; Philippi, A.G.; Pala, L.O.d.O.; Pauletto, P.; Gonçalves, T.M.S.V. Effect of Thickness on Color Stability of Gingiva-Colored Composite Resins Applied to 3D-Printed Resin. Materials 2025, 18, 4757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204757
Drummond LdRB, Reginaldo I, Duarte L, Wanghon ZML, Philippi AG, Pala LOdO, Pauletto P, Gonçalves TMSV. Effect of Thickness on Color Stability of Gingiva-Colored Composite Resins Applied to 3D-Printed Resin. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204757
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrummond, Liliane da Rocha Bonatto, Isabela Reginaldo, Laís Duarte, Zuila Maria Lobato Wanghon, Analucia Gebler Philippi, Luiz Otávio de Oliveira Pala, Patrícia Pauletto, and Thais Marques Simek Vega Gonçalves. 2025. "Effect of Thickness on Color Stability of Gingiva-Colored Composite Resins Applied to 3D-Printed Resin" Materials 18, no. 20: 4757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204757
APA StyleDrummond, L. d. R. B., Reginaldo, I., Duarte, L., Wanghon, Z. M. L., Philippi, A. G., Pala, L. O. d. O., Pauletto, P., & Gonçalves, T. M. S. V. (2025). Effect of Thickness on Color Stability of Gingiva-Colored Composite Resins Applied to 3D-Printed Resin. Materials, 18(20), 4757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204757






