Abstract
How to rationally design composition of alloys with desired properties has always been an open and challenging question, especially for high-entropy alloy (HEA) which has huge selections of composition due to the feature of multi-principal elements. Although great efforts have been made in the past decades, such as approaches based on thermo-kinetic analysis and simulations, strategies to quick determine the optimal HEA composition remain lacking. In this study, based on the effective estimations of elastic modulus of alloys from compositions, we proposed a strategy to design intrinsically strong, ductile, and low-weight refractory HEA (RHEA) compositions. First, the Young’s moduli of three RHEAs were experimentally measured using uniaxial tensile test and impulse excitation of vibration (IEV) test. Then, the present results, combining with the data of elastic moduli of ~130 HEAs in literature, were utilized to validate the prediction of elastic moduli from compositions of HEAs. Finally, based on the property maps that containing 38,326 compositions, a novel RHEA was designed and experimentally tested, exhibiting superior strength, ductility, and low density compared to the equimolar NbMoTaVW alloy. This study provides a new strategy for developing HEAs and contributes to the development of new refractory HEAs with desired properties.
1. Introduction
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) have recently received extremely high research attention owing to their very promising mechanical properties and interesting structure characteristics [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. A well-known advantage of HEAs is their wide range of compositional space, because these alloys are often composed of multiple principal components [8,9]. There are more than three kinds of principal elements in HEAs, and HEAs are also called multiple-principal element alloys (MPEAs) [2,8]. This naturally raises a question: What is the direction for designing the HEA composition to achieve the optimal properties?
Material design for promising mechanical properties, such as high strength and high ductility, has always been a hot topic in the field of metallic structural materials, and many strategies have been proposed [10,11], e.g., the generalized stability principle based on thermodynamics and kinetics [12,13,14,15]. In recent years, great efforts and significant approaches have been made for the composition design of HEAs [16,17,18,19,20,21]. For example, researchers have designed the HfNbTiVAl10 alloy with a hierarchical heterostructure featuring multilevel chemical fluctuations, which exhibits an excellent combination of tensile strength and yield strength [19]. In addition, researchers have also applied various computational simulation methods for material design. For example, thermodynamic calculations based on thermophysical parameters and calculation of phase diagram (CALPHAD) [22,23], first-principle calculations combined with high-throughput calculations [24,25,26], and machine learning modeling have already discovered some alloys with excellent properties [27,28,29,30]. Despite the great progress, the large calculation amount and relatively low efficiency in simulations, as well as the difficulty in predicting the fracture property such as toughness, limit the quick discovery of new good HEAs. So, can we predict the properties of HEAs, such as Young’s modulus or yield strength, directly from their composition?
In 2012, Wang [31] proposed a prediction method for the mechanical and physical properties of metallic glasses based on their compositions, linked to the elastic modulus, providing a unique approach to designing the composition of metallic glasses from an elastic perspective. Further efforts, including the precise prediction of elastic modulus by Liu et al. [32,33] and the prediction of failure behavior by Wu et al. [34,35,36], confirm the significance of the concept of composition design for metallic glasses from elastic modulus, all of which have demonstrated high prediction accuracy. Inspired by these approaches, in this study, we investigate the elastic modulus of HEAs and attempt to examine the feasibility of the above concept of composition design from an elastic perspective for HEAs.
On the other hand, there have been numerous discussions on the correlations between elastic modulus and the mechanical properties of various materials. For instance, both the strength and hardness of materials scale with Young’s modulus, and Poisson’s ratio or Pugh’s ratio [37] (i.e., the ratio of bulk modulus B to shear modulus G) have been considered to be closely related to ductility and/or toughness. Besides the elastic criteria, there are also studies on predicting the ductility of body-centered cubic (BCC) HEAs from valence electron concentration (VEC) [38] and predicting the formation of single-phase structure from the atomic size difference [39]. The atomic size difference can be expressed by the following formula:
where and represent the atomic percentage and atomic radius of the i-th element, respectively, and denotes the average atomic radius. When < 0.066, the alloy tends to form a single-phase solid solution. These approaches are also important for the composition optimization of HEAs.
Refractory high-entropy alloys (RHEAs) exhibit excellent high-temperature strength and stability. For example, NbMoTaVW maintains a stable BCC single-phase structure at 1400 °C, with a yield strength of 477 MPa at 1600 °C [40]. However, it shows less than 5% compression fracture strain at room temperature, exhibiting significant brittle cleavage fracture behavior, which severely limits its application. Therefore, this study focuses on the NbMoTaVW alloy system, aiming to design new RHEAs that offer strength similar to NbMoTaVW but with better plasticity, lower density, and greater potential for practical applications.
In this study, we first measured the elastic modulus of three RHEAs using two experimental methods, i.e., uniaxial tension and impulse excitation of vibration (IEV). We then studied the data of elastic modulus in the literature for many alloys with different compositions, including both experimentally measured data and computer-simulated values of elastic modulus. Based on the elastic modulus data in the present study and in the literature, we examine the validity of the mixture law for predicting the elastic modulus. Finally, based on the NbMoTaVW alloy system, property maps were generated through the predictions of Young’s modulus, valence electron concentration, and density, and a new alloy composition was designed and experimentally tested. Unlike traditional methods, which often rely heavily on large-scale simulations and complex computational models, our approach offers a more direct and efficient prediction of the elastic modulus of HEAs based on their composition. This method provides a simpler framework, enabling faster and more accessible composition optimization. The novelty lies in applying this composition design concept, inspired by previous work on metallic glasses, to RHEAs, thus paving the way for the design of high-performance alloys with optimized properties.
2. Composition Design Strategy
The key to the concept of designing HEAs from an elasticity perspective includes two aspects: (1) the predictions of the elastic modulus from composition, and (2) the predictions of properties from the elastic modulus. Although some approaches to studying the elastic modulus of HEAs have been studied, they mainly focused on the experimental measurement of modulus, the comparison between experiments and simulation, and the factors affecting the elastic modulus. These approaches are helpful for understanding the elastic properties of HEAs; however, they do not provide direct predictions of the elastic modulus. In order to predict the elastic modulus directly from the composition, there are two methods, as discussed in the following section.
- (1)
- The ROM method
Greer et al. [41] proposed the rule of mixtures (ROM) method to estimate the elastic modulus of an alloy from its composition. In this approach, two limiting assumptions are considered. Under the iso-strain condition (uniform strain in all constituent elements), the alloy modulus is obtained as a volume fraction weighted average of the elemental moduli, which provides the upper bound of the alloy modulus. Conversely, under the iso-stress condition (uniform stress across all constituents), the alloy modulus is calculated as the harmonic mean of the elemental moduli, which gives the lower bound. Mathematically, these can be expressed as
where is the elastic modulus of alloy (could be E, G, or B); and are the modulus and molar volume of the i-th element, respectively; is its atomic fraction; and is the average molar volume of alloy, given by . The values predicted by these two assumptions, therefore, represent the theoretical bounds of the alloy modulus. For metallic glasses, the ROM method has been proven to be a useful method for predicting the elastic modulus [31,32], while the applicability of this method for HEAs remains unknown.
