Fabrication of Graphite Flake/Al Composites via the Hybrid Powder-Melt Process: Synergistic Enhancement of Strength and Conductivity Through Low Content Addition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Raw Materials and Fabrication Process
2.2. Performance Testing
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
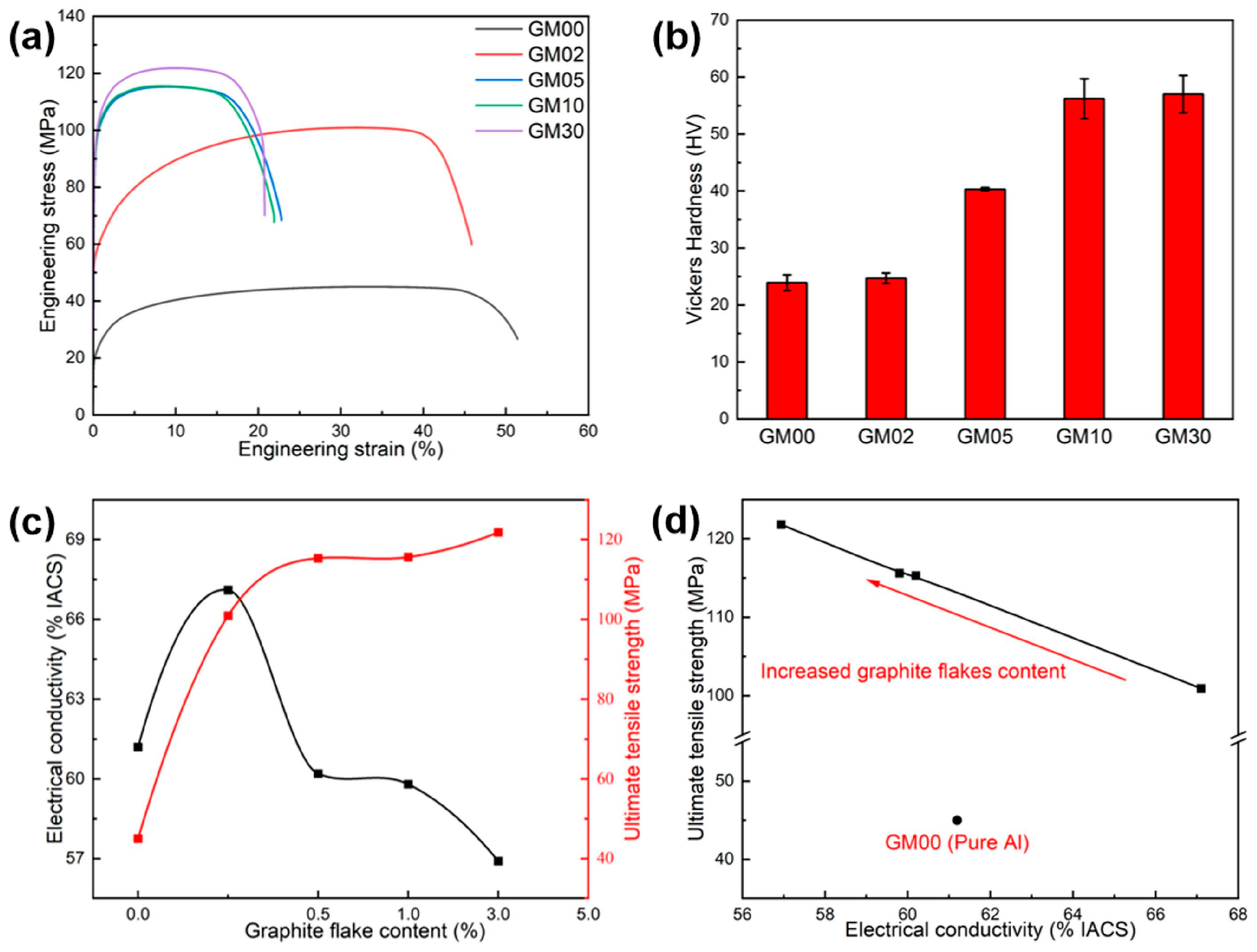
3.1. Properties of Graphite Flakes/Al Composites
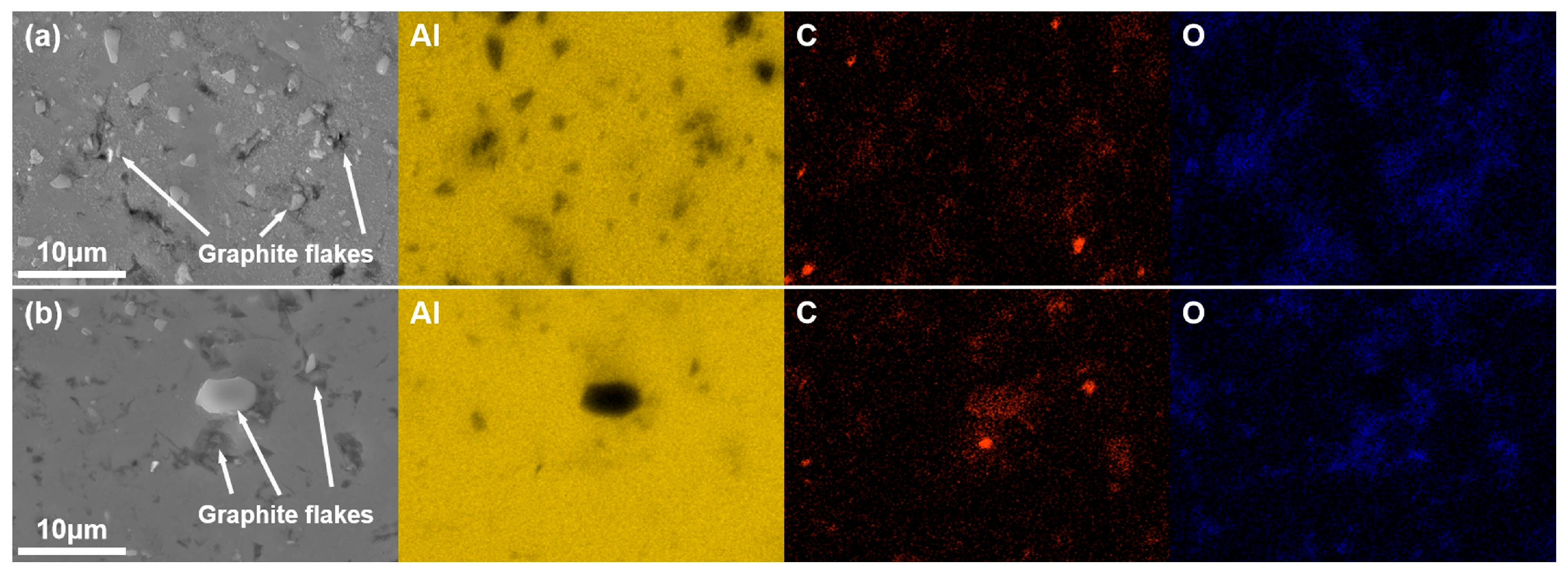
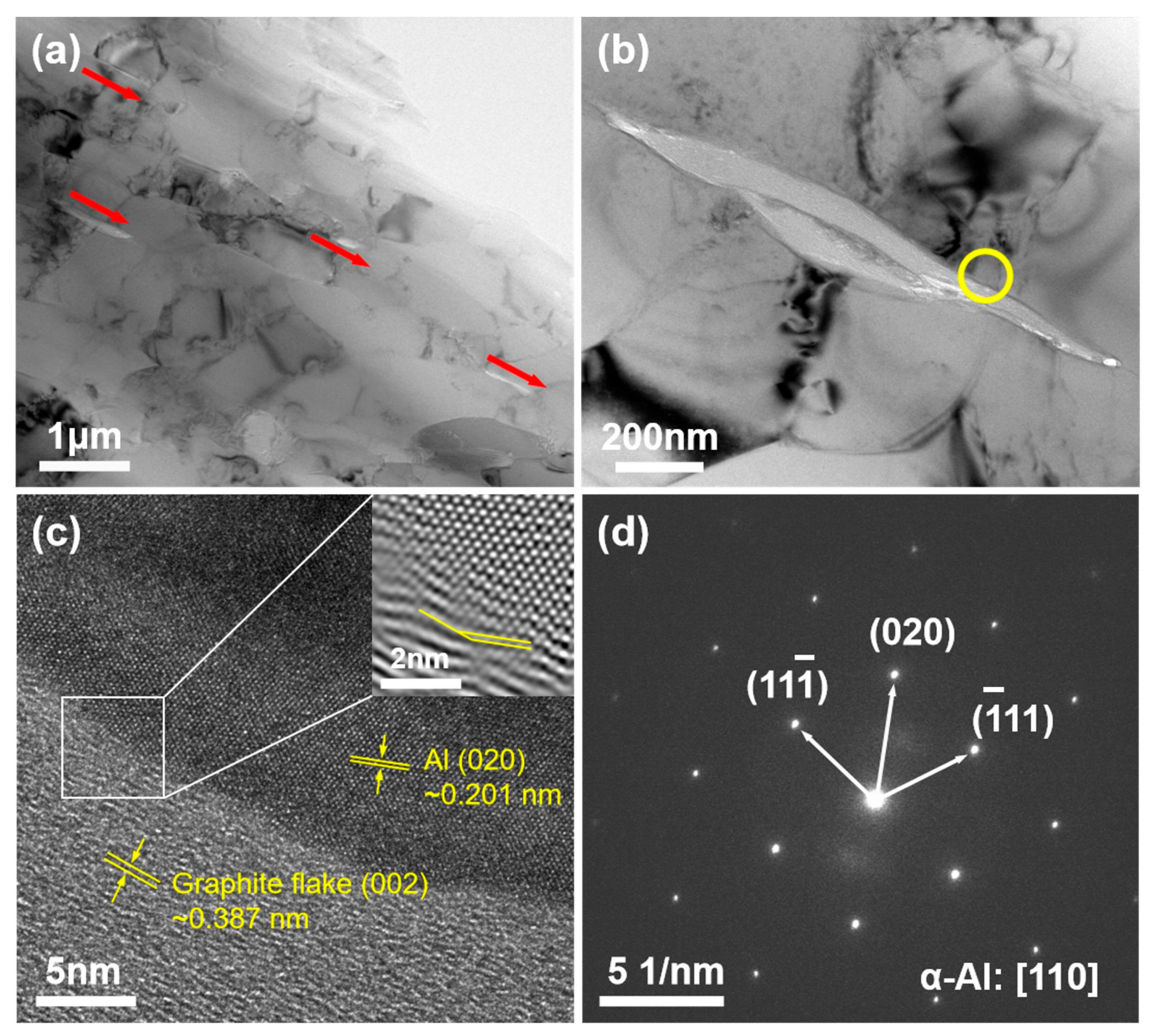
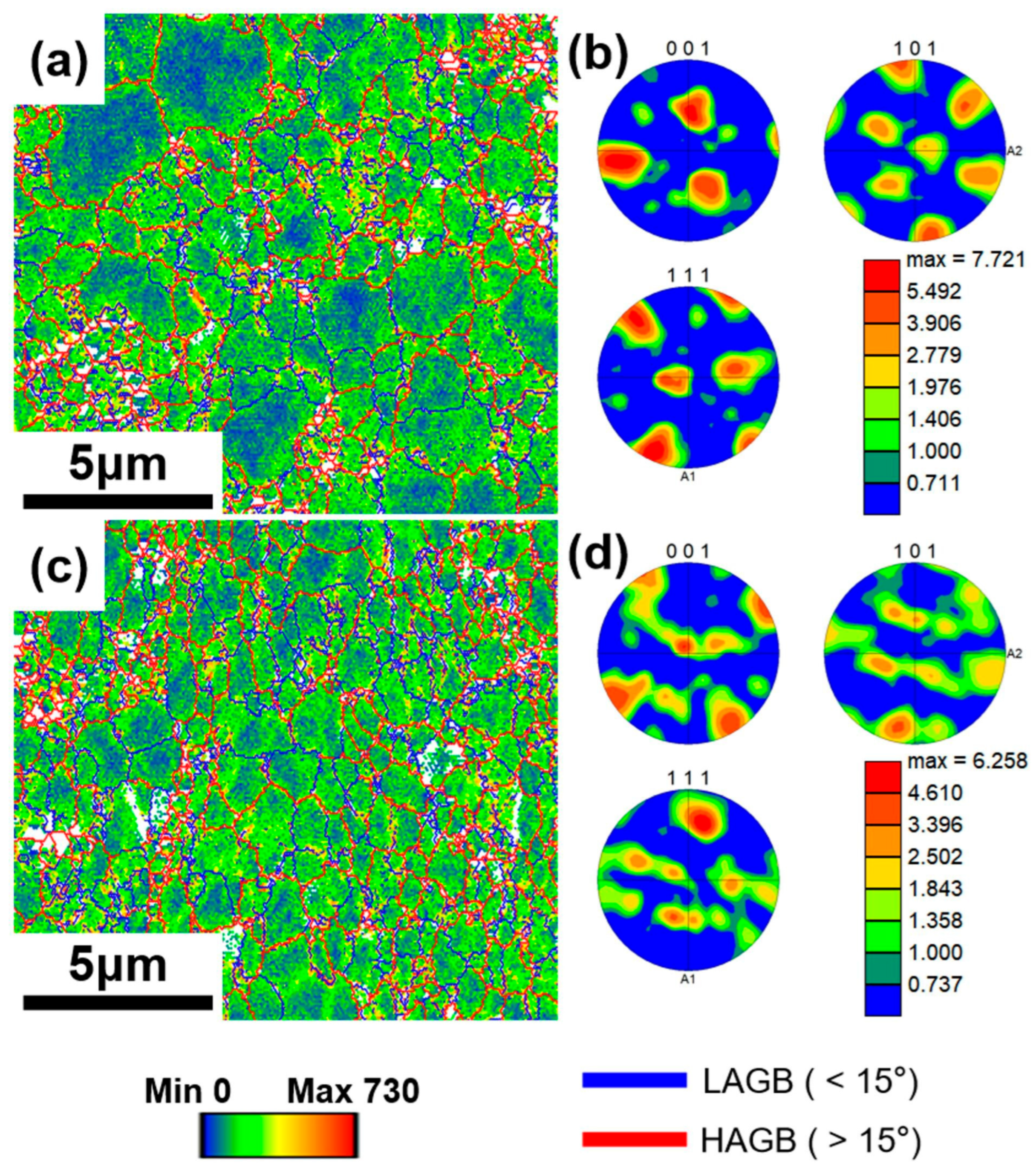
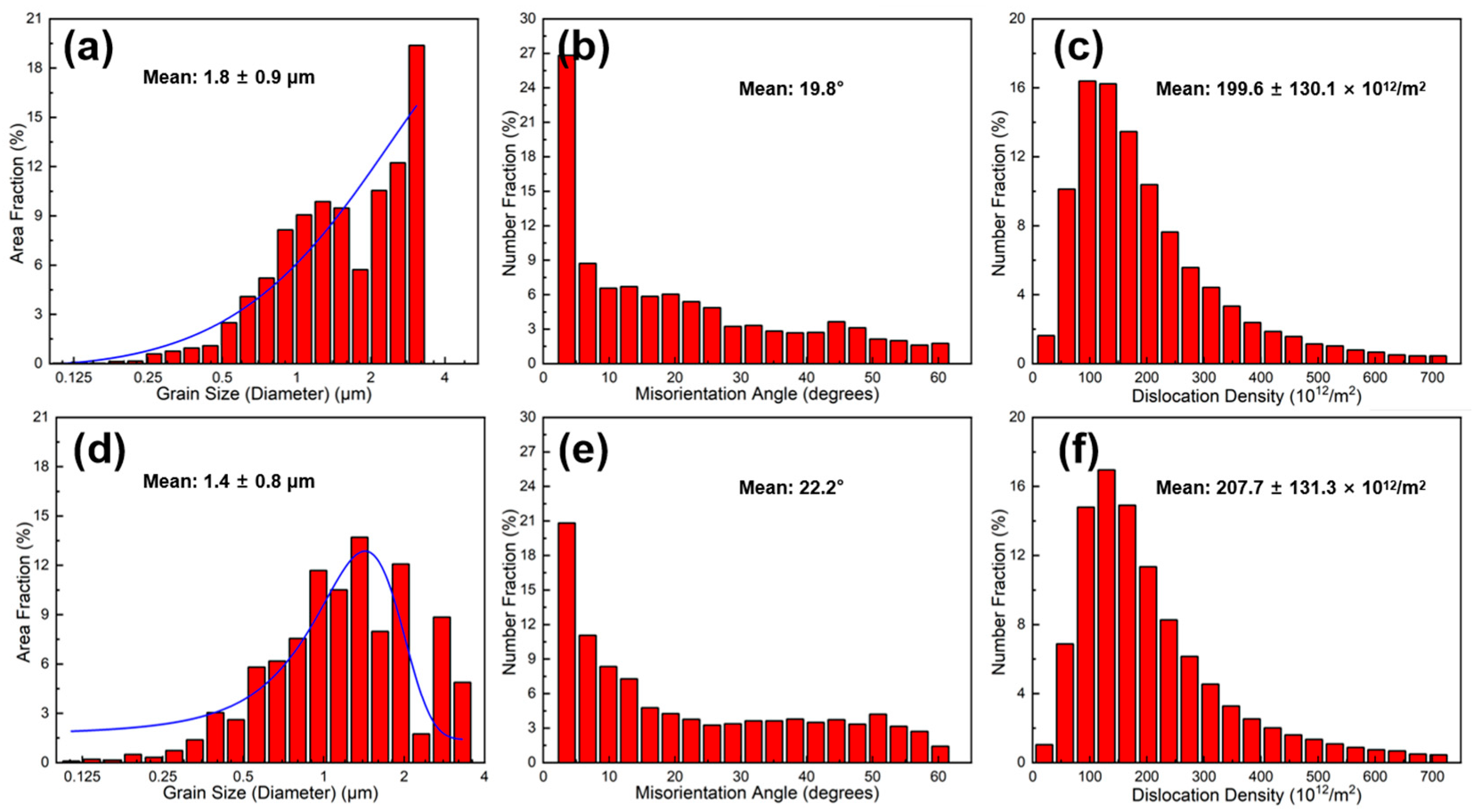
3.2. Distribution of the Graphite Flake
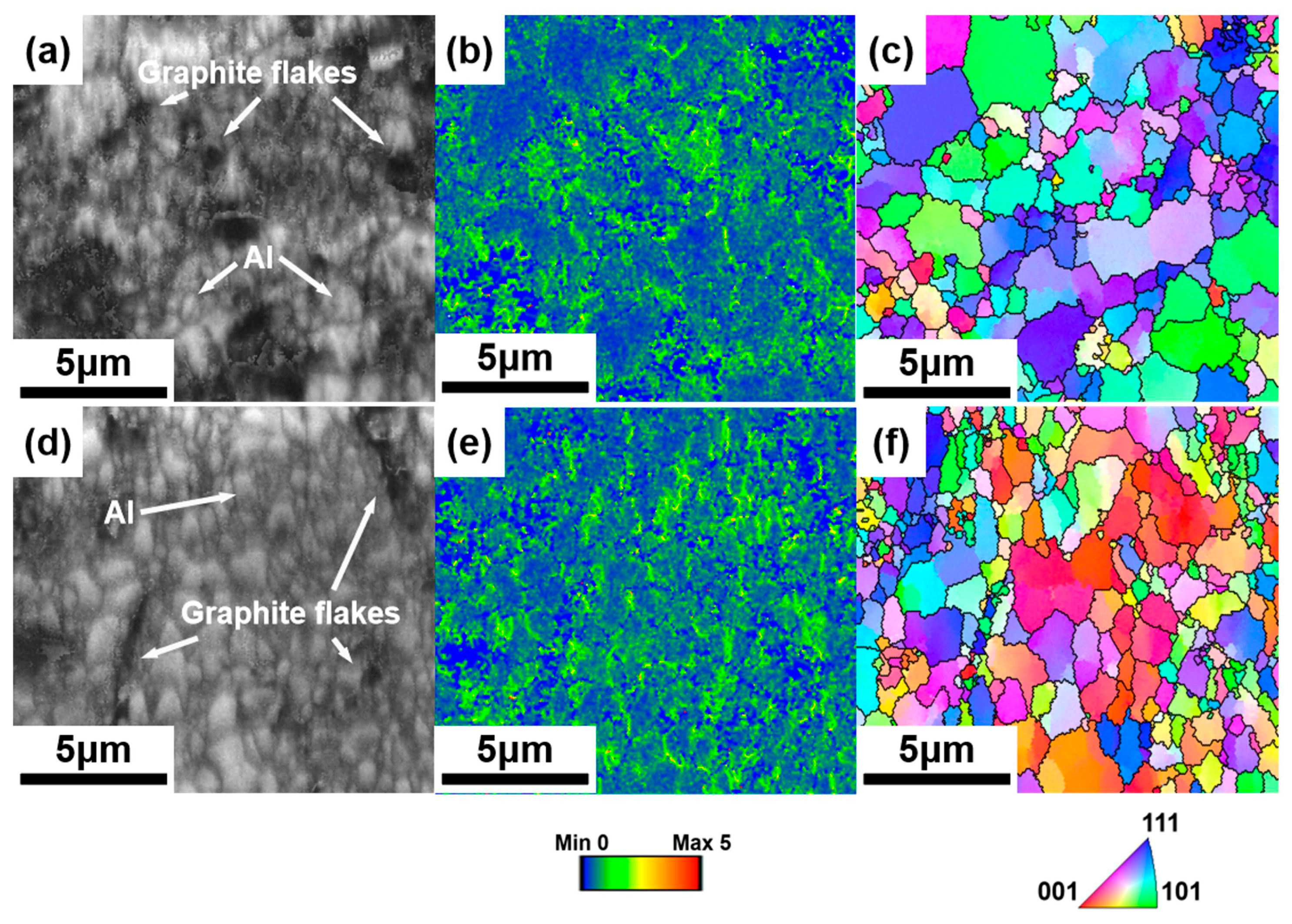
3.3. Effect of the Graphite Flakes on Microstructure
3.4. Effect of the Graphite Flakes on Properties
4. Conclusions
- Slight Grf (0.2 wt.%) can be uniformly dispersed via the HP-MP, forming clean, low-resistance semi-coherent interfaces with the Al matrix, which is key to conductivity enhancement.
- Grf synergistically enhances strength through Orowan strengthening, grain refinement strengthening, and Al4C3 second-phase strengthening.
- Excessive Grf (>0.5 wt.%) causes severe agglomeration, porosity defects, increased Al4C3 phase content, excessive grain refinement, and weakened texture. These factors collectively induce strong grain boundary/interface scattering and stress concentration, leading to a drastic deterioration in conductivity and plasticity (elongation below 10%).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desai, P.D.; James, H.M.; Ho, C.Y. Electrical Resistivity of Aluminum and Manganese. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1984, 13, 1131–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-x.; Zhang, X.; Jing, X.