Dynamic Properties of Mineral-Based Cementitious Material-Stabilized Slurry Soil Under Vehicle Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Design
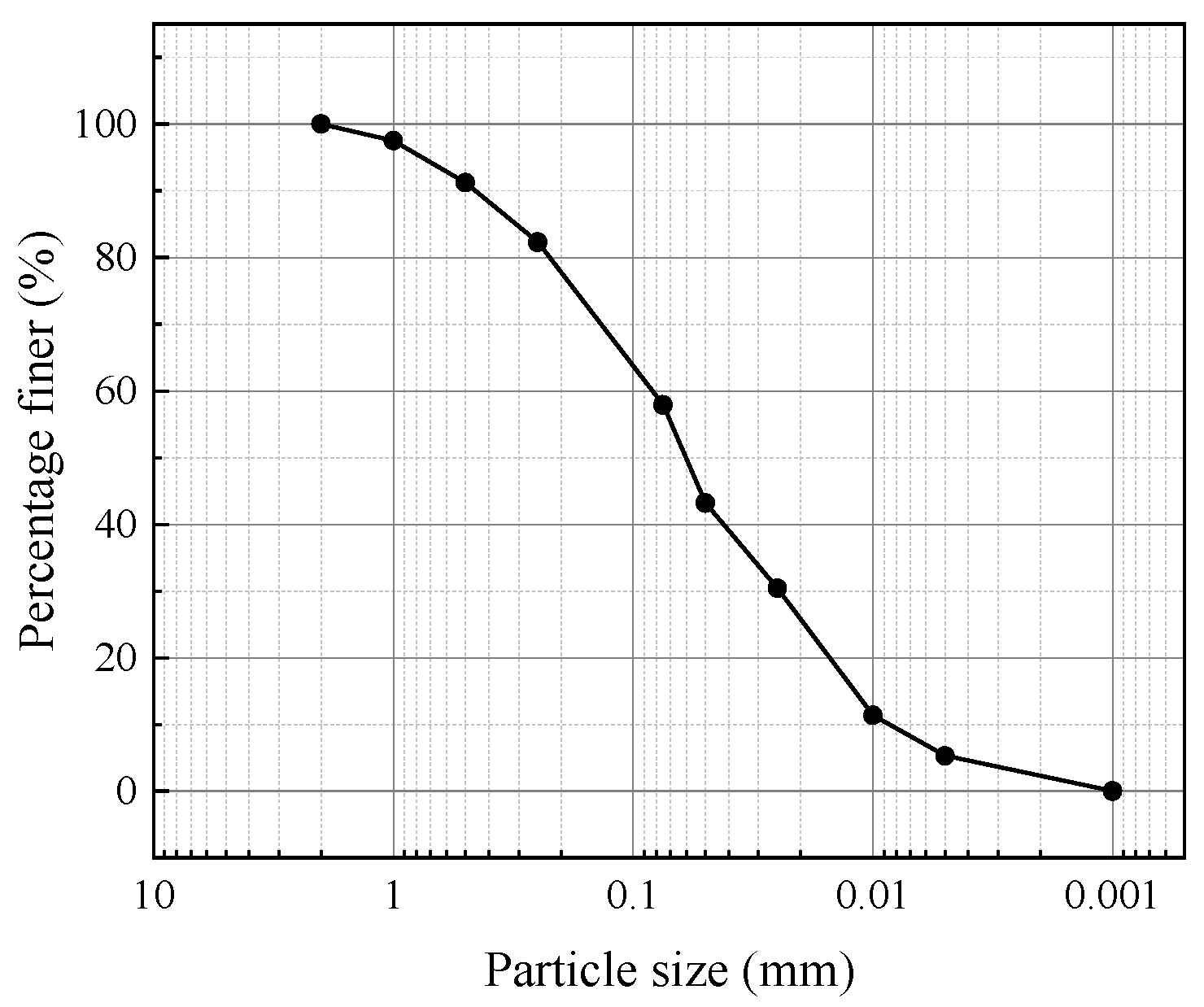
2.1. Experimental Materials
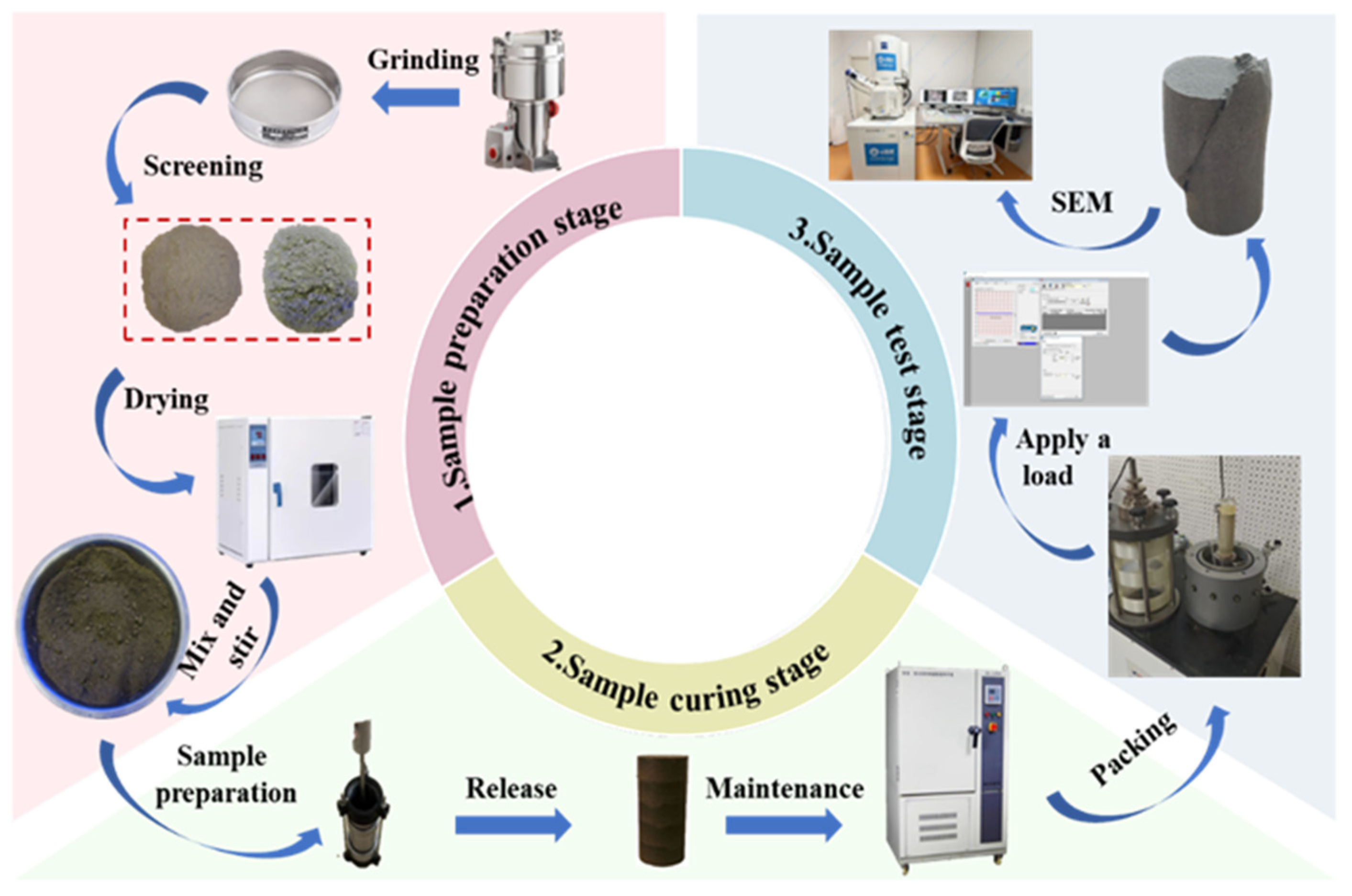
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Experimental Methods
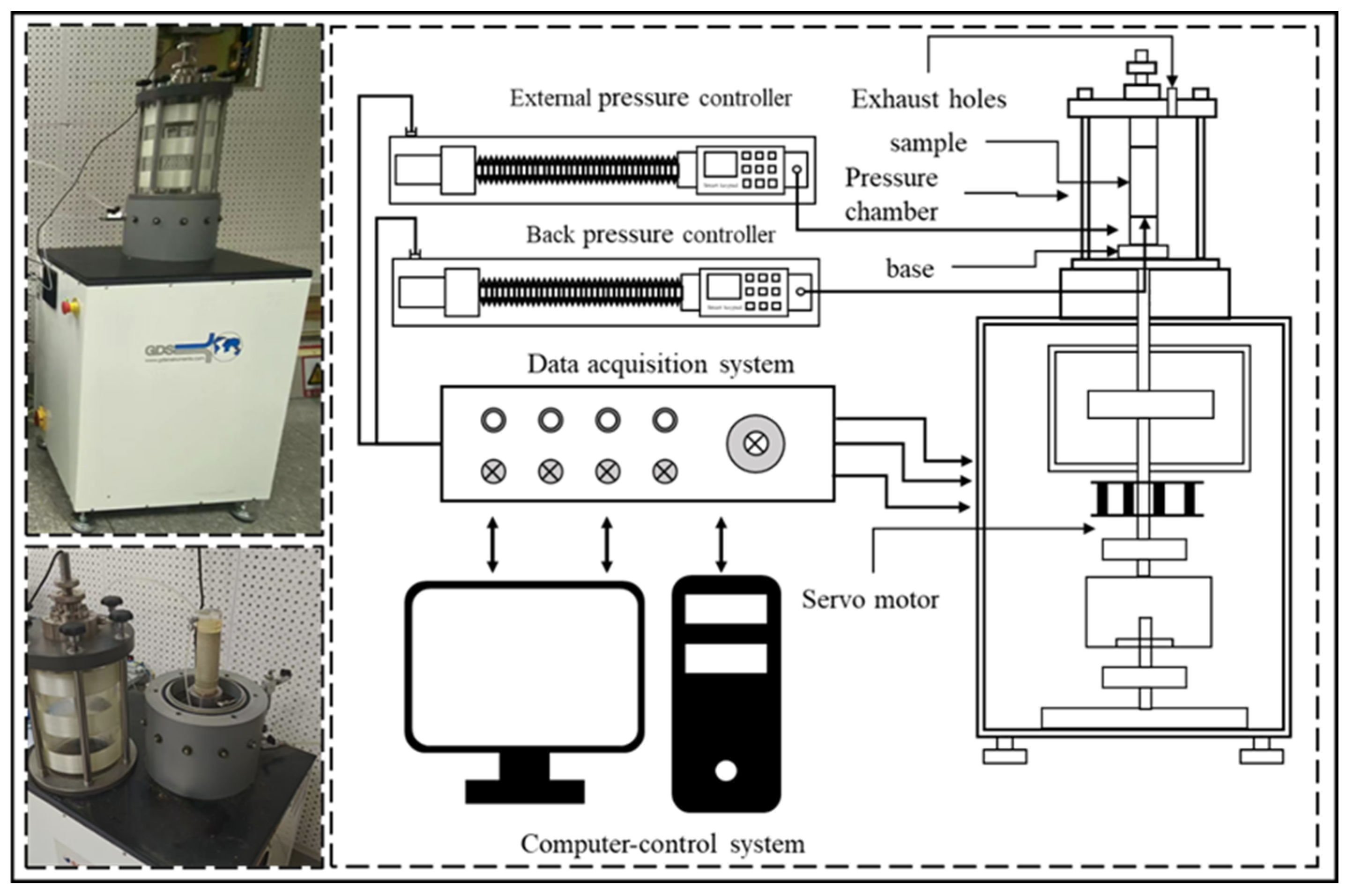
2.3.1. Dynamic Triaxial Test
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Test
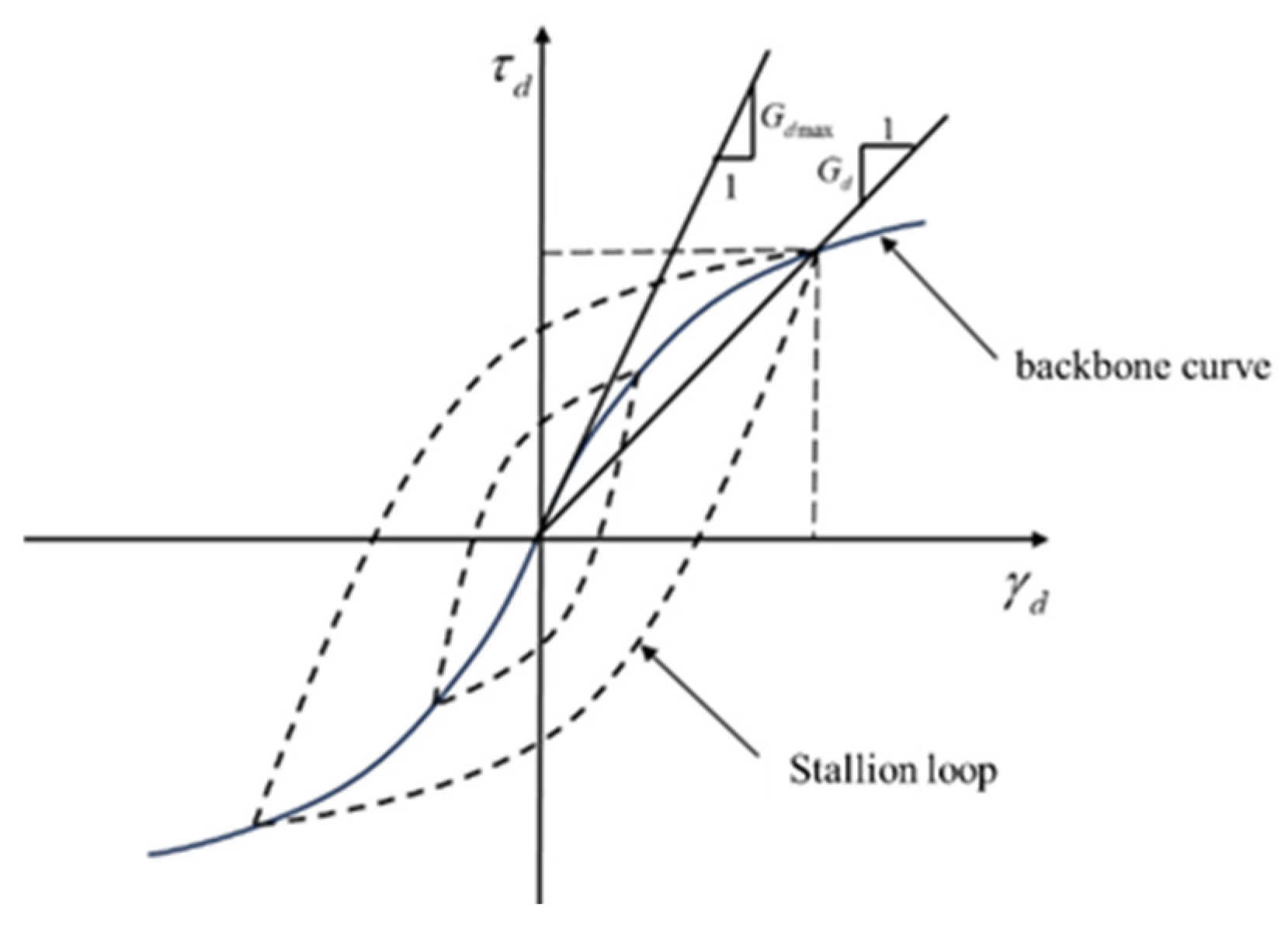
3. Data Processing Methods and Constitutive Model
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
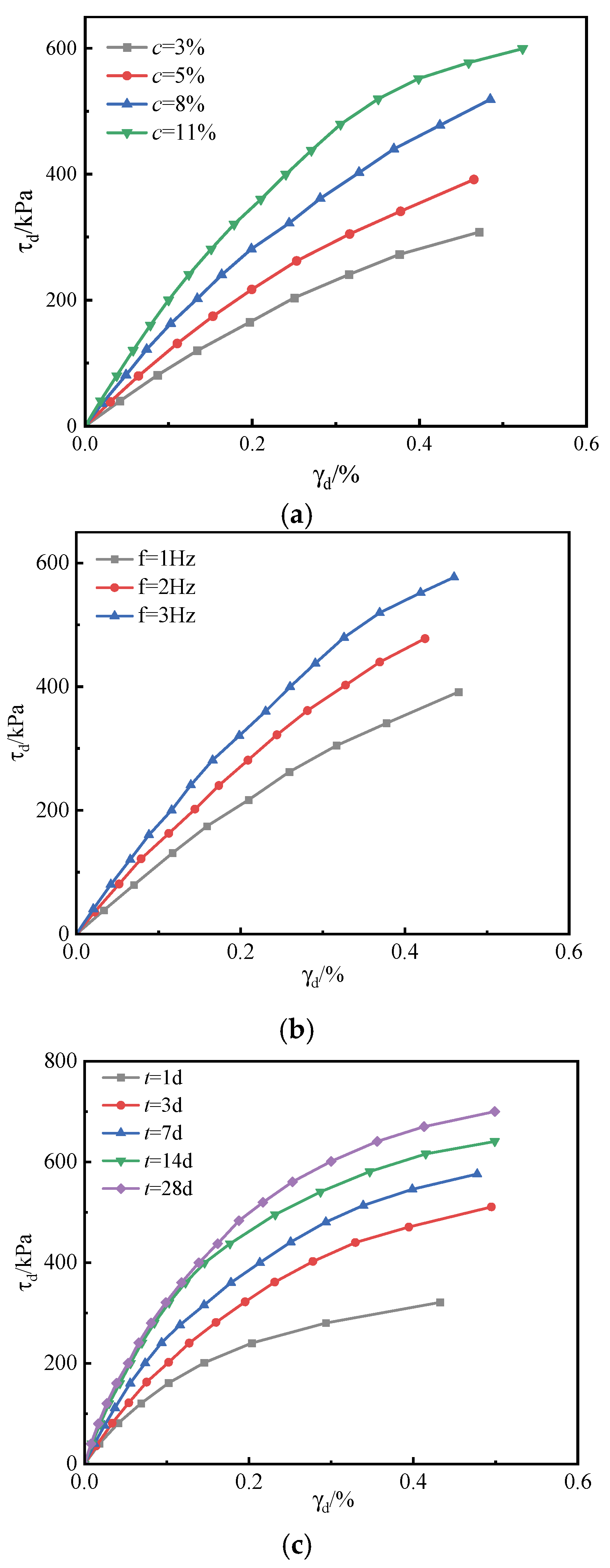
4.1. Backbone Curve Analysis
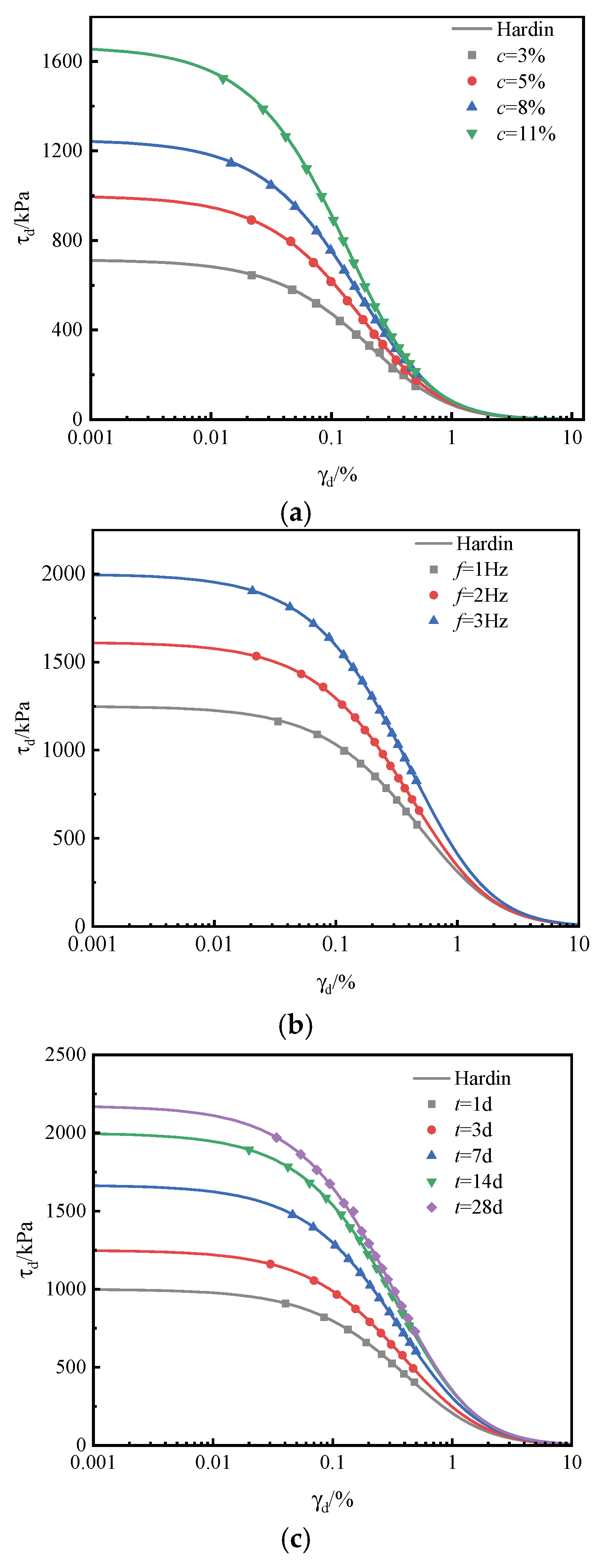
4.2. Analysis of Dynamic Shear Modulus
4.3. Maximum Shear Modulus and Ultimate Stress Amplitude
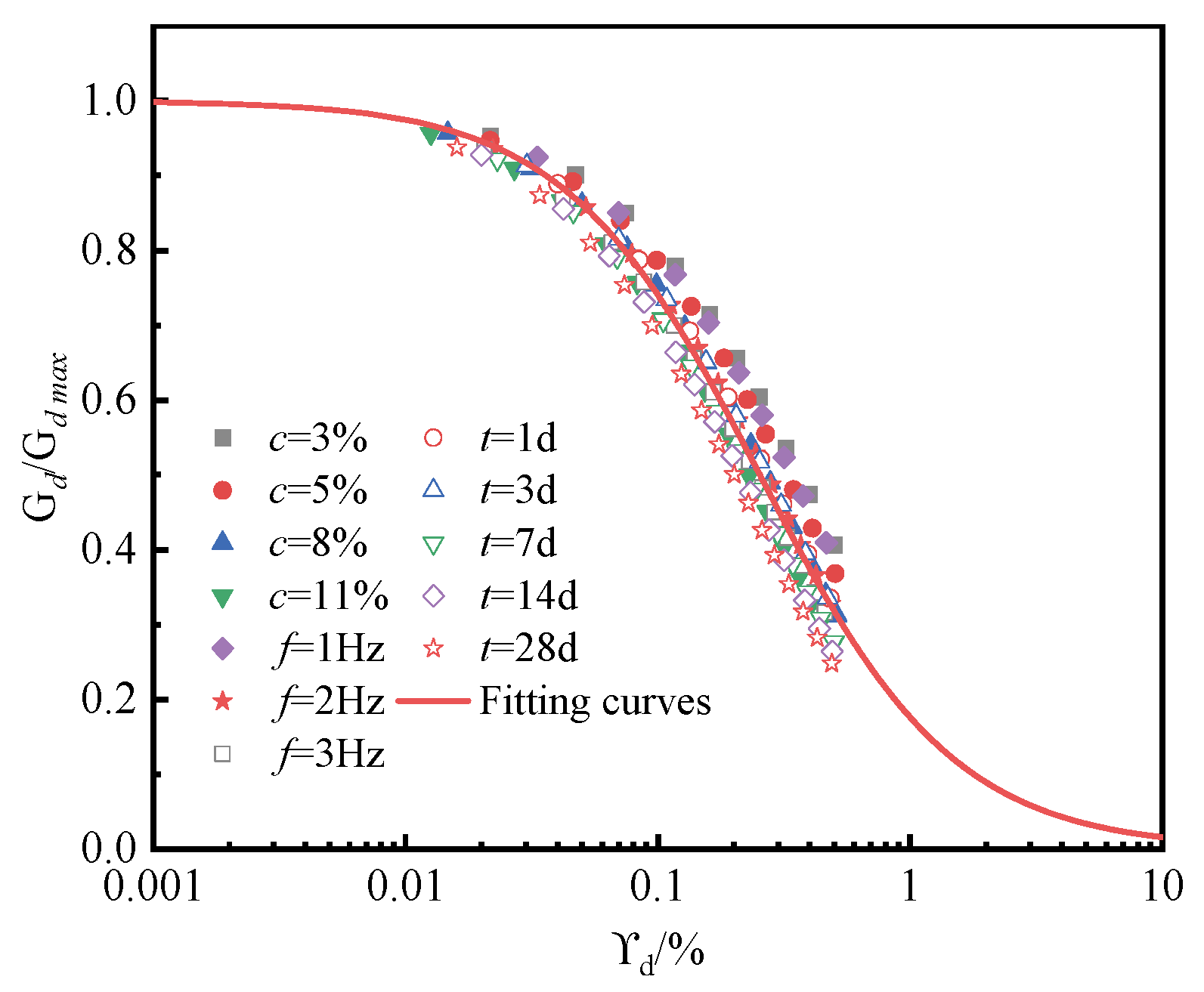
4.4. Empirical Model for Normalized Dynamic Shear Modulus
4.5. Damping Ratio
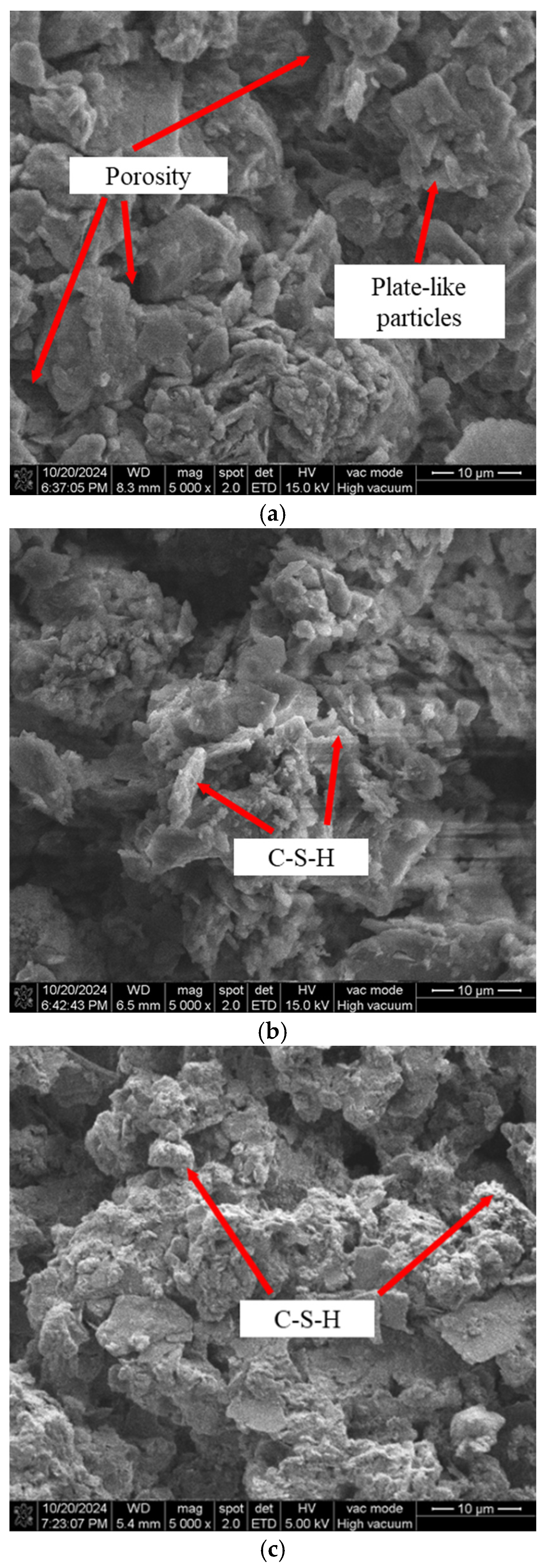
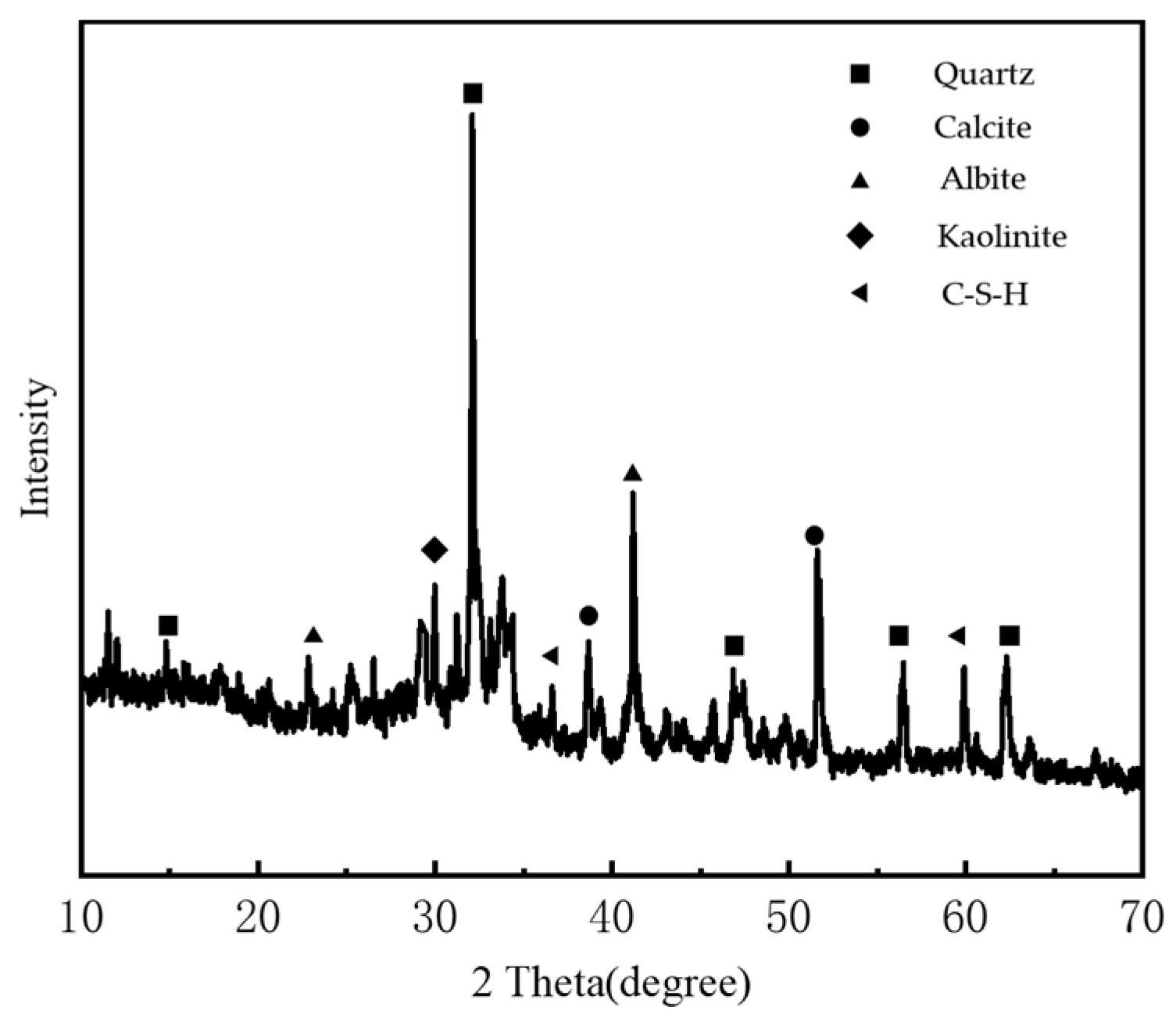
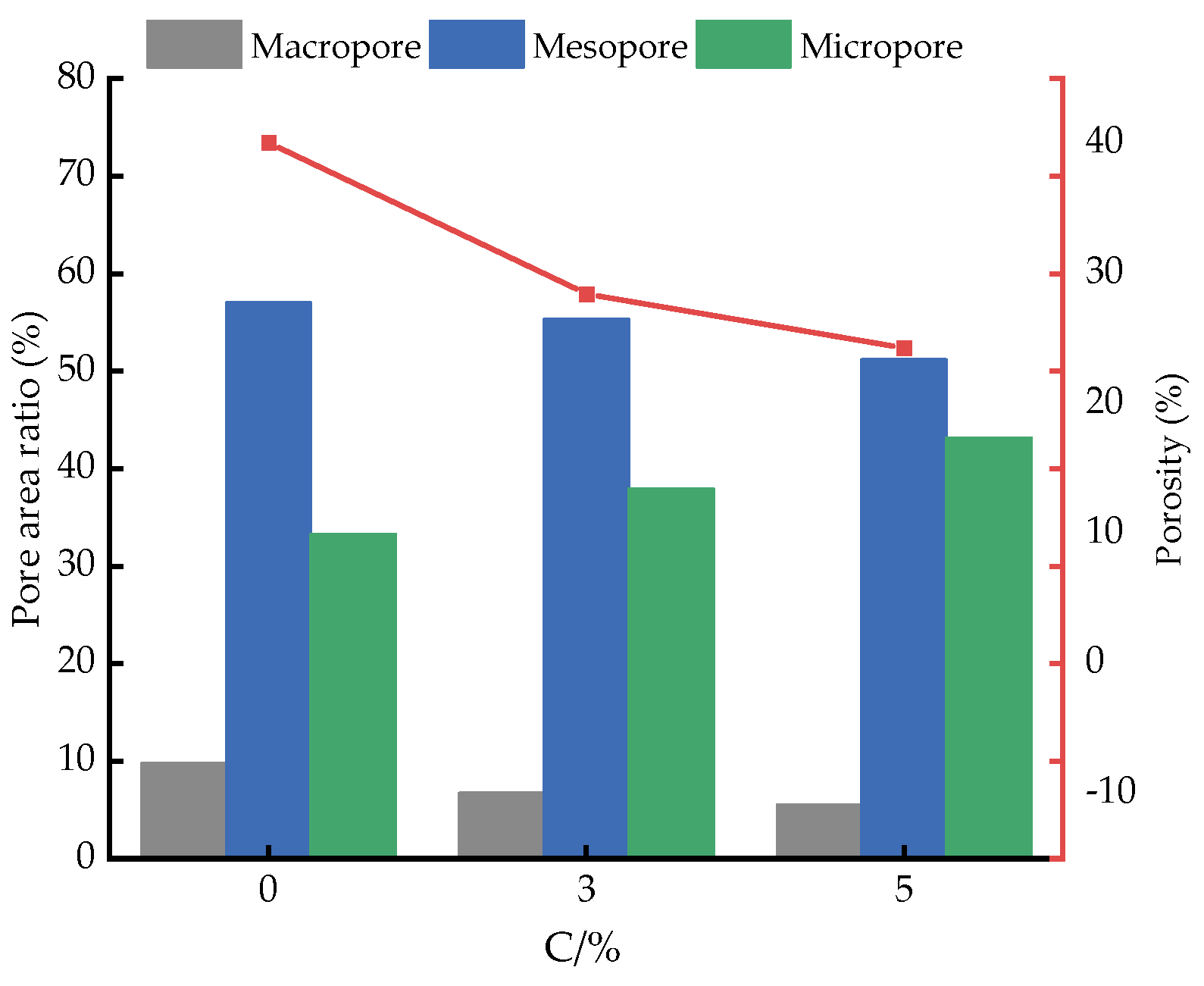
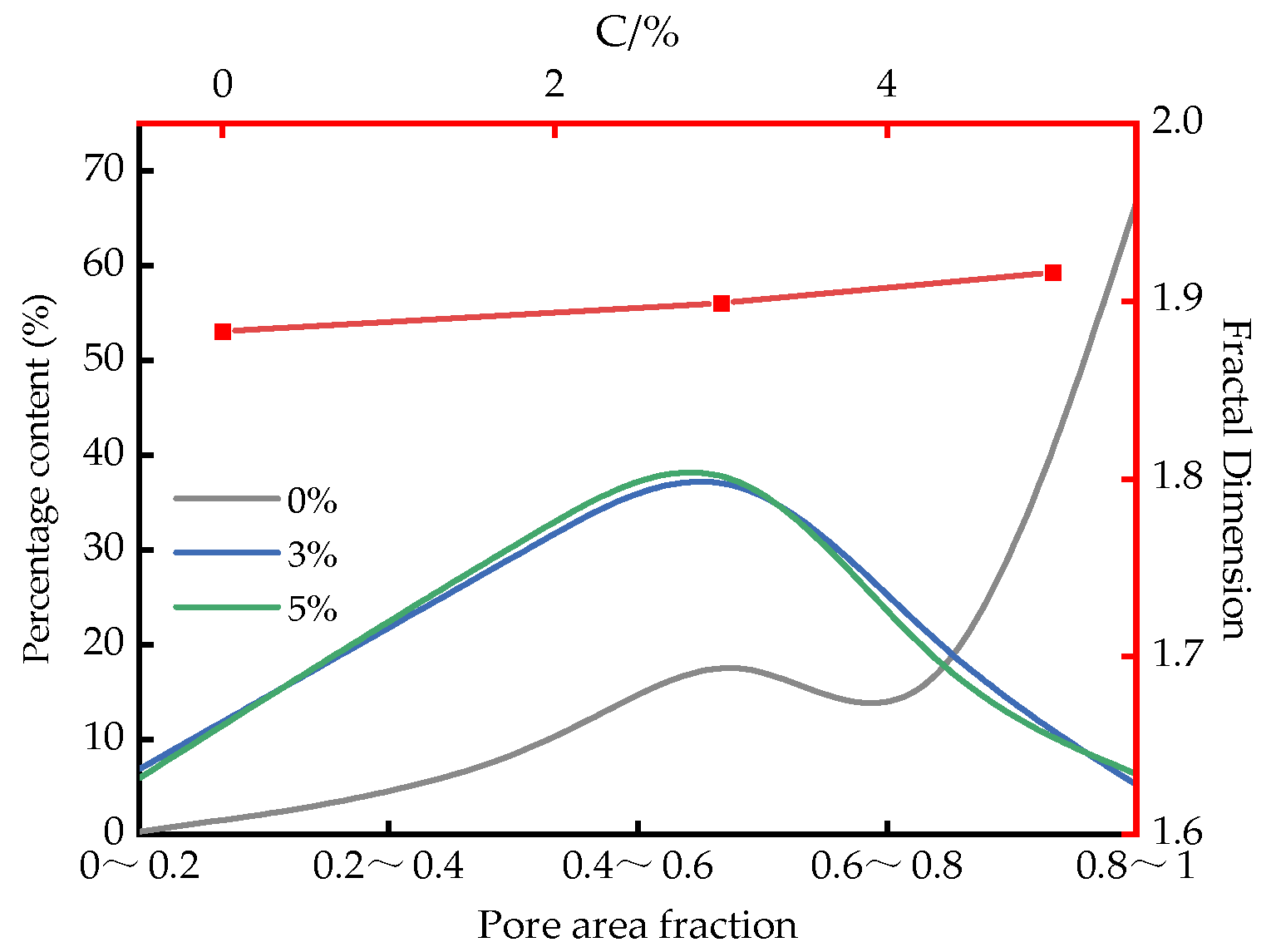
4.6. Microscopic Structure Analysis
4.6.1. Qualitative Analysis
4.6.2. Quantitative Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
5.2. Mechanism Interpretation
5.3. Engineering Implications
5.4. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Unlike previous studies that mainly focused on static properties, this work systematically elucidates the dynamic response of stabilized sludge under varying binder contents, curing ages, and loading frequencies, thereby bridging a critical research gap.
- (2)