- (2)
- The Johnson method
Recently, Johnson et al. [42] found direct correlations between elastic moduli, strengths, and properties of the electron gas for various alloys, and hence proposed a method to quickly estimate the modulus and strength of HEA. The relation between the bulk modulus B and rs, the local exchange correlation parameter related to the interstitial electron density (i.e., ), can be written as follows [42]:
Johnson et al. [42] also calculated the rs of all metal elements in the periodic table, and thus the rs of the alloy was obtained by the rule-of-mixture. They further assumed Poisson’s ratio ν = 1/3; thus, Young’s modulus, E = 3(1 − 2v)B = B, can be estimated.
The applicability of the two Young’s modulus calculation methods to HEAs is discussed in detail in Section 4.2. The problem of predicting the elastic modulus from the composition is solved, and there is a further need to predict the properties from the elastic modulus. We note that the ideal tensile strength scales with the Young’s modulus for various materials [43,44], i.e.,
here, α is a material constant. Hence, materials with a higher Young’s modulus usually tend to intrinsically possess greater strength. Therefore, in this paper, alloy compositions with high Young’s modulus are selected, which are considered to have high strength.
On the other hand, regarding the ductility of materials, there are also some relations for prediction [37]. For HEAs, Qi et al. [45] found that reducing the valence electron concentration on the one hand causes the Fermi energy level to move down relative to the band structure, resulting in earlier shear instability of the material. On the other hand, it is also possible to increase the density of states (DOS) near the Fermi level, thereby increasing the driving force of the Jahn–Teller distortion. After the Jahn–Teller distortion, the DOS peaks slightly below and above the Fermi level move further away from the Fermi level to reduce energy. In this way, the alloy exhibits intrinsic ductility. In addition, Chan proposed [46] that reducing the VEC in the Nb-based alloy can reduce the Peierls–Nabarro energy barrier, thereby improving the dislocation mobility and improving the ductility of the alloy. Sheikh et al. [38] proved that the criterion based on the VEC could predict the intrinsic ductility, especially for the refractory HEAs. Given the alloy composition, the VEC of the alloy can be obtained according to
where and VECi denote the atomic percentage and the VEC of the ith elements, respectively. Recently, Mak et al. [47] proposed that the VEC criterion for intrinsic ductility indicates that materials are brittle when VEC > 5 and ductile when VEC ≤ 5. Thus, HEAs with low VEC values can be selected and expected to show good plasticity. However, high-VEC HEAs, such as NbMoTaVW (VEC = 5.4), exhibit low fracture strain (less than 5%) [40], further supporting the notion that high VEC values tend to limit ductility.
Moreover, it has been proven that the density of HEAs can be predicted well according to the following equation [48]:
where , , and denote the atomic concentration, mass, and density of the ith elements, respectively.
Equations (2)–(7) present the correlations between the HEA composition and properties. Based on these equations, one could expect an approach to design HEA compositions with excellent properties, such as high modulus (high intrinsic strength), high potential ductility, and low weight, as illustrated in Figure 1. To sum up, the composition design strategy includes three steps:
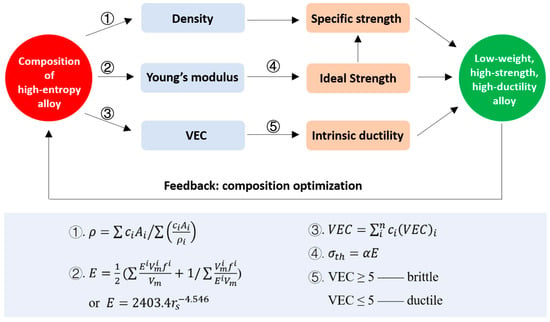
Figure 1.
Illustration of a design strategy for composition of HEAs.
First, select the composition system. We chose the Nb-Mo-Ta-V-W system as an example. The atomic concentrations of the elements are then varied step by step to change the composition systematically.
Second, the elastic modulus, VEC, and density are calculated according to the relevant equations for each composition.
Third, the predicted property maps, such as plots of E vs. VEC and density vs. E, can be drawn, and the specific material composition with the required property can be obtained from the maps. For instance, the HEA with the composition of low VEC and high E is expected to show intrinsically high strength and high ductility, while the alloy composition with high specific modulus can be found in the property map of density vs. E.
3. Experimental Methods
Three refractory HEA ingots with compositions of Al0.5Mo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr, NbTaTiV, and HfNbTaTiZr were prepared via vacuum levitation melting (VLM) and casting. During VLM, the molten liquid alloy was electromagnetically stirred, which enabled the melts to be fully mixed and led to a uniform and accurate composition. Moreover, the alloy was suspended in the crucible in the VLM process; thus, a high-purity alloy can be prepared without contamination. The ingots have dimensions of Ø50 mm × 50 mm, which are large enough for the subsequent measurements of tensile properties and elastic modulus.
Tensile specimens in the shape of a dog bone with gauge dimensions of 3 × 1.7 × 1 mm3 were processed from NbTaTiV and HfNbTaTiZr alloy ingots by an electric spark cutting machine. Figure 2c shows the dimensions and shape of the specimen for tensile testing. Before testing, all specimens were ground and polished to remove surface impurities. Uniaxial tensile testing was performed at room temperature using an Instron 5967 testing machine with a strain rate of 5 × 10−4 s−1. To ensure the reliability and repeatability of the results, at least three specimens were tested for each alloy under the same experimental conditions. A video-based extensometer was used to record the deformation features on the specimen surfaces and to measure the strains. During the tensile tests, the applied load and elongation were continuously recorded. These data were converted into engineering stress–strain curves, from which the yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and total elongation were obtained. The elastic modulus was determined from the linear portion of the stress–strain curve according to Hooke’s law. For the Al0.5Mo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr HEA, no valid tensile data were obtained because the material was too brittle to be tested correctly.
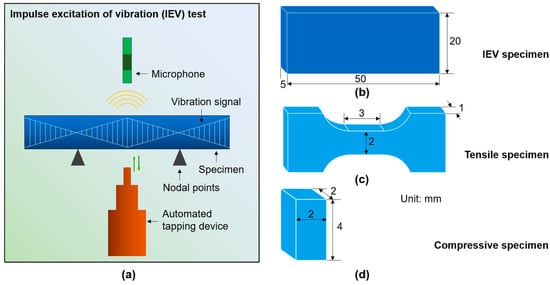
Figure 2.
(a) Sketch of experimental set-up of IEV for testing the elastic moduli. (b–d) Shapes and dimensions of the IEV, tensile, and compression specimens, respectively.
