The Influence of Laser Shock Peening on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AH32 Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and LSP Experiment
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Mechanical Testing
2.4. Friction
3. Result
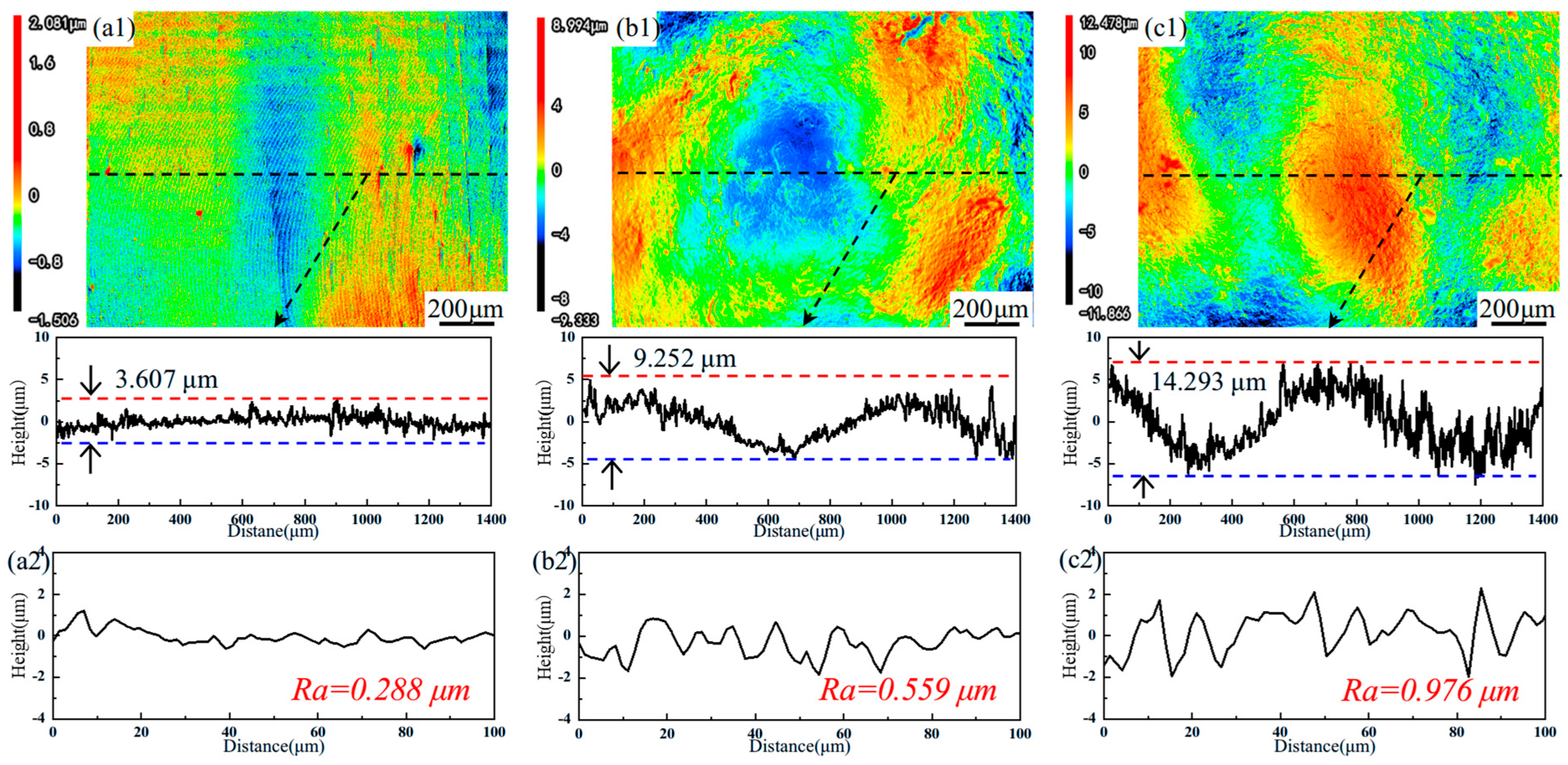
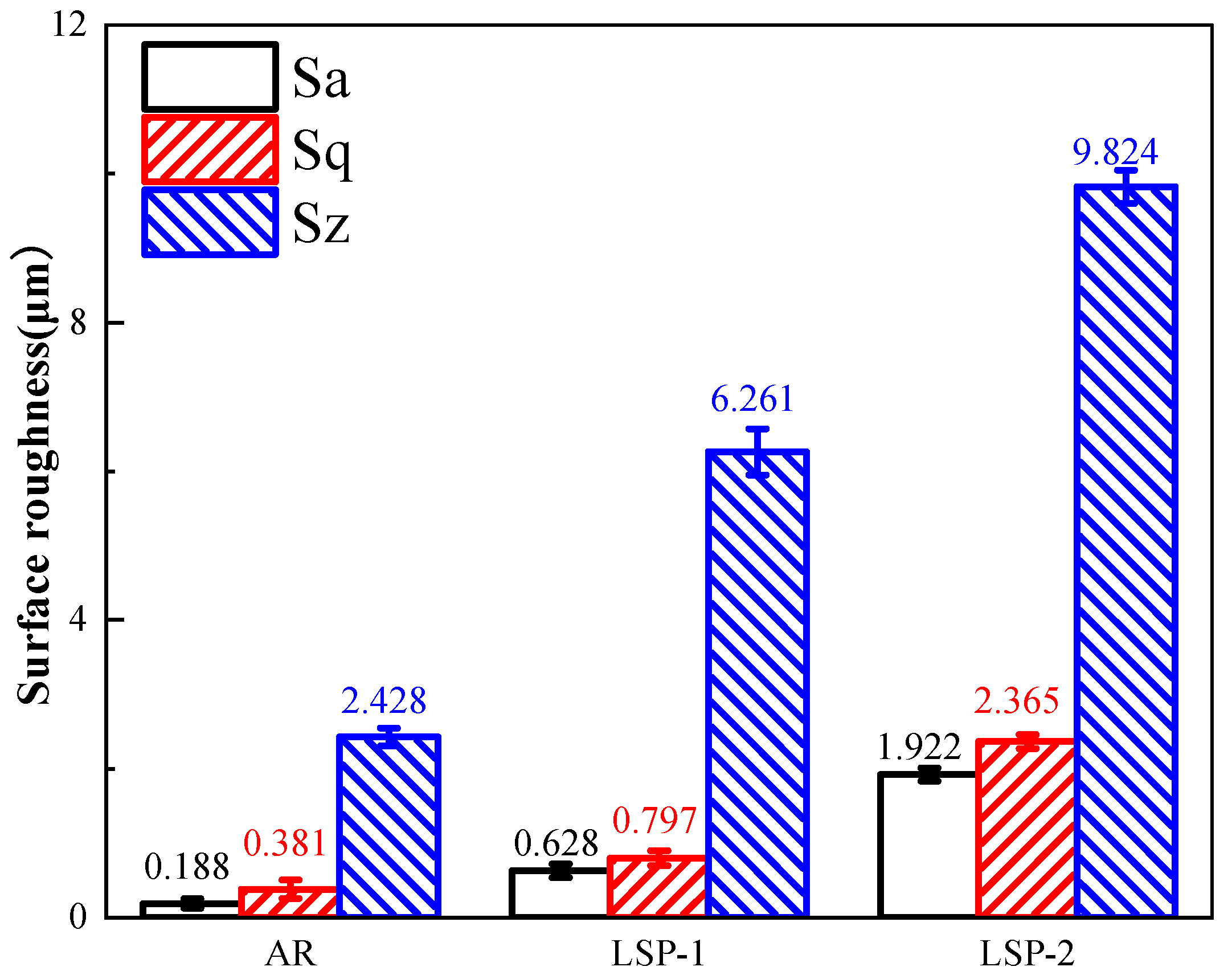
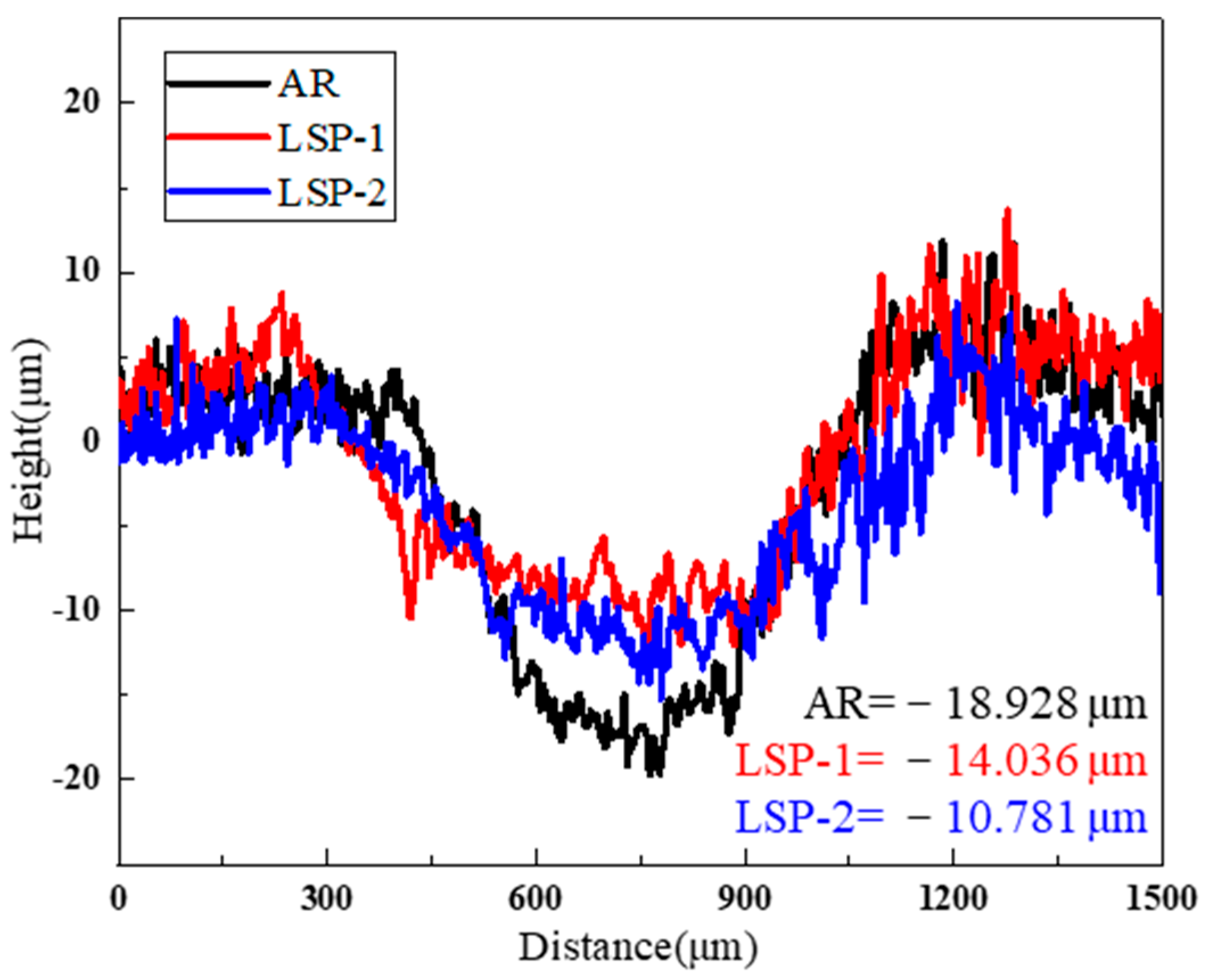
3.1. Roughness
3.2. XRD and Residual Stress Analysis
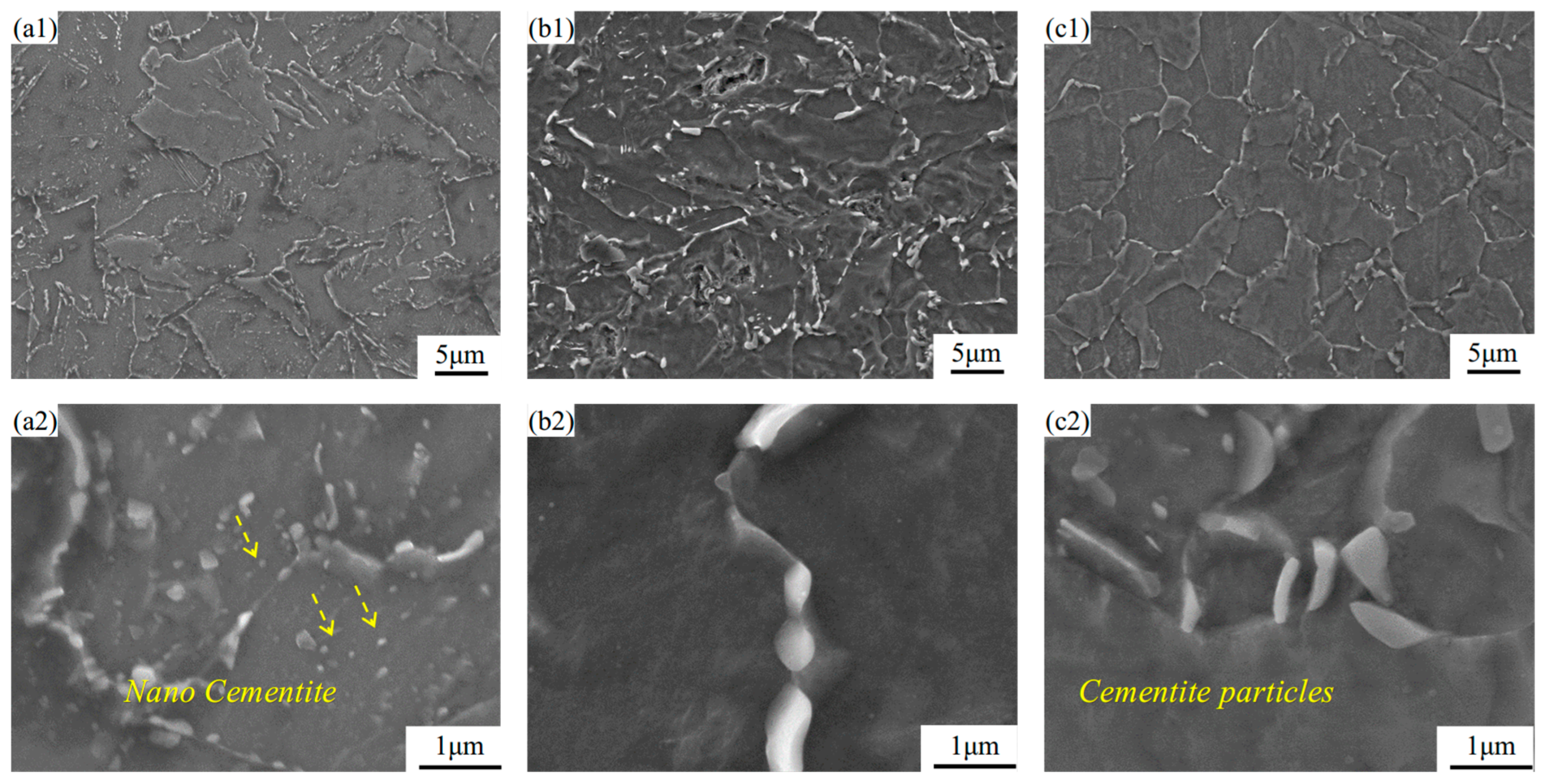
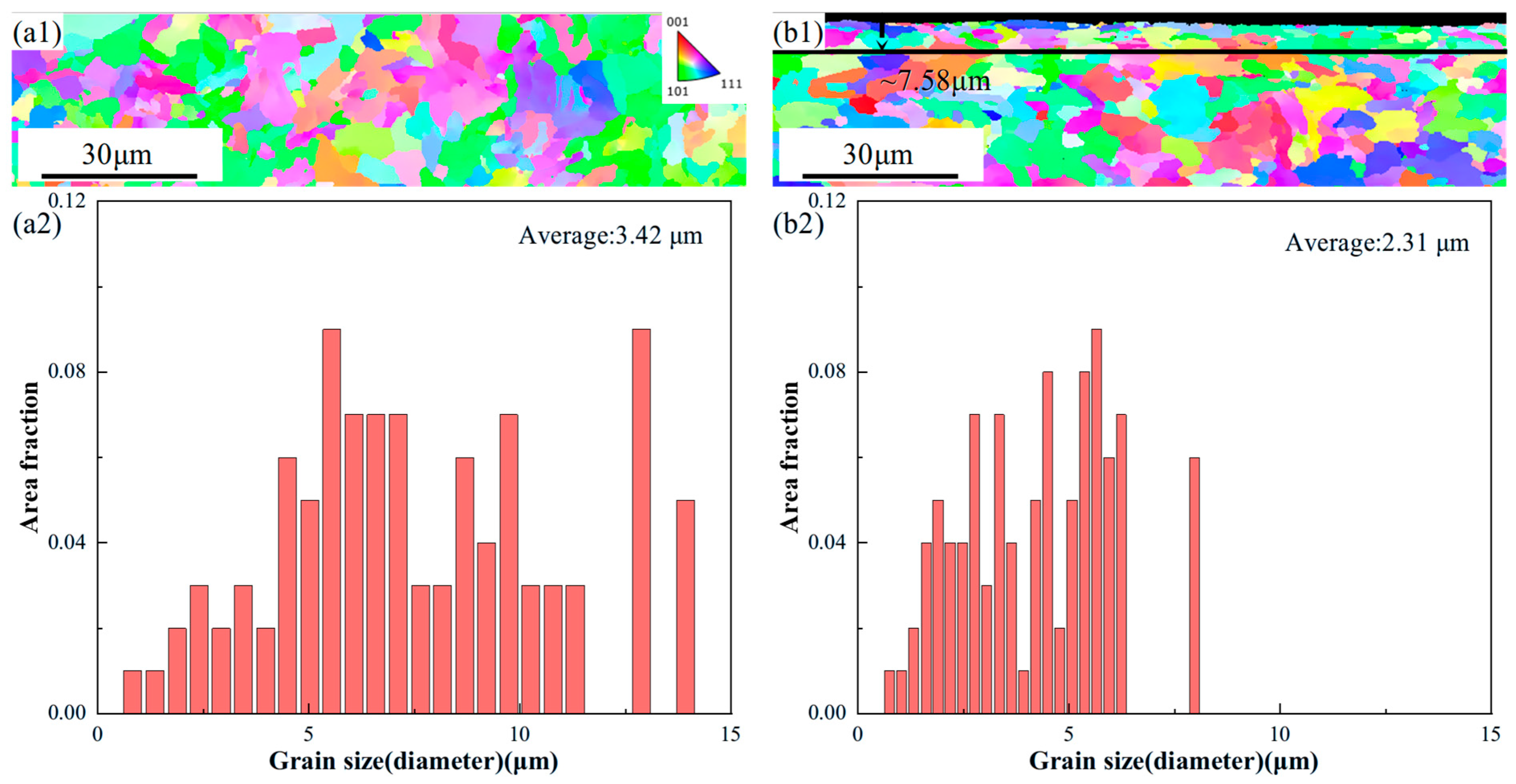
