Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of P92 Main Steam Pipelines After Long-Term Service
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Experimental Procedures
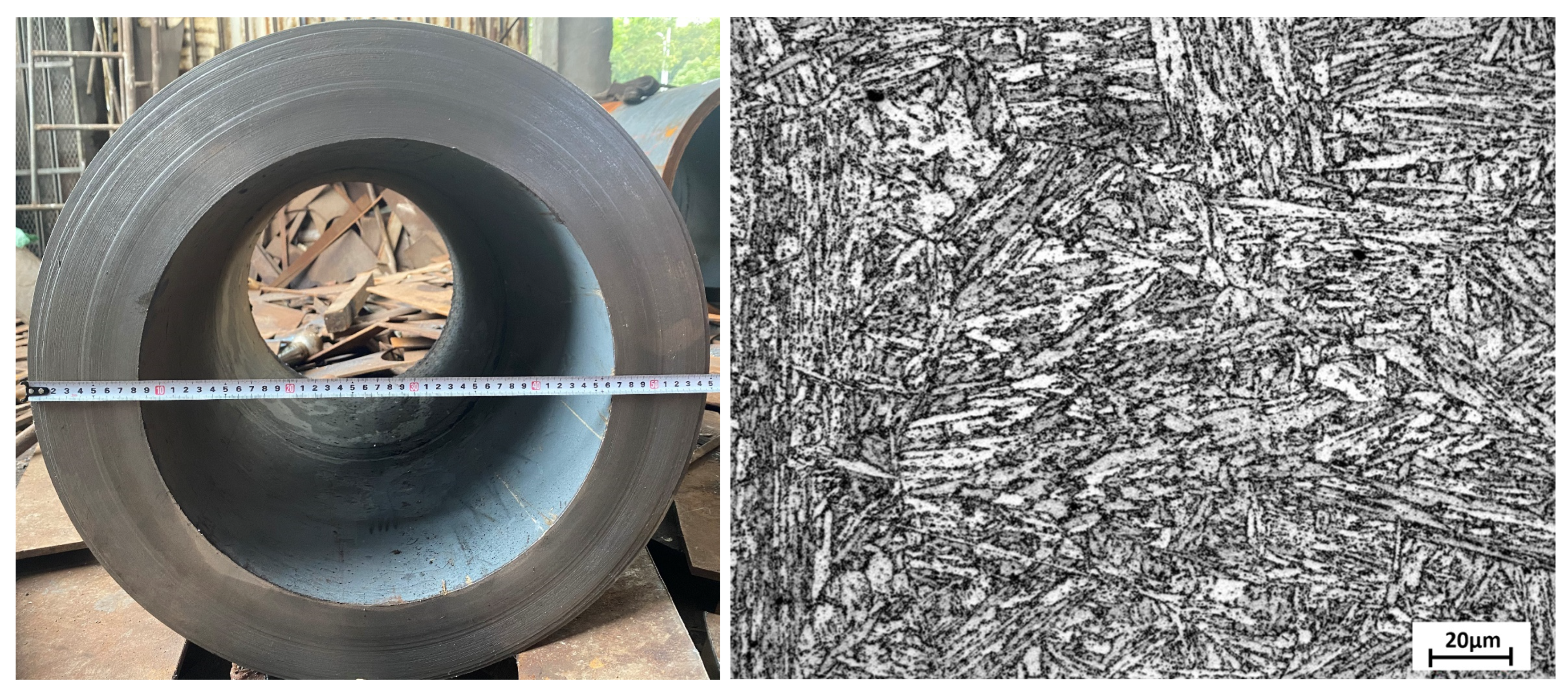
2.1. Material
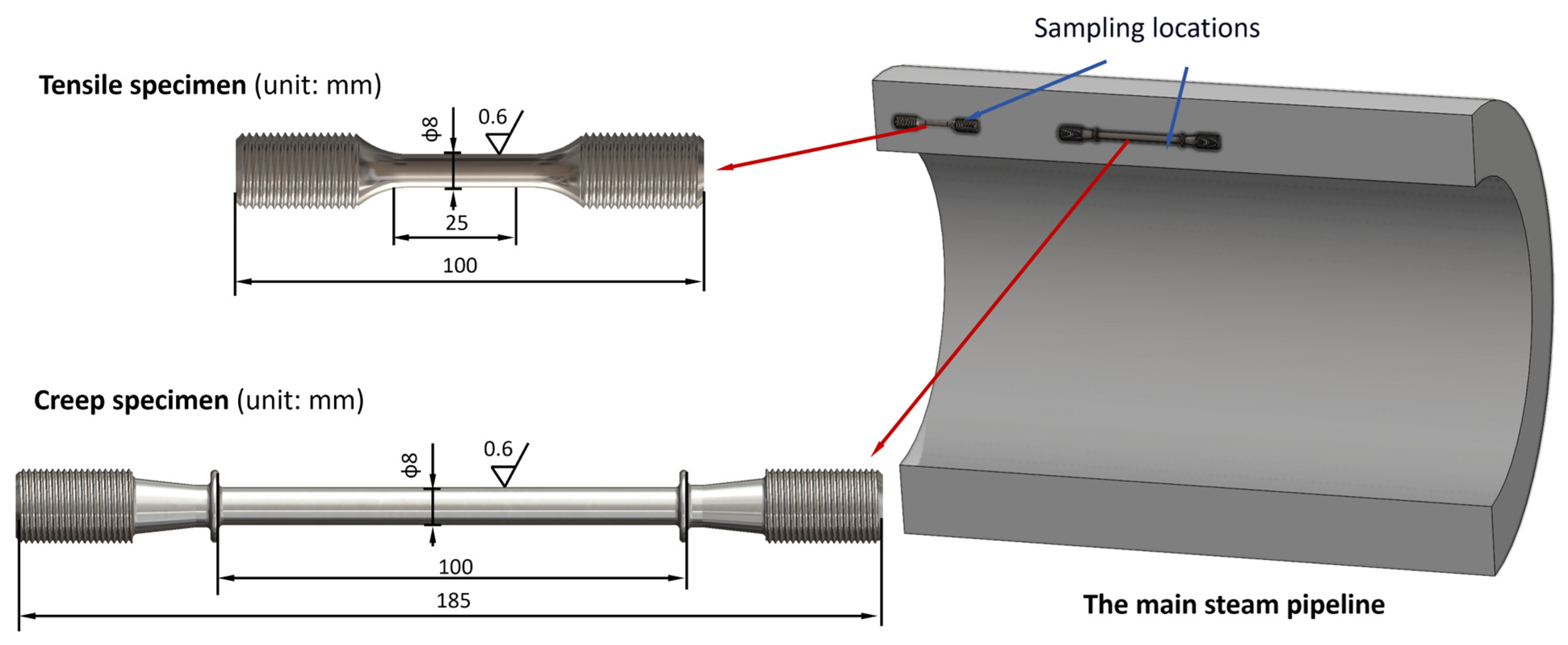
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Material Characterization
