Optimizing the Y Content of Welding Wire for TIG Welding of Sand-Cast Mg-Y-RE-Zr Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
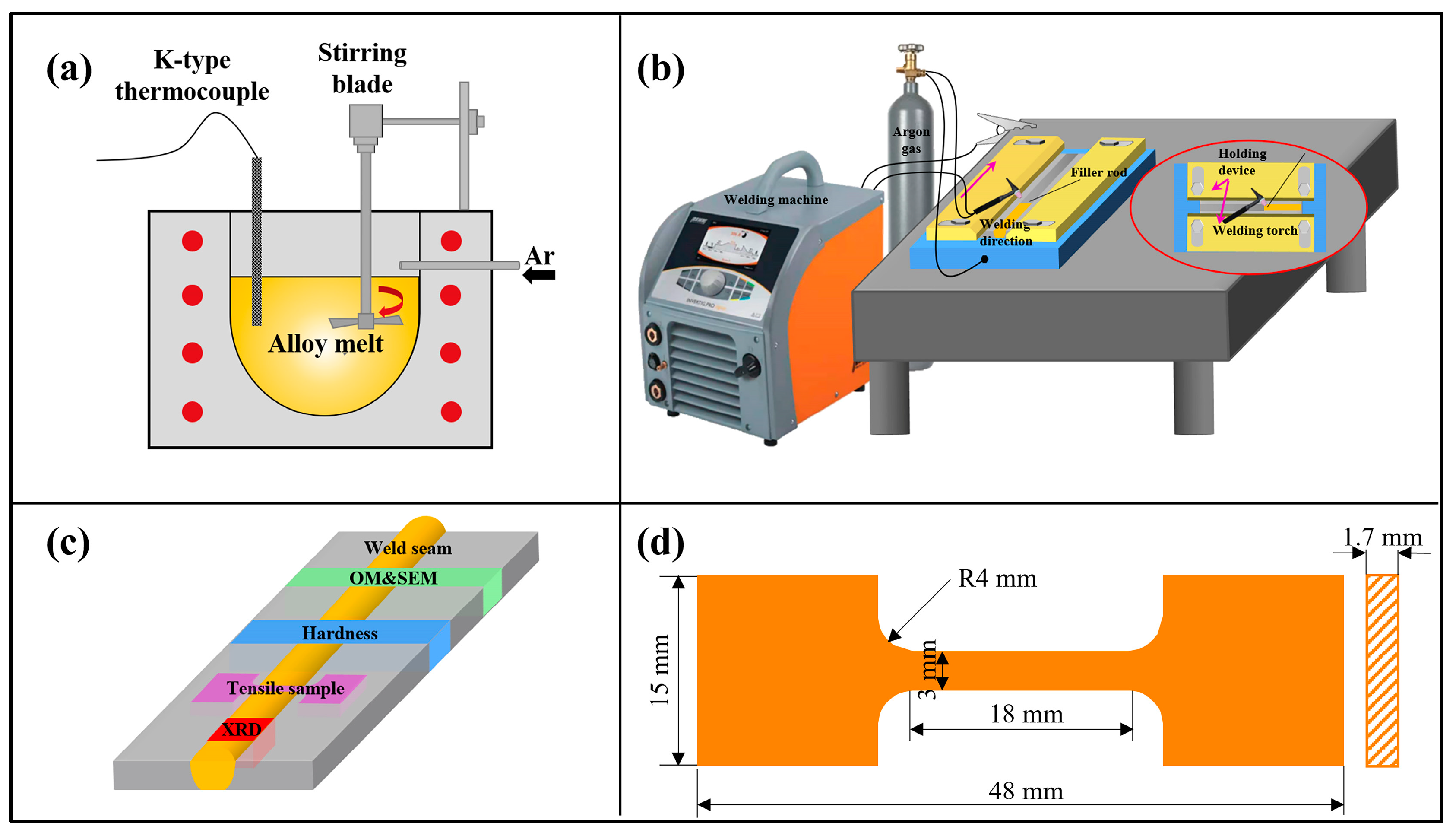
2.1. Preparation of the Gravity Sand-Cast Alloy
2.2. Welding Process
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
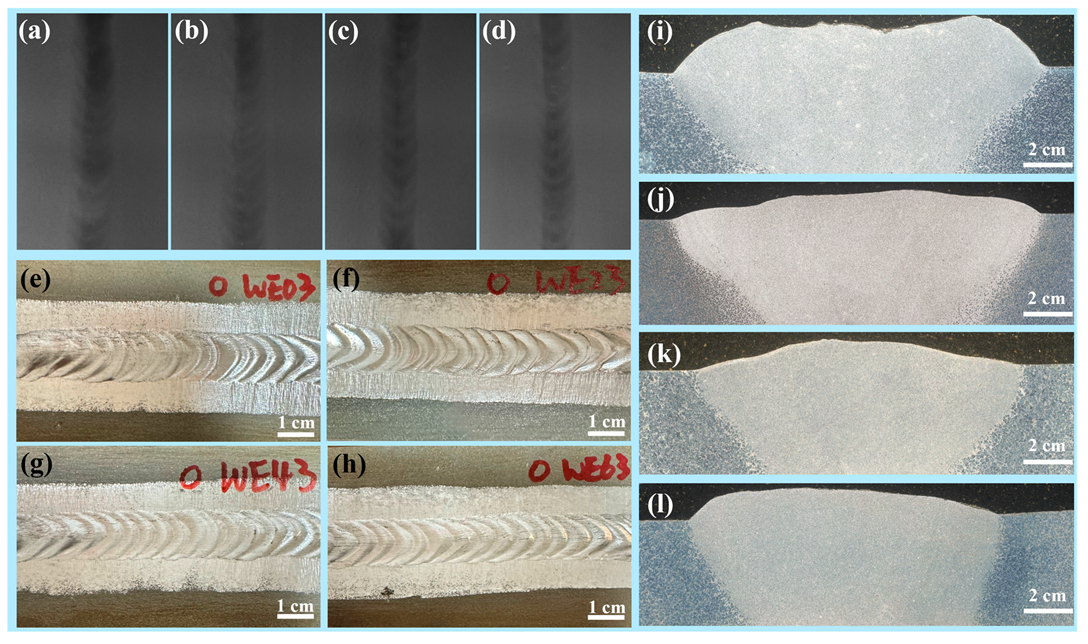
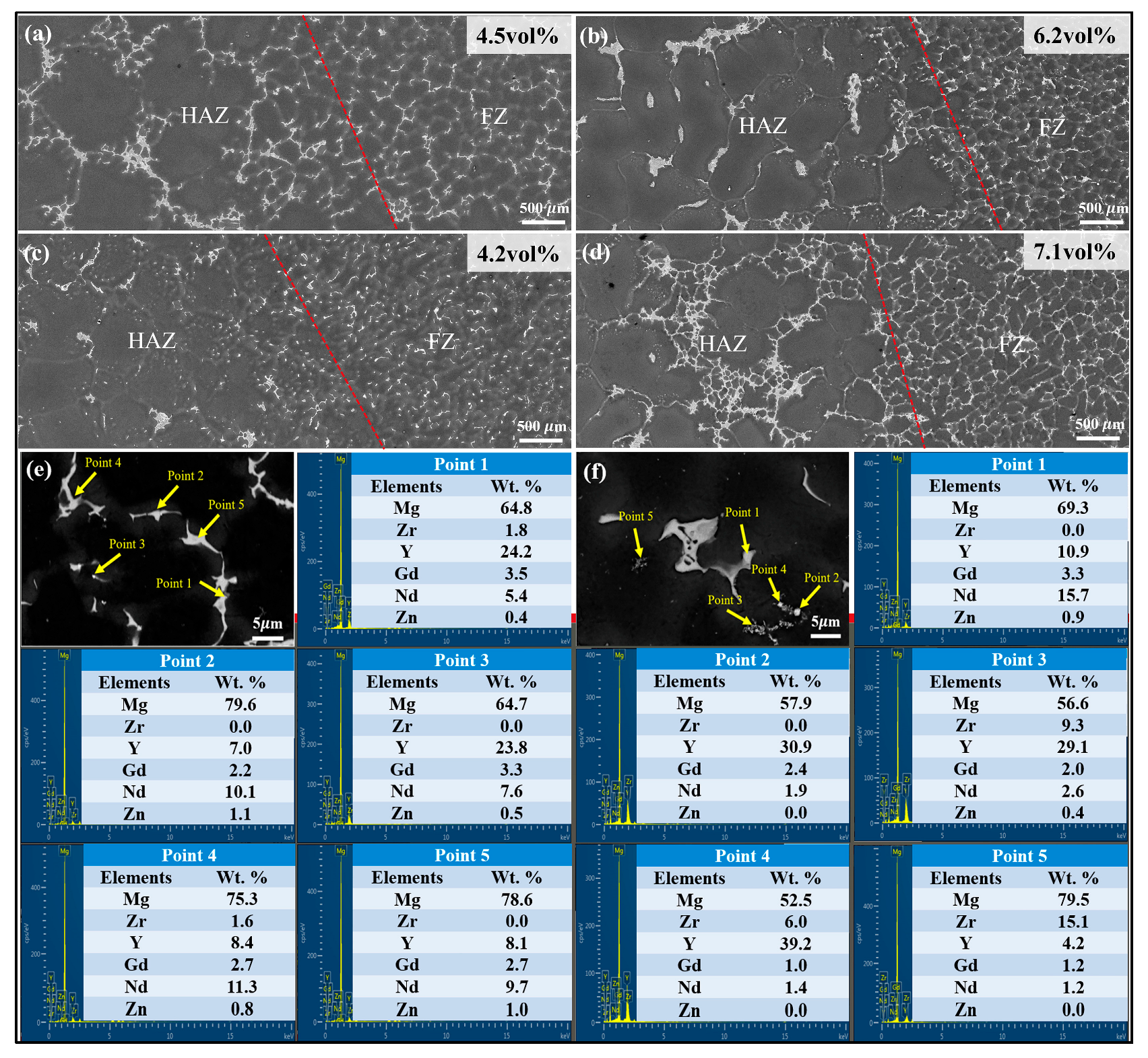
3.1. Macrostructure of the Welded Joints
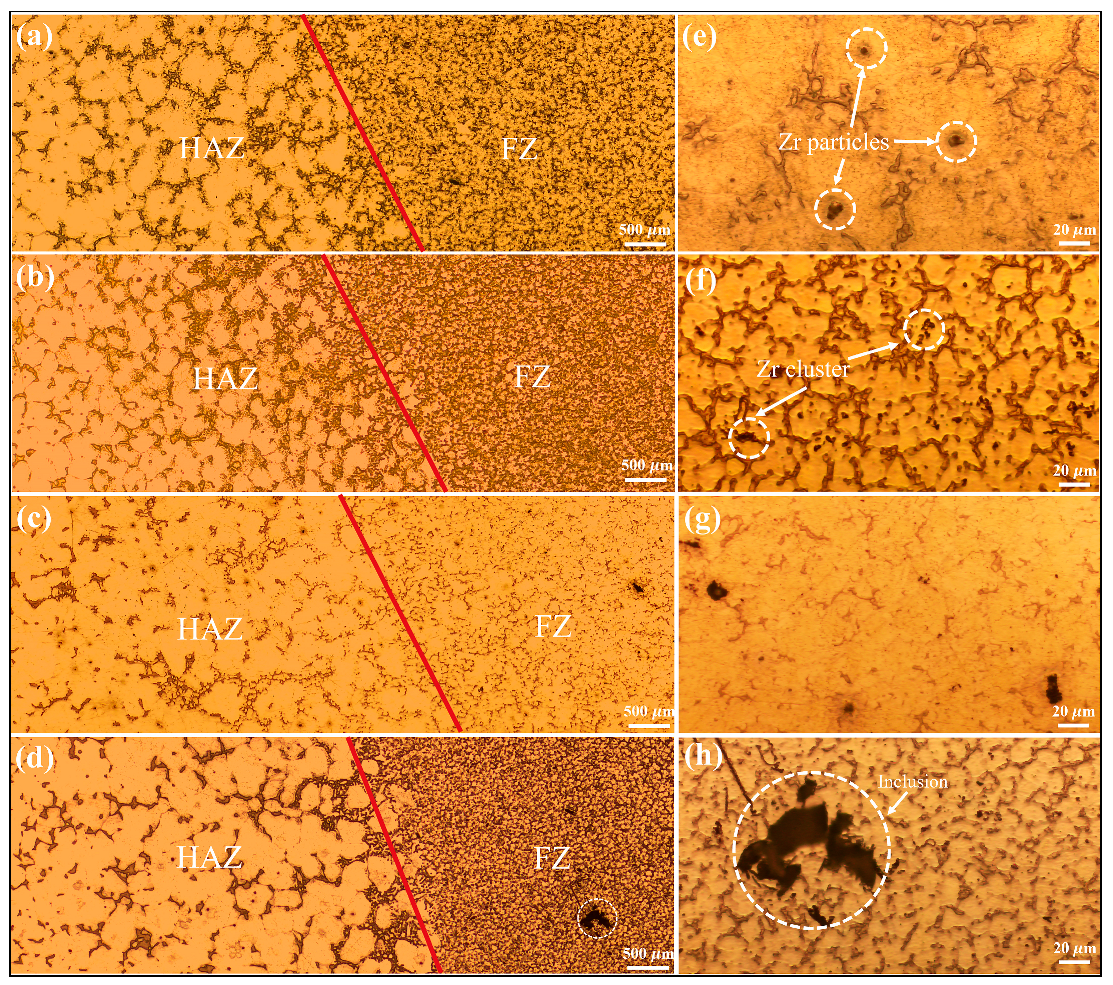
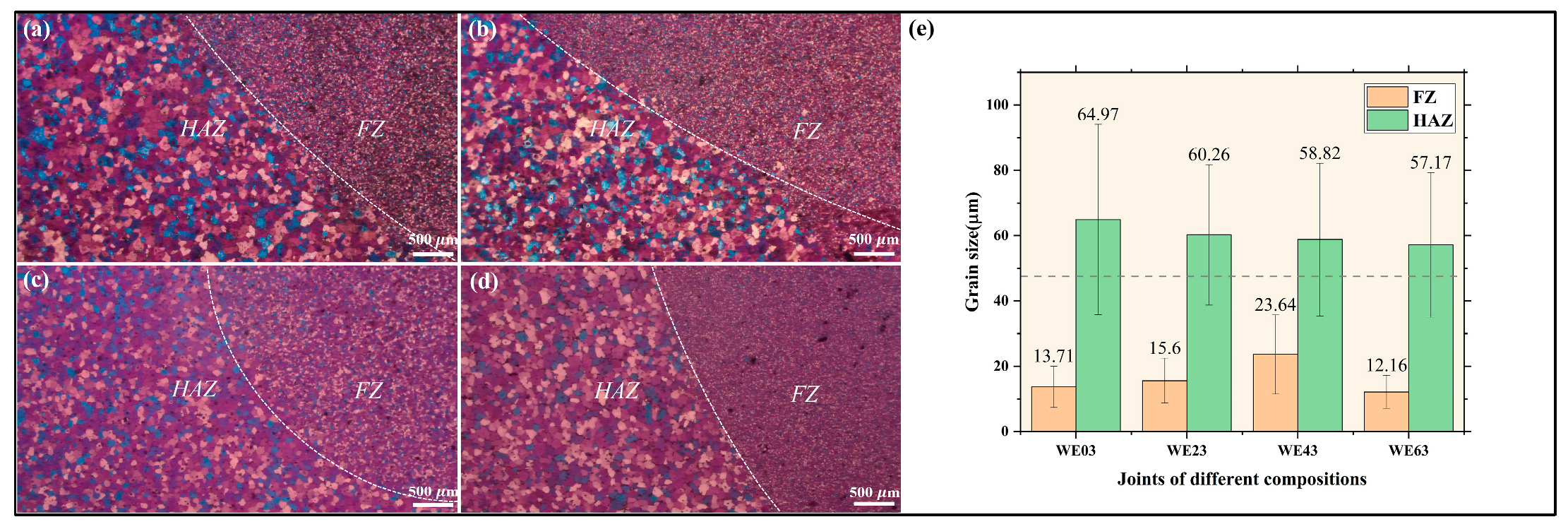
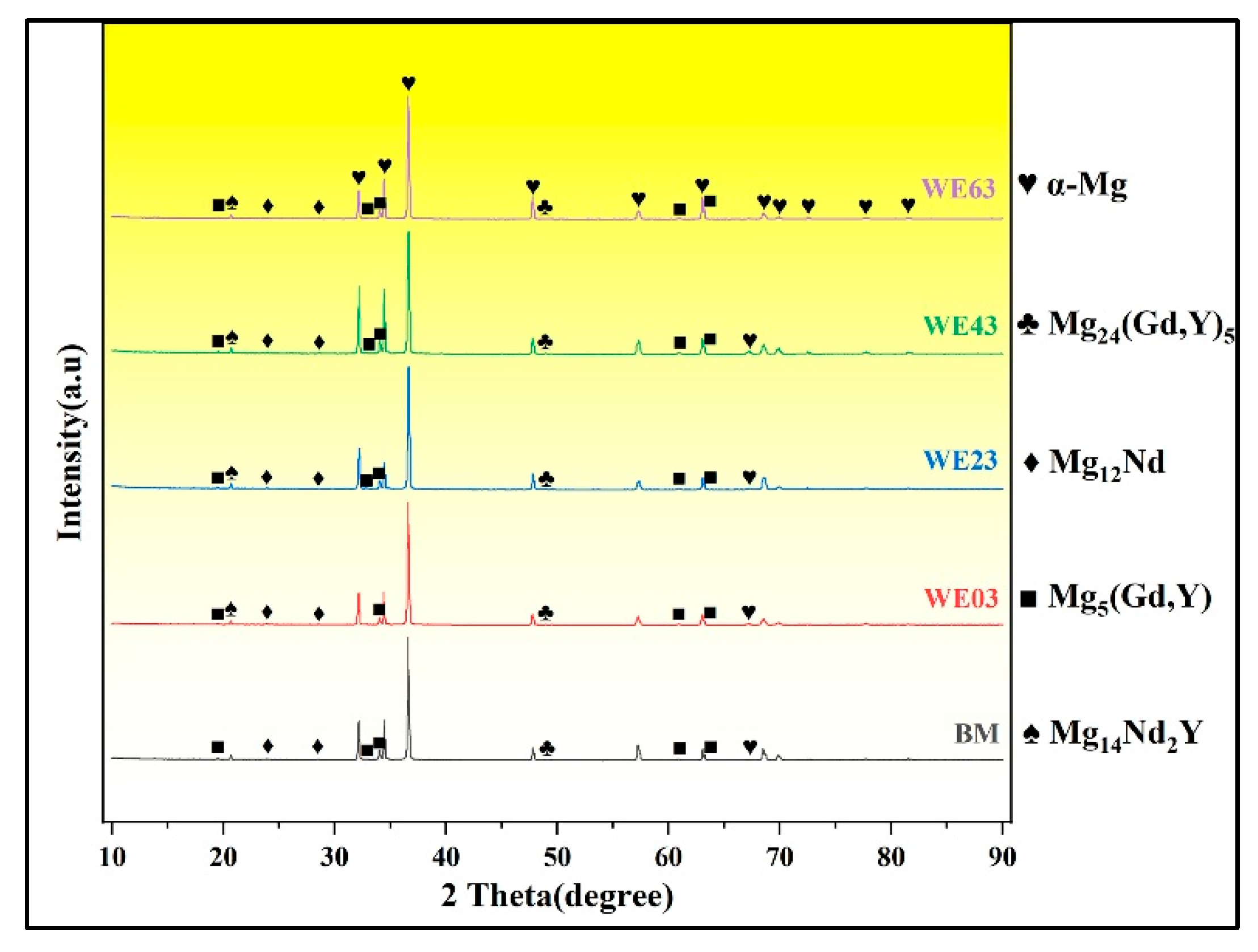
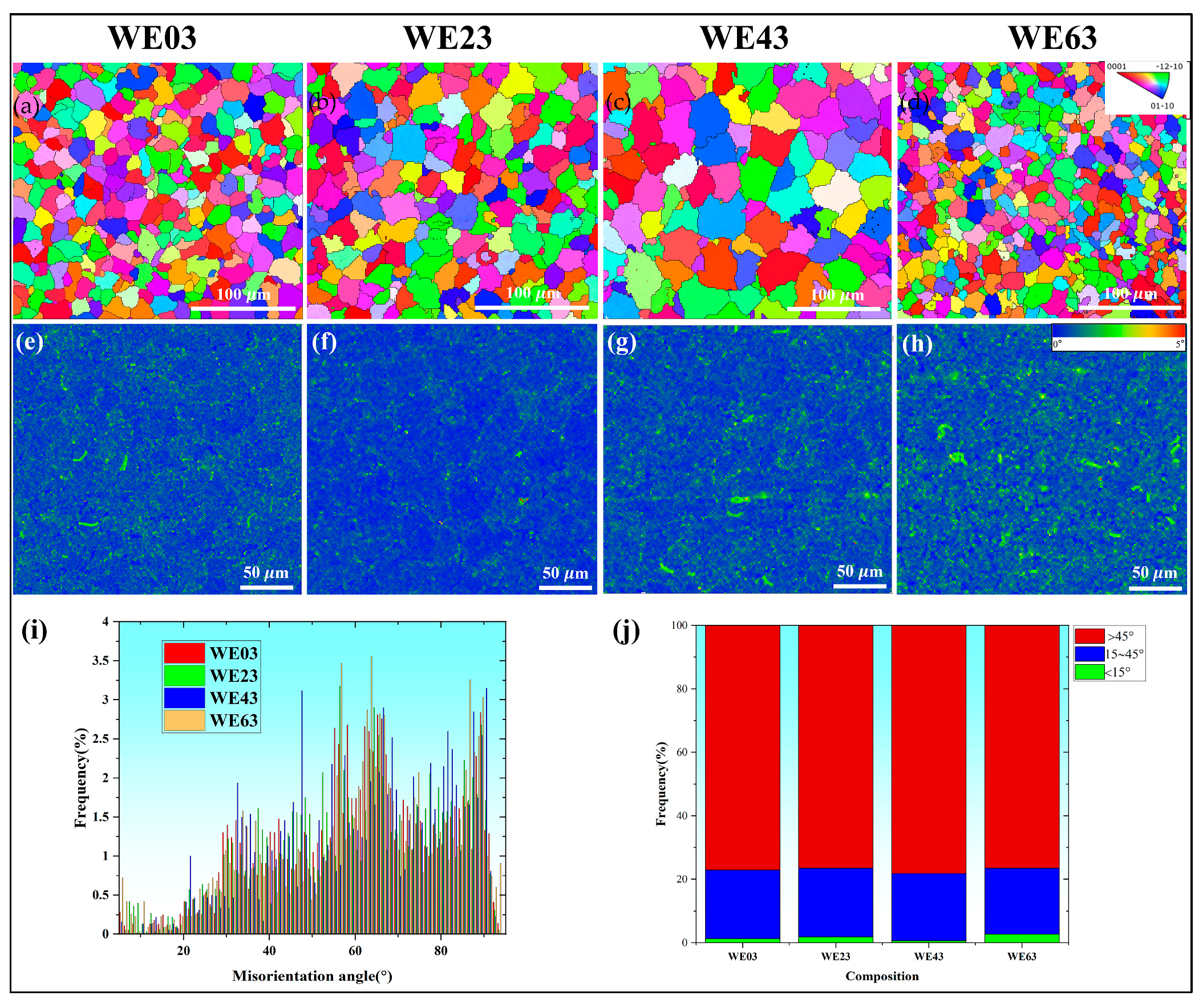
3.2. Microstructure of the Welded Joints
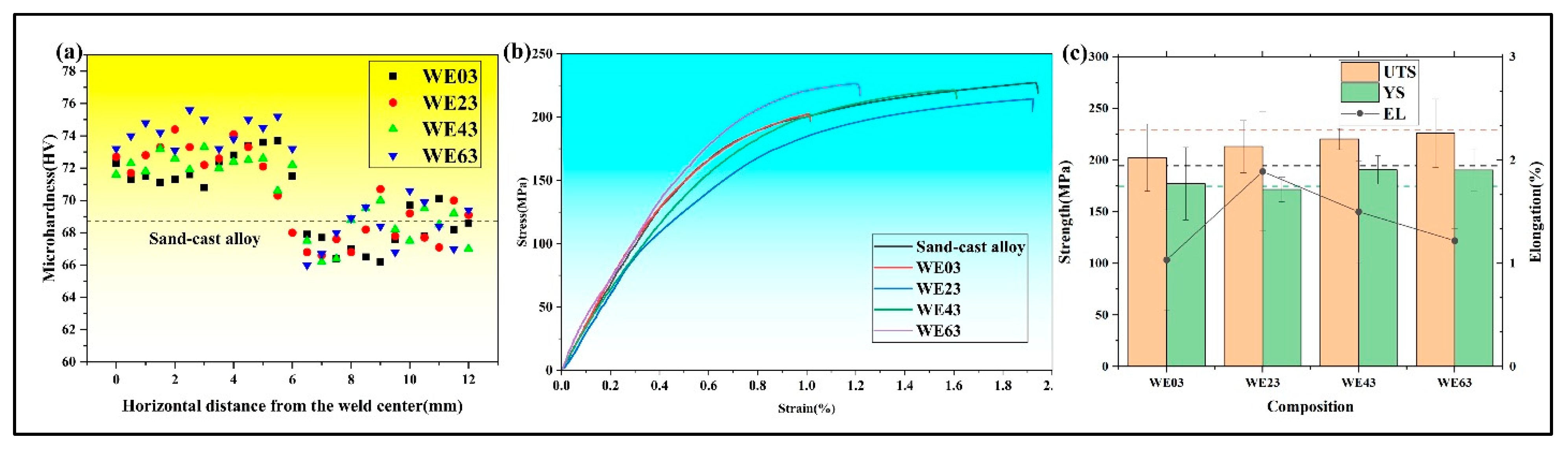
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. Fracture Behavior
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstructural Evolution
4.1.1. Evolution of the Grain
4.1.2. Evolution of the Second Phase
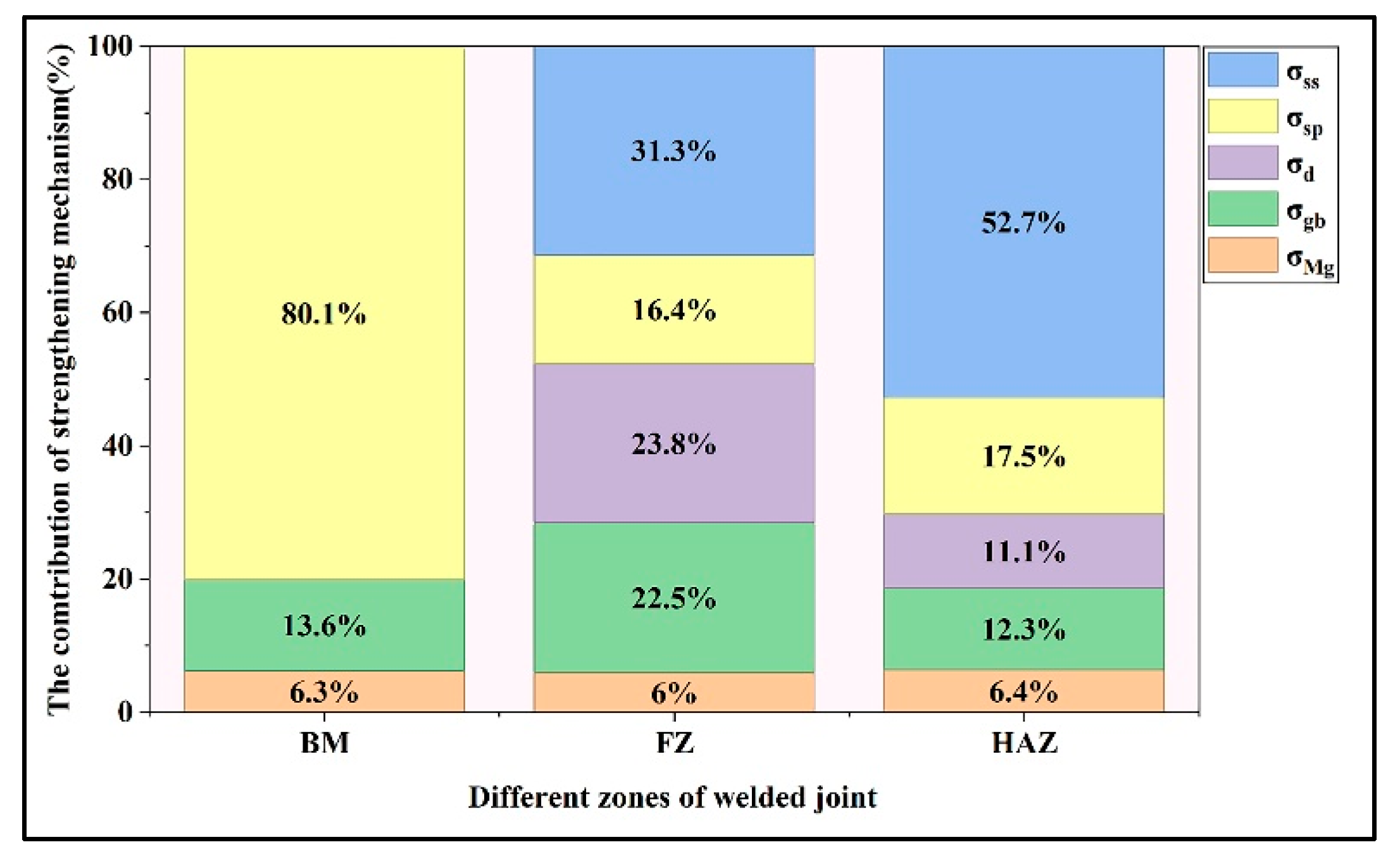
4.2. Strengthening Mechanism
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- With increasing Y content in the welding wire, the second phase in FZ transforms from a semi-continuous to a more continuous network, accompanied by more severe inclusions. The grain size of FZ initially increased, reaching a maximum grain size of 24 µm for the WE43 joint, and then decreased with further Y content.
- (2)
- Increasing Y content in welding wire leads to a weaker effect of thermal undercooling. However, constitutional supercooling induced by more Y elements in FZ promotes grain refinement. Abnormal grain coarsening occurs with WE43 filler wire due to the combined effects of thermal undercooling and constitutional supercooling.
- (3)
- The fracture occurs at the HAZ for joints of WE03, WE23, and WE43. All of them show brittle fracture features, while joints using WE43 show more microcracks. However, the joints of WE63 fracture at FZ, and exhibit extensive microcracking and oxidized inclusion zones.