-y.; Yuan, J.-c.; Song, W. Severe plastic deformation of commercially pure aluminum using novel equal channel angular expansion extrusion with spherical cavity. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 2613–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashkin, M.Y.; Sabirov, I.; Medvedev, A.E.; Enikeev, N.A.; Lefebvre, W.; Valiev, R.Z.; Sauvage, X. Mechanical and electrical properties of an ultrafine grained Al–8.5wt. % RE (RE = 5.4wt.% Ce, 3.1wt.% La) alloy processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramono, A.; Zulfia, A.; Dhoska, K.; Suryana, S.; Milandia, A.; Zulaida, Y.M.; Juniarsih, A. High Strength of Aluminium-Based Composites by Different Methods of Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD). Mater. Sci. Forum 2022, 1057, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lv, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. High strength high electrical conductivity ultrafine-grained Al–Y alloy processed via cold drawing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-y.; Zhang, H.; Kong, X.-x.; Fu, D.-f. Microstructure and properties of Al–0.70Fe–0.24Cu alloy conductor prepared by horizontal continuous casting and subsequent continuous extrusion forming. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanacio-Sánchez, X.; Garay-Reyes, C.G.; Martínez-García, A.; Estrada-Guel, I.; Mendoza-Duarte, J.M.; Guerrero-Seañez, P.; González-Sánchez, S.; Rocha-Rangel, E.; de Jesús Cruz-Rivera, J.; Gutiérrez-Castañeda, E.J.; et al. Enhancement of the Electrical Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of