3. Results
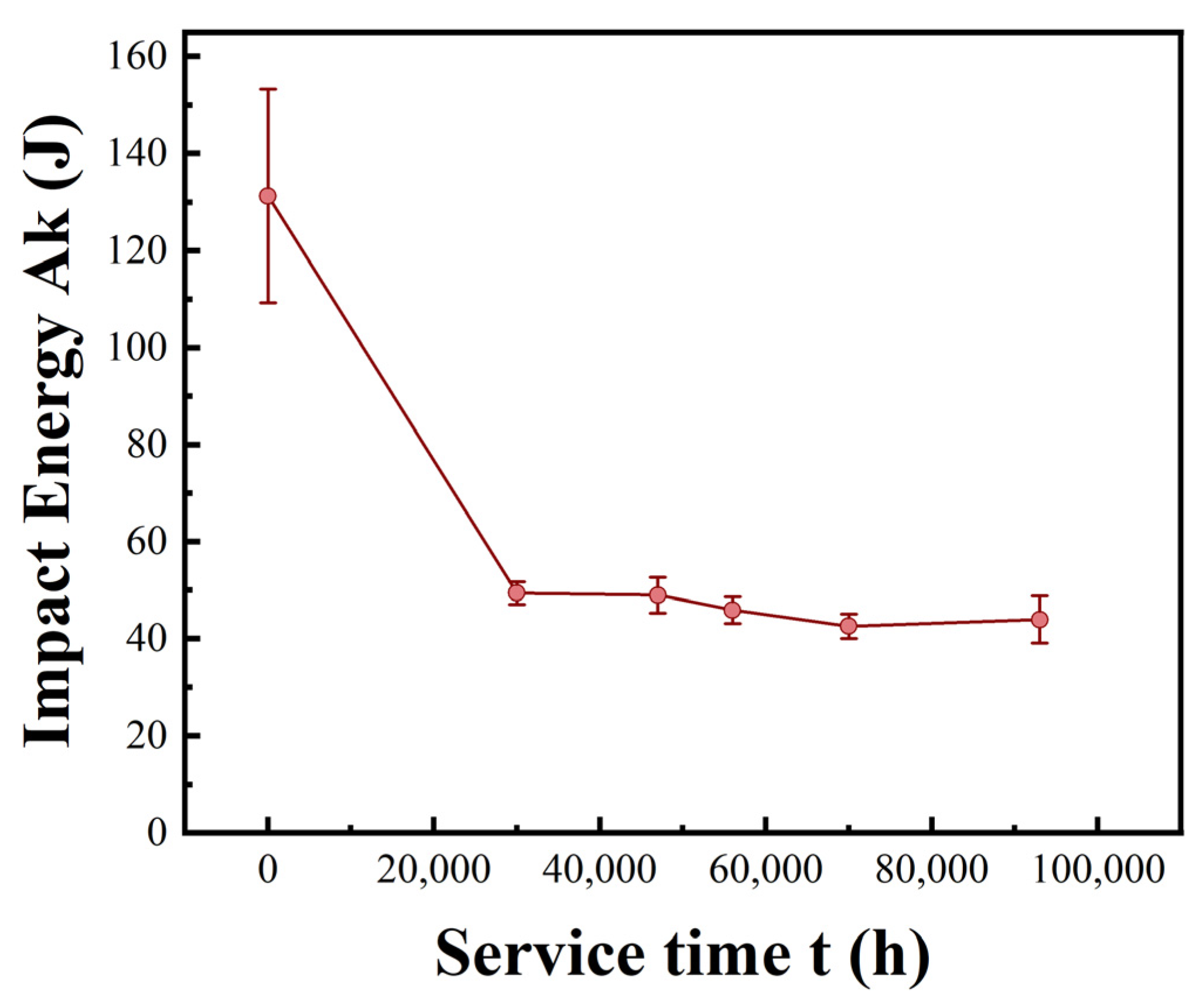
3.1. Impact and Tensile Test
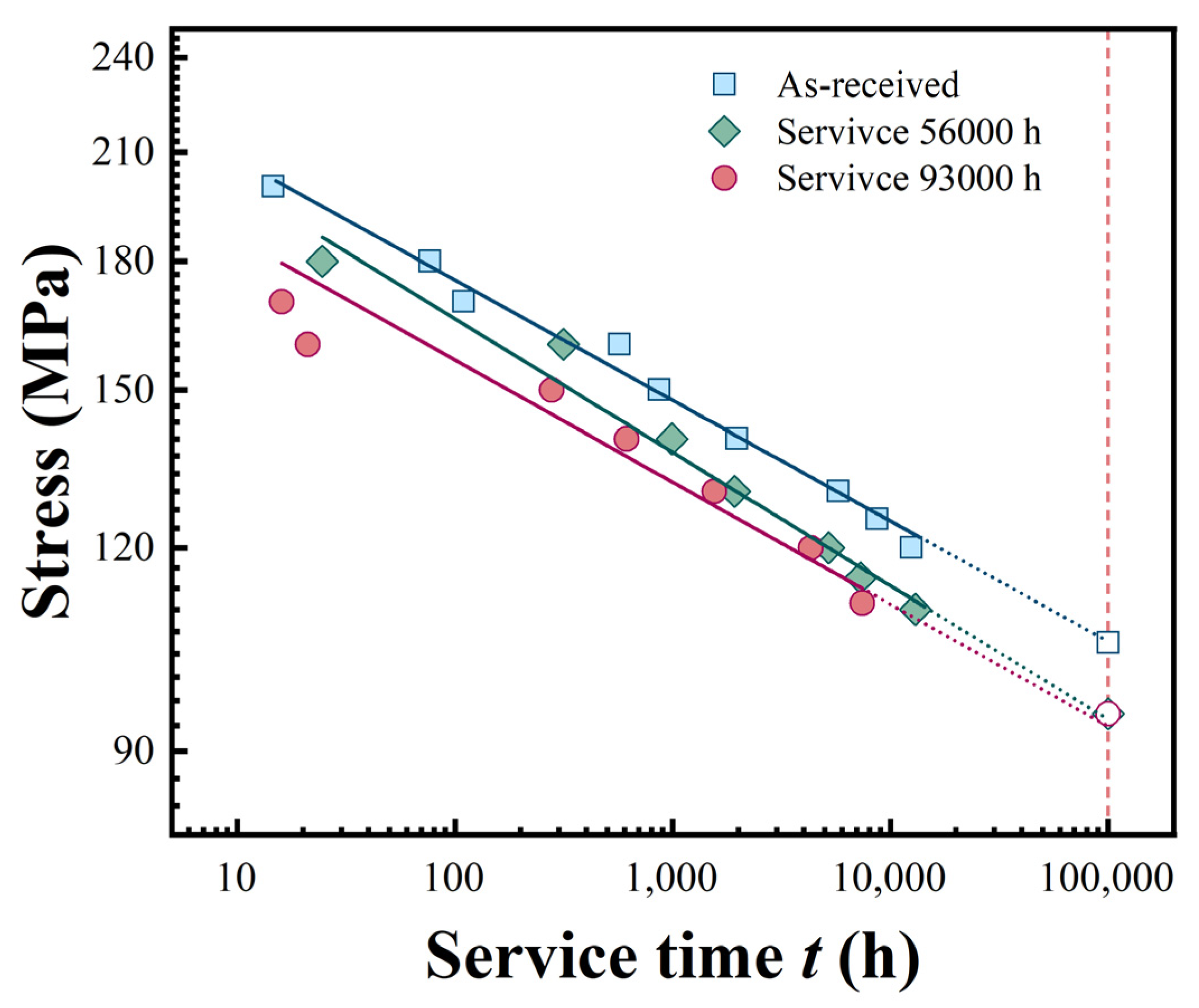
3.2. Creep Rupture Strength and Extrapolation
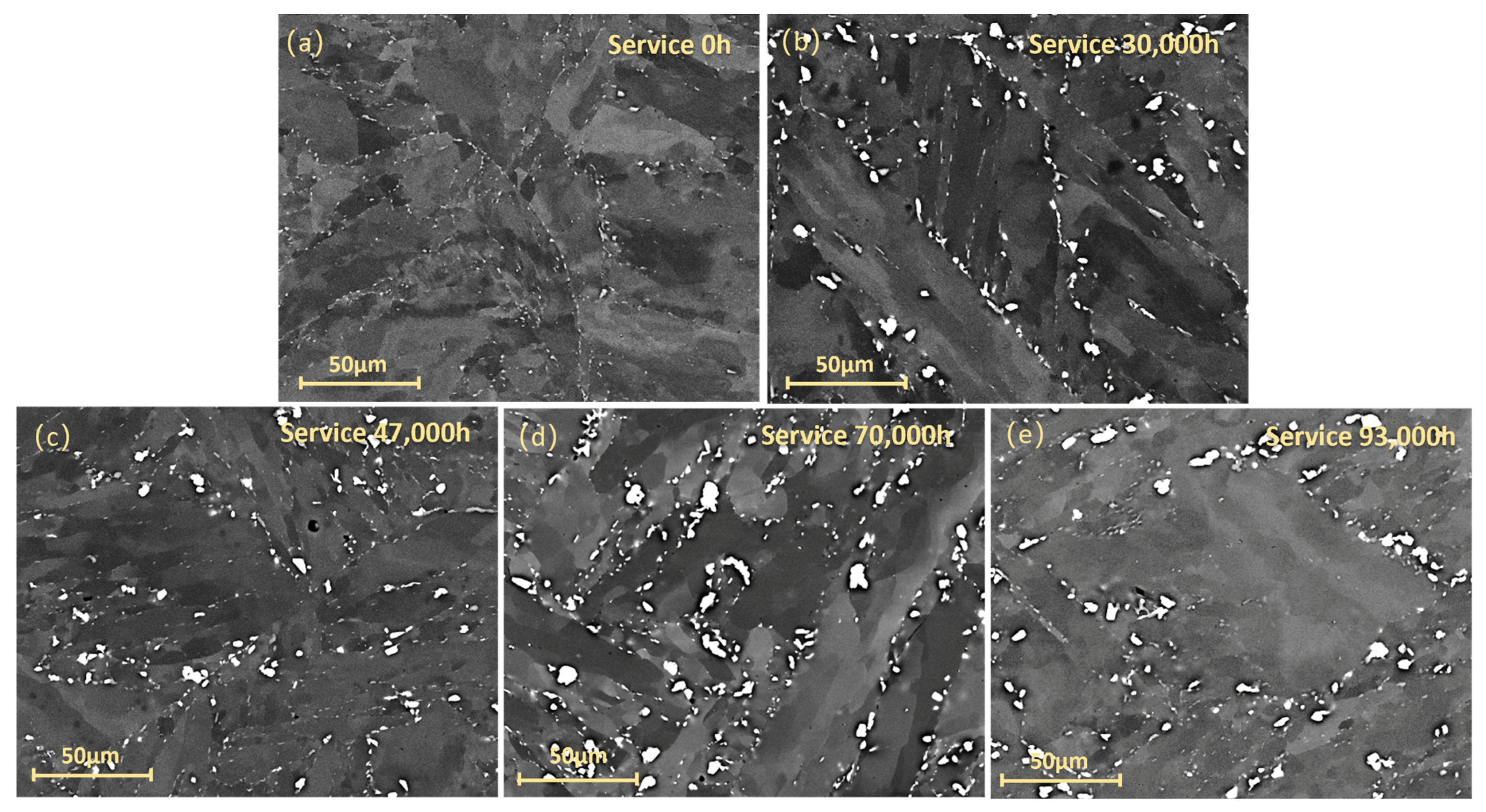
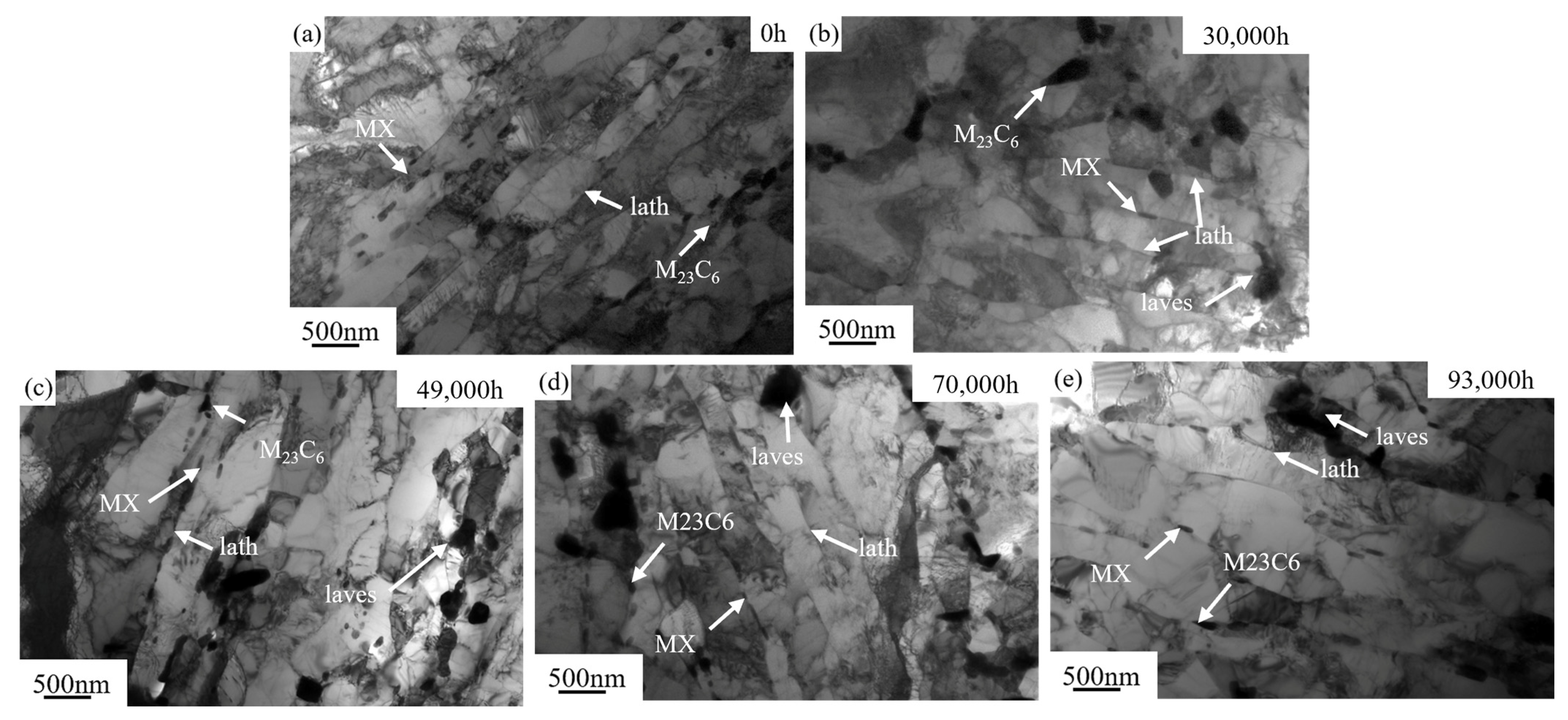
3.3. Microstructural Evolution Under Long-Term Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- RT and HT tensile properties and creep rupture strength decrease with service time. Reduced impact energy lowers material toughness, increasing brittle fracture risk. Declining tensile and yield strength weaken resistance to deformation and fracture. Reduced creep rupture strength deteriorates long-term resistance to deformation and fracture under high temperature and constant load.
- (2)
- Under long-term high-temperature service, P92 steel undergoes significant microstructural changes. SEM images reveal increased precipitate quantity and size, forming cluster-like or chain-like structures. TEM observations show blurred, merged, or coarsened martensite lath boundaries, reduced dislocation density, and severe grain coarsening over time.
- (3)
- Precipitate coarsening weakens the bonding force at the precipitate–matrix interface, facilitating micro-crack formation or reducing dislocation hindrance during impact and tension, thus decreasing impact energy and tensile strength. Widening martensite laths reduce lath boundaries, lowering resistance to crack propagation and dislocation movement, decreasing impact energy and tensile strength, accelerating creep deformation, and reducing creep resistance. Precipitate and martensite lath size changes are interrelated and jointly affect tensile and creep properties.