Moreover, the IEV test was also carried out to measure the elastic moduli for the three HEAs. A sketch of the IEV test setup is shown in Figure 2a. In the IEV tests, the recorded quantities included the flexural and torsional resonance frequencies, together with the specimen mass and dimensions. The IEV test measures the elastic properties based on the measurement of the mechanical resonance frequency of a specimen with regular geometry, because the specific mechanical resonance frequency of the material is determined by the elastic modulus, mass, and the specimen geometry. For a rectangular bar specimen, the Young’s modulus (E) and shear modulus (G) are measured based on the flexural and torsional resonance frequencies, respectively, according to the following equations [49]:
Here m, b, L, and t represent the mass, width, length, and thickness of the specimen, respectively; and are the flexural and torsional resonance frequencies, respectively; T1 and R are specimen size dependent correction factors. For Poisson’s ratio, it is calculated based on the measured Young’s modulus and shear modulus, assuming the isotropic elastic behavior of the materials, according to
Rectangular bar specimens with dimensions of 50 mm × 20 mm × 5 mm were processed from the ingots of the three HEAs via wire cutting for IEV tests. Figure 2b illustrates the specimen dimension and shape for IEV testing. According to the ASTM E1876 standard, the IEV test was performed by using the IMCE NV elastic modulus analyzer (RFDA HT1600). It is important to note that Raggio et al. [48] performed IEV tests using seventeen steel specimens and found that the variation of the measured acoustic velocities is less than 1% for compressional wave velocity and 0.2% for shear wave velocity. Since the compressional and shear wave velocities were determined directly by the density and elastic moduli of materials, these results suggest that the errors (variation) for testing elastic moduli by IEV are expected to be rather limited. Owing to the large size of the IEV specimen and the limitation of the casting alloy, one IEV specimen for each HEA was tested.
Finally, for the testing of the designed new HEA, as discussed in Section 4.3, we prepared the alloy ingot using the electric arc melting method under argon protection. The phase composition of the HEA was then characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Co Kα radiation, Bruker D8 DISCOVER A25 model) from 2θ = 20° to 140°. We also performed backscattered electron (BSE) imaging using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to confirm the microstructure of the as-cast alloy. The specimens for XRD and SEM were ground using 2000-grit sandpaper and then polished with diamond paste. The SEM and BSE analyses were carried out using a ZEISS Sigma300 field emission scanning electron microscope under a voltage of 20 kV. To measure the mechanical property, uniaxial compression tests were carried out using an Instron 5967 testing machine. Before compression, the specimen surfaces were carefully ground and polished with a final specimen size of ~2 × 2 × 4 mm3 (as sketched in Figure 2d). The tests were performed at room temperature and a quasi-static strain rate of 5 × 10−4 s−1. At least three specimens were tested to ensure the reproducibility of the results. After compression, the surface morphologies of the deformed specimens were observed using SEM. Moreover, to further characterize the mechanical properties of the new alloy, Vickers hardness testing and nanoindentation were performed on the polished specimen surface. For the Vickers hardness test, the load for all the specimen positions was 200 g and held for 5 s. A nanoindentation test was conducted using a Bruker Hysitron TI 980 nanoindenter.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Elastic Modulus Experimentally Measured by Tension and IEV
The engineering stress–strain curves of NbTaTiV and HfNbTaTiZr HEAs are shown in Figure 3. Both HEAs exhibit good tensile plasticity, in contrast to many brittle refractory HEAs, such as the Al0.5Mo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr HEA, which broke abnormally and catastrophically under tensile loading, as described above. The uniform elongation (εu) and total elongation (εt) were measured to be εu = 12.1 ± 0.3% and εt = 40.1 ± 3.3% for NbTaTiV HEA, and εu = 2.8 ± 0.6% and εt = 33.6 ± 1.8% for HfNbTaTiZr HEA. Obviously, the quaternary alloy shows better plastic deformation ability than the quinary alloy.
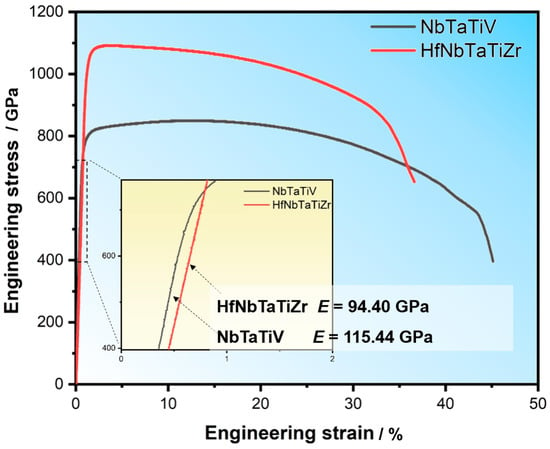
Figure 3.
Typical tensile engineering stress–strain curves of two HEAs. The inset figure displays the enlarged parts of the curves in the elastic stage. The values of Young’s modulus (E) shown in the figure are the measured values for the individual typical specimens, not the average values.
However, the strengths of NbTaTiV are a bit lower than those of HfNbTaTiZr. The former has a yield strength (σy) of 770 ± 16 MPa and an ultimate tensile strength (σuts) of 835 ± 11 MPa, while for HfNbTaTiZr, σy = 992 ± 21 MPa, σuts = 1064 ± 20 MPa. The inset figure in Figure 3 shows enlarged parts of the elastic stage of the stress–strain curves. According to Hooke’s law, the values of Young’s modulus (E) of NbTaTiV and HfNbTaTiZr HEAs, measured using uniaxial tension tests, are 113.66 ± 6.09 GPa and 94.53 ± 1.69 GPa, respectively.
The elastic properties for the three HEAs were also measured using IEV tests. The results are listed in Table 1, in which the Young’s modulus measured by tension was also included. Comparing the E values for the same alloy obtained with the two different methods, it can be found that the value measured using the tension method is a little lower than that determined by IEV, namely, 3.1% lower for NbTaTiV and 0.7% lower for HfNbTaTiZr. The small difference in E between the two methods is consistent with the observations in steels [49] and possibly due to the loading rate effect, i.e., quasi-static loading for tension vs. dynamic loading for IEV.

Table 1.
Elastic properties of the studied three HEAs experimentally measured using uniaxial tension and IEV tests.
In addition to Young’s modulus, the shear modulus (G) and Poisson’s ratio (ν) were also measured using IEV tests. The shear moduli of Al0.5Mo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr, NbTaTiV, and HfNbTaTiZr are 43.98 GPa, 42.80 GPa, and 34.98 GPa, respectively, and the Poisson’s ratios are 0.352, 0.371, and 0.362, respectively. All the measured values of elastic properties are listed in Table 1.
4.2. Prediction of Elastic Modulus from Composition
To further study the elastic properties of HEAs, we collected a lot of modulus data of about 130 HEAs with different compositions from published papers (e.g., [50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60]), including both experimentally measured data and computational simulation values. It is important to note that for Young’s modulus measured by tension or compression, to guarantee the validity of measurement, only data measured in the studies where the strains were accurately determined using an extensometer or a strain gauge were collected.
Based on the compositions of the studied HEAs in this manuscript as well as those in the literature, we estimated the E values for the two assumptions (i.e., Estress for iso-stress and Estrain for iso-strain) according to the ROM of Equations (2) and (3). The specific values are listed in Table 2 and Table 3. To more vividly observe the predictions, we also plotted the estimated E values vs. experimentally measured E values (Eexp) in Figure 4a,b and the estimated E vs. computer-simulated values (Ecom) in Figure 4c. It can be found that the Young’s modulus values of HEAs measured using various test methods are within the range of the estimated values of the ROM and are closer to the lower limits estimated by the assumption of iso-stress (Estress). However, for the computer-simulated E values, the estimation based on the assumption of iso-strain (Estrain) seems to be more proper to predict the Ecom, i.e., the Ecom is closer to the upper limit.

