Recyclable MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT as Sulfur and Water-Resistant Sorbent for Gaseous Elemental Mercury Removal from Coal Combustion Flue Gas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT
2.2. Characterization Methods
2.3. Hg0 Removal Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
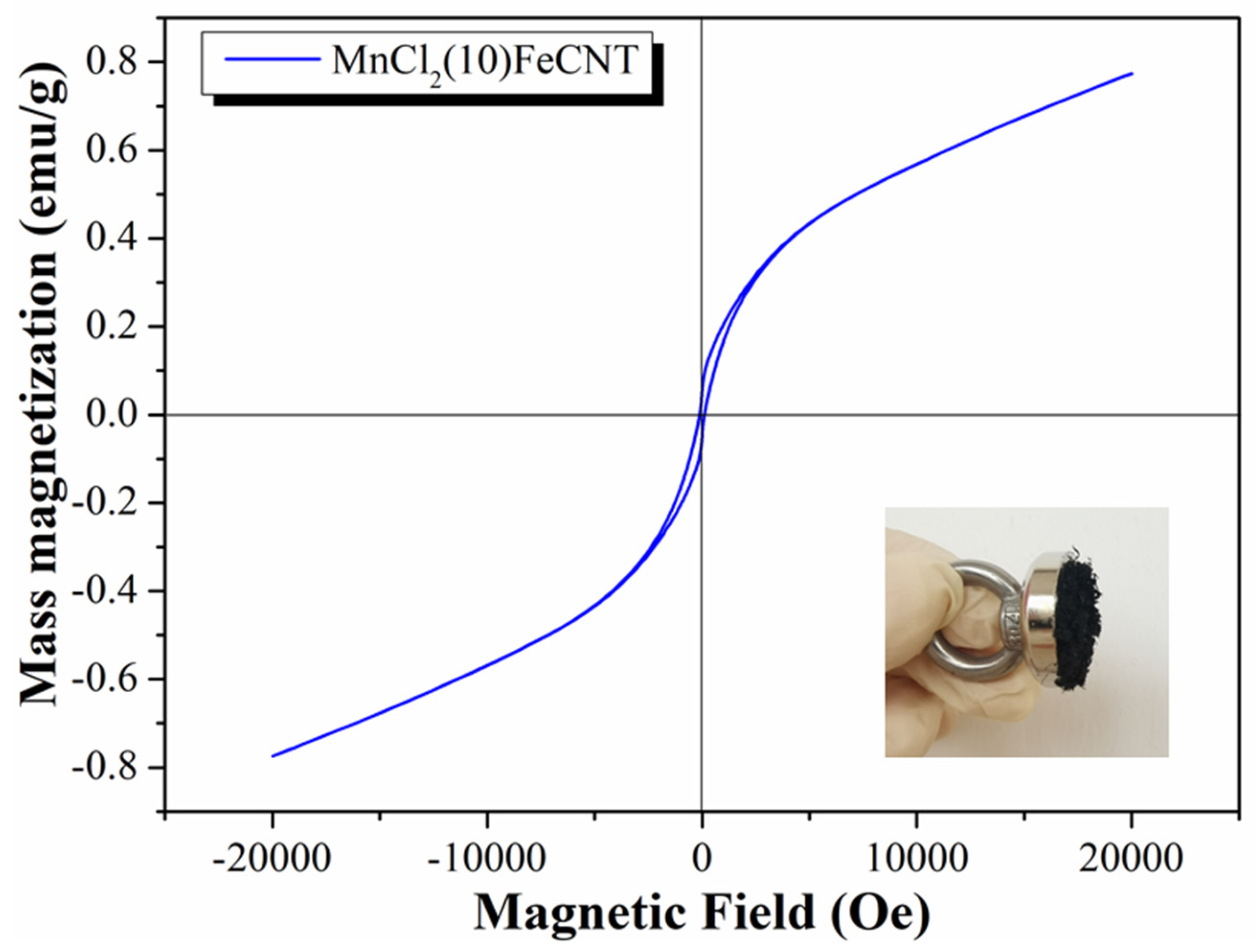
3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT
3.2. Hg0 Removal Performance of MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT
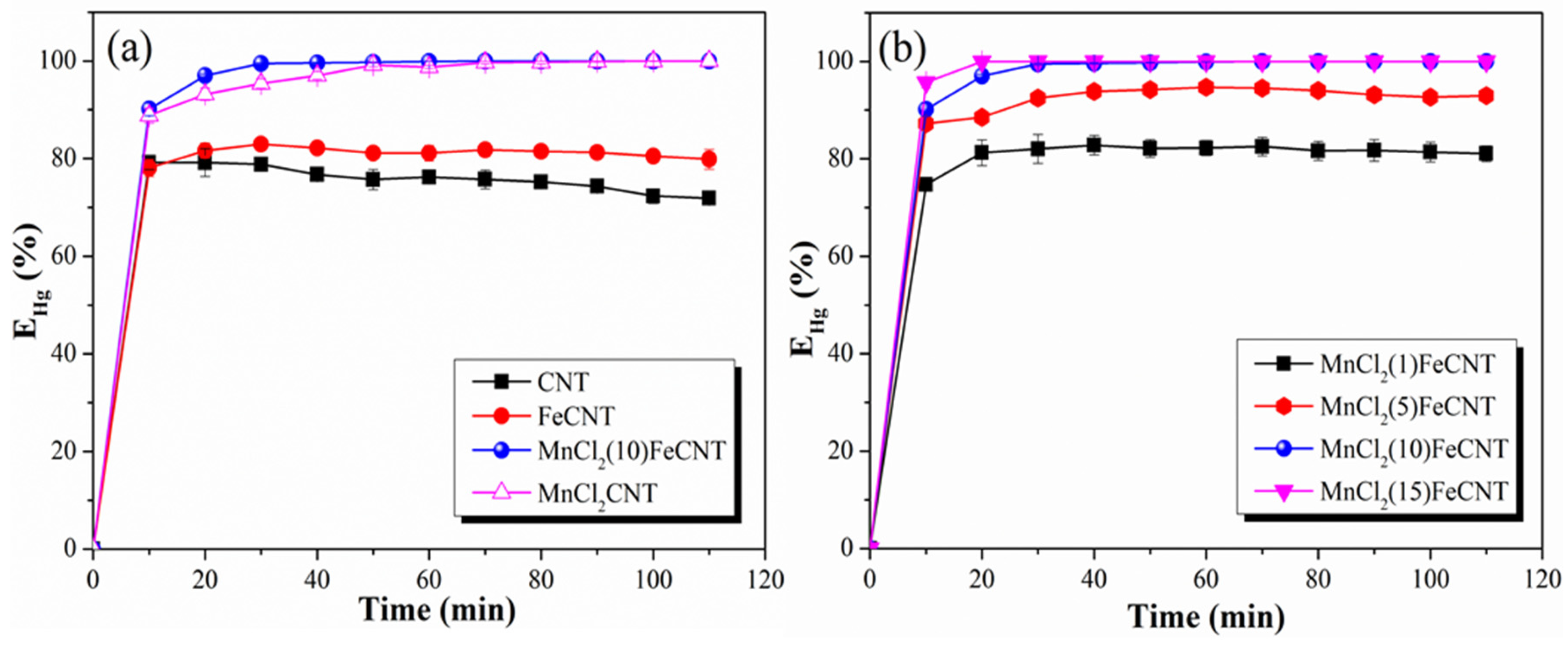
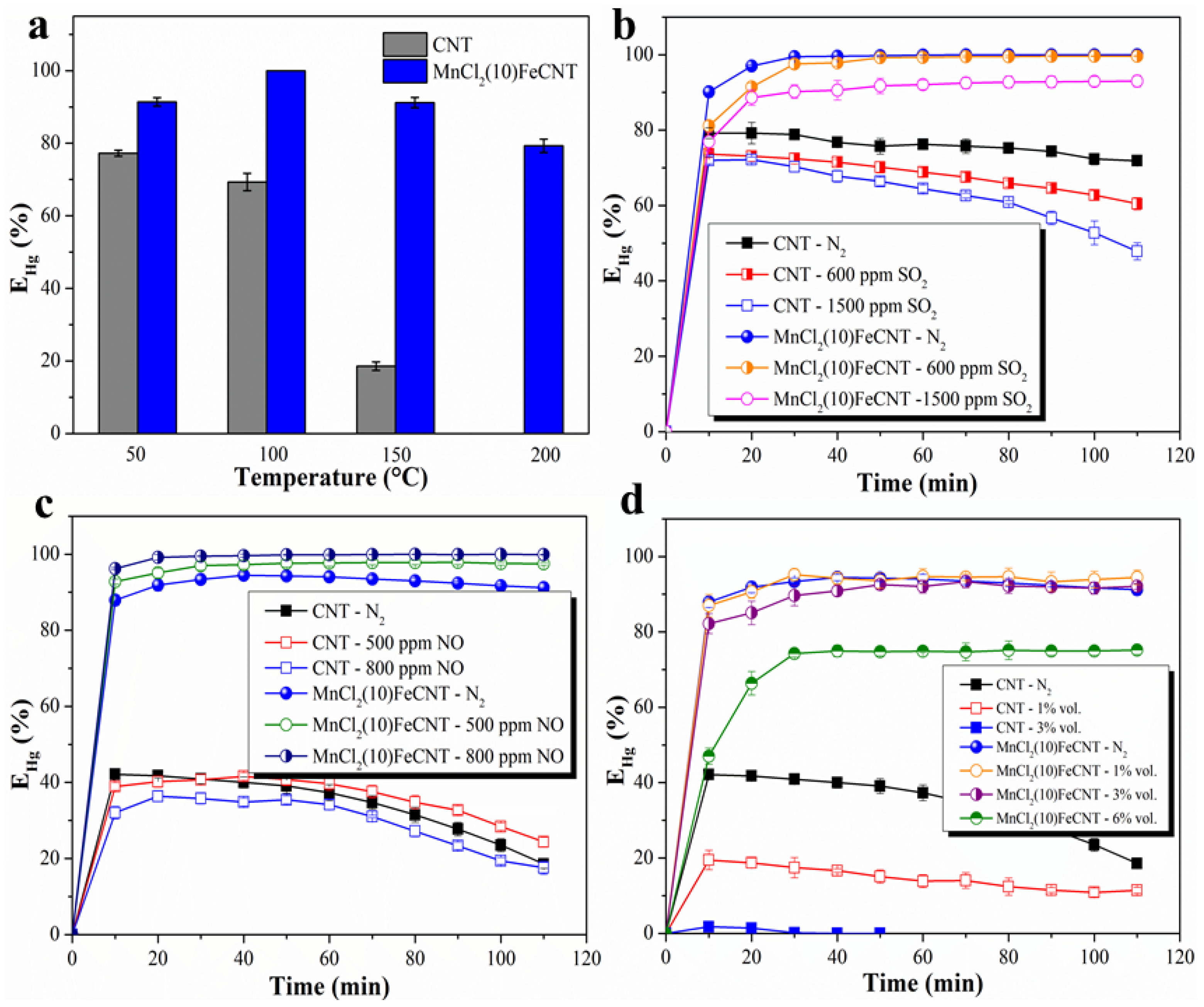
3.2.1. Hg0 Removal Performance of Different MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT Samples
3.2.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature
3.2.3. Effect of SO2
3.2.4. Effect of NO
3.2.5. Effect of H2O