Al-Mg-Si and Al-Mg-Zn Ternary Systems After a T8 Heat Treatment. Metals 2024, 14, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, X.S.; Gao, J.S.; Huang, H.; Ma, Z.Q.; Guo, L.J. Effects of welding parameters and post-heat treatment on mechanical properties of friction stir welded AA2195-T8 Al-Li alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Anderson, I.; Riedemann, T.; Russell, A. Modeling the electrical resistivity of deformation processed metal–metal composites. Acta Mater. 2014, 77, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, G.A.; Anderson, I.E.; Verhoeven, J.D. Strength and electrical conductivity of deformation-processed Cu-15 Vol Pct Fe alloys produced by powder metallurgy techniques. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisinia, B.; Poole, W.J.; Lloyd, D.J. Examination of precipitation in the aluminum alloy AA6111 using electrical resistivity measurements. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 420, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the Elastic Properties and Intrinsic Strength of Monolayer Graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Dahi Taleghani, A. Engineering of polymer nanocomposites using acid-functionalized graphite nanoplatelets for high-temperature sealing purposes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 306, 112772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingione, E.; Salvi, D.; Almonti, D.; Ponticelli, G.S. Improvement of thermal, electrical, and tribological performances of GnPs composites produced by selective laser sintering. Polym. Compos. 