Improvement of Environment and Mechanical Behaviour of Filling Material of Phosphate Solid Waste Using Natural Fibre
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Aggregate
2.1.2. Binder
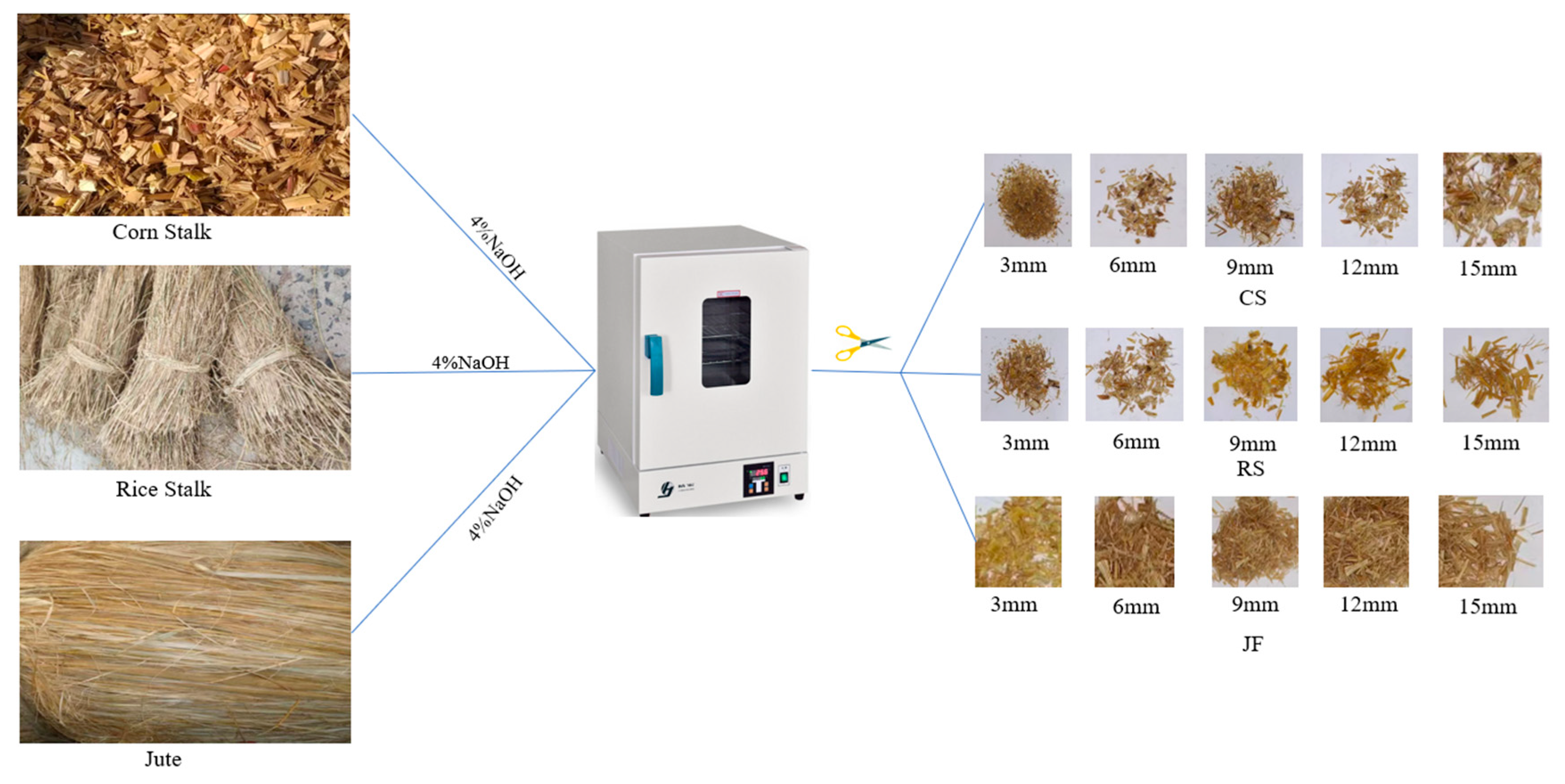
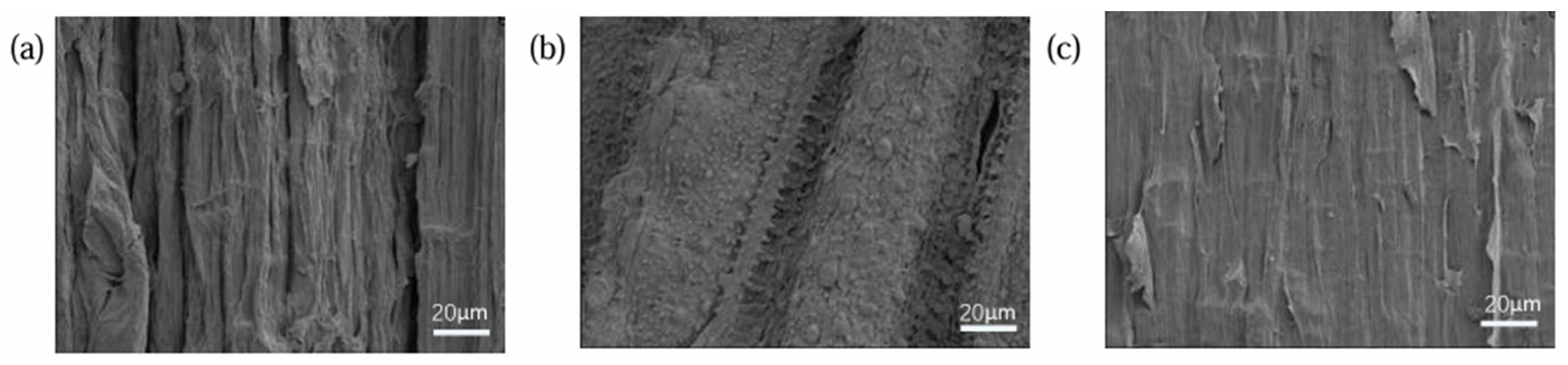
2.1.3. Natural Fibres
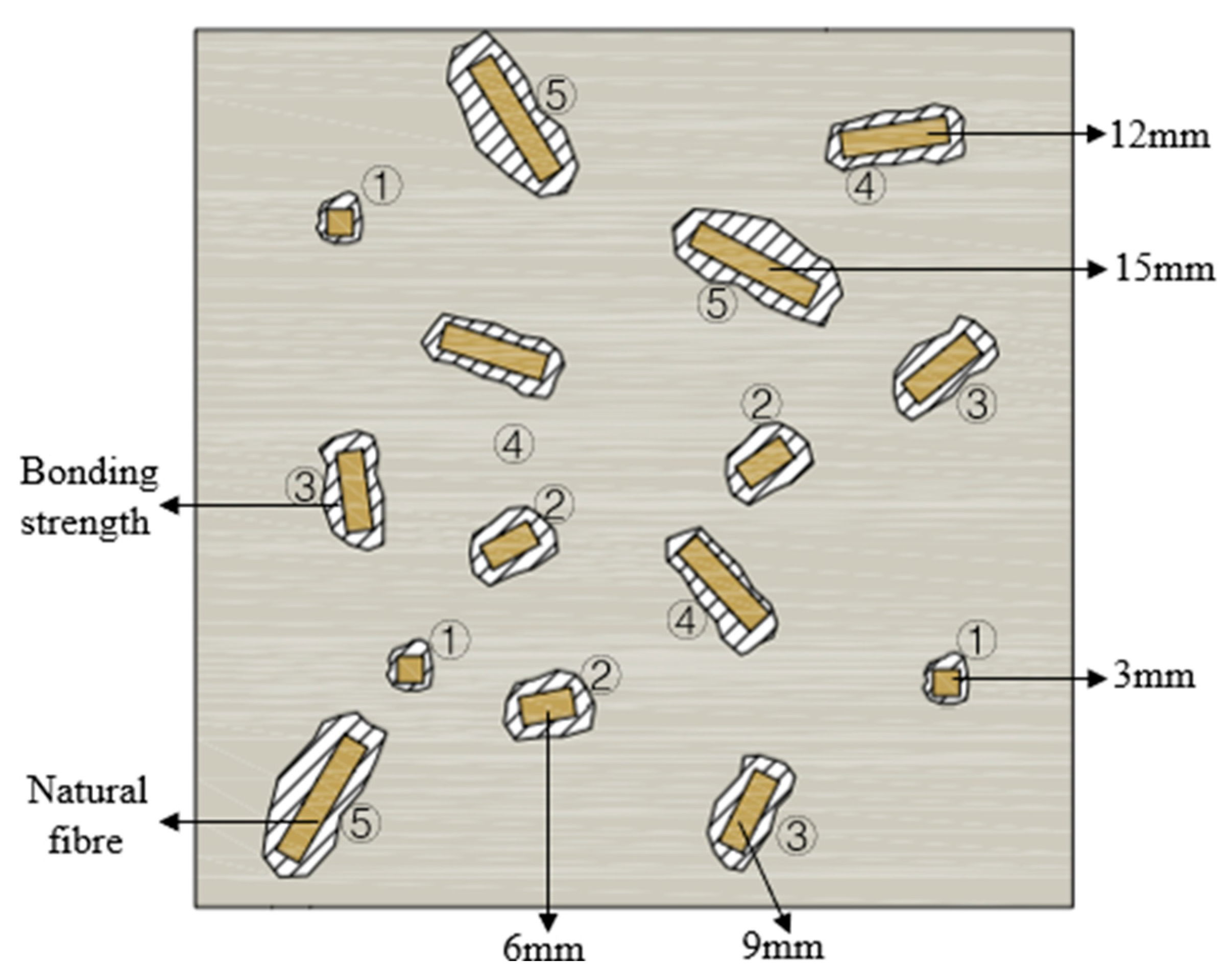
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Flowability Test
2.3.2. Mechanical Strength
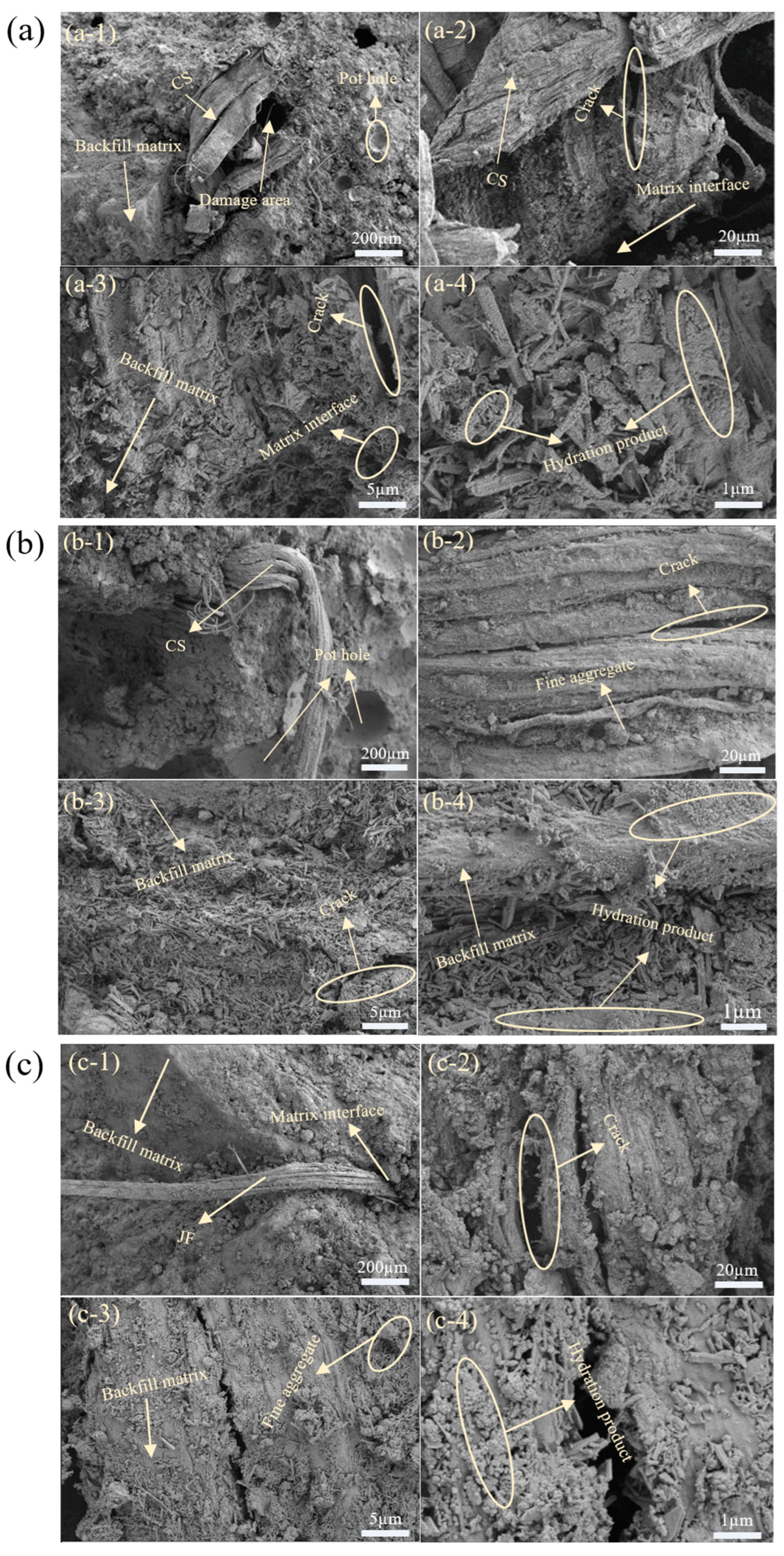
2.3.3. SEM Analysis
2.3.4. XRD Analysis
