Comparison of Cu(II) Adsorption Using Fly Ash and Natural Sorbents During Temperature Change and Thermal–Alkaline Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
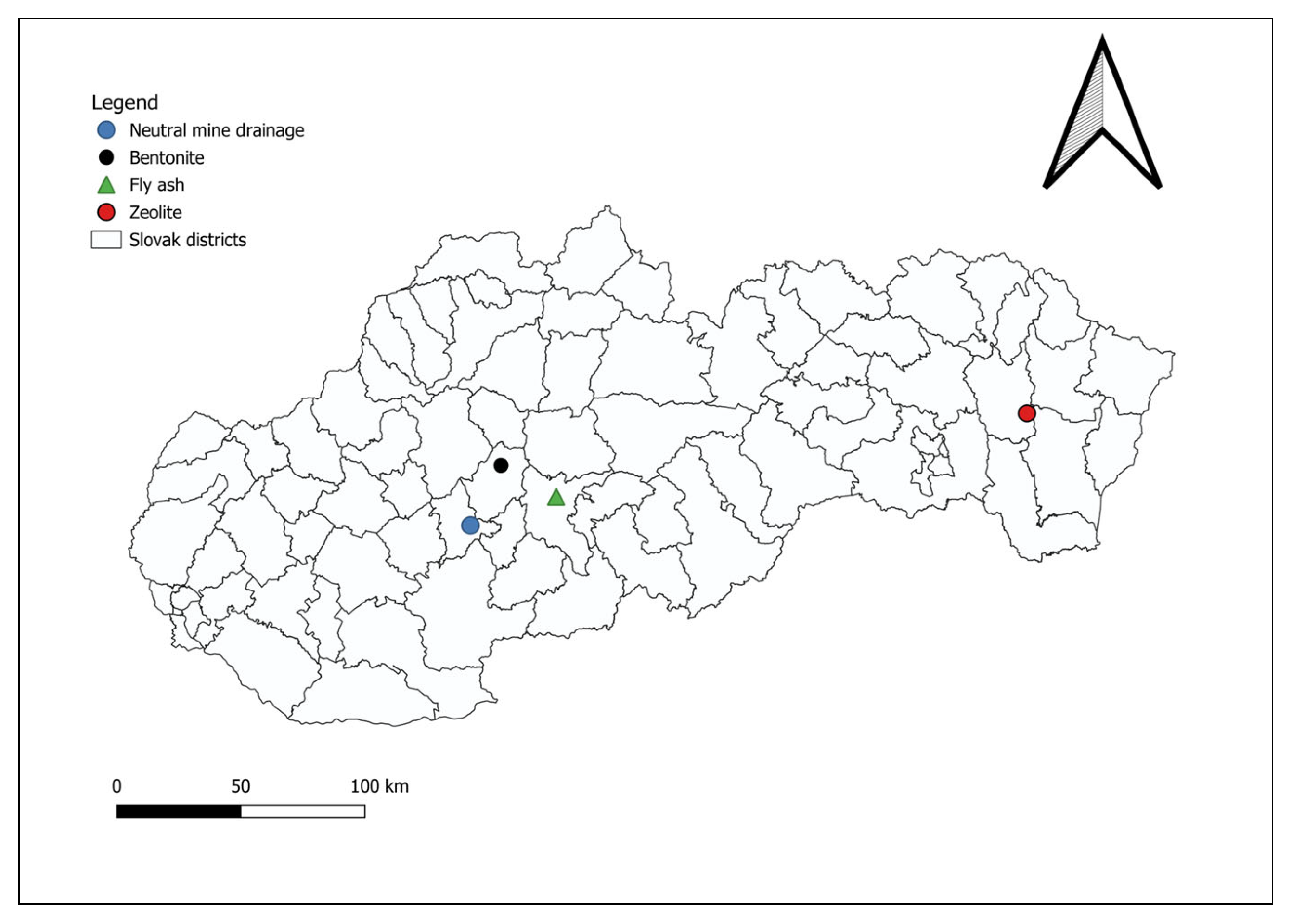
2.1. Sampling Locations
2.2. Analysis Methods
2.3. Calculations
2.3.1. Freundlich, Langmuir and Temkin Adsorption Isotherms
2.3.2. Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm
2.3.3. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
2.3.4. Temkin Adsorption Isotherm
2.3.5. Adsorption Capacity
2.3.6. Kinetics of Sorption
2.3.7. Thermodynamic Quantities
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Neutral Mine Drainage
3.2. Characteristics of Natural Sorbents
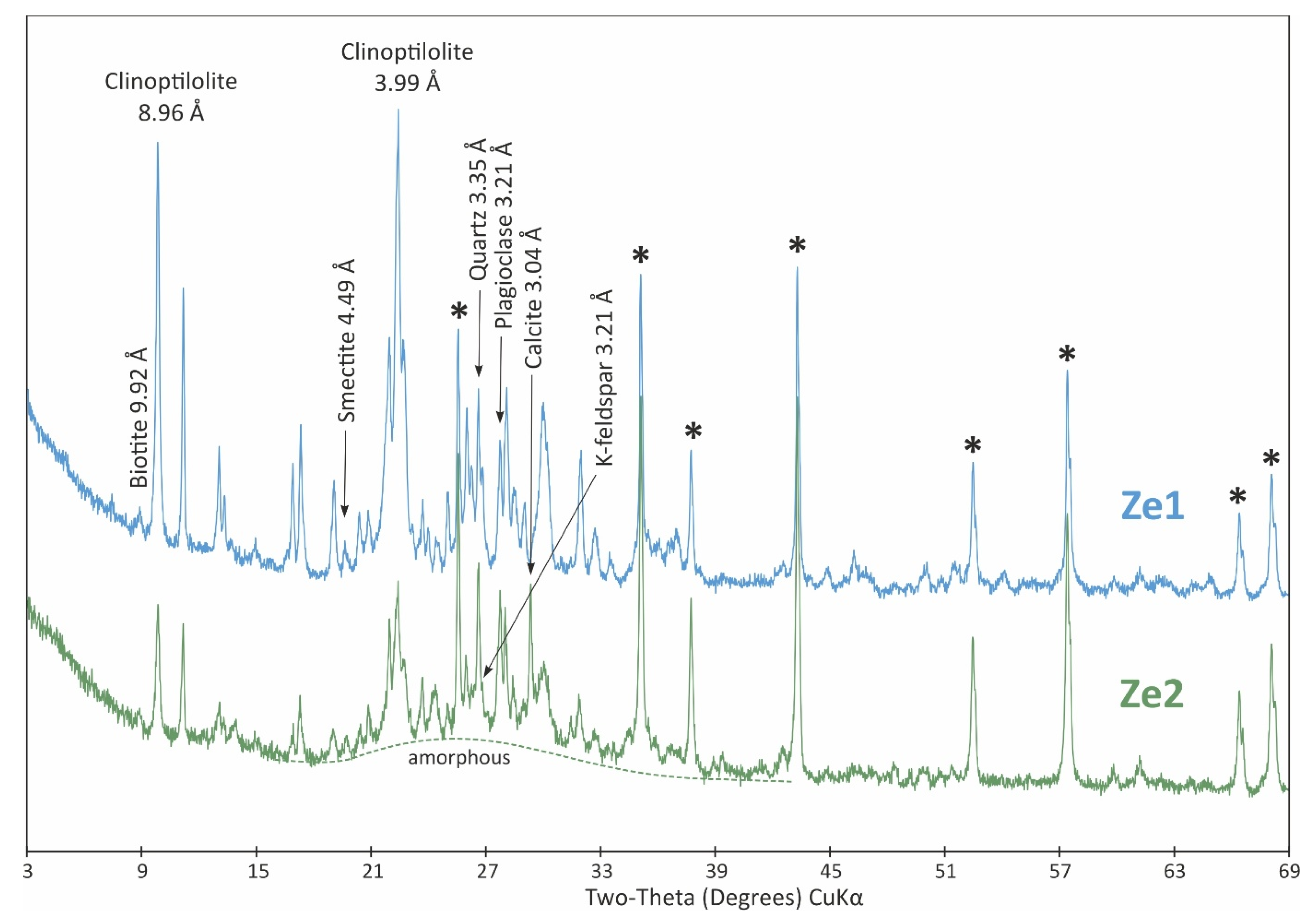
3.3. Characteristics of Fly Ash
3.4. Nonlinear Regression Analysis, Nonlinear Adsorption Isotherm Models
3.5. Models of Pseudo-First-Order and Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics
3.6. Thermodynamic Parameters
3.7. Adsorption Capacities
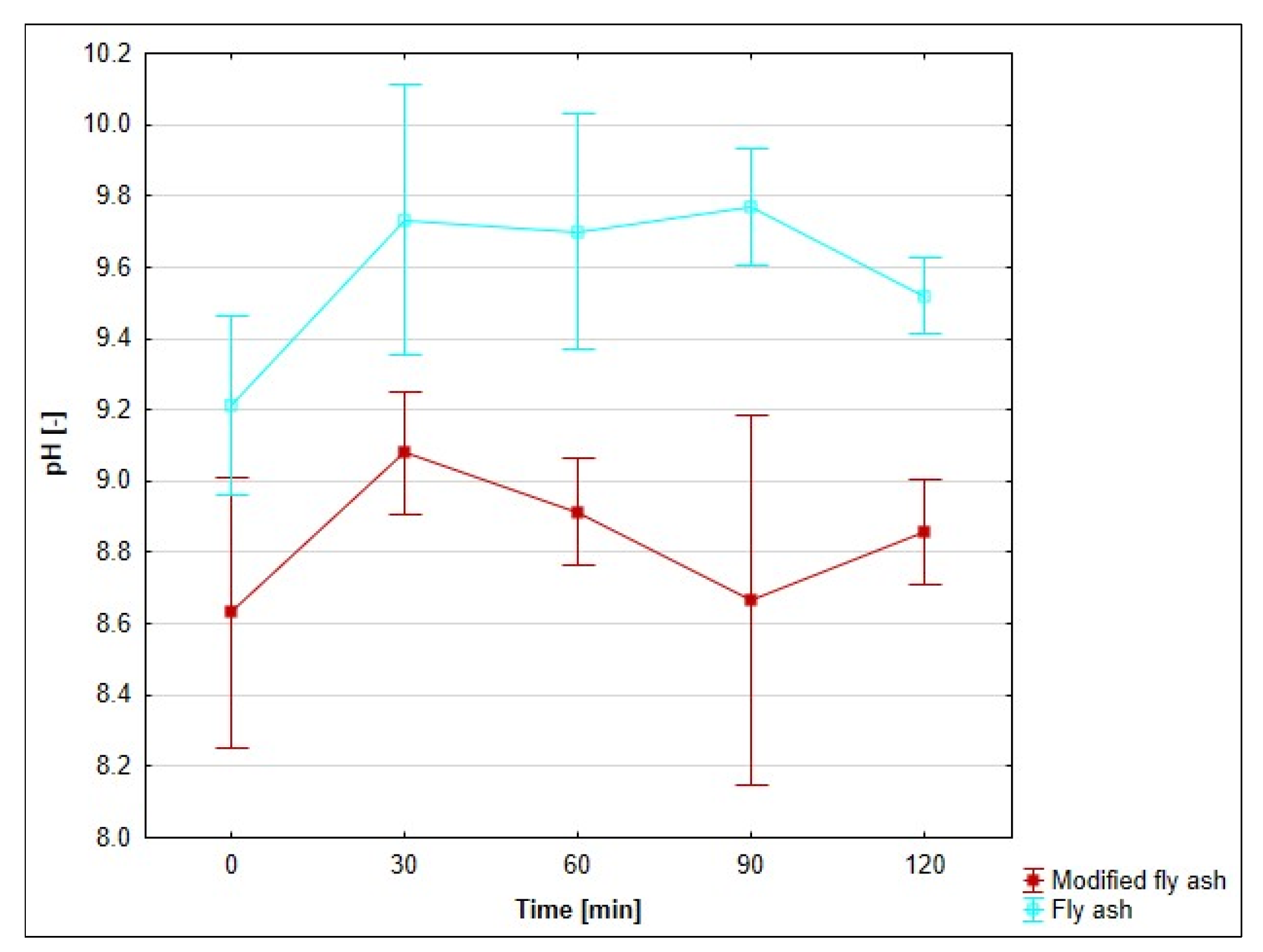