3.3. Microstructural Analysis
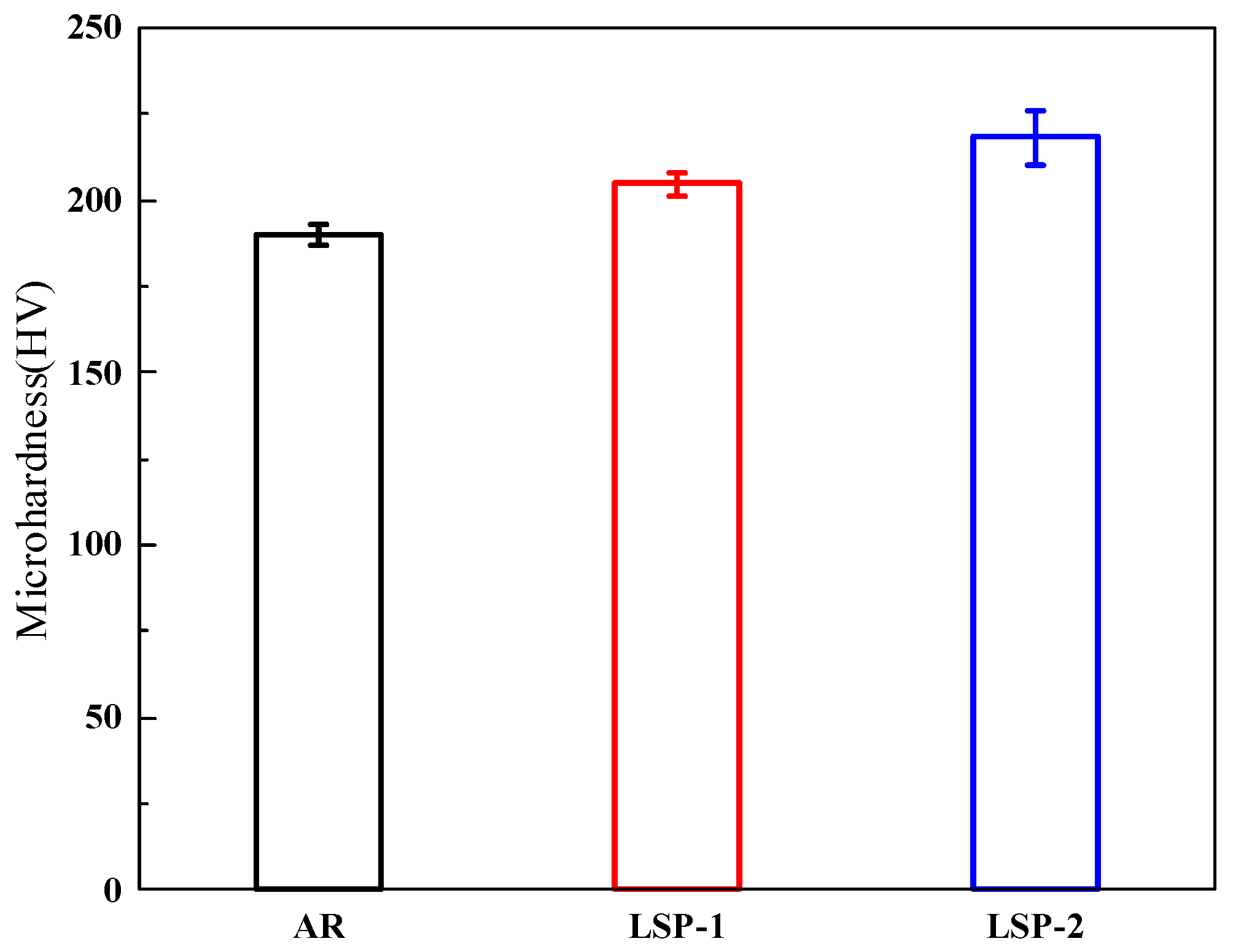
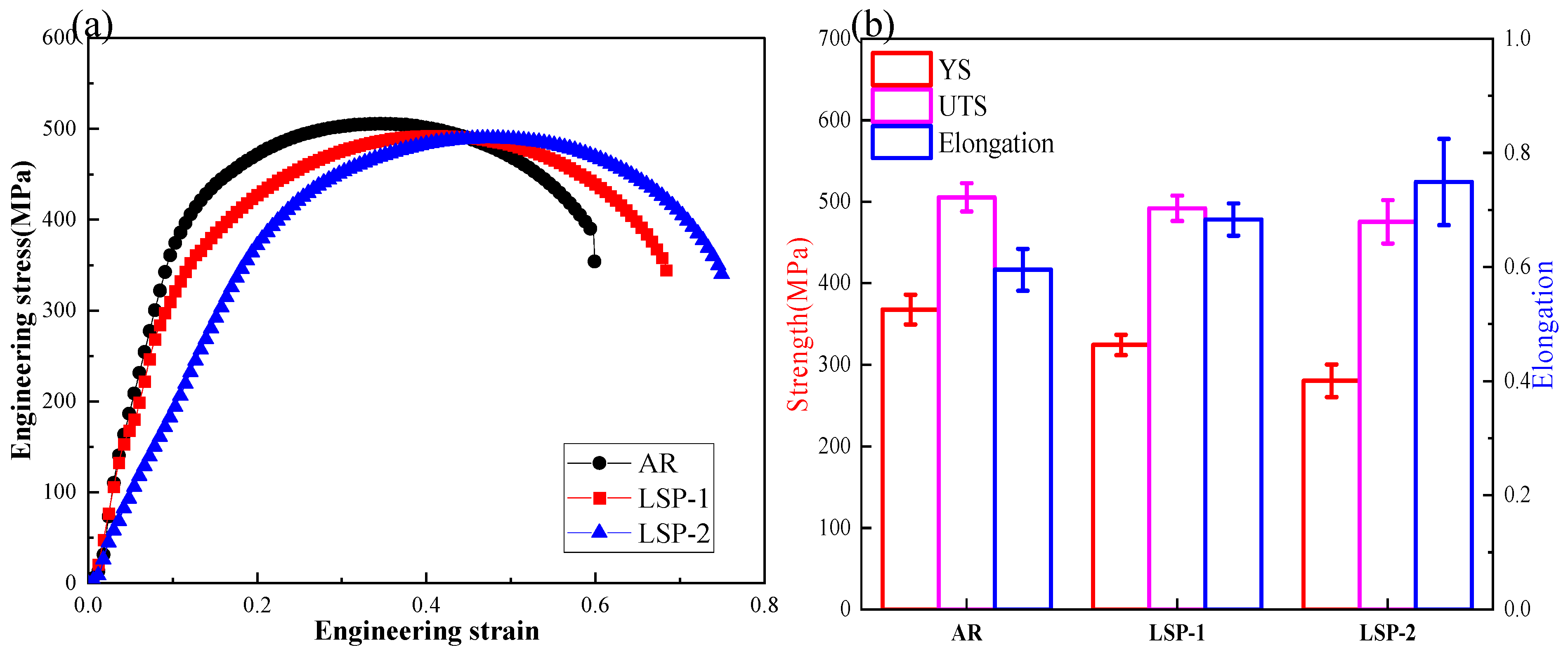
3.4. Microhardness and Tensile Properties
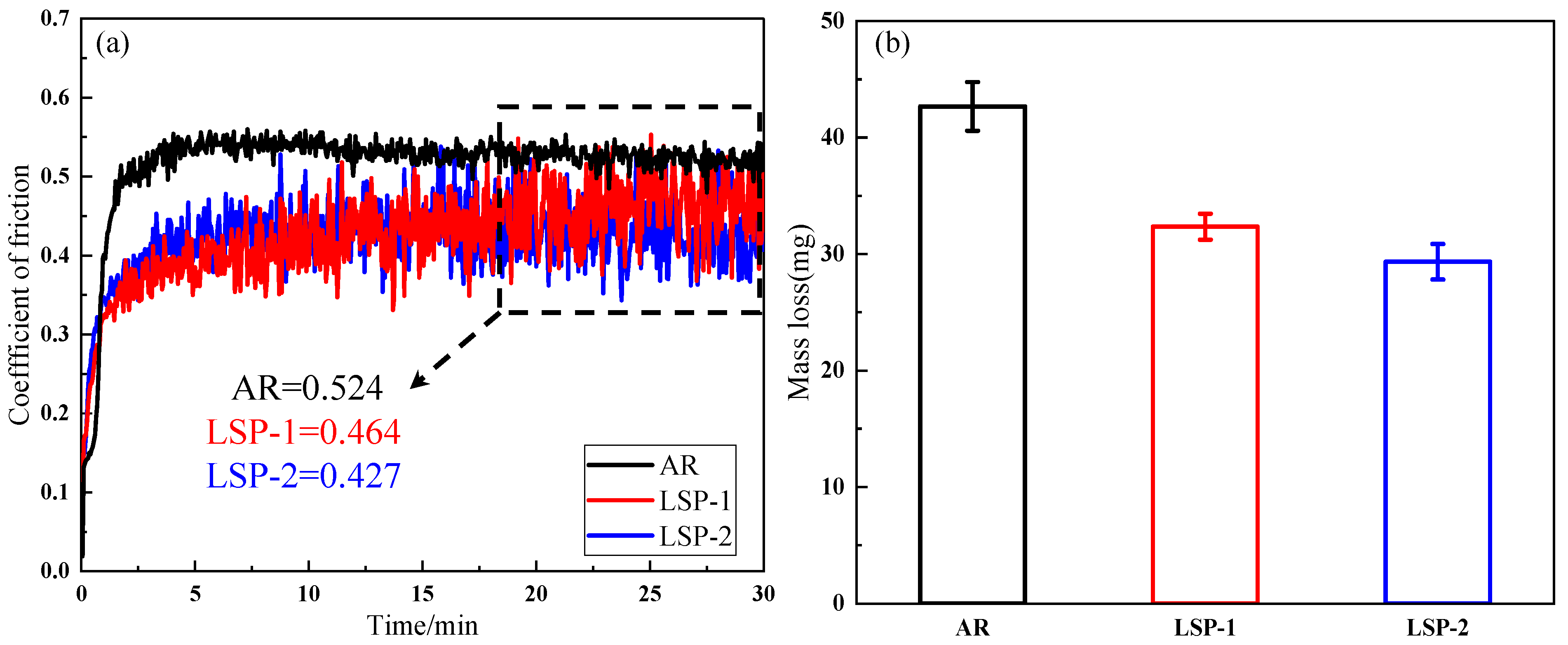
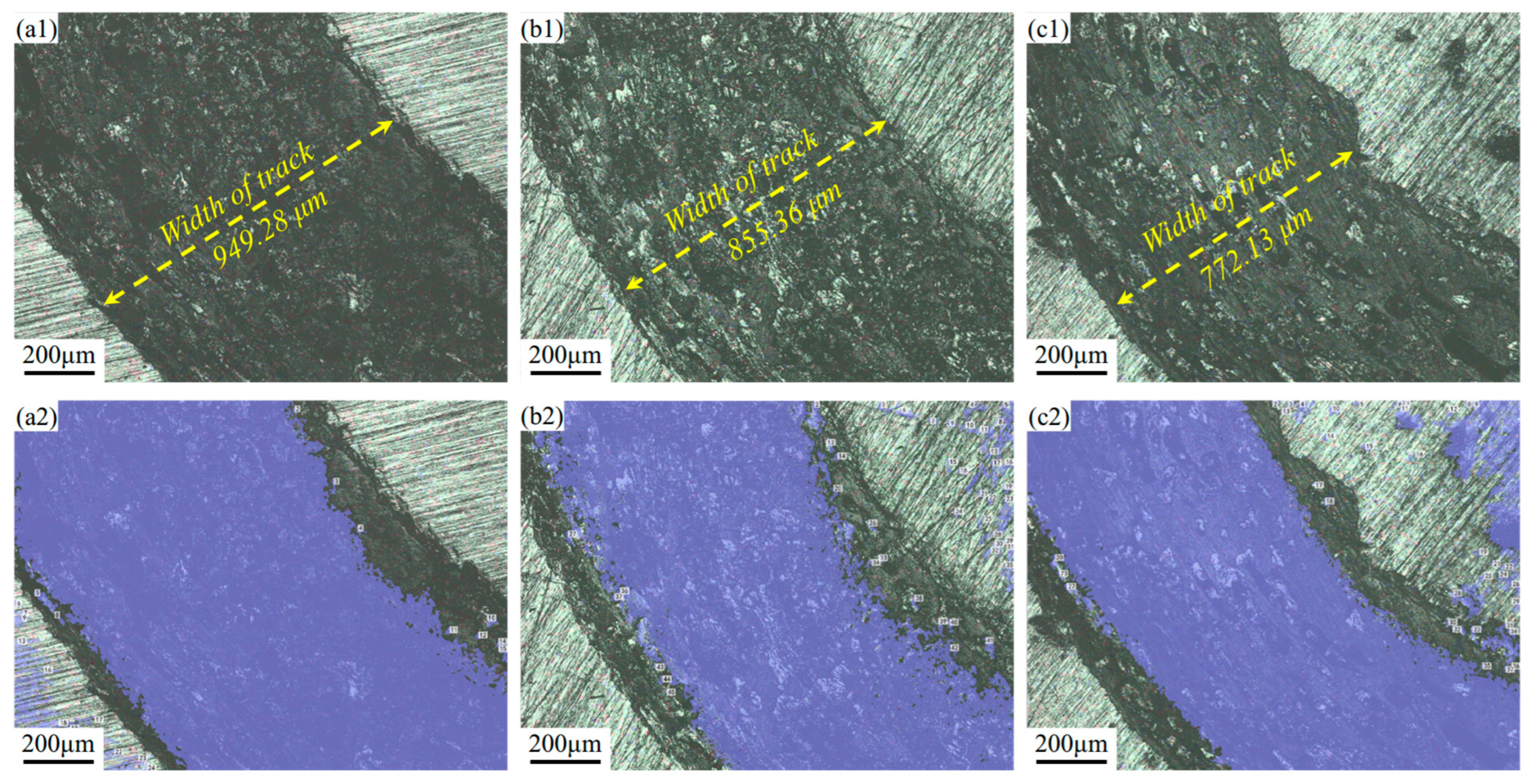
3.5. Friction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The plastic deformation induced by LSP increases the surface roughness of AH32, while also inducing high-magnitude residual stress on the surface. The residual stress for the LSP-2 sample reaches −162 MPa.
- (2)
- The typical microstructure of AH32 steel mainly consists of ferrite and carbides. The microstructural evolution after LSP treatment is primarily characterized by a significant reduction in cementite within the grain boundaries, while cementite particles precipitate along the boundaries of the grains. The LSP-2 sample exhibited an affected layer depth of approximately 7.58 μm, which was accompanied by a 32.4% refinement in grain size compared to the AR sample.
- (3)
- After LSP treatment, the surface hardness of the samples increased by 7.3% and 14.7%, respectively. The tensile results indicate that LSP-2 exhibits a 25.8% enhancement in elongation while demonstrating only a marginal 5.9% reduction in ultimate tensile strength.
