Performance of Self-Compacting Mortars Using Ground Seashells as Recycled Sand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. SC Mortar Design
2.3. Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
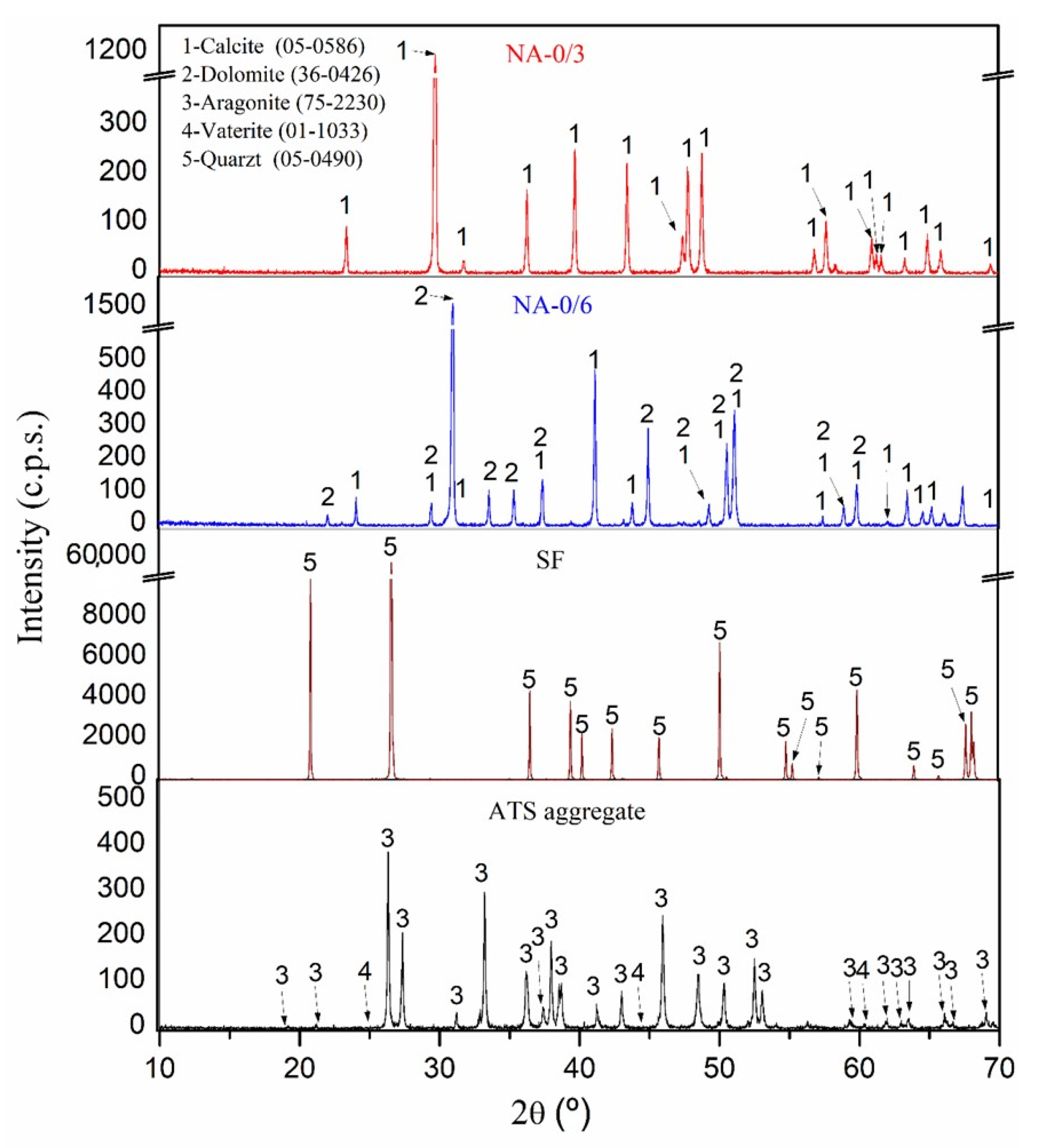
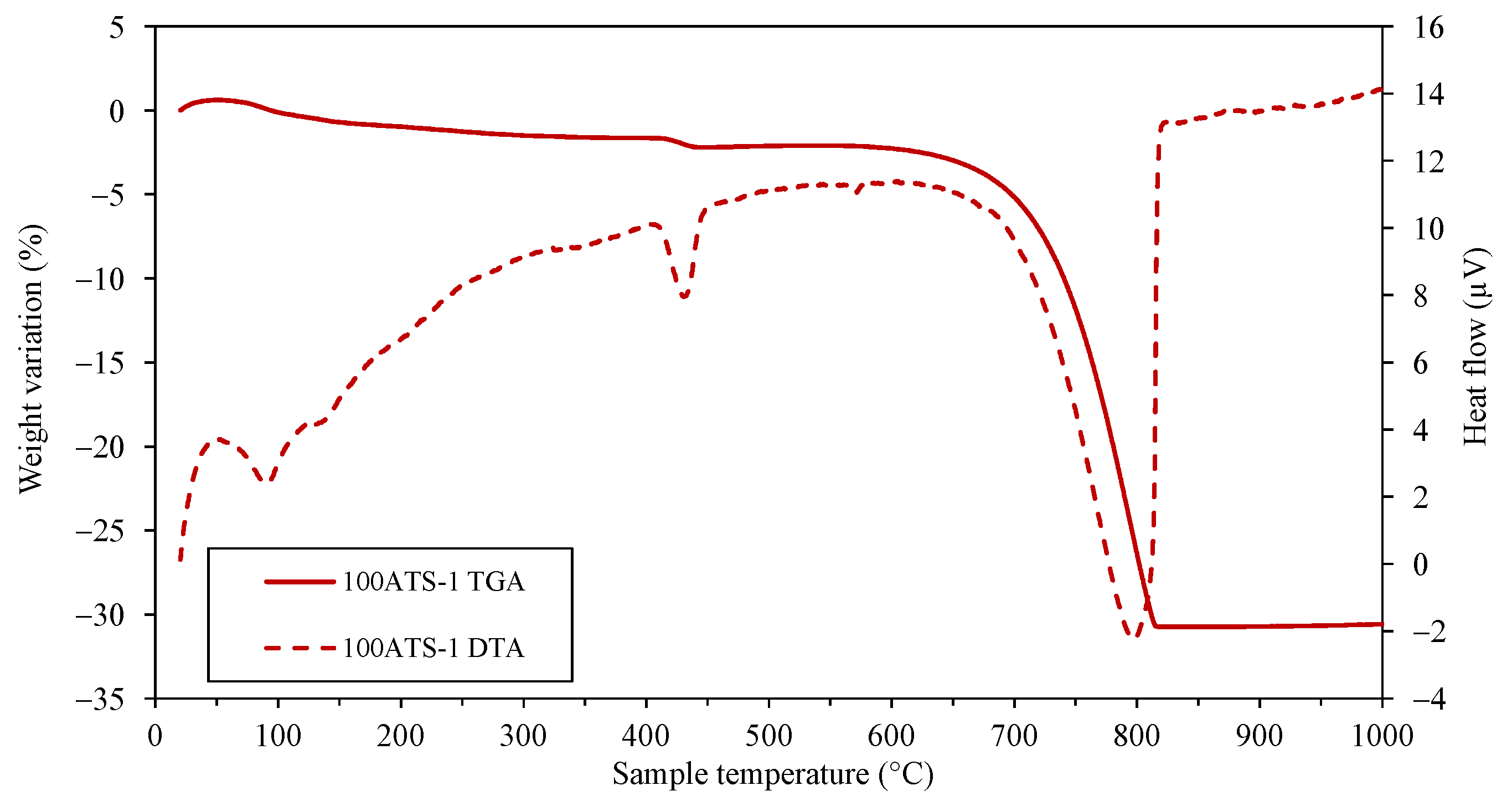
3.1. Chemical Assessment of Primary Materials
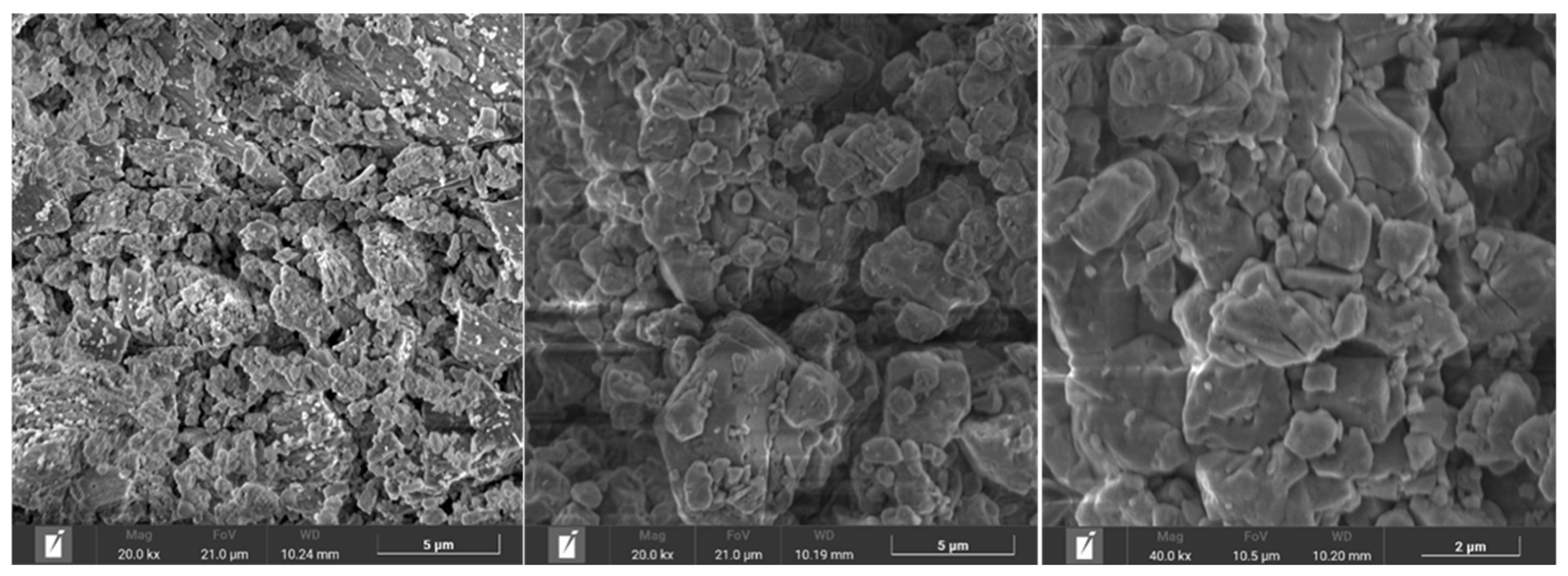
3.2. SEM of Aggregates
3.3. Workability Characteristics of Mixtures
3.4. Hardened Properties of the Mixtures
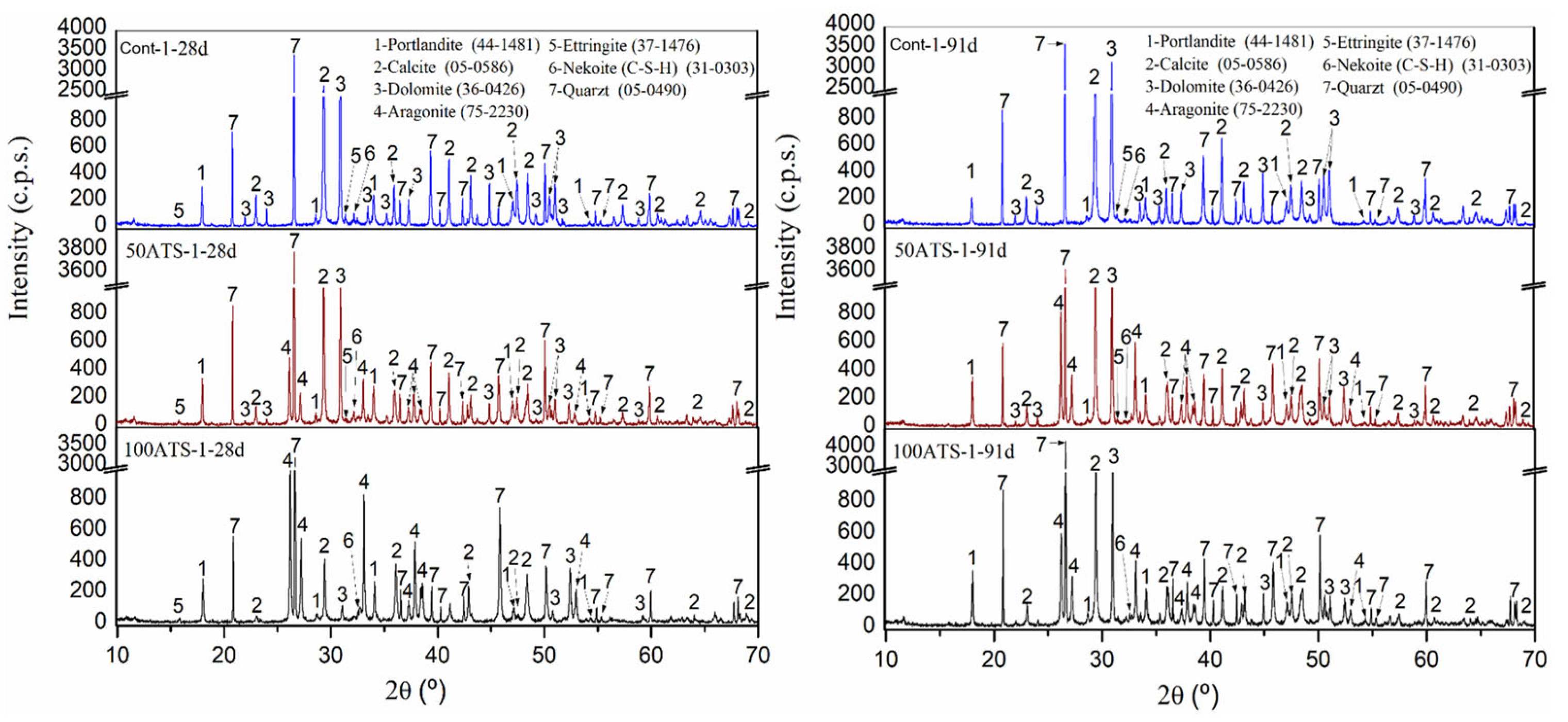
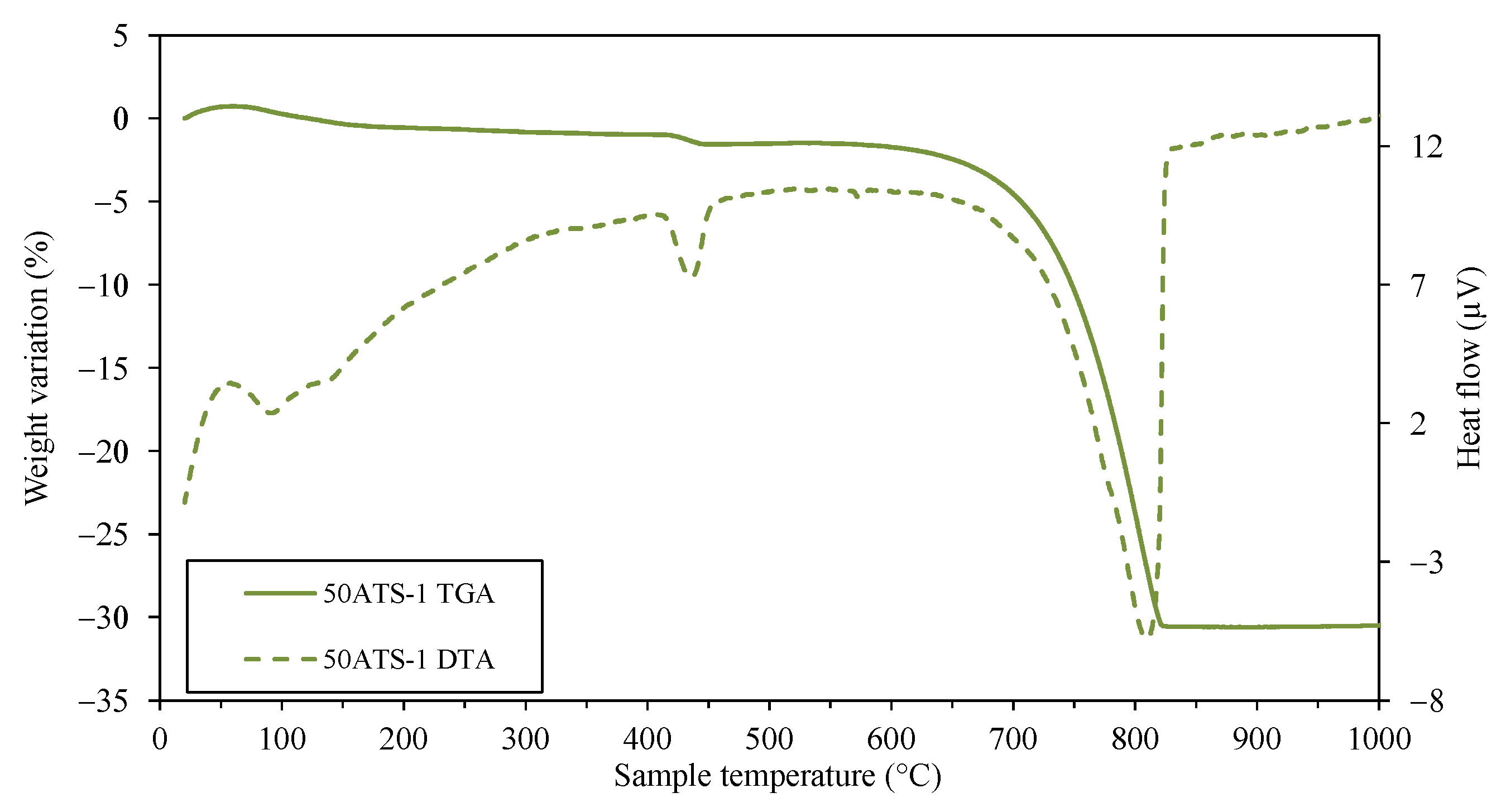
3.4.1. Analysis of Cured Mortar Properties
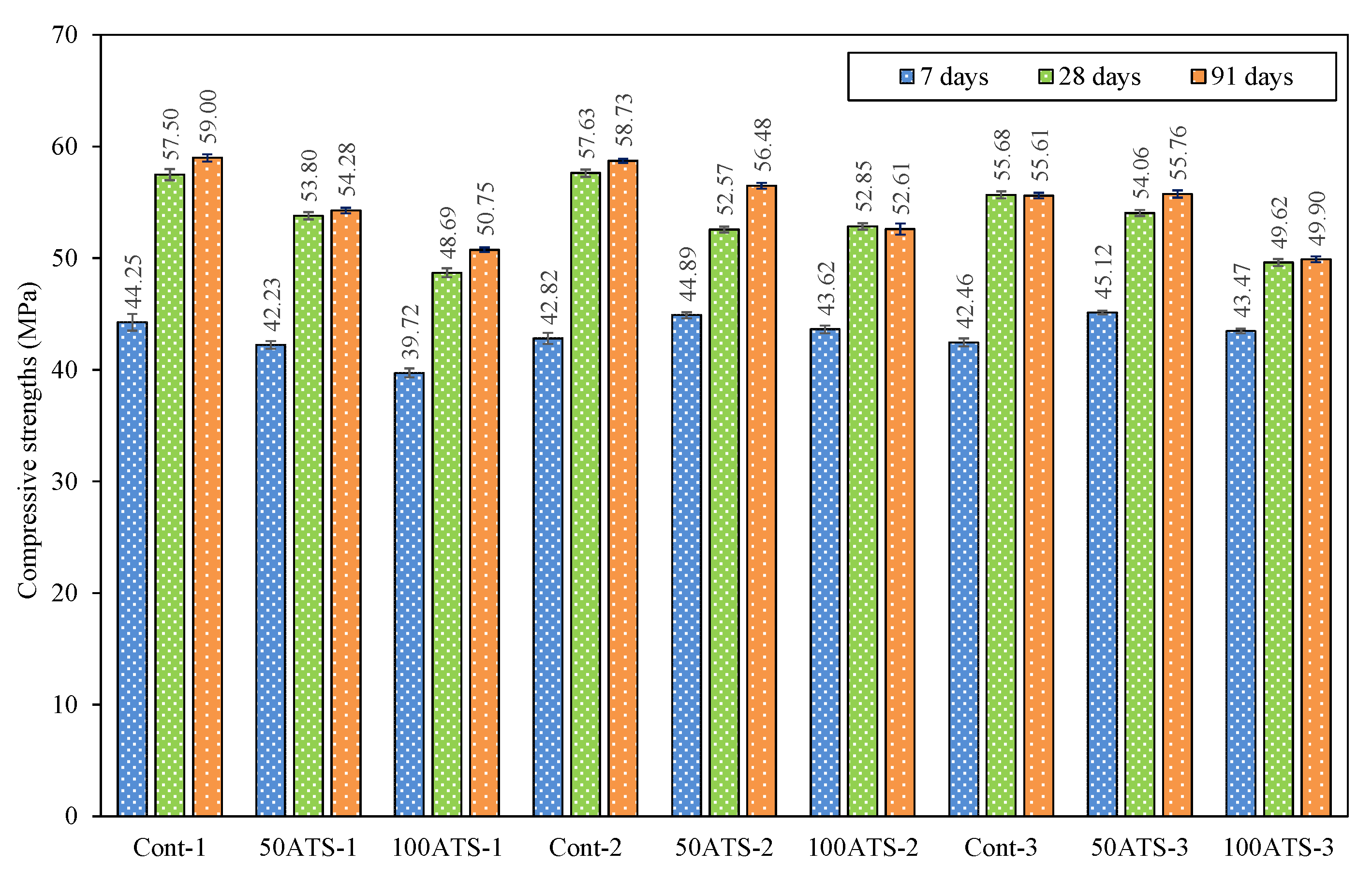
3.4.2. Mechanical Strength
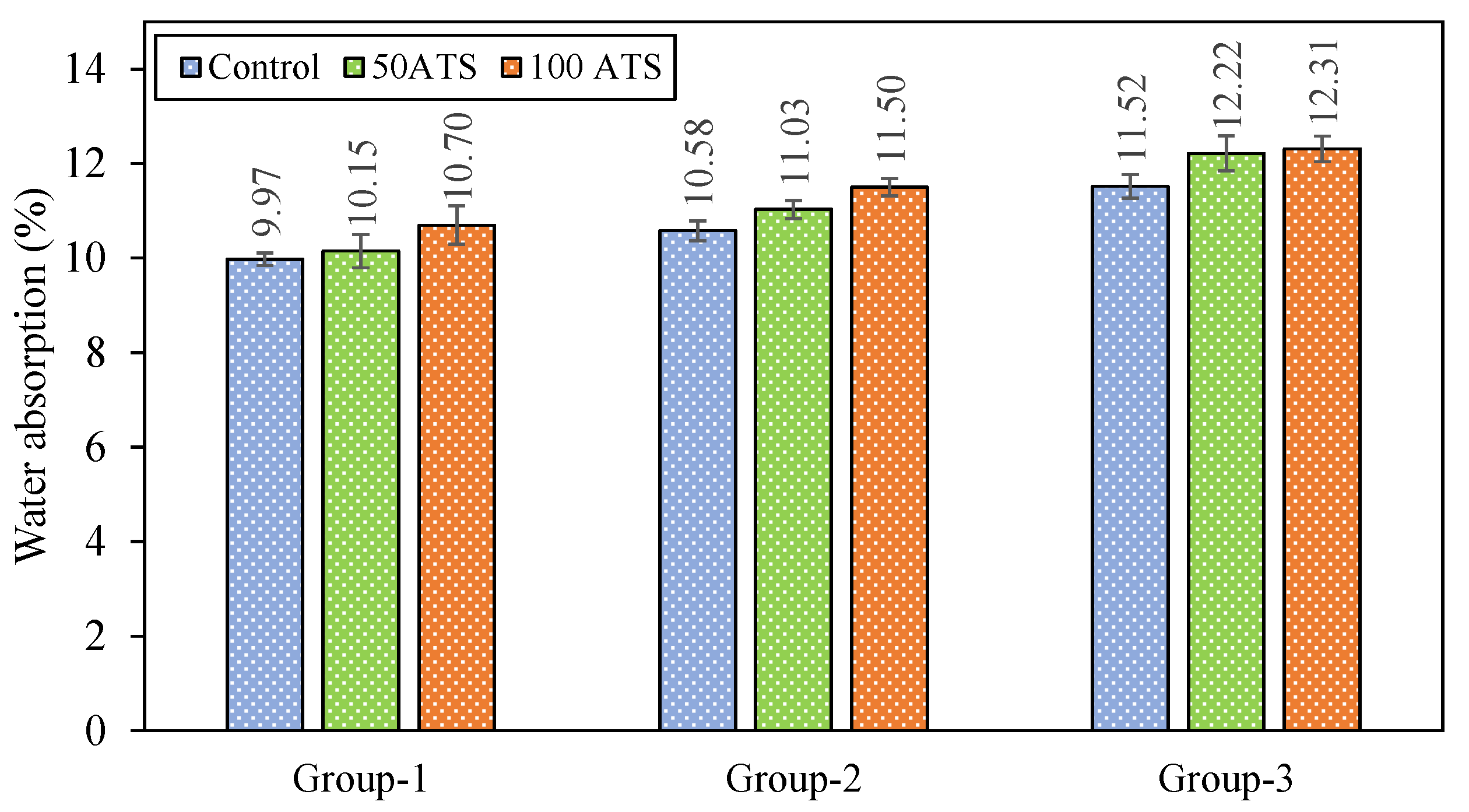
3.4.3. Dry Bulk Density, Accessible Porosity of Water, and Water Absorption
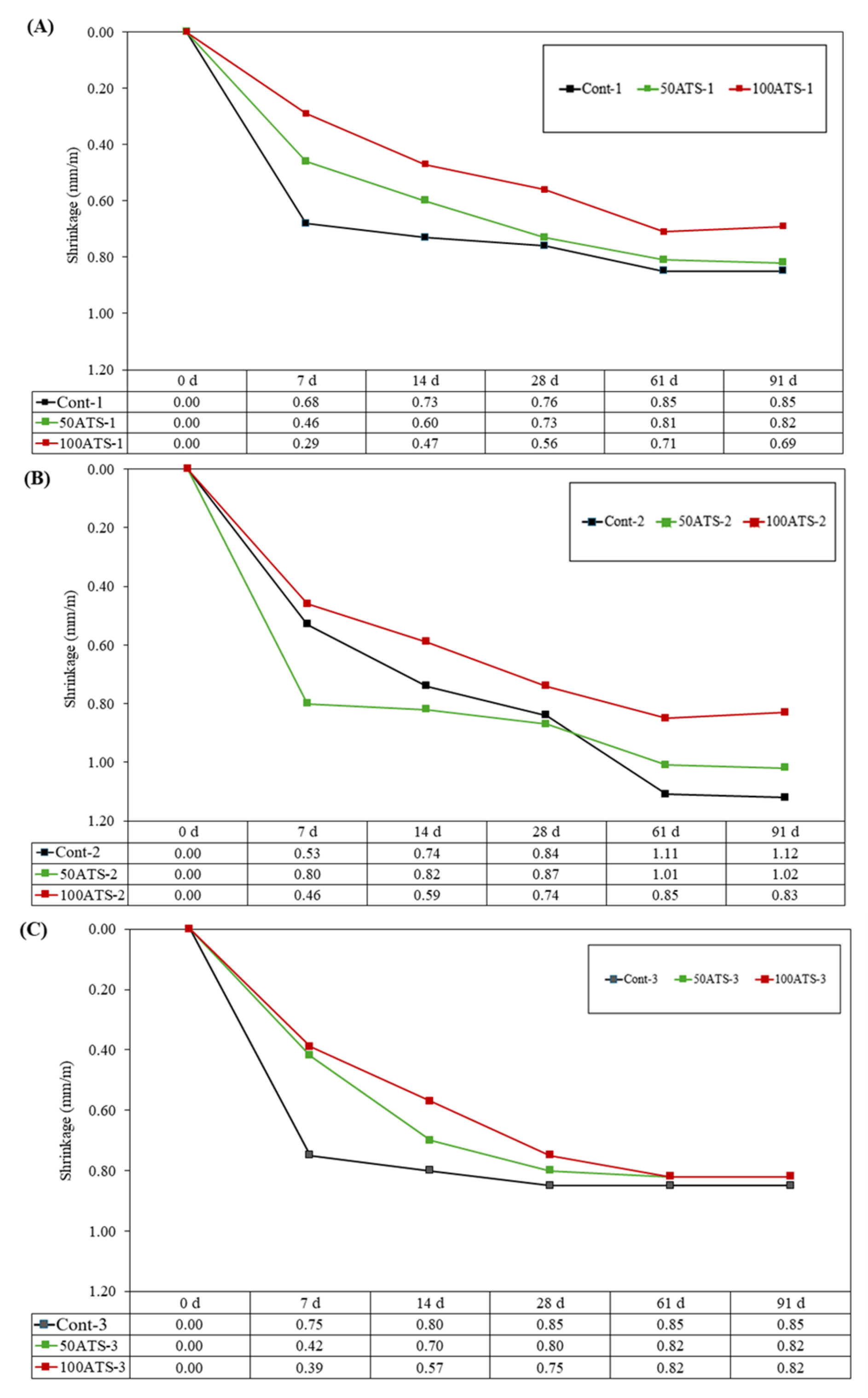
3.4.4. Dimensional Stability
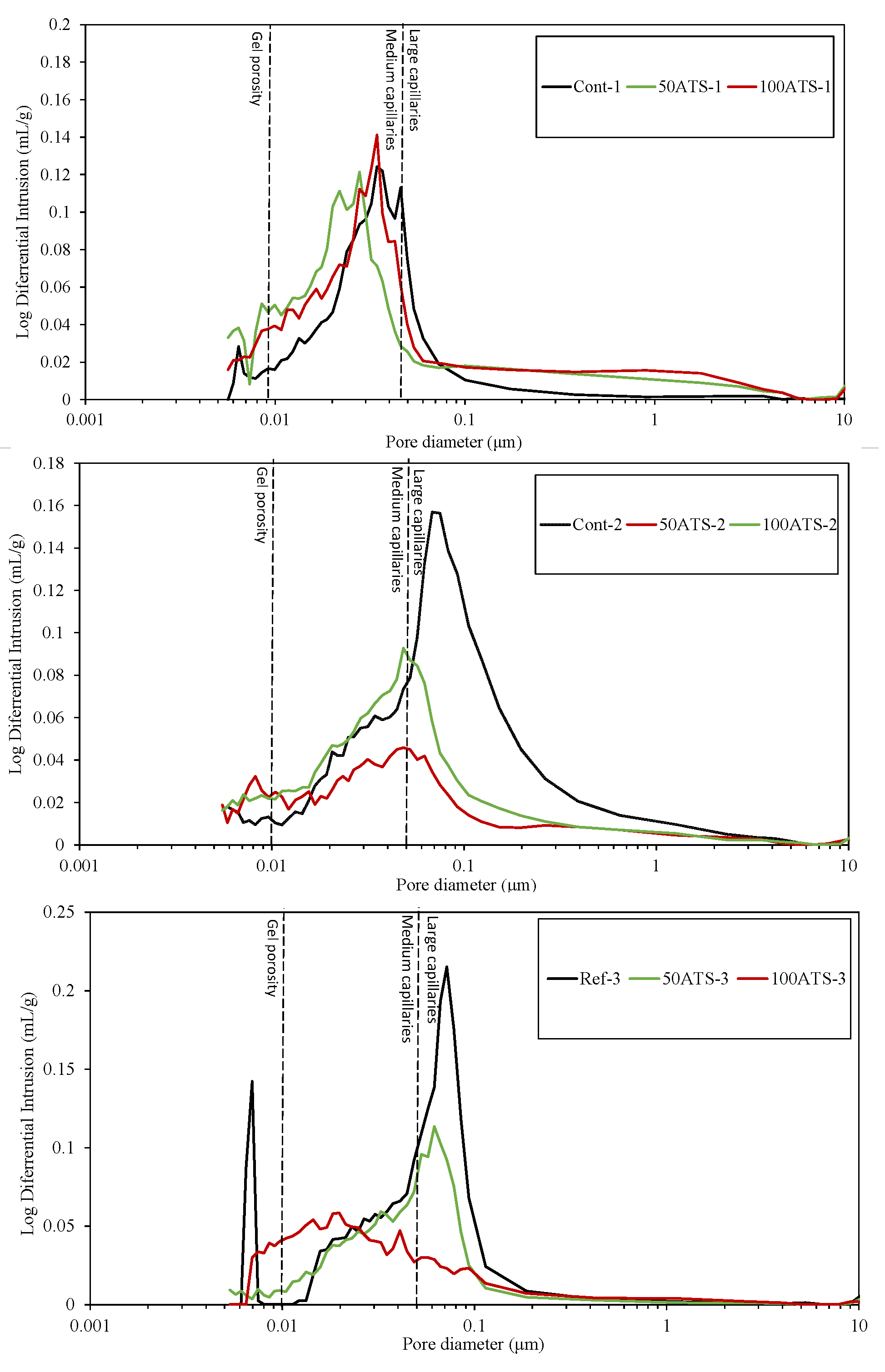
3.4.5. MIP
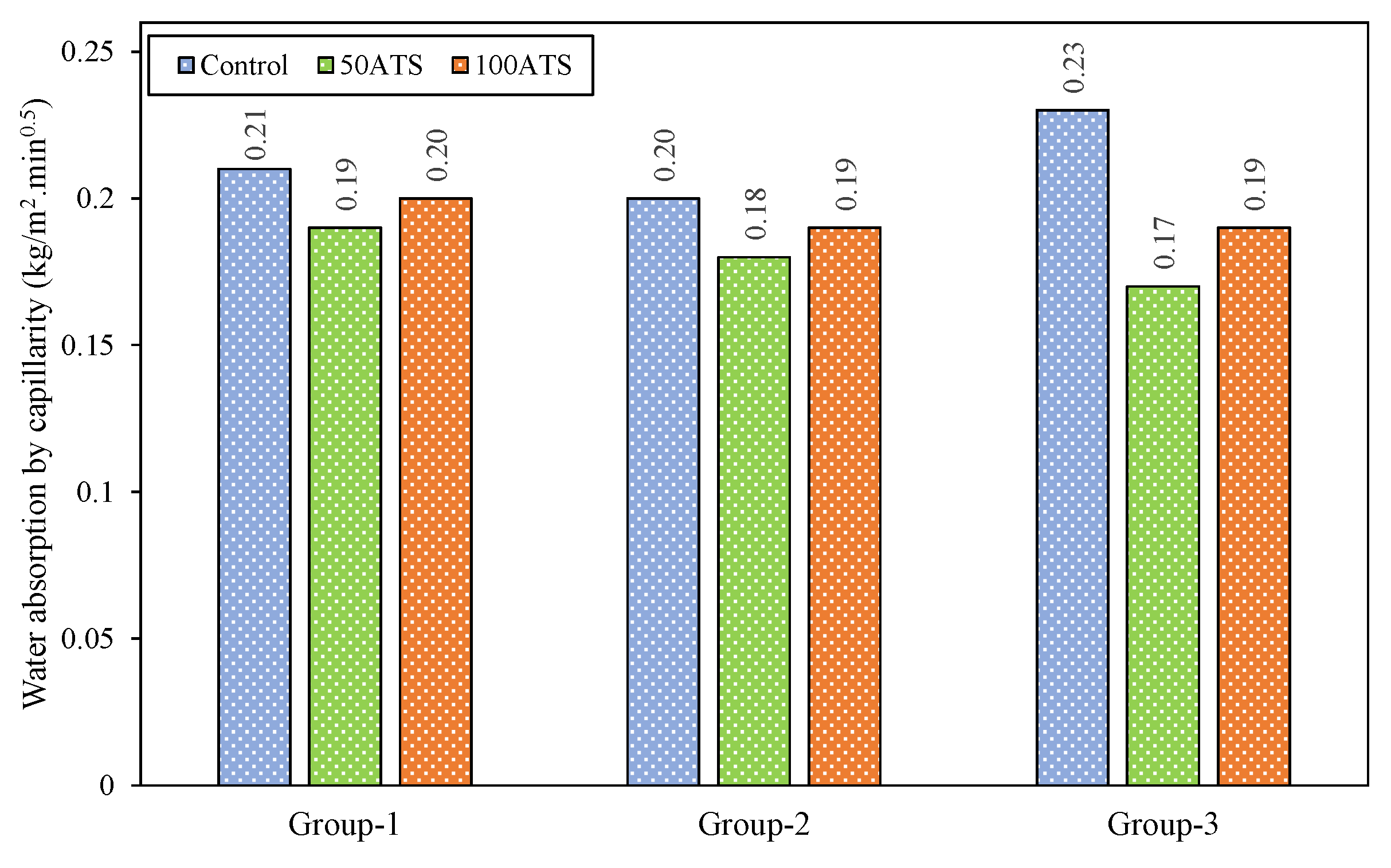
3.4.6. Water Absorption by Capillarity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, B.; Peng, L.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, T.; Zhang, B. Improving the Mechanical Properties of Mussel Shell Aggregate Concrete by Aggregate Modification and Mixture Design. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampanis, I.; Vasilatos, C. Recycling Concrete to Aggregates. Implications on CO2 Footprint. Mater. Proc. 2023, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Market, C.I.; Persistence Market Research. Healthcare Cloud Computing Market—Global Study on Healthcare Cloud. Available online: https://www.persistencemarketresearch.com/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024—Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COM(2020)98, 2020. European Commission, Report from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions on the Implementation of the Circular Economy Action Plan. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/circular-economy-action-plan_en (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Bellei, P.; Torres, I.; Solstad, R.; Flores-Colen, I. Potential Use of Oyster Shell Waste in the Composition of Construction Composites: A Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eziefula, U.G.; Ezeh, J.C.; Eziefula, B.I. Properties of Seashell Aggregate Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 192, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaoka, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kondo, S.; Hayakawa, S. Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide Using Crushed Oyster Shell from Pore Water to Remediate Organically Enriched Coastal Marine Sediments. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4127–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivia, M.; Oktaviani, R. Properties of Concrete Containing Ground Waste Cockle and Clam Seashells. Procedia Eng. 2017, 171, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, C.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Martínez-Abella, F.; López, D.C. Performance of Mussel Shell as Aggregate in Plain Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.H.; Polprasert, C. Roles of Oyster Shells in an Integrated Constructed Wetland System Designed for P Removal. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 34, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E.; Fuller, T. Sea Shells Used as Partial Aggregate Replacement in Concrete. Struct. Surv. 2013, 31, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, X.; Chen, E.; Fan, J.; Xiong, G. Properties of Cement-Based Bricks with Oyster-Shells Ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.-T.; Wang, H.Y.; Shu, C.Y.; Su, D.S. Engineering Properties of Controlled Low-Strength Materials Containing Waste Oyster Shells. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 46, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbede, O.I.; Manasseh, J. Suitability of Periwinkle Shell as Partial Replacement for River Gravel in Concrete. Leonardo Electron. J. Pract. Technol. 