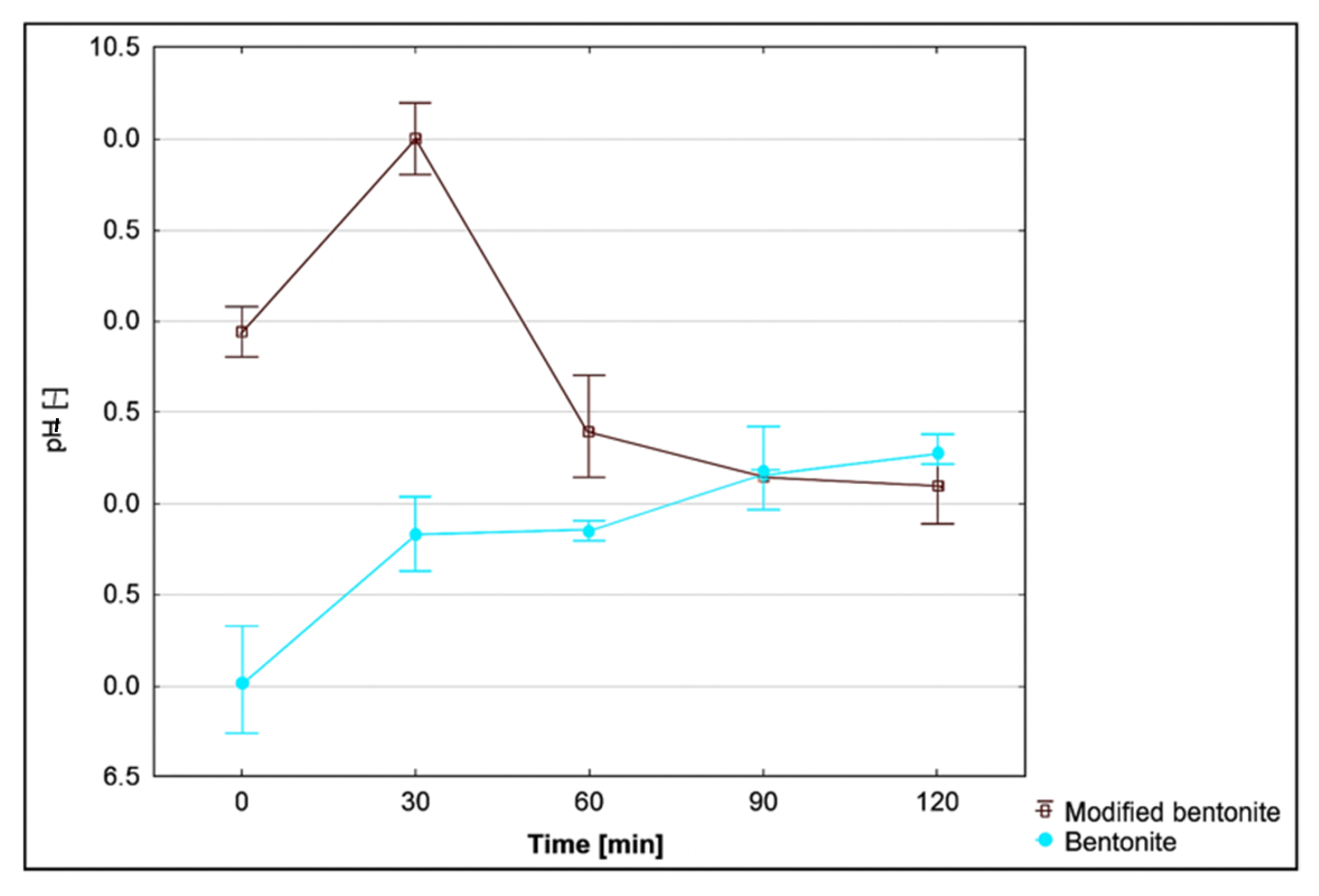
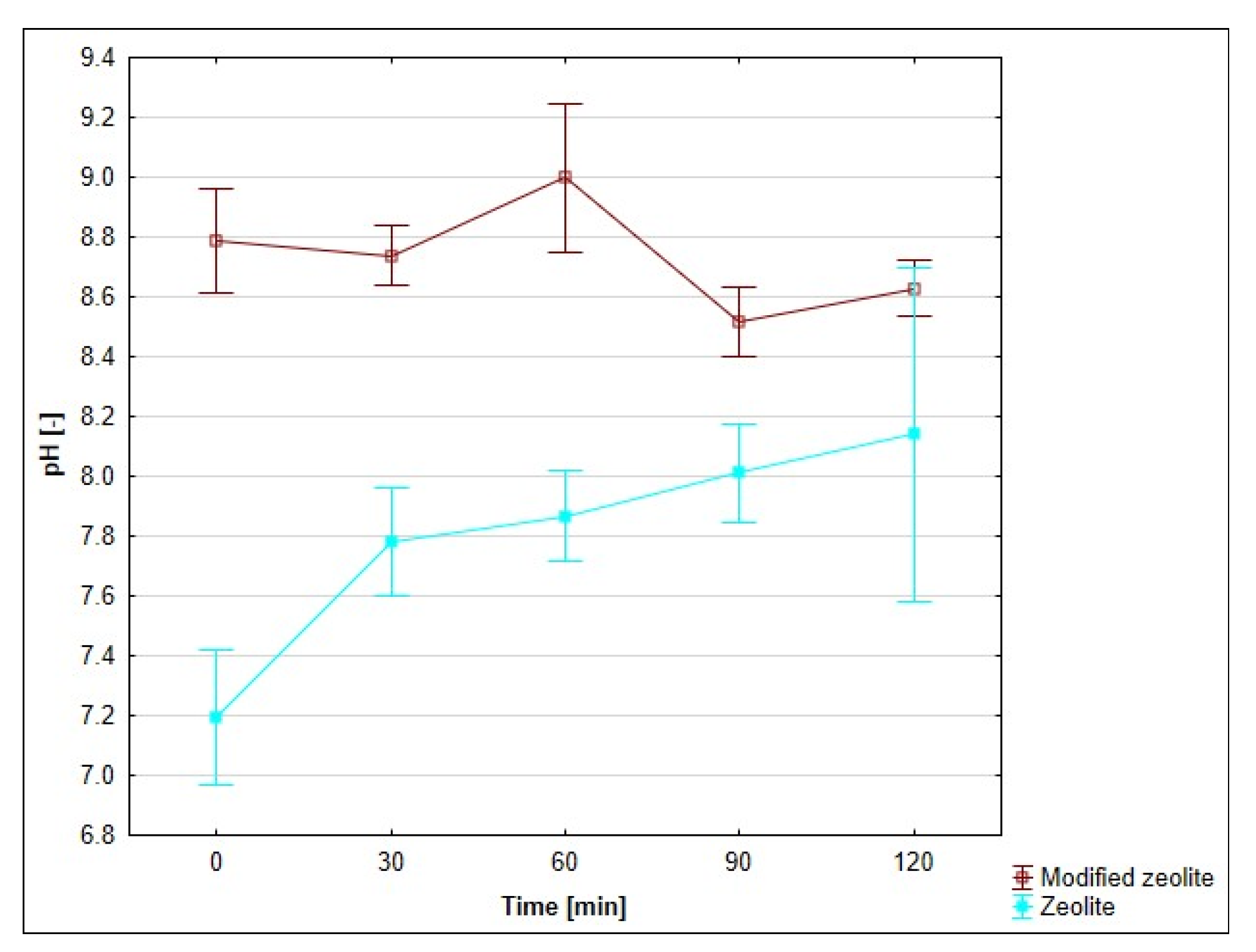
3.8. Effect of pH on the Adsorption Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of the Nonlinear Correlation of Adsorption Isotherms
4.2. Evaluation of the Parameters of Adsorption Isotherms
- High initial adsorbate concentrations;
- The initial stage of adsorption;
- An adsorbent that contains few active sites.
- High initial adsorbate concentrations;
- The final stage of adsorption;
- An adsorbent surface rich in active sites.
4.3. Evaluation of the Separation Factor
4.4. Evaluation of the Models of Pseudo-First-Order and Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics
- Low initial concentration of the adsorbate;
- Description of the process in the final phase;
- Adsorbents rich in active sites.
- 4.
- External diffusion of the adsorbate through the liquid film around the solid particle of the adsorbent;
- 5.
- Internal diffusion into the pores of the adsorbent;
- 6.
- Adsorption of the adsorbate at the active sites of the adsorbent.
