Quasi-Static and High Strain-Rate Behavior of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Modified BOFS Concrete
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
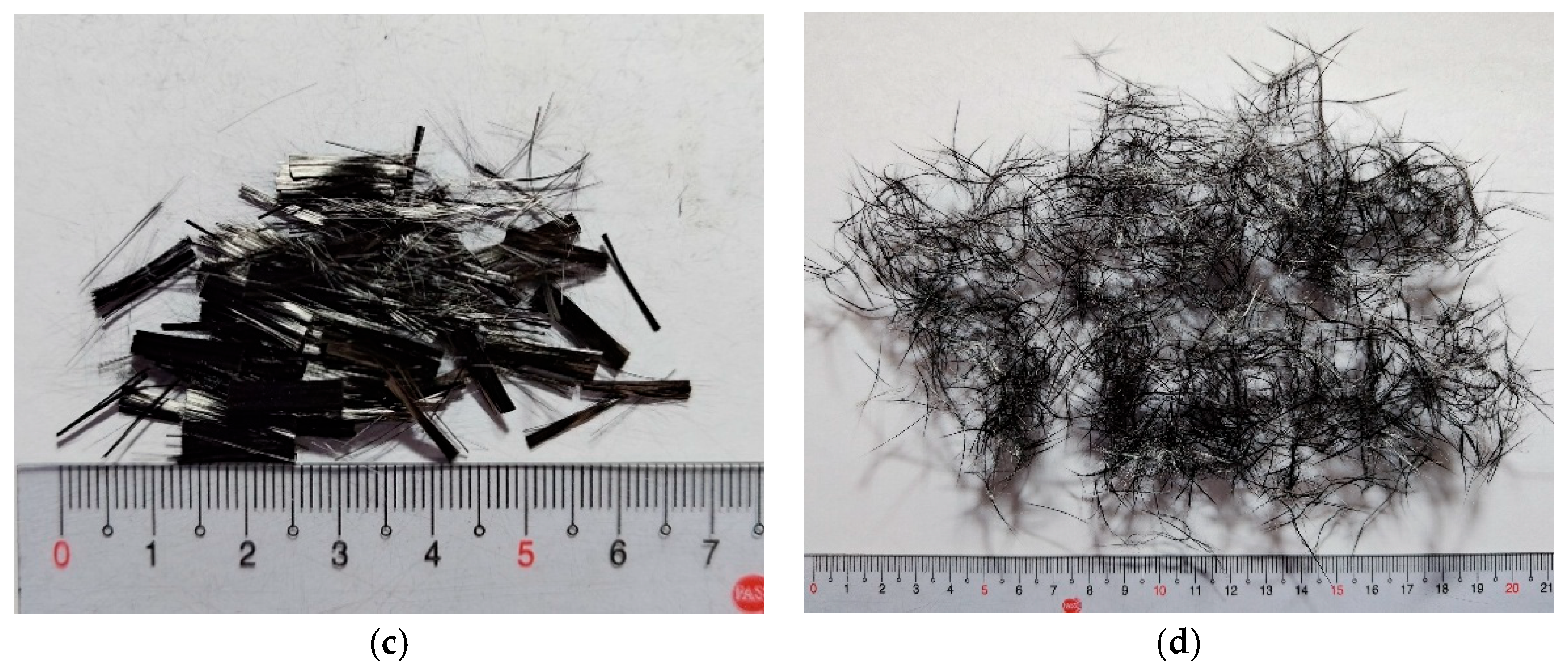
2.1. Chopped Carbon Fiber
- Thermogravimetric analysis of CF
- Heating from 40 °C temperature to 700 °C at 20 °C/min.
- Heating from 40 °C to 550 °C at 20 °C/min, holding for 30 min, then heating to 700 °C at 20 °C/min.
- Tensile strength of CF filament
- Pneumatic dispersion of CF
2.2. Modified Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag and Natural Aggregate