2009, 15, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani, N.; Takamori, H.; Takeda, K.; Sakugawa, H. Transesterification of Soybean Oil Using Combusted Oyster Shell Waste as a Catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1510–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivia, M.; Mifshella, A.A.; Darmayanti, L. Mechanical Properties of Seashell Concrete. Procedia Eng. 2015, 125, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Liang, Y.; Qu, K.; Lu, K.; Chen, S.; Kong, M. Study on Engineering Properties of Foam Concrete Containing Waste Seashell. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, B.A.; Hasaniyah, M.W.; Zeyad, A.M.; Yusuf, M.O. Properties of Concrete Containing Recycled Seashells as Cement Partial Replacement: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Caro, Á.; Merino-Lechuga, A.M.; Fernández-Ledesma, E.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.M.; Jiménez, J.R.; Suescum-Morales, D. The Effect of Acanthocardia Tuberculata Shell Powder as Filler on the Performance of Self-Compacting Mortar. Materials 2023, 16, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, R.; Da, B.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y. Influence of the Usage of Waste Oyster Shell Powder on Mechanical Properties and Durability of Mortar. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, D.; Da, B.; Chen, D. Experiment Research on Effect of Oyster Shell Particle Size on Mortar Transmission Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 375, 131012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.I.; Yi, S.T.; Leem, Y.M. Effect of Oyster Shell Substituted for Fine Aggregate on Concrete Characteristics: Part I. Fundamental Properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billberg, P. Fine Mortars Rheology in Mix Design of SCC. In First International RILEM Symposium on Self-Compacting Concrete; RILEM Publications SARL: Reykjavik, Iceland, 1999; pp. 47–58. ISBN 2912143721. [Google Scholar]