4.5. Evaluation of the Thermodynamic Parameters—Changes in ΔG° ΔH° and ΔS°
4.6. Evaluation of Adsorption Capacity
4.7. Evaluation of the Effect of pH on the Adsorption Process
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, L.B.; Vicentini, R.; Ottoboni, L.M.M. Changes in the Bacterial Community of Soil from a Neutral Mine Drainage Channel. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.Y.; Acuña, C.R.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Esslemont, G.; Douglas, G.B. Sequential Hydrotalcite Precipitation, Microbial Sulfate Reduction and In Situ Hydrogen Sulfide Removal for Neutral Mine Drainage Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, A.P.; Gandy, C.J.; Webb, J.A. Controls on the Generation and Geochemistry of Neutral Mine Drainage: Evidence from Force Crag Mine, Cumbria, UK. Minerals 2023, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, J.; Timms, W. Mine Water Discharge Quality—A Review of Classification Frameworks. In Mining Meets Water—Conflicts and Solutions; Drebenstedt, C., Paul, M., Eds.; IMWA (International Mine Water Association): Freiberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Marmier, V.; Plante, B.; Demers, I.; Benzaazoua, M. Neutral Mine Drainage Prediction for Different Waste Rock Lithologies—Case Study of Canadian Malartic. J. Geochem. Explor. 2025, 271, 107685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Shen, S.Z.; Sun, H.; Sun, K.; Liu, F. Synthesis of L-Glutathione-Capped-ZnSe Quantum Dots for the Sensitive and Selective Determination of Copper Ion in Aqueous Solutions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, S.T.; Akar, T.; Kaynak, Z.; Anilan, B.; Cabuk, A.; Tabak, Ö.; Demir, T.A.; Gedikbey, T. Removal of Copper(II) Ions from Synthetic Solution and Real Wastewater by the Combined Action of Dried Trametes versicolor Cells and Montmorillonite. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prepilková, V.; Poništ, J.; Belčáková, I.; Ďuricová, A.; Salva, J.; Schwarz, M.; Samešová, D. Comparison of Copper and Zinc Sorption Depending on Temperature and Sorbents. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 2241–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samešová, D.; Pochyba, A.; Ďuricová, A.; Poništ, J.; Prepilková, V.Š.; Schwarz, M.; Veverková, D.; Salva, J.; Schmidtová, J. Comparative Adsorption of Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(II), and Mn(II) from Aquatic Solution and Neutral Mine Drainage Using Paper Sludge. Water 2025, 17, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Naidu, G.; Hasan Johir, M.A.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S. Acid Mine Drainage Treatment by Integrated Submerged Membrane Distillation–Sorption System. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olegario-Sanchez, E.; Pelicano, C.M. Characterization of Philippine Natural Zeolite and Its Application for Heavy Metal Removal from Acid Mine Drainage (AMD). Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 737, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wang, S. Magnetic Natural Composite Fe3O4-Chitosan@bentonite for Removal of Heavy Metals from Acid Mine Drainage. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 538, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulandari, E.; Hidayat, A.E.; Moersidik, S.S. Comparison of Copper Adsorption Effectivity in Acid Mine Drainage Using Natural Zeolite and Synthesized Zeolite. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 473, 012143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.H.; Atta, M.; Yaacub, W.Z.W. Remediation of Heavy Metals by Using Industrial Waste by Products in Acid Mine Drainage. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2017, 10, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tu, Z.; Lu, G.; Duan, X.; Yi, X.; Guo, C.; Dang, Z. Removal of Heavy Metals from Acid Mine Drainage Using Chicken Eggshells in Column Mode. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Yin, S.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Ju, S.; Miller, J.D.; Wang, X. Solvent Extraction of Cu(II) from Sulfate Solutions Containing Zn(II) and Fe(III) Using an Interdigital Micromixer. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 177, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edebali, S.; Pehlivan, E. Evaluation of Chelate and Cation Exchange Resins to Remove Copper Ions. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for Heavy Metals Removal and Their Future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Nayak, A.; Agarwal, S. Bioadsorbents for Remediation of Heavy Metals: Current Status and Their Future Prospects. Environ. Eng. Res. 2015, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, M.; İnce, O.K. An Overview of Adsorption Technique for Heavy Metal Removal from Water/Wastewater: A Critical Review. Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2017, 3, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucaci, A.R.; Bulgariu, D.; Popescu, M.-C.; Bulgariu, L. Adsorption of Cu(II) Ions on Adsorbent Materials Obtained from Marine Red Algae Callithamnion corymbosum Sp. Water 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastru, E.; Bulgariu, D.; Zamfir, C.-I.; Bulgariu, L. Application of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Biosorption of Co(II), Zn(II) and Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Media. Water 2022, 14, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Ji, P. Effect and Mechanisms of Synthesis Conditions on the Cadmium Adsorption Capacity of Modified Fly Ash. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Ji, P. Potential of Removing Cd(II) and Pb(II) from Contaminated Water Using a Newly Modified Fly Ash. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hu, Y. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution by Zeolite Synthesized from Fly Ash. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2778–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Zeolite Aggregate with Potential Use as a Sorbent of Heavy Metal Cations. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1183, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiya, T.K.; Bhattacharya, A.K.; Mandal, S.; Das, S.K. The Sorption of Lead(II) Ions on Rice Husk Ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rate, A.W. Sorption of Cadmium(II) and Copper(II) by Soil Humic Acids: Temperature Effects and Sorption Heterogeneity. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.D.T.; Samri, D.; Rahim, M.; Douzane, O.; Promis, G.; Langlet, T. Effect of Temperature-Dependent Sorption Characteristics on the Hygrothermal Behavior of Hemp Concrete. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston, J.E.; Apel, W.A.; Lee, B.D.; Peyton, B.M. Effects of Cell Condition, pH, and Temperature on Lead, Zinc, and Copper Sorption to Acidithiobacillus caldus Strain BC13. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Dai, Q.; Yu, X.; Yu, P.; Zhai, S.; Liu, R.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. Effects of Sludge Thermal-Alkaline Pre-treatment on Cationic Red X-GRL Adsorption onto Pyrolysis Biochar of Sewage Sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.L.; Park, M.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.-E.; Park, B.-Y.; Choi, J. Salt-Thermal Zeolitization of Fly Ash. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2812–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Moreno, N.; Umaña, J.C.; Alastuey, A.; Hernández, E.; López-Soler, A.; Plana, F. Synthesis of Zeolites from Coal Fly Ash: An Overview. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Števulová, N.; Junák, J. Alkalicky aktivované spojivo na báze popolčeka. Chem. Listy 2014, 108, 620–623. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Masto, R.E.; Hazra, B.; Esterle, J.; Singh, P.K. Genesis and Characteristics of Coal and Biomass Ash. In Ash from Coal and Biomass Combustion; Singh, A.K., Masto, R.E., Hazra, B., Esterle, J., Singh, P.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 15–36. ISBN 978-3-030-56981-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lexa, J.; Štohl, J.; Konečný, V. The Banská Štiavnica Ore District: Relationship between Metallogenetic Processes and the Geological Evolution of a Stratovolcano. Miner. Depos. 1999, 34, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Števko, M.; Sejkora, J.; Malíková, R. New Data on Supergene Minerals from the Banská Štiavnica Deposit (Slovak Republic). Bull. Mineral. Petrol. 2018, 26, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- STN EN ISO 5667-1 (757051); Kvalita Vody. Odber Vzoriek. Časť 1: Pokyny na Návrhy Programov Odberu Vzoriek a Techniky Odberu Vzoriek. NORMSERVIS s.r.o.: Hamry nad Sázavou, Czech Republic, 2023. Available online: https://eshop.normservis.sk/norma/stneniso-5667-1-1.1.2023.html (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- STN EN ISO 19458 (757770); Kvalita Vody. Odber Vzoriek na Mikrobiologickú Analýzu. NORMSERVIS s.r.o.: Hamry nad Sázavou, Czech Republic, 2007. Available online: https://eshop.normservis.sk/norma/stneniso-19458-1.2.2007.html (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- ISO 11885:2007; Water Quality—Determination of Selected Elements by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/36250.html (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- STN ISO 11465 (465211); Kvalita Pôdy. Stanovenie Obsahu Sušiny a Hmotnostného Obsahu Vody. Gravimetrická Metóda. NORMSERVIS s.r.o.: Hamry nad Sázavou, Czech Republic, 2001. Available online: https://eshop.normservis.sk/norma/stniso-11465-1.3.2001.html (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- STN EN ISO 10390 (838445); Zemina, Upravené Bioodpady a Kaly. Stanovenie PH. NORMSERVIS s.r.o.: Hamry nad Sázavou, Czech Republic, 2022. Available online: https://eshop.normservis.sk/norma/stneniso-10390-1.6.2022.html (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- ISO 15178:2000; Soil Quality—Determination of Total Sulfur by Dry Combustion. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/26682.html (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- eStudio.cz ČSN 75 7440 (757440). Available online: https://www.technicke-normy-csn.cz/csn-75-7440-757440-226378.html (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Skousen, J.; Jacobs, J.A. Stream Characterization for Acid Mine Drainage. In Acid Mine Drainage, Rock Drainage, and Acid Sulfate Soils; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 105–118. ISBN 978-1-118-74919-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, S. Use of an Air Brush to Spray Dry Samples for X-Ray Powder Diffraction. Clay Miner. 1999, 34, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumpu.com. DIFFRAC.EVA Tutorial. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/34435692/diffraceva-tutorial (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- DIFFRAC.TOPAS. Available online: https://www.bruker.com/en/products-and-solutions/diffractometers-and-x-ray-microscopes/x-ray-diffractometers/diffrac-suite-software/diffrac-topas.html (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Cheary, R.W.; Coelho, A. A Fundamental Parameters Approach to X-Ray Line-Profile Fitting. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1992, 25, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnety, J.A. Redetermination of the Structures of Potassium Sulphate and Potassium Chromate: The Effect of Electrostatic Crystal Forces upon Observed Bond Lengths. Acta Crystallogr. B 1972, 28, 2845–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.; Grundy, H.D. The Crystal Structure of Basic Cancrinite, Ideally Na8Al6Si6O242·3H2O. Can. Mineral. 1991, 29, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Comodi, P.; Fumagalli, P.; Montagnoli, M.; Zanazzi, P.F. A Single-Crystal Study on the Pressure Behavior of Phlogopite and Petrological Implications. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.M.; Cameron, M.; Crowley, K.D. Structural Variations in Natural F, OH, and Cl Apatites. Am. Mineral. 1989, 74, 870–876. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, R.J.; Ross, N.L.; Zhao, J.; Sochalski-Kolbus, L.; Krüger, H.; Schmidt, B.C. Structural Controls on the Anisotropy of Tetrahedral Frameworks: The Example of Monoclinic Feldspars. Eur. J. Mineral. 2013, 25, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, R. Effects of Temperature and Pressure on the Cell Dimension and X-Ray Temperature Factors of Periclase. Am. Mineral. 1976, 61, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, A.F. Accuracy of XRPD QPA Using the Combined Rietveld–RIR Method. J. Appl. Cryst. 2000, 33, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgranges, L.; Grebille, D.; Calvarin, G.; Chevrier, G.; Floquet, N.; Niepce, J.-C. Hydrogen Thermal Motion in Calcium Hydroxide: Ca(OH)2. Acta Crystallogr. B 1993, 49, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antao, S.M.; Hassan, I.; Wang, J.; Lee, P.L.; Toby, B.H. State-of-the-Art High-Resolution Powder X-Ray Diffraction (HRPXRD) Illustrated with Rietveld Structure Refinement of Quartz, Sodalite, Tremolite, and Meionite. Can. Mineral. 2008, 46, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gournis, D.; Lappas, A.; Karakassides, M.A.; Többens, D.; Moukarika, A. A Neutron Diffraction Study of Alkali Cation Migration in Montmorillonites. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2008, 35, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberl, D.D. User Guide to RockJock—A Program for Determining Quantitative Mineralogy from X-Ray Diffraction Data; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003.
