Properties of ZnO Prepared by Polymeric Citrate Amorphous Precursor Method: Influence of Cobalt Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussions
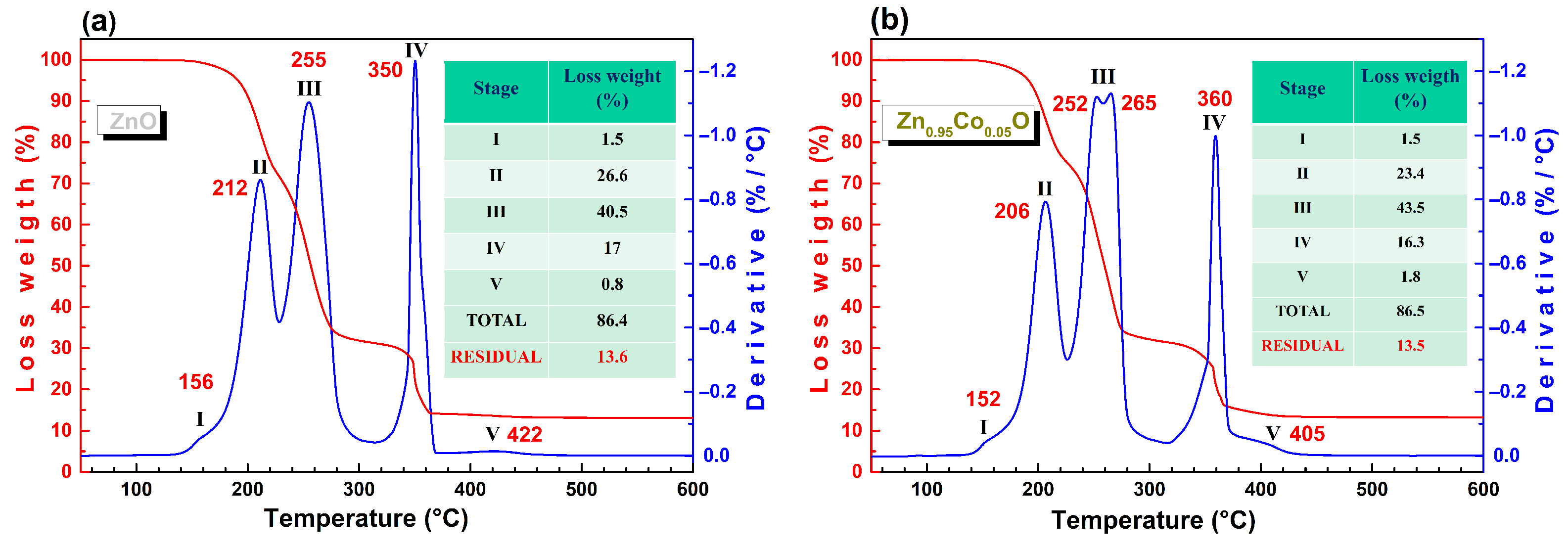
3.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
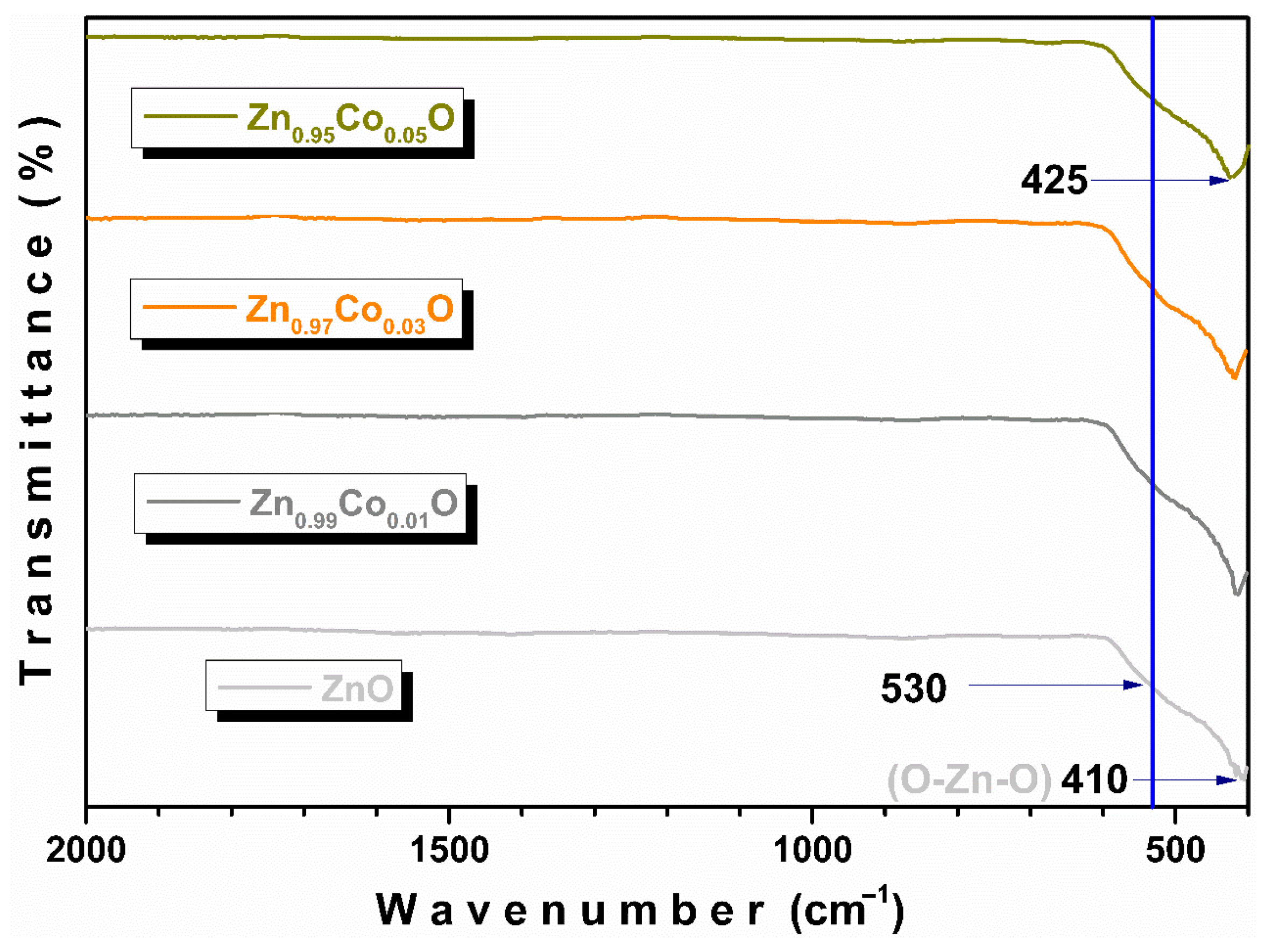
3.2. FTIR-ATR
3.3. SEM Micrographs
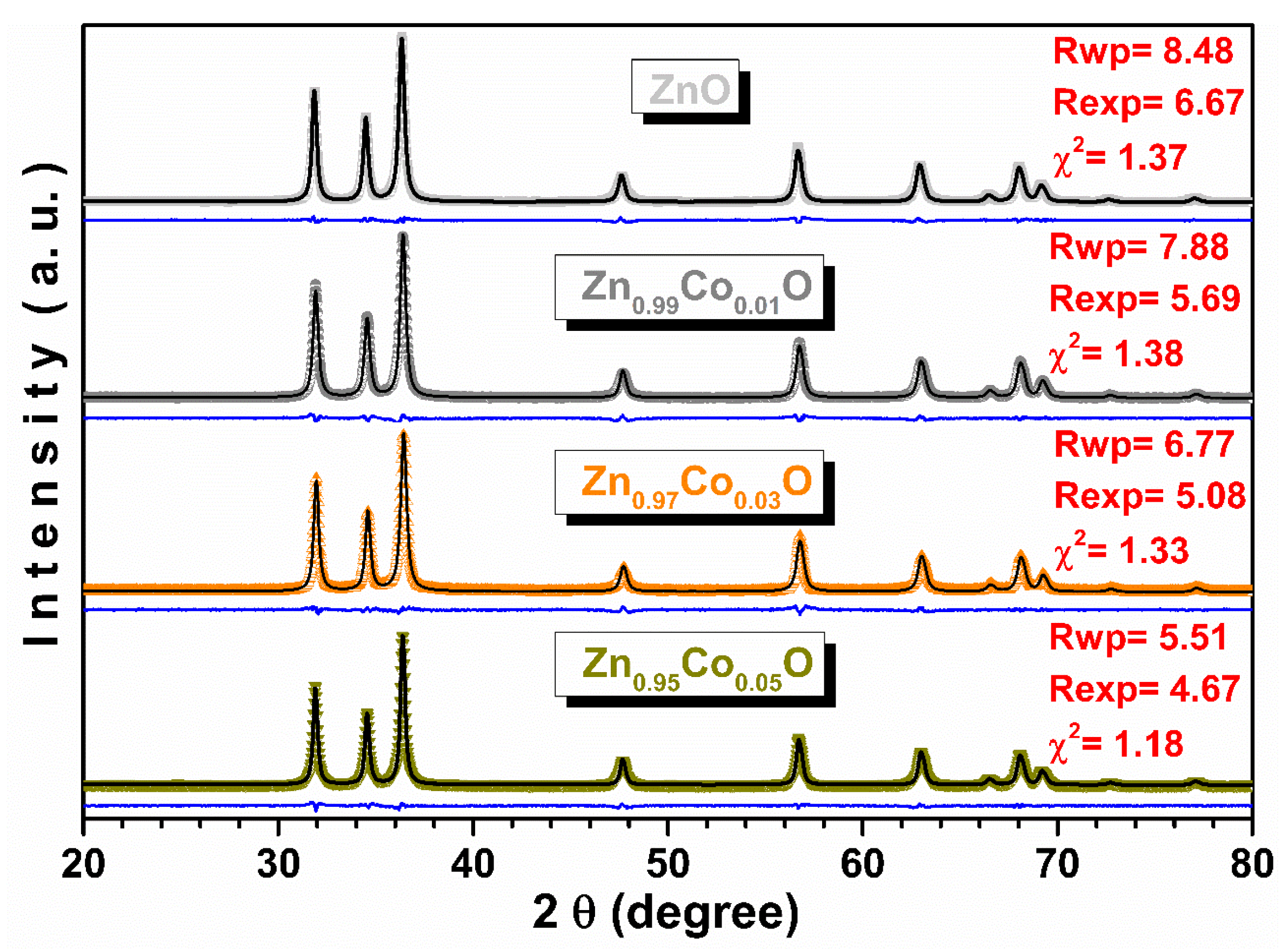
3.4. XRD
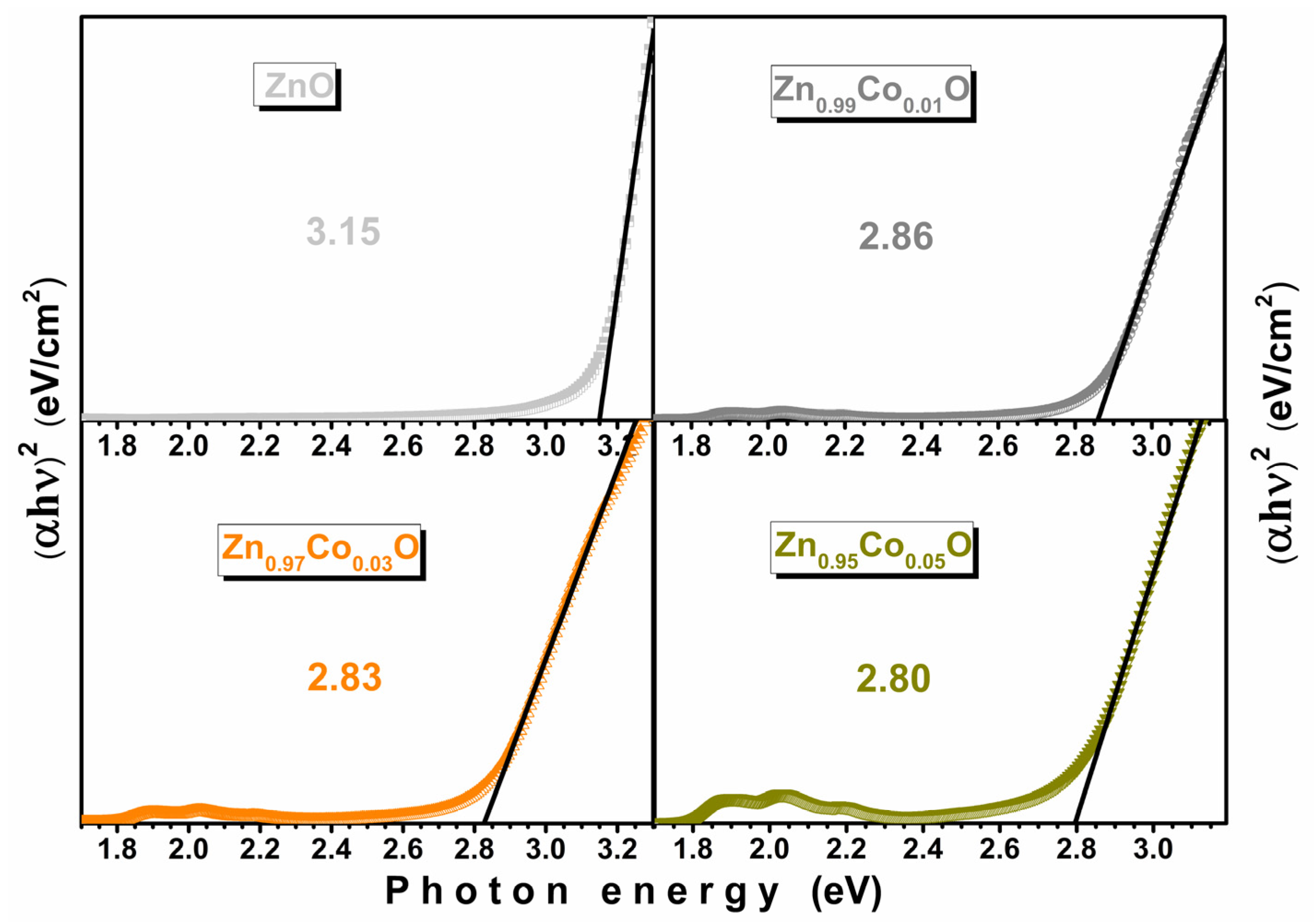
3.5. Optical Properties
3.6. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hossain, N.; Afroz, M.F.; Alam, M.; Shuvo, M.A.I.; Mohiuddin, M.; Hossen, M.N.; Iqbal, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.M. Advances and significances of nanoparticles in semiconductor applications—A review. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Ansari, A.; Lv, R.; Gai, S.; Parchur, A.K.; Solanki, P.R.; Archana; Ansari, Z.; Dhayal, M.; Yang, P.; Nazeeruddin, M.; et al. ZnO nanostructures—Future frontiers in photocatalysis, solar cells, sensing, supercapacitor, fingerprint technologies, toxicity, and clinical diagnostics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 515, 215942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.T.; Amor, N.; Petru, M. Synthesis and applications of ZnO nanostructures (ZONSs): A review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2021, 47, 99–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, S. Ahmaruzzaman, M. ZnO nanostructured materials and their potential applications: Progress, challenges and perspectives. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 1868–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Mohanty, D.L.; Divya, N.; Bakshi, V.; Mohanty, A.; Rath, D.; Das, S.; Mondal, A.; Roy, S.; Sabui, R. A critical review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. Intell. Pharm. 