Table 2.
Young’s modulus (E), shear modulus (G), and bulk modulus (B) of various HEAs experimentally measured using static tests and dynamic tests in references, as well as the estimated E values according to Equations (2) and (3).

Table 3.
Elastic modulus by computer simulation of various HEAs in the literature, as well as the estimated E according to Equations (2) and (3).
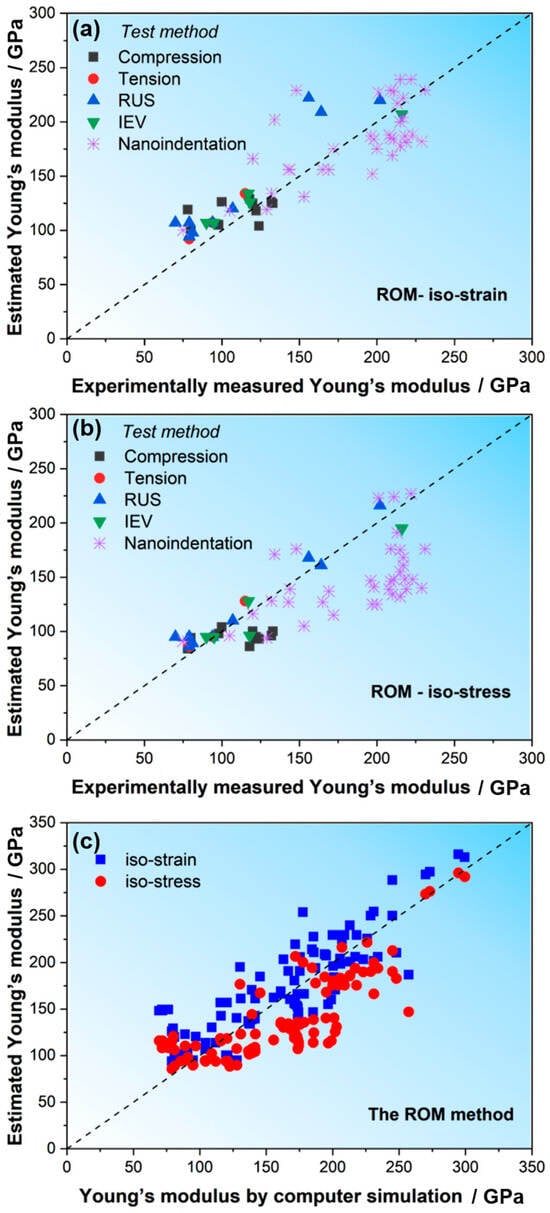
Figure 4.
E estimated from ROM of HEAs versus experimental and computational simulations: (a) Estrain vs. Eexp, (b) Estress vs. Eexp, (c) Ecom vs. EROM.
The difference between experiments and simulations may originate from several factors. While defects in material microstructures are a major cause, other factors, such as microstructural heterogeneities and stresses induced by the solidification process, can also significantly influence the observed properties. In simulations, the material is often assumed to be defect-free or to have a controlled microstructure, leading to a closer match with the upper bound of elastic properties. However, real materials may exhibit variations in microstructure and stresses, which can affect the measured properties, particularly in localized tests such as nanoindentation. Nanoindentation, due to its localized nature, is especially sensitive to such microstructural variations and may show different results compared to bulk tests like uniaxial tension or IEV tests. This can also be illustrated by the E values measured by nanoindentation, which are closer to the upper limit of Estrain, as shown in Figure 4a. This is in contrast to the E values measured using tension and IEV tests, where large specimens were usually used. As discussed above, during the nanoindentation, the volume of the materials deformed is very small and could be much smaller than the size of a grain; hence, the results of the nanoindentation are more sensitive to the local microstructure under the indenter and are less likely to be affected by defects, leading to scatter and higher values than the data obtained using other methods.
Since there is a discrepancy between the E values estimated using Equations (2) and (3) and the experimental or simulation data, we took the averages of the above two assumptions and calculated the average value of ROM using the following equation:
The comparisons between the calculated average modulus values (Eavg) according to Equation (11) and the experimental data or the simulation modulus vales are presented in Figure 5a,b. Apparently, the average modulus value of ROM can better estimate the Young’s modulus value of HEAs for both experiments and simulations.
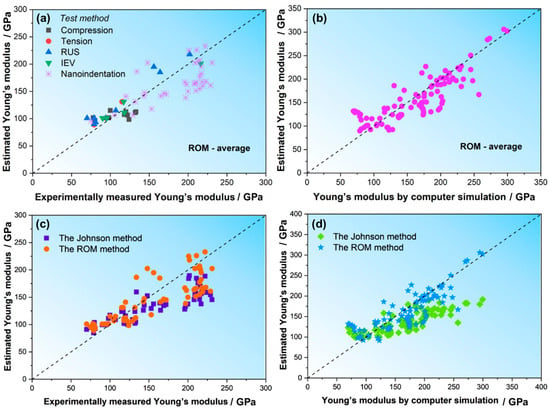
Figure 5.
(a,b) Comparison between the E estimated by the average value of ROM and the experimental and simulated values. (c,d) Comparison of the experimental E values and computer-simulated E values with the E values estimated using the Johnson method and the ROM method.
Furthermore, we calculated the Young’s modulus of the above ~130 HEAs using the Johnson method (Equation (4)) and compared it with the experimental and calculated E values in the literature. The results are shown in Figure 5c,d. For comparison, the predicted E calculated using the above ROM method is also plotted. Apparently, the Johnson method predicts the E values well when the E is lower than ~150 GPa, while for HEAs with higher E, the predicted E values are obviously smaller than the experimental or simulated values. In contrast, the prediction of Eavg using the ROM method is better.
4.3. Experimental Verification of the Strategy
The results above demonstrate the effectiveness of the ROM method for predicting the Young’s modulus for the composition design of HEAs, which facilitates the application of the present composition design strategy discussed in Section 2. To further verify this strategy experimentally, we designed new alloys using this method and measured the properties of the designed alloys using experiments. NbMoTaVW alloy has excellent high-temperature strength, especially above 1000 °C, but it is prone to brittle fracture and has less than 5% compressive plasticity at room temperature [40]. In order to improve the mechanical properties, we selected this alloy system and used the composition design strategy to achieve property optimization.