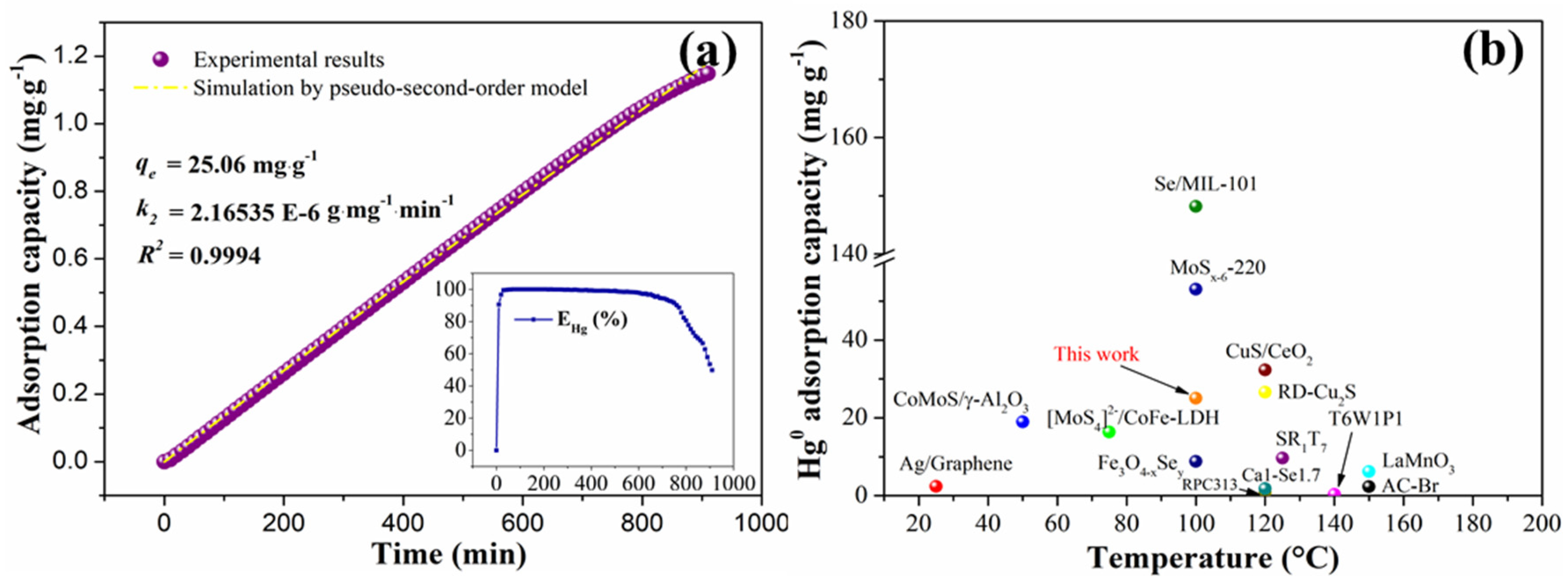
3.2.6. Kinetic Analysis
3.2.7. Regeneration Capability
3.3. Hg0 Removal Mechanism
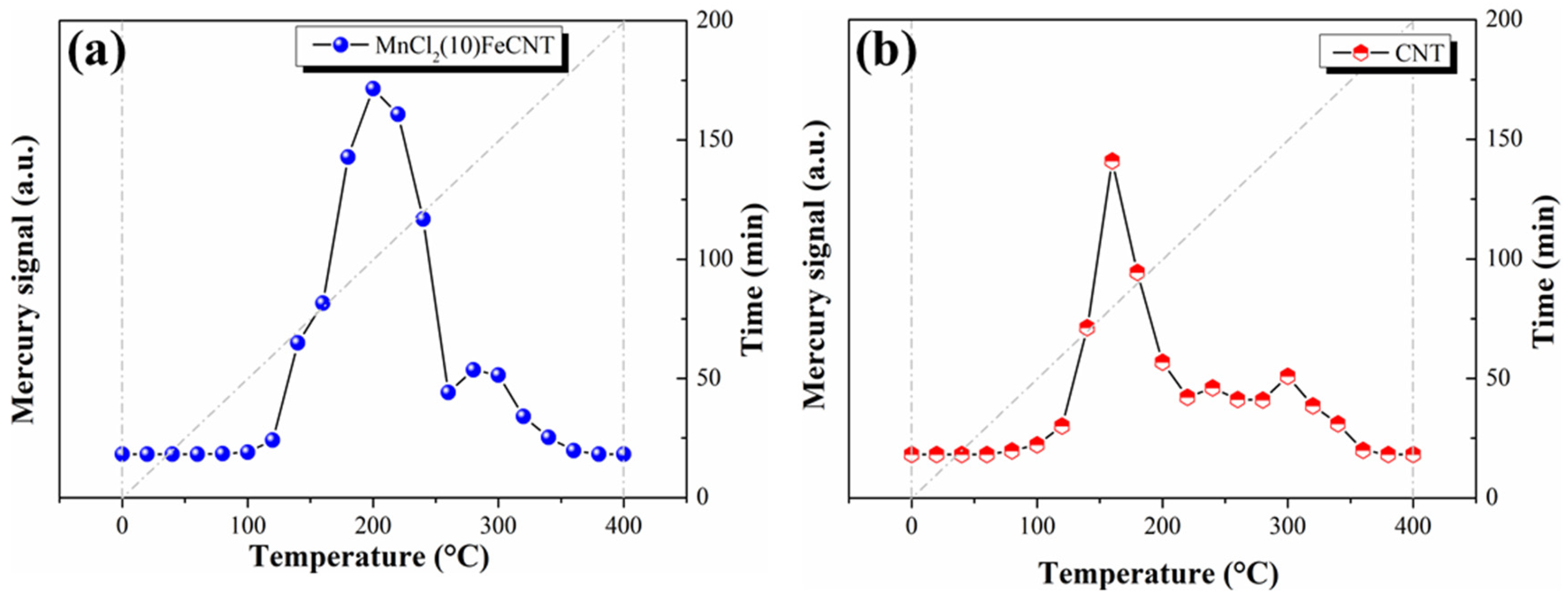
3.3.1. Hg-TPD Analysis
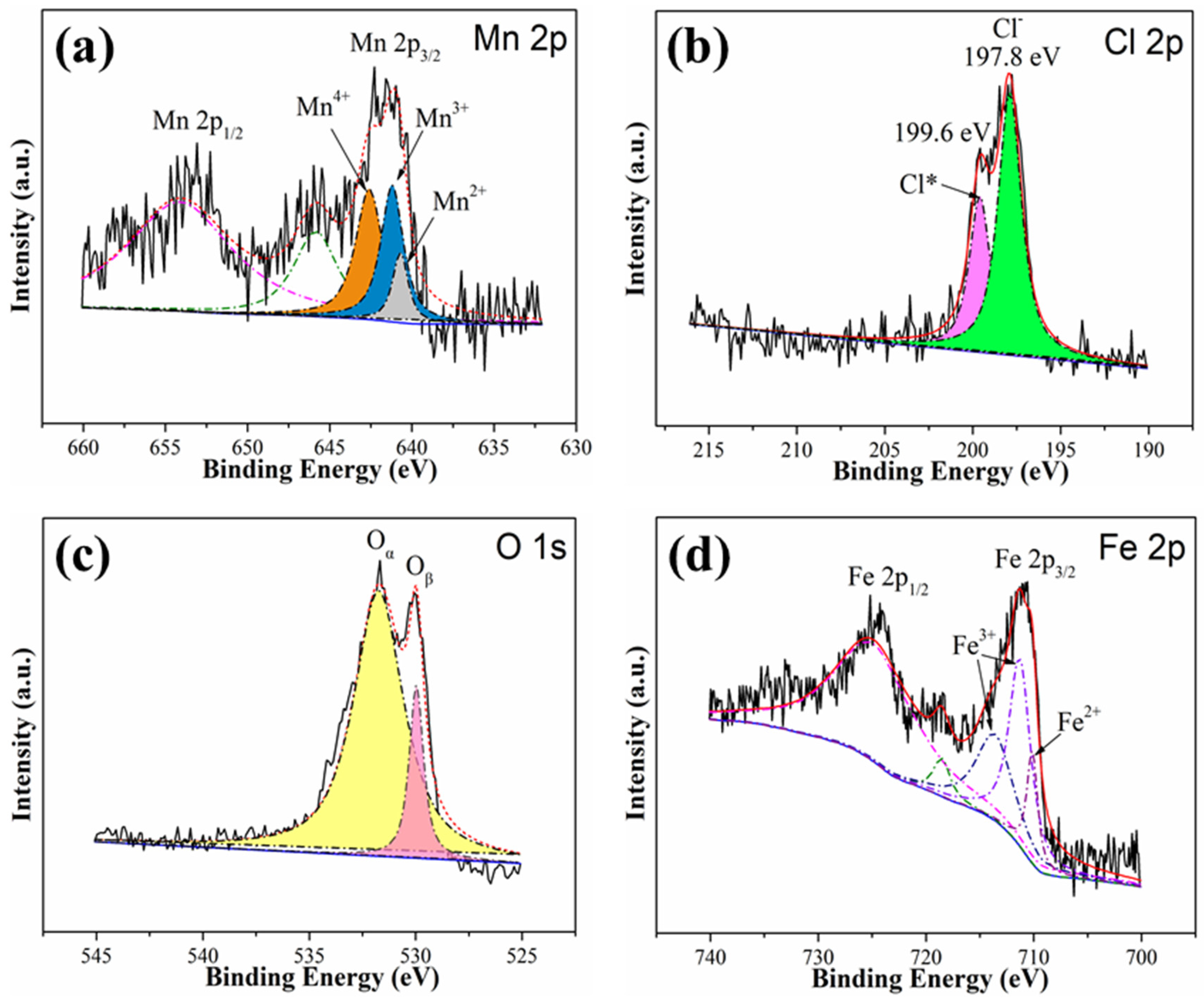
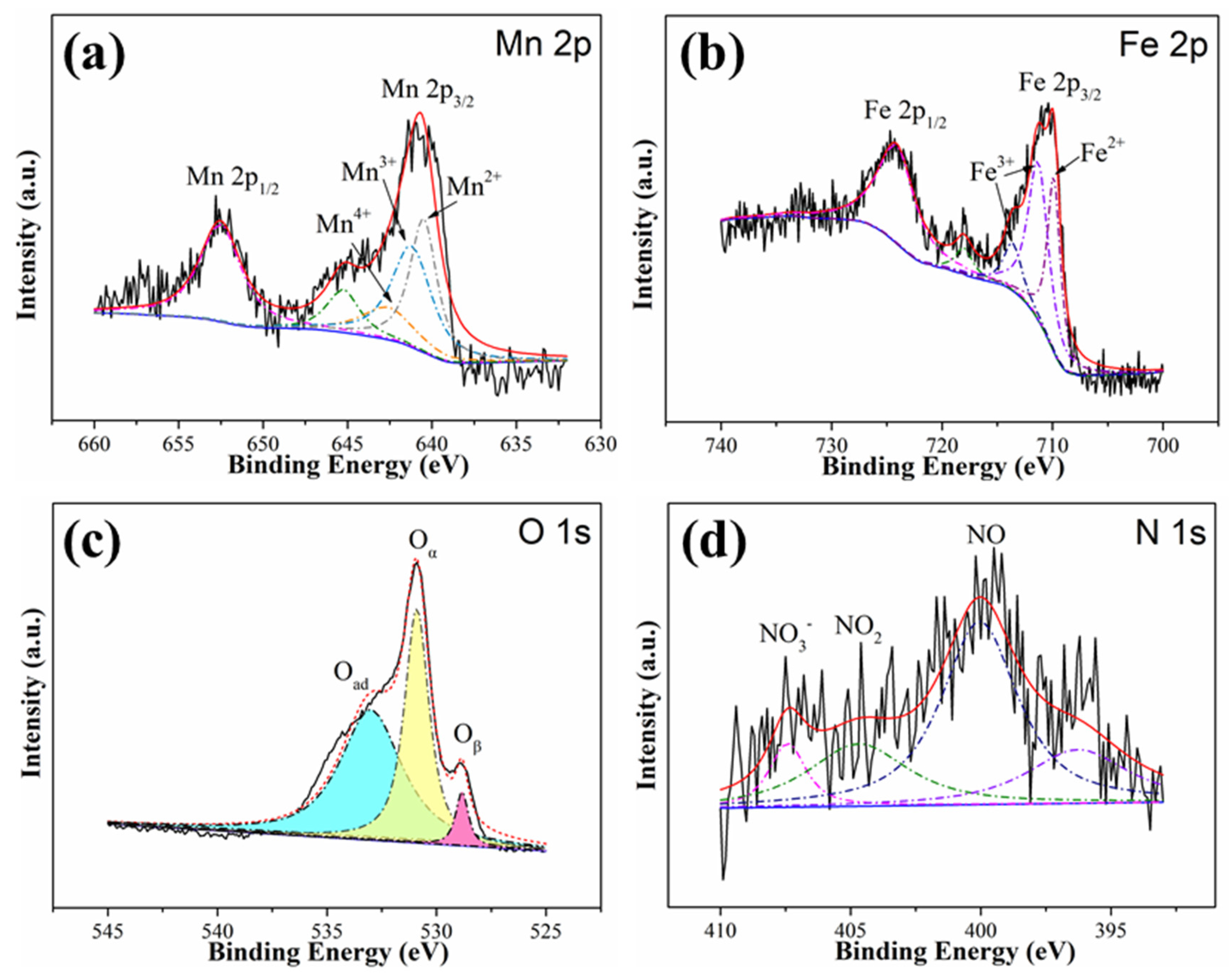
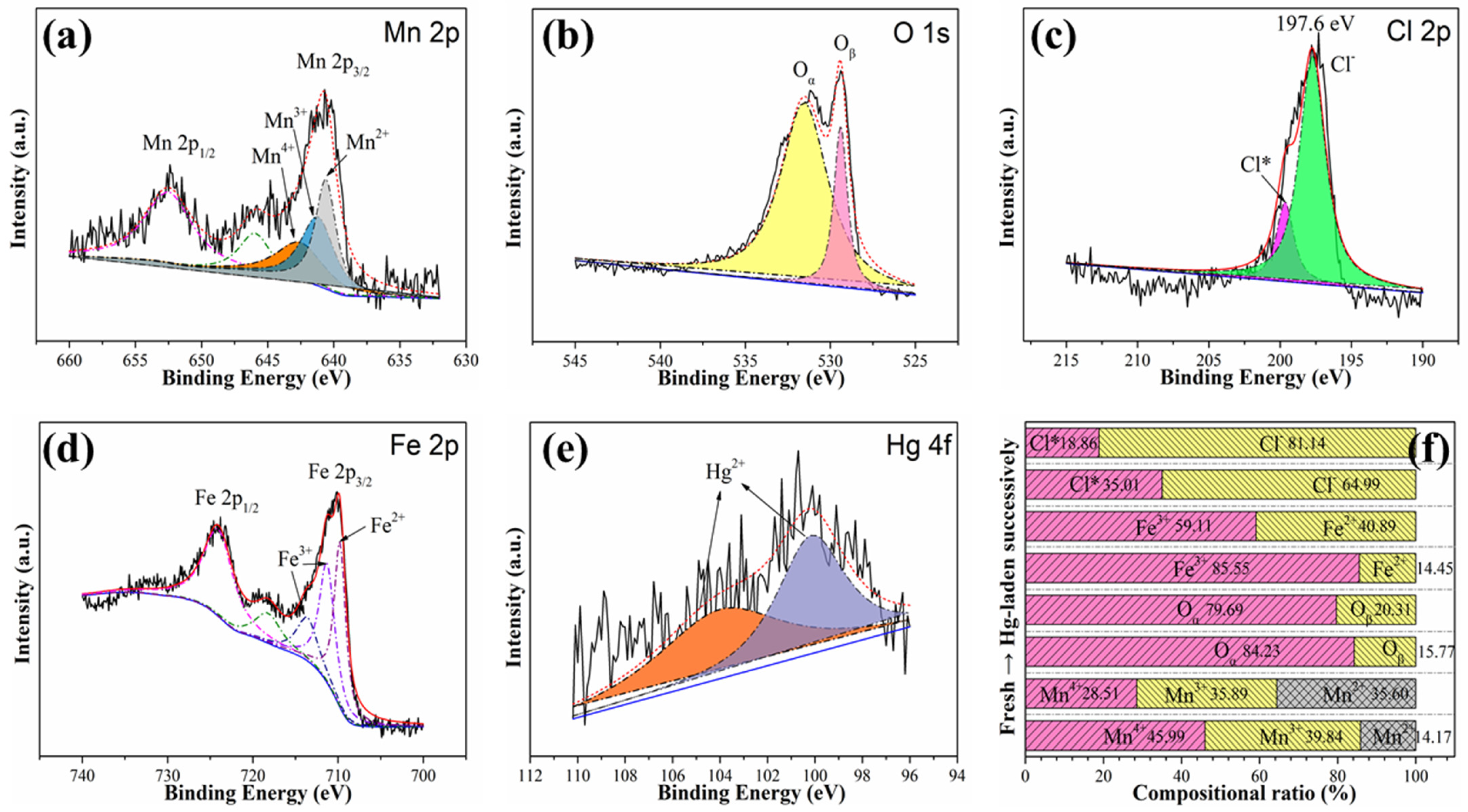
3.3.2. XPS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mercury and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mercury-and-health (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.M.; Sundseth, K.; Munthe, J.; Kindbom, K.; Wilson, S.; Steenhuisen, F.; Maxson, P. Global emission of mercury to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in 2005 and projections to 2020. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2487–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Liang, S.