- (4)
- Although the UTS reached the maximum when using welding wire of WE63, the joints welded with WE23 exhibited a minimal reduction in overall performance. Relative to the sand-cast alloy, the property losses were 7.0%, 2.0%, and 2.6% for UTS, YS, and EL, respectively.
- (5)
- The joint of WE23 wire serves as an exemplary case for analyzing strengthening contributions. Second phase strengthening serves as the primary strengthening mechanism in BM. With grain refinement in FZ, a greater proportion of grain boundary strengthening contributes to the strength. However, the dominant strengthening mechanism for HAZ was second phase strengthening, due to its large number of eutectics and precipitates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, C.; Wen, M.; Wang, R.; Wu, D.; Wu, Z.; Yang, F.; Sheng, L. The Recent Developments of Thermomechanical Processing for Biomedical Mg Alloys and Their Clinical Applications. Materials 2025, 18, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, R.; Hou, L.; Zhang, M. Recent developments in high-strength Mg-RE-based alloys: Focusing on Mg-Gd and Mg-Y systems. J. Magnes. Alloys 2018, 6, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, A.; Saal, J.; Wolverton, C. Formation of high-strength β′ precipitates in Mg–RE alloys: The role of the Mg/β″ interfacial instability. Acta Mater. 2015, 83, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Tong, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Qi, F.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, P. A high-strength Mg-RE alloy fabricated by directed energy deposition: Microstructural evolution and strengthening mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 928, 148072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhao, H.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Song, J.