- (4)
- In the process of pipeline design, it is essential to thoroughly account for the disparities in creep properties to ascertain the operational stress and temperature for ensuring long-term safe functioning. Enhanced service inspections and monitoring should be implemented to swiftly identify and rectify potential creep-induced damage, thereby prolonging the service life of the pipeline and guaranteeing the stable operation of the system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abe, F. Research and Development of Heat-Resistant Materials for Advanced USC Power Plants with Steam Temperatures of 700 °C and Above. Engineering 2015, 1, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, R.; Coleman, K.; Rao, U. Materials for ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plant boilers. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2006, 83, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagode, A.; Kosec, L.; Ule, B.; Kosec, G. Review of creep resistant alloys for power plant applications. Metalurgija 2011, 50, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bhiogade, D.S. Ultra supercritical thermal power plant material advancements: A review. J. Alloys Metall. Syst. 2023, 3, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tao, Z.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Hao, K. Microstructure and High-Temperature Properties Changes of P92 Welded Joints in Ultra-supercritical Units after Long-Term Service. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 6671–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, M.; Skobir Balantič, D.A. Coarsening behaviour of M23C6 carbides in creep-resistant steel exposed to high temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Jiang, Y.; Weng, X.; Gong, J. Microstructural Evolution of P92 Steel During Long-Term Aging. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2017, 17, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Velázquez, J.L. Strengthening Mechanisms. In Mechanical Behavior and Fracture of Engineering Materials; González-Velázquez, J.L., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 103–133. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, B.Y.; Xia, X.X.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xu, C.L.; Yin, J.; Jia, W.Q. Study on the microstructure evolution and effect on mechanical properties of P92 steel during long term service. Materialia 2024, 35, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, F.; Zhang, G. Effect of the microstructure evolution on the high-temperature strength of P92 heat-resistant steel for different service times. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2020, 186, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Shen, J.; Xie, J. Effects of Precipitates Evolution on Low Stress Creep Properties in P92 Heat-resistant Steel. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, N.; Pandey, C.; Mahapatra, M.M. Characterization and evaluation of mechanical properties of CSEF P92 steel for varying normalizing temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, J.; Weng, X. The influence of long-term thermal exposure on microstructural stabilization and mechanical properties in 9Cr-0.5Mo-1.8W-VNb heat-resistant steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 672, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, J.; Ge, W.; Bao, H.; Zhou, L.; Yin, F.; Zhang, Y. Cavity growth behavior and fracture mechanism of 9.5Cr-1.5MoCoVNbNB heat-resistant steel during long-term tensile rupture at 620 °C. Mater. Charact. 2023, 203, 113130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroux, P.-F.; Dalle, F.; Sauzay, M.; Malaplate, J.; Fournier, B.; Gourgues-Lorenzon, A.-F. Mechanical and microstructural stability of P92 steel under uniaxial tension at high temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3984–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayatzadeh, S.; Tanner, D.W.J.; Truman, C.E.; Flewitt, P.E.J.; Smith, D.J. Influence of thermal ageing on the creep behaviour of a P92 martensitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 708, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, V.K.; Singh, L.P.; Tariq, M. Study of Steel P92 Microstructure and Mechanical Properties after Different Heat Treatment Regimes. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2022, 64, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM A335/A335M-15; Standard Specification for Seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- GB/T 229-2020; Metallic Materials—Charpy Pendulum Impact Test Method. National Market Supervision Administration and Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 228.1-2021; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. National Market Supervision Administration and Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 228.2-2015; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 2: Method of Test at Elevated Temperature. National Market Supervision Administration and Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB/T 2039-2024; Metallic Materials—Uniaxial Creep Testing Method in Tension. National Market Supervision Administration and Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Hertzberg, R.W.; Vinci, R.P.; Hertzberg, J.L. Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Shi, D.; Yang, J. Creep rupture limit analysis for engineering structures under high-temperature conditions. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 199, 104763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Fan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Bao, H.