2025, 3, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, H.; Bhushan, M.; Singh, L.R. A comprehensive review on theoretical concepts, types and applications of magnetic semiconductors. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 288, 116201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, A.; Zuo, W.-L.; Song, X.; Ghani, A.; Saeed, A.; Yaseen, M.; Tian, F.; Yang, S. Robust ferromagnetism in rare-earth and transition metal co-doped ZnO nanoparticles for spintronics applications. Mater. Lett. 2022, 310, 131479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziba, A.T.; Nafisa, M.T.; Sultana, R.; Ehsan, F.; Tareq, A.; Rashid, R.; Das, H.; Ullah, A.A.; Kibria, A.F. Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanorods: Advancements in room temperature ferromagnetic behavior for spintronic applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2024, 593, 171836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habanjar, K.; Almoussawi, M.; Abdallah, A.; Awad, R. Magneto-optical effect of (Sm, Co) co-doping in ZnO semiconductor. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 598, 412444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, I.; Zaman, Y.; Althubeiti, K.; Al Otaibi, S.; Ishaque, M.Z.; Rahman, N.; Sohail, M.; Khan, A.; Ullah, A.; Del Rosso, T.; et al. Diluted magnetic semiconductor properties in TM doped ZnO nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 13456–13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelekew, O.A.; Aragaw, S.G.; Sabir, F.K.; Andoshe, D.M.; Duma, A.D.; Kuo, D.-H.; Chen, X.Y.; Desissa, T.D.; Tesfamariam, B.B.; Feyisa, G.B.; et al. Green synthesis of Co-doped ZnO via the accumulation of cobalt ion onto Eichhornia crassipes plant tissue and the photocatalytic degradation efficiency under visible light. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogwuegbu, M.C.; Olatunde, O.C.; Pfukwa, T.M.; Mthiyane, D.M.N.; Fawole, O.A.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of ZnO and Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles obtained using aqueous extracts of Platycladus orientalis leaves. Discov. Mater. 2025, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, L.B.; Leite, D.M.G.; Orlandi, M.O.; Ortiz, W.A.; Lisboa-Filho, P.N. Sonochemical Synthesis and Magnetism in Co-doped ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2012, 26, 2515–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.; Kumar, M.; Chauhan, S.; Raman, R.S. Microwave-assisted sol-gel synthesis of Li-Co doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: Investigating the effects of codoping on structural, optical, and magnetic properties for spintronic applications. J. Cryst. Growth 2025, 652, 128053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Cai, C.; Zhou, S.; Liu, W. Structure, photoluminescence, and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 12917–12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elilarassi, R.; Chandrasekaran, G. Influence of Co-doping on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized using auto-combustion method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2012, 24, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkar, K.Y.; Tangsali, R.; Gad, R.; Jeyakanthan, M.; Subramanian, U. Preparation characterization and magnetic properties of ZnCoO nanoparticle Dilute magnetic semiconductors. Superlattices Microstruct. 2019, 126, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, J.; Barrero, C.; Punnoose, A. Identifying the sources of ferromagnetism in sol-gel synthesized Zn1−xCoxO (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.10) nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 240, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhusha, M.S.M.; Kavitha, B.; Rajarajan, M.; Tharmaraj, P.; Suganthi, A. Synthesis of Co and Cu codoped ZnO nanoparticles by citrate gel combustion method: Photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2022, 7, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, M.; Shah, P.; Ramaswamy, V. Synthesis of nanocrystalline SnO2 powder by amorphous citrate route. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbun, I.A.; Romanova, I.V.; Terikovskaya, T.E.; Dzanashvili, D.I.; Kirillov, S.A. Complex formation in the course of synthesis of zinc oxide from citrate solutions. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2007, 80, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Werde, K.; Mondelaers, D.; Vanhoyland, G.; Nelis, D.; Van Bael, M.K.; Mullens, J.; Van Poucke, L.C.; Van Der Veken, B.; Desseyn, H.O. Thermal decomposition of the ammonium zinc acetate citrate precursor for aqueous chemical solution deposition of ZnO. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Shao, J.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Chi, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, G. Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 2012, 50, 4738–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorna, K.S.V. Metal citrate nanoparticles: a robust water-soluble plant micronutrient source. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 20370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, D.S.; Aziz, D.M.; Aziz, S.B. Zinc metal complexes synthesized by a green method as a new approach to alter the structural and optical characteristics of PVA: New field for polymer composite fabrication with controlled optical band gap. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 26362–26387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Anusuya, S.; Anbazhagan, V. Anticancer, anti-diabetic, antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A comparative analysis. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1263, 133139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillip, G.R.; Banerjee, A.N.; Anitha, V.C.; Raju, B.D.P.; Joo, S.W.; Min, B.K. Oxygen Vacancy-Induced Structural, Optical, and Enhanced Supercapacitive Performance of Zinc Oxide Anchored Graphitic Carbon Nanofiber Hybrid Electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5025–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán, J.J.; Barrero, C.A.; Punnoose, A. Relationship between ferromagnetism and formation of complex carbon bonds in carbon doped ZnO powders. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 8808–8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Pal, U.; Serrano, J.G.; Ucer, K.B.; Williams, R.T. Photoluminesence and FTIR study of ZnO nanoparticles: The impurity and defect perspective. Phys. Status Solidi (C) 2006, 3, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xie, G.; Du, H.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.; Tai, H.; Xu, M.; Zhao, K. Adsorption behaviors of gas molecules on the surface of ZnO nanocrystals under UV irradiation. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Samanta, P.K. Peak Profile Analysis of X-ray Diffraction Pattern of Zinc Oxide Nanostructure. J. Nano-Electron. Phys. 2021, 13, 05001-1–05001-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Sotelo, A.; Avila-Meza, M.; Melendez-Lira, M.A.; Fernandez-Muñoz, J.L.; Zelaya-Angel, O. Modification of the Crystalline Structure of ZnO Nanoparticles Embedded Within a SiO2 Matrix due to Thermal Stress Effects. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20190105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, M.G.; Busacca, C.; Mauriello, F.; Pietropaolo, R. Aliphatic carbonyl reduction promoted by palladium catalysts under mild conditions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 379, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Synthesis and low-temperature sensing property of the porous ZnCo2O4 nanosheets. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 5357–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, J.; Reddy, K.M.; Graces, N.Y.; Engelhard, M.H.; Shutthanandan, V.; Luo, M.; Xu, C.; Giles, N.C.; Wang, C.; Thevuthasan, S.; et al. Effect of Co doping on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 266203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon Radii. Database of Ionic Radii. 2020. Available online: http://abulafia.mt.ic.ac.uk/shannon/ptable.php (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Shi, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, G.-H.; Dang, Z.-M. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanorods prepared by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 576, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hao, W.; Li, B. Controllable synthesis and magnetic investigation of ZnO: Co nanowires and nanotubes. Mater. Lett. 2012, 87, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, J.J.; Barrero, C.A.; Punnoose, A. Understanding