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F. Recent progress on cast magnesium alloy and components. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 9969–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Xiao, L.; Xu, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, F.; Kurz, G.; Sun, B.; Li, Z. Microstructure, mechanical properties and fracture behaviors of large-scale sand-cast Mg-3Y-2Gd-1Nd-0.4 Zr alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, B.; Li, D.; Zeng, X. A study on the high-temperature oxidation of ZM6 alloy through advanced characterization. Corros. Sci. 2023, 218, 111150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lozano-Perez, S.; Zeng, X. The effect of LPSO phase on the high-temperature oxidation of a stainless Mg-Y-Al alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 4045–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaprakash, N.; Haile, A.; Arunprasath, M. The parameters and equipments used in TIG welding: A review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2015, 4, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, G.; Shen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Ding, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, K.; Lin, K.; Hua, X. Welding of thick Ti-6Al-4V plate via narrow gap oscillating laser tungsten inert gas (NG-OL-TIG) hybrid welding: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 139, 741–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badkoobeh, F.; Mostaan, H.; Rafiei, M.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Berto, F. Friction stir welding/processing of Mg-based alloys: A critical review on advancements and challenges. Materials 2021, 14, 6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedjaoui, W.; Boumerzoug, Z.; Delaunois, F. Solid-state diffusion welding of commercial aluminum alloy with pure copper: Welding of aluminum alloy to copper. