Effect of Cooling/Lubrication Conditions on Machining Performance: An Experimental Investigation of 1040 Steel Under Dry, MQL, and Nano-MQL Environments
Highlights
- TiC nano-MQL significantly improved surface quality in AISI 1040 turning.
- Nano-MQL noticeably decreased energy consumption and cutting forces.
- TiC-based lubrication minimized tool wear and prolonged tool life.
- Nano-MQL resulted in stable cutting and favorable chip-breaking performance.
- Results confirm that nano-MQL is a green, high-performance lubrication method.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Roughness
3.2. Energy Consumption
3.3. Cutting Force
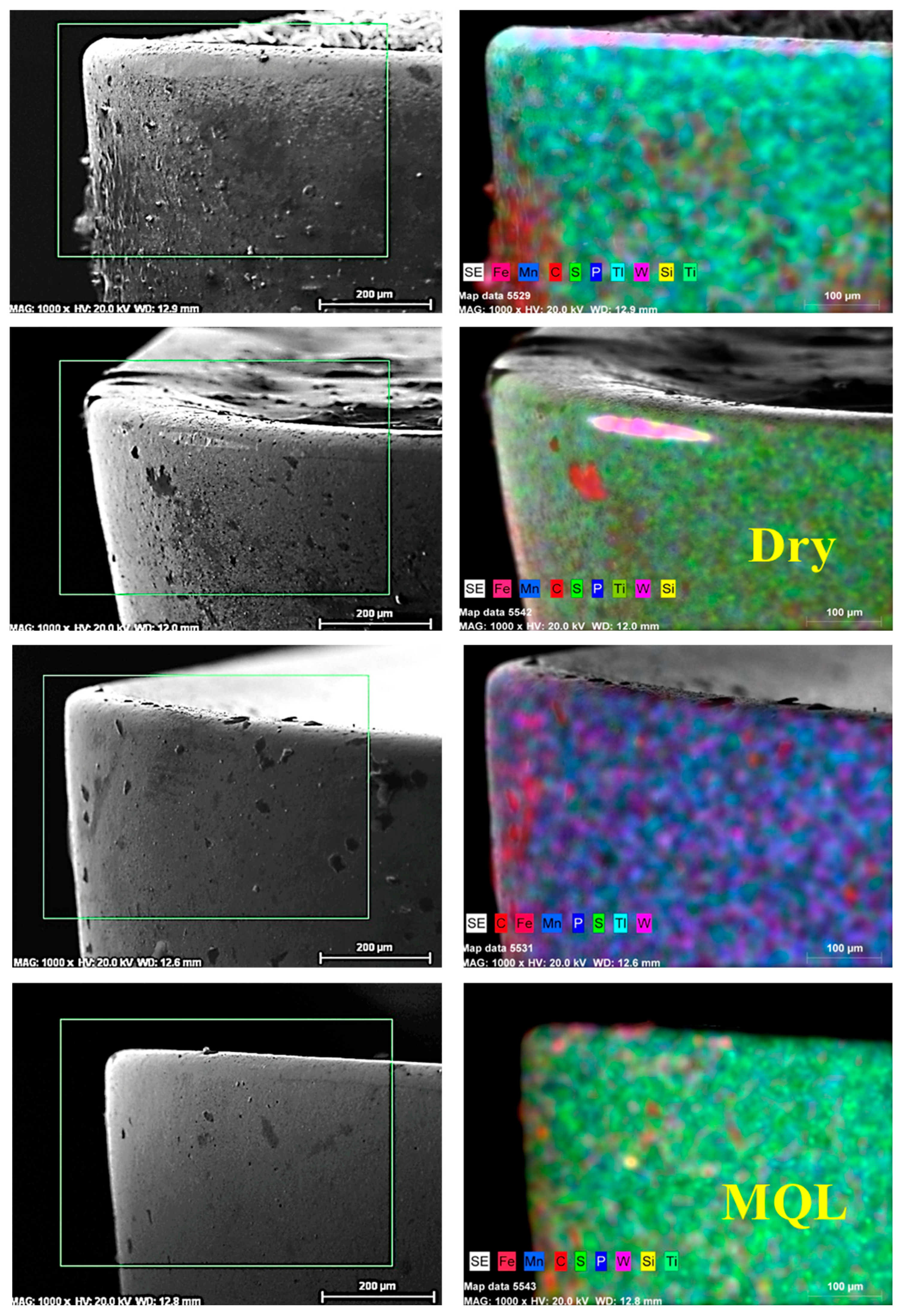
3.4. Tool Wear
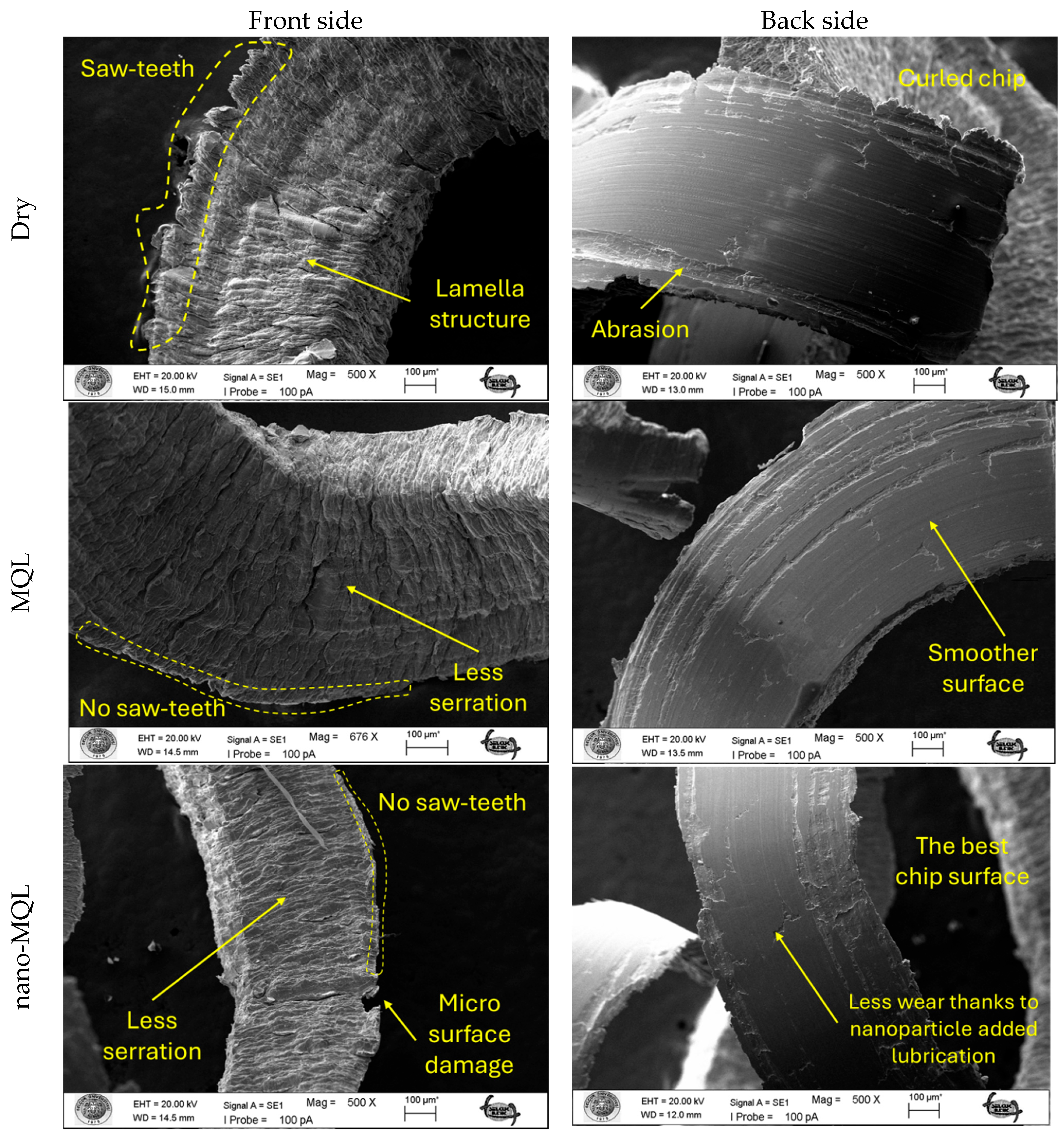
3.5. Chip Morphologies
3.6. Machining Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Said, Z.; Gupta, M.; Hegab, H.; Arora, N.; Khan, A.M.; Jamil, M.; Bellos, E. A comprehensive review on minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) in machining processes using nano-cutting fluids. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 2057–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntoglu, M. Machining induced tribological investigations in sustainable milling of Hardox 500 steel: A new approach of measurement science. Measurement 2022, 201, 111715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntoğlu, M.; Aslan, A. AISI 5140 Çeliğinin tornalanması esnasında yaklaşma açısı ve kesme parametrelerinin işlenebilirliğe etkisinin incelenmesi. Politek. Derg. 2021, 25, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P. Machining: Fundamentals and Recent Advances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Usca, Ü.A.; Uzun, M.; Kuntoğlu, M.; Sap, E.; Gupta, M.K. Investigations on tool wear, surface roughness, cutting temperature, and chip formation in machining of Cu-B-CrC composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 116, 3011–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salur, E. Understandings the tribological mechanism of Inconel 718 alloy machined under different cooling/lubrication conditions. Tribol. Int. 2022, 174, 107677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhshim, N.; Mativenga, P.; Sheikh, M.A. Heat generation and temperature prediction in metal cutting: A review and implications for high speed machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 782–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binali, R.; Demirpolat, H.; Kuntoğlu, M.; Sağlam, H. Machinability investigations based on tool wear, surface roughness, cutting temperature, chip morphology and material removal rate during dry and MQL-assisted milling of Nimax mold steel. Lubricants 2023, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Rong, Y.; Wang, G. The effect of cutting fluids applied in metal cutting process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 230, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Xu, H.; Jin, G.; Lu, Y.; Chen, B.; Xu, S.; Shi, J.; Fan, X. Boundary slip and lubrication mechanisms of organic friction modifiers with effect of surface moisture. Friction 2024, 12, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiran Gabriel, D.; Parthiban, M.; Kantharaj, I.; Beemkumar, N. A review on sustainable alternatives for conventional cutting fluid applications for improved machinability. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2023, 27, 157–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiang, S.; Zhou, X.; Lin, S.; Dong, K.; Liu, Y.; He, D.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, B. Lubrication Performance Promotion of GTL Base Oil by BN Nanosheets via Cascade Centrifugation-Assisted Liquid-Phase Exfoliation. Lubricants 2025, 13, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandekar, S.; Sankar, M.R.; Agnihotri, V.; Ramkumar, J. Nano-cutting fluid for enhancement of metal cutting performance. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2012, 27, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntoğlu, M.; Binali, R.; Makhesana, M. Characterizing Machining Indicators with Machine Learning Models Under Cellulose Nanocrystal and Graphene-Based Nanofluid Conditions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.S.; Singh, G.; Sørby, K. A review on minimum quantity lubrication for machining processes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 935–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamran, N.N.; Ghani, J.; Ramli, R.; Haron, C.C. A review on recent development of minimum quantity lubrication for sustainable machining. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, S.A.; Choudhury, I.A.; Nukman, Y. A critical assessment of lubrication techniques in machining processes: A case for minimum quantity lubrication using vegetable oil-based lubricant. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, B.S.; Yamaner, A.S. A Comparative Evaluation of Dry-MQL Turning Applications for AISI 5115 Steel. Manuf. Technol. Appl. 2025, 6, 23–32. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/mateca/issue/91625/1571978 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H.A. Towards sustainable machining of Inconel 718 using nano-fluid minimum quantity lubrication. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2018, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellán-Nebot, J.V.; Andreu-Sánchez, O.; Fito-López, C.; Mondragón, R. Nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication (NMQL): Overview of nanoparticle toxicity and safer-design guidelines. Lubricants 2024, 12, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Dixit, A.R. Tribological investigation of TiO2 nanoparticle based cutting fluid in machining under minimum quantity lubrication (MQL). Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Voort, G.F.; Lampman, S.R.; Sanders, B.R.; Anton, G.J.; Polakowski, C.; Kinson, J.; Muldoon, K.; Henry, S.D.; Scott, W.W., Jr. ASM Handbook: Metallography and Microstructures; ASM International: Russell Township, OH, USA, 2004; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sabarivasan, V.; Sivaraj, P.; Balasubramanian, V.; Malarvizhi, S. Analysis of Failure Modes of Resistance Spot Welded Dissimilar Thickness DP800/AISI 1040 Steel Joints: An Effect of Welding Current. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2025, 25, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, M.S.; Rajpal, S.J. Comparative analysis of tractor’s trolley axle by using FEA. (by considering change in materials existing shape and size). Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2013, 2, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, A.N.; Kibria, M.G.; Ahmed, M.R. An experimental study on the effect of minimum quantity lubrication on drilling AISI 1040 steel. GAZI Univ. J. Sci. 2015, 28, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S.; Amarnath, M.; Gupta, M.K.; Makhesana, M.A. Performance assessment of nano-Al2O3 enriched coconut oil as a cutting fluid in MQL-assisted machining of AISI-1040 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, K.; Anjum, I.; Pruncu, C.I.; Amjad, M.; Kumar, M.S.; Maqsood, M.A. Progressing towards sustainable machining of steels: A detailed review. Materials 2021, 14, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, N.M.; Duc, T.M.; Long, T.T.; Hoang, V.L.; Ngoc, T.B. Investigation of machining performance of MQL and MQCL hard turning using nano cutting fluids. Fluids 2022, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldin, V.; da Silva, L.R.R.; Davis, R.; Jackson, M.J.; Amorim, F.L.; Houck, C.F.; Machado, Á.R. Dry and MQL milling of AISI 1045 steel with vegetable and mineral-based fluids. Lubricants 2023, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salur, E.; Kuntoğlu, M.; Aslan, A.; Pimenov, D.Y. The effects of MQL and dry environments on tool wear, cutting temperature, and power consumption during end milling of AISI 1040 steel. Metals 2021, 11, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, F. Investigation of the effect of Al2O3 nanoparticle-added MQL lubricant on sustainable and clean manufacturing. Lubricants 2024, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, J.A.; Hamran, N.N.N. Nano-Additives-Assisted MQL Machining. In Tribology in Sustainable Manufacturing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 110–124. [Google Scholar]
- Şirin, Ş.; Sarıkaya, M.; Yıldırım, Ç.V.; Kıvak, T. Machinability performance of nickel alloy X-750 with SiAlON ceramic cutting tool under dry, MQL and hBN mixed nanofluid-MQL. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabgard, M.; Seyedzavvar, M.; Mohammadpourfard, M. Experimental investigation into lubrication properties and mechanism of vegetable-based CuO nanofluid in MQL grinding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 3807–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Krishna, V.M. An investigation on turning AISI 1018 steel with hybrid biodegradeable nanofluid/MQL incorporated with combinations of CuO-Al2O3 nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 24, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Cui, Z.; Wu, C.; Sun, J.; Zhou, J. Evaluation of MQL broaching AISI 1045 steel with sesame oil containing nano-particles under best concentration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, S.; Wagri, N.K.; Dash, L.; Das, A.; Das, S.R.; Rafighi, M.; Sharma, P. Investigation on surface integrity in hard turning of AISI 4140 steel with SPPP-AlTiSiN coated carbide insert under nano-MQL. Lubricants 2023, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Patel, S.K.; Arakha, M.; Dey, A.; Biswal, B.B. Processing of hardened steel by MQL technique using nano cutting fluids. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2021, 36, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Aravindan, S. Machining performance evaluation of Ti6Al4V alloy with laser textured tools under MQL and nano-MQL environments. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 53, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Sen, B.; Ghosh, S.; Rao, P. Strategic enhancement of machinability in nickel-based superalloy using eco-benign hybrid nano-MQL approach. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 127, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salur, E.; Acarer, M.; Şavkliyildiz, İ. Improving mechanical properties of nano-sized TiC particle reinforced AA7075 Al alloy composites produced by ball milling and hot pressing. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, G.; Acarer, M.; Uyaner, M. Effect of Co addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of new generation 3Cr-3W and 5Cr-3W steels. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Olortegui-Yume, J.; Yoon, M.-C.; Kwon, P. A study on droplets and their distribution for minimum quantity lubrication (MQL). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; Dixit, A.R. Effects of Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) in machining processes using conventional and nanofluid based cutting fluids: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhesana, M.A.; Patel, K.M.; Bagga, P.J. Evaluation of surface roughness, tool wear and chip morphology during machining of nickel-based alloy under sustainable hybrid nanofluid-MQL strategy. Lubricants 2022, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ÖZLÜ, B. Evaluation of energy consumption, cutting force, surface roughness and vibration in machining toolox 44 steel using taguchi-based gray relational analysis. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2022, 29, 2250103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şencan, A.Ç.; Duran, A.; Şeker, U. The effect of different cooling methods to hole quality and tool life in the drilling of AA7075 and AA2024 aluminum alloys. Manuf. Technol. Appl. 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Benardos, P.; Vosniakos, G.