the role of iron in the magnetism of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 15284–15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, S.S.; Güner, S.; Koseoglu, Y.; Musa, I.M.; Adamu, B.I.; Abdulhamid, M.I. Simple method for the determination of band gap of a nanopowdered sample using Kubelka Munk theory. J. Niger. Assoc. Math. Phys. 2016, 35, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Repp, S.; Erdem, E. Controlling the exciton energy of zinc oxide (ZnO) quantum dots by changing the confinement conditions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 152, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaung, D.E.; Mhlongo, G.H.; Nkosi, S.S.; Malgas, G.F.; Mwakikunga, B.W.; Coetsee, E.; Swart, H.C.; Abdallah, H.M.I.; Moyo, T.; Ray, S.S. Shape-Selective Dependence of Room Temperature Ferromagnetism Induced by Hierarchical ZnO Nanostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8981–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Xu, C.; Dai, J.; Hu, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, S. Size Dependence of Defect-Induced Room Temperature Ferromagnetism in Undoped ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8813–8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Rao, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y. Ferromagnetism of lightly Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 2008, 145, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.; Boguslavskiy, L.; Feshchenko, A.; Andreev, S.; Lepalovskij, V. Topological study of the rearrangement of the magnetic vector field using magneto-optical images. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 590, 171681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punnoose, A.; Hays, J.; Thurber, A.; Engelhard, M.H.