2025, 46, 7924–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyada, F.A.; Jabur, A.R.; Alwan, H.A. Effect addition of graphene on electrical conductivity and tensile strength for Recycled electric power transmission wires. Energy Procedia 2017, 119, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Mikulova, P.; Fan, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Nomura, N.; Kawasaki, A. Interfacial reaction induced efficient load transfer in few-layer graphene reinforced Al matrix composites for high-performance conductor. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 167, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittala, A.; Smith, J.; Gwalani, B.; Silverstein, J.; Kraft, F.F.; Kappagantula, K. Simultaneously improved electrical and mechanical performance of hot-extruded bulk scale aluminum-graphene wires. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 293, 116452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nam, S.; Roh, A.; Yoo, S.; Quevedo-Lopez, M.; Choi, H. Effect of interfacial features on the mechanical and electrical properties of rGO/Al composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 12001–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, H.; Liang, J.; Gu, S.; You, W.; Shu, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Microstructure evolution and properties of graphene nanoplatelets reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Charact. 2018, 140, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ud Din, R.; Wadood, A.; Syed, W.H.; Akhtar, S.; Aune, R.E. Effect of graphene nanoplatelets on the physical and mechanical properties of Al6061 in fabricated and T6 thermal conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 790, 1076–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, L.H.; Zan, Y.N.; Wang, W.G.; Xiao, B.L.