2.3.5. Porosity Test
2.3.6. Ion Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flowability
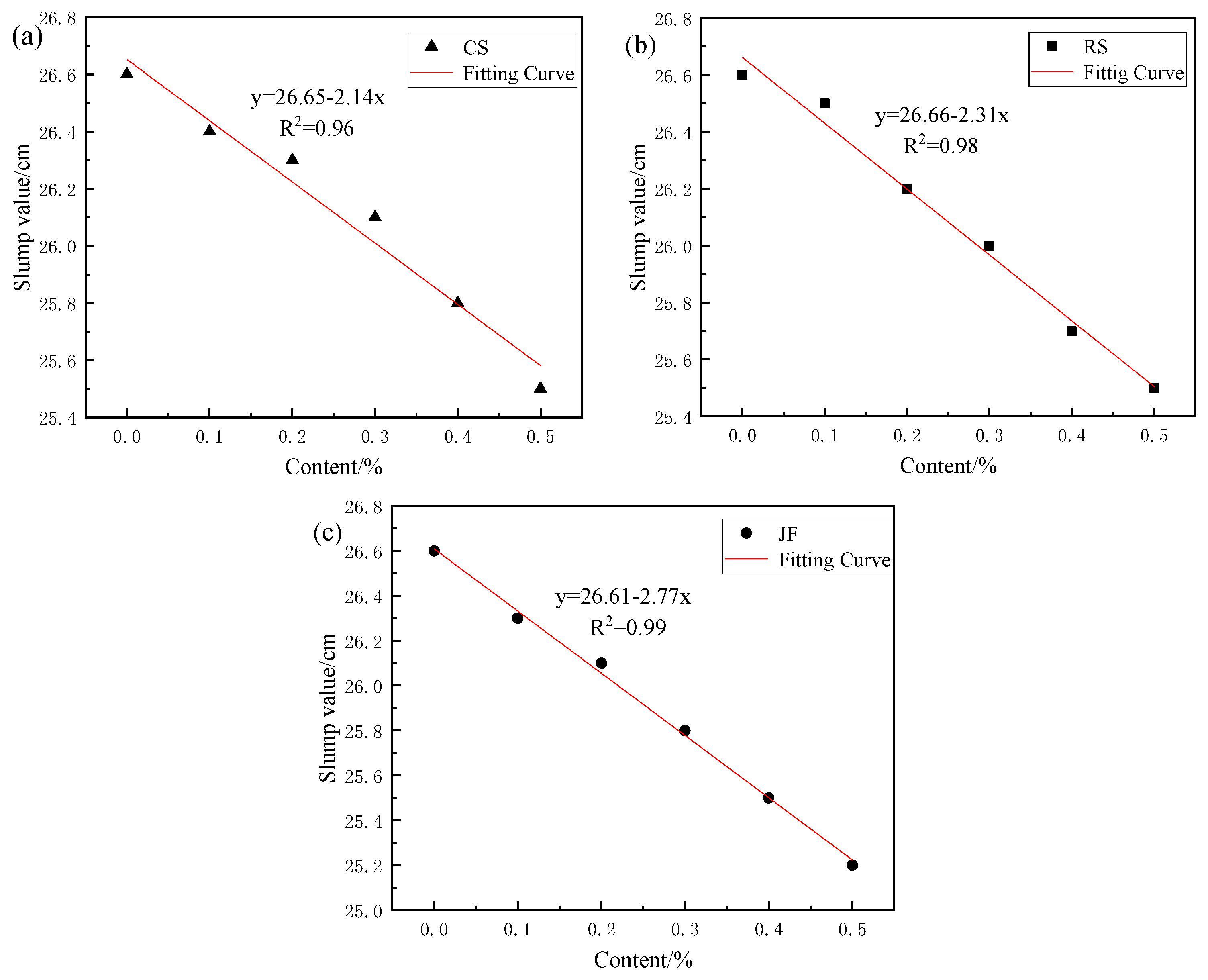
3.1.1. Slump
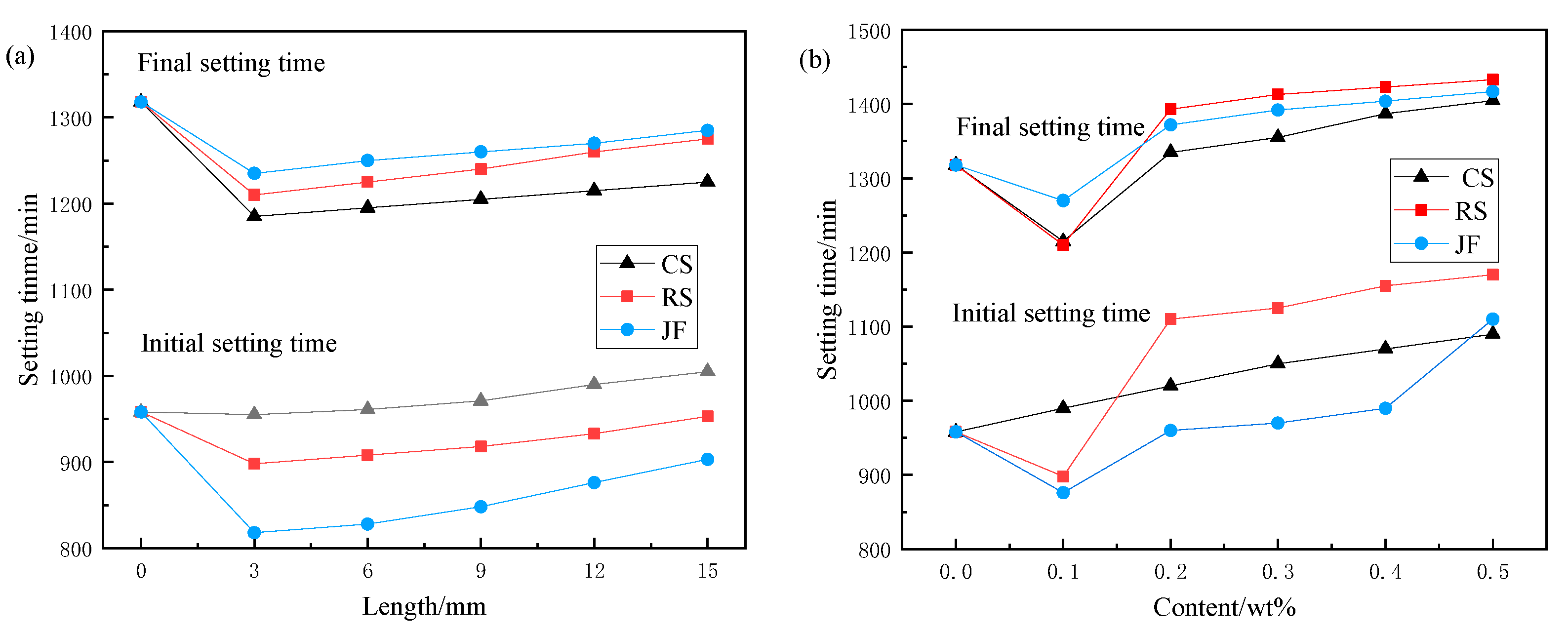
3.1.2. Setting Time
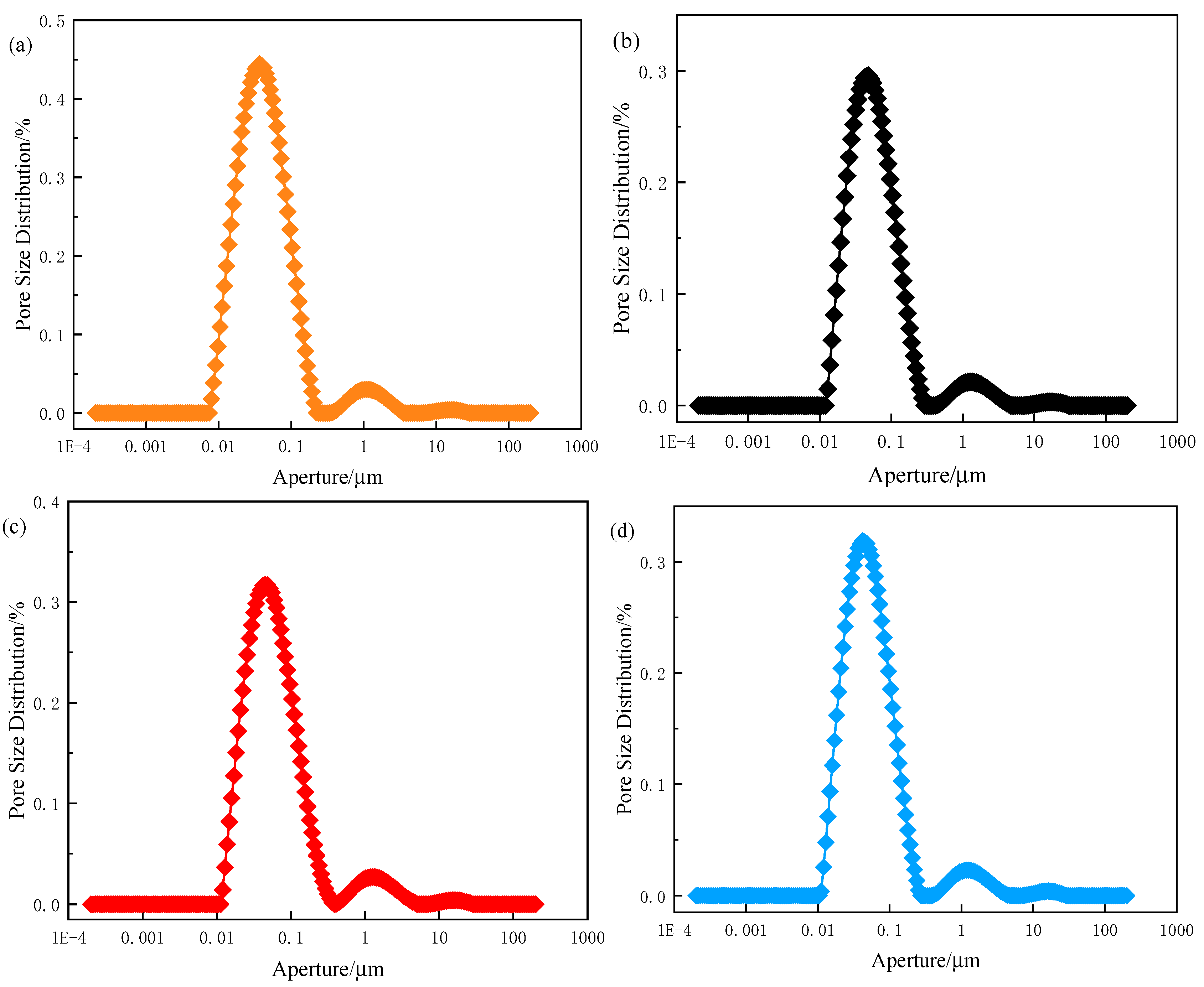
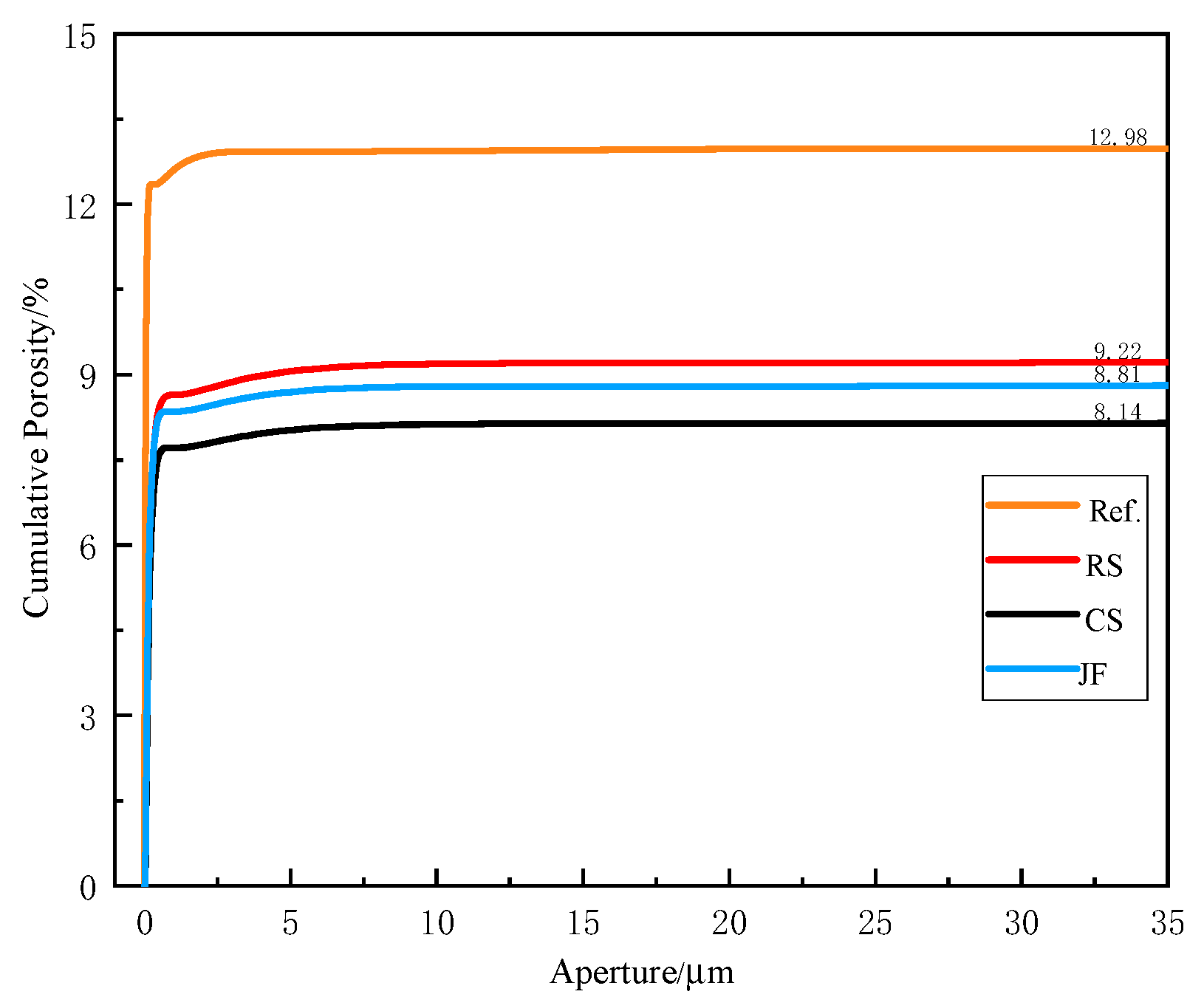
3.2. Porosity
3.3. XRD
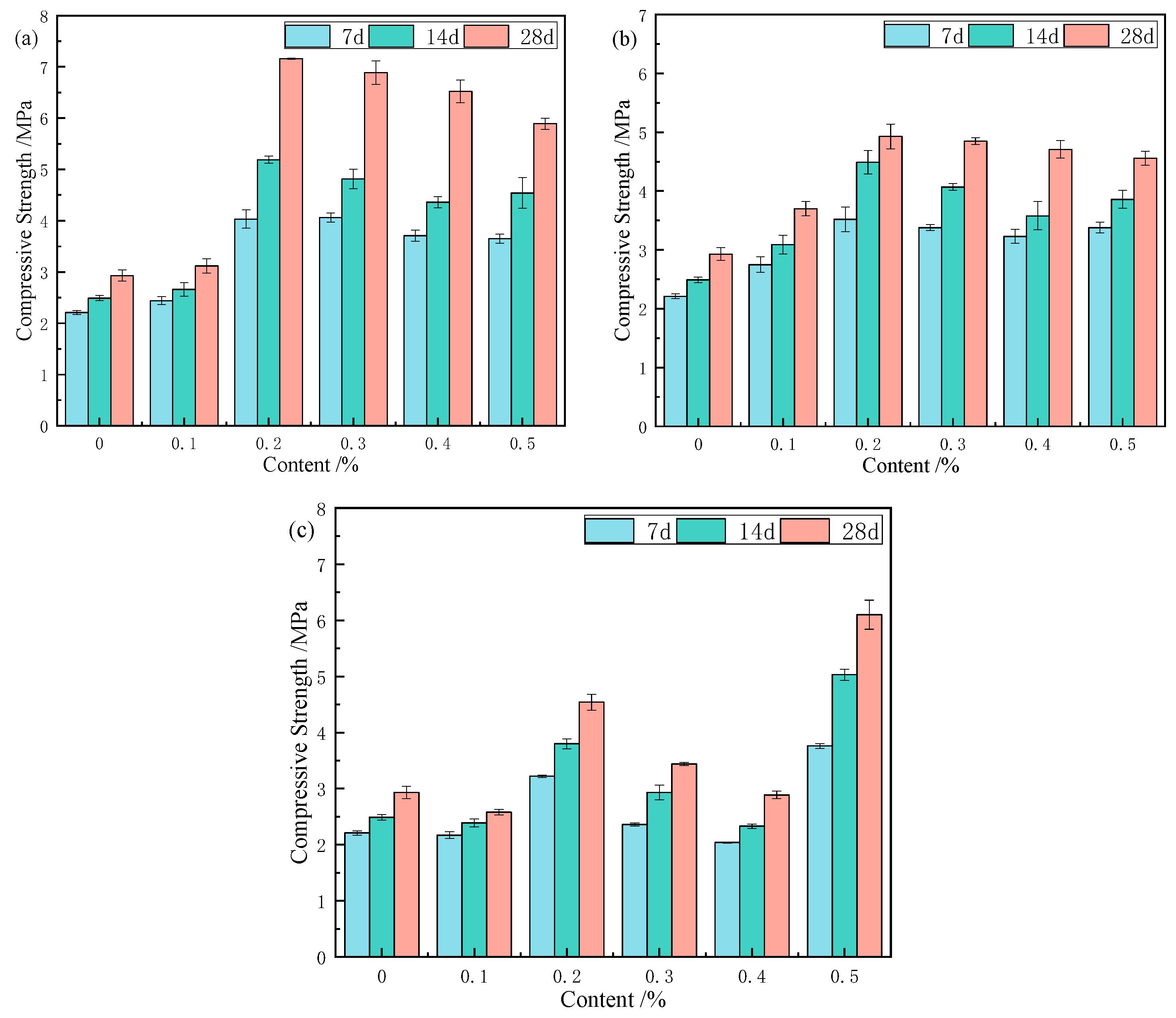
3.4. Compressive Strength
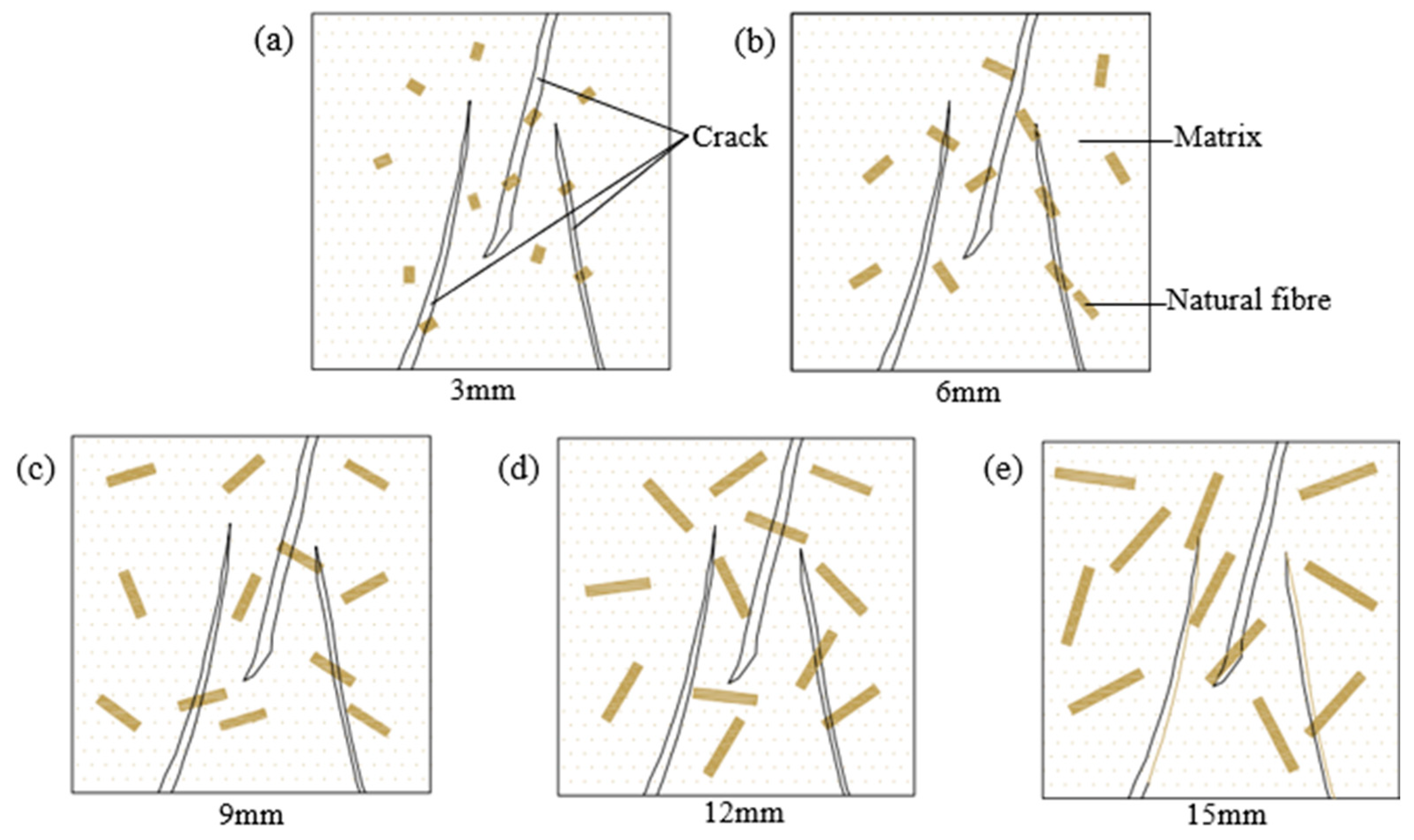
3.4.1. Effect of Fibre Length on Compressive Strength
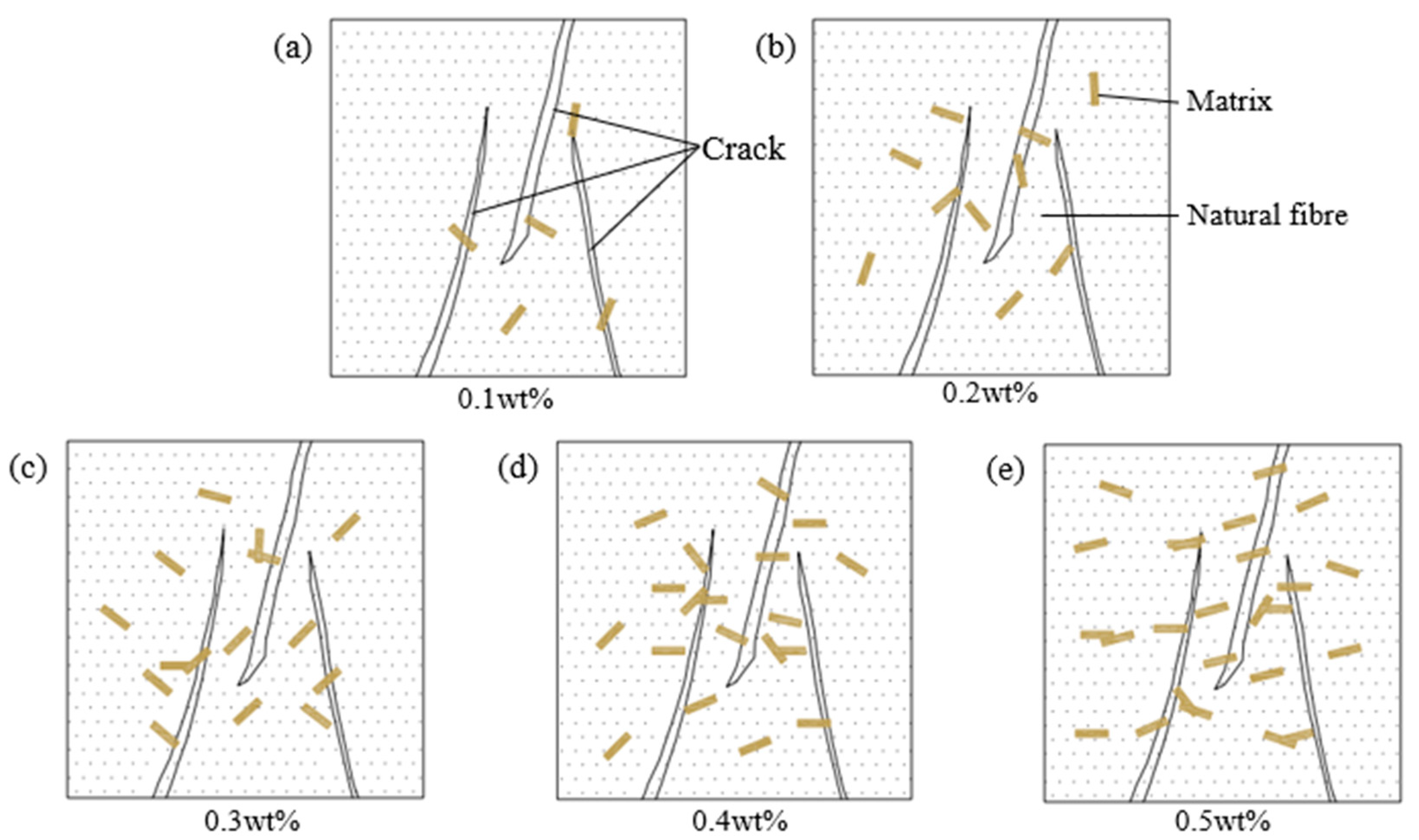
