Interfacial Defect Suppression and Enhanced Optical Properties in InP Quantum Dots via Two-Step ZnSe Shelling Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Precursors
2.3. 2-Step ZnSe Shelling
2.4. 1-Step ZnSe Shelling
2.5. ZnS Shelling
2.6. Characterization
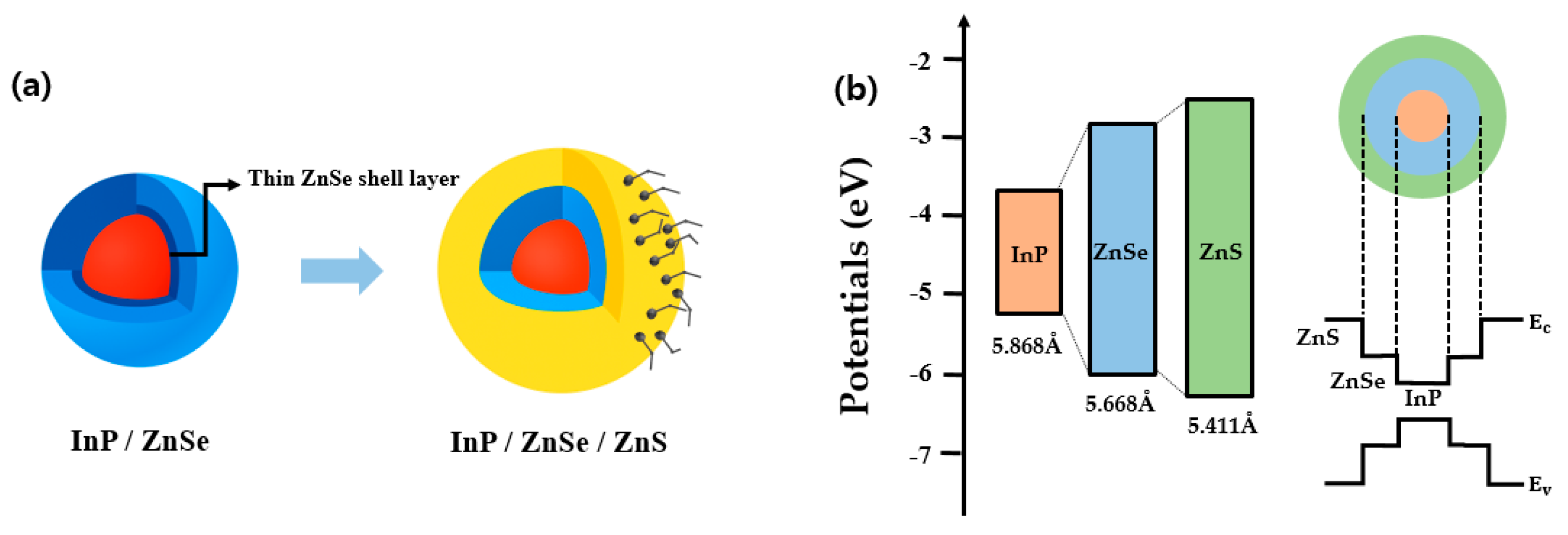
3. Results and Discussion
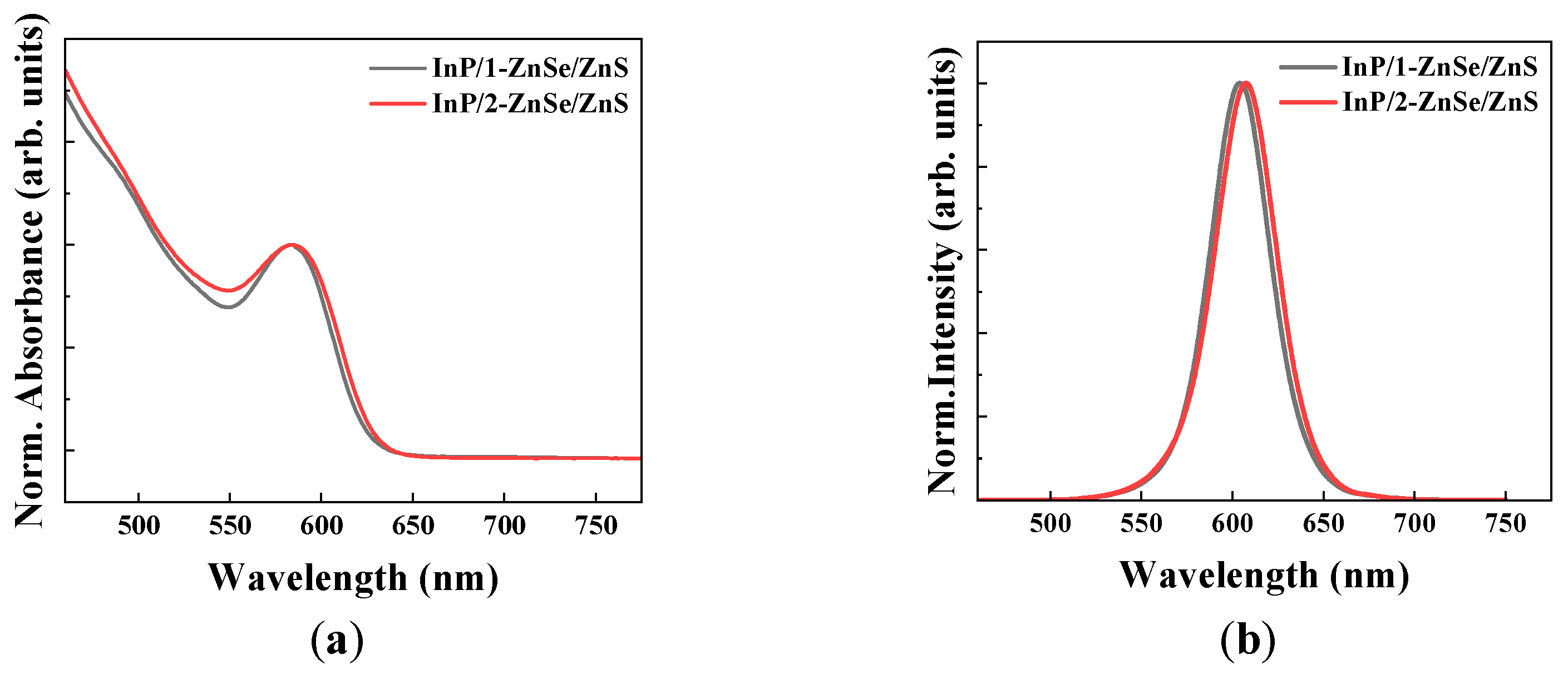
3.1. Optical Characteristics
Photoluminescence Efficiency
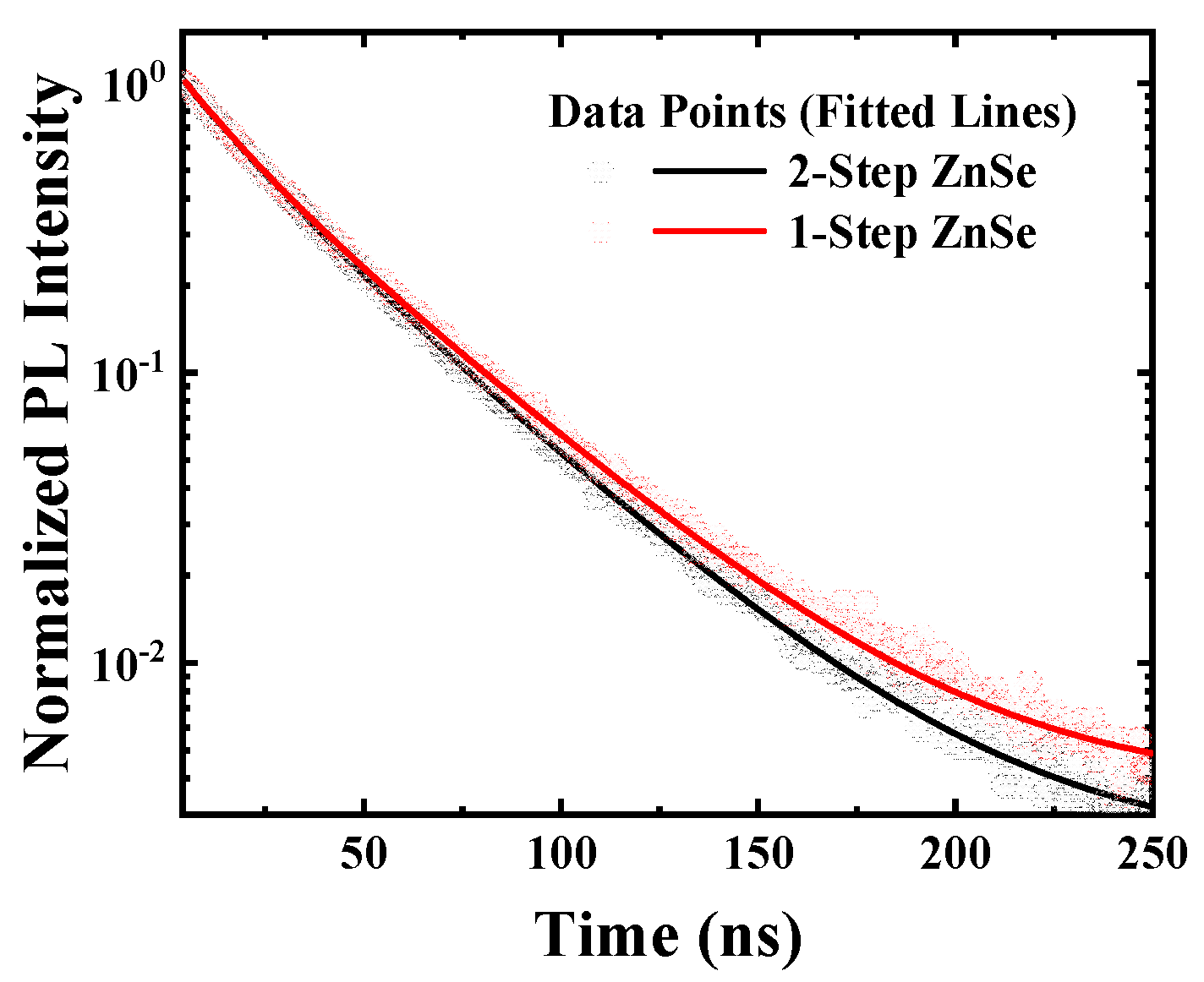
3.2. Time-Resolved Photoluminescence Characteristics
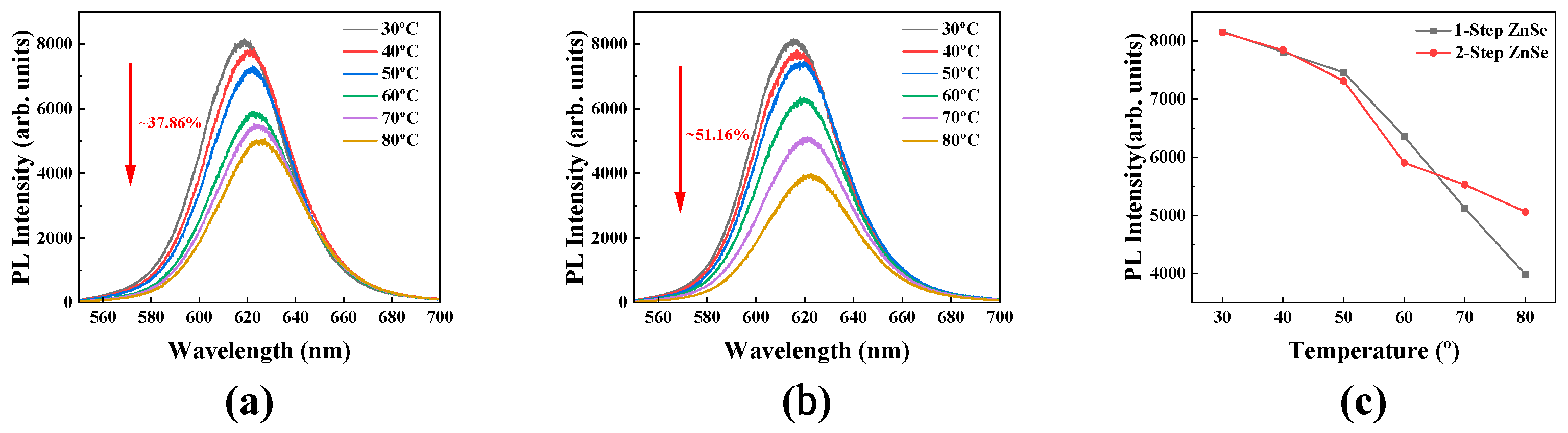
3.3. Temperature-Dependent Photoluminescence
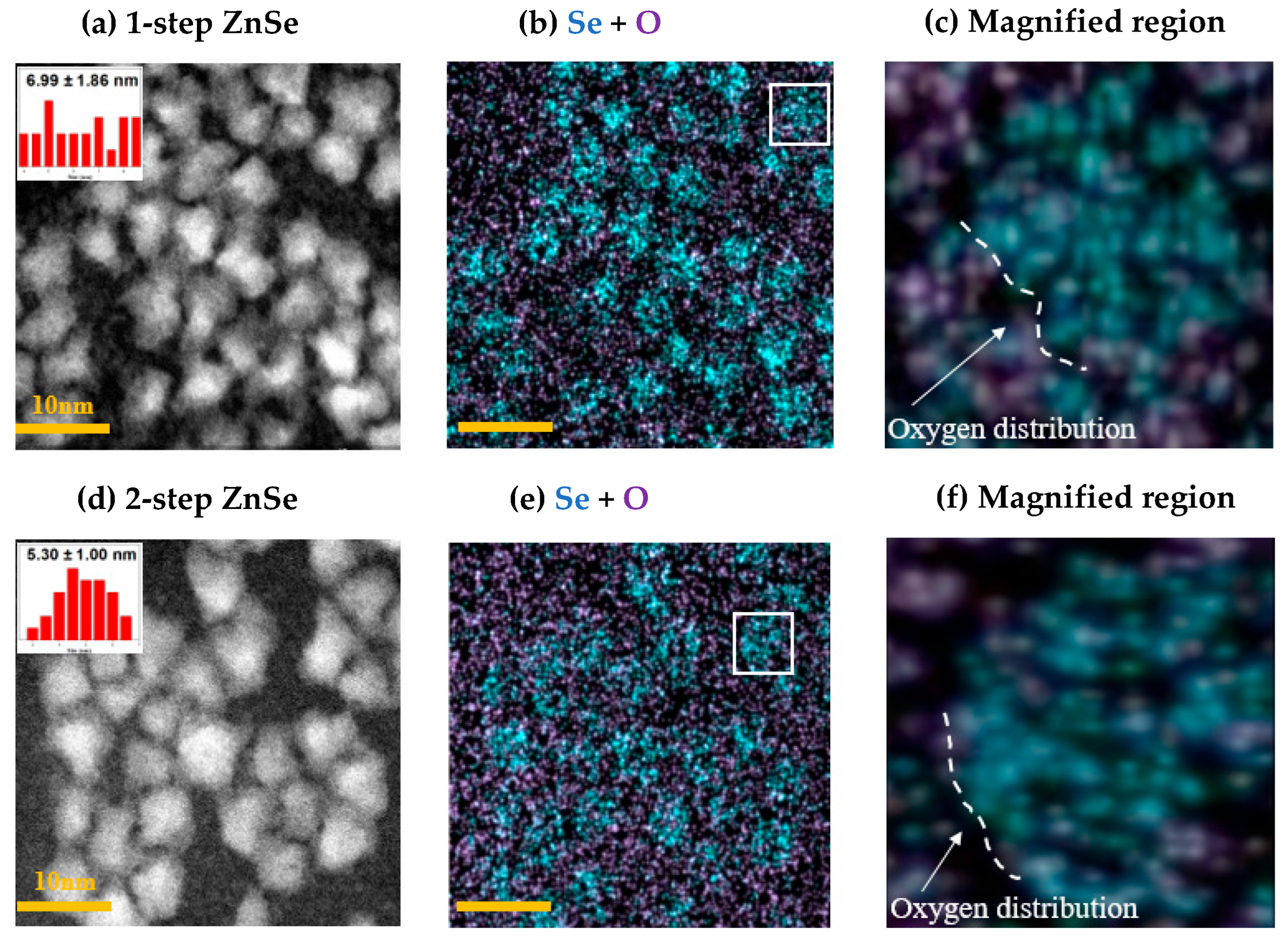
3.4. Structural Characterization by Transmission Electron Microscopy and Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (TEM-EDS)
3.5. Lattice Pattern
3.6. Selenium Distribution Uniformity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, G.; Ubbink, R.F.; Stam, M.; Fossé, I.D.; Houtepen, A.J. InP colloidal quantum dots for visible and near-infrared photonics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 742–758. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, O.; Niu, W.; Yang, C.; Tang, A. Development and challenges of indium phosphide-based quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2023, 55, 100588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, R.; Huang, M.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Tian, P.; Wang, J.; Guo, R.; Mei, S. Advancing Ecofriendly Indium Phosphide Quantum Dots: Comprehensive Strategies toward Color-Pure Luminescence for Wide Color Gamut Displays. ACS Energy Lett. 2025, 10, 2096–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, M.; Almeida, G.; Ubbink, R.F.; van der Poll, L.M.; Vogel, Y.B.; Chen, H.; Giordano, L.; Schiettecatte, P.; Hens, Z.; Houtepen, A.J. Near-Unity Photoluminescence Quantum Yield of Core-Only InP Quantum Dots via a Simple Postsynthetic InF3 Treatment. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 14685–14695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Bian, Y.; Ahn, T.; Shen, H.; Ji, B. ZnF2-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Luminescent InP/ZnSe/ZnS Quantum Dots for Efficient and Stable Electroluminescence. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 4067–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.J.; Kim, D.; Park, J.W.; Yu, Y.; Hwang, S.J. Coordination Chemistry of Ligands Bearing Heavy Group 14 and 15 Elements: Comparative Analysis of Their Influence on Transition Metal Chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 526, 216317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yan, L.; Fu, S.; Lv, Y. Shell thickness influence on the carrier dynamics of InP/ZnS QDs. Chem. Phys. Impact 2024, 8, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.T.; Viscomi, F.N.; Chamberlain, T.W.; Hendow, N.; Adawi, A.M.; Sturge, J.; Erwin, S.C.; Bouillard, J.-S.G.; Tamang, S.; Stasiuk, G.J. Synthesis of super bright indium phosphide colloidal quantum dots through thermal diffusion. Commun. Chem. 2019, 2, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wegner, K.D.; Stiegler, L.M.S.; Zhou, X.; Rezvani, A.; Odungat, A.S.; Zubiri, B.A.; Wu, M.; Spiecker, E.; Walter, J.; et al. Optimizing the shelling process of InP/ZnS quantum dots using a single-source shell precursor: Implications for lighting and display applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 24262–24273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.S.; Ko, M.; Nam, S.; Oh, J.H.; Jeong, S.; Yang, Y.; Park, S.M.; Do, Y.R.; Song, J.K. InP/ZnSeS/ZnS quantum dots with high quantum yield and color purity for display devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Tao, H.; Zou, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, G. Highly luminescent InP–In(Zn)P/ZnSe/ZnS core/shell/shell colloidal quantum dots with tunable emissions synthesized based on growth-doping. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, M.D.; Baquero, E.A.; Dupont, D.; Grigel, V.; Bladt, E.; Bals, S.; Coppel, Y.; Hens, Z.; Nayral, C.; Delpech, F. Interfacial oxidation and photoluminescence of InP-based core/shell quantum dots. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 6877–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-B.; Shin, D.-W.; Lee, S.; Ye, J.; Yu, S.; Morgan, D.J.; Arbab, A.; Yang, J.; Jo, J.-W.; Kim, Y.; et al. InP/ZnS quantum dot photoluminescence modulation via in situ H2S interface engineering. Nanoscale Horiz. 2023, 8, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubbink, R.F.; Speelman, T.; Esteban, D.A.; van Leeuwen, M.; Stam, M.; Bals, S.; De Wijs, G.A.; van Eck, E.R.H.; Houtepen, A.J. Phosphorus oxidation controls epitaxial shell growth in InP/ZnSe quantum dots. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, T.; Kumamoto, A.; Kido, M.; Sasaki, H.; Novet, T.; Shibata, N.; Ikuhara, Y. Highly luminescent and narrow-band-emitting InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot synthesis by halide modified shell reaction. Appl. Phys. Express 2023, 16, 015504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.-H.; Cho, O.; Kim, T.; Chung, D.-Y.; Kim, T.; Chung, H.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Jang, E. Highly efficient and stable InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nature 2019, 575, 634–638. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Kaledin, A.L.; He, S.; Jin, T.; McBride, J.R.; Lian, T. Surface passivation extends single and biexciton lifetimes of InP quantum dots. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-G.; Zherebetskyy, D.; Bekenstein, Y.; Oh, M.H.; Wang, L.-W.; Jang, E.; Alivisatos, A.P. Trap passivation in indium-based quantum dots through surface fluorination: Mechanism and applications. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11529–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Rehman, F.; Das, T.; Imran, M.; Park, J.; Oh, S.; Seo, H.; Choi, Y.K.; Goddard, W.A., III; Oh, S.J. Experimental and first-principles analyses of oxidative defect removal in eco-friendly InP quantum dot synthesis via in situ HF etching. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 511, 162134. [Google Scholar]
- Ubbink, R.F.; Almeida, G.; Iziyi, H.; Fossé, I.D.; Verkleij, R.; Ganapathy, S.; van Eck, E.R.H.; Houtepen, A.J. A water-free in situ HF treatment for ultrabright InP quantum dots. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 10093–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, S.-Y.; Yoon, B.; Shin, D.; Bae, W.K.; Lee, S.-S.; Lee, H. Time-Resolved Mechanism of Positive Aging in InP Quantum-Dot Light-Emitting Diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 55848–55856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippen, C.; Greco, T.; Wedel, A. InP/ZnSe/ZnS: A novel multishell system for InP quantum dots for improved luminescence efficiency and its application in a light-emitting device. J. Inf. Disp. 2012, 13, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; He, M.; Liao, X.; Wan, Q.; Zhan, W.; Kong, L.; Li, L. A Novel Strategy to Enhance the Photostability of InP/ZnSe/ZnS Quantum Dots with Zr Doping. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Fan, Z.; Luo, L.; Wang, L. Advances and challenges in heavy-metal-free InP quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Micromachines 2022, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafipoor, M.; Dupont, D.; Tornatzky, H.; Tessier, M.D.; Maultzsch, J.; Hens, Z.; Lange, H. Strain engineering in InP/(Zn,Cd)Se core/shell quantum dots. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 4393–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, N.; Monchen, J.O.V.; Crisp, R.W.; Grimaldi, G.; Bergstein, H.A.C.; du Fossé, I.; van der Stam, W.; Infante, I.; Houtepen, A.J. Finding and Fixing Traps in II–VI and III–V Colloidal Quantum Dots: The Importance of Z-Type Ligand Passivation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15712–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yang, Y.; Gong, G.; Feng, S.; Liu, D. One-step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent MoS2 Quantum Dots for Lead Ion Detection in Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachurski, J.; Tamariz, S.; Callsen, G.; Buttè, R.; Grandjean, N. Single Photon Emission and Recombination Dynamics in Self-Assembled GaN/AlN Quantum Dots. Light: Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Li, X.; Tsai, H.; Hou, C.-H.; Huang, H.-H.; Ghosh, D.; Shyue, J.-J.; Wang, L.; Tretiak, S.; Ma, X.; et al. Long carrier diffusion length in two-dimensional lead halide perovskite single crystals. Chem 2022, 8, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, S.S.; Vokhmintsev, A.S.; Weinstein, I.A. Activation Energy Distribution in Thermal Quenching of Exciton and Defect-Related Photoluminescence of InP/ZnS Quantum Dots. J. Lumin. 2022, 242, 118550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Riemersma, C.; Pietra, F.; Koole, R.; de Mello Donegá, C.; Meijerink, A. High-Temperature Luminescence Quenching of Colloidal Quantum Dot. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9058–9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C. High-Performance Giant InP Quantum Dots with Stress-Released Morphological ZnSe–ZnSeS–ZnS Shell. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2407026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhuang, W.; Liu, R.; Xing, X.; Qu, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, B.; Wang, K.; Sun, X. Double-Shelled InP/ZnMnS/ZnS Quantum Dots for Light-Emitting Devices. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 18961–18968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride James, R.; Rosenthal Sandra, J. Real colloidal quantum dot structures revealed by high resolution analytical electron microscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 160903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, H.; Kang, S.; Heo, J.; Choi, S.; Kim, R.; Kim, K.; Ahn, N.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, T.; Chang, J.; et al. Insights into structural defect formation in individual InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots under UV oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Hahm, D.; Bae, W.K.; Lim, J. Heteroepitaxial chemistry of zinc chalcogenides on InP nanocrystals for defect-free interfaces with atomic uniformity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullum, P.E.; Nord, M.; Vatanparast, M.; Thomassen, S.F.; Boothroyd, C.; Holmestad, R.; Fimland, B.-O.; Reenaas, T.W. Quantitative strain analysis of InAs/GaAs quantum dot materials. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Koley, S.; Slobodkin, I.; Remennik, S.; Banin, U. ZnSe/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots with Superior Optical Properties through Thermodynamic Shell Growth. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Shelling Method | Peak Wavelength (nm) | PLQY (%) | FWHM (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-step ZnSe | 603.9 | 94.0 ± 1.1 | 38.0 ± 0.1 |