- Środoń, J.; Drits, V.A.; McCarty, D.K.; Hsieh, J.C.C.; Eberl, D.D. Quantitative X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of Clay-Bearing Rocks from Random Preparations. Clays Clay Miner. 2001, 49, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuránek, M.; Melichová, Z.; Mirković, M.M.; Ivanović, M.; Pavlović, V.B.; Kljajević, L.; Nenadović, S. The Study of Cu(II) Adsorption onto Synthetically Modified Geopolymers. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer Technology: The Current State of the Art. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, A.; Tuzen, M.; Citak, D.; Soylak, M. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies of Adsorption of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution onto Turkish Kaolinite Clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Zhang, J.; Zou, W.; Shi, J.; Liu, H. Equilibrium Biosorption Isotherm for Lead Ion on Chaff. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 125, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melichová, Z.; Ľuptáková, A. Removing Lead from Aqueous Solutions Using Different Low-Cost Abundant Adsorbents. Desal. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 5025–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, S.A. Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics for the Removal of Artichoke Tournefortii Straw from Agricultural Waste. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1664, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampranpiboon, P. Equilibrium Isotherm Models for Adsorption of Zinc(II) Ion from Aqueous Solution on Pulp Waste. Wseas Trans. Environ. Dev. 2014, 10, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Edet, U.A.; Ifelebuegu, A.O. Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamic Modeling of the Adsorption of Phosphates from Model Wastewater Using Recycled Brick Waste. Processes 2020, 8, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadian, H.; Ghorbani, F.; Tayebi, H.; Asl, S.H. Study of the Adsorption of Cd(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Zeolite-Based Geopolymer, Synthesized from Coal Fly Ash; Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie der sogenannten Adsorption gelöster Stoffe. Z. Phys. Chem. Kolloid. 1907, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-Second Order Model for Sorption Processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walpole, R.E. Probability & Statistics for Engineers & Scientists; Pearson: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- El-Enein, S.A.; Okbah, M.A.; Hussain, S.G.; Soliman, N.F.; Ghounam, H.H. Adsorption of Selected Metals Ions in Solution Using Nano-Bentonite Particles: Isotherms and Kinetics. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitek, R.; Masini, J.C. Nonlinear Regression for Treating Adsorption Isotherm Data to Characterize New Sorbents: Advantages over Linearization Demonstrated with Simulated and Experimental Data. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, Z.; Karim, A.; Karam, A.; Khalloufi, S. Adsorption of Heavy Metals: Mechanisms, Kinetics, and Applications of Various Adsorbents in Wastewater Remediation—A Review. Waste 2023, 1, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elovich, S.Y.; Larinov, O.G. Theory of Adsorption from Solutions of Non Electrolytes on Solid (I) Equation Adsorption from Solutions and the Analysis of Its Simplest Form, (II) Verification of the Equation of Adsorption Isotherm from Solutions. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Otd. Khimicheskikh Nauk 1962, 2, 209–216. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=1418178 (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Melichová, Z.; Ďuricová, A.; Samešová, D.; Nagyová, I. Hodnotenie Rizík Vybraných Kovových Prvkov vo Vodách; Univerzita Mateja Bela, Fakulta prírodných vied: Banská Bystrica, Slovakia, 2017; Volume 1, p. 1. Available online: https://www.library.sk/arl-sldk/sk/detail-sldk_un_epca-0020016 (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Vengris, T.; Binkienė, R.; Sveikauskaitė, A. Nickel, Copper and Zinc Removal from Waste Water by a Modified Clay Sorbent. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 18, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melichová, Z.; Handzušová, M. Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Natural Bentonites. Solid State Phenom. 2016, 244, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, H.; Kul, A.R. An Investigation of Cu(II) Adsorption by Native and Activated Bentonite: Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmayanti, L.; Notodarmodjo, S.; Damanhuri, E.; Mukti, R.R. Removal of Copper(II) Ions in Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Alkali Activated Fly Ash. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 147, 04007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harja, M.; Buema, G.; Sutiman, D.-M.; Munteanu, C.; Bucur, D. Low Cost Adsorbents Obtained from Ash for Copper Removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 29, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavouraki, A.; Bartzas, G.; Komnitsas, K. Synthesis of Zeolites from Greek Fly Ash and Assessment of Their Copper Removal Capacity. Minerals 2020, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, I.V.; Tosheva, L.; Doyle, A.M. Simultaneous Removal of Cd(II), Co(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), and Zn(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions via Adsorption on FAU-Type Zeolites Prepared from Coal Fly Ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of Copper and Nickel on Na-Bentonite. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2010, 88, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Han, R.; Chen, Z.; Jinghua, Z.; Shi, J. Kinetic Study of Adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions Using Manganese Oxide Coated Zeolite in Batch Mode. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 279, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczuk, A.; Kołodyńska, D. Equilibrium, Thermodynamic and Kinetic Studies on Removal of Chromium, Copper, Zinc and Arsenic from Aqueous Solutions onto Fly Ash Coated by Chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 274, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apiratikul, R.; Pavasant, P. Sorption of Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ Using Modified Zeolite from Coal Fly Ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Kinetic Models: Physical Meanings, Applications, and Solving Methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmayanti, L.; Notodarmodjo, S.; Damanhuri, E. Removal of Copper(II) Ions in Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Fly Ash. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2017, 49, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapinar, N.; Donat, R. Adsorption Behaviour of Cu2+ and Cd2+ onto Natural Bentonite. Desalination 2009, 249, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotova, M.I. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Copper Ions Removal from Wastewater by Use of Zeolite. Waste Manag. 2001, 21, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.S.; Al Zboon, K.; Al-Makhadmeh, L.; Hararah, M.; Mahasneh, M. Fly Ash Based Geopolymer for Heavy Metal Removal: A Case Study on Copper Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, J.; Sheng, G.; Zhao, G.; Huang, Q. Effect of pH, Ionic Strength, Foreign Ions and Temperature on the Adsorption of Cu(II) from Aqueous Solution to GMZ Bentonite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 349, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, A.; Javid, N.; Malakootian, M. Investigation of Adsorption Efficiency of Cu2+ and Zn2+ by Red Soil and Activated Bentonite from Acid Copper Mine Drainage. Desal. Water Treat. 2019, 144, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, S.M. Towards a Safer Environment: Zeolitization of Bentonite and Its Potentialities for Removing Heavy Metals from Wastewater. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2010, 1, 533–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.R. Effects of pH on Isotherms Modeling for Cu(II) Ions Adsorption Using Maple Wood Sawdust. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikkaliotis, D.G.; Christoforidis, A.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Adsorption of Copper Ions onto Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Beads Functionalized with Poly(Ethylene Glycol). Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloussaief, M.; Jarraya, I.; Benzina, M. Adsorption of Copper Ions on Two Clays from Tunisia: pH and Temperature Effects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleraky, M.I.; Razek, T.M.A.; Hasani, I.W.; Fahim, Y.A. Adsorptive Removal of Lead, Copper, and Nickel Using Natural and Activated Egyptian Calcium Bentonite Clay. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