We adjusted the composition of the Nb-Mo-Ta-V-W system by varying the atomic concentrations of each element in the range from 2.5 to 40 at.% with a step size of 2.5%. We then calculated the VEC, density, and E according to Equations (6)–(8), respectively. A total of 38,326 compositions were calculated, and the maps of predicted properties can finally be plotted, as shown in Figure 6a,b. The predicted variation trend for E against VEC is a trade-off, which is consistent with the strength–ductility trade-off for metallic materials [96]. The goal for this composition design is to enhance the intrinsic ductility but reduce the loss of strength or elastic modulus. Thus, we selected the alloy composition with the smallest VEC and also a relatively high E. According to Figure 6a, a new HEA with a composition of Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 (at.%) was finally designed. The further property map in Figure 6b illustrates that the Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 alloy is expected to have a lower density than the equimolar NbMoTaVW HEA. We then experimentally prepared the alloy with the composition of Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 (at.%) using the electric arc melting method, characterized the microstructure using XRD and SEM, and measured the mechanical properties using uniaxial compression tests.
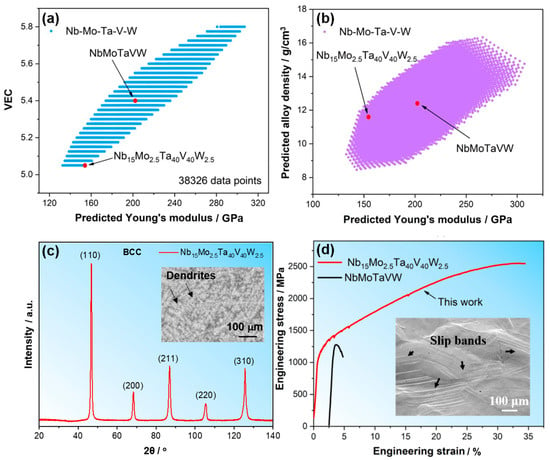
Figure 6.
(a,b) Predicted property maps for Nb-Mo-Ta-V-W HEA system: the predicted VEC vs. the predicted Young’s modulus (a) and the predicted density vs. the predicted Young’s modulus (b). (c,d) Experimental results of the newly designed Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 refractory HEA, including the XRD profile (c), the BSE image of microstructure (inset of (c)), the typical compressive engineering stress–strain curves (d) of Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 and NbMoTaVW [40] HEAs, and the SEM image on the surface of a deformed specimen of Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 (inset of (d)).
The experimental results are shown in Figure 6c,d. The XRD profile suggests that the as-cast Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 alloy is a single-phase BCC structure. The BSE image inset of Figure 6c reveals a dendritic microstructure in this alloy, which is the typical microstructure feature of the as-cast alloy in BCC HEA and consistent with other ones [5,17,40]. The grain size for the new alloy is measured to be ~240 μm, which is a little larger than the equimolar NbMoTaVW alloy (~200 μm) prepared with a similar casting method [40]. The compressive engineering stress–strain curves of both the present new alloy and the equimolar NbMoTaVW alloy in the literature [40] are displayed in Figure 6d for comparison. Accordingly, the yield strength of Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 is 1115 ± 18 MPa, slightly lower than that of the as-cast equimolar NbMoTaVW alloy (~1246 MPa), which is consistent with the predicted decreasing trend of elastic modulus. However, the compressive fracture strain (plasticity) of the new Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 alloy is greatly improved to 35.7 ± 0.9%, much higher than ~2% for NbMoTaVW HEA. This demonstrates that by reducing VEC, the intrinsic shear plastic deformation ability is effectively enhanced. In addition, the initiation of brittle cracking is severely delayed, and many slip lines can be observed on the specimen surface (see the inset figure in Figure 6d). The dislocation slip that dominates the work-hardening ability of the material is fully developed, and a very high compressive strength of 2550 ± 75 MPa was observed. These results indicate that new compositions of HEAs with better properties can be effectively designed using the present composition design strategy.
To further confirm the promising properties, the Vickers hardness and nanoindentation tests were performed for the new HEA. The results suggest that the Vickers hardness is 4.13 ± 0.09 GPa and the nanohardness is 8.90 ± 0.91 GPa. The difference in hardness values between Vickers hardness and nanohardness originates from the indentation size effect [97]. The volume beneath the indenter is much smaller in nanoindentation than that in Vickers hardness, which significantly limits the dislocation activity and thus increases the difficulty for deformation. Nevertheless, the high hardness values suggest a high resistance to plastic deformation in the present new HEA. Moreover, it is found that the ratio between Vickers hardness and the compressive yield strength for the present HEA is 3.65, which is much higher than 3, usually for brittle BCC HEA, but agrees with ductile HEAs [98], indirectly implying the ductile nature of the present new alloy.
4.4. Limitations and Further Discussion
The success of the current strategy for designing new RHEAs with high ductility was verified by experiments. Thereafter, new RHEA compositions with desired properties, such as high elastic modulus, high ductility, and low densities, can thus be discovered from the property map. However, it should be noted that the present composition design strategy has limitations.
First, the yield strength of RHEAs has not yet been predicted or designed. The present strategy estimates the elastic modulus of the HEAs with the ROM and relates the Young’s modulus to the ideal tensile strength, which provides a ceiling of strength for perfect materials, but is far from the strength of real materials. A recent study by Maresca and Curtin et al. [99,100,101] provided a solution for predicting the yield strength of BCC HEAs. The calculation was based on edge dislocation strengthening, and yield strength at finite temperature (T) and finite strain rate () are given below:
where is the zero temperature strength; is the zero temperature energy barrier; = 104 s−1 is a reference strain rate; is the Boltzmann constant. and can be expressed as follows:
Here, α = 1/12 is a line-tension coefficient, G and are the shear modulus and Poisson’s ratio of the alloy, b is the Burgers vector of edge dislocation, cn is the atomic concentration for the nth element, and is the elemental misfit volumes. This approach has been proven to be effective for predicting the yield strengths of BCC HEAs. By combining Equation (12) with the present composition design strategy, it is expected to achieve the ability to design RHEAs with high strength and ductility. However, correctly estimating the values of parameters in Equations (12)–(14) and the scope of application of these calculations requires further investigations.
Second, the effect of microstructure on mechanical properties has not been considered in the present strategy. Actually, the microstructures of crystalline metallic materials, including grain size, phase structures, etc., have significant impacts on strength and ductility. This limits the direct prediction of mechanical properties, which is one of the challenges in this field. To include the microstructure effect, the quantitative relations of microstructure vs. properties and processing conditions vs. microstructure formation should be determined and included in the material design strategy. This requires long-term work and is out of the scope of the present study.
Although there are some limitations, the present strategy provides good estimates on the elastic modulus and VEC of RHEAs and suggests the usage of a property map to find optimal compositions for desired properties. Thus, a direction for discovering light, strong, and intrinsically ductile RHEA compositions that could deform plastically rather than fracture in a brittle manner could be indicated by the present strategy. It is expected that by combining the present strategy with additional theoretical efforts (e.g., thermo-kinetics predictions of microstructures [12,13] and quantitative predictions of mechanical properties [99]) and computational studies (e.g., machine learning [29]), more efficient composition optimization and design of RHEAs will be achieved.
5. Conclusions
In this manuscript, a composition design method for HEAs is proposed. The following conclusions can be drawn:
- (1)
- The Young’s modulus of the NbTaTiV and HfNbTaTiZr HEAs was measured by both the tensile test and IEV test. No significant differences were found between the two test methods. The shear modulus and Poisson’s ratio were also measured with the IEV test for these two alloys and the Al0.5Mo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr HEA.
