New Polycyclic Red Luminescent Compounds Based on Carbonyl/Nitrogen Skeleton for Efficient Narrow-Spectrum OLEDs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
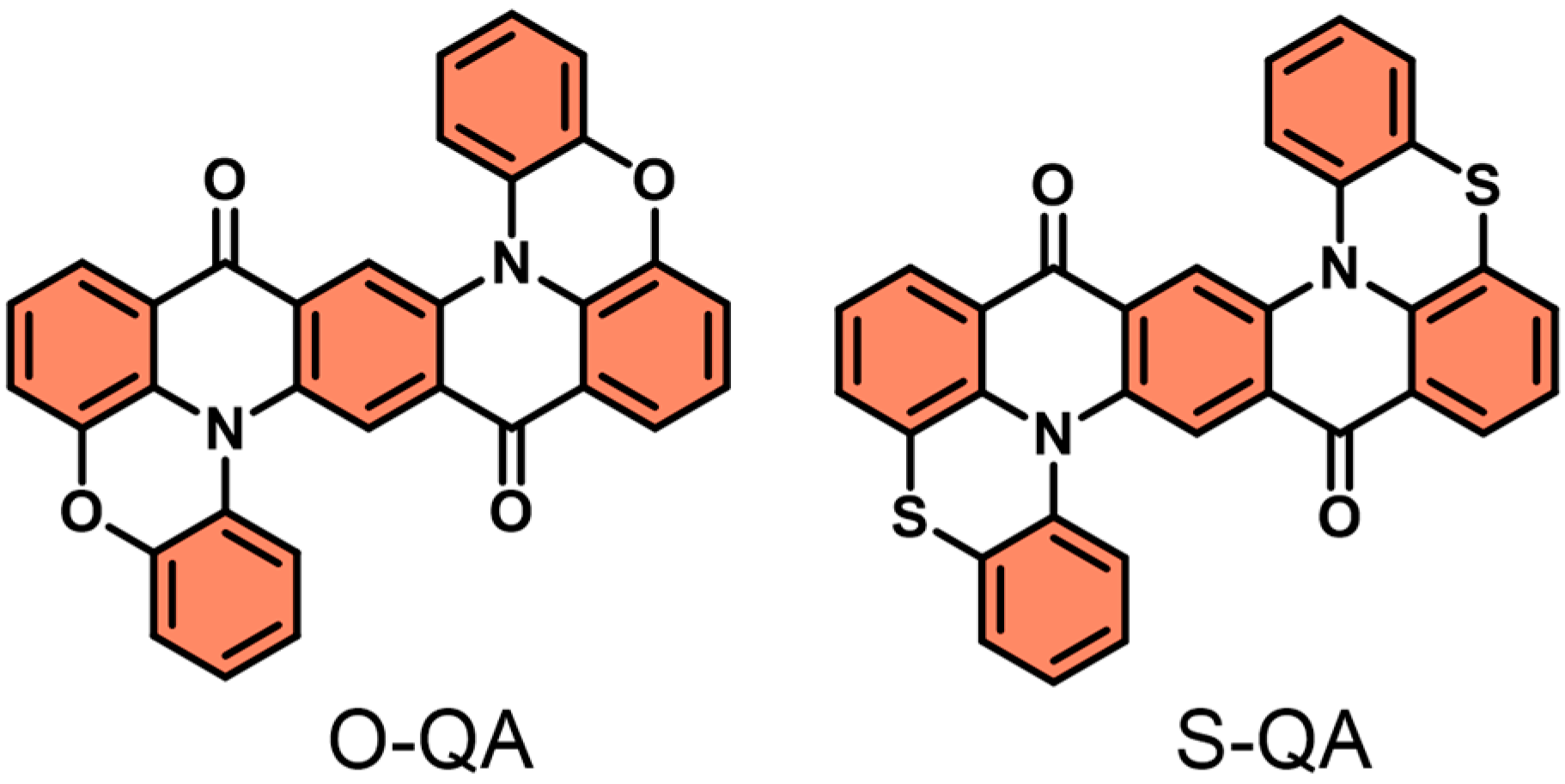
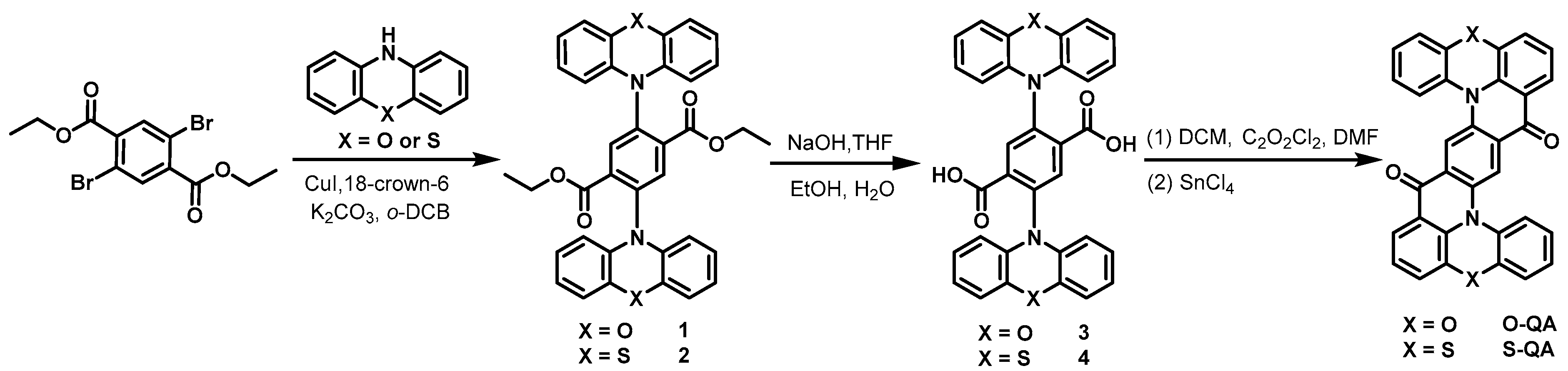
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
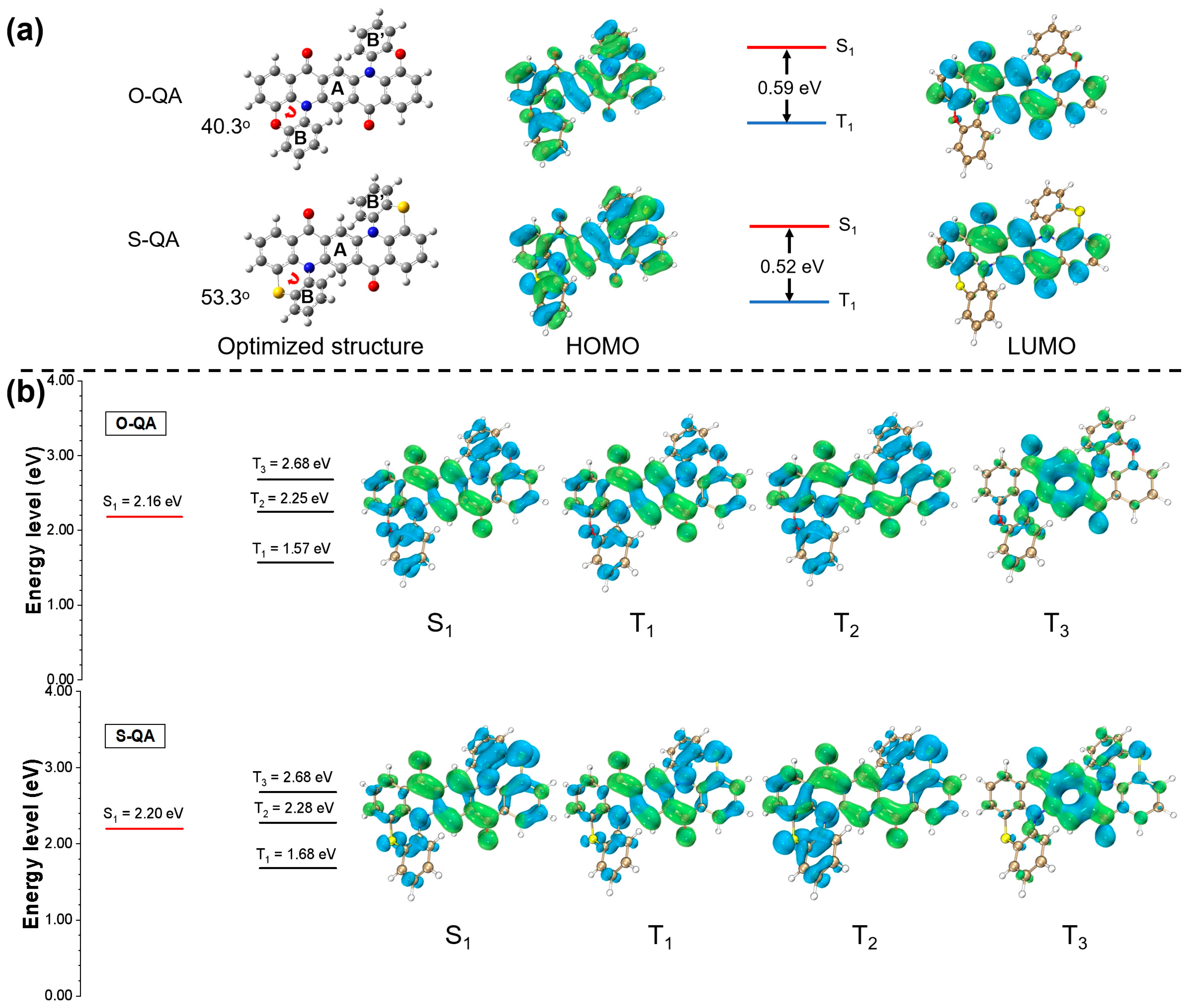
2.2. Theoretical Calculation
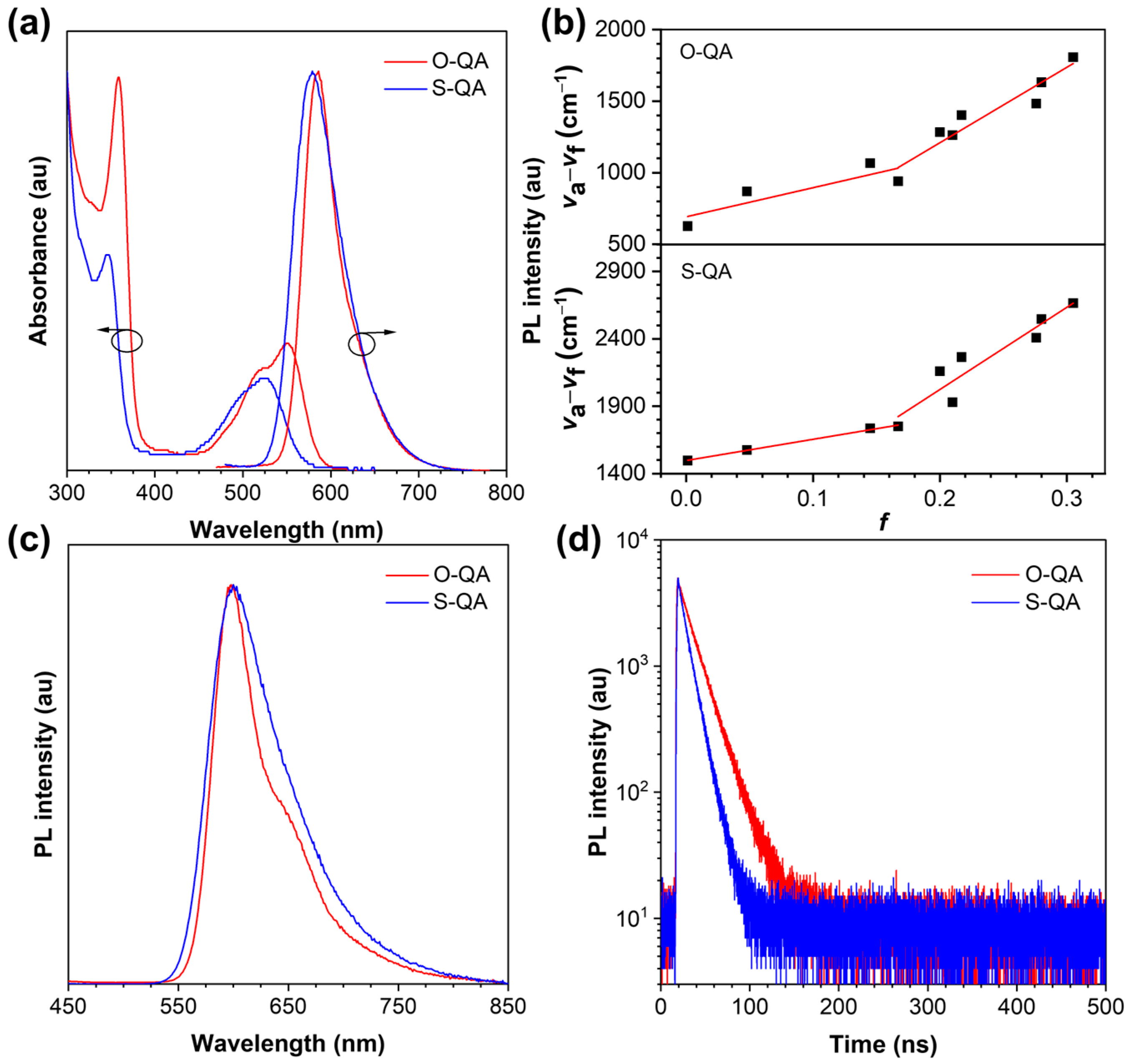
2.3. Photophysical Properties
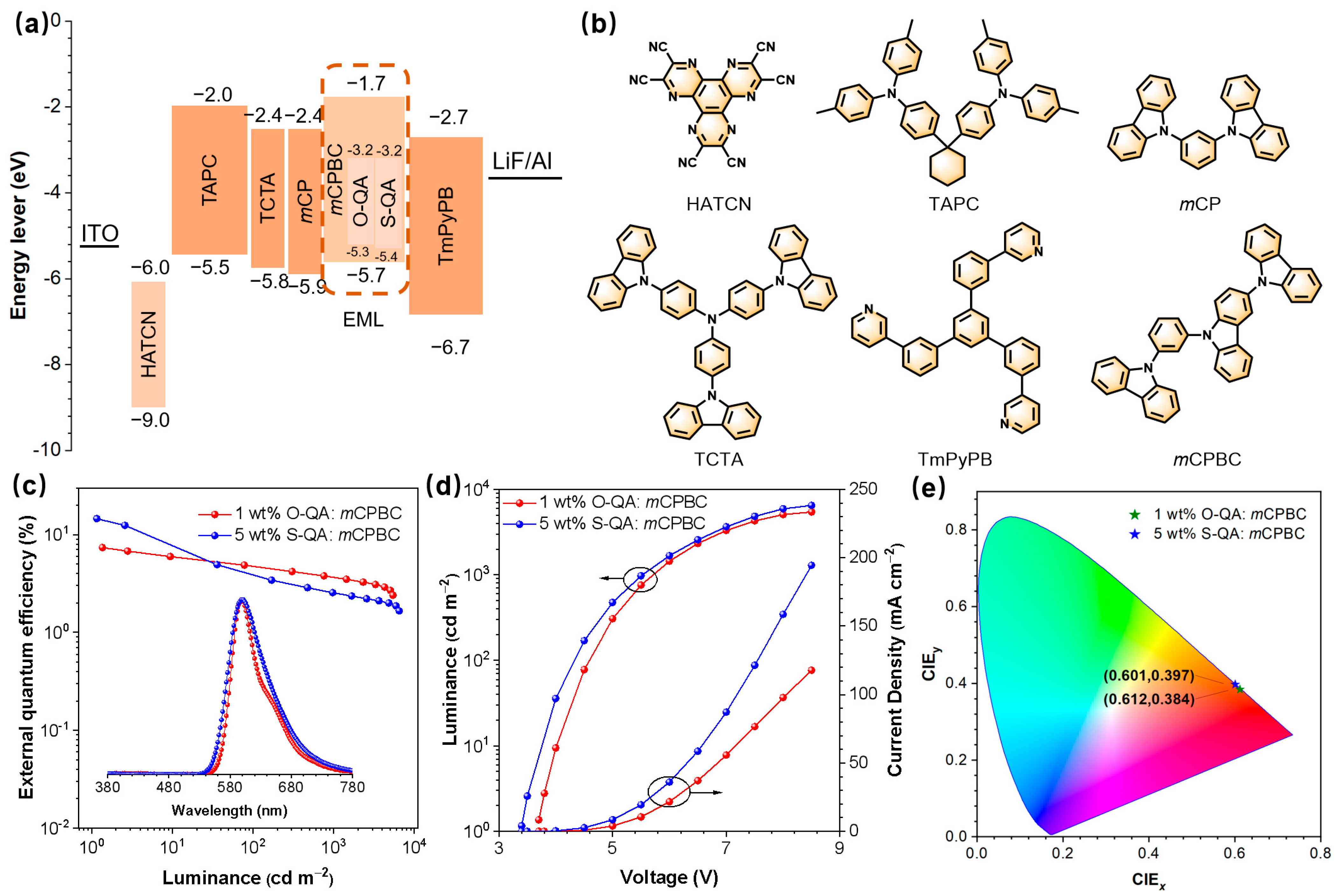
2.4. Electroluminescence Behaviors
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, S.; Hu, Y.-N.; Sun, D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zysman-Colman, E. A Fluorene-Bridged Double Carbonyl/Amine Multiresonant Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitter for Efficient Green OLEDs. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 2489–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Chu, S.; Gao, Y.; Yao, X.; Ji, W.; Li, G.; Ren, Z.; Fei, Z. High-Efficiency Solution-Processed Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Utilizing Multiple-Resonance Emitters Incorporating Thiocarbazole Unit. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2025, 13, 2403566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, J.; Yu, M.; Miao, J.; Xie, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Cao, X.; Yang, C. High-Performance Narrowband Pure-Red OLEDs with External Quantum Efficiencies up to 36.1% and Ultralow Efficiency Roll-Off. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Meng, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Yang, S.; Zhou, D.; Liao, L.; Jiang, Z. Introducing Spiro-locks into the Nitrogen/Carbonyl System towards Efficient Narrowband Deep-Blue Multi-Resonance TADF Emitters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, M.A.; O’Brien, D.F.; Thompson, M.E.; Forrest, S.R. Excitonic Singlet-Triplet Ratio in a Semiconducting Organic Thin Film. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 14422–14428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.; Kimyonok, A.; Etherington, M.K.; Griffiths, G.C.; Jankus, V.; Turksoy, F.; Monkman, A.P. Ultrahigh Efficiency Fluorescent Single and Bi-Layer Organic Light Emitting Diodes: The Key Role of Triplet Fusion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Hu, D.; Qiao, X.; Jiang, X.; et al. Highly Efficient Blue Fluorescent OLEDs Based on Upper Level Triplet–Singlet Intersystem Crossing. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Fang, K.; Mu, X.; Liu, C.; Su, S.-J.; Ge, Z. Decoding the Impact of Molecular Configuration on High-Efficiency Blue Hot Exciton Emitters. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2024, 12, 2400652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uoyama, H.; Goushi, K.; Shizu, K.; Nomura, H.; Adachi, C. Highly Efficient Organic Light-Emitting Diodes from Delayed Fluorescence. Nature 2012, 492, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathiya, S.; Panneerselvam, M.; Costa, L.T. A theoretical investigation of heavy atom and oxidation effects in MR-TADF emitters for OLEDs: A combined DFT, double hybrid DFT, CCSD, and QM/MM approaches. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2025, 27, 7265–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, M.; Kathiravan, A.; Solomon, R.V.; Jaccob, M. The role of π-linkers in tuning the optoelectronic properties of triphenylamine derivatives for solar cell applications–A DFT/TDDFT study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 6153–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liang, J.; Cui, Y.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Su, S.-J.