2.3. The Preparation of Modified Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag Carbon Fiber Reinforced Concrete
3. Test Methods
3.1. Slump Test
3.2. Compressive Strength Test
3.3. Flexural Strength Test
3.4. Splitting Tensile Strength Test
3.5. Drop-Weight Test
3.6. Stress Reversal Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar Test
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Slump Test Results
4.2. Compressive Strength Test Results
4.3. Flexural Strength Test Results
4.4. Splitting Tensile Strength Test Results
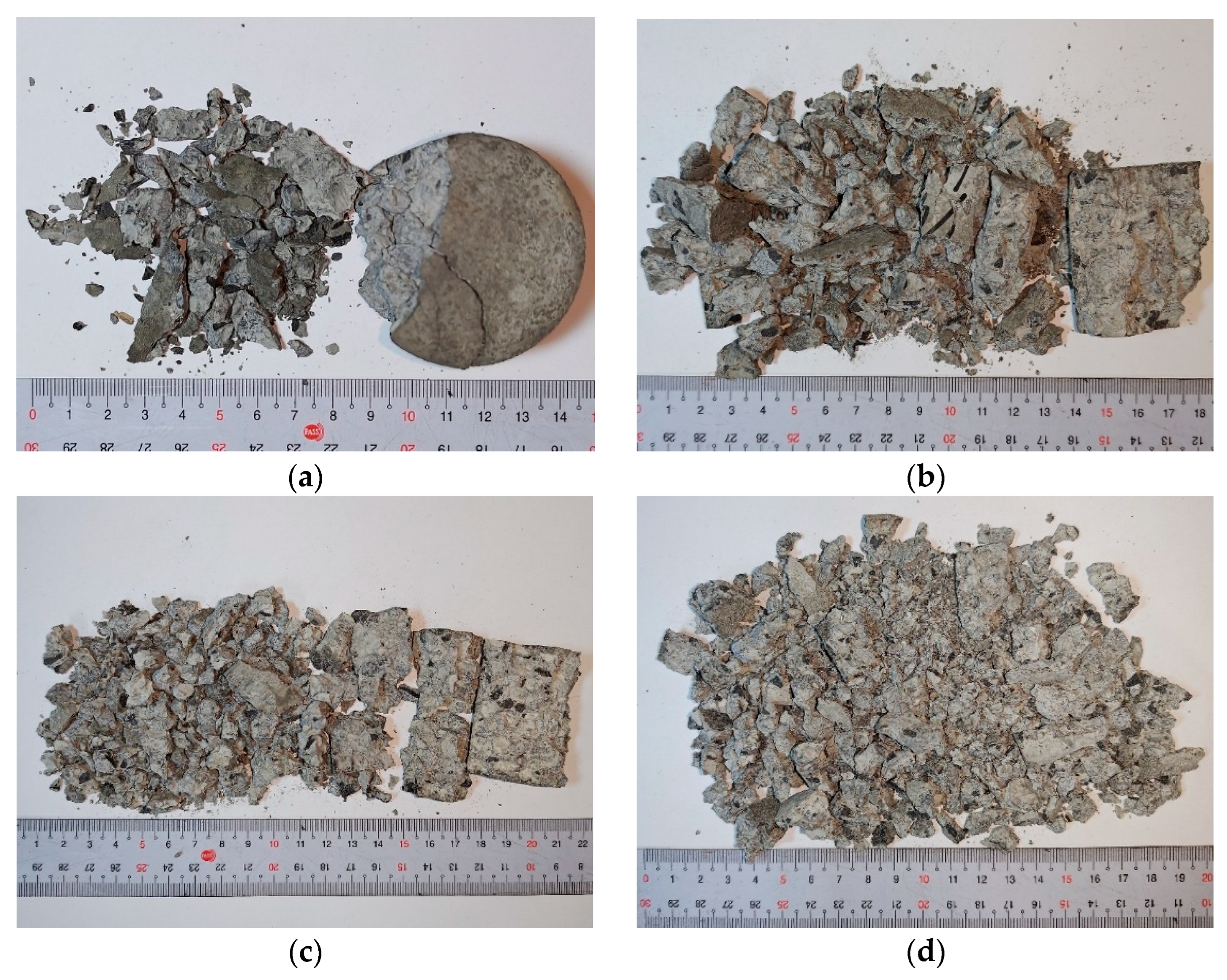
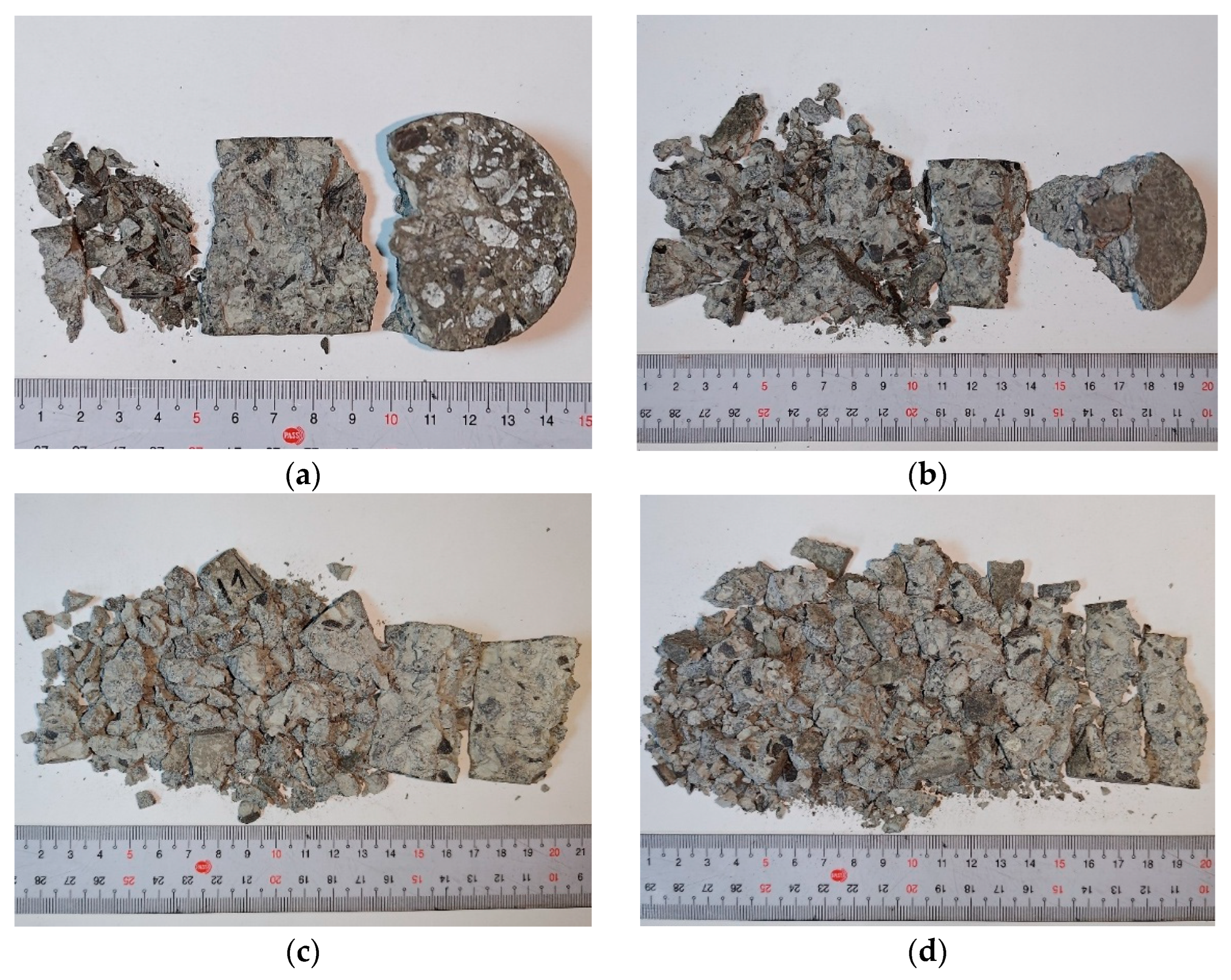
4.5. Drop-Weight Test Results
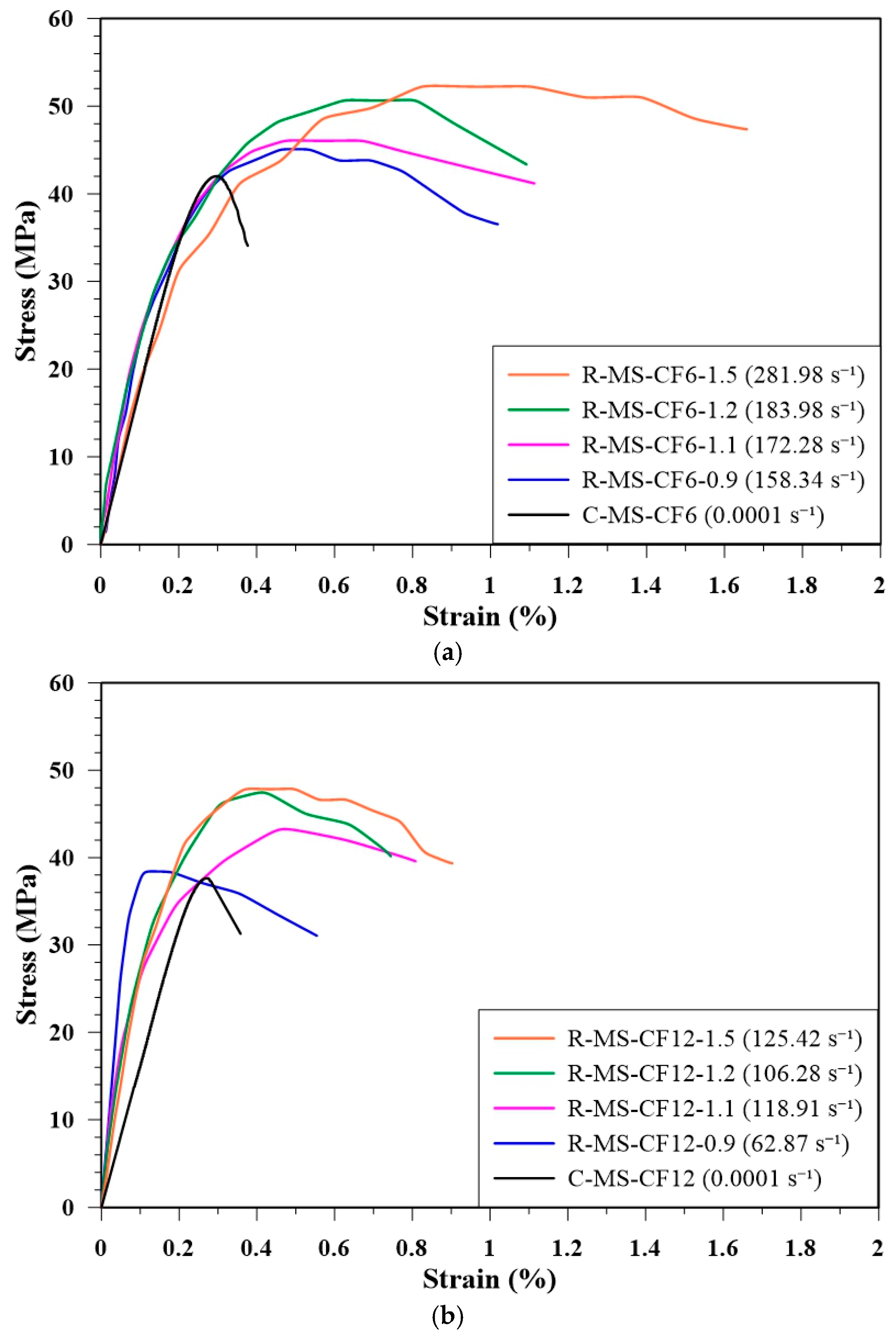
4.6. RSHPB Test
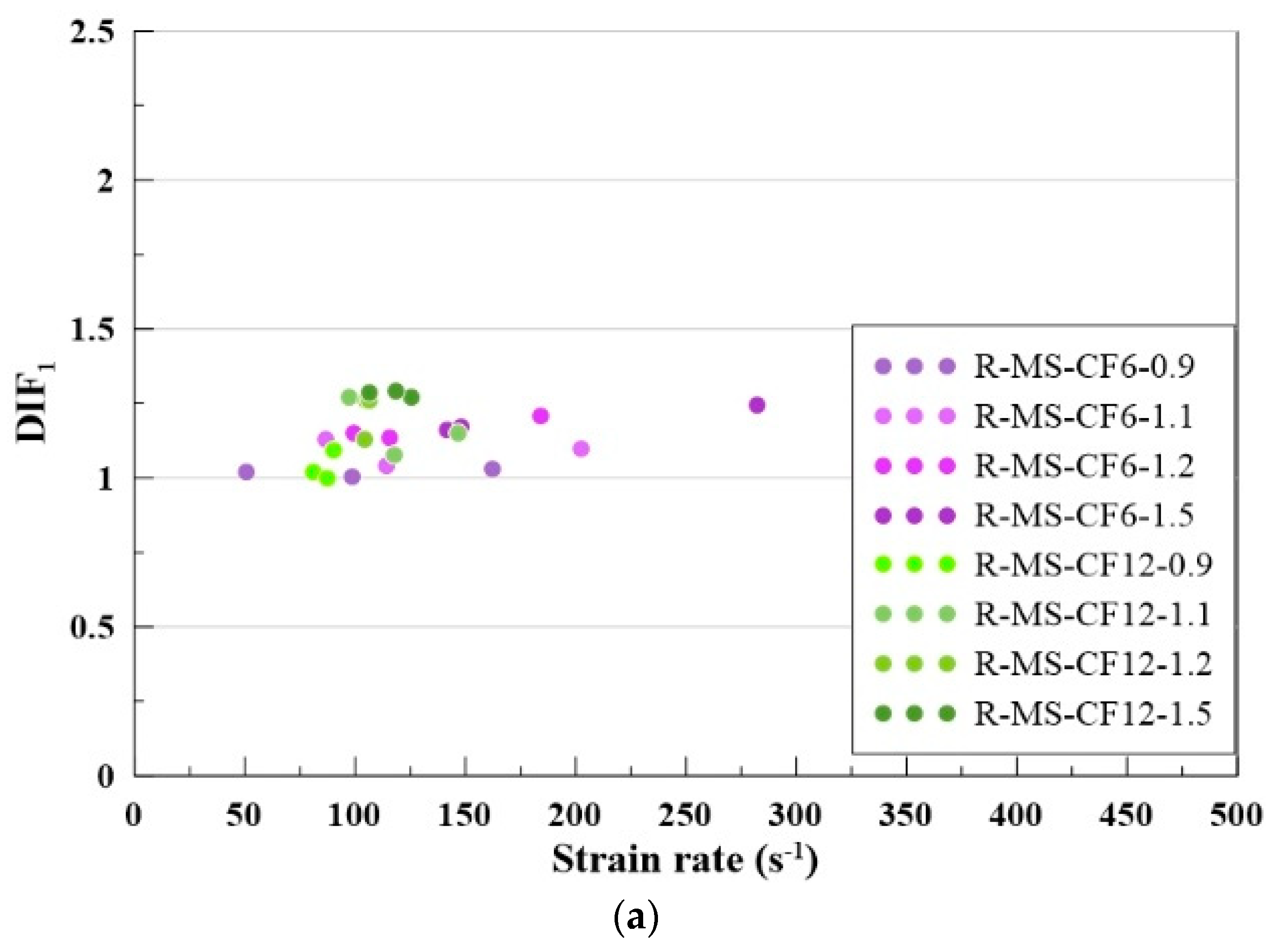
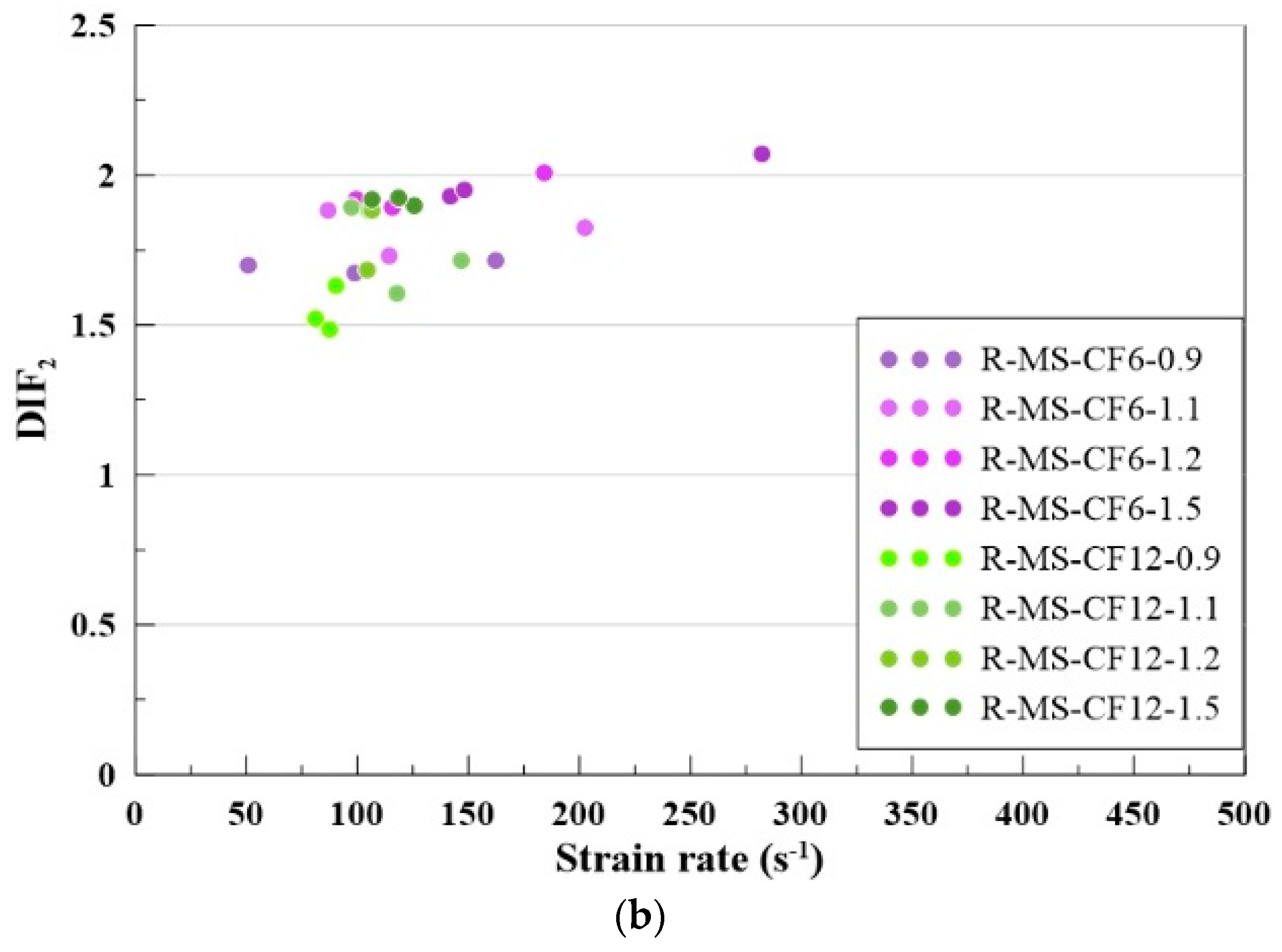
4.7. Dynamic Increase Factor
5. Conclusions
- Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) revealed that heat-treated CF exhibited up to 1.5% weight loss due to the removal of surface sizing. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) further confirmed the effective elimination of sizing through thermal treatment.