- (2)
- According to the ROM, the elastic modulus values of 132 HEAs were estimated based on their compositions. The estimated elastic modulus was compared with the experimental or simulated values in literature and this study, and the results indicate that the average values of the ROM can estimate the elastic modulus of HEAs.
- (3)
- A composition design strategy is proposed based on the correlations between compositions and properties, including Young’s modulus, VEC, density, and atomic size difference. Property maps can be predicted and plotted, and the optimal composition with desired properties can be reached.
- (4)
- According to the composition design strategy, a new HEA with the composition of Nb15Mo2.5Ta40V40W2.5 was designed. Further tests of the as-cast new alloy, including mechanical property measurement and structure characterization, suggest that this HEA has a BCC single phase and much higher compressive strength (2550 ± 75 MPa) and plasticity (35.7 ± 0.9%) than the equimolar NbMoTaVW alloy. The experimental results validate the rationality of the design strategy.
This study justified the applicability of the ROM for predicting the elastic modulus of HEAs and further proposed a composition design strategy to estimate alloy properties directly from composition. This approach provides a practical framework for the design of HEAs with tailored mechanical properties. Nonetheless, the underlying physical mechanisms governing the relationships between composition, elastic modulus, and ductility are not yet fully understood, and further investigations are needed. Future work could focus on exploring these mechanisms through combined computational modeling and experimental studies, as well as extending the design strategy to other HEA systems. Moreover, the methodology and findings presented here can be potentially applied to the development of high-performance alloys for real engineering applications, such as structural components in extreme environments, where both high strength and sufficient plasticity are required.
Author Contributions
F.R.: investigation, visualization, and writing—original draft; Y.H.: investigation and writing—review and editing; R.Q.: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, and supervision; F.L.: conceptualization and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52271072, 52571100, 52431002, and 52130110) and High-level Talent Research Start-up Project Funding of Henan Academy of Sciences (Project No. 242017126).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52271072, 52571100, 52431002, and 52130110) and High-level Talent Research Start-up Project Funding of Henan Academy of Sciences (Project No. 242017126). We thank Chuanyun Wang for the assistance with the IEV test and the helpful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest and also declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the study reported in this paper.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HEAs | High-entropy alloys. |
| MPEAs | Multiple-principal element alloys. |
| CALPHAD | Calculation of phase diagram. |
| BCC | Body-centered cubic. |
| VEC | Valence electron concentration. |
| RHEAs | Refractory high-entropy alloys. |
| IEV | Impulse excitation of vibration. |
| ROM | Rule of mixture. |
| DOS | Density of states. |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction. |
| BSE | Backscattered electron. |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope. |
| Eavg | Average modulus. |
References
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A Critical Review of High Entropy Alloys and Related Concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-Entropy Alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, B. Review on Preparation Technology and Properties of Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Materials 2022, 15, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Maresca, F.; Feng, R.; Chou, Y.; Ungar, T.; Widom, M.; An, K.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Chou, Y.-C.; Liaw, P.K.; et al. Strength Can Be Controlled by Edge Dislocations in Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Wang, X.D.; Lu, J.T.; Qu, R.T.; Zhang, Z.F. Room-Temperature Mechanical Properties of V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 High-Entropy Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1800028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.J.; Qu, R.T.; Zhang, Z.F. Remarkably High Fracture Toughness of HfNbTaTiZr Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Wu, S.; Volkert, C.A.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F. Significantly Improved Strength and Plasticity of a Refractory High-Entropy Alloy at Small Length Scale. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 867, 144729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural Development in Equiatomic Multicomponent Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wu, C.; Cheng, B.; Xu, Z. The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys with High Plasticity. Materials 2018, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, K.; Kou, Z.; Gong, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, Q.; Sun, H.; Liu, P.; Qu, R.; Hu, L.; et al. Synergistic Grain Boundary Engineering for Achieving Strength-Ductility Balance in Ultrafine-Grained High-Cr-Bearing Multicomponent Alloys. Int. J. Plast. 2024, 177, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Niu, K.; Liu, F. Generalized Stability Criterion for Exploiting Optimized Mechanical Properties by a General Correlation between Phase Transformations and Plastic Deformations. Acta Mater. 2020, 201, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Song, S.; Du, J.; Peng, H.; Ding, Z.; Hou, H.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F. Thermo-Kinetic Connectivity by Integrating Thermo-Kinetic Correlation and Generalized Stability. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, H.; Huang, L.; Liu, F. Materials Design by Generalized Stability. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 147, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, P.D.; Huang, L.K.; Song, K.X.; Qin, G.; Liu, F. High-Density Metastable Annealing Twin Boundaries-Induced Extraordinary Strain Hardening in Ultrafine-Grained High-Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2025, 295, 121205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kou, Z.; Qu, R.; Song, W.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C.; Song, K.; et al. Accelerating Matrix/Boundary Precipitations to Explore High-Strength and High-Ductile Co34Cr32Ni27Al3.5Ti3.5 Multicomponent Alloys through Hot Extrusion and Annealing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 143, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Xing, Y.; Wu, P.; Qu, R.; Song, K.; Liu, F. Super Tensile Ductility in an As-Cast TiVNbTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2024, 34, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Qu, R.; Ren, F.; Guo, C.; Xing, Y.; Ma, H.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, K.; Liu, F. New Lightweight and Super-Hard Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Developed by a High-Throughput Method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Li, A.; Mao, S.; Yang, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Shao, R.; Jiang, C.; et al. Negative Mixing Enthalpy Solid Solutions Deliver High Strength and Ductility. Nature 2024, 625, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Qu, R.; Ma, H.; Song, K.; Liu, F. Simultaneously Enhanced Strength and Fracture Resistance in HfNbTaTiZr Refractory High-Entropy Alloy at Higher Strain Rate. Acta Metall. Sin. 2025, 38, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Qu, R.; Liu, F. Property Maps of Single-Phase Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 48, 113444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Nucleation/Growth Design by Thermo-Kinetic Partition. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 155, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, S.; Fan, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Liaw, P.K. CALPHAD-Aided Design for Superior Thermal Stability and Mechanical Behavior in a TiZrHfNb Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xie, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, T. Effect of Ti Content on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of CoCrFeNiTix High Entropy Alloys Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials 2020, 13, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Ding, X.; Sun, J. Rapid Design and Screen High Strength U-Based High-Entropy Alloys from First-Principles Calculations. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 179, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Q.; Ding, X.; Sun, J. First-Principles Design of High Strength Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 3420–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xue, D.; Bai, Y.; Antonov, S.; Dai, L.; Lookman, T.; Su, Y. Machine Learning Assisted Design of High Entropy Alloys with Desired Property. Acta Mater. 