- Nepomuceno, M.; Oliveira, L.; Lopes, S.M.R. Methodology for Mix Design of the Mortar Phase of Self-Compacting Concrete Using Different Mineral Additions in Binary Blends of Powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Caro, Á.; Merino-Lechuga, A.M.; Fernández-Ledesma, E.; María Fernández-Rodríguez, J.; Ramón Jiménez, J.; Suescum-Morales, D. Use of Milled Acanthocardia Tuberculate Seashell as Fine Aggregate in Self-Compacting Mortars. Materials 2024, 17, 4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFNARC. EFNARC Specification and Guidelines for Self-Compacting Concrete; EFNARC: Surrey, UK, 2002; Volume 44, p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-83980; Concrete Durability. Test Methods. Determination of the Water Absorption, Density and Accesible Porosity for Water in Concrete. Asociacion Espanola de Normalizacion: Madrid, Spain, 2014.
- Centro de Investigación, Tecnología e Innovación de La Universidad de Sevilla (CITIUS). Available online: https://citius.us.es/web/ (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- UNE 83831; Mortars. Methods of Test for Hardened Mortar for Mansory—Determination of Dimensional Stability of Hardened Mortar for Mansory. European Standard: Plzen, Czech Republic, 2021.
- UNE-EN 1015-18; Methods of Test for Mortar for Mansory—Part 18: Determination of Water Absorption Coefficient Due to Capillary Action of Hardened Mortar. European Standards: Pilsen, Czech, 2003.
- Merino-Lechuga, A.M.; González-Caro, Á.; Fernández-Ledesma, E.; Jiménez, J.R.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.M.; Suescum-Morales, D. Accelerated Carbonation of Vibro-Compacted Porous Concrete for Eco-Friendly Precast Elements. Materials 2023, 16, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohit, M.; Haftbaradaran, H.; Riahi, H.T. Investigating the Ternary Cement Containing Portland Cement, Ceramic Waste Powder, and Limestone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, K.H.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Lee, S.C.; Goh, W.I.; Yuen, C.W. Recycling of Seashell Waste in Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCPDS. Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 81A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suescum-Morales, D.; Fernández-Ledesma, E.; González-Caro, Á.; Merino-Lechuga, A.M.