- Single-fiber tensile tests indicated that heat treatment did not significantly influence the tensile strength of individual CF filaments.
- Replacing natural aggregates with MBOFS reduced the slump of concrete mixtures but significantly enhanced compressive, flexural, and splitting tensile strengths.
- The incorporation of chopped CF at 1% by weight of cement further improved the mechanical performance of MBOFS concrete. In quasi-static tests, specimens with 6 mm CF exhibited higher compressive strength, whereas those with 12 mm CF showed superior flexural and splitting tensile strengths.
- Drop-weight impact tests demonstrated that MBOFS CFRC specimens exhibited greater impact resistance than non-fiber specimens. Among fiber-reinforced specimens, those with 12 mm CF showed slightly higher impact resistance than those with 6 mm CF.
- RSHPB tests indicated that MBOFS CFRC specimens with 6 mm CF achieved higher dynamic strength than those with 12 mm CF. Increasing gas pressure led to higher dynamic strength, and the dynamic increase factor (DIF) showed an upward trend with increasing strain rate.
- The results of this study indicate that MBOFS CFRC has the potential to utilize industrial by-products as sustainable construction materials.
- The MBOFS material used in this work was supplied by China Steel Corporation (Kaohsiung, Taiwan), and its current production is limited to research purposes, which may constrain broader applicability at present. Future research will therefore focus on conducting large-scale field experiments and evaluating the long-term durability of CFRC incorporating MBOFS to further validate its practical potential.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bendixen, M.; Iversen, L.L.; Best, J.; Franks, D.M.; Hackney, C.R.; Latrubesse, E.M.; Tusting, L.S. Sand, gravel, and UN Sustainable Development Goals: Conflicts, synergies, and pathways forward. One Earth 2021, 4, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Das, B.C.; Ghosh, S.; Saheb, A.M.; Barman, S.D.; Saha, U.D.; Mohinuddin, S.; Pal, S.C.; Quesada-Román, A. Role of riverbed sand mining on planform and cross-sectional morphology of Mayurakshi River, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 963, 178465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, I.M.; Mahto, S.S.; Bhagat, C.; Modi, A.; Jain, V.; Mohapatra, P.K. A Review of River Sand Mining: Methods, Impacts, and Implications. Next Res. 2025, 2, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dering, D.; Swartz, C.; Dogan, N. Dynamic modeling and simulation of basic oxygen furnace (BOF) operation. Processes 2020, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, T.S.; Sheridan, C.M.; van Dyk, L.D. Basic oxygen furnace slag: Review of current and potential uses. Miner. Eng. 2020, 149, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulatbekova, D.; Vashistha, P.; Kim, H.K.; Pyo, S. Effects of basic-oxygen furnace, electric-arc furnace, and ladle furnace slags on the hydration and durability properties of construction materials: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 92, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Ding, W. Evaluation the deleterious potential and heating characteristics of basic oxygen furnace slag based on laboratory and in-place investigation during large-scale reutilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, D.M.; Fehling, K.A.; Shay, E.C.; Wittenborn, J.L.; Green, J.J.; Avent, C.; Bigham, R.D.; Connolly, M.; Lee, B.; Shepker, T.O.; et al. Physical and chemical characteristics of blast furnace, basic oxygen furnace, and electric arc furnace steel industry slags. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Wu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, R.; Yang, T. Environmental performance and functional analysis of chip seals with recycled basic oxygen furnace slag as aggregate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambole, C.; Paige-Green, P.; Kupolati, W.K.; Ndambuki, J.M.; Adeboje, A.O. Basic oxygen furnace slag for road pavements: A review of material characteristics and performance for effective utilisation in southern Africa. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Zhuang, K.W.; Chang, Y.H.; Nagarajan, D.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, J.S. Basic oxygen furnace slag as a support material for the cultivation of indigenous marine microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 125968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, H.D.; de Carvalho, J.M.F.; Costa, L.C.B.; da Fonseca Elói, F.P.; e Silva, K.D.D.C.; Peixoto, R.A.F. Mechanical performance and resistance to carbonation of steel slag reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Structural characteristics and cementitious behavior of basic oxygen furnace slag mud and electric arc furnace slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 219, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Cheng, T.W.; Lin, K.Y.; Lin, K.L.; Wu, C.C.; Tsai, C.T. Geopolymer technologies for stabilization of basic oxygen furnace slags and sustainable application as construction materials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.F.; Schollbach, K.; Melzer, S.; Van Der Laan, S.R.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Quantitative analysis and phase assemblage of basic oxygen furnace slag hydration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, S.C.; Vernilli, F.; Cascudo, O. The reuse of basic oxygen furnace slag as concrete aggregate to achieve sustainable development: Characteristics and limitations. Buildings 2023, 13, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Pham, P.N.; Nam, H.P.; Nguyen, P. Factors affecting compressive strength of steel slag concrete: A systematic literature review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 100, 111686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, H.; Ma, M.; Ling, T.C. A closed-loop recycling of wastewater derived from aqueous carbonation of basic oxygen furnace slag in cement paste production. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, V.A.; Cimentada, A.; Thomas, C.; Borges, P.H. Pre-treatment of BOF steel slag aggregates and effect on the mechanical and microstructure properties of alkali-activated mortars. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.Z.; Vernilli, F.; Almeida, B.; Oliveira, M.D.; Silva, S.N. Reducing environmental impacts: The use of basic oxygen furnace slag in portland cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-González, D.; Prazuch, J.; Ruiz-Bustinza, I.; González-Gasca, C.; Piñuela-Noval, J.; Verdeja, L.F. The treatment of Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) slag with concentrated solar energy. Sol. Energy 2019, 180, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chang, J.; Ansari, W.S. The effects of carbonation and hydration on the mineralogy and microstructure of basic oxygen furnace slag products. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, E.A.; Azevedo, A.G.; Junior, H.S.; Borges, P.H. Accelerated carbonation of steel slag for enhanced carbon capture and utilization as aggregate in alkali-activated materials. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2024, 12, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omur, T.; Miyan, N.; Kabay, N.; Özkan, H. Utilization and optimization of unweathered and weathered basic oxygen furnace slag aggregates in cement based mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 64, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Yu, L.