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2022, 19, 9734–9746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Farshidianfar, A.; Dalir, H. A comprehensive review on recent laser beam welding process: Geometrical, metallurgical, and mechanical characteristic modeling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 4781–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Tong, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Sui, H.; Zhang, X. Research on the post-weld heat treatment of TIG repair welded joint of sand-cast Mg-Y-RE-Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 821, 141577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, G.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Liu, W.; Ding, W. Addressing the abnormal grain coarsening during post-weld heat treatment of TIG repair welded joint of sand-cast Mg-Y-RE-Zr alloy. Mater. Charact. 2021, 176, 111125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, G.; Qi, F.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, L. Microstructure Evolution and Corrosion Behavior of TIG Welded Joint of a New MgGdNdZnZr Alloy during Post-Weld Heat Treatment. J. Magnes. Alloys, 2024; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, G.; Tong, X. An investigation into wire arc additive manufacturing of Mg-Y-RE-Zr alloy. Mater. Lett. 2022, 326, 132922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Ding, W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of repair welds of low-pressure sand-cast Mg–Y–RE–Zr alloy by tungsten inert gas welding. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tong, X.; Wu, G.; Zhan, J.; Qi, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W. Microstructure and strengthening mechanism of TIG welded joints of a Mg-Nd-Gd alloy: Effects of heat input and pulse current. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 869, 144816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Dong, X.; Li, N.