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.Z.; Ni, D.R.; Ma, Z.Y. Enhancing strengthening efficiency of graphene nano-sheets in aluminum matrix composite by improving interface bonding. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 199, 108268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Liu, K.; Yan, Q.; Xiong, W.; Wu, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of graphene nanoplatelets reinforced Al matrix composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 837, 155495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, S.; Quanfang, C. The influence of interface products on the mechanical and electrical properties of graphene aluminum composites. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 104164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bustamante, R.; Bolaños-Morales, D.; Bonilla-Martínez, J.; Estrada-Guel, I.; Martínez-Sánchez, R. Microstructural and hardness behavior of graphene-nanoplatelets/aluminum composites synthesized by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, S578–S582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yi, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Jiang, B.; Wang, H. Mechanical properties and conductivity of graphene/Al-8030 composites with directional distribution of graphene. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 3314–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillari, L.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Murty, S.V.S.N.; Umasankar, V. On the Comparison of Graphene and Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes as Reinforcements in Aluminum Alloy AA2219 Processed by Ball Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Yang, W.; Shao, P.; Hussain, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xiu, Z.; Hou, X.; Qiao, J.; Wu, G. Effect of interfacial microstructure on the mechanical properties of GNPs/Al composites. Carbon 2020, 162, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.; Tyson, W.R. Tensile properties of fibre-reinforced metals: Copper/tungsten and copper/molybdenum. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1965, 13, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.; Kashyap, K.T.; Rahul, R.; Yamdagni, S. Strengthening in carbon nanotube/aluminium (CNT/Al) composites. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.H.; Cha, S.I.; Lim, B.K.; Park, H.M.; Han, D.S.; Hong, S.H. Synergistic strengthening by load transfer mechanism and grain refinement of CNT/Al–Cu composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, D.L. Consideration of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites: A model for predicting their yield strength. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Fang, Y.-Y.; Lu, M.-Y.; Keng, P.Y.; Chang, S.-Y. Grain-boundary/interface structures and scatterings of ruthenium and molybdenum metallization for low-resistance interconnects. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 629, 157440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Shen, Y.; Chen, X.; Qian, L.; Lu, K. Ultrahigh Strength and High Electrical Conductivity in Copper. Science 2004, 304, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Liu, P.; Fan, G.; Xiong, D.