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y.; Lu, D.; Li, N.; Qu, F. Sustainable Asphalt Mixtures Reinforced with Basic Oxygen Furnace Steel Slag: Multi-Scale Analysis of Enhanced Interfacial Bonding. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Sheu, B.L. Application and Breakthrough of BOF Slag Modification; China Steel Technical Report No. 28; China Steel Corporation: Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2015; pp. 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Lin, C.T. Recycling of basic oxygen furnace slag as a raw material for autoclaved aerated concrete production. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Soliman, A.M.; Nehdi, M.L. Exploring Mech. and durability properties of ultra-high performance concrete incorporating various steel fiber lengths and dosages. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 75, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, A.; Jayashree, J.; Abhishek, S.; Prakash, A. Multifunctional properties of carbon fiber integrated cement composite–A review and insights. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Hung, J.Y.; Syu, J.Y.; Chen, S.H.; Huang, C.H.; Chang, S.M.; Kuo, W.S. Effect of the sizing removal methods of fiber surface on the mechanical performance of basalt fiber-reinforced concrete. Fibers 2024, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ding, Y.; Randl, N. Effect of macro polyoxymethylene fibers on shear transfer across a crack and crack surface topography of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 464, 140118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, S.; Thushanthan, K.; Tharmarajah, G. Durability and mechanical performance of glass and natural fiber-reinforced concrete in acidic environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 465, 140262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomb, B.A. Processing, structure, and properties of carbon fibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 91, 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Lee, M.E.; Choi, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Lee, S. Strategies for the production of PAN-Based carbon fibers with high tensile strength. Carbon 2022, 186, 644–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumarana, T.V.; Arachchi, M.A.V.H.M.; Somarathna, H.M.C.C.; Raman, S.N. A review on the variation of mechanical properties of carbon fibre-reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, M.; Xing, T.; He, A.; Huang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Qiao, S.; Tong, A.; Bai, J.; et al. Advances in colored carbon-based fiber materials and their emerging applications. SusMat 2024, 4, e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhuang, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y. Mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced concrete (CFRC) after exposure to high temperatures. Compos. Struct. 2021, 256, 113072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.S.; Qureshi, L.A. Effect of carbon fiber on mechanical properties of reactive powder concrete exposed to elevated temperatures. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 42, 102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, G.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y. Flexural behavior of carbon fiber-reinforced concrete beams under impact loading. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 118, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Ge, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, S. Preparation of carbon fiber conductive concrete and study on its mechanical and heating properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džolan, A.; Fischer, O.; Niedermeier, R. Analyses of the fatigue behavior of carbon short-fiber-reinforced concrete (CSFRC) under tension and flexion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 453, 139058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Gao, S.; Mäder, E.; Sharma, H.; Wei, L.Y.; Bijwe, J. Carbon fiber surfaces and composite interphases. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 102, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyckens, D.J.; Stojcevski, F.; Hendlmeier, A.; Randall, J.D.; Hayne, D.J.; Stanfield, M.K.; Newman, B.; Vukovic, F.; Walsh, T.R.; Henderson, L.C. Carbon fibre surface chemistry and its role in fibre-to-matrix adhesion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 26528–26572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, X.; Bai, H.; Xu, Z.; Ma, D. Effect of fiber dispersion, content and aspect ratio on tensile strength of PP fiber reinforced soil. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalel, H.; Khan, M.; Starr, A.; Khan, K.A.; Muhammad, A. Performance of engineered fibre reinforced concrete (EFRC) under different load regimes: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, H.; Gou, H. Evaluation of carbon fiber dispersion in cement-based materials using mechanical properties, conductivity, mass variation coefficient, and microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 120891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Yang, T.H.; Kuo, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.K. A Study on improving the mechanical performance of carbon-fiber-reinforced cement. Materials 2019, 12, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.; Kim, M. Impact resistance and interlaminar shear strength enhancement of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites by introducing MWCNT-anchored carbon fiber. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 217, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Yang, K.H.; Hsu, P.Y.; Syu, J.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Kuo, W.S.; Tsai, Y.K. Comparing mechanical characterization of carbon, Kevlar, and hybrid-fiber-reinforced concrete under quasistatic and dynamic loadings. Buildings 2023, 13, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1557-20; Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength and Young’s Modulus of Fibers. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM C33/C33M-24a; Standard Specification for Concrete Aggregates. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM C127-24; Standard Test Method for Relative Density (Specific Gravity) and Absorption of Coarse Aggregate. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Li, Y.F.; Li, J.Y.; Ramanathan, G.K.; Chang, S.M.; Shen, M.Y.; Tsai, Y.K.; Huang, C.H. An experimental study on mechanical behaviors of carbon fiber and microwave-assisted pyrolysis recycled carbon fiber-reinforced concrete. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, A.; Lyu, Z.; He, Z.; Nguyen, K.T. Fresh and rheological characteristics of fiber reinforced concrete—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 296, 123734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhuang, Y.; Song, L.; He, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H. Mechanical properties and failure mechanism of fiber-reinforced concrete materials: Effects of fiber type and content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 465, 140190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C143/C143M-20; Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM C39/C39M-24; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- ASTM C78/C78M-22; Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM C496/C496M-17; Standard Test Method for Splitting Tensile Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ACI 544.2R-89; Measurement of Properties of Fiber Reinforced Concrete. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 1999.