2019, 170, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimenko, D.; Stepanov, N.; Li, J.; Fang, Q.; Zherebtsov, S. Machine Learning-Based Strength Prediction for Refractory High-Entropy Alloys of the Al-Cr-Nb-Ti-V-Zr System. Materials 2021, 14, 7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Pei, Z. Machine Learning for High-Entropy Alloys: Progress, Challenges and Opportunities. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 131, 101018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xue, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Gao, S.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; et al. Machine-Learning Design of Ductile FeNiCoAlTa Alloys with High Strength. Nature 2025, 643, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H. The Elastic Properties, Elastic Models and Elastic Perspectives of Metallic Glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 487–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, R.F.; Qu, R.T.; Zhang, Z.F. Precisely Predicting and Designing the Elasticity of Metallic Glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 203513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.F. Strengthening and Toughening Metallic Glasses: The Elastic Perspectives and Opportunities. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 163505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.T.; Zhang, Z.F. A Universal Fracture Criterion for High-Strength Materials. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Eckert, J. Unified Tensile Fracture Criterion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 094301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Liu, Z.Q.; Qu, R.T.; Zhang, Z.F. Designing Metallic Glasses with Optimal Combinations of Glass-Forming Ability and Mechanical Properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 67, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, S.F. XCII. Relations between the Elastic Moduli and the Plastic Properties of Polycrystalline Pure Metals. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1954, 45, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Shafeie, S.; Hu, Q.; Ahlstrom, J.; Persson, C.; Vesely, J.; Zyka, J.; Klement, U.; Guo, S. Alloy Design for Intrinsically Ductile Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 164902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Prediction of High-Entropy Stabilized Solid-Solution in Multi-Component Alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical Properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Greer, A.L. Correlations for Predicting Plasticity or Brittleness of Metallic Glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 434, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.D.; Singh, P.; Smirnov, A.V.; Argibay, N. Universal Maximum Strength of Solid Metals and Alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 130, 166101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, N.H. The Theoretical Strength of Solids. J. Mater. Sci. 1972, 7, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasako, N.; Jahnátek, M.; Asahi, R.; Hafner, J. Anomalies in the Response of V, Nb, and Ta to Tensile and Shear Loading: Ab Initio Density Functional Theory Calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 094108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Chrzan, D.C. Tuning Ideal Tensile Strengths and Intrinsic Ductility of Bcc Refractory Alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 115503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.S. A Computational Approach to Designing Ductile Nb-Ti-Cr-Al Solid-Solution Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 2475–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, E.; Yin, B.; Curtin, W.A. A Ductility Criterion for Bcc High Entropy Alloys. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2021, 152, 104389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.W.; Qiao, J.W.; Hawk, J.A.; Zhou, H.F.; Chen, M.W.; Gao, M.C. Mechanical Properties of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys: Experiments and Modeling. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggio, L.I.; Etcheverry, J.; Sánchez, G.; Bonadeo, N. Error Analysis of the Impulse Excitation of Vibration Measurement of Acoustic Velocities in Steel Samples. Phys. Procedia 2010, 3, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Senkov, O.N.; Jensen, J.K.; Pilchak, A.L.; Miracle, D.B.; Fraser, H.L. Compositional Variation Effects on the Microstructure and Properties of a Refractory High-Entropy Superalloy AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr. Mater. Des. 2018, 139, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Chaput, K.J.; Couzinie, J.-P. Development and Exploration of Refractory High Entropy Alloys—A Review. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3092–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C. Mechanical Properties of Low-Density, Refractory Multi-Principal Element Alloys of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr System. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Guel, I.; Rodríguez-González, C.A.; Hernández-Paz, J.; Jimenez, O.; Santos-Beltran, A.; Martínez-Sánchez, R.; Romero-Romero, M.; Gómez-Esparza, C.D. Phase Composition and Its Effect on the Mechanical Performance of an AlCoCrFeNiTi High-Entropy Alloy. Mater. Lett. 2022, 316, 132035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, M.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, M.; Chakradhar, R.P.; Panigrahi, B.B. Effect of Minute Element Addition on the Oxidation Resistance of FeCoCrNiAl and FeCoCrNi2Al High Entropy Alloy. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, F.; Yang, X.; Sheng, R.; Qiao, J.; Liaw, P.K.; Li, M.; Jiang, L.; Chen, S.; et al. Effect of Zr Addition on the Local Structure and Mechanical Properties of Ti–Ta–Nb–Zr Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 4428–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Yan, L.; Shu-nan, C.; Yi, L.; Gang, J.; Hai-Dong, C.; Yun-Jie, J.; Chang-Jiu, L.; Cheng-Xin, L. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Lightweight Al CrNbTiV(x = 0.2, 0.5, 0.8) Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 104, 105784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Babuska, T.; Krick, B.; Balasubramanian, G. Machine Learned Feature Identification for Predicting Phase and Young’s Modulus of Low-, Medium- and High-Entropy Alloys. Scr. Mater. 2020, 185, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönecker, S.; Li, X.; Wei, D.; Nozaki, S.; Kato, H.; Vitos, L.; Li, X. Harnessing Elastic Anisotropy to Achieve Low-Modulus Refractory High-Entropy Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Des. 2022, 215, 110430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Delczeg, L.; Chen, N.; Varga, L.K.; Shen, J.; Vitos, L. Structural Stability of NiCoFeCrAlx High-Entropy Alloy from Ab Initio Theory. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 085128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Varga, L.K.; Chen, N.; Delczeg, L.; Vitos, L. Ab Initio Investigation of High-Entropy Alloys of 3d Elements. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 075144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C. Effect of Aluminum on the Microstructure and Properties of Two Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2014, 68, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilensten, L.; Couzinié, J.-P.; Bourgon, J.; Perrière, L.; Dirras, G.; Prima, F.; Guillot, I. Design and Tensile Properties of a Bcc Ti-Rich High-Entropy Alloy with Transformation-Induced Plasticity. Mater. Res. Lett. 2017, 5, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglund, A.; Koehler, M.; Catoor, D.; George, E.P.; Keppens, V. Polycrystalline Elastic Moduli of a High-Entropy Alloy at Cryogenic Temperatures. Intermetallics 2015, 58, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirras, G.; Lilensten, L.; Djemia, P.; Laurent-Brocq, M.; Tingaud, D.; Couzinié, J.-P.; Perrière, L.; Chauveau, T.; Guillot, I. Elastic and Plastic Properties of As-Cast Equimolar TiHfZrTaNb High-Entropy Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 654, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.X.; Musico, B.L.; Lu, Z.Z.; Xu, L.B.; Lei, Z.F.; Keppens, V.; Xu, H.X.; Nieh, T.G. Evaluating Elastic Properties of a Body-Centered Cubic NbHfZrTi High-Entropy Alloy—A Direct Comparison between Experiments and Ab Initio Calculations. Intermetallics 2019, 109, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Chen, N.; Zhao, S.F.; Fan, L.W.; Yang, G.N.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. Effect of Ti Additions on Mechanical Properties of NbMoTaW and VNbMoTaW Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Intermetallics 2017, 84, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcik, I.; Cizek, J.; Zapletal, J.; Kovacova, Z.; Vesely, J.; Minarik, P.; Kitzmantel, M.; Neubauer, E.; Dlouhy, I. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ni1,5Co1,5CrFeTi0,5 High Entropy Alloy Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Gadaud, P.; Perrière, L.; Guillot, I.; Couzinié, J.P. Temperature Dependence of Elastic Moduli in a Refractory HfNbTaTiZr High-Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 799, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.K.; Li, Y.T.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, M.; Ye, J.Z.; Qiu, X.L.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Y.X. Effect of Bias Voltage on the Structure and Properties of CuNiTiNbCr Dual-Phase High Entropy Alloy Films. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 931, 167371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiao, Z.B.; Baker, I. A Comparative Study on Microstructure, Nanomechanical and Corrosion Behaviors of AlCoCuFeNi High Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting and Laser Metal Deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 131, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcikova-Gouvea, L.; Moravcik, I.; Omasta, M.; Veselý, J.; Cizek, J.; Minárik, P.; Cupera, J.; Záděra, A.; Jan, V.; Dlouhy, I. High-Strength Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti High-Entropy Alloy Produced by Powder Metallurgy and Casting: A Comparison of Microstructures, Mechanical and Tribological Properties. Mater. Charact. 2020, 159, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Kong, T.; Ryu, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Superior Mechanical Properties and Strengthening Mechanisms of Lightweight AlxCrNbVMo Refractory High-Entropy Alloys (x = 0, 0.5, 1.0) Fabricated by the Powder Metallurgy Process. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 69, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Kong, T.; Dan, N.H.; Phuong, D.D.; Ryu, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Effect of Boron Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory Al0.1CrNbVMo High-Entropy Alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 100, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachani, S.K.; Wang, C.-J.; Lou, B.-S.; Chang, L.-C.; Lee, J.-W. Microstructural Characterization, Mechanical Property and Corrosion Behavior of VNbMoTaWAl Refractory High Entropy Alloy Coatings: Effect of Al Content. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 403, 126351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Fan, J.; Yu, P.; Li, G. Anomalous Microstructure and Excellent Mechanical Behaviors of (CoCrFeNi) Cr Al High-Entropy Alloy Induced by Cr and Al Addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 752, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, L.; Anupam, A.; Karthick, G.; Berndt, C.C.; Ang, A.S.M.; Narayana Murty, S.V.S.; Fabijanic, D.; Murty, B.S.; Kottada, R.S. Strengthening Mechanisms in CrMoNbTiW Refractory High Entropy Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 819, 141503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Scales, R.J.; Li, B.-S.; Goode, M.; Young, B.A.; Hu, J.; Wilkinson, A.J.; Armstrong, D.E.J. Controlling Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-V-Cr-Nb-Ta Refractory High Entropy Alloys through Heat Treatments. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 932, 167651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolskiy, A.V.; Tabachnikova, E.D.; Voloschuk, V.V.; Gorban, V.F.; Krapivka, N.A.; Firstov, S.A. Mechanical Properties and Thermally Activated Plasticity of the Ti30Zr25Hf15Nb20Ta10 High Entropy Alloy at Temperatures 4.2–350 K. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.-B.; Xu, C.-H.; Wang, T.-L.; Feng, C.-S.; Khan, M.A.; Yasin, G. Oxidation Influences on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of W–Nb–Mo–Ta–V–O Refractory High-Entropy Alloy Films. Vacuum 2023, 207, 111586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalali, D.G.; Antharam, S.; Hasan, M.; Karthik, P.S.; Phani, P.S.; Bhanu Sankara Rao, K.; Rajulapati, K.V. On the Origins of Ultra-High Hardness and Strain Gradient Plasticity in Multi-Phase Nanocrystalline MoNbTaTiW Based Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 812, 141098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, T. An Ab Initio and Experimental Studies of the Structure, Mechanical Parameters and State Density on the Refractory High-Entropy Alloy Systems. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Ni, X.; Tian, F.; Varga, L.K.; Vitos, L. Ab Initio Study of Alx MoNbTiV High-Entropy Alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2015, 27, 075401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Tian, F.; Wang, Y. Elastic and Thermal Properties of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys from First-Principles Calculations. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2017, 128, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Chen, S.-M.; Naihua, N.; Zhou, J.; Hu, Q.-M.; Sun, Z. Structural Stability and Mechanical Properties of B2 Ordered Refractory AlNbTiVZr High Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 886, 161289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, B.; Yan, M.; Fu, Y. A Theoretical Study of the Stability, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of AlNiCuCo Equimolar High Entropy Alloy. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, G. Predicting Mechanical Properties of High Entropy Alloys with Face Centered Cubic Structure from First Principles Calculations. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaddach, A.J.; Niu, C.; Koch, C.C.; Irving, D.L. Mechanical Properties and Stacking Fault Energies of NiFeCrCoMn High-Entropy Alloy. JOM 2013, 65, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.; Zhang, J.; Xin, G.X.; Xie, L.; Yang, L.C.; Peng, Q. Tensile Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiTiAl High Entropy Alloy via Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Intermetallics 2022, 142, 107444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Varga, L.K.; Vitos, L. Predicting Single Phase CrMoWX High Entropy Alloys from Empirical Relations in Combination with First-Principles Calculations. Intermetallics 2017, 83, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazakas, É.; Zadorozhnyy, V.; Varga, L.K.; Inoue, A.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V.; Tian, F.; Vitos, L. Experimental and Theoretical Study of Ti20Zr20Hf20Nb20X20 (X = V or Cr) Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 47, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Bai, L.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Influence of Alloying Elements on Mechanical and Electronic Properties of NbMoTaWX (X = Cr, Zr, V, Hf and Re) Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Intermetallics 2020, 126, 106928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiong, K.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y. An Ambient Ductile TiHfVNbTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloy: Cold Rolling, Mechanical Properties, Lattice Distortion, and First-Principles Prediction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 856, 144046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.L.; Bai, L.H.; Tong, Y.G.; Deng, D.Y.; Liang, X.B.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, Y.X. First-Principle Calculation Investigation of NbMoTaW Based Refractory High Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 827, 153963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Hu, Y.; Liang, X.; Tong, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Titanium Alloying Enhancement of Mechanical Properties of NbTaMoW Refractory High-Entropy Alloy: First-Principles and Experiments Perspective. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 157542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Liu, Y.; Min, L.; Lai, Z.; Han, T.; Yang, D.; Zhu, J. Alloying Effect on Phase Stability, Elastic and Thermodynamic Properties of Nb-Ti-V-Zr High Entropy Alloy. Intermetallics 2018, 101, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K. The Future of Metals. Science 2010, 328, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharr, G.M.; Herbert, E.G.; Gao, Y. The Indentation Size Effect: A Critical Examination of Experimental Observations and Mechanistic Interpretations. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2010, 40, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Qu, R.; Zhang, Z. Relation between strength and hardness of high-entropy alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. 2021, 34, 1461–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, F.; Curtin, W.A. Mechanistic Origin of High Strength in Refractory BCC High Entropy Alloys up to 1900K. Acta Mater. 2020, 182, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Maresca, F.; Curtin, W.A. Vanadium Is an Optimal Element for Strengthening in Both Fcc and Bcc High-Entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Baruffi, C.; De Luca, A.; Leinenbach, C.; Curtin, W.A. Theory-Guided Design of High-Strength, High-Melting Point, Ductile, Low-Density, Single-Phase BCC High Entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2022, 237, 118132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).