-B.; Li, Z. Towards an atomic-scale understanding of interface characteristics in graphene/Al composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element | Al (wt.%) | Cu (wt.%) | Fe (wt.%) | Si (wt.%) | Balance (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 99.87 | 0.0010 | 0.0763 | 0.0456 | 0.0071 |
| Sample ID | Master Alloy (kg) | Pure Al (kg) | Master Alloy:CP Al | Graphite Flake Content (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM00 | 0 | 2 | - | 0.0 |
| GM02 | 0.25 | 6 | 1:24 | 0.2 |
| GM05 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 1:9 | 0.5 |
| GM10 | 1 | 4 | 1:4 | 1.0 |
| GM30 | 2 | 1.333 | 1:0.666 (3:2) | 3.0 |
| Sample ID | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Uniform Elongation (%) | Vickers Hardness (HV) | Electrical Conductivity (% IACS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM00 | 44.6 ± 0.4 | 32.9 ± 2.1 | 23.9 ± 1.4 | 61.2 |
| GM02 | 100.4 ± 0.5 | 31.6 ± 1.3 | 24.7 ± 0.9 | 67.1 |
| GM05 | 115.7 ± 0.4 | 9.4 ± 0.2 | 40.3 ± 1.3 | 60.2 |
| GM10 | 116.0 ± 0.4 | 8.6 ± 0.2 | 56.2 ± 3.5 | 59.8 |
| GM30 | 120.9 ± 0.9 | 8.75 ± 0.1 | 57.0 ± 3.3 | 56.9 |
| Composite Material | Preparation Process | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Electrical Conductivity (% IACS) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM00 (CP-Al) | Hybrid Powder-Melt Process | 44.6 | 61.2 | This work |
| GM02 (0.2 wt.% Grf/Al) | 100.4 | 67.1 | ||
| GM05 (0.5 wt.% Grf/Al) | 115.7 | 60.2 | ||
| Ball-milled Al | Ball milling process | (Yield strengths) 298 | 51 | [18] |
| 0.2 vol.% rGO/Al | (Yield strengths) 374 | 51 | ||