3.4.2. Effect of Fibre Content on Compressive Strength
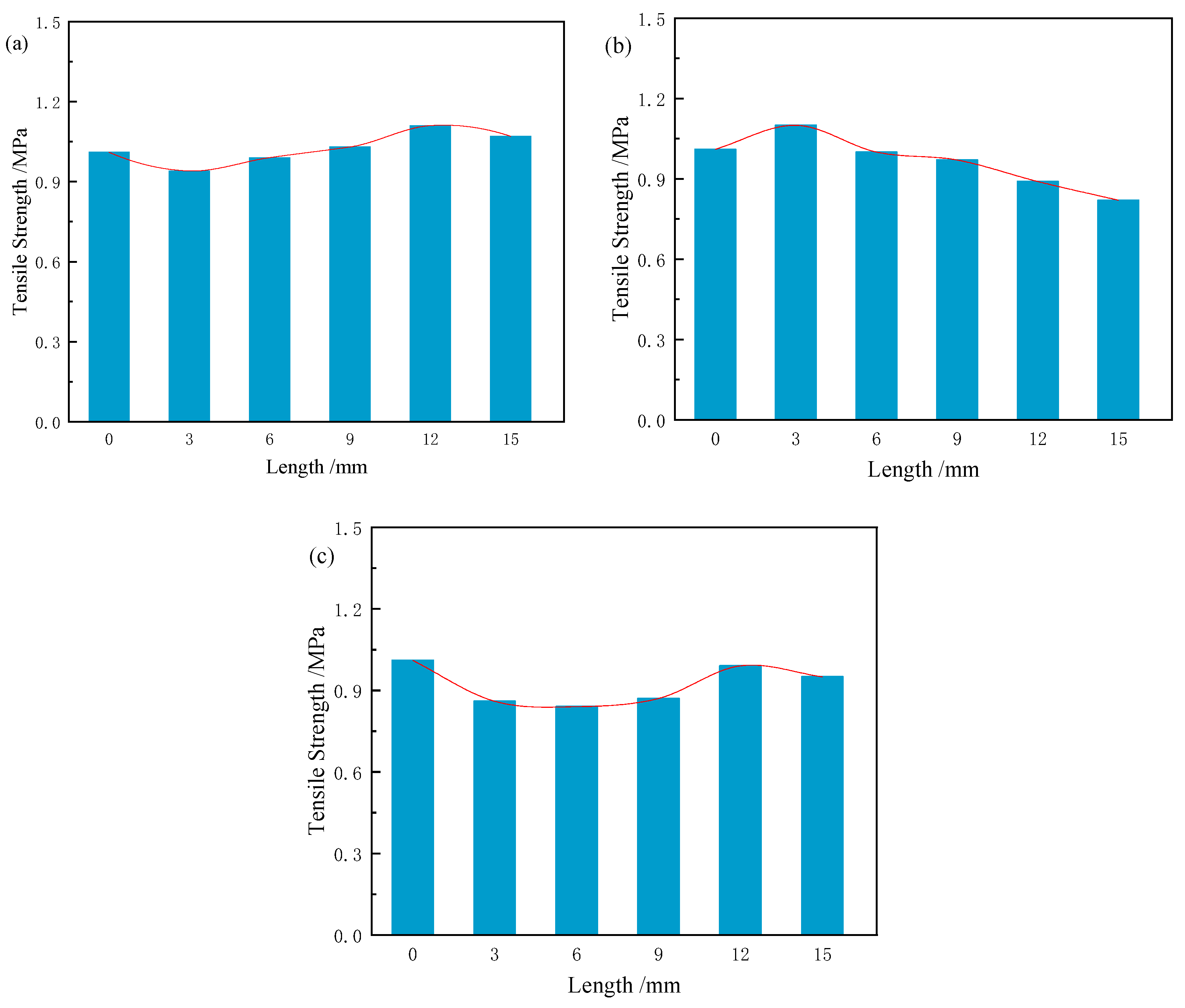
3.5. Tensile Strength
3.5.1. Effect of Fibre Length on Tensile Strength
3.5.2. Effect of Fibre Content on Tensile Strength
3.6. Failure Mode Analysis of Filling Materials
3.6.1. Macroscopic Failure Mode
3.6.2. Microscopic Failure Mode
3.7. Environmental Impact Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Natural fibres reduce backfill fluidity and porosity, particularly 3 mm CS fibres at 0.2 wt%, while increasing pore density and resulting in a denser microstructure, as confirmed by NMR analysis.
- (2)
- Compressive strength increases with fibre length (3–15 mm), with optimal lengths of 12 mm for CS and 3–9 mm for RS. Fibre content (0.1–0.5 wt%) showed an initial increase in compressive strength, followed by a decrease in CS and RS samples. JF samples exhibited an increase–decrease–increase pattern, with the greatest improvement for 0.2 wt% CS (12 mm), achieving compressive strength increases of 82.3%, 108.4%, and 144.4% at 7, 14, and 28 days, respectively.
- (3)
- Tensile strength increased with fibre length (3–15 mm), with CS (9, 12, and 15 mm) and RS (3 mm) samples showing the most significant improvement. As fibre content increased (0.1–0.5 wt%), tensile strength in CS and RS initially rose, then declined, while JF samples showed a similar pattern. The greatest improvement was observed for CS at 0.4 wt% (12 mm), with an 18.8% increase in tensile strength compared to the reference.
