An Elastoplastic Constitutive Model for Steel Slag Aggregate Concrete Under Multiaxial Stress States Based on Non-Uniform Hardening Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Form of Incremental Constitutive Relation
2.1. Incremental Form of Stress–Strain Relationship for SAC
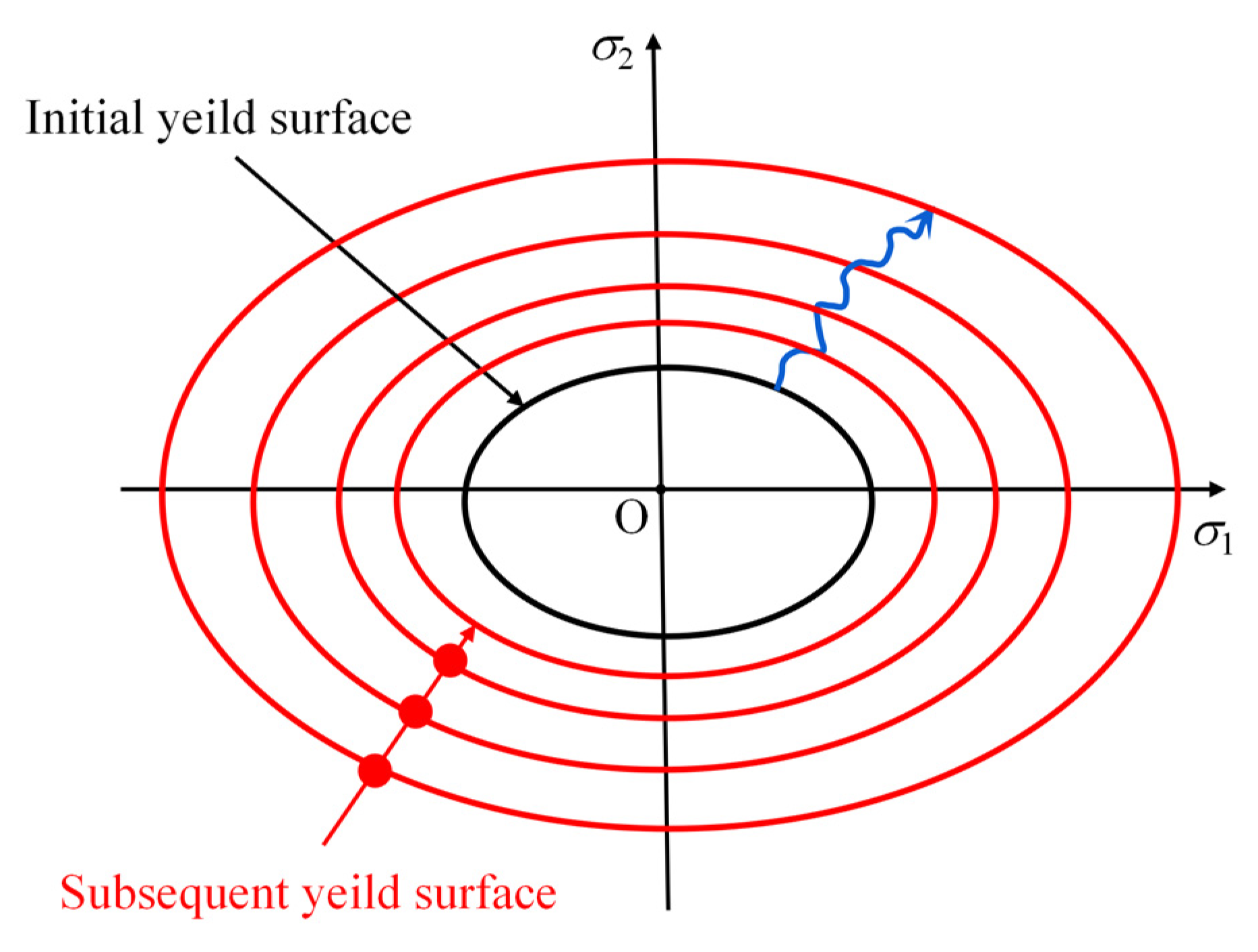
2.2. Flow Rule
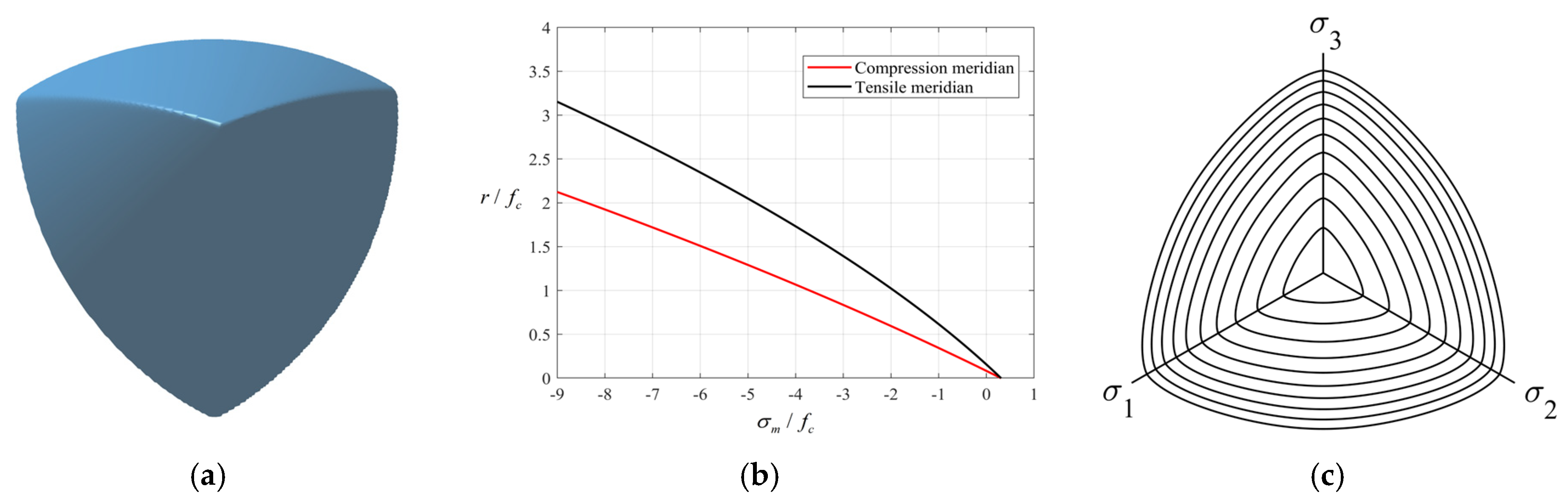
2.3. Failure Surface and Yield Criterion
2.4. Effective Stress τ and Stress Scalar Function ϕ