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, H.; Yang, Z. Looping Mercury Cycle in Global Environmental–Economic System Modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2861–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, F.; Rinklebe, J. Cycling of mercury in the environment: Sources, fate, and human health implications: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 693–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczak, M.; Wierońska, F.; Burmistrz, P.; Strugała, A.; Kogut, K.; Lech, S. Investigation of subbituminous coal and lignite combustion processes in terms of mercury and arsenic removal. Fuel 2019, 251, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xiong, Z.; Ni, P.; Ma, Z.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H. Review on adsorbents in elemental mercury removal in coal combustion flue gas, smelting flue gas and natural gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 45, 140095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilar, L.; Borovec, K.; Szeliga, Z.; Górecki, J. Mercury emission from three lignite-fred power plants in the Czech Republic. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 212, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, J.; Rupp, E.; Ying, S.C.; Lim, D.H.; Negreira, A.S.; Kirchofer, A.; Feng, F.; Lee, K. Mercury adsorption and oxidation in coal combustion and gasification processes. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 90–91, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, F.; Clack, H. Mercury emissions from coal combustion: Modeling and comparison of Hg capture in a fabric filter versus an electrostatic precipitator. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Ma, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yuan, B.; Wang, L. Removal and recovery of gaseous elemental mercury using a Cl-doped protonated polypyrrole@MWCNTs composite membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 56, 3689–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Lai, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Chai, L. In-situ synthesis of monodispersed CuxO heterostructure on porous carbon monolith for exceptional removal of gaseous Hg0. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 265, 118556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Global Mercury Assessment 2018. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/publication/global-mercury-assessment-2018 (accessed on 25 September 2025).
- Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Tian, H.; Duan, L.; Hao, J. A highly resolved mercury emission inventory of Chinese coal-fired power plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Minamata Convention on Mercury. Available online: https://www.mercuryconvention.org/en (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Liu, H.; Chang, L.; Liu, W.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Advances in mercury removal from coal-fired flue gas by mineral adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Hussain, A.; Liu, Y.X. A review on modification methods of adsorbents for elemental mercury from flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, E.; Kellartzis, I.; Diamantopoulou, I.; Stavropoulos, G.; Vourlias, G.; Mitrakas, M. Study of elemental mercury removal from flue gases using tetravalent manganese feroxyhyte. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Elemental mercury removal from flue gas using heat and Co2+/Fe2+ coactivated oxone oxidation system. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nick, R.K.; Hutson, D.; Srivastava, R.K. simultaneous removal of SO2, NOX, and Hg from coal flue gas using a NaClO2-enhanced wet scrubber. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 5825–5831. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Hu, J. Promotional effect of Mo addition on CoOx/Ti-Ce catalyst for oxidation removal of elemental mercury in flue gas. Fuel 2018, 224, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, M.; Huang, H.; Ding, X.; Wu, C.; Gates, I.D.; Gao, Z. Theoretical prediction of graphene-based single atom iron as a novel catalyst for catalytic oxidation of Hg0 by O2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Liang, P. Satisfactory anti-interference and high performance of the 1Co-1Ce/Mn@ZSM-5 catalyst for simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 in abominable flue gas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3596–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granite, E.J.; Pennline, H.W. Photochemical removal of mercury from flue gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 5470–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Dai, B.; Sheng, W.; Su, S.; Xiang, J. Photocatalytic oxidation removal of Hg0 by ternary Ag@AgCl/Ag2CO3 hybrid under fluorescent light. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 159, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Q.; Qi, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, T.; Cao, Y. Photocatalytic oxidation of gas-phase Hg0 by CuO/TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Shen, Q. Electrochemical removal of gaseous elemental mercury in liquid phase with a novel foam titanium-based DSA anode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Yan, N.; Wu, D.; He, H.; Xie, J.; Qu, Z.; Jia, J. Remarkable effect of the incorporation of titanium on the catalytic activity and SO2 poisoning resistance of magnetic Mn-Fe spinel for elemental mercury capture. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 101, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, X.; An, M.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W. Negative effect of SO2 on mercury removal over catalyst/sorbent from coal-fired flue gas and its coping strategies: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y. Novel carbon-based sorbents for elemental mercury removal from gas streams: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Hao, L.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Liang, P. Enhanced SO2 tolerance of FeCeOX/CNTs catalyst for NO and Hg0 removal by coating shell SiO2. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 201, 106342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacha, A.W.; Milowska, K.Z.; Payne, M.C.; Greer, H.F.; Terzyk, A.P.; Korczeniewski, E.; Cyganiuk, A.; Boncel, S. The origin of amphipathic nature of short and thin pristine carbon nanotubes-fully recyclable 1D water-in-oil emulsion stabilizers. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2202407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Long, Y.; Hu, J. Removal of elemental mercury from coal combustion flue gas using recyclable Dy modified Mn-Fe mixed oxide nanoparticles. J. Environ. Che. Eng. 2022, 10, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shao, H.; Xu, M. Catalytic oxidation of elemental mercury y Mn-Mo/CNT at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, Z.; Huang, S.; Chi, J.; Zhao, S. Efficient mercury removal in chlorine-free flue gas by doping Cl into Cu2O nanocrystals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Cheng, H.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Zha, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, S.; et al. Elemental mercury removal from coal-fired flue gas using recyclable magnetic Mn-Fe based attapulgite sorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, H. Cobalt doped ceria for abundant storage of surface active oxygen and efficient elemental mercury oxidation in coal combustion flue gas. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 239, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, Q.; Shen, B.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X. MIL-100(Fe) supported Mn-based catalyst and its behavior in Hg0 removal from flue gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Hua, M.; Dong, X.; Chen, C.; Duan, Y.; Tang, H. From scrap polystyrene foam to efficient demercurizer: In-situ synthesis of Fe-embedded hyper-cross-linked polymers. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 285, 119791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, H.; Han, X.; Ding, S.