-C. Predicting surface roughness in machining: A review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2003, 43, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaner, A.S.; Kul, B.S. Evaluation of tool radius and machining parameters on cutting forces and surface roughness for AA 6082 aluminum alloy. Eur. Mech. Sci. 2025, 9, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özlü, B.; Ulaş, H.B.; Kara, F. Investigation of the Effects of Cutting Tool Coatings and Machining Conditions on Cutting Force, Specific Energy Consumption, Surface Roughness, Cutting Temperature, and Tool Wear in the Milling of Ti6Al4V Alloy. Lubricants 2025, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binali, R.; Demirpolat, H.; Kuntoğlu, M.; Kaya, K. Exploring the Tribological Performance of Mist Lubrication Technique on Machinability Characteristics During Turning S235JR Steel. Manuf. Technol. Appl. 2024, 5, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldum, B.B.; Leksycki, K.; Cagan, S.C. Comparative Analysis of Dry, Minimum Quantity Lubrication, and Nano-Reinforced Minimum Quantity Lubrication Environments on the Machining Performance of AZ91D Magnesium Alloy. Machines 2025, 13, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Gong, Z.; Liu, A.; Cai, Y.; Wang, B.; Song, Q.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Comparison of surface morphology and tool wear in the machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloys with uncoated and TiAlN tools under dry, minimum quantity lubrication, flood cooling, and low-temperature spray jet cooling conditions. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedai, Y. Exploring the impact of the turning of AISI 4340 steel on tool wear, surface roughness, sound intensity, and power consumption under dry, MQL, and nano-MQL conditions. Lubricants 2023, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P. Design of optimisation of cutting parameters for turning metal matrix composites based on the orthogonal arrays. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 132, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, Ş.; Güllü, A. Farklı yanaşma açıları ile vermiküler grafitli dökme demirin frezelenmesinde kesme kuvvetlerinin araştırılması ve analitik modellenmesi. Gazi Üniversitesi Mühendislik Mimar. Fakültesi Derg. 2013, 28, 135–143. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/gazimmfd/issue/6702/89067 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Uluğ, D. Kaplamalı ve Kaplamasız Sementit Karbür Takımlar İçin Taylor Takım Ömrü Modeli’ndeki “n” Üstel Değerinin Deneysel Olarak Araştırılması. Master’s Thesis, Gazi Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Ankara, Turkey, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dilipak, H.; Gezgin, A. AISI D3 çeliğinin frezelenmesinde, kesici uç sayısı, kesme hızı ve ilerleme miktarının yüzey pürüzlülüğü üzerindeki etkilerinin araştırılması. Politek. Derg. 2010, 13, 29–32. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/politeknik/issue/33052/367854 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Gökkaya, H.; Sur, G.; Dilipak, H. Kaplamasiz Sementit Karbür Kesici Takim Ve Kesme Parametrelerinin Yüzey Pürüzlülüğüne Etkisinin Deneysel Olarak İncelenmesi. Pamukkale Üniversitesi Mühendislik Bilim. Derg. 2006, 12, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ciftci, I. Machining of austenitic stainless steels using CVD multi-layer coated cemented carbide tools. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özlü, B.; Akgün, M.; Demir, H. AA 6061 Alaşımının tornalanmasında kesme parametrelerinin yüzey pürüzlülüğü üzerine etkisinin analizi ve optimizasyonu. Gazi Mühendislik Bilim. Derg. 2019, 5, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binali, R.; Demirpolat, H.; Kuntoğlu, M.; Salur, E. Different aspects of machinability in turning of AISI 304 stainless steel: A sustainable approach with MQL technology. Metals 2023, 13, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.E.; Gupta, M.K.; Çelik, E.; Ross, N.S.; Günay, M. A sustainable cooling/lubrication method focusing on energy consumption and other machining characteristics in high-speed turning of aluminum alloy. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 40, e00919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtkuran, H.; Günay, M. Analyzing the effects of cutting parameters on Machinability Criteria in Milling of 17-4PH Stainless Steel under Dry Environment. Manuf. Technol. Appl. 2022, 3, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.E.; Gupta, M.K.; Çelik, E.; Ross, N.S.; Günay, M. Tool wear and its mechanism in turning aluminum alloys with image processing and machine learning methods. Tribol. Int. 2024, 191, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, N.; Hayat, F.; Günay, M. Sertleştirilmiş 1.2367 takım çeliğinin işlenmesinde enerji tüketiminin analizi ve modellenmesi. İmalat Teknol. Uygulamaları 2020, 1, 41–49. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/article-file/1377847 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Yavaşcı, E.; Kardökmak, A.; Demirsöz, R. Talaşlı imalatta kesme hızı, ilerleme ve kesme derinliği değişkenlerinin torna tezgâhı güç tüketimi üzerine etkileri. Çelik Araştırma Geliştirme Derg. 2022, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Karabulut, Ş.; Şahinoğlu, A. R260 çeliklerinin işlenmesinde kesme parametrelerinin yüzey pürüzlülüğü, güç tüketimi ve makine gürültüsü üzerine etkileri. Politek. Derg. 2018, 21, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Serin, G.; Kahya, M.; Özbayoğlu, M.; Ünver, H.Ö. TI6AL4V Malzemesinin Tornalama İşleminde Özgül Kesme Enerjisi Ve Yüzey Pürüzlüğünün İncelenmesi Ve Yapay Sinir Ağlari Temelli Tahmin Modeli Geliştirilmesi. Uludağ Üniversitesi Mühendislik Fakültesi Derg. 2019, 24, 517–536. [Google Scholar]
- Şap, S. AISI 5140 Çeliğinin Farklı Soğutma Teknikleri Kullanılarak Frezelenmesinin Güç Tüketimi Üzerine Etkileri. Fırat Üniversitesi Mühendislik Bilim. Derg. 2023, 35, 313–320. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/doi/10.35234/fumbd.1227075 (accessed on 22 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Kazan, H.; Ergül, E.U. Kesme Parametrelerinin Haynes 242 Nikel Bazlı Süper Alaşım Malzemenin Tornalamasında Güç Tüketimi Üzerindeki Etkilerinin RSM ve GA ile İncelenmesi. Afyon Kocatepe Üniversitesi Fen Mühendislik Bilim. Derg. 2022, 22, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Cönger, D.; Emiroğlu, U.; Uysal, A.; Altan, E. Alüminyum 6061 Malzemenin MQL Yöntemi ile Frezelenmesinde Nano MoS2 Katkılı Kesme Sıvısı Kullanımının Kesme Kuvvetleri ve Yüzey Pürüzlülüğüne Etkilerinin İncelenmesi. Makina Tasarım İmalat Derg. 2019, 17, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kursuncu, B.; Yaraş, A. AISI O2 çeliğinin frezelenmesinde minimum miktarda yağlama (MQL) sisteminin kesme performansına etkisi. J. Bartin Univ. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2017, 5, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, J.; Jadhav, B. Experimental study of effect of cutting parameters on cutting force in turning process. Int. J. Innov. Res. Adv. Eng. 2014, 1, 240–248. [Google Scholar]
- Tazehkandi, A.H.; Pilehvarian, F.; Davoodi, B. Experimental investigation on removing cutting fluid from turning of Inconel 725 with coated carbide tools. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 80, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazehkandi, A.H.; Shabgard, M.; Kiani, G.; Pilehvarian, F. Investigation of the influences of polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (PCBN) tool on the reduction of cutting fluid consumption and increase of machining parameters range in turning Inconel 783 using spray mode of cutting fluid with compressed air. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, Y. Matkap Ile Delik Delme Esnasında Kesme Parametrelerinin Kesme Kuvveti ve Sıcaklığın Değişimine Etkisinin Deneysel Olarak Incelenmesi. Master’s Thesis, Marmara Universitesi, İstanbul, Turkey, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Korkut, İ.; Dönertaş, M.A. Kesme parametrelerinin frezelemede oluşan kesme kuvvetleri üzerindeki etkileri. Politek. Derg. 2003, 6, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaş, H.B. AISI D2 ve AISI D3 soğuk iş takım çeliklerinin delinmesinde kesme parametrelerinin kesme kuvvetleri üzerindeki etkisinin incelenmesi. Politek. Derg. 2018, 21, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güral, A.; Erdoğan, M.; Şeker, U.; Korkut, İ. Çift Fazlı Çeliklerde Martensit Hacim Oranı ve Parçacık Boyutunun Kesici Uçta Aşınma ve Sıvanma BUE Oluşma Eğilimleri Üzerine Etkileri. GÜ Fen Bilim. Derg. 2000, 13, 741–753. [Google Scholar]
- Gürbüz, H.; Kafkas, F.; Şeker, U. AISI 316L Çeliğinin İşlenmesinde Kesici Takim Kesici Kenar Formu Ve Talaş Kirici Formlarinin Kesme Kuvvetleri Ve Yüzey Pürüzlülüğü Üzerine Etkisi. Batman Üniversitesi Yaşam Bilim. Derg. 2012, 1, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Tang, S.; Guo, S.; Song, X. Tool wear analysis in turning inconel-657 using various tool materials. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2024, 39, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.E.; Gupta, M.K.; Kuntoğlu, M.; Patange, A.D.; Ross, N.S.; Yılmaz, H.; Chauhan, S.; Vashishtha, G. Prediction and classification of tool wear and its state in sustainable machining of Bohler steel with different machine learning models. Measurement 2023, 223, 113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; Sharif, A.; Hussain, A.; Aamir, M.; Giasin, K.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Ali, U. Analysis of hole quality and chips formation in the dry drilling process of Al7075-T6. Metals 2021, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, O.; Altan Özbek, N.; Kara, F.; Saruhan, H. Effect of vibration and cutting zone temperature on surface topography during hybrid cooling/lubrication assisted machining of Vanadis 10. Mater. Test. 2023, 65, 1437–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