3. Parameter Calibration
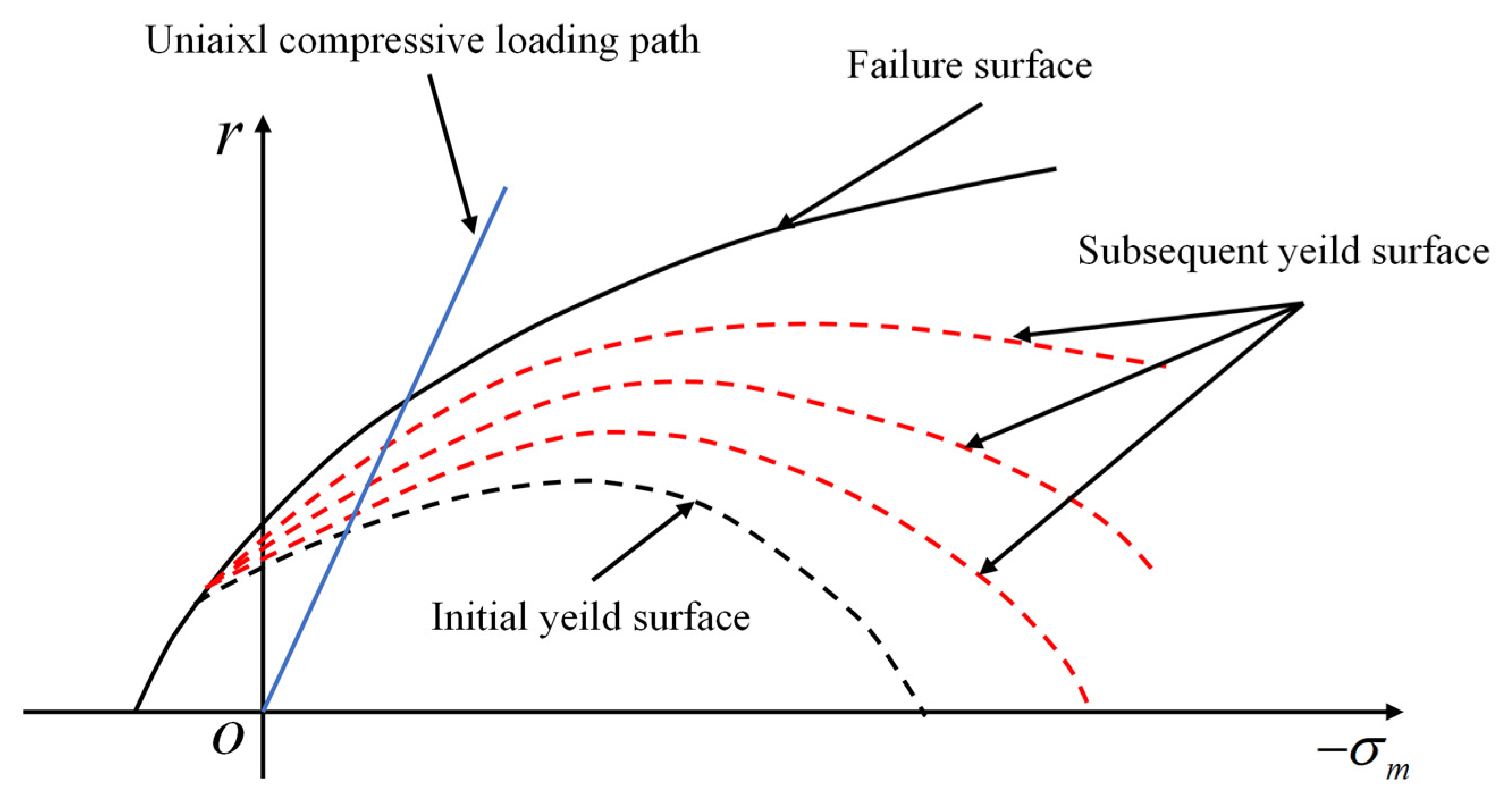
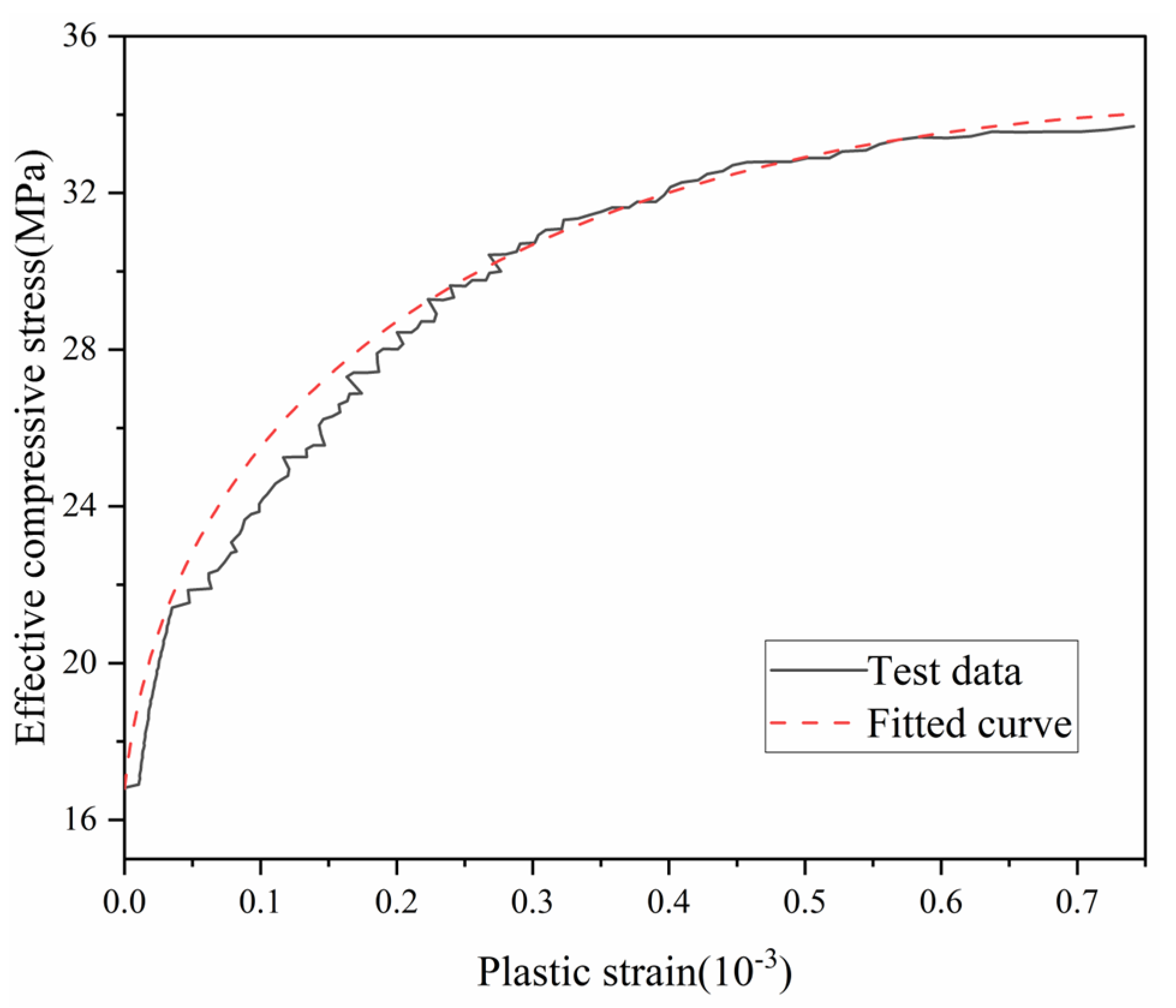
3.1. Hardening Parameter k0
3.2. Plastic Modulus Hp
3.3. Coefficient of Cubical Expansion αp
4. Numerical Calculation and Model Verification