- (4)
- The addition of natural fibres changed failure modes from tensile-dominated (reference) to predominantly shear failure, improving sample integrity and fibre–matrix bonding. SEM and XRD analyses confirmed that fibre incorporation strengthened the matrix and provided bridging effects, reducing crack propagation. Ion leaching tests and XPS analysis revealed that fibres effectively adsorb and immobilize phosphorus (P) and fluorine (F), reducing the environmental impact of phosphate tailings.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, J.; Shuai, Q.; Cui, H. Research Status and Breakthrough Ideas of Green Full Utilization Technology of Phosphate Resources. Chem. Bioeng. 2024, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Hou, S.; Li, Z.; Xu, G.; Chi, R.; Xi, B. Current situation and prospect of comprehensive utilization of phosphogypsum. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2024, 56, 1–8+22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yu, J.; Li, Y. Research progress of pretreatment and comprehensive utilization of phosphogypsum. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2024, 31, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, C.; You, C.; Li, J. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of major pollutants inregional water environment of phosphogypsum yard. Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind. 2024, 44, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Tayibi, H.; Mohamed, C.; Félix A, L.; Francisco J, A.; Aurora, L. Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Feng, W.; Su, Y. Research Progress on Comprehensive Utilization of Phosphogypsum andIts Application in the Field of Building Materials. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 43, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Yang, W.; He, B. The General Introduction of Phosphogypsum Comprehensive Utilization Technology in China. Yunnan Chem. Technol. 2021, 48, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmanović, P.; Leposava Filipović, P.; Jan, H.; Sofija, F.; Dušan, M.; Jovana Knežević, R. Radioactivity of phosphate rocks and products used in Serbia and assessment of radiation risk for workers. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2023, 332, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, M.F.; Metwally, S.S.; Moussa, S.I.; Soliman, M.A. Environmental impact assessment of phosphate fertilizers and phosphogypsum waste: Elemental and radiological effects. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dai, J. Current status and prospect of comprehensive utilization of phosphate tailings. Ind. Miner. Process. 2015, 44, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, B. A Critical Review on Approaches for Phosphorus Ore Flotation Tailings Treatment and Disposal Technology: Environment Properties, Comprehensive Utilization, and Resource Utilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Hu, C. Effect of phosphate tailings and tailing mud on properties of cemented filling materials. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 41, 973–977. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huo, H.; Chen, B.; Cui, Q. Development and optimization of phosphogypsum-based geopolymer cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Chen, H.; Wei, Z. Optimization of technical parameters for making light-basis-weightand environment-friendly rice straw fiber film. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, C.-S.; Lin, S.-H.; Lu, W.-C. Preparation and characterization of solid biomass fuel made from rice straw and rice bran. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ali, M. Use of agriculture waste as short discrete fibers and glass-fiber-reinforced-polymer rebars in concrete walls for enhancing impact resistance. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X. Structure-Activity Relationship of Ion-Exchange Cellulose Fibers and Its Application in Wastewater Filters; Shanxi University of Science and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hajilou, N.; Mostafayi, S.S.; Yarin, A.L.; Shokuhfar, T.A. Comparative Review on Biodegradation of Poly(Lactic Acid) in Soil, Compost, Water, and Wastewater Environments: Incorporating Mathematical Modeling Perspectives. AppliedChem 2025, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mo, C.; Deng, D.; Liao, D.; Cao, C.; Xu, X. Performance and mechanism of La-Fe modified vermiculite adsorbent forefficient phosphorus removal. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2024, 41, 5412–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Qi, T.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. Influence of the use of corn straw fibers to connect the interfacial transition zone with the mechanical properties of cemented coal gangue backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, W.; Hu, N.; Su, H. Optimization Research and Application of Paste Filling Modified by Pretreated Jute Fiber. Min. Res. Dev. 2024, 44, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Zhou, J.; Huang, P. Determination of mechanical, flowability, and microstructural properties of cemented tailings backfill containing rice straw. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Hao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Yong, F.; Dong, Z.; Yuan, Q. Dynamic mechanical response and damage evolution of cemented tailings backfill with alkalized rice straw under SHPB cycle impact load. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 127009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Wei, M.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Ke, Y.; Tao, T. Effect of the Alkalized Rice Straw Content on Strength Properties and Microstructure of Cemented Tailings Backfill. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 727925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Z.; Wu, A.; Fu, H.; Wang, S. Influence mechanism of straw fiber on uniaxial compressivestrength cemented paste backfill body of sulfur-bearing tailings. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2023, 54, 837–848. [Google Scholar]