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Wang, C.; Shutthanandan, V.; Thevuthasan, S. Development of high-temperature ferromagnetism in SnO2 and paramagnetism in SnO by Fe doping. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 054402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




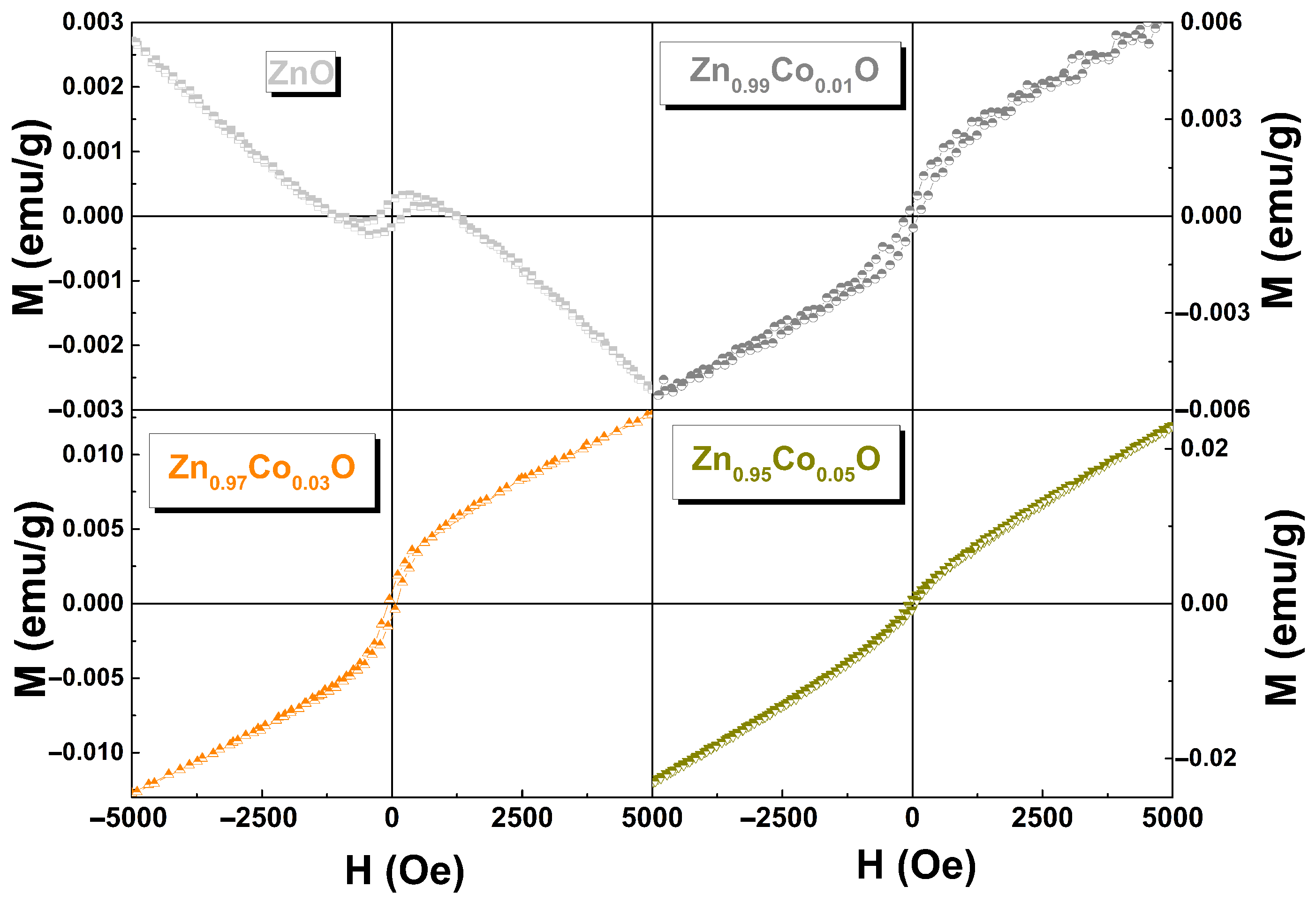
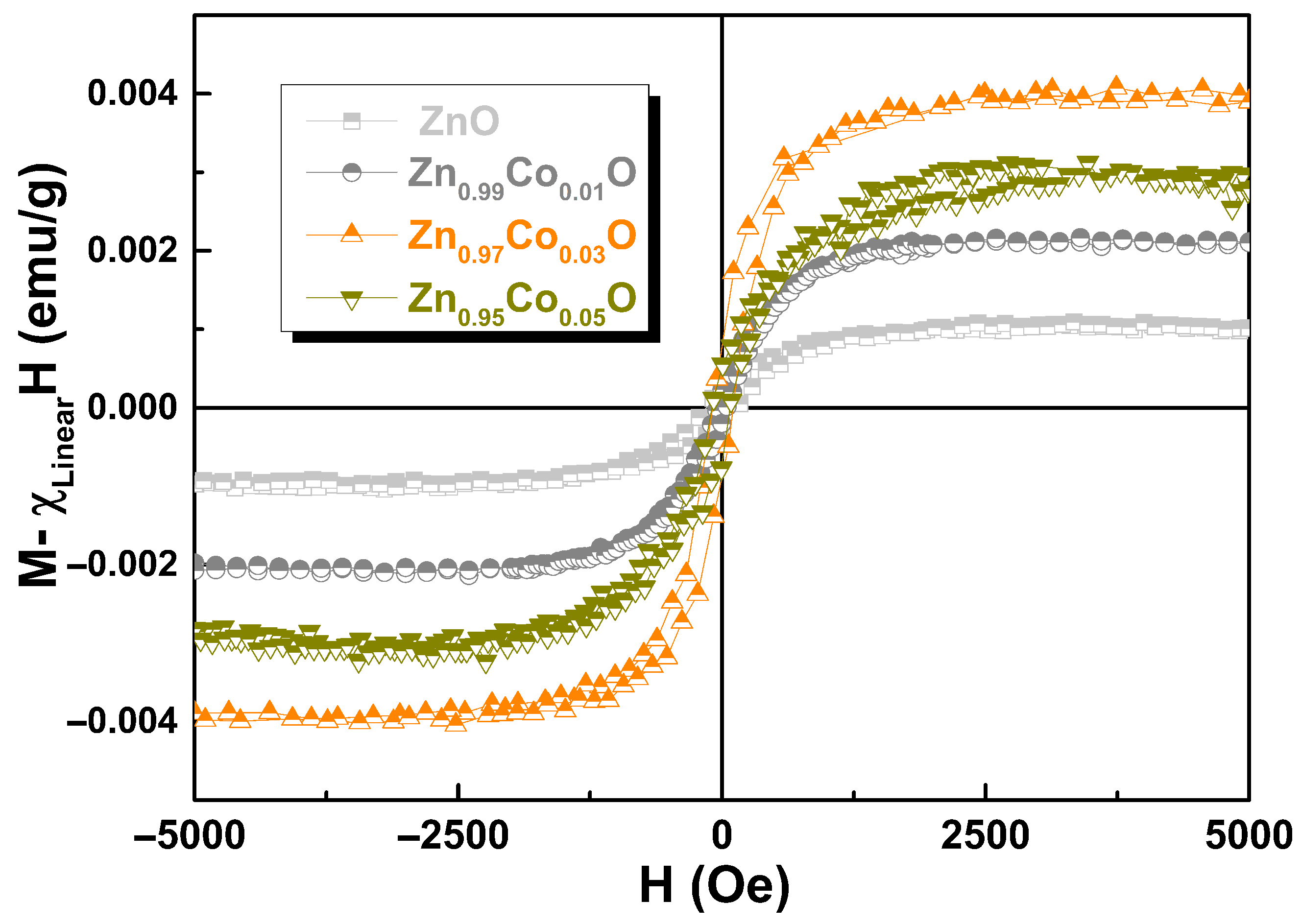
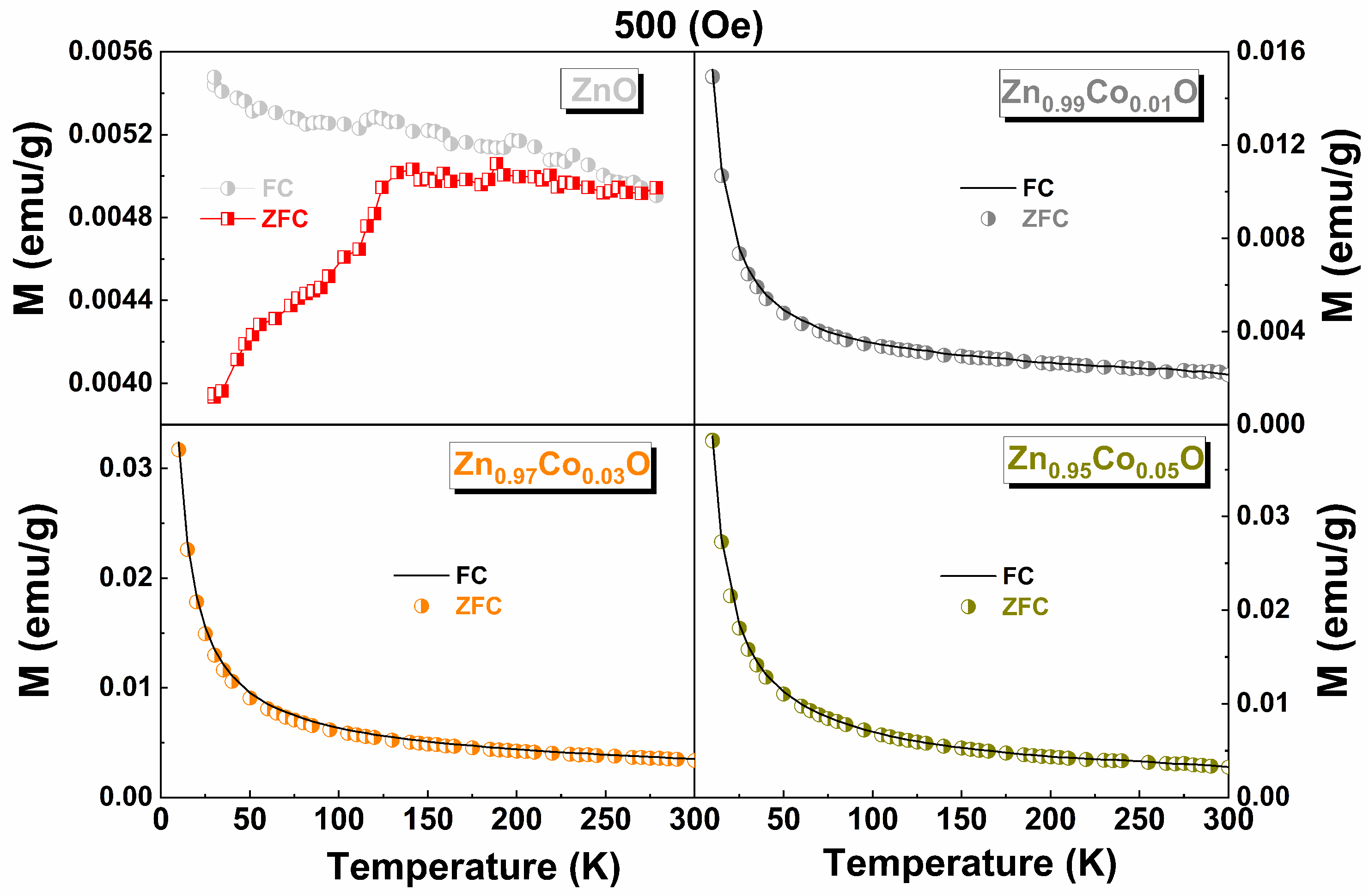
| x in Zn1−xCoxO | Mo (emu/g) | C (emu K/g Oe) | θ (K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.94 | 0.15 | 1.26 |
| 0.03 | 1.29 | 0.33 | 1.41 |
| 0.05 | 1.09 | 0.45 | 2.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beltrán, J.J.; Flórez, L.A.; Sánchez, L.C. Properties of ZnO Prepared by Polymeric Citrate Amorphous Precursor Method: Influence of Cobalt Concentration. Materials 2025, 18, 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173991
Beltrán JJ, Flórez LA, Sánchez LC. Properties of ZnO Prepared by Polymeric Citrate Amorphous Precursor Method: Influence of Cobalt Concentration. Materials. 2025; 18(17):3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173991
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeltrán, Jailes J., Luis A. Flórez, and Luis C. Sánchez. 2025. "Properties of ZnO Prepared by Polymeric Citrate Amorphous Precursor Method: Influence of Cobalt Concentration" Materials 18, no. 17: 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173991
APA StyleBeltrán, J. J., Flórez, L. A., & Sánchez, L. C. (2025). Properties of ZnO Prepared by Polymeric Citrate Amorphous Precursor Method: Influence of Cobalt Concentration. Materials, 18(17), 3991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173991