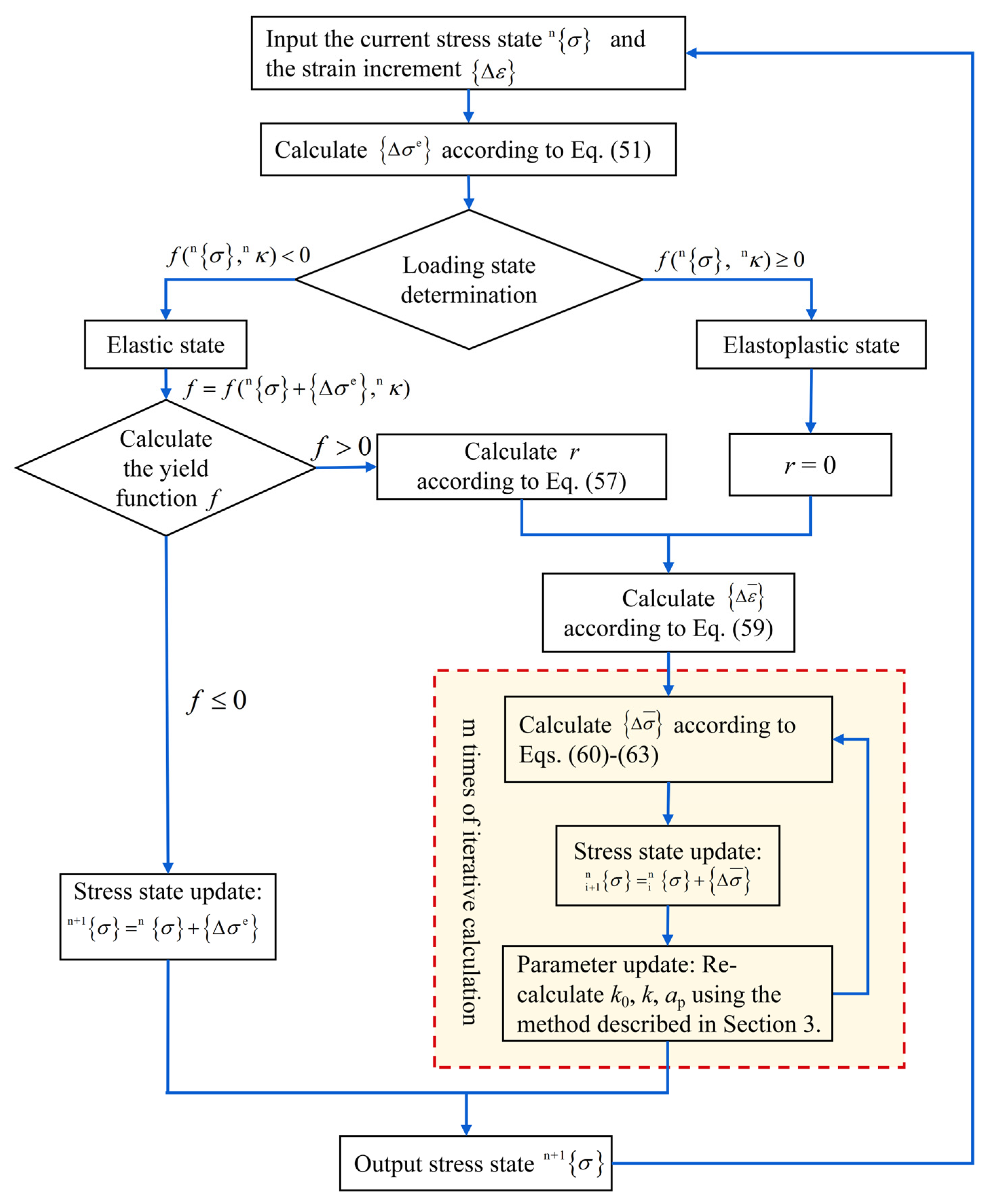
4.1. Numerical Calculation Methodology
4.1.1. Matrix-Form Multiaxial Stress–Strain Relationship
4.1.2. Analysis of the Numerical Computation Procedure
- Loading State Analysis
- 2.