- A normalized constitutive model for the dynamic shear modulus ratio was proposed and validated, achieving a correlation coefficient of 0.96. This provides a novel predictive tool for describing the modulus–strain evolution of stabilized sludge soils with high accuracy.
- (3)
- By integrating SEM and XRD evidence, this study revealed the coupling mechanism between microstructural evolution (C–S–H formation and porosity reduction) and macroscopic dynamic response. This micro–macro linkage offers a new mechanistic explanation for the improved stiffness and damping characteristics.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jongpradist, P.; Youwai, S.; Jaturapitakkul, C. Effective void ratio for assessing the mechanical properties of cement-clay admixtures at high water content. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzababaei, M.; Arulrajah, A.; Haque, A.; Nimbalkar, S.; Mohajerani, A. Effect of fiber reinforcement on shear strength and void ratio of soft clay. Geosynth. Int. 2018, 25, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, D.J. Application of construction waste in the reinforcement of soft soil foundation in coastal cities. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Zhang, K.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, G.; Yu, X.; Xu, W. Study on the Mechanical Properties of Modified Sludge Soil Based on an SM-C Modifier. Materials 2025, 18, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.X.; Liu, H.L.; Zhu, W. Experimental research on engineering characteristics of cement solidified soil. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2000, 549–554. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, A.S.; Dayioglu, A.Y.; Aydilek, A.H. Geoenvironmental behavior of lime-treated marine sediments. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2021, 39, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, C.; Guo, J.; Chu, Z.; Li, Y. Mechanical properties and microscopic mechanism of dredged silt solidification by slag-chlorine oxygen magnesium cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 448, 138211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentar, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, D. Comparative study of stabilization/solidification of dredged sediments with ordinary Portland cement and calcium sulfo-aluminate cement in the framework of valorization in road construction material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 279, 122447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Castillo, A.; Andrés-Castro, F.; Gómez-Casero, M.Á.; Eliche-Quesada, D. Olive Pomace Fly Ash as an Alternative Alkaline Activator for Electric Arc Furnace Slag for Sustainable Cementitious Materials. Materials 2025, 18, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ciais, P.; Deng, Z.; Davis, S.J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, Y.; Cui, D.; Zhu, B.; Dou, X.; Ke, P.; et al. Carbon Monitor, a near-real-time daily dataset of global CO2 emission from fossil fuel and cement production. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.X.; Abriak, N.E.; Zentar, R.; Xu, W. Solidification/stabilization of dredged marine sediments for road construction. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoobanpot, N.; Jamsawang, P.; Simarat, P.; Jongpradist, P.; Likitlersuang, S. Sustainable reuse of dredged sediments as pavement materials by cement and fly ash stabilization. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3807–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, F. Deterioration Effects and Microscopic Mechanisms of Solidified/Stabilized Red Mud by CGFPA Binders Under Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Materials 2025, 18, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huaihe, F.U.; Mingzhi, Z.H.A.N.G.; Shuaidong, M.A.O.; Youzhi, B.A.O.; Yinghao, H.U.A.N.G. Experimental study on combined solidification of sludge using industrial wastes reinforced alkali slag-cement. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 47 (Suppl. S1), 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.W.; Zhang, S.; Hong, Z.S.; Liu, S.Y. Experimental study of solidification of dredged clays with high water content by adding cement and phosphogypsum synchronously. Rock Soil Mech. 2010, 31, 2817–2822. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Yin, S.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Study on dynamic characteristics of cement-modified red mud-based silty soil under traffic load. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 198, 109650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.N. Physical and mechanical properties of saline soil stabilized by combined slag, fly ash and polyacrylamide. Rock Soil Mech. 2024, 45 (Suppl. S1), 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Fang, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, C.; Yao, Z.; Tan, X.; Lv, Y. Solidification of loess using a composite geopolymer based on slag powder and fly ash: Influencing factors and mechanism analysis. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 04024428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.M.; Jian, W.