| Al | Continuous casting and rolling processes | 114 | 62.5 | [19] |
| Al-0.2 wt.% GNPs | 156 | 61.8 | ||
| Al2219 | Spark plasma sintering | - | 50 | [26] |
| Al2219-0.5 wt.% graphene | - | 36 | ||
| Al2219-1 wt.% graphene | - | 11 | ||
| Al-8030 | Semisolid extrusion | 130.6 | 62.2 | [25] |
| 0.5 wt% GNPs/Al-8030 | 212.7 | 61.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Qian, Q.; Yan, M.; Lin, H. Fabrication of Graphite Flake/Al Composites via the Hybrid Powder-Melt Process: Synergistic Enhancement of Strength and Conductivity Through Low Content Addition. Materials 2025, 18, 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204683
Luo J, Lu C, Liu F, Yang X, Wang Z, Qian Q, Yan M, Lin H. Fabrication of Graphite Flake/Al Composites via the Hybrid Powder-Melt Process: Synergistic Enhancement of Strength and Conductivity Through Low Content Addition. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204683
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jiapeng, Chunyang Lu, Feihua Liu, Xinwei Yang, Ziren Wang, Qian Qian, Ming Yan, and Haihui Lin. 2025. "Fabrication of Graphite Flake/Al Composites via the Hybrid Powder-Melt Process: Synergistic Enhancement of Strength and Conductivity Through Low Content Addition" Materials 18, no. 20: 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204683
APA StyleLuo, J., Lu, C., Liu, F., Yang, X., Wang, Z., Qian, Q., Yan, M., & Lin, H. (2025). Fabrication of Graphite Flake/Al Composites via the Hybrid Powder-Melt Process: Synergistic Enhancement of Strength and Conductivity Through Low Content Addition. Materials, 18(20), 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204683