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Achieving 34.3% External Quantum Efficiency for Red Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Organic Light-Emitting Diode by Molecular Isomer Engineering. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2201191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, G.; Duan, L. High-Efficiency Narrow-Band Electro-Fluorescent Devices with Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Sensitizers Combined Through-Bond and Through-Space Charge Transfers. CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Peng, X.; Chen, L.; Tang, B.Z.; Zhao, Z. Through-Space Conjugated Molecule with Dual Delayed Fluorescence and Room-Temperature Phosphorescence for High-Performance OLEDs. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Evans, E.W.; Dong, S.; Gillett, A.J.; Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Hele, T.J.H.; Friend, R.H.; Li, F. Efficient Radical-Based Light-Emitting Diodes with Doublet Emission. Nature 2018, 563, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, Z. Bay/Ortho-Octa-Substituted Perylene: A Versatile Building Block toward Novel Polycyclic (Hetero)Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, T.; Shiren, K.; Nakajima, K.; Nomura, S.; Nakatsuka, S.; Kinoshita, K.; Ni, J.; Ono, Y.; Ikuta, T. Ultrapure Blue Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Molecules: Efficient HOMO-LUMO Separation by the Multiple Resonance Effect. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2777–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Yoshiura, K.; Kitera, S.; Nishi, H.; Oda, S.; Gotoh, H.; Sasada, Y.; Yanai, M.; Hatakeyama, T. Narrowband Deep-Blue Organic Light-Emitting Diode Featuring an Organoboron-Based Emitter. Nat. Photon. 2019, 13, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tang, X.; Du, X.