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Fang, Z.H. Experimental study on performance of sludge stabilized by CSFG-FR synergy. Rock Soil Mech. 2022, 43, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.; Wang, J.; Feng, D.; Liang, S.; Liu, F.; Wu, S. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Sodium Silicate-Activated Slag/Fly Ash Solidified South China Coastal Soft Soil: Areas of specialization: Geotechnical Engineering. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2025, 29, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Miao, S.D.; Zhang, M.Z.; Wang, S.; Lei, G.H. Mechanical strength and microscopic mechanism of different industrial waste-cement co-curing sludges. Mater. Rep. 2025, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeev, P.; Kohees, M.; Sanjayan, J.G. Stress–strain model for geopolymer mortar under active confinement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.W.; Wan, X.; Gao, H.M.; Wang, Z.H.; Jiao, N. Mechanical Behavior and Microscopic Mechanism of Soft Clay Stabilized by Red Mud, Phosphogypsum and Cement. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; He, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, N.; Cao, J.; Yang, T.; Sun, X. On shear strength and microstructure characteristics of dredged sludge treated synergistically by aggregates recycled from building demolition waste, blast furnace powder, and cement. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 677–689. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, G.; Shu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q. Solidification and field assessment of soft soil stabilized by a waste-based binder using deep mixing method. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 5061–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wei, J. Strength and solidified mechanism of slag−steel slag−desulfurization gypsum−cement stabilized silt. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 54, 2382–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Luo, J.; Yue, M.; Fan, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Ding, X. Study of dynamic characteristics and damage mechanism of pile–net composite roadbeds in high-speed railways under seismic action. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 190, 109177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Indraratna, B.; Singh, M. Dynamic parameters of subgrade soils prone to mud pumping considering the influence of kaolin content and the cyclic stress ratio. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 29, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Xie, M. Study on seismic response and running safety of the heavy-haul railway train-track-bridge system under spatially varying ground motions. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 196, 109450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Wu, H.-J.; Lu, J.-T.; Liu, Y.; Diab, A.; Zheng, J.-J.; Miao, Y. Dynamic viscoelastic response of asphalt pavement with random transversely isotropic base courses. Transp. Res. Rec. 2023, 2677, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, I.M.; Al-Qadi, I. Incorporation of Pavement Dynamic Loading in Mechanistic–Empirical Design Frameworks. Transp. Res. Rec. 2023, 2677, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-C.; Yan, Q.-F. Horizontal Vibration of Pile in Transversely Isotropic Saturated Soil Based on Saturated Porous Medium Theory. J. Appl. Math. 2023, 2023, 8103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method. National Standards of People, Republic’s of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Zhang, X.D.; Cao, Q.K.; Pan, Y. Experiment research of lime-fly ash Soil’s dynamics characteristics. Rock Soil Mech. 2010, 31, 2560–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Y. Mechanical Properties of Plain Soils and Improved Soils Subjected to Heavy-Haul Train Load. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J. Determination of traffic load parameters on indoor test highways. Low Temp. Archit. Technol. 2015, 37, 121–123. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, B.O.; Drnevich, V.P. Shear modulus and damping in soils: Measurement and parameter effects (terzaghi leture). J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1972, 98, 603–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Chen, W.-S. Research on large-scale dynamic triaxial test of geocell-reinforced sand. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 683–690. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, D.; Ge, B.; Jiang, Y. Dynamic behavior and characteristics of geogrid-reinforced sand under cyclic loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 180, 108630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| /% | /% | /% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35.2 | 19.6 | 15.5 | 1.69 | 17.0 |
| Chemical Composition | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | NaO | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage | 56.24 | 25.67 | 9.34 | 1.63 | 2.68 | 3.24 | 0.24 | 0.96 |