- Nemat-Nasser, S.; Isaacs, J.B.; Starrett, J.E. Hopkinson techniques for dynamic recovery experiments. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci 1991, 435, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

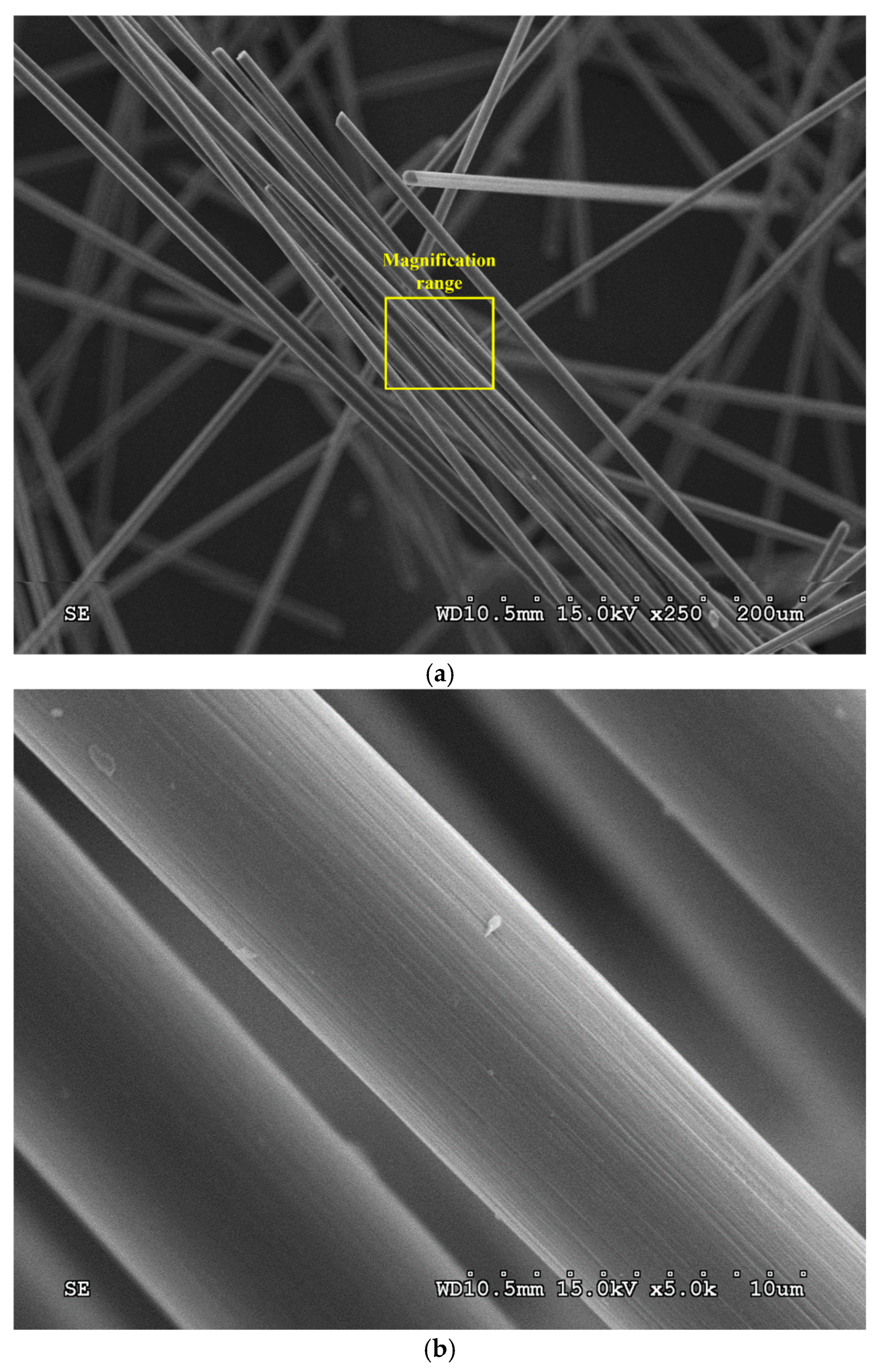
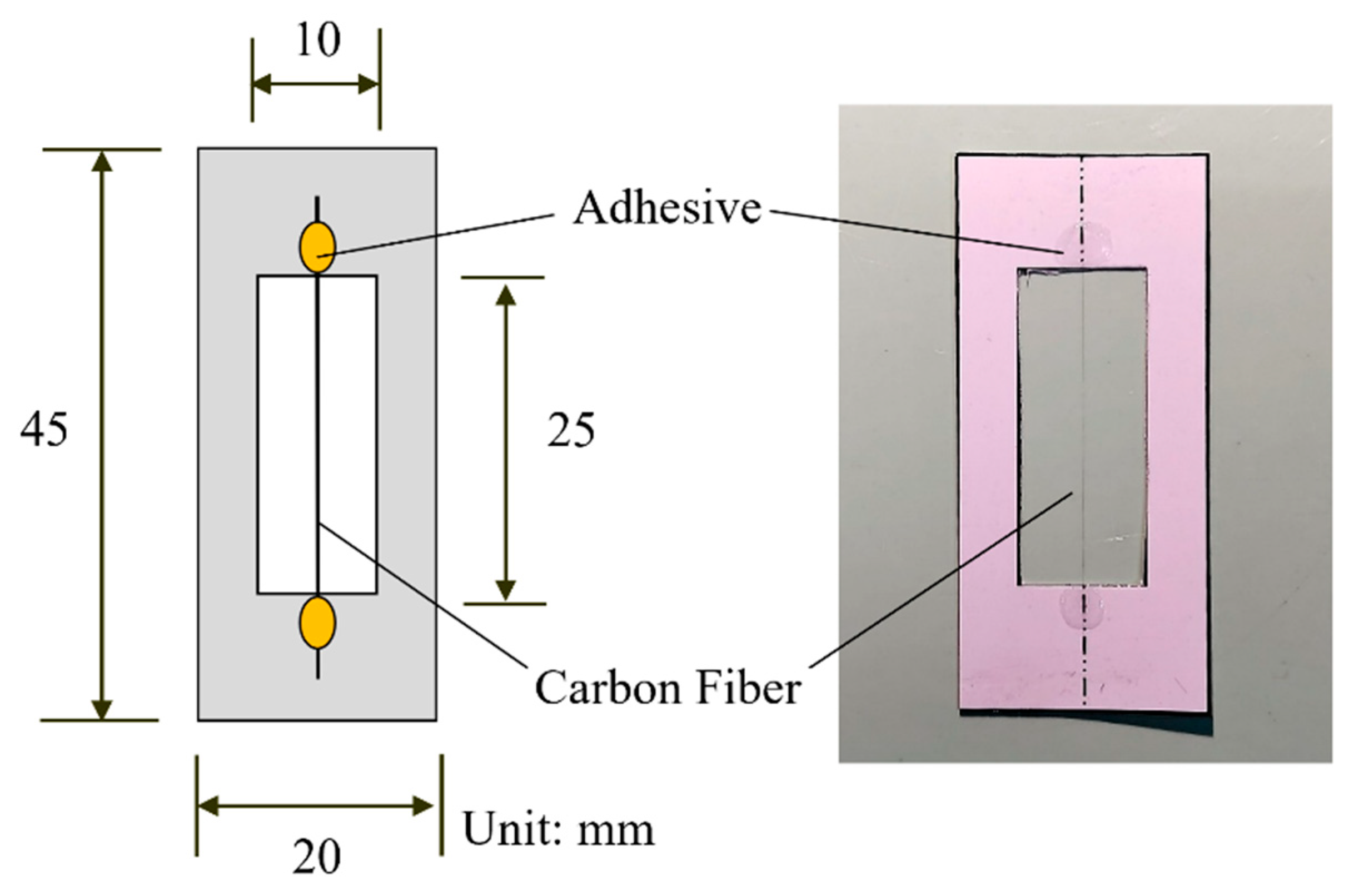




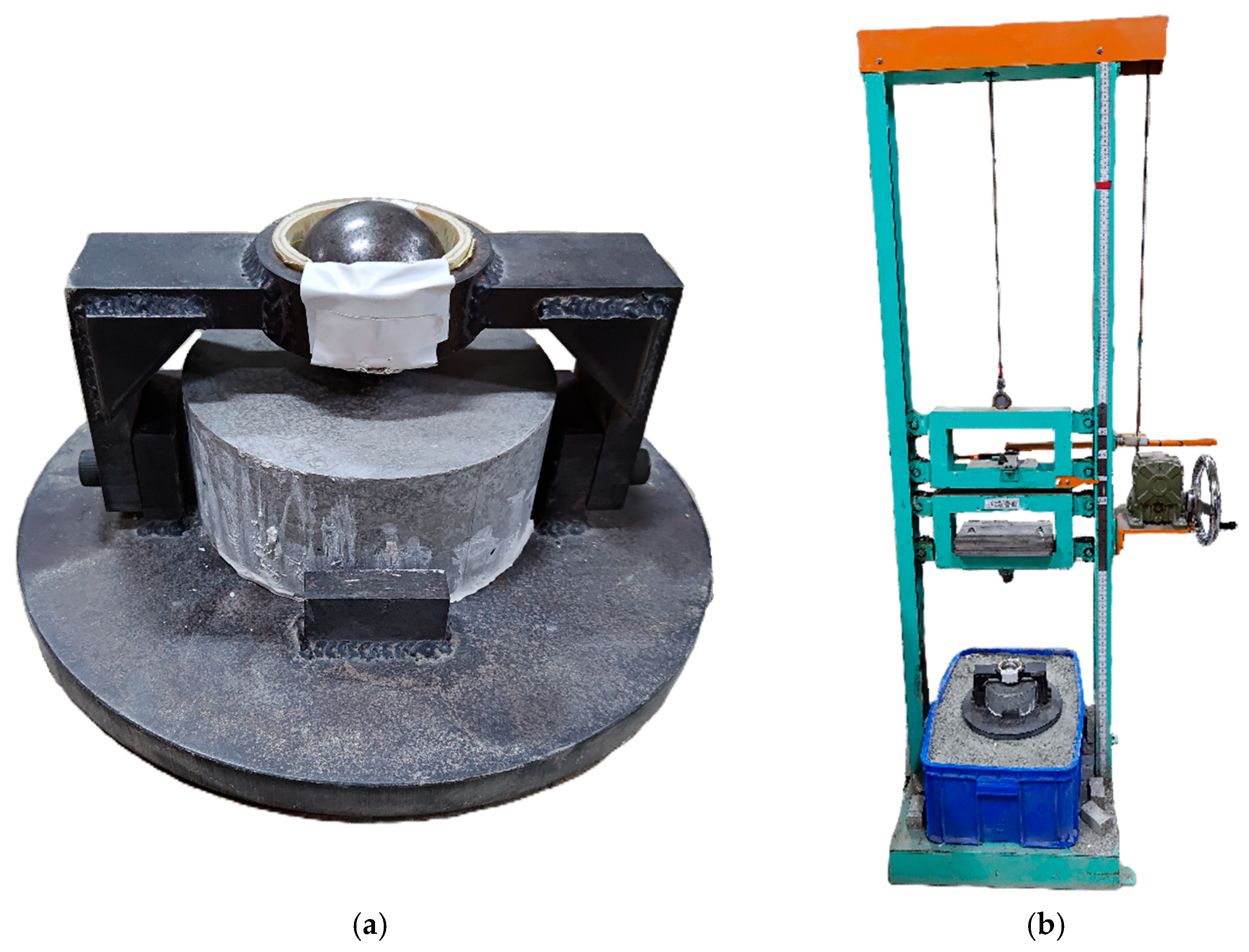

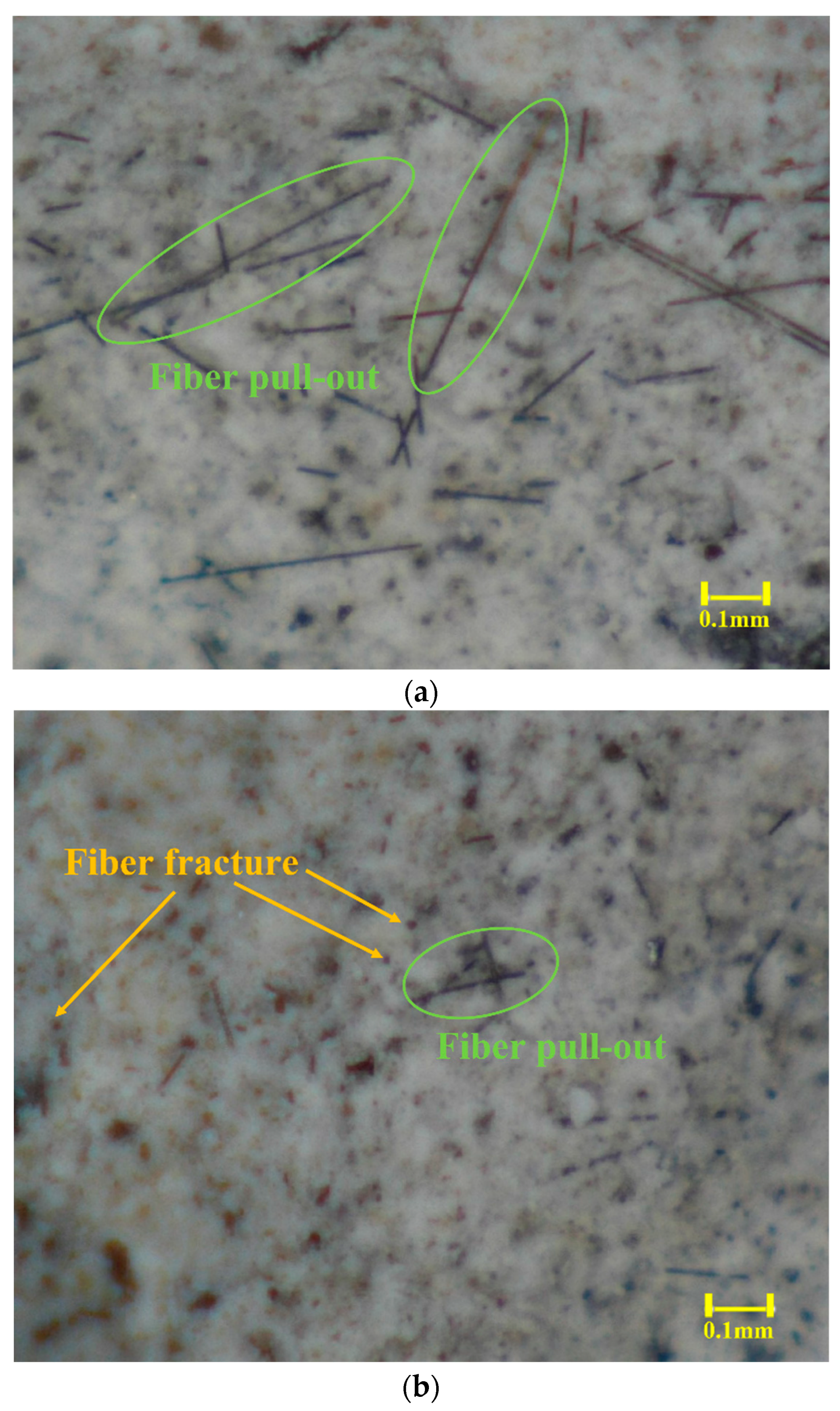


| No. | Untreated CF | Heat-Treated CF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Force (gf) | Displ. (mm) | Slope (gf/mm) | Force (gf) | Displ. (mm) | Slope (gf/mm) | |
| 1 | 8.96 | 0.27 | 33.82 | 10.84 | 0.28 | 38.86 |
| 2 | 12.99 | 0.39 | 33.57 | 12.85 | 0.34 | 37.35 |
| 3 | 12.29 | 0.36 | 33.75 | 13.30 | 0.36 | 36.73 |
| 4 | 13.33 | 0.37 | 36.32 | 12.01 | 0.35 | 34.82 |
| 5 | 9.99 | 0.30 | 33.19 | 14.57 | 0.40 | 36.69 |
| 6 | 14.36 | 0.40 | 35.54 | 12.72 | 0.36 | 35.53 |
| 7 | 9.80 | 0.28 | 35.24 | 11.07 | 0.33 | 33.94 |
| 8 | 9.04 | 0.27 | 33.37 | 13.09 | 0.38 | 34.72 |
| 9 | 12.50 | 0.33 | 37.52 | 13.09 | 0.37 | 35.38 |
| 10 | 10.84 | 0.32 | 34.20 | 9.56 | 0.27 | 35.92 |
| 11 | 10.76 | 0.33 | 32.91 | 10.04 | 0.26 | 39.06 |
| 12 | 11.00 | 0.32 | 34.92 | 14.70 | 0.41 | 36.02 |
| 13 | 12.53 | 0.36 | 34.89 | 12.16 | 0.35 | 35.24 |
| 14 | 14.29 | 0.42 | 34.11 | 14.82 | 0.40 | 36.78 |
| 15 | 12.29 | 0.34 | 35.72 | 11.32 | 0.33 | 34.62 |
| 16 | 14.78 | 0.41 | 36.12 | 11.69 | 0.34 | 34.29 |
| 17 | 10.79 | 0.31 | 35.38 | 12.32 | 0.31 | 39.23 |
| 18 | 11.48 | 0.33 | 34.90 | 11.84 | 0.33 | 35.54 |
| 19 | 11.80 | 0.33 | 35.66 | 10.74 | 0.33 | 32.76 |
| 20 | 12.53 | 0.37 | 33.67 | 11.98 | 0.37 | 32.73 |
| 21 | 10.84 | 0.32 | 34.31 | 10.25 | 0.28 | 37.26 |
| 22 | 13.59 | 0.38 | 35.85 | 11.16 | 0.30 | 36.96 |
| 23 | 13.68 | 0.38 | 36.49 | 13.38 | 0.36 | 36.85 |
| 24 | 11.64 | 0.31 | 37.93 | 10.15 | 0.29 | 34.76 |
| 25 | 11.19 | 0.30 | 36.94 | 12.53 | 0.34 | 36.95 |
| 26 | 11.72 | 0.35 | 33.98 | 15.47 | 0.43 | 36.39 |
| 27 | 14.23 | 0.42 | 34.20 | 15.42 | 0.43 | 36.02 |
| 28 | 13.72 | 0.38 | 35.72 | 12.53 | 0.40 | 31.47 |
| 29 | 10.52 | 0.31 | 33.50 | 12.19 | 0.34 | 35.44 |
| 30 | 9.41 | 0.26 | 36.62 | 15.90 | 0.44 | 35.97 |
| Avg. | 11.90 | 0.34 | - | 12.46 | 0.35 | |