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z. Correlation of creep fracture lifetime with microstructure evolution and cavity behaviors in G115 martensitic heat-resistant steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 788, 139468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, T.; Selvi, S.P.; Parameswaran, P.; Laha, K. Influence of Thermal Ageing on Microstructure and Tensile Properties of P92 Steel. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2018, 37, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.; Mohan Mahapatra, M.; Kumar, P.; Thakre, J.G.; Saini, N. Role of evolving microstructure on the mechanical behaviour of P92 steel welded joint in as-welded and post weld heat treated state. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 263, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.B.; Chang, X.F.; Key, J. New insight into high-temperature creep deformation and fracture of T92 steel involving precipitates, dislocations and nanovoids. Mater. Charact. 2017, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, Y.; Ali, K.; Akhtar, K.; Jawaria; Hussain, M.I.; Ahmad, G.; Arif, T. TEM for Atomic-Scale Study: Fundamental, Instrumentation, and Applications in Nanotechnology. In Handbook of Materials Characterization; Sharma, S.K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 147–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.T.; Bushby, A.J.; Dunstan, D.J. Materials mechanical size effects: A review. Mater. Technol. 2008, 23, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, N.; Mulik, R.S.; Mahapatra, M.M. Study on the effect of ageing on laves phase evolution and their effect on mechanical properties of P92 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 716, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, A.; Laurson, L.; Granberg, F.; Nordlund, K.; Alava, M.J. Effects of precipitates and dislocation loops on the yield stress of irradiated iron. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Shang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Liu, H. The nature of nano-sized precipitates in ferritic/martensitic steel P92 produced by thermomechanical treatment. Mater. Charact. 2016, 119, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| C | S | P | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | W | B | V | Nb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 0.10 | 0.0033 | 0.018 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 8.93 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 1.85 | 0.0012 | 0.17 | 0.067 |
| 30,000 h | 0.10 | 0.001 | 0.018 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 8.86 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 1.51 | 0.0024 | 0.19 | 0.076 |
| 49,000 h | 0.11 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.32 | 0.53 | 8.95 | 0.40 | 0.44 | 1.67 | 0.0019 | 0.21 | 0.057 |
| 70,000 h | 0.094 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.26 | 0.47 | 8.68 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 1.58 | 0.0021 | 0.17 | 0.053 |
| 90,000 h | 0.093 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.26 | 0.47 | 8.86 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 1.72 | 0.0015 | 0.16 | 0.064 |
| ASME A335 | 0.07–0.13 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.5 | 0.3–0.6 | 8.5–9.5 | ≤0.4 | 0.30–0.60 | 1.5–2.0 | 0.001–0.006 | 0.15–0.25 | 0.03–0.07 |
| Tests | Service Time t/h | Temperature T/°C | Yield Strength σs/MPa | Tensile Strength σt/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT | 0 | 25 | 593.36 | 743.13 |
| 30,000 | 25 | 512.95 | 685.59 | |
| 47,000 | 25 | 502.70 | 685.59 | |
| 56,000 | 25 | 471.96 | 657.99 | |
| 70,000 | 25 | 464.87 | 655.63 | |
| 93,000 | 25 | 494.03 | 669.03 | |
| HT | 0 | 610 | 378.94 | 412.26 |
| 30,000 | 610 | 259.12 | 297.75 | |
| 47,000 | 610 | 263.85 | 286.71 | |
| 56,000 | 610 | 259.91 | 291.44 | |
| 70,000 | 610 | 259.12 | 283.56 | |
| 93,000 | 610 | 256.76 | 282.72 |
| Material Type | Service Time t/h | Temperature T/°C | Stress σ/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| P92 steel | 0 | 610 | 200~120 |
| 56,000 | 610 | 200~110 | |
| 93,000 | 610 | 170~110 |
| Material Type | Service Time t/h | a | b | A | B | 105 h Rupture Strength MPa | Coefficient of Determination R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P92 steel | 0 | 2.392 | −0.074 | 0.028 | 13.51 | 105 | 0.993 |
| 56,000 | 2.384 | −0.082 | 0.0279 | 12.19 | 94.9 | 0.982 | |
| 93,000 | 2.323 | −0.0697 | 0.0271 | 14.34 | 94.4 | 0.958 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, H.; Xia, X.; Ma, Q.; Lai, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, B. Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of P92 Main Steam Pipelines After Long-Term Service. Materials 2025, 18, 4432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194432
Dong H, Xia X, Ma Q, Lai Y, Jin X, Zhu B. Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of P92 Main Steam Pipelines After Long-Term Service. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194432
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Haitao, Xianxi Xia, Qinzheng Ma, Yunting Lai, Xiao Jin, and Baoyin Zhu. 2025. "Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of P92 Main Steam Pipelines After Long-Term Service" Materials 18, no. 19: 4432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194432
APA StyleDong, H., Xia, X., Ma, Q., Lai, Y., Jin, X., & Zhu, B. (2025). Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of P92 Main Steam Pipelines After Long-Term Service. Materials, 18(19), 4432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194432