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Y. Preparation of magnetic Co-Fe modified porous carbon from agricultural wastes by microwave and steam activation for mercury removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, X.; Shen, B.; Ren, K.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J. Enhanced elemental mercury removal via chlorine-based hierarchically porous biochar with CaCO3 as template. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wu, J.; Jin, B. Development of copper sulfide functionalized CeO2 nanoparticle for strengthened removal of gaseous elemental mercury from flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Pan, J.; Fan, B.; Liu, Y. Removal of gaseous elemental mercury using seaweed chars impregnated by NH4Cl and NH4Br. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 216, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, Y.; Luo, G.; Zhang, Q.; Du, L.; Cui, X.; Li, Z. Facile synthesis of phosphorus-doped porous biochars for efficient removal of elemental mercury from coal combustion flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.S.S.; Dwivedi, V.; Dasgupta, K.; Musharaf, A.S.; Shenoy, K.T. Novel amidoamine functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for removal of mercury (II) ions from wastewater: Combined experimental and density functional theoretical approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Shi, J.; Fan, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Niu, C. “Fast SCR” reaction over Sm-modified MnOX-TiO2 for promoting reduction of NOX with NH3. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 564, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Li, F.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Long, Y.; et al. Enhanced performance and SO2 tolerance of Ce modified TiO2 supported Mn-Sm catalyst for synergetic removal of Hg0 and NO from flue gas. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 227, 107136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shen, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, F.; He, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. Removal of element mercury by medicine residue derived biochars in presence of various gas compositions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Song, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y. Role of acid gases in Hg0 removal from flue gas over a novel cobalt-containing biochar prepared from harvested cobalt-enriched phytoremediation plant. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 207, 106478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, S.; Huang, W.; Qu, Z. Interface modulation of Mn-N4-C with optimized oxygen-containing functional groups for highly efficient mercury adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Díaz-Somoano, M.; Dang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Influence of SO3 on the MnOX/TiO2 SCR catalyst for elemental mercury removal and the function of Fe modification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Bisson, T.; Xu, Z. Magnetically responsive catalytic sorbent for removal of Hg0 and NO. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 160, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mu, B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Gao, L.; Li, B.; Tian, J. Ag-Fe3O4@rGO ternary magnetic adsorbent for gaseous elemental mercury removal from coal-fired flue gas. Fuel 2019, 239, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lisbona, P.; Perez, V.; Guo, X. Performance of MnCl2 doped magnetic iron-carbon sorbent on mercury removal from flue gas: The effect of O2 and SO2. Fuel 2021, 285, 119064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Shen, Z.; Fan, M.; Su, P.; Tang, Q.; Zou, C. Adsorption mechanism of elemental mercury (Hg0) on the surface of MnCl2 (110) studied by Density Functional Theory. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; He, P.; Wu, J.; Chen, N.; Xu, T.; Shi, E.; Pan, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y. Conversion of 2H MoS2 to 1 T MoS2 via lithium ion doping: Effective removal of elemental mercury. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Shi, W.; Sun, W.; Pan, L. Hg0 removal performance and mechanisms of FeOCl regulated by CuCl2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Xu, H.; Liu, D. Removal of elemental mercury from simulated flue gas by ZSM-5 modified with Mn-Fe mixed oxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Fe-modified MnOX/TiO2 as the SCR catalyst for simultaneous removal of NO and mercury from coal combustion flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presto, A.A.; Granite, E.J. Impact of sulfur oxides on mercury capture by activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6579–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J. Preparation of microwave-activated magnetic bio-char adsorbent and study on removal of elemental mercury from flue gas. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente-Cuesta, A.; Lopez-Anton, M.A.; Diaz-Somoano, M.; Martínez-Tarazona, M.R. Retention of mercury by low-cost sorbents: Influence of flue gas composition and fly ash occurrence. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 213, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, A.; Dhanak, V.R.; Kiskinova, M.; Rosei, R. Molecular and mixed coadsorbed layers produced by NO adsorption on (1×1) and (1×2) Rh (110). Appl. Surf. Sci. 1994, 78, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; You, X.; Shao, S.; Liu, K. Exploration of reaction mechanism between acid gases and elemental mercury on the CeO2-WO3/TiO2 catalyst via in situ DRIFTS. Fuel 2019, 239, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, K.