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.M.; Jiménez, J.R. Carbon Emission Evaluation of CO2 Curing in Vibro-Compacted Precast Concrete Made with Recycled Aggregates. Materials 2023, 16, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suescum-Morales, D.; Silva, R.V.; Bravo, M.; Jiménez, J.R.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.M.; de Brito, J. Effect of Incorporating Municipal Solid Waste Incinerated Bottom Ash in Alkali-Activated Fly Ash Concrete Subjected to Accelerated CO2 Curing. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska-Wichrowska, K.; Pawluczuk, E.; Bołtryk, M.; Jimenez, J.R.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, J.M.; Morales, D.S. The Performance of Concrete Made with Secondary Products—Recycled Coarse Aggregates, Recycled Cement Mortar, and Fly Ash–Slag Mix. Materials 2022, 15, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, I.N.; Rao, J.B. Investigations on Physical and Chemical Properties of High Silica Sand, Fe-Cr Slag and Blast Furnace Slag for Foundry Applications. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perić, J.; Vueak, M.; Krstulovib, R.; Breeevib, L.; Kralj, D. Phase Transformation of Calcium Carbonate Polymorphs. Thermochim. Acta 1996, 277, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.C.; Bello, P.M.; Bao, M.; Torrado, J.J. From Waste to Commodity: Transforming Shells into High Purity Calcium Carbonate. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Rashidi, N.A.; Yusup, S.; Teong, L.K.; Rashid, U.; Ali, R.M. Effects of Experimental Variables on Conversion of Cockle Shell to Calcium Oxide Using Thermal Gravimetric Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 37, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, M.; Guendouz, M.; Boukhelkhal, D. The Effect of Using Seashells as Cementitious Bio-Material and Granite Industrial Waste as Fine Aggregate on Mechanical and Durability Properties of Green Flowable Sand Concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 87, 108968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, B.; Saidi, M.; Daoui, A.; Bellal, A.; Mechekak, A.; Toumi, K. The Use of Seashells as a Fine Aggregate (by Sand Substitution) in Self-Compacting Mortar (SC mortar). Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.E.; Chung, S.Y.; Kim, K.; Han, S.H. Comparative Analysis of the Effects of Waste Shell Aggregates on the Material Properties of Cement Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Lunar, A.; Dubchenko, I.; Bashynskyi, S.; Rodero, A.; Fernández, J.M.; Jiménez, J.R. Performance of Self-Compacting Mortars with Granite Sludge as Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nduka, D.O.; Akanbi, E.T.; Ojo, D.O.; Babayemi, T.E.; Jolayemi, K.J. Investigation of the Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Masonry Mortar Made with Seashell Particles. Materials 2023, 16, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Riera, D.; Merlo, A.; Lavagna, L.; Nisticò, R.; Pavese, M. Mechanical Properties of Mortar Containing Recycled Acanthocardia Tuberculata Seashells as Aggregate Partial Replacement. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2021, 60, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalat-Behbahani, A.; Soltanzadeh, F.; Emam-Jomeh, M.; Soltan-Zadeh, Z. Sustainable Approaches for Developing Concrete and Mortar Using Waste Seashell. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 1874–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Rica, H.; Sebaibi, N.; Boutouil, M.; Boudart, B. Properties of Ordinary Concretes Incorporating Crushed Queen Scallop Shells. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2016, 49, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, S.H.; Yi, S.T. Effect of Oyster Shell as an Aggregate Replacement on the Characteristics of Concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertwattanaruk, P.; Makul, N.; Siripattarapravat, C. Utilization of Ground Waste Seashells in Cement Mortars for Masonry and Plastering. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Lu, J.; Nie, Y.; He, W. Effect of Seashell Powder as Binder Material on the Performance and Microstructure of Low-Carbon Sustainable Alkali-Activated Concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 90, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, A.B.; Willis, K.L.; Lange, D.A. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry and Image Analysis of Cement-Based Materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 211, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.A.; John, V.M.; Ribeiro, J.L.D.; Roman, H.R. Pore Size Distribution of Hydrated Cement Pastes Modified with Polymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Uceda, A.; Cantador-Fernández, D.; Da Silva, P.R.; de Brito, J.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.M.; Jiménez, J.R. Mechanical and Durability Performance of Self-Compacting Mortars Made with Different Industrial by-Products as Fillers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 431, 136536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista Junior, G.; Nascimento, L.C.; de Xavier, G.C.; Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F.; Marvila, M.T.; Alledi, C.T.D.B. Durability for Coating Mortars: Review of Methodologies. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, C.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Carro-López, D.; Martínez-Abella, F. Effects of Mussel Shell Aggregates on Hygric Behaviour of Air Lime Mortar at Different Ages. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, C.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Carro-López, D.; Martínez-Abella, F. Mussel Shell Mortars Durability: Study of Aggregate Replacement Limit. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Group-1 | Group-2 | Group-3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cont-1 | 50ATS | 100ATS | Cont-2 | 50ATS | 100ATS | Cont-3 | 50ATS | 100ATS | ||
| Powders | CEM | 490.0 | 490.0 | 490.0 | 525.4 | 525.4 | 525.4 | 556.1 | 556.1 | 556.1 |
| Siliceous Filler (SF) | 293.9 | 293.9 | 293.9 | 315.1 | 315.1 | 315.1 | 333.5 | 333.5 | 333.5 | |
| Fine aggregates | NA-0/3 | 617.0 | 308.5 | 0 | 567.0 | 283.5 | 0 | 525.2 | 262.6 | 0 |