| Sample No. | f/Hz | c/% | t/d |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1-f 1-c 8-t 3 | 1 | 8 | 3 |
| X2-f 2-c 8-t 3 | 2 | 8 | 3 |
| X3-f 3-c 8-t 3 | 3 | 8 | 3 |
| X4-f 2-c 3-t 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| X5-f 2-c 5-t 3 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
| X6-f 2-c 8-t-3 | 2 | 8 | 3 |
| X7-f 2-c 11-t 3 | 2 | 11 | 3 |
| X8-f 2-c 8-t 1 | 2 | 8 | 1 |
| X9-f 2-c 8-t 3 | 2 | 8 | 3 |
| X10-f 2-c 8-t 7 | 2 | 8 | 7 |
| X11-f 2-c 8-t 14 | 2 | 8 | 14 |
| X12-f 2-c 8-t 28 | 2 | 8 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhou, F.; Ling, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Han, S. Dynamic Properties of Mineral-Based Cementitious Material-Stabilized Slurry Soil Under Vehicle Loading. Materials 2025, 18, 4539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194539
Sun Z, Zhao Y, Luo J, Zhou F, Ling X, Wang Y, Yang Y, Han S. Dynamic Properties of Mineral-Based Cementitious Material-Stabilized Slurry Soil Under Vehicle Loading. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194539
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhenlong, Yingying Zhao, Jun Luo, Fengxi Zhou, Xianzhang Ling, Yongbo Wang, Yaping Yang, and Sanping Han. 2025. "Dynamic Properties of Mineral-Based Cementitious Material-Stabilized Slurry Soil Under Vehicle Loading" Materials 18, no. 19: 4539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194539
APA StyleSun, Z., Zhao, Y., Luo, J., Zhou, F., Ling, X., Wang, Y., Yang, Y., & Han, S. (2025). Dynamic Properties of Mineral-Based Cementitious Material-Stabilized Slurry Soil Under Vehicle Loading. Materials, 18(19), 4539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194539