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liang, P. Inhibitory effects of water vapor on elemental mercury removal performance over cerium-oxide-modified semi-coke. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 324, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Sui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B.; Pan, W. Enhanced mercury removal by transplanting sulfur-containing functional groups to biochar through plasma. Fuel 2019, 253, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Katayama, R.; Uddin, M.A.; Sasaoka, E.; Xie, Z. Study on reactivity of HgO over activated carbon with HCl and SO2 in the presence of moisture by temperature-programmed decomposition desorption mass spectrometry. Energy Fuel 2015, 29, 6598–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Du, X.; Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zeng, G. Superior performance and resistance to SO2 and H2O over CoOX-modifed MnOX/biomass activated carbons for simultaneous Hg0 and NO removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Duan, Y.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, C.; She, M.; Zhang, J.; Wei, H. Experimental and kinetic studies of gas-phase mercury adsorption by raw and bromine modified activated carbon. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 134, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Huang, W.; Mei, J.; Chen, W.; Zhao, S.; Yan, N. Regenerable Ag/graphene sorbent for elemental mercury capture at ambient temperature. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 476, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liao, Y.; Xie, J.; Qu, Z.; Shangguan, W.; Yan, N. [MoS4]2- cluster bridges in Co-Fe layered double hydroxides for mercury uptake from S-Hg mixed flue gas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10109–10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, G.; Gao, X.; Pang, C.; Kingman, S.W.; Wu, T. Hg0 capture over CoMoS/γ-Al2O3 with MoS2 nanosheets at low temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Zong, C.; Quan, F.; Mei, J.; Yan, N. Catalytic oxidation and adsorption of Hg0 over low-temperature NH3-SCR LaMnO3 perovskite oxide from flue gas. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 186, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Deng, F.; Pang, Q.; He, S.; Xu, Y.; Luo, G.; Yao, H. Development of waste-derived sorbents from biomass and brominated flame retarded plastic for elemental mercury removal from coal-fired flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ji, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, K.; Xu, H.; Huang, W.; Yan, N.; Qu, Z. Fabrication of Cu2S hollow nanocages with enhanced high-temperature adsorption activity and recyclability for elemental mercury capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Qu, W.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Shih, K. Development of selenized magnetite (Fe3O4-xSey) as an efficient and recyclable trap for elemental mercury sequestration from coal combustion flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 125022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; LiLiu, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J. Removal of elemental mercury from flue gas over a low-cost and magnetic sorbent derived from FeSO4-flocculated sludge and rice straw. J. Energy Inst. 2022, 105, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, W.; Qu, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, H. Selenium functionalized metal-organic framework MIL-101 for efficient and permanent sequestration of mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; He, G.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Bao, J. Industrial grade calcium sulfide modified by selenium for elemental mercury removal from flue gas. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Yan, K.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Engineering sulfur-rich MoS2 adsorbent with abundant unsaturated coordination sulfur sites for gaseous mercury capture from high-concentration SO2 smelting flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

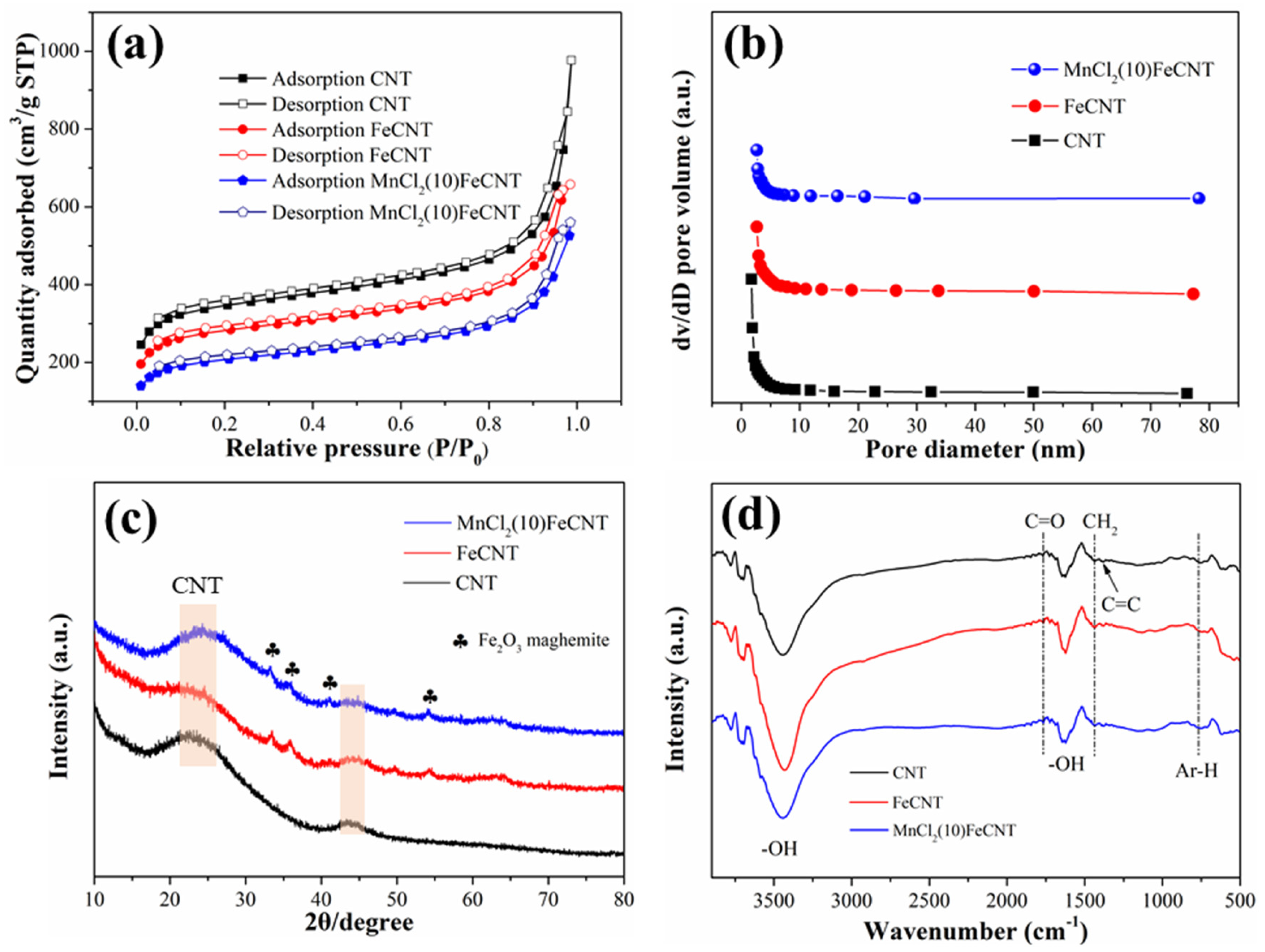

| Samples | BET Surface Area | Pore Volume | Pore Size | Micropore Area | External Surface Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m2·g−1) | (cm3·g−1) | (nm) | (m2·g−1) | (m2·g−1) | |
| CNT | 1307.01 | 1.27 | 8.29 | 971.45 | 335.56 |
| FeCNT | 1065.14 | 0.78 | 7.31 | 790.13 | 275.01 |
| MnCl2(10)FeCNT | 775.76 | 0.70 | 8.27 | 560.49 | 215.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Rong, H.; Jie, C.; Peng, X.; Li, H. Recyclable MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT as Sulfur and Water-Resistant Sorbent for Gaseous Elemental Mercury Removal from Coal Combustion Flue Gas. Materials 2025, 18, 4573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194573
Liu Z, Chen Y, Rong H, Jie C, Peng X, Li H. Recyclable MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT as Sulfur and Water-Resistant Sorbent for Gaseous Elemental Mercury Removal from Coal Combustion Flue Gas. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194573
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhuo, Yuchi Chen, Hao Rong, Cui Jie, Xiyan Peng, and Honghu Li. 2025. "Recyclable MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT as Sulfur and Water-Resistant Sorbent for Gaseous Elemental Mercury Removal from Coal Combustion Flue Gas" Materials 18, no. 19: 4573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194573
APA StyleLiu, Z., Chen, Y., Rong, H., Jie, C., Peng, X., & Li, H. (2025). Recyclable MnCl2-Fe2O3@CNT as Sulfur and Water-Resistant Sorbent for Gaseous Elemental Mercury Removal from Coal Combustion Flue Gas. Materials, 18(19), 4573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194573