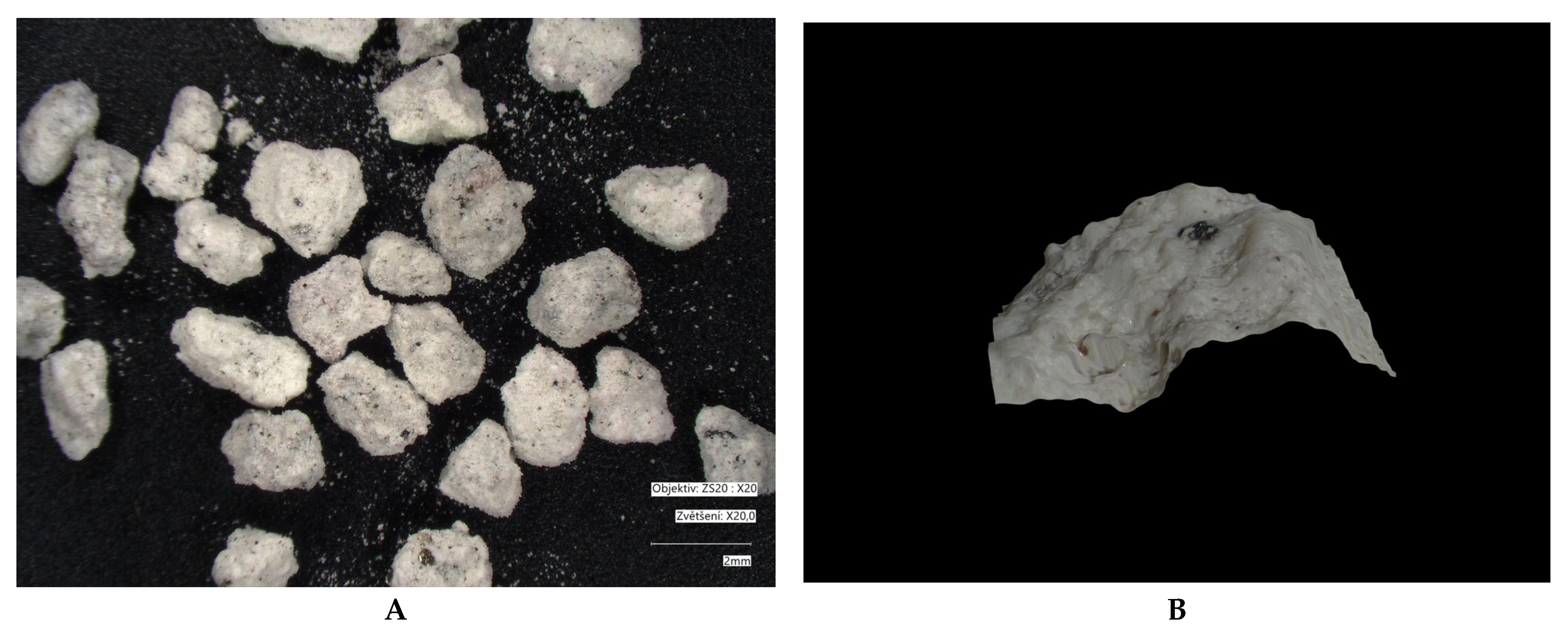







| Parameter /Metal | Method | |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Marking | |
| Cu | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) [41] |
| Mn | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Zn | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Fe | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Pb | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Cd | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Al | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Parameter /Metal | Method | |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Marking | |
| dry matter | gravimetrically | STN ISO 11465 < (SWP 2) [42] |
| pH/H2O | potentiometrically | ISO 10390 (SWP 8) [43] |
| S | EA-TCD | SWP 4 (ISO 15178) [44] |
| Al | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| B | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Cr | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Mn | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Cu | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Na | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Zn | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Fe | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Cd | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Pb | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Ni | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885) |
| Hg | AAS AMA | SWP 15 (CSI) 75 7440 l [45] |
| Mg | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885). SWP 19 Mehlich III |
| Ca | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885). SWP 19 Mchlich III |
| K | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885). SWP 19 Mehlich III |
| P | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885). SWP 19 Mehlich III |
| Cu | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885). SWP 19 Mehlich III |
| Fe | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885). SWP 19 Mehlich III |
| Mn | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885). SWP 19 Mehlich III |
| Zn | AES-ICP | SWP 6 (ISO 11885). SWP 19 Mehlich III |
| Adsorbent Sample | Fly Ash, Before Treatment | Fly Ash, After Treatment | Bentonite, Before Treatment | Bentonite, After Treatment | Zeolite, Before Treatment | Zeolite, After Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Rie | Rie | RJ | Rie | RJ | RJ |
| Mineral | [wt.%] | |||||
| quartz | 22 | 24 | 6 | 3 | - | - |
| K-feldspar | - | 7 | 11 | 5 | <1 | 3 |
| plagioclase | 5 | 35 | - | - | 4 | 11 |
| biotite | - | - | 2 | 2 | <1 | 3 |
| clinoptilolite/heulandite | - | - | - | - | 76 | 29 |
| opal-CT | - | - | 6 | - | 15 | - |
| arcanite | 17 | - | - | - | - | - |
| cancrinite | - | - | - | 16 | - | - |
| calcite | 29 | 34 | - | <1 | - | 4 |
| portlandite | 16 | - | - | - | - | - |
| hydroxylapatite | 5 | - | - | - | - | - |
| periclase | 6 | - | - | - | - | - |
| kaolinite | - | - | 2 | - | - | - |
| smectite | - | - | 73 | 1 | 3 | <1 |
| amorphous content | - | - | - | 72 | - | 50 |
| Sum | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Metal Content [µg·dm−3] | Ag | Ba | Cd | Co | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LV | 5 | 0.08 for the 1st hardness class up to 0.25 5th hardness class | 50 | 7.5 | |
| MV | <0.05 | 12.66 | 21.43 | 11.14 | 1 |
| Metal Content [µg·dm−3] | Pb | Se | Sb | Sn | Sr |
| LV | 7.2 | 20 | |||
| MV | 1.7 | 1.3 | 0.61 | 0.39 | 1814.39 |
| Metal Content [µg·dm−3] | Cu * | Fe | Zn | Tl | Al |
| LV | 1.1 for the 1st and 2nd hardness class and 8.8 for 4th and 5th hardness class | total Fe 2 mg·dm−3 | 7.8 for the 1st and 2nd hardness class and 52 for 4th and 5th hardness class | 200 | |
| MV | 17.2 | <10 | 4821.6 | 0.48 | 141 |
| pH [-] | 7.6 | ||||
| Chemical Composition [%] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | Na2O | K2O | MnO |
| Bentonite | 60.18–73.8 | 11.56–24.90 | 2.15–3.39 | 1.23–2.17 | 1.09–3.29 | 0.11–0.20 | 0.29–0.91 | 0.42–1.18 | 0.02–0.06 |
| Zeolite | 64.18–75.50 | 10.93–14.80 | 0.12–2.45 | 1.43–11.68 | 0.29–1.43 | - | 0.10–2.97 | 1.24–4.24 | – |
| Elemental Analysis [mg·kg−1] | |||||||||
| Adsorbent | Copper | Antimony | Zinc | Iron | Lead | Cadmium | Arsenic | Aluminium | |
| Bentonite | 7.40 | 23.4 | 64.4 | 23.711 | 12.4 | - | 6.3 | 121.198 | |
| Zeolite | 3.12 | 0.15 | - | 8.044 | 8.39 | 0.045 | 0.91 | 66.685 | |
| Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter | pH/H2O | S | Al | B | Cr |
| % | - | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 |
| 99.97 | 12.11 | 19,400 | 17,448 | 295 | 14.5 |
| Mn | Cu | Na | Zn | Fe | Cd |
| mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 |
| 4771 | 117 | 2099 | 1649 | 11,253 | 11.8 |
| Pb | Ni | Hg | Mg | Ca | K |
| mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | μg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 |
| 43.0 | 15.6 | 3.04 | 0.561 | 62,419 | 88,632 |
| Adsorbent | BET Surface Area (m2·g−1) |
|---|---|
| fly ash | 15.433 |
| bentonite | 43.098 |
| zeolite | 33.506 |
| modified fly ash | 16.449 |
| modified bentonite | 27.472 |
| modified zeolite | 10.098 |
| Adsorbent | Temperature | Freundlich Constants | Langmuir Constants | Temkin Constants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t [°C] | Kf [mg·g−1] | n | qm [mg·g−1] | b [dm3·mg−1] | A [dm3·g−1] | bt [J·mol−1] | |
| Fly ash | 10 | 4.630 | 2.091 | 7.819 | 1.611 | 17.546 | 1451.230 |
| 20 | 6.582 | 3.688 | 6.549 | 9.828 | 103.571 | 1743.130 | |
| 30 | 19.059 | 1.134 | 36.467 | 0.735 | 21.089 | 694.579 | |
| Modified fly ash | 10 | 9.368 | 2.057 | 8.484 | 5.783 | 72.422 | 1401.750 |
| 20 | 10.127 | 1.934 | 10.087 | 4.236 | 46.214 | 1140.310 | |
| 30 | 8.162 | 4.564 | 7.685 | 15.949 | 18 778 | 3975.660 | |
| Bentonite | 10 | 5.061 | 4.766 | 5.937 | 5.831 | 136.082 | 2350.720 |
| 20 | 5.530 | 2.810 | 7.222 | 3.184 | 24.269 | 1390.920 | |
| 30 | 5.512 | 3.199 | 7.541 | 3.567 | 31.875 | 1523.130 | |
| Modified bentonite | 10 | 14.233 | 1.447 | 15.962 | 2.142 | 23.974 | 771.812 |
| 20 | 18.681 | 1.798 | 23.083 | 2.923 | 130.58 | 1150.080 | |
| 30 | 7.732 | 4.970 | 34.109 | 1.319 | 9483.3 | 3289.896 | |
| Zeolite | 10 | 2.991 | 2.083 | 8.839 | 0.482 | 2.951 | 998.073 |
| 20 | 2.096 | 1.482 | 8.540 | 0.478 | 2.651 | 1152.540 | |
| 30 | 5.665 | 1.316 | 22.162 | 0.347 | 10.314 | 1020.170 | |
| Modified zeolite | 10 | 16.530 | 1.595 | 12.588 | 4.520 | 29.748 | 708.488 |
| 20 | 9.447 | 1.299 | 19.405 | 0.812 | 13.139 | 806.982 | |
| 30 | 8.024 | 2.194 | 9.610 | 3.311 | 25.902 | 1046.620 | |
| Temperature (°C) | Adsorbent c0 [mg·dm−3] | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash | Bentonite | Zeolite | |||||||||||||
| 5 | 9 | 12 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 16 | 18 | |
| 10 | 0.083 | 0.048 | 0.037 | 0.028 | 0.025 | 0.086 | 0.049 | 0.038 | 0.028 | 0.025 | 0.429 | 0.294 | 0.238 | 0.190 | 0.173 |
| 20 | 0.052 | 0.030 | 0.023 | 0.017 | 0.015 | 0.053 | 0.030 | 0.023 | 0.017 | 0.015 | 0.379 | 0.253 | 0.202 | 0.160 | 0.145 |
| 30 | 0.303 | 0.195 | 0.153 | 0.120 | 0.108 | 0.106 | 0.062 | 0.047 | 0.036 | 0.032 | 0.205 | 0.125 | 0.097 | 0.075 | 0.067 |
| Modified fly ash | Modified bentonite | Modified zeolite | |||||||||||||
| 5 | 9 | 12 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 16 | 18 | |