- Numerical integration method
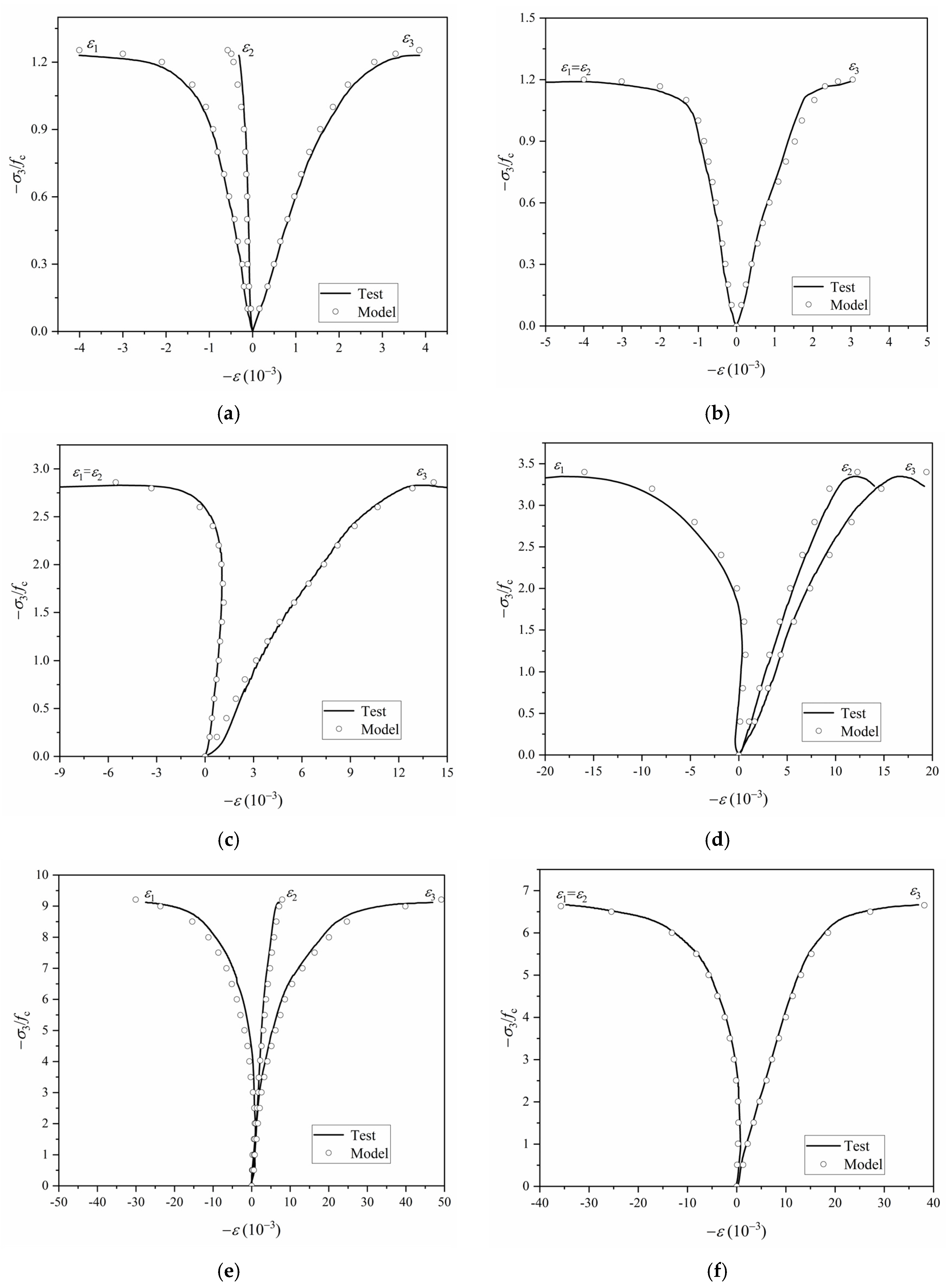
4.2. Numerical Implementation and Validation Results of the Constitutive Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Notation
| σ1, σ2, σ3 | Principal stresses (tension-positive) |
| σij | Stress tensor |
| sij | Deviatoric stress tensor |
| σm | Mean normal stress |
| τm | Mean shear stress |
| ε1, ε2, ε3 | Principal strain |
| εij | Strain tensor |
| εv | Volumetric strain |
| I1 = σkk | The first invariant of the stress tensor |
| The second invariant of the deviatoric stress tensor | |
| The third invariant of the deviatoric stress tensor | |
| θ | Lode angle |
| Length of the deviatoric part of the stress tensor | |
| E | Elasticity modulus |
| v | Poisson’s ratio |
| Elastic stiffness tensor | |
| Elastoplastic stiffness tensor | |
| Permutation operator (Kronecker symbol) | |
| { } | Vector |
| [ ] | Matrix |
Appendix A
References
- Jiang, Y.; Ling, T.C.; Shi, C.; Pan, S.-Y. Characteristics of steel slags and their use in cement and concrete—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Kasiri, A.M. Producing Portland cement from iron and steel slags and limestone. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, R.; Zhang, P. Applications of Steel Slag Powder and Steel Slag Aggregate in Ultra—High Performance Concrete. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z. Comparison of the properties between high-volume fly ash concrete and high-volume steel slag concrete under temperature matching curing condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 649–655. [Google Scholar]
- Gencel, O.; Karadag, O.; Oren, O.H.; Bilir, T. Steel slag and its applications in cement and concrete technology: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 283, 122783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F. Utilization of steel slag in ultra-high performance concrete with enhanced eco-friendliness. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Dong, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y. Microscopic characterizations of pervious concrete using recycled Steel Slag Aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.S.; Roesler, J.R. Steel furnace slag aggregate expansion and hardened concrete properties. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baalamurugan, J.; Kumar, V.G.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Balasundar, S.; Venkatraman, B.; Padmapriya, R.; Raja, V.K.B. Recycling of steel slag aggregates for the development of high density concrete: Alternative & environment-friendly radiation shielding composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 216, 108885. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.; Wang, G.; Chen, X.; Tan, J.; Gu, X. Recycling of steel slag aggregate in portland cement concrete: An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Eishah, S.I.; El-Dieb, A.S.; Bedir, M.S. Performance of concrete mixtures made with electric arc furnace (EAF) steel slag aggregate produced in the Arabian Gulf region. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.H.; Zou, J.; Yao, B.; Ho, J.C.M.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, Q. Improving mechanical behavior and microstructure of concrete by using BOF steel slag aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, I.; Santamaría, A.; Ruiz, E.; Ortega-López, V.; Manso, J.M. Electric arc furnace slag and its use in hydraulic concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 90, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.S.; Roesler, J.R. Interfacial transition zone of cement composites with steel furnace slag aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 86, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Yan, P. Cementitious properties of super-fine steel slag. Powder Technol. 2013, 245, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooholamini, H.; Sedghi, R.; Ghobadipour, B.; Adresi, M. Effect of electric arc furnace steel slag on the mechanical and fracture properties of roller-compacted concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, J.; Zheng, W.; Li, J. Effects of steel slag as fine aggregate on static and impact behaviours of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 192, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondi, L.; Bregoli, G.; Sorlini, S.; Cominoli, L.; Collivignarelli, C.; Plizzari, G. Concrete with EAF steel slag as aggregate: A comprehensive technical and environmental characterization. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 90, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Václavík, V.; Ondová, M.; Dvorský, T.; Eštoková, A.; Fabiánová, M.; Gola, L. Sustainability Potential Evaluation of Concrete with Steel Slag Aggregates by the LCA Method. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhao, J.; Zuo, K. Utilization of unprocessed steel slag as fine aggregate in normal- and high-strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasrawi, H.; Shalabi, F.; Asi, I. Use of low CaO unprocessed steel slag in concrete as fine aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, N.H.; Ismail, M.; Khalid, N.H.A.; Muhammad, B. Properties of concrete containing electric arc furnace steel slag and steel sludge. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 28, 101060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, T.; Song, T.; Pan, Z. Performance of concrete made with steel slag and waste glass. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malathy, R.; Arivoli, M.; Chung, I.-M.; Prabakaran, M. Effect of surface-treated energy optimized furnace steel slag as coarse aggregate in the performance of concrete under corrosive environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 284, 122840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, H. Utilization of carbonated and granulated steel slag aggregate in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 84, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palankar, N.; Shankar, A.U.R.; Mithun, B.M. Durability studies on eco-friendly concrete mixes incorporating steel slag as coarse aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 129, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortega, M.A.; Cavalaro, S.H.P.; Rodríguez de Sensale, G.; Aguado, A. Durability of concrete with electric arc furnace slag aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 217, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortega, M.A.; Segura, I.; Cavalaro, S.H.P.; Toralles-Carbonari, B.; Aguado, A.; Andrello, A.C. Radiological protection and mechanical properties of concretes with EAF steel slags. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 51, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Xue, G.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Dong, W. Mechanical performance, microstructure, and damage model of concrete containing steel slag aggregate. Struct. Concr. 2022, 24, 2189–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, B.; Deng, Z.; Liu, B. Mechanical Performance of Steel Slag Concrete under Biaxial Compression. Materials 2020, 13, 3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, B.; Wen, X.; Liu, B. Triaxial Compression Performance Research of Steel Slag Concrete on the Unified Strength Theory. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.C.; Liao, J.; Zeng, J.J.; Ma, C.L.; Li, Y.L.; Zhuge, Y. Tri-axial compressive behavior of coal reject concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.J.; Hu, X.; Sun, H.Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.J.; Zhuge, Y. Triaxial compressive behavior of 3D printed PE fiber-reinforced ultra-high performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 155, 105816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, L.; Yan, L.; Li, S.; Cai, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, X. Characterising mechanical properties and failure criteria of steel slag aggregate concrete under multiaxial stress states. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 424, 135903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, L.; Yan, L.; Cai, H.; Luo, X.; Li, Y. Autoclaved steel slag coarse aggregate: A potential solution for sustainable concrete production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, J.E. Mechanics of Materials 2: The Mechanics of Elastic and Plastic Deformation of Solids and Structural Materials, 3rd ed.; Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK; Auckland, New Zealand; Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 61–86. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.J.; Chen, W.F. A nonuniform hardening plasticity model for concrete materials. Mech. Mater. 1985, 4, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Han, D.J. Plasticity for Structural Engineers, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; 1988; pp. 345–380. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.F.; Han, D.J. Constitutive modeling in analysis of concrete structures. J. Eng. Mech. 1987, 113, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Constitutive Relationship of Autoclaved Steel Slag Aggregate Concrete. Doctoral Dissertation, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.F.; Yu, T. Constitutive Equations for Materials of Concrete and Soil, 1st ed.; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 312–317. [Google Scholar]

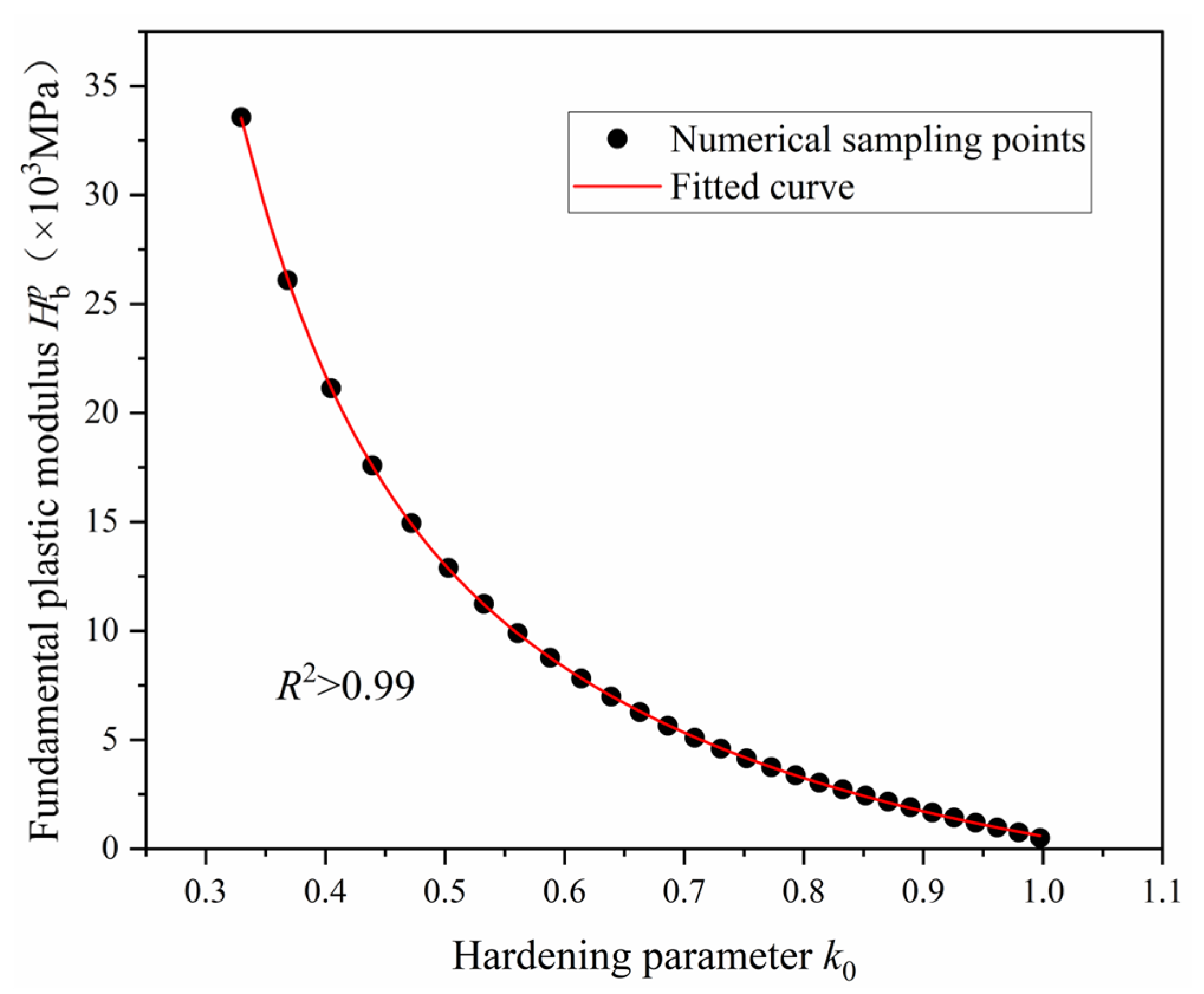
| Parameters | a | b | ct | cc | d | α | β |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 10.0632 | 0.0976 | 17.8701 | 11.0764 | 0.9326 | 1.6 | 2.0 |
| Parameters | A1 | A2 | A3 | t1 | t2 | Correlation Coefficient R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 6.67 × 106 | 5.60 × 105 | −2.99 × 104 | 0.0852 | 0.3632 | >0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Dong, T. An Elastoplastic Constitutive Model for Steel Slag Aggregate Concrete Under Multiaxial Stress States Based on Non-Uniform Hardening Theory. Materials 2025, 18, 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174124
Chen Z, Huang L, Yang Y, Dong T. An Elastoplastic Constitutive Model for Steel Slag Aggregate Concrete Under Multiaxial Stress States Based on Non-Uniform Hardening Theory. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174124
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhijun, Liang Huang, Yiwei Yang, and Teng Dong. 2025. "An Elastoplastic Constitutive Model for Steel Slag Aggregate Concrete Under Multiaxial Stress States Based on Non-Uniform Hardening Theory" Materials 18, no. 17: 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174124
APA StyleChen, Z., Huang, L., Yang, Y., & Dong, T. (2025). An Elastoplastic Constitutive Model for Steel Slag Aggregate Concrete Under Multiaxial Stress States Based on Non-Uniform Hardening Theory. Materials, 18(17), 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174124