| 2-step ZnSe | 607.6 | 95.7 ± 1.4 | 39.0 ± 0.1 |
| Shelling | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-step ZnSe | 0.28 | 0.72 | 14.34 | 37.19 | 34.20 |
| 2-step ZnSe | 0.31 | 0.69 | 16.94 | 36.28 | 32.93 |
| Temperature Range | Reduction Rate (%) (1-Step Shelling) | Reduction Rate (%) (2-Step Shelling) |
|---|---|---|
| 30 °C → 40 °C | 4.28 | 3.74 |
| 40 °C → 50 °C | 4.51 | 6.74 |
| 50 °C → 60 °C | 14.73 | 19.24 |
| 60 °C → 70 °C | 19.39 | 6.36 |
| 70 °C → 80 °C | 22.26 | 8.46 |
| Shelling | Se Count | O Count | O/Se ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-step ZnSe | 1425 | 1486 | 104.3% |
| 2-step ZnSe | 1247 | 977 | 78.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, J.; Joe, S.-Y.; Ko, J.-H. Interfacial Defect Suppression and Enhanced Optical Properties in InP Quantum Dots via Two-Step ZnSe Shelling Strategy. Materials 2025, 18, 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174172
Yoo J, Joe S-Y, Ko J-H. Interfacial Defect Suppression and Enhanced Optical Properties in InP Quantum Dots via Two-Step ZnSe Shelling Strategy. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174172
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Jaehyeong, Sung-Yoon Joe, and Jae-Hyeon Ko. 2025. "Interfacial Defect Suppression and Enhanced Optical Properties in InP Quantum Dots via Two-Step ZnSe Shelling Strategy" Materials 18, no. 17: 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174172
APA StyleYoo, J., Joe, S.-Y., & Ko, J.-H. (2025). Interfacial Defect Suppression and Enhanced Optical Properties in InP Quantum Dots via Two-Step ZnSe Shelling Strategy. Materials, 18(17), 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174172