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, Y.-J.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Liao, L.-S.; Lee, S.-T. The Design of Fused Amine/Carbonyl System for Efficient Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence: Novel Multiple Resonance Core and Electron Acceptor. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1801536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhuang, N.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Tang, B.Z.; Zhao, Z. Deciphering Intermediate Excited States in Spin-Flip Transition in Carbonyl-Nitrogen Multi-Resonance Molecule. Innov. Mater. 2025, 3, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Yasuda, T. Narrowband Emissive Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Materials. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2201714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Xie, F.M.; Li, Y.Q.; Tang, J.X. Recent Progress and Prospects of Fluorescent Materials Based on Narrow Emission. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 6471–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.C.; Wang, K.; Shi, Y.Z.; Chen, J.X.; Huang, F.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.N.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Ou, X.M.; Yu, J.; et al. Managing Intersegmental Charge-Transfer and Multiple Resonance Alignments of D3-A Typed TADF Emitters for Red OLEDs with Improved Efficiency and Color Purity. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Kumar Gupta, A.; Yoshida, K.; Gong, J.; Hall, D.; Cordes, D.B.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Zysman-Colman, E. Highly Efficient Green and Red Narrowband Emissive Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Employing Multi-Resonant Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 134, e202213697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zou, P.; Xu, J.; Dong, X.; Tang, B.Z.; Zhao, Z. Carbonyl-Nitrogen Multi-Resonance Emitters for Efficient OLEDs with High Color Purity. Commun. Chem. 2025, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Pu, J.; Guo, D.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Su, S.J.; Deng, H.; Zhao, J.; Chi, Z. Multiple-Resonance Thermally Activated Delayed Emitters through Multiple Peripheral Modulation to Enable Efficient Blue OLEDs at High Doping Levels. Aggregate 2024, 5, e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hafeez, H.; Tang, S.; Matulaitis, T.; Edman, L.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Zysman-Colm, E. Highly Efficient Organic Light-Emitting Diodes and Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells Employing Multiresonant Thermally Activated Delayed Fuorescent Emitters with Bulky Donor or Acceptor Peripheral Groups. Aggregate 2024, 5, e571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, S.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, X.J.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, H. High Steric-Hindrance Windmill-Type Molecules for Efficient Ultraviolet to Pure-Blue Organic Light-Emitting Diodes via Hybridized Local and Charge-Transfer Excited-State. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Liu, Z.; Han, Y.; Long, J.; Guo, T.; Lan, X.; Yu, M.; Fan, T.; Ma, H.; Wei, Y.; et al. Introducing Electron-Rich Thiophene Bridges in Hot Exciton Emitter for Efficient Non-Doped Near-Infrared OLEDs with Low Turn-on Voltages. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Ding, Z.; Liu, D.; Zheng, W.; Ma, B.; Zhang, H.; Chang, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. High-Efficiency and Narrow-Band Near-Ultraviolet Emitters with Low CIEy of 0.03 by Incorporating Extra Weak Charge Transfer Channel into Multi-Resonance Skeleton. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2300195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, D.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Lin, J.; Xing, L.; Huo, Y.; Ji, S. Phosphorus-Oxygen Modified Anthracene-Based Emitters for High-Efficiency Deep-Blue OLEDs Approaching the BT.2020 Blue Standard. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wu, C.; Tong, K.N.; Shi, K.; Jung, S.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; He, W.; Ye, M.; et al. Boosting Electroluminescence Efficiency Based on TADF Emitters Featuring Multiple Resonance Segment Integrated with a Co-Host Exciplex. Mater. Today Energy 2025, 49, 101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Geng, S.; Zhong, Z.; Li, H.; Feng, X.J.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, H. Donor–Acceptor–Donor Molecules for High Performance Near Ultraviolet Organic Light-Emitting Diodes via Hybridized Local and Charge-Transfer Processes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 5316–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhong, Z.; Feng, X.J.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, H. Bipolar Molecules with Hybridized Local and Charge-Transfer State for Highly Efficient Deep-Blue Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with EQE of 7.4% and CIEy ~0.05. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | λabs (a) [nm] | εmax (b) [104] | λem (c) [nm] | FWHM (d) [nm] | ΔEST (e) [eV] | ΦPL (f) [%] | τ (g) [ns] | kr (h) [107 s−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-QA | 550 | 3.15 | 586/598 | 48/55 | 0.29 | 55/67 | 18.6 | 3.60 |
| S-QA | 524 | 2.28 | 579/600 | 64/79 | 0.26 | 49/60 | 11.1 | 5.41 |