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, H. The effect of Rare Earth (RE) elements on corrosion and mechanical properties of Magnesium (Mg) alloys: A review. Phys. Scr. 2025, 100, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, D.; Li, X.; Hu, S. Mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and biocompatibilities of degradable Mg-RE alloys: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Wang, C.; Jiang, B.; Bai, S.; Dong, Z.; Qian, X.; He, C.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Q. Role of Y on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 861, 144371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, C.; Xie, H.; Hu, H.; Gao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, T.; Jiang, B. Insight into Y Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Tong, X.; Jiang, R.; Liu, W. Characterization of complex surface oxide layers formed during the solidification of distinct Mg-RE alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 13, 3055–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, H.; An, G.; Shi, H.; Cai, C.; Jiang, W.; Li, W.; Wei, Q. Laser powder bed fusion of WE43 magnesium alloy with superior balance of strength and ductility. J. Magnes. Alloys 2025, 13, 1275–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Murakawa, H. Prediction of welding distortion and residual stress in a thin plate butt-welded joint. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, K.; Dong, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, C.; Gan, W.; Maawad, E.; Sun, B. Achieving high mechanical performance of the large-scale sand-casting Mg–4Y–x nd–y Gd–0.4 Zr alloys by tailoring Nd and Gd contents. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 900, 146476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Ding, W. Effect of Y and Gd content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Y–RE alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2019, 7, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Guo, E. Effect of TIG repaired welding process on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg-4Y-3Nd-1.5 Al alloy. Mater. Charact. 2025, 219, 114622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qin, G.; Ren, Y.; Pei, W.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y. The maximum solubility of Y in α-Mg and composition ranges of Mg24Y5−x and Mg2Y1−x intermetallic phases in Mg–Y binary system. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.A.; StJohn, D.H. A model of grain refinement incorporating alloy constitution and potency of heterogeneous nucleant particles. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; StJohn, D.H.; Easton, M.A.; Wang, K.; Ni, J. Effect of cooling rate on the grain refinement of Mg-Y-Zr alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Meng, J.; Zhang, D.; Tang, D. Effect of Y for enhanced age hardening response and mechanical properties of Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 456, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.; Bunn, A.; Tronche, A.; Evans, P.; Bristow, D. Modelling of inoculation of metallic melts: Application to grain refinement of aluminium by Al–Ti–B. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 2823–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaz, M.; Thevoz, P. Solute diffusion model for equiaxed dendritic growth. Acta Metall. 1987, 35, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; Sun, B.; Mi, J.; Grant, P. A quantitative study of solute diffusion field effects on heterogeneous nucleation and the grain size of alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penghuai, F.; Liming, P.; Haiyan, J.; Jianwei, C.; Chunquan, Z. Effects of heat treatments on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg–3Nd–0.2 Zn–0.4 Zr (wt.%) alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 486, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Hu, Y.; He, B.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, T.; Pan, F. Effect of manganese on microstructure and properties of Mg-2Gd magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 765, 138292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starink, M.J.; Cheng, X.; Yang, S. Hardening of pure metals by high-pressure torsion: A physically based model employing volume-averaged defect evolutions. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, N.; Sha, G.; Ringer, S.P.; Starink, M.J. Microstructural evolution, strengthening and thermal stability of an ultrafine-grained Al–Cu–Mg alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 109, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Qiao, X.; Zheng, M.; Xu, C.; Gao, N.; Starink, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a nanostructured Mg-8.2 Gd-3.8 Y-1.0 Zn-0.4 Zr supersaturated solid solution prepared by high pressure torsion. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, K.; Bachmaier, A.; Beloshenko, V.A.; Beygelzimer, Y.; Blank, V.D.; Botta, W.J.; Bryła, K.; Čížek, J.; Divinski, S.; Enikeev, N.A. Nanomaterials by severe plastic deformation: Review of historical developments and recent advances. Mater. Res. Lett. 2022, 10, 163–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fu, P.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H. Strengthening mechanisms in solution treated Mg–y Nd–z Zn–x Zr alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 6367–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, N.; Sha, X.; Xu, M.; Chen, B.; Gao, B.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, H. Mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of Mg-Gd alloy during aging treatment. Metals 2021, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