| 10 | 0.024 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.118 | 0.069 | 0.053 | 0.040 | 0.036 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 20 | 0.040 | 0.022 | 0.017 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 6.18 × 10−4 | 3.44 × 10−4 | 2.58 × 10−4 | 1.93 × 10−4 | 1.72 × 10−4 | 1.80 × 10−1 | 1.09 × 10−1 | 8.37 × 10−2 | 6.41 × 10−2 | 5.74 × 10−2 |
| 30 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | * | * | * | * | * | 0.105 | 0.061 | 0.047 | 0.035 | 0.032 |
| Adsorbent | Isotherm | F-Test | p-Level * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bentonite 10 °C | Freundlich | 89.46 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 91.09 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 89.91 | 0.000 | |
| Bentonite 20 °C | Freundlich | 107.39 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 112.48 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 110.30 | 0.000 | |
| Bentonite 30 °C | Freundlich | 276.68 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 389.02 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 335.48 | 0.000 | |
| Zeolite 10 °C | Freundlich | 207.76 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 242.03 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 250.50 | 0.000 | |
| Zeolite 20 °C | Freundlich | 175.21 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 180.63 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 184.42 | 0.000 | |
| Zeolite 30 °C | Freundlich | 1439.30 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 1217.71 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 693.33 | 0.000 | |
| Fly ash 10 °C | Freundlich | 311.94 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 318.06 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 309.29 | 0.000 | |
| Fly ash 20 °C | Freundlich | 107.23 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 113.41 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 109.95 | 0.000 | |
| Fly ash 30 °C | Freundlich | 1220.39 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 1261.66 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 1087.93 | 0.000 | |
| Modified bentonite 10 °C | Freundlich | 469.78 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 485.05 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 494.01 | 0.000 | |
| Modified bentonite 20 °C | Freundlich | 19.04 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 500.27 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 610.23 | 0.000 | |
| Modified bentonite 30 °C | Freundlich | 92.31 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 408.56 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 320.79 | 0.000 | |
| Modified zeolite 10 °C | Freundlich | 126.54 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 90.40 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 70.45 | 0.000 | |
| Modified zeolite 20 °C | Freundlich | 1777.37 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 1597.5 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 1371.74 | 0.000 | |
| Modified zeolite 30 °C | Freundlich | 167.97 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 167.56 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 169.88 | 0.000 | |
| Modified fly ash 10 °C | Freundlich | 387.57 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 379.54 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 365.31 | 0.000 | |
| Modified fly ash 20 °C | Freundlich | 1328.07 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 1550.38 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 1243.12 | 0.000 | |
| Modified fly ash 30 °C | Freundlich | 286.93 | 0.000 |
| Langmuir | 185.54 | 0.000 | |
| Temkin | 357.03 | 0.000 |
| Adsorbent | Temperature | qe Experim. [mg·g−1] | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [°C] | k1 [dm3·min−1] | qe [mg·g−1] | R2 | Equation | k2 [g·mg−1 min−1] | qe [mg·g−1] | R2 | Equation | ||
| 5 [mg·dm−3] | ||||||||||
| Fly ash | 10 | 1.934 | 0.0109 | 1.745 | 0.579 | y = 0.0109x + 0.5565 | 0.903 | 0.389 | 0.998 | y = 2.5728x + 7.3327 |
| 20 | 1.951 | 0.0108 | 1.830 | 0.534 | y = 0.0108x + 0.6045 | 2.579 | 0.393 | 1 | y = 2.546x + 2.513 | |
| 30 | 1.968 | 0.0108 | 1.837 | 0.532 | y = 0.0108x + 0.6084 | 2.408 | 0.396 | 1 | y = 2.5264x + 2.6508 | |
| Modified fly ash | 10 | 1.984 | 0.0107 | 1.876 | 0.512 | y = 0.0107x + 0.6289 | 6.069 | 0.397 | 1 | y = 2.5191x + 1.0457 |
| 20 | 1.981 | 0.0107 | 1.879 | 0.509 | y = 0.0107x + 0.6309 | 7.774 | 0.396 | 1 | y = 2.5243x + 0.8197 | |
| 30 | 2.000 | 0.0107 | 1.899 | 0.502 | y = 0.0107x + 0.6413 | 24.300 | 0.400 | 1 | y = 2.4995x + 0.2571 | |
| Bentonite | 10 | 1.860 | 0.0133 | 1.214 | 0.886 | y = 0.0133x + 0.1939 | 0.089 | 0.439 | 0.824 | y = 2.2801x + 58.422 |
| 20 | 1.871 | 0.0111 | 1.653 | 0.634 | y = 0.0111x + 0.5027 | 0.569 | 0.384 | 0.994 | y = 2.6014x + 11.893 | |
| 30 | 1.832 | 0.0106 | 1.755 | 0.559 | y = 0.0106x + 0.5625 | 1.707 | 0.390 | 1 | y = 2.5664x + 3.8582 | |
| Modified bentonite | 10 | 1.967 | 0.0106 | 1.881 | 0.505 | y = 0.0106x + 0.632 | 13.184 | 0.394 | 1 | y = 2.5412x + 0.4898 |
| 20 | 2.000 | 0.6295 | 1.877 | 0.516 | y = 0.0108x + 0.6295 | 5.342 | 0.161 | 1 | y = 2.4949x + 1.1651 | |
| 30 | 2.000 | 0.0108 | 1.894 | 0.506 | y = 0.0108x + 0.6385 | 15.777 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4967x + 0.3951 | |
| Zeolite | 10 | 1.578 | 0.0108 | 1.182 | 0.922 | y = 0.0108x + 0.1674 | 0.140 | 0.330 | 0.839 | y = 3.032x + 65.646 |
| 20 | 1.656 | 0.0096 | 1.484 | 0.673 | y = 0.0096x + 0.3948 | 0.416 | 0.316 | 0.953 | y = 3.1679x + 24.097 | |
| 30 | 1.926 | 0.0115 | 1.518 | 0.727 | y = 0.0115x + 0.4177 | 0.284 | 0.390 | 0.974 | y = 2.5667x + 23.22 | |
| Modified zeolite | 10 | 1.979 | 0.0107 | 1.880 | 0.5068 | y = 0.0107x + 0.6315 | 8.161 | 0.395 | 1 | y = 2.5314x + 0.7852 |
| 20 | 1.942 | 0.0106 | 1.866 | 0.509 | y = 0.0106x + 0.6236 | 8.394 | 0.388 | 1 | y = 2.5741x + 0.7894 | |
| 30 | 1.938 | 0.0108 | 1.806 | 0.5441 | y = 0.0108x + 0.5911 | 1.676 | 0.390 | 1 | y = 2.5627x + 3.9187 | |
| 9 [mg·dm−3] | ||||||||||
| Fly ash | 10 | 3.331 | 0.0145 | 2.186 | 0.552 | y = 0.0145x + 0.7821 | 1.043 | 0.373 | 0.998 | y = 2.6843x + 6.9117 |
| 20 | 3.476 | 0.0145 | 2.351 | 0.509 | y = 0.0145x + 0.8549 | 7.848 | 0.387 | 1 | y = 2.5811x + 0.8489 | |
| 30 | 3.513 | 0.0147 | 2.297 | 0.531 | y = 0.0147x + 0.8315 | 1.845 | 0.393 | 0.999 | y = 2.5437x + 3.5069 | |
| Modified fly ash | 10 | 3.530 | 0.0145 | 2.377 | 0.504 | y = 0.0145x + 0.866 | 14.673 | 0.392 | 1 | y = 2.5498x + 0.4431 |
| 20 | 3.539 | 0.0145 | 2.380 | 0.503 | y = 0.0145x + 0.8673 | 14.325 | 0.393 | 1 | y = 2.544x + 0.4518 | |
| 30 | 3.562 | 0.0146 | 2.390 | 0.502 | y = 0.0146x + 0.8715 | 17.820 | 0.396 | 1 | y = 2.5258x + 0.358 | |
| Bentonite | 10 | 3.244 | 0.0146 | 1.879 | 0.659 | y = 0.0146x + 0.6305 | 0.127 | 0.298 | 0.961 | y = 2.8046x + 26.378 |
| 20 | 3.228 | 0.0147 | 2.073 | 0.593 | y = 0.0147x + 0.7291 | 0.663 | 0.368 | 0.995 | y = 2.7159x + 11.127 | |
| 30 | 3.478 | 0.0152 | 2.130 | 0.592 | y = 0.0152x + 0.7561 | 3.092 | 0.385 | 1 | y = 2.5943x + 2.177 | |
| Modified bentonite | 10 | 3.518 | 0.0145 | 2.381 | 0.502 | y = 0.0145x + 0.8675 | 37.302 | 0.391 | 1 | y = 2.5579x + 0.1754 |
| 20 | 3.600 | 0.0148 | 2.336 | 0.524 | y = 0.0148x + 0.8484 | 5.322 | 0.161 | 1 | y = 2.49x + 2.5051 | |
| 30 | 3.600 | 0.0147 | 2.399 | 0.503 | y = 0.0147x + 0.8751 | 21.811 | 0.400 | 1 | y = 2.4976x + 0.286 | |
| Zeolite | 10 | 3.113 | 0.0163 | 1.485 | 0.849 | y = 0.0163x + 0.3957 | 0.101 | 0.389 | 0.841 | y = 2.5689x + 65.018 |
| 20 | 3.002 | 0.0145 | 1.929 | 0.635 | y = 0.0145x + 0.657 | 0.463 | 0.348 | 0.987 | y = 2.8755x + 17.859 | |
| 30 | 3.376 | 0.0146 | 2.100 | 0.583 | y = 0.0146x + 0.7418 | 0.596 | 0.373 | 0.991 | y = 2.68x + 12.044 | |
| Modified zeolite | 10 | 3.599 | 0.0147 | 2.385 | 0.507 | y = 0.0147x + 0.869 | 7.085 | 0.400 | 1 | y = 2.4989x + 0.8814 |
| 20 | 3.510 | 0.0146 | 2.323 | 0.519 | y = 0.0146x + 0.8429 | 2.472 | 0.390 | 1 | y = 2.5611x + 2.6529 | |
| 30 | 3.478 | 0.0145 | 2.325 | 0.515 | y = 0.0145x + 0.8438 | 3.140 | 0.386 | 1 | y = 2.5929x + 2.1411 | |