- (4)
- Compared to the AR samples, the LSP samples exhibited lower friction coefficients and wear rates, with the wear coefficients decreasing by 11.4% and 18.5%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mostafanejad, A.; Iranmanesh, M.; Zarebidaki, A. An experimental study on stress corrosion behavior of A131/A and A131/AH32 low carbon steels in simulated seawater. Ocean Eng. 2019, 188, 106204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Yang, P.; Xu, G. Low cycle fatigue and ratcheting failure behavior of AH32 steel under uniaxial cyclic loading. Int. J. Nav. Arch. Ocean Eng. 2019, 11, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Huang, G.; Wu, W. Effect of tensile stress on the corrosion morphology and multifractal characteristics of DH36 steel in a neutral salt spray environment. Corros. Sci. 2024, 243, 112583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shen, Y.; Hua, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, S. Improvement in electrochemical and long-term immersion corrosion resistance of AH32 marine steel using laser shock peening. Surfaces Interfaces 2025, 72, 107183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, H.; Xing, S.; Jiang, C.; Ji, V. Surface mechanical property and residual stress stability of nanostructured CNT/Al-Cu-Mg composites induced by shot peening. Mater. Charact. 2024, 218, 114515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, W.; Li, J.; Pan, H.; Liu, L. Corrosion behavior of laser powder bed fusion TA2-Cu-Q345 composite plate subjected to picosecond laser shock peening. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 189, 113120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, K.; Cai, J.; Lu, J. Obvious improvement in electrochemical and long-term immersion corrosion resistance of AISI 420 martensitic stainless steel using laser shock peening. Corros. Sci. 2022, 209, 110688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wang, Z.; Deng, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Luo, K.; Lu, J. Gradient microstructural evolution and mechanical property enhancement mechanisms in laser shock peened IN718 superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 944, 148905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Deng, W.; Du, J.; Luo, K.; Cai, J.; Lu, J. Improvement of strength-ductility synergy of Mg–Al–Mn alloy using laser shock peening-induced gradient nanostructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 871, 144844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Liu, D.; Dang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, L. Surface strengthening and wear resistance enhancement of electron beam powder bed fusion fabricated Ni-based superalloys via laser shock peening. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2025, 513, 132443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Niu, W.; Zhou, L.; Han, P.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Song, P.; Hu, N.; Guo, N.; et al. Effects of multiple laser shock peening impacts on microstructure and wear performance of wire-based laser directed energy deposition 17-4PH stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 3222–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Sun, M.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C.; Lu, J. The effect of laser shock peening with and without coating on microstructure and electrochemical corrosion behavior of AZ31b magnesium alloy. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2024, 496, 131709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Xing, Y.; Sun, M.; Xu, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, C.; Lu, J. Effect of laser shock peening on the dissolution of precipitates and pitting corrosion of AA6061-T6 with different original surface roughness. Corros. Sci. 2023, 228, 111794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Taji, I.; Hajilou, T.; Palencsár, S.; Dugstad, A.; Barnoush, A.; Verbeken, K.; Depover, T.; Johnsen, R. Role of cementite morphology on corrosion layer formation of high-strength carbon steels in sweet and sour environments. Corros. Sci. 2023, 214, 111031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lv, B.; Ma, H.; Sun, D.; Zhang, F. Wear behavior and the corresponding work hardening characteristics of Hadfield steel. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Kong, D.; Ma, R.; Liu, L.; Li, P. Microstructure evolution of 2205 duplex stainless steel (DSS) and inconel 718 dissimilar welded joints and impact on corrosion and mechanical behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 929, 148136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-M.; Liu, X.-B.; He, B.-M.; Zhang, F.-Z.; Liang, J.-X.; Liu, X.-Y.; Zheng, J. Laser cladding Ni60-SiC/Ti3SiC2 self-lubricating composite coatings on IN718 alloy: Wear mechanisms and oxidation behaviors. Wear 2024, 560–561, 205611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cao, F.; Sun, T.; Huang, G.; Li, M.; Hou, W.; Piao, Z.; Shen, Z.; Shen, Y. Developing ultrafine-grained structure with balanced α/γ fraction via underwater friction stir processing enables enhanced wear and corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2023, 457, 129295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, Q.; Li, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of in situ synthesized ceramic reinforced 316L/IN718 matrix composites. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 93, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yue, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, G.; Huang, M.; Yang, S. Enhancing strength performance of laser welded 7075 aluminum alloy joints with TiC nanoparticle-mixed filler powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 915, 147285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, J.; Ma, F.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, X.; Gao, X.; Xie, K. Effect of the microstructure and residual stress on tribological behavior of induction hardened GCr15 steel. Tribol. Int. 2017, 115, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, F.; Qu, S.; Ji, V.; Liu, H.; Li, X. Effect of shot peening on residual stress distribution and tribological behaviors of 17Cr2Ni2MoVNb steel. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2020, 386, 125497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| C | S | P | Cr | Ni | Mn | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AH32 | ≤0.18 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.4 | 0.9–1.6 | Balanced |
| Lattice Plane | AR | LSP-1 | LSP-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (110) | 0.208 | 0.223 | 0.241 |
| (200) | 0.342 | 0.346 | 0.416 |
| (211) | 0.433 | 0.442 | 0.473 |
| Samples | Total Worn Volume/μm3 | Cross-Section Area/μm2 | Area Ration/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR | 10,872,236.220 | 1,085,310.616 | 71.335 |
| LSP-1 | 9,680,137.442 | 920,414.825 | 62.468 |
| LSP-2 | 5,680,900.656 | 872,829.626 | 57.369 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, X.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, P.; Peng, Y. The Influence of Laser Shock Peening on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AH32 Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204679
Pei X, Shen Y, Xu Z, Li P, Peng Y. The Influence of Laser Shock Peening on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AH32 Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(20):4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204679
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Xu, Yiming Shen, Zhaomei Xu, Pengfei Li, and Yuchun Peng. 2025. "The Influence of Laser Shock Peening on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AH32 Steel" Materials 18, no. 20: 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204679
APA StylePei, X., Shen, Y., Xu, Z., Li, P., & Peng, Y. (2025). The Influence of Laser Shock Peening on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AH32 Steel. Materials, 18(20), 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18204679