- Kirubai, S.; Padmavathy, S.; Ganesh, N.; Rajaguru, K. Study of mechanical behaviour on jute fiber and rice straw reinforced hybrid silica filled composite material. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 69, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Hao, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L. Study on Mechanical Behavior and Damage Characteristics of Cemented Tailings Backfill with Different Water Content Under Different Loading Rates. Mater. Rep. 2022, 36, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, W. Investigation on the Morphology, Microstructure and Chemical Component of Jute Fiber. Plant Fibers Prod. 2005, 27, 239, 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Hua, Z.; Sun, W. Morphological structure and properties of rice-straw fibers. J. Text. Res. 2015, 36, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Xiang, Y.; Yue, J. Analysis of Chemical Composition and Fiber Morphology of Different Parts of Corn Stalk. Trans. China Pulp Pap. 2023, 38, 92–97. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2075.ts.20230419.1856.002 (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Shi, W.; Xu, Q.; Chang, J. Softening effect and crack evolution law of fine sandstone with different water contens. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2024, 20, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, T.; Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Du, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q. Effects of Corn Stalk Fly Ash (CSFA) on the Mechanical and Deformation Properties of Cemented Coal Gangue Backfill. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 7421769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Yilmaz, E.; Song, W.; Yilmaz, E. Influence of fiber reinforcement on mechanical behavior and microstructural properties of cemented tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 213, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Effect of alkaline environment on properties of plant fiber cement mortar. Concrete 2023, 8, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, P.; Gong, C. Experimental Study on Energy Damage Evolution Characteristics of FillingSpecimens with Different Sizes Under Uniaxial Compression. Gold Sci. Technol. 2022, 30, 540–549. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50080-2016; Standard for Test Method of Performance on Ordinary Fresh Concrete. The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 23561.12-2010; Methods for Determining the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Coal and Rock—Part 12: Methods for Determining Coal Hardiness Coefficient. The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Sathiparan, N.; De Zoysa, H.T.S.M. The effects of using agricultural waste as partial substitute for sand in cement blocks. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 19, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Guo, L.; Chen, X. Study on Bleeding Characteristics of Tailings Backfill Slurry and Its Influence on Cemented Backfill. Nonferrous Met. Eng. 2022, 12, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, S. Research Progress of Natural Fiber Reinforce Concrete. J. Chang. Inst. Technol. 2023, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Study on Mechanical Properties of a Fine Aggregate Fly Ash Based Filling Grouting Specimen. Mod. Min. 2024, 40, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; He, C.; Tang, H.; Fu, J.; Wang, M. Performance Comparison of Three Kinds of Plant Fibers Modified Polylactic Acid Composites. Eng. Plast. Appl. 2016, 44, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, R.; Wang, S. Effect of thickeners on the flow characteristics of paste fillingslurry and its engineering application. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2024, 15, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Huang, W. Quantitative study on pore structure of saturated fine-grained soil. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2019, 41, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Influence of temperature on compressive strength, microstructure properties and failure pattern of fiber-reinforced cemented tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-W.; Choi, Y.-C. Effect of abaca natural fiber on the setting behavior and autogenous shrinkage of cement composite. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 56, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xia, D. Effect of mixed fibers on the basic mechanical properties offull desert sand concrete. J. Shihezi Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 42, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Letelier, G.; Concha-Riedel, J.; Antico, F.C.; Valdés, C.; Cáceres, G. Influence of natural fiber dosage and length on adobe mixes damage-mechanical behavior. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yu, Q.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Effects of treated miscanthus on performance of bio-based cement mortar. J. Sustain. Cem. Based Mater. 2022, 12, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qi, T.; Feng, G.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.; Shi, X.; Du, X. Effect of partial substitution of corn straw fly ash for fly ash as supplementary cementitious material on the mechanical properties of cemented coal gangue backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 280, 122553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xia, C.; Wu, L.; Mou, C.; Liu, Z. Development Status and Prospect of Strength Demand for Backfill in Metal Mines. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2024, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Shi, C. Effect of Poplar Fiber on Flowability, Mechanical Propertyand Auto-Shrinkage of Mortar. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 43, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabi, E.; Doko, V.; Hounkpè, S.; Adjovi, E. Study of cement composites on addition of rice husk. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 12, e00345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Song, W.; Yilmaz, E.; Xue, G. Loading rate effect on uniaxial compressive strength behavior and acoustic emission properties of cemented tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 213, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.R.; Pan, Y.; Chen, B. Physical and mechanical properties of sustainable vegetal concrete exposed to extreme weather conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 287, 123024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Feng, M.; Mao, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Ni, X.; Han, G. Particle size distribution of aggregate effects on mechanical and structural properties of cemented rockfill: Experiments and modeling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Tensile properties of chemically treated hemp fibres as reinforcement for composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 53, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, J.; Picado-Santos, L.; Neves, J. Mechanical Performance of Cement Bound Granular Mixtures Using Recycled Aggregate and Coconut Fiber. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gan, D.; Xue, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X. Correlation Mechanism Between Pore Structure and Backfill Strength Based on NMR Technology. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2022, 54, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Hou, E.; Duan, Z.; Wen, Q.; Huang, M.; He, D. Fractal characteristics of pores and microfractures of coals with different structureand their effect on permeability. Coal Geol. Explor. 2019, 47, 70–78. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1155.P.20190403.1457.004 (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Li, J.; Wei, J.; Yuan, G.; Shi, Y. Study on the influence mechanism of porosity on the mechanical properties, deformation and failure characteristics of coal samples. J. Min. Strat. Control Eng. 2024, 6, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, G.; Yilmaz, E.; Song, W.; Cao, S. Mechanical, flexural and microstructural properties of cement-tailings matrix composites: Effects of fiber type and dosage. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 172, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.R.; Chen, B. Influence of type of binder and size of plant aggregate on the hygrothermal properties of bio-concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, L.; Fang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Sun, W. Effect of polypropylene fiber on properties of modified magnesium-coal-based solid waste backfill materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 362, 129695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, D.; Thapa, V.; Dahm, F.; Faltz, C. Masonry Blocks from Lightweight Concrete on the Basis of Miscanthus as Aggregates. In Perennial Biomass Crops for a Resource-Constrained World; Barth, S., Murphy-Bokern, D., Kalinina, O., Taylor, G., Jones, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Ke, Y.; Luo, Z. Mechanical properties of cemented tailings backfill containing alkalized rice straw of various lengths. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Xing, J.; Xiang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, J. Mechanical behavior and microscopic mechanism of synergistically enhanced cemented ultra-fine tailings backfill with polypropylene fiber and silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kundu, S.P.; Roy, A.; Adhikari, B.; Majumder, S.B. Polymer modified jute fibre as reinforcing agent controlling the physical and mechanical characteristics of cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.A.; Amir, M.T.; Ali, B.; El Ouni, M.H. Mechanical performance and environmental impact of normal strength concrete incorporating various levels of coconut fiber and recycled aggregates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 83636–83651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Zhou, Z. Mechanical Properties of Natural as well as Synthetic Fiber Reinforced Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 333, 127353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, Z.; Yi, X.; Guo, L. Macro-meso Experiment of Fiber-reinforced Cement Paste Filling Material. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2016, 42, 406–412. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2286.t.20160304.1504.024 (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Rahim, M.; Douzane, O.; Tran Le, A.D.; Promis, G.; Langlet, T. Characterization and comparison of hygric properties of rape straw concrete and hemp concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Hu, X.; Lin, H.; Li, E. Study on the Selective Flotation Separation Mechanism of Feldspar and Quartz by NaF Inhibitor. Nonferrous Met. (Miner. Process. Sect.) 2025, 4, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Li, X.; Sun, H. Activation Mechanism of Coal Gangue and Effect of Activated Gangue on Cement Mechanics. Contemp. Chem. Ind. 2025, 54, 294–301. [Google Scholar]
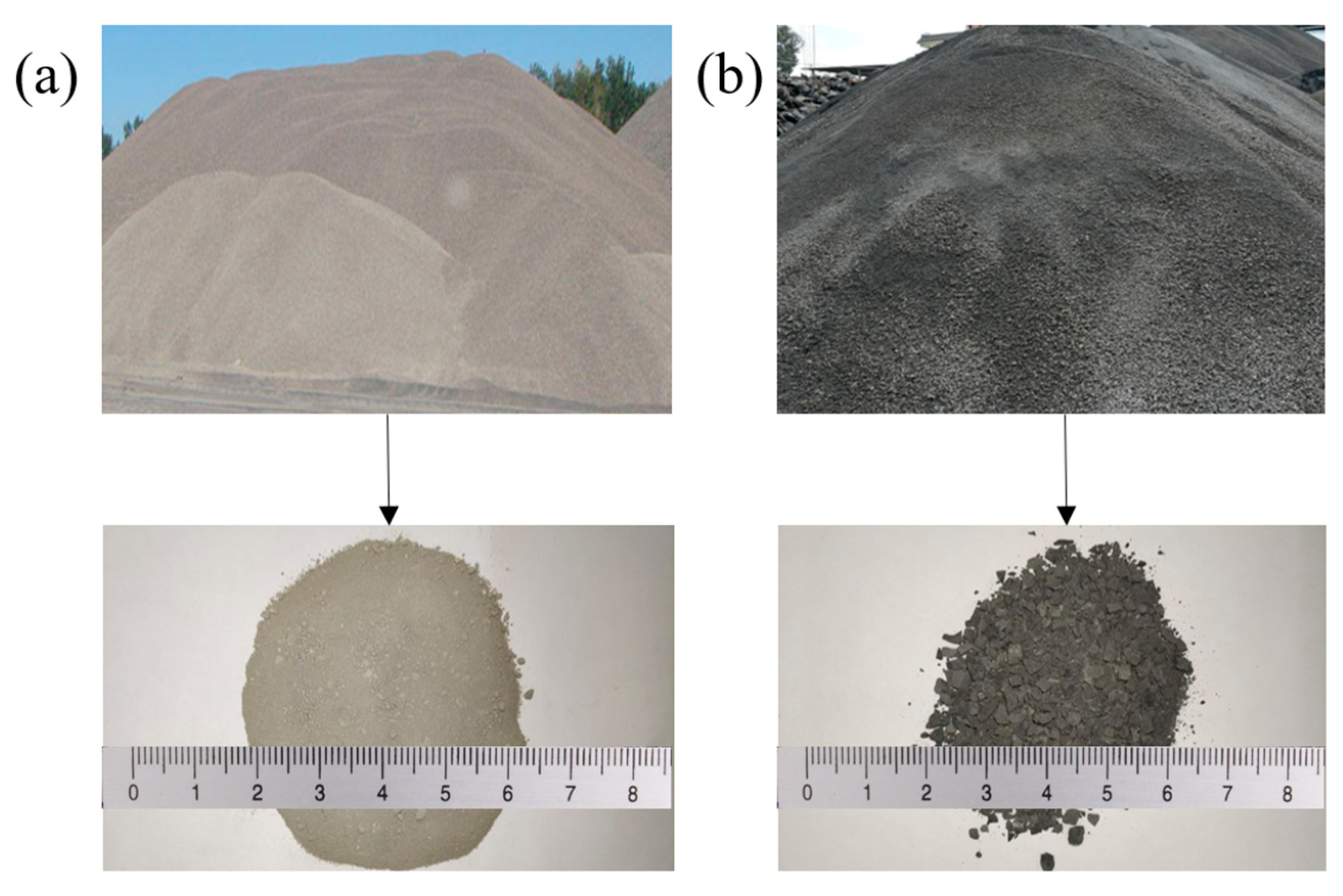



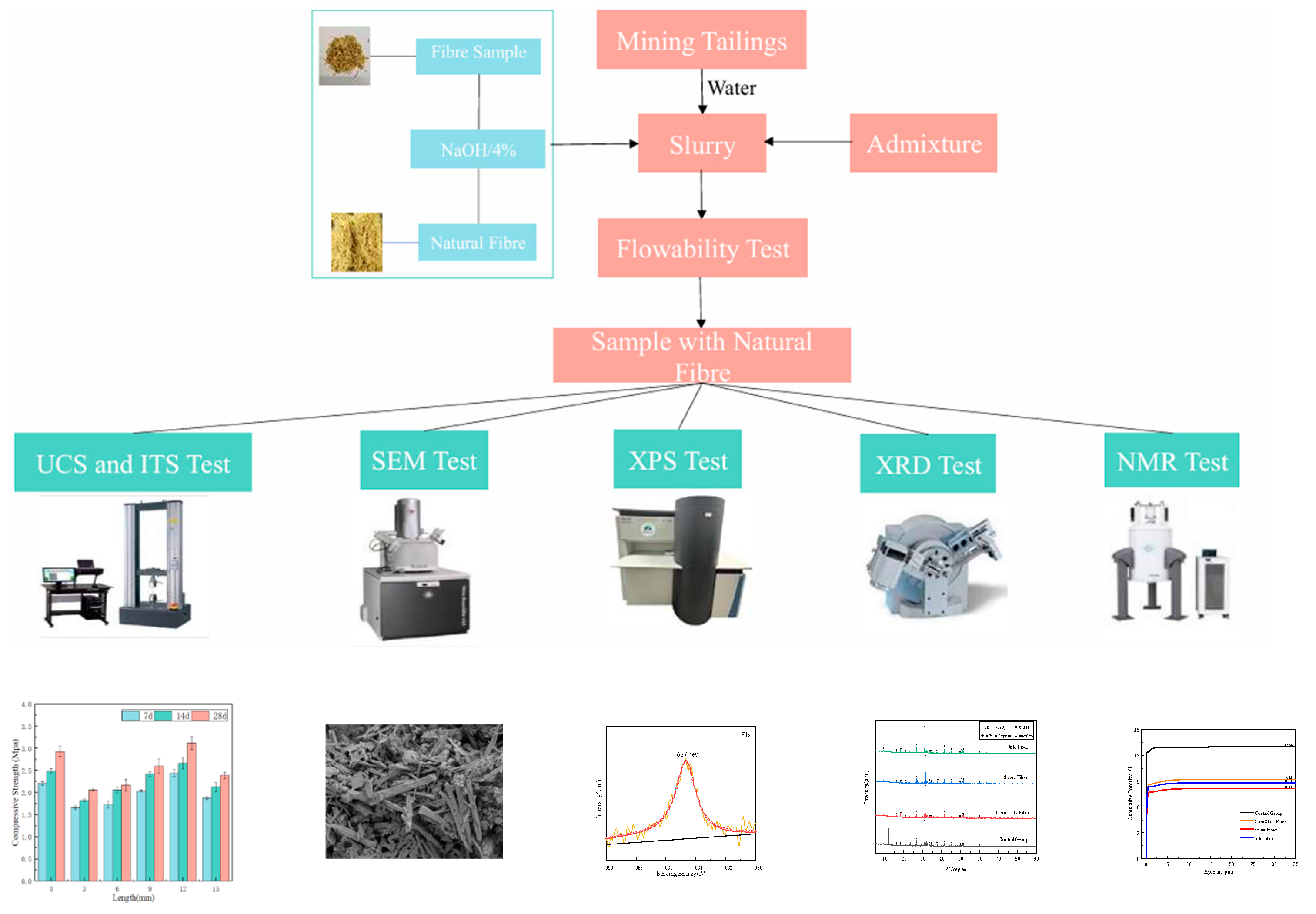






| Types (%) | CaO | MgO | SO3 | P2O5 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | K2O | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flotation tailings | 61.04 | 20.56 | 1.06 | 6.59 | 6.40 | 2.07 | 1.23 | 0.68 | 0.11 |
| Gravity tailings | 38.76 | 9.47 | 2.82 | 12.97 | 25.04 | 3.50 | 3.82 | 2.23 | 0.67 |
| Types (%) | SO3 | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | P2O5 | K2O | MgO | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphogypsum | 43.09 | 38.29 | 12.64 | 1.66 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.77 | 0.47 |
| Slag powder | 2.10 | 44.40 | 27.85 | 14.46 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.35 | 7.92 | 1.53 |
| Cement | 0 | 65.90 | 22.27 | 5.59 | 3.47 | 0.07 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 0.31 |
| Types (%) | Cellulose | Hemicellulose | Lignin |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 21.98~28.40 | 25.12~27.87 | 14.27~15.82 |
| RS | 24.91~52.26 | 8.39~32.74 | 10.40~33.36 |
| JF | 55.36~65.58 | 19.46~25.50 | 8.68~13.37 |
| Mix No. | Ref. | RS1~5 | CS1~5 | JF1~5 | RS6~9 | CS6~9 | JF6~9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid content (wt%) | 76 wt% | ||||||
| Natural fibre length (mm) | 0 | 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 | 12 | 3 | 12 | ||
| Natural fibre content (wt%) | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 | ||||
| Research item | 0 | Fibre length effect | Fibre content effect | ||||
| Fibre Type | Backfill Material | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Amplify (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Amplify (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn straw | Phosphorus tailings | 7.16 | 144.4% | 1.20 | 18.8% | This study |
| Rice straw | 4.93 | 68.3% | 1.13 | 11.9% | ||
| Jute | 6.10 | 108.2% | 1.16 | 14.9% | ||
| Corn straw | Coal gangue | 5.22 | 10.6% | 0.85 | 14.8% | [20] |
| Polypropylene | Coal gangue | 5.24 | 63.8% | —— | —— | [63] |
| Rice straw | Copper mine tailings | 6.43 | 16.9% | 1.05 | 31.2% | [66] |
| Rice straw | Lead and zinc mine tailings | 3.38 | 19% | —— | —— | [25] |
| Polypropylene | Gold mine tailings | 3.43 | 19.9% | —— | —— | [33] |
| Polyacrylonitrile | 3.31 | 25.4% | —— | —— | ||
| Glass | 3.02 | 14.4% | —— | —— | ||
| Polypropylene | Copper tailings | 4.87 | 55.6% | 0.33 | 21.7% | [67] |
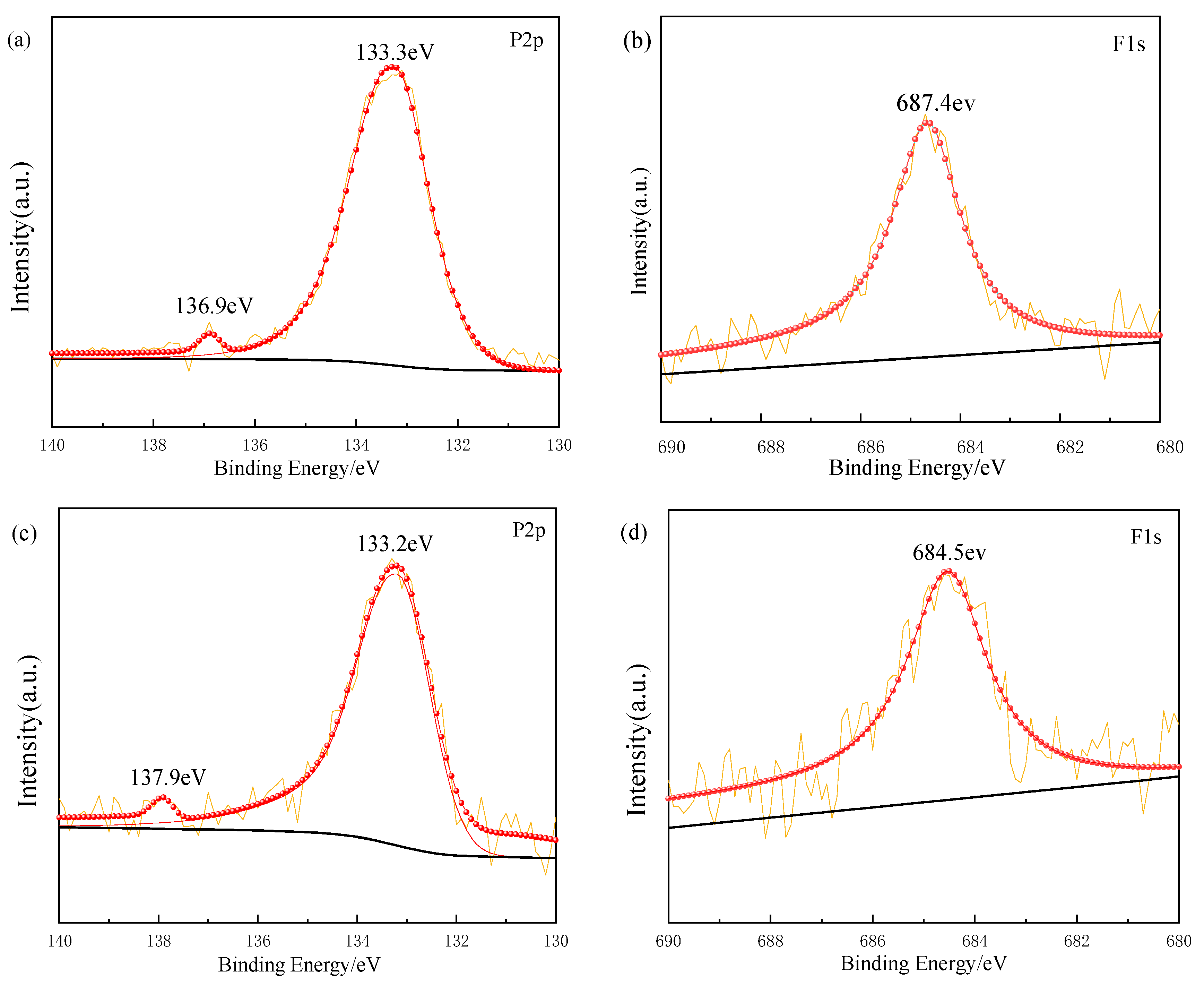
| P (mg/L) | F (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| Ref. | 0.198 | 0.83 |
| CS | 0.063 | 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Ke, C.; Wu, F.; Zheng, Y. Improvement of Environment and Mechanical Behaviour of Filling Material of Phosphate Solid Waste Using Natural Fibre. Materials 2025, 18, 3978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173978
Liu D, Ke C, Wu F, Zheng Y. Improvement of Environment and Mechanical Behaviour of Filling Material of Phosphate Solid Waste Using Natural Fibre. Materials. 2025; 18(17):3978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173978
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Defeng, Chenglin Ke, Fan Wu, and Yantao Zheng. 2025. "Improvement of Environment and Mechanical Behaviour of Filling Material of Phosphate Solid Waste Using Natural Fibre" Materials 18, no. 17: 3978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173978
APA StyleLiu, D., Ke, C., Wu, F., & Zheng, Y. (2025). Improvement of Environment and Mechanical Behaviour of Filling Material of Phosphate Solid Waste Using Natural Fibre. Materials, 18(17), 3978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173978