| 12 [mg·dm−3] | ||||||||||
| Fly ash | 10 | 4.181 | 0.0184 | 1.750 | 0.772 | y = 0.0184x + 0.5597 | 0.117 | 0.400 | 0.865 | y = 2.5027x + 53.539 |
| 20 | 4.616 | 0.0166 | 2.545 | 0.531 | y = 0.0166x + 0.9342 | 5.728 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4952x + 1.0869 | |
| 30 | 4.707 | 0.0169 | 2.520 | 0.545 | y = 0.0169x + 0.9242 | 1.161 | 0.397 | 0.999 | y = 2.5212x + 5.4732 | |
| Modified fly ash | 10 | 4.635 | 0.0163 | 2.675 | 0.497 | y = 0.0163x + 0.9839 | 14.858 | 0.386 | 1 | y = 2.5906x − 0.4517 |
| 20 | 4.716 | 0.0164 | 2.675 | 0.501 | y = 0.0164x + 0.984 | 5.728 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4952x + 1.0869 | |
| 30 | 4.726 | 0.0165 | 2.664 | 0.504 | y = 0.0165x + 0.9798 | 7.841 | 0.393 | 1 | y = 2.5438x + 0.8253 | |
| Bentonite | 10 | 4.597 | 0.0177 | 2.191 | 0.643 | y = 0.0177x + 0.7844 | 0.303 | 0.405 | 0.979 | y = 2.4698x + 20.162 |
| 20 | 4.674 | 0.0179 | 2.150 | 0.661 | y = 0.0179x + 0.7654 | 5.728 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4952x + 1.0869 | |
| 30 | 4.200 | 0.0162 | 2.394 | 0.553 | y = 0.0162x + 0.8731 | 5.527 | 0.391 | 1 | y = 2.5566x + 1.1827 | |
| Modified bentonite | 10 | 4.743 | 0.0165 | 2.671 | 0.504 | y = 0.0165x + 0.9823 | 9.691 | 0.395 | 1 | y = 2.5311x + 0.6611 |
| 20 | 4.800 | 0.0166 | 2.652 | 0.511 | y = 0.0166x + 0.9752 | 5.728 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4952x + 1.0869 | |
| 30 | 4.800 | 0.0166 | 2.672 | 0.508 | y = 0.0166x + 0.983 | 5.728 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4952x + 1.0869 | |
| Zeolite | 10 | 4.111 | 0.0164 | 2.268 | 0.588 | y = 0.0164x + 0.8189 | 0.682 | 0.352 | 0.994 | y = 2.8409x + 11.84 |
| 20 | 3.585 | 0.0153 | 2.050 | 0.621 | y = 0.0153x + 0.7176 | 5.728 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4952x + 1.0869 | |
| 30 | 4.453 | 0.0166 | 2.411 | 0.561 | y = 0.0166x + 0.8801 | 0.879 | 0.375 | 0.997 | y = 2.6643x + 8.0793 | |
| Modified zeolite | 10 | 4.721 | 0.0166 | 2.659 | 0.509 | y = 0.0166x + 0.9778 | 8.540 | 0.396 | 1 | y = 2.5251x + 0.7466 |
| 20 | 4.613 | 0.0164 | 2.616 | 0.511 | y = 0.0164x + 0.9615 | 5.728 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4952x + 1.0869 | |
| 30 | 4.685 | 0.0165 | 2.642 | 0.509 | y = 0.0165x + 0.9717 | 5.542 | 0.391 | 1 | y = 2.5559x + 1.1788 | |
| 16 [mg·dm−3] | ||||||||||
| Fly ash | 10 | 5.898 | 0.0192 | 2.355 | 0.642 | y = 0.0192x + 0.8564 | 0.253 | 0.383 | 0.964 | y = 2.6128x + 27.027 |
| 20 | 6.205 | 0.0187 | 2.800 | 0.542 | y = 0.0187x + 1.0295 | 0.944 | 0.392 | 0.997 | y = 2.5529x + 6.9036 | |
| 30 | 6.302 | 0.0186 | 2.901 | 0.523 | y = 0.0186x + 1.0651 | 1.795 | 0.396 | 0.999 | y = 2.5253x + 3.5534 | |
| Modified fly ash | 10 | 6.255 | 0.0183 | 2.982 | 0.504 | y = 0.0183x + 1.0925 | 9.881 | 0.390 | 1 | y = 2.5639x + 0.6653 |
| 20 | 6.210 | 0.0182 | 3.011 | 0.497 | y = 0.0182x + 1.1023 | 10.971 | 0.387 | 1 | y = 2.581x − 0.6072 | |
| 30 | 6.296 | 0.0184 | 3.005 | 0.501 | y = 0.0184x + 1.1002 | 29.117 | 0.394 | 1 | y = 2.5407x + 0.2217 | |
| Bentonite | 10 | 5.991 | 0.0189 | 2.569 | 0.591 | y = 0.0189x + 0.9437 | 0.438 | 0.386 | 0.988 | y = 2.5883x + 15.311 |
| 20 | 6.105 | 0.0194 | 2.412 | 0.635 | y = 0.0194x + 0.8804 | 0.249 | 0.400 | 0.959 | y = 2.4998x + 25.106 | |
| 30 | 6.235 | 0.0187 | 2.861 | 0.532 | y = 0.0187x + 1.0512 | 3.247 | 0.394 | 1 | y = 2.5391x + 1.9858 | |
| Modified bentonite | 10 | 6.299 | 0.0185 | 2.980 | 0.507 | y = 0.0185x + 1.092 | 7.320 | 0.395 | 1 | y = 2.5344x + 0.8775 |
| 20 | 6.382 | 0.0185 | 2.988 | 0.508 | y = 0.0185x + 1.0945 | 4.831 | 0.400 | 1 | y = 2.5015x + 1.2952 | |
| 30 | 6.400 | 0.0186 | 2.988 | 0.509 | y = 0.0186x + 1.0946 | 4.973 | 0.401 | 1 | y = 2.4921x + 1.2489 | |
| Zeolite | 10 | 5.703 | 0.0187 | 2.242 | 0.659 | y = 0.0187x + 0.8073 | 0.220 | 0.361 | 0.937 | y = 2.7723x + 34.893 |
| 20 | 5.704 | 0.0189 | 2.268 | 0.655 | y = 0.0189x + 0.8187 | 0.218 | 0.369 | 0.930 | y = 2.7077x + 33.705 | |
| 30 | 6.000 | 0.0184 | 2.785 | 0.536 | y = 0.0184x + 1.0244 | 1.127 | 0.377 | 0.998 | y = 2.65x + 6.2315 | |
| Modified zeolite | 10 | 6.374 | 0.0185 | 3.004 | 0.505 | y = 0.0185x + 1.1001 | 9.829 | 0.399 | 1 | y = 2.5081x + 0.64 |
| 20 | 6.164 | 0.0183 | 2.953 | 0.507 | y = 0.0183x + 1.0829 | 7.039 | 0.386 | 1 | y = 2.589x + 0.9523 | |
| 30 | 6.319 | 0.0185 | 2.956 | 0.511 | y = 0.0185x + 1.084 | 3.270 | 0.394 | 1 | y = 2.5386x + 1.9709 | |
| 18 [mg·dm−3] | ||||||||||
| Fly ash | 10 | 6.654 | 0.0193 | 2.624 | 0.589 | y = 0.0193x + 0.9647 | 0.391 | 0.367 | 0.978 | y = 2.7266x + 19.033 |
| 20 | 7.123 | 0.0196 | 3.000 | 0.533 | y = 0.0196x + 1.0985 | 1.361 | 0.399 | 0.999 | y = 2.5055x + 4.6108 | |
| 30 | 7.067 | 0.0192 | 3.104 | 0.509 | y = 0.0192x + 1.1328 | 4.218 | 0.393 | 1 | y = 2.5451x + 1.5356 | |
| Modified fly ash | 10 | 7.055 | 0.0191 | 3.149 | 0.500 | y = 0.0191x + 1.147 | 63.965 | 0.391 | 1 | y = 2.5543x + 0.102 |
| 20 | 7.045 | 0.0191 | 3.151 | 0.499 | y = 0.0191x + 1.1478 | 54.778 | 0.391 | 1 | y = 2.5585x + 0.1195 | |
| 30 | 7.144 | 0.0193 | 3.127 | 0.507 | y = 0.0193x + 1.1401 | 5.627 | 0.397 | 1 | y = 2.5182x + 1.127 | |
| Bentonite | 10 | 7.026 | 0.0202 | 2.613 | 0.614 | y = 0.0202x + 0.9605 | 0.285 | 0.407 | 0.970 | y = 2.4587x + 21.188 |
| 20 | 6.897 | 0.0207 | 2.411 | 0.664 | y = 0.0207x + 0.8799 | 0.193 | 0.411 | 0.951 | y = 2.4345x + 30.643 | |
| 30 | 6.482 | 0.0192 | 2.823 | 0.552 | y = 0.0192x + 1.0378 | 29.836 | 0.384 | 1 | y = 2.6019x + 0.2269 | |
| Modified bentonite | 10 | 7.051 | 0.0195 | 3.004 | 0.530 | y = 0.0195x + 1.1001 | 1.560 | 0.395 | 1 | y = 2.5321x + 4.1095 |
| 20 | 7.200 | 0.0194 | 3.106 | 0.513 | y = 0.0194x + 1.1334 | 3.157 | 0.160 | 1 | y = 2.4964x + 1.9742 | |
| 30 | 7.200 | 0.0193 | 3.162 | 0.503 | y = 0.0193x + 1.1513 | 13.032 | 0.400 | 1 | y = 2.4979x + 0.4788 | |
| Zeolite | 10 | 5.513 | 0.019 | 2.273 | 0.657 | y = 0.019x + 0.8212 | 0.297 | 0.325 | 0.969 | y = 3.079x + 31.961 |
| 20 | 5.967 | 0.0186 | 2.556 | 0.586 | y = 0.0186x + 0.9383 | 0.467 | 0.334 | 0.982 | y = 2.9962x + 19.214 | |
| 30 | 6.729 | 0.0189 | 2.983 | 0.518 | y = 0.0189x + 1.093 | 1.870 | 0.371 | 0.998 | y = 2.6971x + 3.8898 | |
| Modified zeolite | 10 | 7.200 | 0.0193 | 3.160 | 0.503 | y = 0.0193x + 1.1507 | 11.797 | 0.400 | 1 | y = 2.4976x + 0.5288 |
| 20 | 6.955 | 0.0192 | 3.087 | 0.5096 | y = 0.0192x + 1.1272 | 5.063 | 0.388 | 1 | y = 2.5794x + 1.3141 | |
| 30 | 6.918 | 0.019 | 3.119 | 0.5017 | y = 0.019x + 1.1375 | 27.124 | 0.385 | 1 | y = 2.6004x + 0.2493 | |
| Adsorbent | Temperature | ΔG0 | ΔH0 | ΔS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [°C] | [kJ·mol−1] | [kJ·mol−1] | [J·mol−1·K−1] | |
| Fly ash | 10 | −18.113 | 31.09 | 173.89 |
| 20 | −19.969 | |||
| 30 | −21.586 | |||
| Modified fly ash | 10 | −20.312 | 72.10 | 324.08 |
| 20 | −21.522 | |||
| 30 | −26.888 | |||
| Bentonite | 10 | −17.861 | 32.34 | 177.61 |
| 20 | −19.924 | |||
| 30 | −21.400 | |||
| Modified bentonite | 10 | −20.634 | 49.10 | 246.63 |
| 20 | −23.434 | |||
| 30 | −25.551 | |||
| Zeolite | 10 | −13.144 | 37.88 | 179.28 |
| 20 | −14.119 | |||
| 30 | −16.768 | |||
| Modified zeolite | 10 | −15.578 | 29.11 | 157.23 |
| 20 | −16.614 | |||
| 30 | −18.748 |
| Adsorbent | Time [min] | Valid N | Mean [mg·g−1] | Confidence | Confidence | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash | 30 | 6 | 1.67 | 1.64 | 1.70 | 0.03 |
| Fly ash | 30 | 6 | 2.93 | 2.92 | 2.95 | 0.02 |
| Fly ash | 30 | 6 | 1.77 | 1.74 | 1.79 | 0.02 |
| Fly ash | 30 | 6 | 3.92 | 3.84 | 3.99 | 0.07 |
| Fly ash | 30 | 6 | 5.00 | 4.93 | 5.07 | 0.06 |
| Fly ash | 60 | 6 | 1.79 | 1.79 | 1.80 | 0.01 |
| Fly ash | 60 | 6 | 3.09 | 3.07 | 3.11 | 0.02 |
| Fly ash | 60 | 6 | 3.52 | 3.43 | 3.60 | 0.08 |
| Fly ash | 60 | 6 | 4.45 | 4.44 | 4.47 | 0.02 |
| Fly ash | 60 | 6 | 5.30 | 5.28 | 5.32 | 0.02 |
| Fly ash | 90 | 6 | 1.87 | 1.86 | 1.87 | 0.01 |
| Fly ash | 90 | 6 | 3.26 | 3.25 | 3.26 | 0.01 |
| Fly ash | 90 | 6 | 4.07 | 4.04 | 4.09 | 0.02 |
| Fly ash | 90 | 6 | 5.64 | 5.61 | 5.67 | 0.03 |
| Fly ash | 90 | 6 | 5.85 | 5.84 | 5.87 | 0.01 |
| Fly ash | 120 | 6 | 1.93 | 1.93 | 1.94 | 0.01 |
| Fly ash | 120 | 6 | 3.33 | 3.32 | 3.35 | 0.01 |
| Fly ash | 120 | 6 | 4.18 | 4.17 | 4.19 | 0.01 |