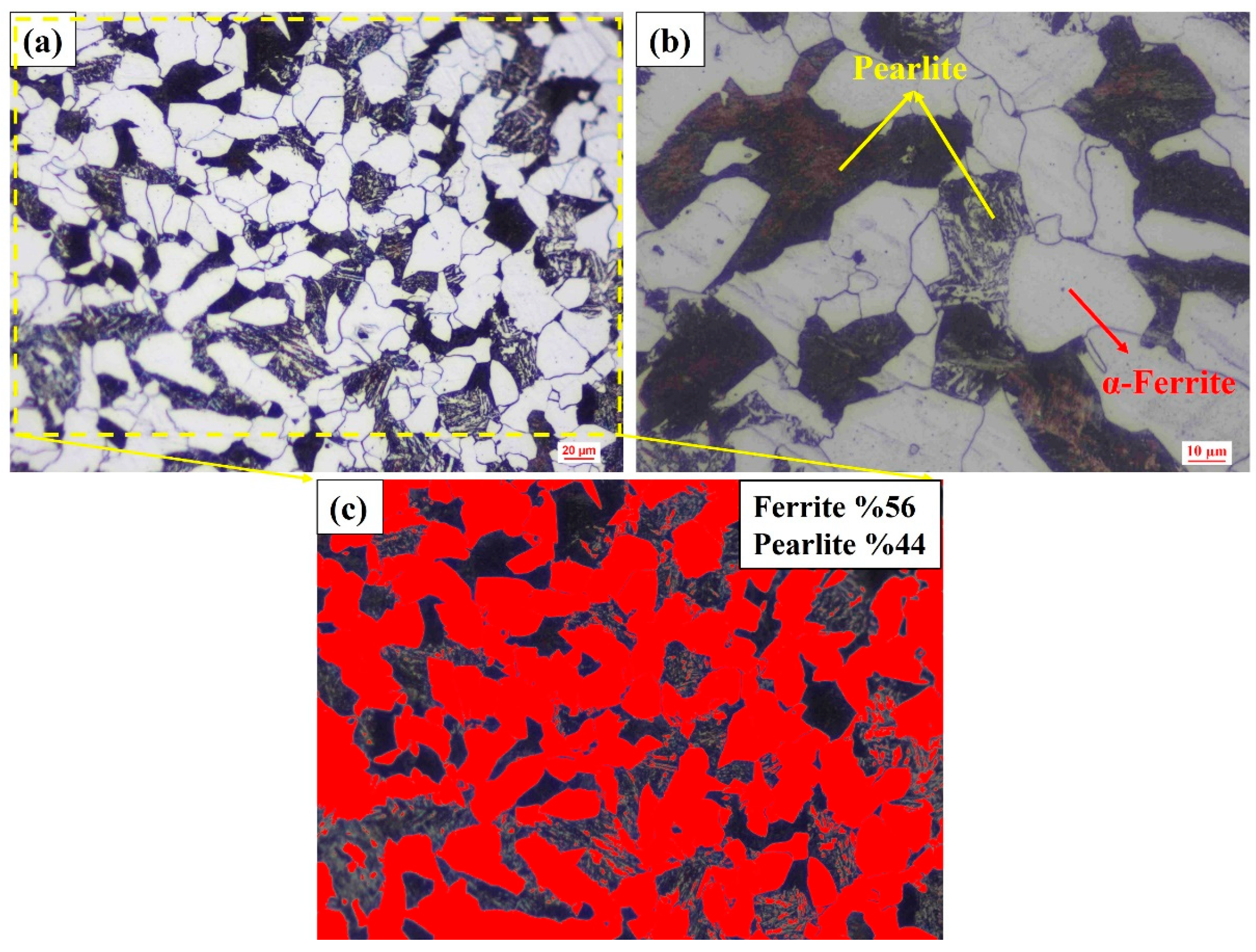
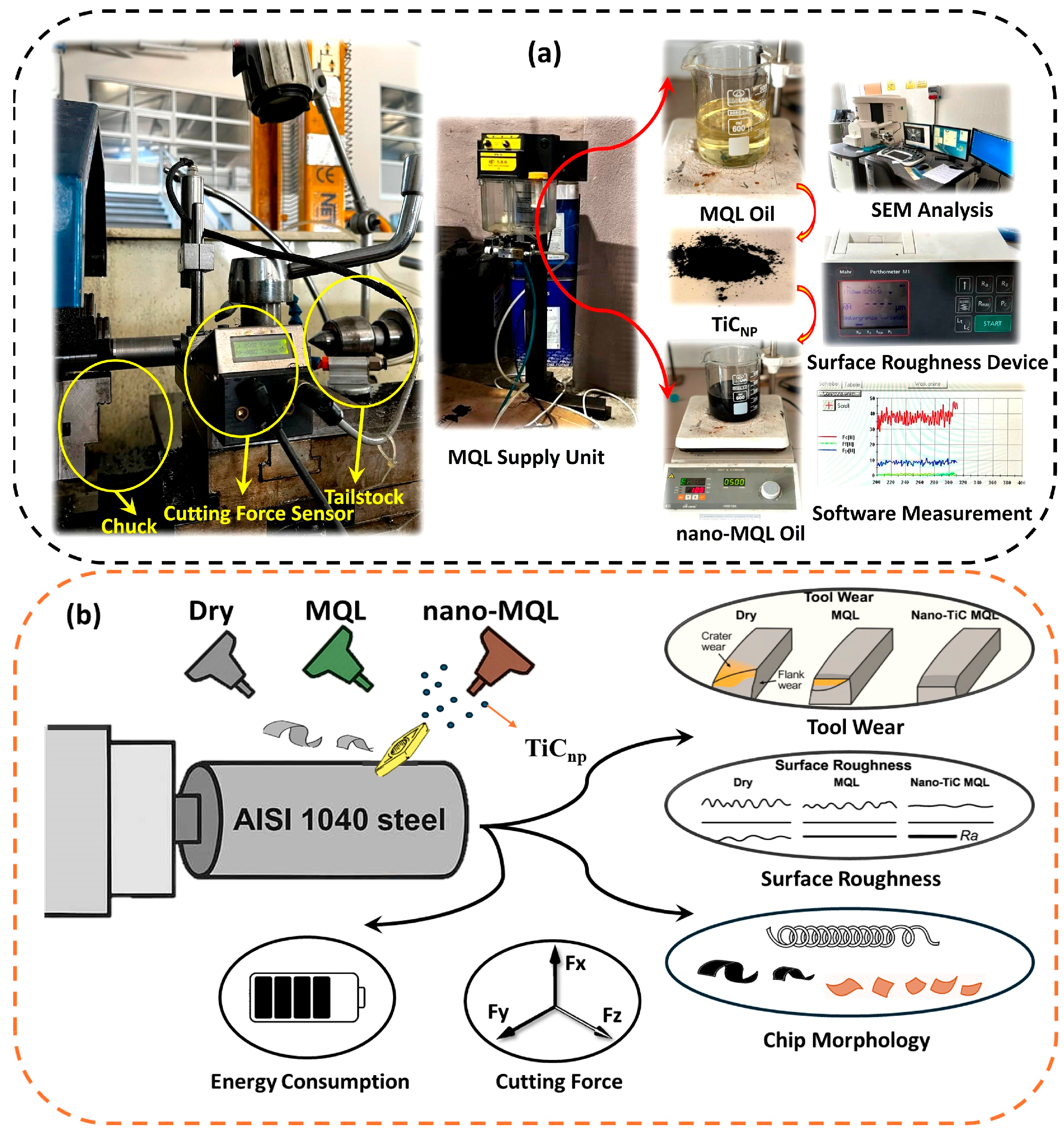
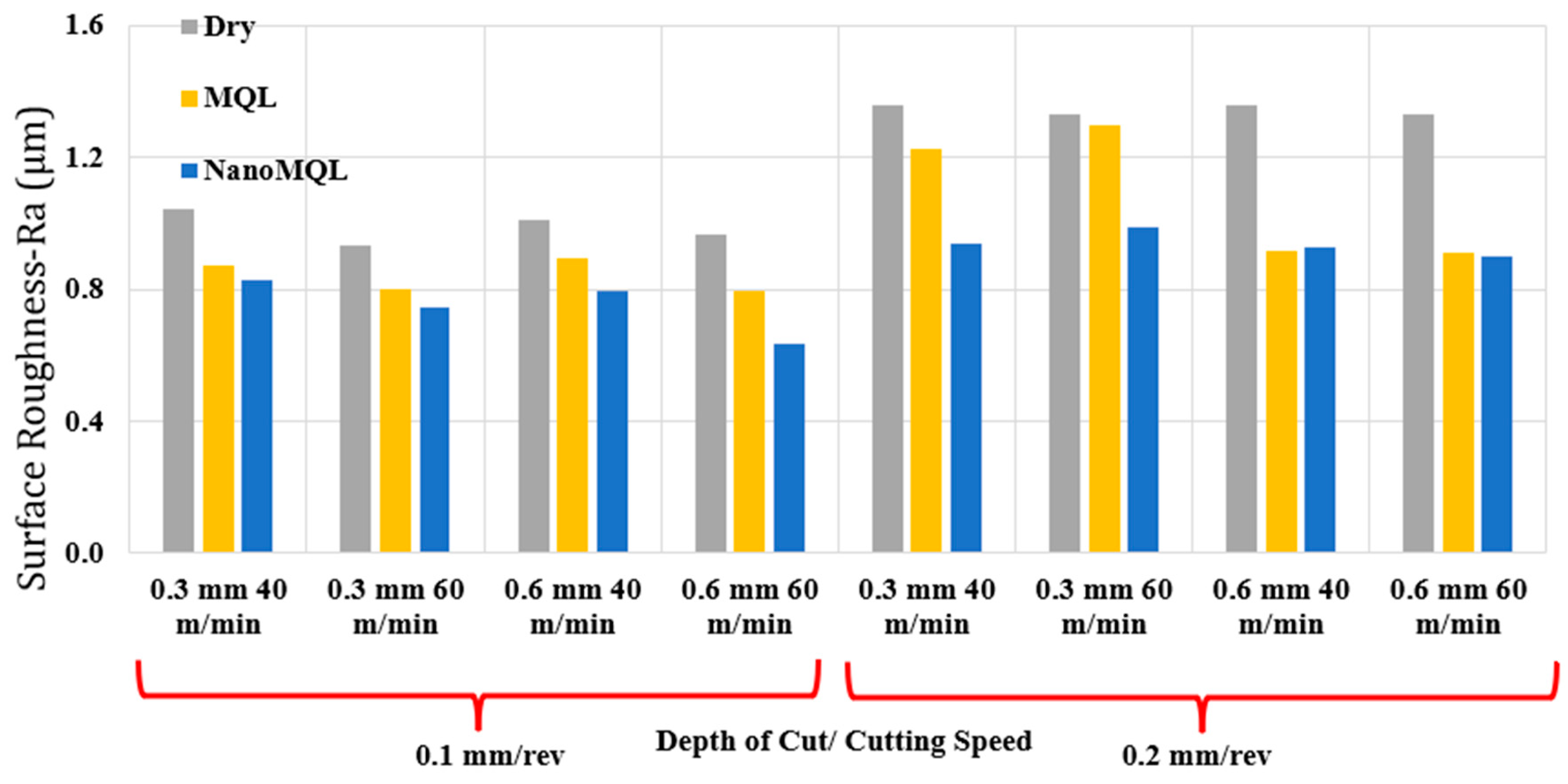
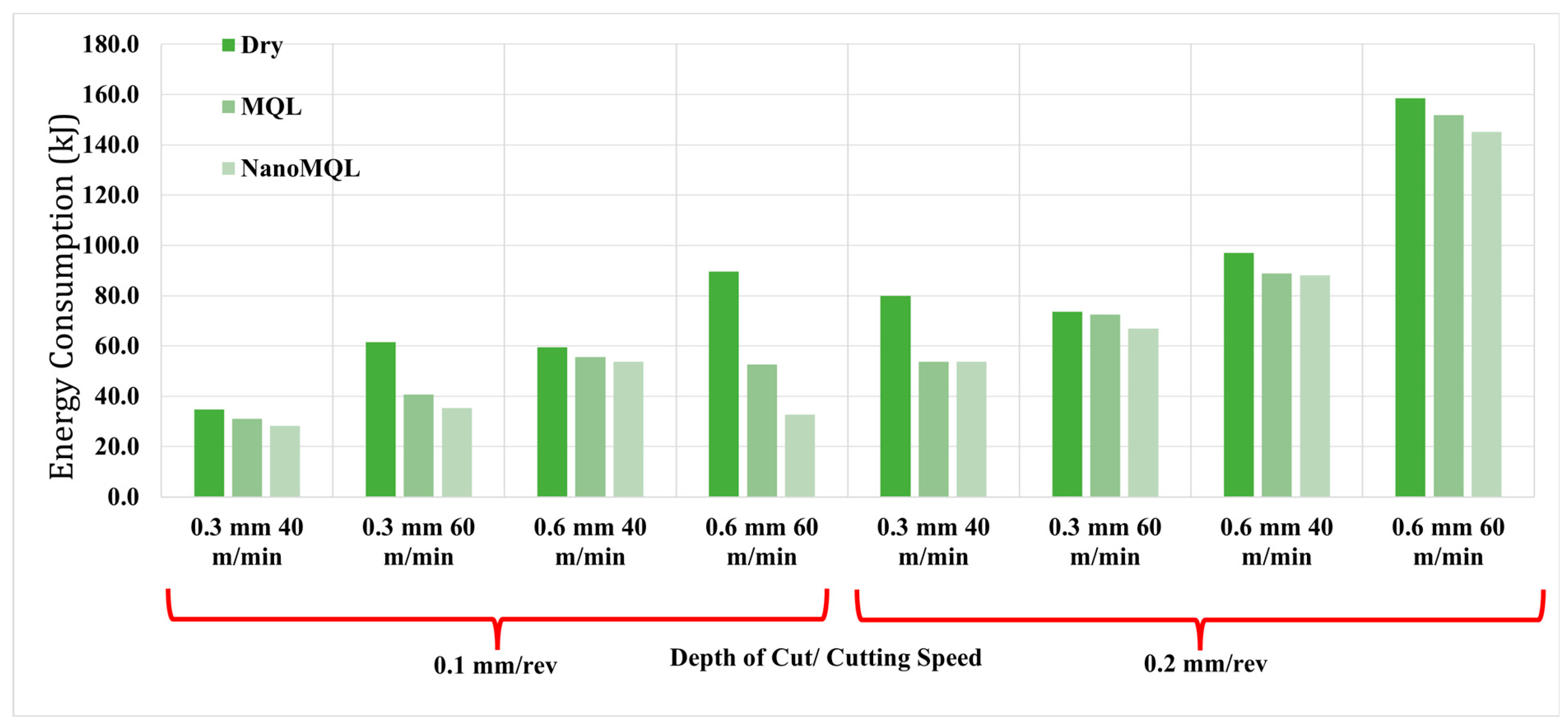


| Input Parameters | Output Parameters | Result Evaluations |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Depth | Surface Roughness | Graphical |
| Cooling Medium | Cutting Force | Machine Learning |
| Cutting Speed | Tool Wear | SEM |
| Feed Rate | Energy Consumption | Modeling |
| C %wt. | Mn %wt. | P %wt. | S %wt. | Si %wt. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.37–0.44 | 0.60–0.90 | ~0.04 | ~0.05 | 0.15–0.30 |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 580–700 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 320–530 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 13–20% |
| Brinell Hardness | 160–180 HB |
| Shear Strength | 350–390 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 190–210 GPa |
| Poisson Ratio | 0.27–0.30% |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 12 µm/m·°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 51 W/m·K |
| Density | 7.8 g/cm3 |
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Cutting speed (m/min) | 40, 60 |
| Feed rate (mm/rev) | 0.1, 0.2 |
| Cutting depth (mm) | 0.3, 0.6 |
| Cutting environment | Dry, MQL, and nano-TiC/mQL |
| Cutting Environments | MEI Values |
|---|---|
| Dry | 2.8922% |
| MQL | 4.4622% |
| Nano-MQL | 6.1605% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salur, E.; Okcu, N.; Korkmaz, M.E.; Kaya, K.; Binali, R.; Çetinkal, S.B. Effect of Cooling/Lubrication Conditions on Machining Performance: An Experimental Investigation of 1040 Steel Under Dry, MQL, and Nano-MQL Environments. Materials 2025, 18, 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174063
Salur E, Okcu N, Korkmaz ME, Kaya K, Binali R, Çetinkal SB. Effect of Cooling/Lubrication Conditions on Machining Performance: An Experimental Investigation of 1040 Steel Under Dry, MQL, and Nano-MQL Environments. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174063
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalur, Emin, Nursena Okcu, Mehmet Erdi Korkmaz, Kübra Kaya, Rüstem Binali, and Salih Bilal Çetinkal. 2025. "Effect of Cooling/Lubrication Conditions on Machining Performance: An Experimental Investigation of 1040 Steel Under Dry, MQL, and Nano-MQL Environments" Materials 18, no. 17: 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174063
APA StyleSalur, E., Okcu, N., Korkmaz, M. E., Kaya, K., Binali, R., & Çetinkal, S. B. (2025). Effect of Cooling/Lubrication Conditions on Machining Performance: An Experimental Investigation of 1040 Steel Under Dry, MQL, and Nano-MQL Environments. Materials, 18(17), 4063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174063