| Emitter | λEL [nm] | Von [V] | Lmax [cd m−2] | CEmax [cd A−1] | PEmax [lm W−1] | EQEmax [%] | CIE (x, y) | FWHM [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 wt% O-QA | 598 | 3.7 | 5439 | 13.58 | 11.53 | 7.36 | (0.612, 0.384) | 56 |
| 3 wt% O-QA | 602 | 3.6 | 4601 | 11.18 | 9.7 | 6.70 | (0.625, 0.373) | 59 |
| 5 wt% O-QA | 604 | 3.6 | 4039 | 8.70 | 7.59 | 5.46 | (0.629, 0.369) | 63 |
| 10 wt% O-QA | 606 | 3.5 | 3494 | 5.71 | 5.13 | 3.80 | (0.634, 0.364) | 68 |
| 1 wt% S-QA | 594 | 3.5 | 7784 | 18.96 | 17.01 | 8.76 | (0.578, 0.417) | 72 |
| 3 wt% S-QA | 598 | 3.5 | 7392 | 26.20 | 23.52 | 13.27 | (0.591, 0.405) | 73 |
| 5 wt% S-QA | 602 | 3.4 | 6482 | 26.62 | 24.60 | 14.54 | (0.601, 0.397) | 76 |
| 10 wt% S-QA | 602 | 3.4 | 6483 | 13.89 | 12.84 | 8.02 | (0.607, 0.391) | 77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Zou, P.; Chen, Z.; Tang, B.Z.; Zhao, Z. New Polycyclic Red Luminescent Compounds Based on Carbonyl/Nitrogen Skeleton for Efficient Narrow-Spectrum OLEDs. Materials 2025, 18, 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174000
Wu Z, Zou P, Chen Z, Tang BZ, Zhao Z. New Polycyclic Red Luminescent Compounds Based on Carbonyl/Nitrogen Skeleton for Efficient Narrow-Spectrum OLEDs. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174000
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhiwei, Peng Zou, Ziwei Chen, Ben Zhong Tang, and Zujin Zhao. 2025. "New Polycyclic Red Luminescent Compounds Based on Carbonyl/Nitrogen Skeleton for Efficient Narrow-Spectrum OLEDs" Materials 18, no. 17: 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174000
APA StyleWu, Z., Zou, P., Chen, Z., Tang, B. Z., & Zhao, Z. (2025). New Polycyclic Red Luminescent Compounds Based on Carbonyl/Nitrogen Skeleton for Efficient Narrow-Spectrum OLEDs. Materials, 18(17), 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174000