| NA-0/6 | 617.9 | 310.8 | 0 | 567.9 | 285.7 | 0 | 526.0 | 264.6 | 0 | |
| ATS sand | 0 | 641.2 | 1282.5 | 0 | 589.3 | 1178.6 | 0 | 545.8 | 1091.6 | |
| Water | 240.2 | 240.2 | 240.2 | 257.5 | 257.5 | 257.5 | 272.6 | 272.6 | 272.6 | |
| Workability parameters | Vp/Vs | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Vw/Vp | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | |
| Sp/p % | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 | |
| Group-1 | Group-2 | Group-3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cont-1 | 50ATS-1 | 100ATS-1 | Cont-2 | 50ATS-2 | 100ATS-2 | Cont-3 | 50ATS-3 | 100ATS-3 | |
| Gm | 5.25 | 5.00 | 4.86 | 5.50 | 5.25 | 4.90 | 5.76 | 5.55 | 5.25 |
| Rm (s−1) | 1.25 | 1.33 | 1.43 | 1.11 | 1.18 | 1.25 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Caro, Á.; Merino-Lechuga, A.M.; Suescum-Morales, D.; Fernández-Ledesma, E.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.M.; Jiménez, J.R. Performance of Self-Compacting Mortars Using Ground Seashells as Recycled Sand. Materials 2025, 18, 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020418
González-Caro Á, Merino-Lechuga AM, Suescum-Morales D, Fernández-Ledesma E, Fernández-Rodríguez JM, Jiménez JR. Performance of Self-Compacting Mortars Using Ground Seashells as Recycled Sand. Materials. 2025; 18(2):418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020418
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Caro, Ágata, Antonio Manuel Merino-Lechuga, David Suescum-Morales, Enrique Fernández-Ledesma, José María Fernández-Rodríguez, and José Ramón Jiménez. 2025. "Performance of Self-Compacting Mortars Using Ground Seashells as Recycled Sand" Materials 18, no. 2: 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020418
APA StyleGonzález-Caro, Á., Merino-Lechuga, A. M., Suescum-Morales, D., Fernández-Ledesma, E., Fernández-Rodríguez, J. M., & Jiménez, J. R. (2025). Performance of Self-Compacting Mortars Using Ground Seashells as Recycled Sand. Materials, 18(2), 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020418