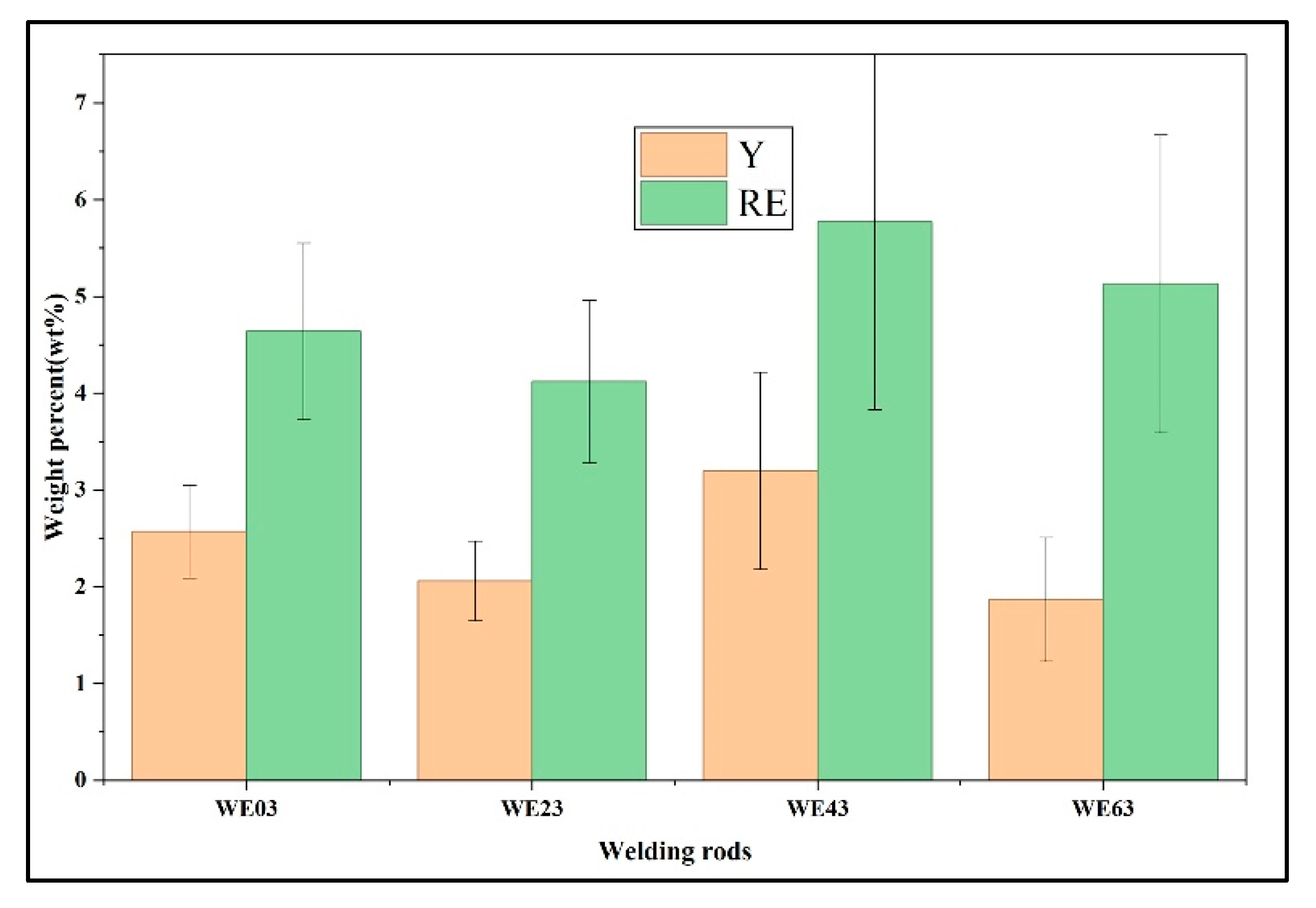

| Material | Element | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Nd | Gd | Zn | Zr | Mg | |
| Base material | 3.99 | 2.46 | 1.29 | 0.20 | 0.48 | Bal. |
| WE03 | 0.00 | 2.53 | 1.22 | 0.19 | 0.46 | Bal. |
| WE23 | 2.05 | 2.51 | 1.29 | 0.17 | 0.47 | Bal. |
| WE43 | 3.97 | 2.50 | 1.26 | 0.18 | 0.52 | Bal. |
| WE63 | 6.04 | 2.54 | 1.27 | 0.20 | 0.53 | Bal. |
| Welding Current (A) | Tungsten Electrode Diameter (mm) | Filler Wire Diameter (mm) | Welding Speed (mm/s) | Ar Flow Rate (L/min) | Wire Feeding Speed (mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160 | 2.4 | 5 | 2 | 10 | 4 |
| Welding Wires | Liquidus Temperature |
|---|---|
| WE03 | 647 °C |
| WE23 | 642 °C |
| WE43 | 640 °C |
| WE63 | 630 °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Y.; Wei, G.; Tong, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W. Optimizing the Y Content of Welding Wire for TIG Welding of Sand-Cast Mg-Y-RE-Zr Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 4549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194549
Gong Y, Wei G, Tong X, Liu G, Wang Y, Ding W. Optimizing the Y Content of Welding Wire for TIG Welding of Sand-Cast Mg-Y-RE-Zr Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194549
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Yikai, Guangling Wei, Xin Tong, Guonan Liu, Yingxin Wang, and Wenjiang Ding. 2025. "Optimizing the Y Content of Welding Wire for TIG Welding of Sand-Cast Mg-Y-RE-Zr Alloy" Materials 18, no. 19: 4549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194549
APA StyleGong, Y., Wei, G., Tong, X., Liu, G., Wang, Y., & Ding, W. (2025). Optimizing the Y Content of Welding Wire for TIG Welding of Sand-Cast Mg-Y-RE-Zr Alloy. Materials, 18(19), 4549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194549