| Fly ash | 120 | 6 | 5.90 | 5.89 | 5.90 | 0.01 |
| Fly ash | 120 | 6 | 6.65 | 6.64 | 6.67 | 0.02 |
| Bentonite | 30 | 6 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.78 | 0.04 |
| Bentonite | 30 | 6 | 2.25 | 2.22 | 2.27 | 0.02 |
| Bentonite | 30 | 6 | 2.99 | 2.96 | 3.02 | 0.03 |
| Bentonite | 30 | 6 | 4.58 | 4.55 | 4.60 | 0.03 |
| Bentonite | 30 | 6 | 5.01 | 4.87 | 5.15 | 0.13 |
| Bentonite | 60 | 6 | 1.44 | 1.42 | 1.46 | 0.02 |
| Bentonite | 60 | 6 | 2.41 | 2.38 | 2.43 | 0.03 |
| Bentonite | 60 | 6 | 4.16 | 4.14 | 4.18 | 0.02 |
| Bentonite | 60 | 6 | 5.13 | 5.10 | 5.15 | 0.02 |
| Bentonite | 60 | 6 | 5.46 | 5.42 | 5.51 | 0.04 |
| Bentonite | 90 | 6 | 1.86 | 1.85 | 1.87 | 0.01 |
| Bentonite | 90 | 6 | 2.74 | 2.71 | 2.77 | 0.03 |
| Bentonite | 90 | 6 | 4.60 | 4.58 | 4.61 | 0.01 |
| Bentonite | 90 | 6 | 5.99 | 5.97 | 6.01 | 0.02 |
| Bentonite | 90 | 6 | 7.03 | 7.02 | 7.03 | 0.01 |
| Bentonite | 120 | 6 | 1.86 | 1.85 | 1.87 | 0.01 |
| Bentonite | 120 | 6 | 3.24 | 3.16 | 3.32 | 0.08 |
| Bentonite | 120 | 6 | 4.60 | 4.58 | 4.61 | 0.01 |
| Bentonite | 120 | 6 | 5.99 | 5.97 | 6.01 | 0.02 |
| Bentonite | 120 | 6 | 7.03 | 7.02 | 7.03 | 0.01 |
| Zeolite | 30 | 6 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.01 |
| Zeolite | 30 | 6 | 1.34 | 1.32 | 1.36 | 0.02 |
| Zeolite | 30 | 6 | 3.15 | 3.12 | 3.18 | 0.03 |
| Zeolite | 30 | 6 | 3.66 | 3.63 | 3.69 | 0.03 |
| Zeolite | 30 | 6 | 3.42 | 3.39 | 3.44 | 0.03 |
| Zeolite | 60 | 6 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.03 |
| Zeolite | 60 | 6 | 2.01 | 1.98 | 2.03 | 0.02 |
| Zeolite | 60 | 6 | 3.98 | 3.96 | 4.01 | 0.03 |
| Zeolite | 60 | 6 | 3.86 | 3.73 | 3.99 | 0.12 |
| Zeolite | 60 | 6 | 4.58 | 4.54 | 4.63 | 0.04 |
| Zeolite | 90 | 6 | 1.35 | 1.32 | 1.38 | 0.03 |
| Zeolite | 90 | 6 | 2.91 | 2.90 | 2.92 | 0.01 |
| Zeolite | 90 | 6 | 4.06 | 4.03 | 4.08 | 0.02 |
| Zeolite | 90 | 6 | 4.97 | 4.93 | 5.01 | 0.04 |
| Zeolite | 90 | 6 | 5.43 | 5.37 | 5.50 | 0.06 |
| Zeolite | 120 | 6 | 1.58 | 1.56 | 1.59 | 0.02 |
| Zeolite | 120 | 6 | 3.11 | 3.07 | 3.15 | 0.04 |
| Zeolite | 120 | 6 | 4.11 | 4.11 | 4.12 | 0.00 |
| Zeolite | 120 | 6 | 5.70 | 5.66 | 5.75 | 0.04 |
| Zeolite | 120 | 6 | 5.51 | 5.47 | 5.56 | 0.04 |
| Modified fly ash | 30 | 6 | 1.94 | 1.93 | 1.94 | 0.01 |
| Modified fly ash | 30 | 6 | 3.49 | 3.49 | 3.50 | 0.01 |
| Modified fly ash | 30 | 6 | 4.66 | 4.65 | 4.66 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 30 | 6 | 6.16 | 6.16 | 6.16 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 30 | 6 | 7.04 | 7.03 | 7.06 | 0.01 |
| Modified fly ash | 60 | 6 | 1.96 | 1.96 | 1.97 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 60 | 6 | 3.52 | 3.51 | 3.52 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 60 | 6 | 4.68 | 4.67 | 4.69 | 0.01 |
| Modified fly ash | 60 | 6 | 6.26 | 6.20 | 6.32 | 0.05 |
| Modified fly ash | 60 | 6 | 7.07 | 7.03 | 7.11 | 0.04 |
| Modified fly ash | 90 | 6 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 90 | 6 | 3.52 | 3.51 | 3.52 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 90 | 6 | 4.63 | 4.63 | 4.64 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 90 | 6 | 6.18 | 6.17 | 6.18 | 0.01 |
| Modified fly ash | 90 | 6 | 7.03 | 7.02 | 7.03 | 0.01 |
| Modified fly ash | 120 | 6 | 1.98 | 1.98 | 1.99 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 120 | 6 | 3.53 | 3.53 | 3.53 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 120 | 6 | 4.64 | 4.63 | 4.64 | 0.01 |
| Modified fly ash | 120 | 6 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.26 | 0.00 |
| Modified fly ash | 120 | 6 | 7.05 | 7.05 | 7.06 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 30 | 6 | 1.95 | 1.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 30 | 6 | 3.50 | 3.49 | 3.51 | 0.01 |
| Modified bentonite | 30 | 6 | 4.68 | 4.67 | 4.69 | 0.01 |
| Modified bentonite | 30 | 6 | 6.14 | 6.13 | 6.16 | 0.01 |
| Modified bentonite | 30 | 6 | 6.31 | 6.28 | 6.34 | 0.03 |
| Modified bentonite | 60 | 6 | 1.96 | 1.95 | 1.96 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 60 | 6 | 3.52 | 3.51 | 3.52 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 60 | 6 | 4.70 | 4.70 | 4.71 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 60 | 6 | 6.28 | 6.27 | 6.28 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 60 | 6 | 6.93 | 6.90 | 6.96 | 0.03 |
| Modified bentonite | 90 | 6 | 1.96 | 1.96 | 1.96 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 90 | 6 | 3.51 | 3.51 | 3.51 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 90 | 6 | 4.72 | 4.71 | 4.72 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 90 | 6 | 6.29 | 6.29 | 6.30 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 90 | 6 | 6.97 | 6.96 | 6.97 | 0.01 |
| Modified bentonite | 120 | 6 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 120 | 6 | 3.52 | 3.52 | 3.52 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 120 | 6 | 4.74 | 4.74 | 4.75 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 120 | 6 | 6.30 | 6.30 | 6.30 | 0.00 |
| Modified bentonite | 120 | 6 | 7.05 | 7.04 | 7.06 | 0.01 |
| Modified zeolite | 30 | 6 | 1.95 | 1.95 | 1.95 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 30 | 6 | 3.53 | 3.53 | 3.53 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 30 | 6 | 4.61 | 4.61 | 4.62 | 0.01 |
| Modified zeolite | 30 | 6 | 6.28 | 6.28 | 6.28 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 30 | 6 | 7.13 | 7.13 | 7.13 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 60 | 6 | 1.96 | 1.96 | 1.96 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 60 | 6 | 3.56 | 3.56 | 3.57 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 60 | 6 | 4.72 | 4.72 | 4.72 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 60 | 6 | 6.34 | 6.33 | 6.34 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 60 | 6 | 7.14 | 7.14 | 7.15 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 90 | 6 | 1.96 | 1.95 | 1.96 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 90 | 6 | 3.58 | 3.58 | 3.59 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 90 | 6 | 4.79 | 4.79 | 4.79 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 90 | 6 | 6.36 | 6.36 | 6.36 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 90 | 6 | 7.17 | 7.12 | 7.22 | 0.05 |
| Modified zeolite | 120 | 6 | 1.98 | 1.98 | 1.98 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 120 | 6 | 3.60 | 3.60 | 3.60 | 0.00 |
| Modified zeolite | 120 | 6 | 4.72 | 4.58 | 4.86 | 0.13 |
| Modified zeolite | 120 | 6 | 6.37 | 6.37 | 6.38 | 0.01 |
| Modified zeolite | 120 | 6 | 7.17 | 7.12 | 7.22 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ďuricová, A.; Prepilková, V.Š.; Sečkár, M.; Schwarz, M.; Samešová, D.; Murajda, T.; Andráš, P.; Eštoková, A.; Hološová, M.Č.; Poništ, J.; et al. Comparison of Cu(II) Adsorption Using Fly Ash and Natural Sorbents During Temperature Change and Thermal–Alkaline Treatment. Materials 2025, 18, 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194552
Ďuricová A, Prepilková VŠ, Sečkár M, Schwarz M, Samešová D, Murajda T, Andráš P, Eštoková A, Hološová MČ, Poništ J, et al. Comparison of Cu(II) Adsorption Using Fly Ash and Natural Sorbents During Temperature Change and Thermal–Alkaline Treatment. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194552
Chicago/Turabian StyleĎuricová, Anna, Veronika Štefanka Prepilková, Michal Sečkár, Marián Schwarz, Dagmar Samešová, Tomáš Murajda, Peter Andráš, Adriana Eštoková, Miriama Čambál Hološová, Juraj Poništ, and et al. 2025. "Comparison of Cu(II) Adsorption Using Fly Ash and Natural Sorbents During Temperature Change and Thermal–Alkaline Treatment" Materials 18, no. 19: 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194552
APA StyleĎuricová, A., Prepilková, V. Š., Sečkár, M., Schwarz, M., Samešová, D., Murajda, T., Andráš, P., Eštoková, A., Hološová, M. Č., Poništ, J., Zacharová, A., Schmidtová, J., Veverková, D., & Biroň, A. (2025). Comparison of Cu(II) Adsorption Using Fly Ash and Natural Sorbents During Temperature Change and Thermal–Alkaline Treatment. Materials, 18(19), 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194552