| σ | 1.65 | 0.05 | - | 1.70 | 0.05 | |
| F value | - | - | - | - | - | 0.766 |
| p value | - | - | - | - | - | 0.385 |
| t value | - | - | - | - | - | −1.963 |
| p value | - | - | - | - | - | 0.0545 |
| Specific Gravity | BOF | Natural |
|---|---|---|
| Specimen weight (g) | 2000 | 2000 |
| Oven-dry weight (g) | 1992 | 1995.2 |
| Saturated-surface-dry weigh (g) | 2022.7 | 2006 |
| Specimen weight in water (g) | 1405 | 1241.7 |
| Bulk specific gravity | 3.23 | 2.61 |
| Apparent specific gravity | 3.39 | 2.65 |
| Absorbed moisture (%) | 1.54 | 0.54 |
| Moisture content (%) | 0.40 | 0.24 |
| Specimen | SL-B | SL-MS | SL-MS-CF6 | SL-MS-CF12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slump (mm) | 239 | 130 | 48 | 36 |
| Specimen | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Average Compressive Strength (MPa) | Increment Based on C-B (%) | Increment Based on C-MS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-B | 29.88 | 30.30 | - | - |
| 30.42 | ||||
| 30.60 | ||||
| C-MS | 36.80 | 37.80 | 24.75 | - |
| 38.24 | ||||
| 38.37 | ||||
| C-MS-CF6 | 42.95 | 44.21 | 45.89 | 16.95 |
| 44.45 | ||||
| 45.22 | ||||
| C-MS-CF12 | 40.52 | 41.29 | 36.26 | 9.23 |
| 41.67 | ||||
| 41.67 |
| Specimen | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Average Flexural Strength (MPa) | Increment Based on F-B (%) | Increment Based on F-MS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-B | 4.19 | 4.37 | - | - |
| 4.22 | ||||
| 4.69 | ||||
| F-MS | 4.59 | 5.00 | 14.41 | - |
| 4.98 | ||||
| 5.43 | ||||
| F-MS-CF6 | 5.78 | 6.35 | 45.29 | 26.99 |
| 6.55 | ||||
| 6.71 | ||||
| F-MS-CF12 | 6.42 | 6.74 | 54.34 | 34.91 |
| 6.84 | ||||
| 6.98 |
| Specimen | Splitting Strength (MPa) | Average Splitting Strength (MPa) | Increment Based on S-B (%) | Increment Based on S-MS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-B | 2.31 | 2.35 | - | - |
| 2.37 | ||||
| 2.38 | ||||
| S-MS | 2.17 | 2.57 | 9.1 | - |
| 2.64 | ||||
| 2.89 | ||||
| S-MS-CF6 | 2.95 | 3.32 | 41.08 | 29.31 |
| 3.42 | ||||
| 3.60 | ||||
| S-MS-CF12 | 2.85 | 3.35 | 42.23 | 30.36 |
| 3.22 | ||||
| 3.98 |
| Specimens | Impact Energy (J) | Impact Number | Average Impact Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-B | 150 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 3.3 |
| 100 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 8.7 | |
| 75 | 27 | 28 | 34 | 29.7 | |
| I-MS | 150 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 100 | 8 | 9 | 16 | 11 | |
| 75 | 65 | 133 | 185 | 127.7 | |
| I-MS-CF6 | 150 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 10 |
| 100 | 14 | 16 | 30 | 20 | |
| 75 | 280 | 376 | 388 | 348 | |
| I-MS-CF12 | 150 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 10.3 |
| 100 | 19 | 20 | 29 | 22.7 | |
| 75 | 401 | 457 | 489 | 449 | |
| Specimens | Gas Pressure (MPa) | Failure Strain Rate (s−1) | Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| R-MS-CF6 | 0.09 | 158.34 | 45.03 |
| 0.11 | 172.28 | 46.04 | |
| 0.12 | 183.98 | 50.64 | |
| 0.15 | 281.98 | 52.22 | |
| R-MS-CF12 | 0.09 | 62.87 | 38.34 |
| 0.11 | 118.91 | 43.22 | |
| 0.12 | 106.28 | 47.45 | |
| 0.15 | 125.42 | 47.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.-F.; Chien, C.-W.; Syu, J.-Y.; Huang, C.-H.; Kuo, W.-S.; Tsai, Y.-K. Quasi-Static and High Strain-Rate Behavior of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Modified BOFS Concrete. Materials 2025, 18, 4497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194497
Li Y-F, Chien C-W, Syu J-Y, Huang C-H, Kuo W-S, Tsai Y-K. Quasi-Static and High Strain-Rate Behavior of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Modified BOFS Concrete. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194497
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yeou-Fong, Chun-Wei Chien, Jin-Yuan Syu, Chih-Hong Huang, Wen-Shyong Kuo, and Ying-Kuan Tsai. 2025. "Quasi-Static and High Strain-Rate Behavior of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Modified BOFS Concrete" Materials 18, no. 19: 4497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194497
APA StyleLi, Y.-F., Chien, C.-W., Syu, J.-Y., Huang, C.-H., Kuo, W.-S., & Tsai, Y.-K. (2025). Quasi-Static and High Strain-Rate Behavior of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Modified BOFS Concrete. Materials, 18(19), 4497. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194497








